A Case Report of Malignant Cerebellopontine Angle Lesion Highlighting the Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Challenge in the Case of Unilateral Progressive Hearing Loss
Abstract
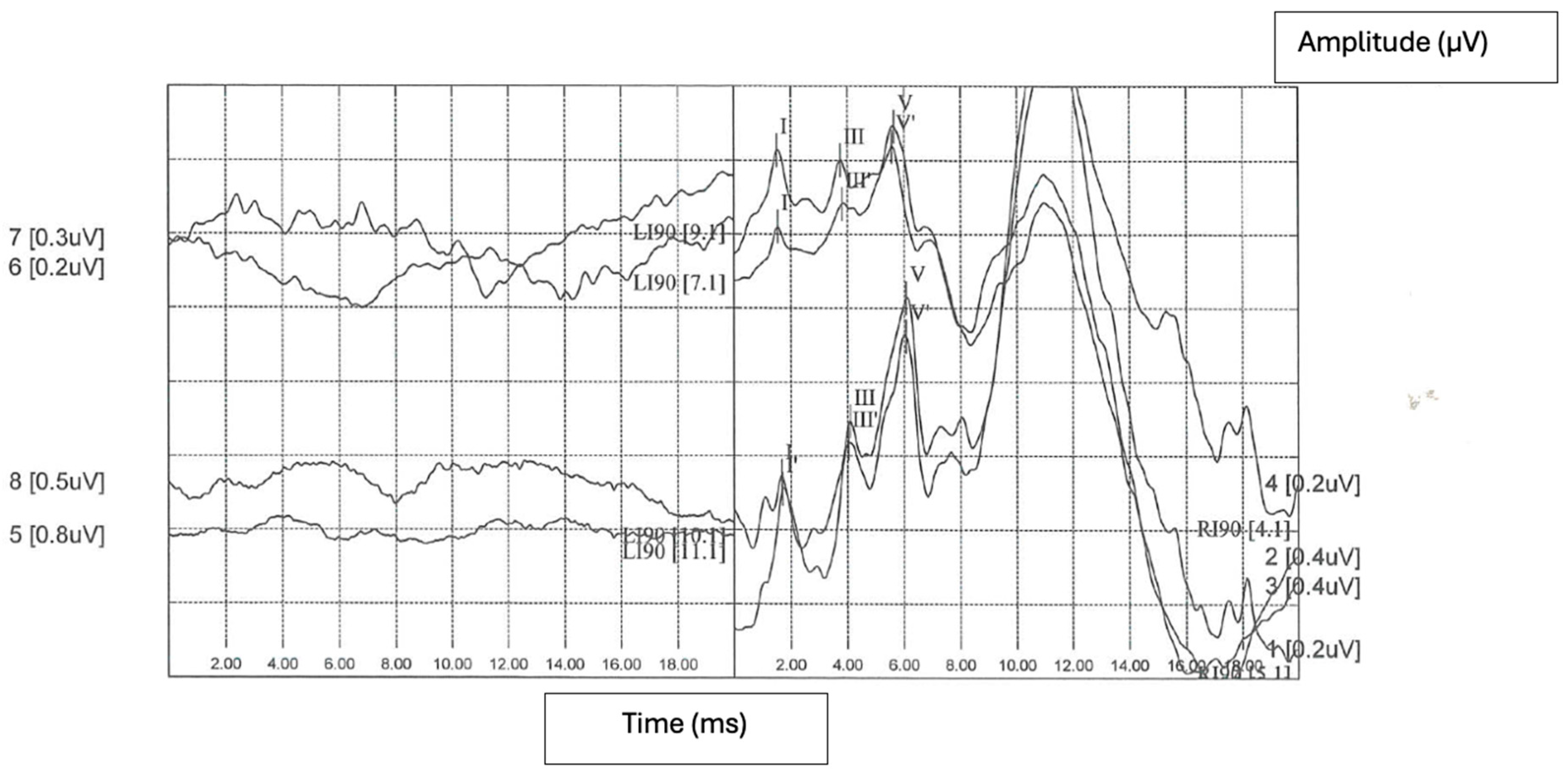
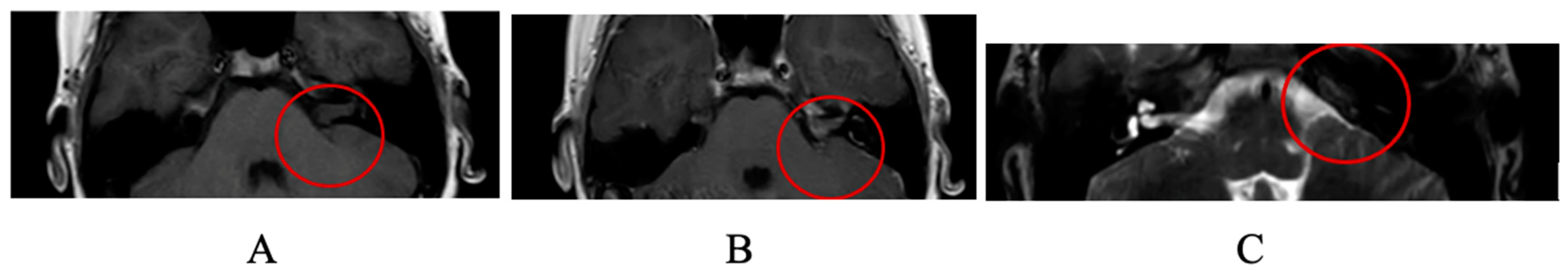
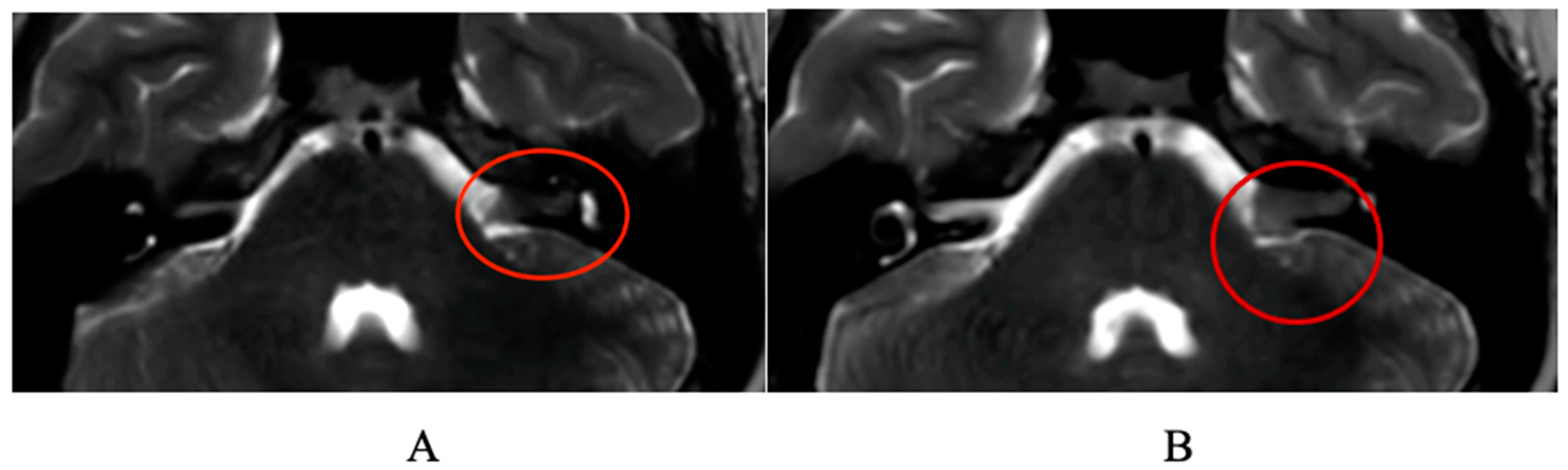
:1. Case Report
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bess, F.H.; Dodd-Murphy, J.; Parker, R.A. Children with minimal sensorineural hearing loss: Prevalence, educational performance, and functional status. Ear Hear. 1998, 19, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, J.; West, K.P., Jr.; Khatry, S.K.; Wu, L.; LeClerq, S.C.; Karna, S.L.; Katz, J.; Sommer, A.; Pillion, J. Vitamin A supplementation in preschool children and risk of hearing loss as adolescents and young adults in rural Nepal: Randomised trial cohort follow-up study. BMJ 2012, 344, d7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinwald, J.; DeAlarcon, A.; Cohen, A.; Uwiera, T.; Zhang, K.; Benton, C.; Halstead, M.; Meinzen-Derr, J. Significance of unilateral enlarged vestibular aqueduct. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Audiology Pediatric Amplification (2013) Updated Clinical Practice Guidelines for Unilateral Hearing Loss Document. Available online: https://audiology-web.s3.amazonaws.com/migrated/PediatricAmplificationGuidelines.pdf_539975b3e7e9f1.74471798.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2013).
