The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological Data
3. Clinical and Immunopathological Features
4. Pathogenetic Insights
4.1. Psoriasis
4.2. Bullous Pemphigoid
4.3. Bullous Pemphigoid–Psoriasis Association
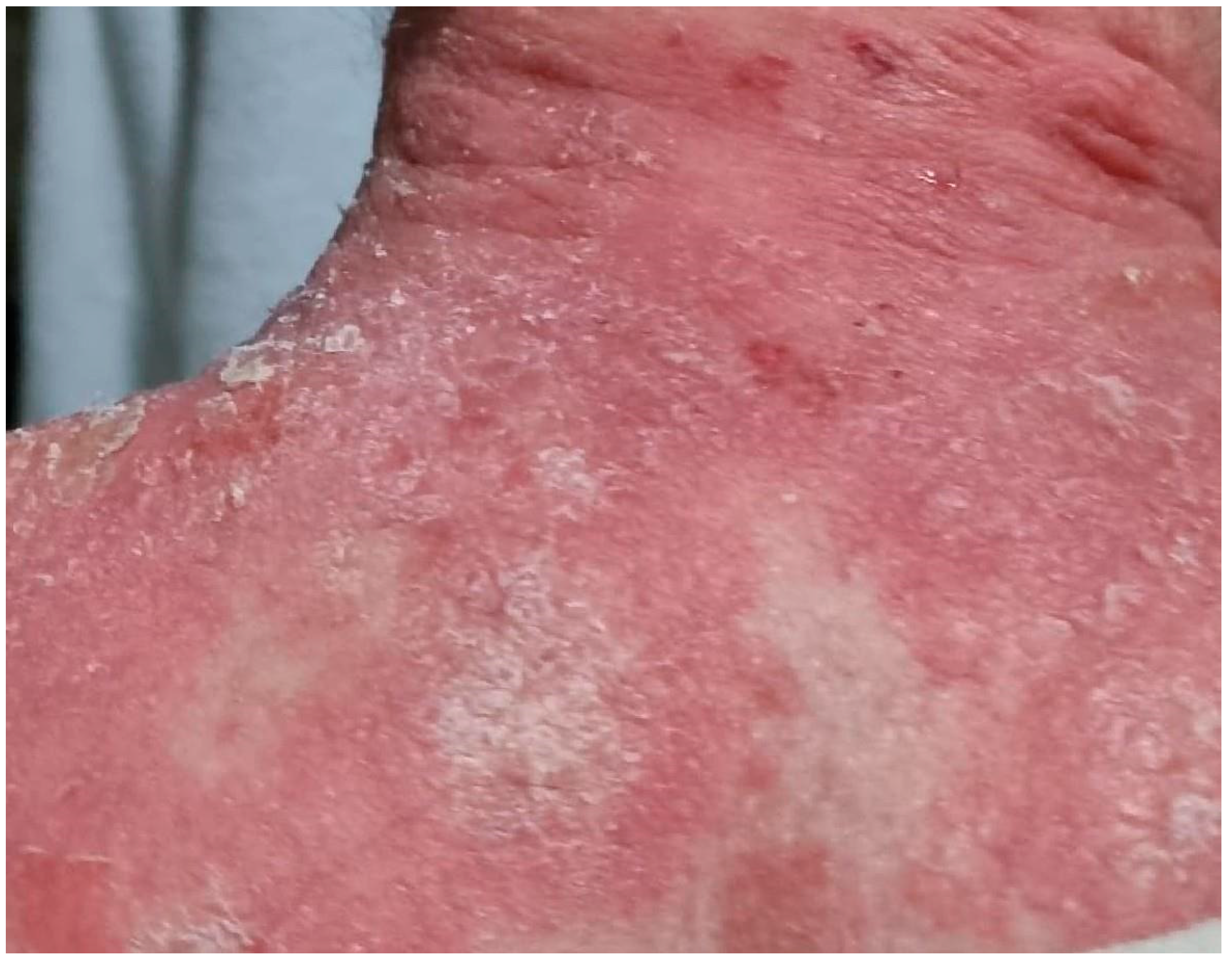
Treatments for Psoriasis as Triggers of BP
5. Management of Concurrent Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naldi, L.; Gambini, D. The clinical spectrum of psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deotto, M.L.; Spiller, A.; Sernicola, A.; Alaibac, M. Bullous pemphigoid: An immune disorder related to aging (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zenzo, G.; Della Torre, R.; Zambruno, G.; Borradori, L. Bullous pemphigoid: From the clinic to the bench. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairley, J.A.; Bream, M.; Fullenkamp, C.; Syrbu, S.; Chen, M.; Messingham, K.N. Missing the target: Characterization of bullous pemphigoid patients who are negative using the BP180 enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohata, C.; Ishii, N.; Koga, H.; Fukuda, S.; Tateishi, C.; Tsuruta, D.; Furumura, M.; Hashimoto, T. Coexistence of autoimmune bullous diseases (AIBDs) and psoriasis: A series of 145 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainichi, T.; Kabashima, K. Interaction of Psoriasis and Bullous Diseases. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genovese, G.; Moltrasio, C.; Cassano, N.; Maronese, C.A.; Vena, G.A.; Marzano, A.V. Pustular Psoriasis: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.F.; Wang, T.S.; Hung, S.T.; Tsai, P.I.; Schenkel, B.; Zhang, M.; Tang, C.H. Epidemiology and comorbidities of psoriasis patients in a national database in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 63, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.H.; Hu, H.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Li, C.P.; Wu, C.Y. Psoriasis is associated with increased risk of bullous pemphigoid: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.M.; Ferris, L.K.; Kaffenberger, J.A. A Systematic Review of Concomitant Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2016, 1, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.; Goyal, S.; Murrell, D.F. Association between bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2019, 60, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kridin, K.; Ludwig, R.J.; Schonmann, Y.; Damiani, G.; Cohen, A.D. The bidirectional association between bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: A population-based cohort study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Ludwig, R.J. The Growing Incidence of Bullous Pemphigoid: Overview and Potential Explanations. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kridin, K.; Bergman, R. Association between bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: A case-control study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ständer, S.; Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D.; Thaçi, D.; Ludwig, R.J.; Kridin, K. Patients with bullous pemphigoid and comorbid psoriasis present with less blisters and lower serum levels of anti-BP180 autoantibodies. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, L.; Gatti, S.; Nini, G. Bullous pemphigoid and severe erythrodermic psoriasis: Combined low-dose treatment with cyclosporine and systemic steroids. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 27, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Peng, C.; Zheng, J.; Lu, X.; Ding, Y.; Su, L. Bullous Pemphigoid Associated with Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A Case Report. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, C.; Driesch, P.V. Psoriatic erythroderma and bullous pemphigoid treated successfully with acitretin and azathioprine. Eur. J. Dermatol. 1999, 9, 537–539. [Google Scholar]
