Deep Learning-Based Detection of Bone Tumors around the Knee in X-rays of Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Model Training
2.4. Algorithm
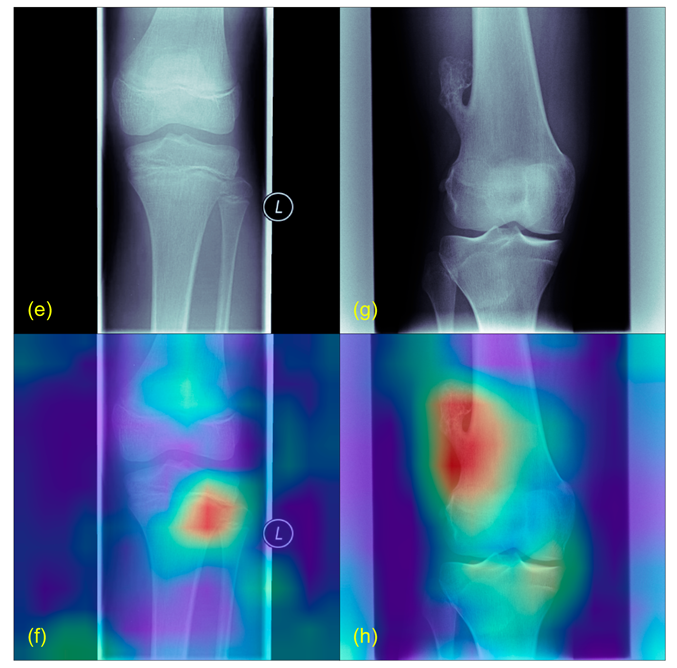
2.5. Plausibility
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Algorithm
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrasser, N.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Biberthaler, P. Facharztwissen Orthopädie Unfallchirurgie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, R.M.; Walton, M.A.; Carter, P.M. The Major Causes of Death in Children and Adolescents in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Colombet, M.; Ries, L.A.G.; Moreno, F.; Dolya, A.; Bray, F.; Hesseling, P.; Shin, H.Y.; Stiller, C.A. International incidence of childhood cancer, 2001–10: A population-based registry study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, M.C.; Ready, J.E.; Mankin, H.J. Tumors about the knee in children. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1990, 255, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breden, S.; Lallinger, V.; Stephan, M.; Mogler, C.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Lenze, U.; Knebel, C. Knochentumoren des kindlichen Knies. Knie J. 2021, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widhe, B.; Widhe, T. Initial symptoms and clinical features in osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2000, 82, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenze, U.; Breden, S.; Rechl, H.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Knebel, C. Knochensarkome des Kindesalters: Diagnostik und Therapie von Osteosarkom und Ewing-Sarkom. Trillium Krebsmed. 2020, 6, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goedhart, L.M.; Gerbers, J.G.; Ploegmakers, J.J.; Jutte, P.C. Delay in Diagnosis and Its Effect on Clinical Outcome in High-grade Sarcoma of Bone: A Referral Oncological Centre Study. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 8, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, G.; Ferrari, S.; Longhi, A.; Mellano, D.; Giacomini, S.; Forni, C. Delay in diagnosis of high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities. Has it any effect on the stage of disease? Tumori 2000, 86, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.L.; Chan, W.H.; Chia, Y.Y. Initial symptoms and delayed diagnosis of osteosarcoma around the knee joint. J. Orthop. Surg. 2010, 18, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneppen, O.; Hansen, L.M. Presenting symptoms and treatment delay in osteosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma. Acta Radiol. Oncol. 1984, 23, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, W.H.; Song, W.S.; Koh, J.S.; Lee, J.A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Shin, D.S.; Jeon, D.G. Prognostic effects of doctor-associated diagnostic delays in osteosarcoma. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2009, 129, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreou, D.; Ruppin, S.; Fehlberg, S.; Pink, D.; Werner, M.; Tunn, P.U. Survival and prognostic factors in chondrosarcoma: Results in 115 patients with long-term follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2011, 82, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, J.; Klein, A.; Baur-Melnyk, A.; Knösel, T.; Lindner, L.; Birkenmaier, C.; Roeder, F.; Jansson, V.; Dürr, H.R. Survival and prognostic factors in conventional central chondrosarcoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosma, S.E.; Ayu, O.; Fiocco, M.; Gelderblom, H.; Dijkstra, P.D.S. Prognostic factors for survival in Ewing sarcoma: A systematic review. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterwimmer, F.; Consalvo, S.; Neumann, J.; Rueckert, D.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Burgkart, R. Applications of machine learning for imaging-driven diagnosis of musculoskeletal malignancies—A scoping review. