The Prevalence and Risk Analysis of Cerebral Palsy and Other Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Children with Low Birth Weight in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definition of Comorbidities
2.2. Maternal Biopsychosocial Factors
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Comorbidities of Premature Infants Stratified by Family Income Levels
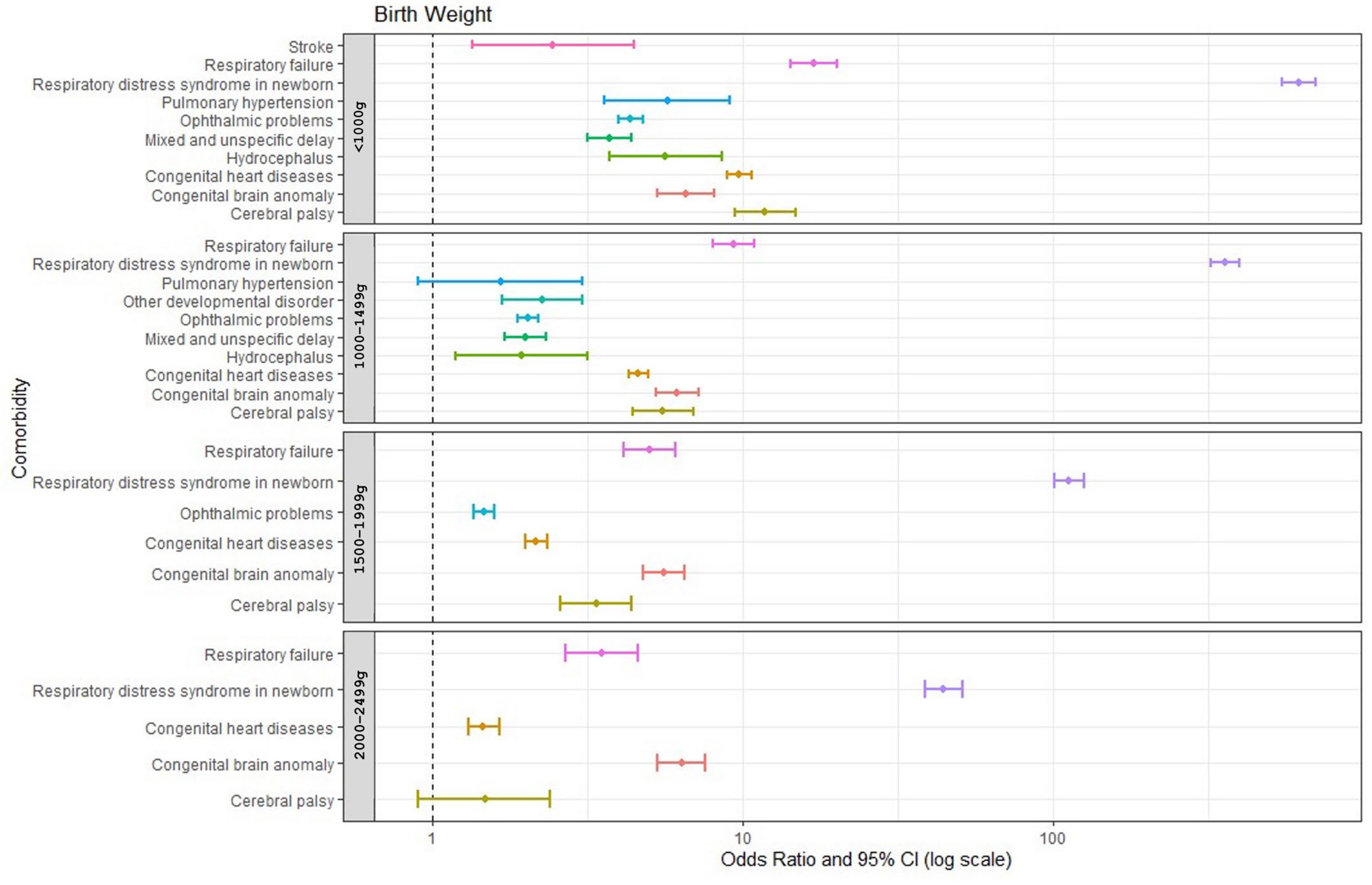
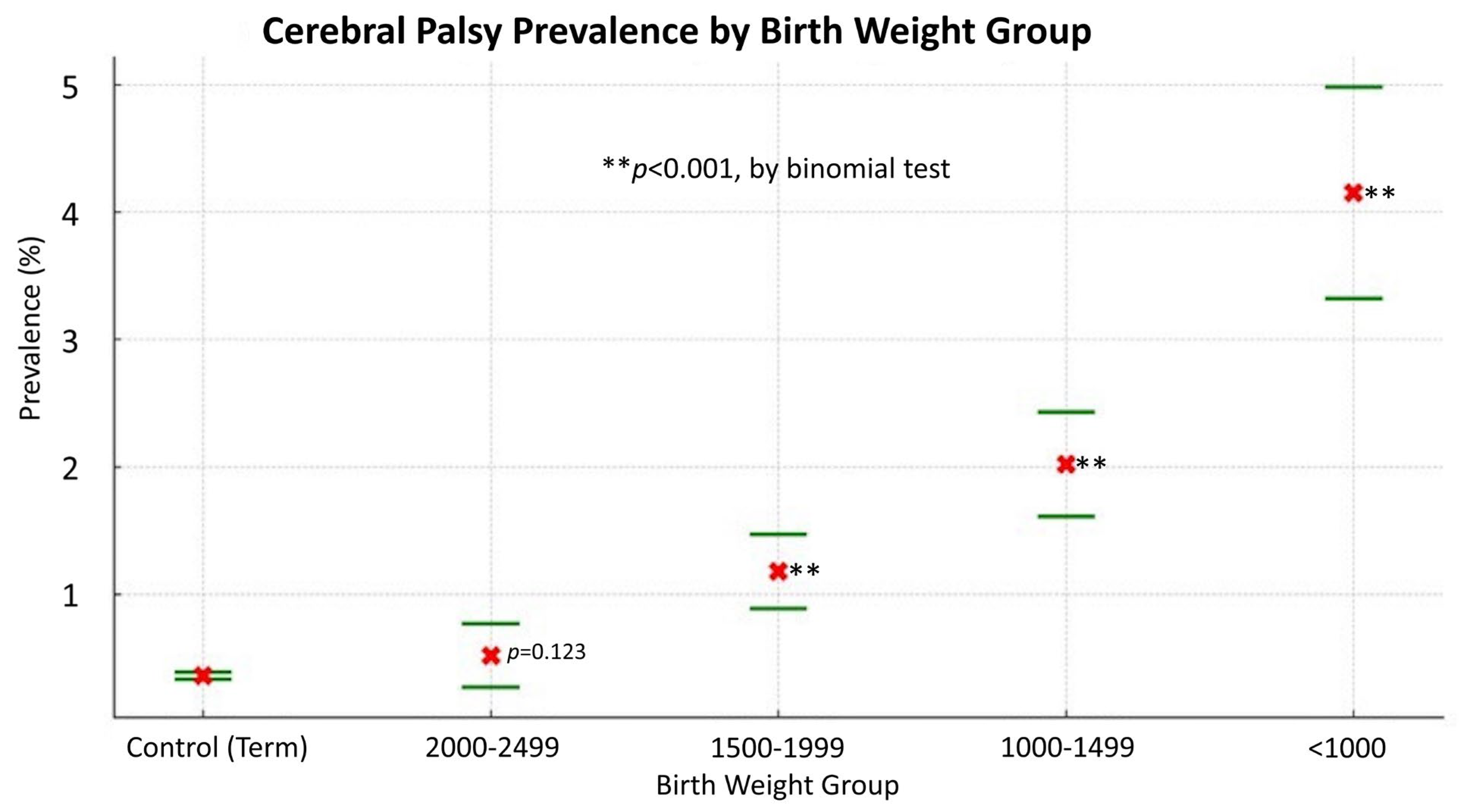
3.3. Common Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Infants Born Prematurely and the Association with Birth Weight
3.4. Inpatient Care Use
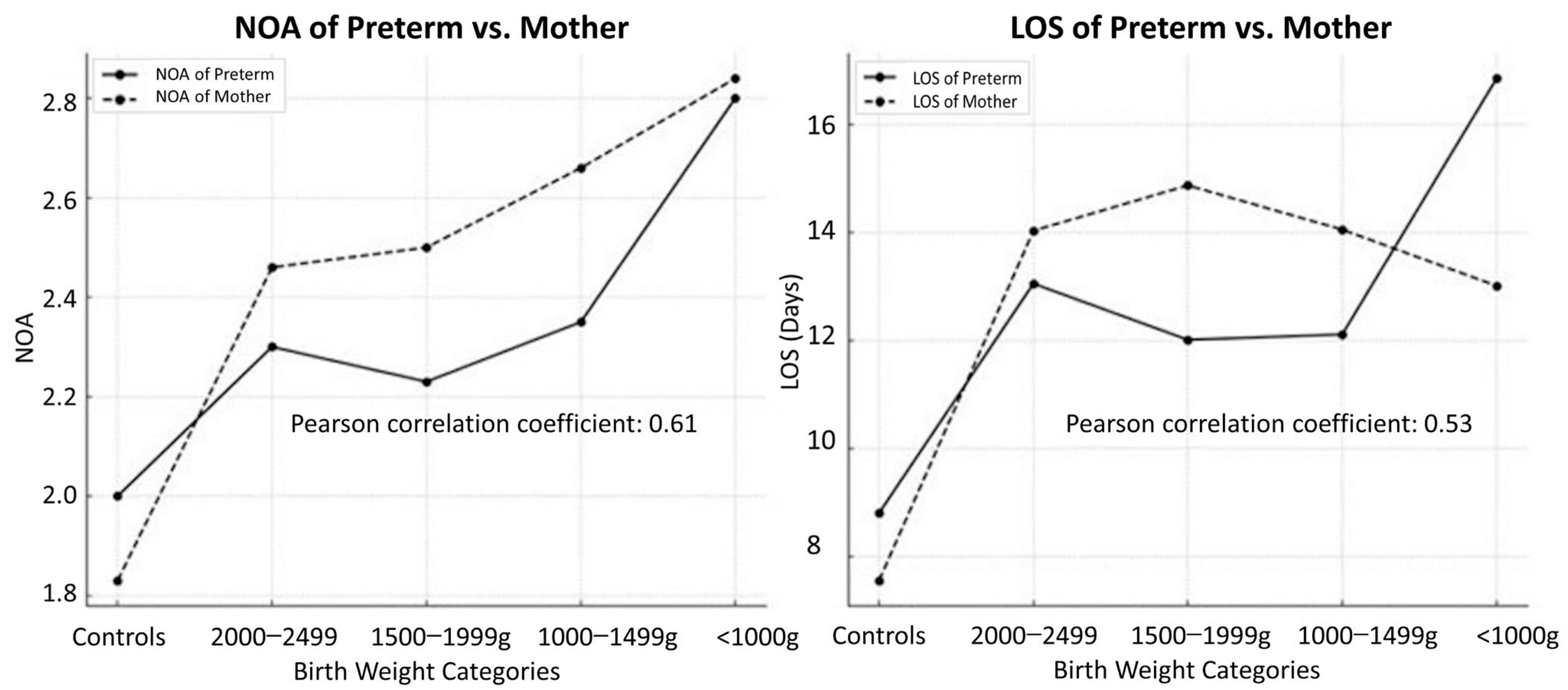
3.5. NOA and LOS Correlations for Preterm Infants and Mothers
3.6. Association between Low Birth Weight and Maternal Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, H.C.; Ho, L.I.; Chi, C.S.; Cheng, S.N.; Juan, C.J.; Chiang, K.L.; Lin, S.Z.; Harn, H.J. Current proceedings of cerebral palsy. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P. Cerebral palsy: What parents and doctors want to know. BMJ 2003, 326, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneth, N. Cerebral palsy as a public health indicator. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2023, 37, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, N.; McIntyre, S.; Hunt, R.W. Perinatal care with a view to preventing cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021, 63, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskoui, M.; Coutinho, F.; Dykeman, J.; Jette, N.; Pringsheim, T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.T.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; Hsu, C.T.; Lin, M.C. Maternal risk factors for preterm birth in Taiwan, a nationwide population-based cohort study. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2024, 65, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Hwang, Y.S.; Ho, C.H.; Lai, M.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsai, W.H. Prevalence and Initial Diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy in Preterm and Term-Born Children in Taiwan: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, S.; Goldsmith, S.; Webb, A.; Ehlinger, V.; Hollung, S.J.; McConnell, K.; Arnaud, C.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Oskoui, M.