Benralizumab Efficacy in Late Non-Responders to Mepolizumab and Variables Associated with Occurrence of Switching: A Real-Word Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
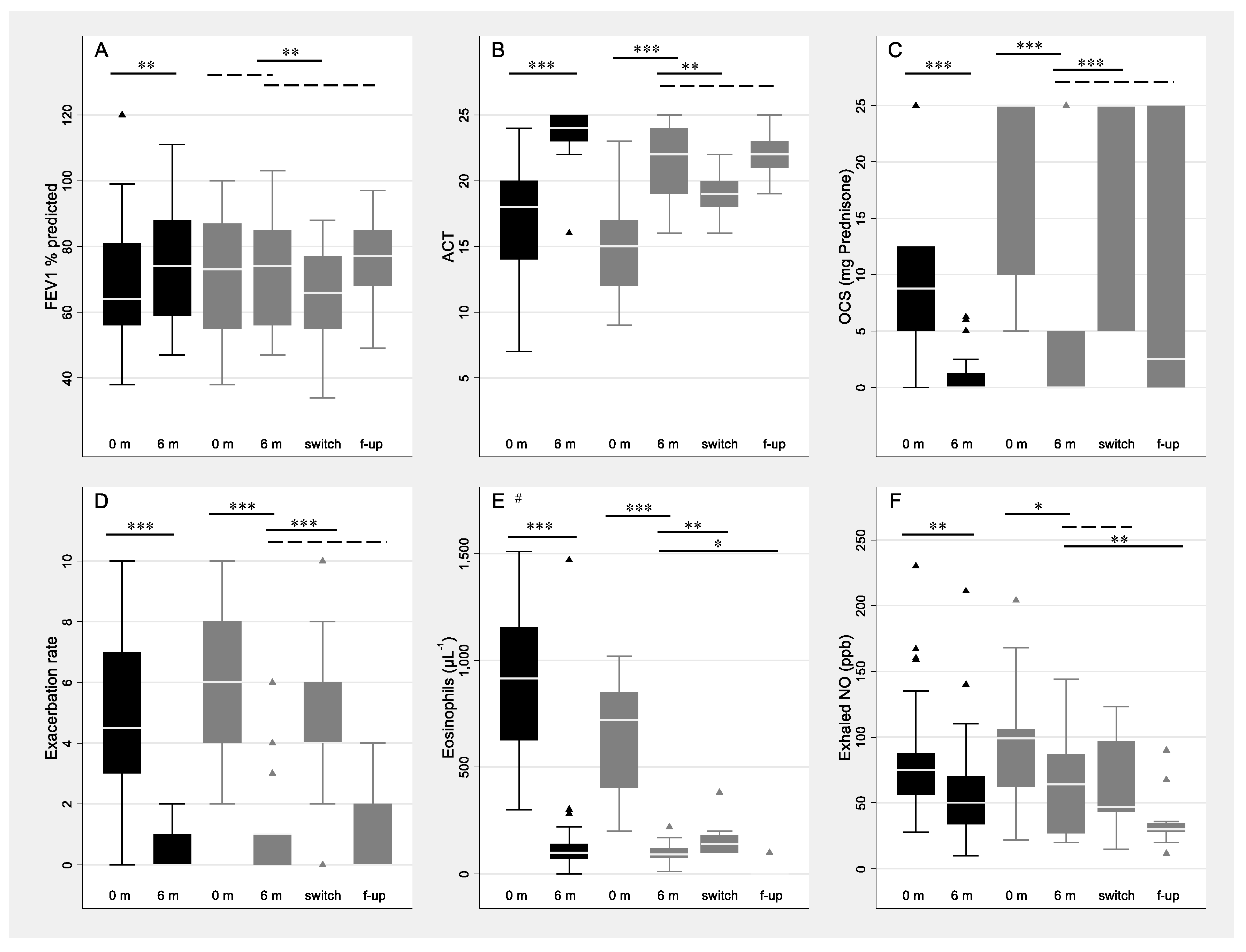
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caminati, M.; Bagnasco, D.; Rosenwasser, L.J.; Vianello, A.; Senna, G. Biologics for the Treatments of Allergic Conditions: Severe Asthma. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2020, 40, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency, Nucala European Public Assessment Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/nucala (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- European Medicines Agency, Fasenra European Public Assessment Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/fasenra (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Drick, N.; Milger, K.; Seeliger, B.; Fuge, J.; Korn, S.; Buhl, R.; Schuhmann, M.; Herth, F.; Kendziora, B.; Behr, J.; et al. Switch from IL-5 to IL-5-Receptor α Antibody Treatment in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 11, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yasuba, H. Role of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in switching to benralizumab treatment in mepolizumab responders. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 58, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, J.E.; Hearn, A.P.; d’Ancona, G.; Dhariwal, J.; Roxas, C.; Green, L.; Thomson, L.; Fernandes, M.; Kent, B.D.; Nanzer, A.M.; et al. Benralizumab after sub-optimal response to mepolizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma. Allergy 2021, 76, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khatri, S.; Moore, W.; Gibson, P.G.; Leigh, R.; Bourdin, A.; Maspero, J.; Barros, M.; Buhl, R.; Howarth, P.; Albers, F.C.; et al. Assessment of the long-term safety of mepolizumab and durability of clinical response in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1742–1751.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, T.; Canonica, G.W.; Chupp, G.; Lee, J.; Schleich, F.; Welte, T.; Valero, A.; Gemzoe, K.; Maxwell, A.; Joksaite, S.; et al. Real-world mepolizumab in the prospective severe asthma REALITI-A study: Initial analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminati, M.; Senna, G.; Guerriero, M.; Dama, A.R.; Chieco-Bianchi, F.; Stefanizzi, G.; Montagni, M.; Ridolo, E. Omalizumab for severe allergic asthma in clinical trials and real-life studies: What we know and what we should address. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffler, E.; Paoletti, G.; Giorgis, V.; Puggioni, F.; Racca, F.; Del Giacco, S.; Bagnasco, D.; Caruso, C.; Brussino, L.; Rolla, G.; et al. Real-life studies of biologics used in asthma patients: Key differences and similarities to trials. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J. Variability of Type 2 inflammatory markers guiding biologic therapy of severe asthma: A 5-year retrospective study from a single tertiary hospital. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, M.; Koenderman, L. Immunological and hematological effects of IL-5(Rα)-targeted therapy: An overview. Allergy 2018, 73, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bleecker, E.R.; Wechsler, M.E.