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 7173–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Chen, E.; Banerjee, O.; Topol, E.J. AI in health and medicine. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlap, P.; Min, H.; Vandenberg, N.; Dowling, J.; Holloway, L.; Haworth, A. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, P.; Singh, P.; Gupta, P.; Bhatia, T. Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Transfer Learning for Detecting Pneumonia on Chest X-rays. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Pan, I.; Bao, B.; Halsey, K.; Chang, M.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Sebro, R.A.; Guan, J.; Yi, T.; et al. Deep learning-based classification of primary bone tumors on radiographs: A preliminary study. EBioMedicine 2020, 62, 103121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consalvo, S.; Hinterwimmer, F.; Neumann, J.; Steinborn, M.; Salzmann, M.; Seidl, F.; Lenze, U.; Knebel, C.; Rueckert, D.; Burgkart, R.H.H. Two-Phase Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection and Differentiation of Ewing Sarcoma and Acute Osteomyelitis in Paediatric Radiographs. Anticancer. Res. 2022, 42, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.T.; Jung, S.T.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Multi-Level Seg-Unet Model with Global and Patch-Based X-ray Images for Knee Bone Tumor Detection. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scitkit. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Cai, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ye, J.; Yang, D. A multimodal transformer to fuse images and metadata for skin disease classification. Vis. Comput. 2022, 39, 2781–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, K.; Zhao, S.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Hua, X.-S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. RemixFormer: A Transformer Model for Precision Skin Tumor Differential Diagnosis via Multi-Modal Imaging and Non-Imaging Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 624–633. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Hafeez, A. COVID-ResNet: A Deep Learning Framework for Screening of COVID19 from Radiographs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14395. [Google Scholar]



| Entity | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Ewing’s sarcoma | 1 | 0.6% |
| Chondrosarcoma | 3 | 1.7% |
| Giant cell tumor | 3 | 1.7% |
| Enchondroma | 5 | 2.8% |
| Chondroblastoma | 10 | 5.7% |
| Non-ossifying Fibroma | 25 | 14.2% |
| Osteosarcoma | 41 | 23.3% |
| Osteochondroma | 88 | 50.0% |
| Total | 176 | 100.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breden, S.; Hinterwimmer, F.; Consalvo, S.; Neumann, J.; Knebel, C.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Burgkart, R.H.; Lenze, U. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Bone Tumors around the Knee in X-rays of Children. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185960
Breden S, Hinterwimmer F, Consalvo S, Neumann J, Knebel C, von Eisenhart-Rothe R, Burgkart RH, Lenze U. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Bone Tumors around the Knee in X-rays of Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185960
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreden, Sebastian, Florian Hinterwimmer, Sarah Consalvo, Jan Neumann, Carolin Knebel, Rüdiger von Eisenhart-Rothe, Rainer H. Burgkart, and Ulrich Lenze. 2023. "Deep Learning-Based Detection of Bone Tumors around the Knee in X-rays of Children" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185960
APA StyleBreden, S., Hinterwimmer, F., Consalvo, S., Neumann, J., Knebel, C., von Eisenhart-Rothe, R., Burgkart, R. H., & Lenze, U. (2023). Deep Learning-Based Detection of Bone Tumors around the Knee in X-rays of Children. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185960