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Sjolander, A.; Johansson, S.; Lu, D.; Razaz, N.; Tedroff, K.; Villamor, E.; Cnattingius, S. Impact of gestational age on risk of cerebral palsy: Unravelling the role of neonatal morbidity. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 50, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Ehlinger, V.; Delobel-Ayoub, M.; Klapouszczak, D.; Perra, O.; Hensey, O.; Neubauer, D.; Hollody, K.; Virella, D.; Rackauskaite, G.; et al. Trends in Prevalence and Severity of Pre/Perinatal Cerebral Palsy Among Children Born Preterm From 2004 to 2010: A SCPE Collaboration Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 624884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Fan, H.C.; Kuo, F.C. Prolonged length of stay for acute hospital admissions as the increasing of age: A nationwide population study for Taiwan’s patients with cerebral palsy. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2019, 60, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.L.; Kuo, F.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Chang, K.P. Prevalence and demographic characteristics of comorbid epilepsy in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: A nationwide population-based study. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2019, 35, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Su, C.C.; Shao, S.C.; Sung, S.F.; Lin, S.J.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lai, E.C. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.J.; Ma, H.I.; Lu, T.H. Estimating the prevalence of cerebral palsy in Taiwan: A comparison of different case definitions. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 36C, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.J.; Hope, P.L.; Johnson, A. Neonatal risk factors for cerebral palsy in very preterm babies: Case-control study. BMJ 1997, 314, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyama, M.; Touyama, J.; Toyokawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Trends in the prevalence of cerebral palsy in children born between 1988 and 2007 in Okinawa, Japan. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeon, H.R.; Shin, J.C.; Youk, T.; Kim, J. Incidence of Cerebral Palsy in Korea and the Effect of Socioeconomic Status: A Population-Based Nationwide Study. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Chen, L.S.; Yen, M.F.; Chen, H.H.; Liou, H.H. Geographic variation in the age- and gender-specific prevalence and incidence of epilepsy: Analysis of Taiwanese National Health Insurance-based data. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, N.; Hurvitz, E.A.; Peterson, M.D. Multimorbidity in Middle-Aged Adults with Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 744.e749–744.e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, K.; Metsala, J.; Pulakka, A.; Nilsen, S.M.; Kivimaki, M.; Risnes, K.; Kajantie, E. Preterm birth and the risk of multimorbidity in adolescence: A multiregister-based cohort study. Lancet Public Health 2023, 8, e680–e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.K.; Tseng, Y.T.; Chen, K.T. The epidemiologic characteristics and associated risk factors of preterm birth from 2004 to 2013 in Taiwan. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laverty, C.; Surtees, A.; O’Sullivan, R.; Sutherland, D.; Jones, C.; Richards, C. The prevalence and profile of autism in individuals born preterm: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2021, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spittle, A.J.; Morgan, C.; Olsen, J.E.; Novak, I.; Cheong, J.L.Y. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Cerebral Palsy in Children with a History of Preterm Birth. Clin. Perinatol. 2018, 45, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaski, M.; Majnemer, A.; Oskoui, M. Contribution of socio-economic status on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic search and review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faramarzi, R.; Darabi, A.; Emadzadeh, M.; Maamouri, G.; Rezvani, R. Predicting neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants: A comprehensive evaluation of neonatal and maternal risk factors. Early Hum. Dev. 2023, 184, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadi, J.; Hyder, S.; Rodriguez Ormaza, N.P.; Twer, E.; Phillips, M.; Akinkuotu, A.; Reid, T.D. Evaluation of Complications and Weight Outcomes in Pediatric Cerebral Palsy Patients With Gastrostomy Tubes. Am. Surg. 2023, 89, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehretie, Y.; Amare, A.T.; Getnet, G.B.; Mekonnen, B.A. Length of hospital stay and factors associated with very-low-birth-weight preterm neonates surviving to discharge a cross-sectional study, 2022. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.P.; Chawanpaiboon, S.; Moller, A.B.; Watananirun, K.; Bonet, M.; Lumbiganon, P. The global epidemiology of preterm birth. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 52, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, A.M.; Salinas, Y.D.; DeWan, A.T.; Hawley, N.L.; Donohue, P.K.; Strobino, D.M. Risks of preterm birth among non-Hispanic black and non-Hispanic white women: Effect modification by maternal age. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2019, 33, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaz, N.; Cnattingius, S.; Lisonkova, S.; Nematollahi, S.; Oskoui, M.; Joseph, K.S.; Kramer, M. Pre-pregnancy and pregnancy disorders, pre-term birth and the risk of cerebral palsy: A population-based study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundelin, H.E.K.; Stephansson, O.; Johansson, S.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Pregnancy outcome in women with cerebral palsy: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subcategories of Preterm Birth or Low Birth Weight | ICD 9 Codes |
|---|---|
| Extremely preterm (<1000 g) | 765.01, 765.02, 765.03, 765.11, 765.12, 765.13, V21.31, V21.32 |
| Very preterm (1000–1499 g) | 765.04, 765.05, 765.14, 765.15, V21.33 |
| Moderately preterm (1500–1999 g) | 765.06, 765.07, 765.16, 765.17, V21.34 |
| Late preterm (2000–2499 g) | 765.08, 765.18, V21.35 |
| Enrollees n (%) | Controls n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth weight | |||
| Total sample size | 15,181 | 151,810 | |
| <1000 g | 2241 (14.76) | ||
| 1000–1499 g | 4461 (29.39) | ||
| 1500–1999 g | 5240 (34.52) | ||
| 2000–2500 g | 3239 (21.34) | ||
| Sex | |||
| Female | 7119 (46.89) | 71,190 (46.89) | |
| Male | 8062 (53.11) | 80,620 (53.11) | 1.000 1 |
| Income | |||
| 1 (Lowest) | 3447 (22.71) | 17,525 (11.54) | |
| 2 | 5756 (37.92) | 61,905 (40.78) | |
| 3 | 4026 (26.52) | 48,524 (31.96) | |
| 4 (Highest) | 1952 (12.86) | 23,856 (15.71) | <0.001 2 |
| Location | |||
| Northern | 7263 (47.84) | 81,875 (53.93) | |
| Central | 3661 (24.12) | 32,401 (21.34) | |
| Southern | 3982 (26.23) | 35,252 (23.22) | |
| Eastern | 267 (1.76) | 2032 (1.33) | |
| Off-island | 8 (0.05) | 250 (0.18) | <0.001 2 |
| Maternal age | |||
| <20 years | 42 (0.77) | 331 (0.57) | |
| 20–30 years | 1512 (27.66) | 20,286 (34.99) | |
| 30–40 years | 3680 (67.33) | 35,921 (61.96) | |