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wu, Y.; Hirsch, I.; Goldman, M.; Newbold, P.; Zangrilli, J.G. Baseline patient factors impact on the clinical efficacy of benralizumab for severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Baseline Characteristic | Missing Data (n, %) | Non-Switch Subgroup (n = 38) | Switch Subgroup (n = 30) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) Adjusted for Daily OCS Dose at Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | - | 58 (53, 67) | 52.5 (45, 57) | 0.93 (0.89–0.98) ** | 0.95 (0.89–1.01) |
| Sex (Female, n) (%) | - | 22 (58) | 21 (70) | 1.70 (0.62–4.67) | 1.58 (0.46–5.46) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 4 (6%) | 24.1 (22.1, 26.7) | 22.8 (20.8, 27.0) | 0.99 (0.86–1.13) | 1.03 (0.87–1.22) |
| Nasal polyps (n, %) | - | 17 (45) | 19 (63) | 2.13 (0.80–5.68) | 2.54 (0.76–8.55) |
| FEV1, L | 2 (3%) | 1.9 (1.3, 2.4) | 1.9 (1.3, 2.2) | 0.97 (0.46–2.02) | 0.77 (0.31–1.93) |
| FEV1 % predicted | 3 (4%) | 64 (56, 81) | 63.5 (48, 77) | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) | 0.98 (0.95–1.02) |
| Tiffeneau Index, % | 2 (3%) | 64 (59, 68) | 63 (54, 75) | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | 1.00 (0.94–1.05) |
| FeNO, ppb | 5 (7%) | 74.5 (54, 88) | 62 (35, 102) | 0.97 (0.88–1.08) b | 0.97 (0.86–1.10) b |
| Blood eosinophils, µL−1 | 5 (7%) | 860 (560, 1140) | 490 (340, 750) | 0.85 (0.73–0.99) c * | 0.88 (0.75–1.05) c |
| ACT score | 1 (1%) | 18 (14, 20) | 14.5 (12, 18) | 0.92 (0.83–1.03) | 0.96 (0.85–1.08) |
| Exacerbations in the last year (n) | - | 4.5 (3, 7) | 5 (4, 8) | 1.07 (0.90–1.28) | 0.96 (0.78–1.19) |
| OCS, daily prednisone dose (mg) | 6 (9%) | 7.5 (5, 12.5) | 25 (12.5, 25) | 1.15 (1.07–1.24) *** | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caminati, M.; Marcon, A.; Guarnieri, G.; Miotti, J.; Bagnasco, D.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Pelaia, G.; Vaia, R.; Maule, M.; Vianello, A.; et al. Benralizumab Efficacy in Late Non-Responders to Mepolizumab and Variables Associated with Occurrence of Switching: A Real-Word Perspective. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051836
Caminati M, Marcon A, Guarnieri G, Miotti J, Bagnasco D, Carpagnano GE, Pelaia G, Vaia R, Maule M, Vianello A, et al. Benralizumab Efficacy in Late Non-Responders to Mepolizumab and Variables Associated with Occurrence of Switching: A Real-Word Perspective. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051836
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaminati, Marco, Alessandro Marcon, Gabriella Guarnieri, Jessica Miotti, Diego Bagnasco, Giovanna Elisiana Carpagnano, Girolamo Pelaia, Rachele Vaia, Matteo Maule, Andrea Vianello, and et al. 2023. "Benralizumab Efficacy in Late Non-Responders to Mepolizumab and Variables Associated with Occurrence of Switching: A Real-Word Perspective" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051836
APA StyleCaminati, M., Marcon, A., Guarnieri, G., Miotti, J., Bagnasco, D., Carpagnano, G. E., Pelaia, G., Vaia, R., Maule, M., Vianello, A., & Senna, G. (2023). Benralizumab Efficacy in Late Non-Responders to Mepolizumab and Variables Associated with Occurrence of Switching: A Real-Word Perspective. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1836. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051836