- Si, X.; Ge, L.; Xin, H.; Cao, W.; Sun, X.; Li, W. Erythrodermic psoriasis with bullous pemphigoid: Combination treatment with methotrexate and compound glycyrrhizin. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido Colmenero, C.; Arias Santiago, S.; Blasco Morente, G.; Pérez López, I.; Aneiros Fernández, J. Photoletter to the editor: Psoriatic erythroderma associated with bullous pemphigoid: Clinical appearance and histopathology. J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teraki, Y.; Fukuda, T. Pemphigoid nodularis associated with psoriatic erythroderma: Successful treatment with suplatast tosilate. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 424–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskandarli, M.; Gerceker Turk, B.; Yaman, B.; Ozturk, G. Pemphigoid Diseases as a Sign of Active Psoriasis: A Case Report and Brief Review. Dermatology 2015, 231, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.T.; Elston, D.M.; Libow, L.F.; David-Bajar, K. A case of bullous pemphigoid limited to psoriatic plaques. Cutis 2002, 70, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sussman, M.E.; Grossman, S.K.; Hsu, S.; Lee, J.B.; Motaparthi, K. Neutrophil-rich, noncollagenous 16A domain-negative bullous pemphigoid associated with psoriasis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 16, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamura, E.; Tsujiwaki, M.; Ujiie, H.; Nishie, W.; Hata, H.; Shimizu, H.; Iwata, H. Bullous pemphigoid associated with psoriasis showing marked neutrophilic infiltrates. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.D.; Jones, M.S.; Stewart, T.W.; Fernando, M.U. Bullous pemphigoid occurring in psoriatic plaques in association with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1991, 16, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, A.; Kalińska-Bienias, A.; Kowalewski, C.; Schwartz, R.; Wozniak, K. Development of bullous pemphigoid in a patient with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome. Cutis 2016, 98, E19–E23. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, L.E.; Patrascu, V.; Dascalu, R.C.; Ciurea, M.E. Bullous pemphigoid associated with psoriasis, breast cancer and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2014, 40, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Pasić, A.; Ljubojević, S.; Lipozencić, J.; Marinović, B.; Loncarić, D. Coexistence of psoriasis vulgaris, bullous pemphigoid and vitiligo: A case report. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2002, 16, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.; Czajkowski, R.; Scibior, K.; Schwartz, R.A. Coexistence of psoriasis vulgaris and vitiligo with bullous pemphigoid: A case report. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e359–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalas, J.; Del Pozo, L.; Gracia-Darder, I. Psoriasis, sarcoidosis, and bullous pemphigoid: More than a coincidence in a single patient? Dermatol. Online J. 2022, 28, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, N.; Demitsu, T.; Umemoto, N.; Nagashima, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kakurai, M.; Nakamura, S.; Yamada, T.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T. Possible paraneoplastic syndrome case of bullous pemphigoid with immunoglobulin G anti-BP180 C-terminal domain antibodies associated with psoriasis and primary macroglobulinemia. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Ahmed, A.R. Anti-p200 Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, P.; Bergallo, M.; Ponti, R.; Barberio, E.; Cicchelli, S.; Buffa, E.; Comessatti, A.; Costa, C.; Terlizzi, M.E.; Astegiano, S.; et al. Th1, Th2, Th17 and regulatory T cell pattern in psoriatic patients: Modulation of cytokines and gene targets induced by etanercept treatment and correlation with clinical response. Dermatology 2011, 223, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Gilliet, M. Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Targeted Therapies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, L.; Chen, Y.L.; Ogg, G.S. Role of regulatory T cells in psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, N.; Hoashi, T.; Saeki, H. The Defect in Regulatory T Cells in Psoriasis and Therapeutic Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanoni, D.; Venegoni, L.; Vergani, B.; Tavecchio, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Leone, B.E.; Marzano, A.V. Evidence for a role of autoinflammation in early-phase psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 198, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honma, M.; Nozaki, H. Molecular Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Biomarkers Reflecting Disease Activity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Koppu, S.; Perche, P.O.; Feldman, S.R. The Cytokine Mediated Molecular Pathophysiology of Psoriasis and Its Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Brodsky, M.; Atanelov, Z.; Farahnik, B.; Abrouk, M.