| ≥40 years | 232 (4.24) | 1436 (2.48) | <0.001 2 |
| Comorbidities | Income Level (in NTD) | Enrollees | Controls | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10,000 (lowest) | 1506 | 9860 | 2.31 | (2.11, 1.31) | |
| 10,001–25,000 | 3039 | 37,857 | 1.21 | (1.12, 1.31) | |
| Respiratory | 25,001–50,000 | 2003 | 28,374 | 1.07 | (0.98, 1.16) |
| >50,001 (highest) | 872 | 13,197 | --- | --- | |
| 0–10,000 (lowest) | 510 | 1031 | 2.68 | (2.27, 3.10) | |
| 10,001–25,000 | 1343 | 4756 | 1.53 | (1.34, 1.73) | |
| Circulatory | 25,001–50,000 | 906 | 3812 | 1.29 | (1.12, 1.46) |
| >50,001 (highest) | 360 | 1954 | --- | --- | |
| 0–10,000 (lowest) | 72 | 693 | 1.10 | (0.75, 1.45) | |
| 10,001–25,000 | 321 | 3250 | 1.05 | (0.80, 1.29) | |
| Neurological | 25,001–50,000 | 205 | 2314 | 0.94 | (0.71, 1.17) |
| >50,001 (highest) | 105 | 1112 | --- | --- | |
| 0–10,000 (lowest) | 567 | 1835 | 2.61 | (2.25, 2.97) | |
| 10,001–25,000 | 1459 | 8218 | 1.50 | (1.32, 1.67) | |
| Psycho-developmental | 25,001–50,000 | 964 | 6513 | 1.25 | (1.10, 1.40) |
| >50,001 (highest) | 417 | 3517 | --- | --- | |
| 0–10,000 (lowest) | 405 | 6539 | 1.51 | (1.29, 1.73) | |
| 10,001–25,000 | 1091 | 26,420 | 1.01 | (0.88, 1.13) | |
| GI and nutritional | 25,001–50,000 | 721 | 19,508 | 0.90 | (0.78, 1.02) |
| >50,001 (highest) | 362 | 8821 | --- | --- |
| Comorbidities | Birth Weight Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1000 g (OR, 95% CI) | 1000–1499 g (OR, 95% CI) | 1500–1999 g (OR, 95% CI) | 2000–2499 g (OR, 95% CI) | |
| Neurological: | 4.27 (3.92, 4.65) | 2.08 (1.94, 2.23) | 1.53 (1.42, 1.64) | 1.11 (1.01, 1.22) |
| Congenital brain anomaly | 6.55 (5.30–8.09) | 6.14 (5.24–7.20) | 5.54 (4.75–6.47) | 6.35 (5.31–7.59) |
| Cerebral palsy | 11.80 (9.42–14.79) | 5.53 (4.41–6.93) | 3.36 (2.57–4.38) | 1.47 (0.90–2.39) |
| Hydrocephalus | 5.63 (3.71–8.54) | 1.93 (1.18–3.16) | 0.87 (0.44–1.70) | 0.61 (0.22–1.68) |
| Stroke | 2.44 (1.34–4.44) | 0.87 (0.43–1.74) | 0.46 (0.19–1.11) | 0.44 (0.14–1.33) |
| Ophthalmic problems | 4.34 (3.96–4.75) | 2.02 (1.87–2.19) | 1.46 (1.35–1.58) | 0.94 (0.84–1.06) |
| Hearing problems | 1.12 (0.83–1.51) | 0.82 (0.64–1.05) | 0.42 (0.31–0.58) | 0.17 (0.10–0.31) |
| Epilepsy | 0.99 (0.74–1.39) | 0.53 (0.39–0.72) | 0.43 (0.32–0.59) | 0.38 (0.25–0.57) |
| Movement disorders | 0.17 (0.06–0.54) | 0.20 (0.10–0.41) | 0.10 (0.04–0.25) | 0.04 (0.01–0.17) |
| Sleep disorders | 0.44 (0.11–1.67) | 0.22 (0.06–0.82) | 0.10 (0.02–0.57) | 0.00 (0.00–0.60) |
| Psycho-developmental: | 2.09 (1.82–2.41) | 1.27 (1.12–1.44) | 0.62 (0.53–0.73) | 0.35 (0.27–0.45) |
| Developmental delay | 2.69 (2.32–3.12) | 1.58 (1.39–1.80) | 0.78 (0.67–0.92) | 0.43 (0.33–0.56) |
| Mixed and nonspecific delay | 3.70 (3.14–4.36) | 1.99 (1.71–2.31) | 0.94 (0.77–1.14) | 0.44 (0.31–0.62) |
| Other developmental disorder | 2.44 (1.64–3.63) | 2.25 (1.67–3.02) | 1.14 (0.79–1.66) | 0.83 (0.49–1.41) |
| Speech or language developmental disorder | 0.73 (0.51–1.04) | 0.45 (0.33–0.60) | 0.30 (0.21–0.43) | 0.21 (0.12–0.35) |
| Developmental coordination disorder | 0.69 (0.27–1.74) | 0.75 (0.40–1.42) | 0.36 (0.15–0.85) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Learning disability | 1.49 (0.37–6.00) | 1.11 (0.36–3.45) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Childhood emotional disturbances | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.12 (0.02–0.68) | 0.11 (0.02–0.57) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| ADHD | 0.33 (0.13–0.79) | 0.25 (0.13–0.50) | 0.21 (0.10–0.44) | 0.15 (0.05–0.44) |
| Intellectual disabilities | 0.34 (0.05–2.26) | 0.51 (0.17–1.54) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Autistic spectrum disorder | 0.37 (0.10–1.34) | 0.26 (0.09–0.78) | 0.23 (0.08–0.70) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Anxiety | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.22 (0.03–1.58) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Acute stress reaction | 1.80 (0.25–13.24) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Birth Weight | Mean | Standard Deviation | Number of Patients | p-Value 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOA 1 of preterm infants | <1000 g | 2.80 | 2.67 | 1243 | <0.001 |
| 1000–1499 g | 2.35 | 2.30 | 2045 | ||
| 1500–1999 g | 2.23 | 2.27 | 2153 | ||
| 2000–2499 g | 2.30 | 2.32 | 1306 | ||
| Control | 2.00 | 1.89 | 79,466 | ||
| LOS 2 of preterm infants | <1000 g | 16.85 | 26.07 | 1243 | <0.001 |
| 1000–1499 g | 12.11 | 17.55 | 2045 | ||
| 1500–1999 g | 12.01 | 21.28 | 2153 | ||
| 2000–2499 g | 13.05 | 23.25 | 1306 | ||
| Control | 8.80 | 12.96 | 79,466 | ||
| NOA of mothers | <1000 g | 2.84 | 1.79 | 758 | <0.001 |
| 1000–1499 g | 2.66 | 1.97 | 1561 | ||
| 1500–1999 g | 2.50 | 1.53 | 1911 | ||
| 2000–2499 g | 2.46 | 1.51 | 1236 | ||