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; Liao, W. Erythrodermic psoriasis: Pathophysiology and current treatment perspectives. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2016, 6, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Tsai, T.F. Overlapping Features of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: From Genetics to Immunopathogenesis to Phenotypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Liang, Y.; Sarkar, M.K.; Wolterink, L.; Swindell, W.R.; Voorhees, J.J.; Harms, P.W.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Johnston, A.; Gudjonsson, J.E. IL-17 Responses Are the Dominant Inflammatory Signal Linking Inverse, Erythrodermic, and Chronic Plaque Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2498–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.R.; Warren, R.B. Psoriasis and susceptibility to other autoimmune diseases: An outline for the clinician. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Kadono, T.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. Autoimmunity and autoimmune co-morbidities in psoriasis. Immunology 2018, 154, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ten Bergen, L.L.; Petrovic, A.; Aarebrot, A.K.; Appel, S. Current knowledge on autoantigens and autoantibodies in psoriasis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, P.T.; Tseng, H.C. Refractory bullous pemphigoid with prurigo nodularis successfully treated with dupilumab monotherapy. Dermatol. Sin. 2022, 40, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Di Zenzo, G.; Cozzani, E.; Berti, E.; Cugno, M.; Marzano, A.V. New Insights Into the Pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid: 2019 Update. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, G. The role of T cells in pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.M.; Giudice, G.J.; Fairley, J.A. Autoimmunity in bullous pemphigoid. G Ital. Dermatol Venereol. 2009, 144, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freire, P.C.; Muñoz, C.H.; Stingl, G. IgE autoreactivity in bullous pemphigoid: Eosinophils and mast cells as major targets of pathogenic immune reactants. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, L.; Cordiali Fei, P.; Ameglio, F. Cytokines and bullous pemphigoid. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1999, 10, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margaroli, C.; Bradley, B.; Thompson, C.; Brown, M.R.; Giacalone, V.D.; Bhatt, L.; Stoff, B.; Ahuja, S.; Springman, E.; Tirouvanziam, R.; et al. Distinct compartmentalization of immune cells and mediators characterizes bullous pemphigoid disease. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, B.F.; Patsinakidis, N.; Raap, U. Role of the Pruritic Cytokine IL-31 in Autoimmune Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, H.; Li, L. Factors associated with the activity and severity of bullous pemphigoid: A review. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, E.H.; Kneibner, D.; Kridin, K.; Amber, K.T. Serum and blister fluid levels of cytokines and chemokines in pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Jan, S.; Plée, J.; Vallerand, D.; Dupont, A.; Delanez, E.; Durlach, A.; Jackson, P.L.; Blalock, J.E.; Bernard, P.; Antonicelli, F. Innate immune cell-produced IL-17 sustains inflammation in bullous pemphigoid. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plée, J.; Le Jan, S.; Giustiniani, J.; Barbe, C.; Joly, P.; Bedane, C.; Vabres, P.; Truchetet, F.; Aubin, F.; Antonicelli, F.; et al. Integrating longitudinal serum IL-17 and IL-23 follow-up, along with autoantibodies variation, contributes to predict bullous pemphigoid outcome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Jan, S.; Muller, C.; Plee, J.; Durlach, A.; Bernard, P.; Antonicelli, F. IL-23/IL-17 Axis Activates IL-1β-Associated Inflammasome in Macrophages and Generates an Auto-Inflammatory Response in a Subgroup of Patients With Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakievska, L.; Holtsche, M.M.; Künstner, A.; Goletz, S.; Petersen, B.S.; Thaci, D.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Ludwig, R.J.; Franke, A.; Sadik, C.D.; et al. IL-17A is functionally relevant and a potential therapeutic target in bullous pemphigoid. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, D.; Bini, E.; Terryn, C.; Didier, K.; Le Jan, S.; Gatouillat, G.; Durlach, A.; Nesmond, S.; Muller, C.; Bernard, P.; et al. NET Formation in Bullous Pemphigoid Patients With Relapse Is Modulated by IL-17 and IL-23 Interplay. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niebel, D.; Wilsmann-Theis, D.; Bieber, T.; Berneburg, M.; Wenzel, J.; Braegelmann, C. Bullous Pemphigoid in Patients Receiving Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors and Psoriatic Patients-Focus on Clinical and Histopathological Variation. Dermatopathology 2022, 9, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, A.; Sticherling, M. Concomitant psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid: Coincidence or pathogenic relationship? Int. J. Dermatol. 2006, 45, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.S.; Vanderlugt, C.J.; Hashimoto, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Zone, J.J.; Black, M.M.; Wojnarowska, F.; Stevens, S.R.; Chen, M.; Fairley, J.A.; et al. Epitope spreading: Lessons from autoimmune skin diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 110, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glinski, W.; Jarzabek-Chorzelska, M.; Kuligowski, M.; Pierozynska-Dubowska, M.; Glinska-Ferenz, M.; Jabłonska, S. Basement membrane zone as a target for human neutrophil elastase in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1990, 282, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimi, Y.; Pawankar, R.; Kawana, S. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-13 in lesional skin of bullous pemphigoid. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 139, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozó, R.; Flink, L.B.; Belső, N.; Gubán, B.; Széll, M.; Kemény, L.; Bata-Csörgő, Z. Could basement membrane alterations, resembling micro-wounds at the dermo-epidermal junction in psoriatic non-lesional skin, make the skin susceptible to lesion formation? Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Gleñ, J.; Zabłotna, M.; Nedoszytko, B.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M.; Rêbała, K.; Nowicki, R.J. Significance of interleukin-31 (IL-31) gene polymorphisms and IL-31 serum level in psoriasis in correlation with pruritus. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2021, 38, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtschig, G.; Chow, E.T.; Venning, V.A.; Wojnarowska, F.T. Acquired subepidermal bullous diseases associated with psoriasis: A clinical, immunopathological and immunogenetic study. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dănescu, S.; Chiorean, R.; Macovei, V.; Sitaru, C.; Baican, A. Role of physical factors in the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid: Case report series and a comprehen.nsive review of the published work. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caca-Biljanovska, N.; Arsovska-Bezhoska, I.; V’lckova-Laskoska, M. PUVA-induced Bullous Pemphigoid in Psoriasis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2016, 24, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugita, K.; Kabashima, K.; Nishio, D.; Hashimoto, T.; Tokura, Y. Th2 cell fluctuation in association with reciprocal occurrence of bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis vulgaris. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyden, M.J.; Bilgic, A.; Murrell, D.F. A Systematic Review of Drug-Induced Pemphigoid. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svigos, K.; Fried, L.; Yin, L.; Brinster, N.; Lo Sicco, K.; Adotama, P. A new eruption of bullous pemphigoid within psoriatic plaques following cyclosporine withdrawal. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 8, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.G.; Soura, E.; Antoniou, C. Drug-induced pemphigoid: A review of the literature. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 9, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, F.T.; Amber, K.T. Autoimmune blistering diseases provoked during the treatment of chronic inflammatory disease with biologic agents: A systematic review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, M.; Ishii, M.; Takahashi-Shishido, N.; Ichimura, Y.; Morimura, S. Case of bullous pemphigoid under treatment with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, e163–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Sánchez, A.; Bonifaz, A. Simultaneous Bullous Pemphigoid and Vitiligo Associated with Adalimumab Therapy in a Patient with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nin, M.; Tokunaga, D.; Ishii, N.; Komai, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Katoh, N. Case of coexisting psoriatic arthritis and bullous pemphigoid improved by etanercept. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, R.; Citarella, L.; Spallone, G.; Chimenti, S. A biological approach in a patient with psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid associated with losartan therapy. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 33, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusano, F.; Iannazzone, S.S.; Riccio, G.; Piccirillo, F. Coexisting bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis successfully treated with etanercept. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2010, 20, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, P.S.; Lowe, N.J.; Gindi, V. Treatment of coexisting bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis with the tumor necrosis factor antagonist etanercept. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54 (Suppl. 2), S121–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majima, Y.; Yagi, H.; Tateishi, C.; Groth, S.; Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D.; Koga, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Tokura, Y. A successful treatment with ustekinumab in a case of antilaminin-c1 pemphigoid associated with psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 1367–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loget, J.; Plee, J.; Antonicelli, F.; Bernard, P.; Loget, J.; Plée, J. A successful treatment with ustekinumab in a case of relapsing bullous pemphigoid associated with psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e228–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Rahat, S.; Mufti, A.; Witol, A.; Bagit, A.; Sachdeva, M.; Yeung, J. Biologic treatment outcomes in mucous membrane pemphigoid: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, F.; Fania, L.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Salemme, A.; Di Zenzo, G. Bullous Pemphigoid: Trigger and Predisposing Factors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, A.A.; Pelechas, E.; Kaltsonoudis, E.; Markatseli, T.E.; Voulgari, P.V. Biologic Therapies and Autoimmune Phenomena. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Steinhoff, M. Bullous pemphigoid induced by biologic drugs in psoriasis: A systematic review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 2886–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.H.; Tsai, T.F. Development of bullous pemphigoid during secukinumab treatment for psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, e220–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlando, M.; Capurro, N.; Herzum, A.; Cozzani, E.; Parodi, A. Guselkumab-associated bullous pemphigoid in a psoriasis patient: A case report and review of the literature. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, N.; Suzuki, T.; Aoyama, K.; Kinjo, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Sato, T. Bullous pemphigoid during the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris with risankizumab. J. Dermatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borradori, L.; Van Beek, N.; Feliciani, C.; Tedbirt, B.; Antiga, E.; Bergman, R.; Böckle, B.C.; Caproni, M.; Caux, F.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Updated S2 K guidelines for the management of bullous pemphigoid initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L. Rituximab, Omalizumab, and Dupilumab Treatment Outcomes in Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 928621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.N.; Khan, Z.A.; Ali, M.H.; Almas, T.; Khedro, T.; Raj Nagarajan, V. A blistering new era for bullous pemphigoid: A scoping review of current therapies, ongoing clinical trials, and future directions. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 70, 102799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanakos, A.; Vergou, T.; Panopoulos, S.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Stratigos, A.J.; Sfikakis, P.P. Psoriasis as an adverse reaction to biologic agents beyond anti-TNF-α therapy. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, H.S.; Alhowaish, N.Y.; Omair, M.A. Rituximab-Induced Psoriasis in a Patient with Granulomatosis with Polyangitis Treated with Adalimumab. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2019, 2019, 5450863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, F. Pathogenesis of Paradoxical Reactions Associated with Targeted Biologic Agents for Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Kawai, K. Doxycycline as an initial treatment of bullous pemphigoid in Japanese patients. J. Cutan. Immunol. Allergy 2020, 3, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraj, K.H.; Ashok, N.M.; Rashmi, R.; Praveen, T.K. The role of drugs in the induction and/or exacerbation of psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Tsai, T.F. Management of Coexisting Bullous Pemphigoid and Psoriasis: A Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoire, A.R.F.; DeRuyter, B.K.; Stratman, E.J. Psoriasis Flares Following Systemic Glucocorticoid Exposure in Patients with a History of Psoriasis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, N.L.A.; Balak, D.M.W.; Knulst, A.C.; Welsing, P.M.J.; van Laar, J.M. Systemic glucocorticoid use and the occurrence of flares in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4232–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, P.; Giacaman, P.; Fernández, J.; Morales, C. Bullous pemphigoid associated with psoriasis: A good response to methotrexate. An. Bras. De Dermatol. 2019, 94, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.; Gupta, A.; Yunis, F.; Handettu, S.; Chandrashekar, B. Coexistence of psoriasis with bullous pemphigoid. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2012, 3, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, U.; Gunduz, K.; Ermertcan, A.T.; Kandiloğlu, A.R. Coexistence of psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid: Remission with low-dose methotrexate. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwarsa, O.; Herlina, L.; Sutedja, E.; Dharmadji, H.P.; Hindritiani, R.; Gunawan, H. Concurrence of bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: A case report. Serb. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 10, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monnier-Murina, K.; Du Thanh, A.; Merlet-Albran, S.; Guillot, B.; Dereure, O. Bullous pemphigoid occurring during efalizumab treatment for psoriasis: A paradoxical auto-immune reaction? Dermatology 2009, 219, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarczyk, M.; Wozniak, K.; Ishii, N.; Gorkiewicz-Petkov, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Schwarz, R.; Kowalewski, C. Coexistence of psoriasis and pemphigoid—Only a coincidence? Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hisler, B.M.; Aronson, P.J.; Rudner, E.J. Bullous pemphigoid in psoriatic lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 20, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washio, H.; Hara, H.; Suzuki, H.; Yoshida, M.; Hashimoto, T. Bullous pemphigoid on psoriasis lesions after UVA radiation. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2005, 85, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Primka, E.J., 3rd; Camisa, C. Psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid treated with azathioprine. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1998, 39, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boixeda, J.P.; Soria, C.; Medina, S.; Ledo, A. Bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis: Treatment with cyclosporine. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 24, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, E.; Anyfantakis, V. Coexistent psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid responding to mycophenolate mofetil monotherapy. SKINmed Dermatol. Clin. 2008, 7, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, S.; Gundoğdu, M.; Ertop, P.; Şanlı, H.; Korkmaz, P.; Heper, A.O.; Kundakçı, N. Ustekinumab associated bullous pemphigoid in a psoriasis patient and a review of the literature. TURKDERM-Turk. Arch. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 53, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.A.; Buffard, V.; André, C.; Ortonne, N.; Revuz, J.; Bagot, M.; Roujeau, J.C. Efalizumab-induced bullous pemphigoid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Qi, Y.; Lin, B. Incidental amelioration of bullous pemphigoid during ixekizumab treatment for psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, e13–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xia, D.; Zhou, X.; Li, W. Ixekizumab successfully treated refractory psoriasis concurrent bullous pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsun, N.; Sallahoglu, K.; Dizman, D.; Su, O.; Tosuner, Z. Bullous pemphigoid during ustekinumab therapy in a psoriatic patient. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Alzueta, N.; Castresana, M.; Gascon, A.; Pio, M. Bullous pemphigoid induced by ustekinumab: A case report. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2021, 28, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, C.E.H. Evidence of an association between bullous pemphigoid and psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1985, 113, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.S.; Tsai, T.F. Remission of bullous pemphigoid after rituximab treatment in a psoriasis patient on regular low-dose methotrexate. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2014, 94, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.S.; Scardamaglia, L.; Tan, C.G.; McCormack, C.J. Successful secukinumab treatment of active bullous pemphigoid and chronic severe psoriasis: A case report. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, e155–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, K.; Raju, B.P.; Raveendra, L. Epitope Spreading Phenomenon: A Case Report. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 10, 580–584. [Google Scholar]
- Kamata, M.; Asano, Y.; Shida, R.; Maeda, N.; Yoshizaki, A.; Miyagaki, T.; Kawashima, T.; Tada, Y.; Sato, S. Secukinumab decreased circulating anti-BP180-NC16a autoantibodies in a patient with coexisting psoriasis vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, e216–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.M.; Novoa, R.A.; Bui, N.Q.; Zaba, L.C. Successful treatment of HIV-negative Kaposi sarcoma with ipilimumab and nivolumab and concurrent management of baseline psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiang, H.; Li, W. Concurrent bullous pemphigoid and plaque psoriasis successfully treated with Janus kinase inhibitor Baricitinib. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classes | Drugs | References |
|---|---|---|
| Immunomodulating/Immunosuppressant agents | Methotrexate | [17,19,22,27,72,75,85,104,105,106,107,108,109,118,122,124] |
| Cyclosporine | [16,25,75,80,113,119,124] | |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | [83,114] | |
| Azathioprine | [18,92,112,121] | |
| Fumaric acids | [64] | |
| Suplatast tosilate | [21] | |
| Baricitinib | [127] | |
| Cyclophosphamide | [32] * | |
| Agents with antinflammatory properties | Erythromycin | [110] |
| Tetracycline | [30,81,109,110,112] | |
| Doxycycline | [111] | |
| Minocycline | [21] | |
| Dapsone | [64,80,109,110,120,124] | |
| Sulfasalazine | [126] | |
| Nicotinamide | [109,110,111,112] | |
| Compound glycyrrhizin | [19,126] | |
| Retinoids | Acitretin | [18,23,115,116,126] |
| Biologics | ||
| Anti-TNF-alpha | Etanercept | [80,81,82,83] |
| Anti-IL-12/23 | Ustekinumab | [85,91] |
| Anti-IL-17 | Secukinumab | [123,125] |
| Ixekizumab | [117,118] | |
| Anti-CD20 | Rituximab | [32,81,122] * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maronese, C.A.; Cassano, N.; Genovese, G.; Foti, C.; Vena, G.A.; Marzano, A.V. The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010328
Maronese CA, Cassano N, Genovese G, Foti C, Vena GA, Marzano AV. The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(1):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010328
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaronese, Carlo Alberto, Nicoletta Cassano, Giovanni Genovese, Caterina Foti, Gino Antonio Vena, and Angelo Valerio Marzano. 2023. "The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 1: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010328
APA StyleMaronese, C. A., Cassano, N., Genovese, G., Foti, C., Vena, G. A., & Marzano, A. V. (2023). The Intriguing Links between Psoriasis and Bullous Pemphigoid. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(1), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010328