| Control | 1.83 | 1.15 | 57,974 | ||
| LOS of mothers | <1000 g | 13.01 | 13.55 | 758 | <0.001 |
| 1000–1499 g | 14.05 | 16.08 | 1561 | ||
| 1500–1999 g | 14.87 | 16.64 | 1911 | ||
| 2000–2499 g | 14.03 | 14.01 | 1236 | ||
| Control | 7.55 | 8.20 | 57,974 |
| Maternal Age | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <20 Years | 20–30 Years | 30–40 Years | ≥40 Years | |||||
| Birth weight | n, OR 1 (95% CI) | |||||||
| Enrollees | 42 | 1.70 (1.23–2.36) | 1512 | --- | 3680 | 1.37 (1.29–1.46) | 232 | 2.17 (1.86–2.51) |
| <1000 g | 7 | 2.29 (1.07–4.92) | 187 | --- | 530 | 1.60 (1.35–1.89) | 34 | 2.57 (1.78–3.72) |
| 1000–1499 g | 16 | 2.25 (1.35–3.75) | 436 | --- | 1044 | 1.35 (1.21–1.51) | 65 | 2.11 (1.61–2.75) |
| 1500–1999 g | 11 | 1.23 (0.67–2.26) | 546 | --- | 1286 | 1.33 (1.20–1.47) | 68 | 1.76 (1.36–2.28) |
| 2000–2499 g | 8 | 1.43 (0.70–2.91) | 343 | --- | 820 | 1.35 (1.19–1.53) | 65 | 2.68 (2.04–3.51) |
| Control group | 331 | --- | 20,286 | --- | 35,921 | --- | 1436 | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Wang, D.-S.; Chen, C.-M.; Hu, S.-W.; Chiang, K.-L.; Kuo, F.-C. The Prevalence and Risk Analysis of Cerebral Palsy and Other Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Children with Low Birth Weight in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123480
Fan H-C, Chang Y-M, Lee J-Y, Wang D-S, Chen C-M, Hu S-W, Chiang K-L, Kuo F-C. The Prevalence and Risk Analysis of Cerebral Palsy and Other Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Children with Low Birth Weight in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123480
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Hueng-Chuen, Yu-Mei Chang, Jen-Yu Lee, Der-Shiun Wang, Chuan-Mu Chen, Shu-Wei Hu, Kuo-Liang Chiang, and Fang-Chuan Kuo. 2024. "The Prevalence and Risk Analysis of Cerebral Palsy and Other Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Children with Low Birth Weight in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123480
APA StyleFan, H.-C., Chang, Y.-M., Lee, J.-Y., Wang, D.-S., Chen, C.-M., Hu, S.-W., Chiang, K.-L., & Kuo, F.-C. (2024). The Prevalence and Risk Analysis of Cerebral Palsy and Other Neuro-Psychological Comorbidities in Children with Low Birth Weight in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3480. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123480