- Paul, A.; Marlin, S.; Parodi, M.; Rouillon, I.; Guerlain, J.; Pingault, V.; Couloigner, V.; Garabedian, E.N.; Denoyelle, F.; Loundon, N. Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Medical Context and Etiology. Audiol. Neurotol. 2017, 22, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Varshney, S.; Sood, R.; Kumar, A. Role of Blood Investigations in Idiopathic Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74 (Suppl. S3), 3682–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Liu, T.C. Etiologic and audiologic characteristics of patients with pediatric-onset unilateral and asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beeck Calkoen, E.A.; Aliaga, E.S.; Merkus, P.; Smit, C.F.; van de Kamp, J.M.; Mulder, M.F.; Goverts, S.T.; Hensen, E.F. High prevalence of abnormalities on CT and MR imaging in children with unilateral sensorineural hearing loss irrespective of age or degree of hearing loss. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 97, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.; Di Berardino, F.; Sina, C.; Zanetti, D.; Scola, E.; Gavagna, C.; Gaini, L.; Palumbo, G.; Capaccio, P.; Triulzi, F. MR Imaging in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Time to Talk. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.C.; Carlson, M.L.; Lane, J.I. MRI of the Internal Auditory Canal, Labyrinth, and Middle Ear: How We Do It. Radiology 2020, 297, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valesano, J.C.; Carr, C.M.; Eckel, L.J.; Carlson, M.L.; Lane, J.I. MRI screening of the internal auditory canal: Is gadolinium necessary to detect intralabyrinthine schwannomas? Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortnum, H.; O’Neill, C.; Taylor, R.; Lenthall, R.; Nikolopoulos, T.; Lightfoot, G.; O’Donoghue, G.; Mason, S.; Baguley, D.; Jones, H.; et al. The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the identification of suspected acoustic neuroma: A systematic review of clinical and cost effectiveness and natural history. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, iii–iv, ix–xi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, T.A.; Besachio, D.A.; Quigley, E.P.; Gurgel, R.K.; Shelton, C.; Harnsberger, H.R.; Wiggins, R.H. Diagnostic accuracy of screening MR imag- ing using unenhanced axial CISS and coronal T2WI for detection of small internal au- ditory canal lesions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 2366–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, J.P.; Mandell, D.L.; Arjmand, E.M. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric unilateral and asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss. Arch. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropers, F.G.; Pham, E.N.B.; Kant, S.G.; Rotteveel, L.J.C.; Rings, E.H.H.M.; Verbist, B.M.; Dekkers, O.M. Assessment of the Clinical Benefit of Imaging in Children With Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Muzzi, E.; Gregori, M.; Orzan, E. Inner Ear Malformations and Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss-the Elephant in the Room. JAMA Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thigpen, M.C.; Whitney, C.G.; Messonnier, N.E.; Zell, E.R.; Lynfield, R.; Hadler, J.L.; Harrison, L.H.; Farley, M.M.; Reingold, A.; Bennett, N.M.; et al. Emerging Infections Programs Network. Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1998–2007. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, M.A.; Schmitt, W.R.; Carlson, M.L.; Driscoll, C.L.; Beatty, C.W.; Link, M.J. Pediatric cerebellopontine angle and internal auditory canal tumors. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 12, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, S.; Rashid, R.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Santagata, S. An update on the CNS manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 2. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparella, M.M.; Berlinge, N.T.; Oda, M.; El-fiky, F. Otological manifestations of leukemia. Laryngoscope 1973, 83, 1510–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veling, M.C.; Windmill, I.; Bumpous, J.M. Sudden hearing loss as a presenting manifestation of leukemia. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 1999, 120, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donné, A. Cours de Microscopie Complémentaire des Études Médicales: Anatomie Microscopique et Physiologie des Fluides de L’économie; J.B. Bailliere: Paris, France, 1844. [Google Scholar]
- Ulu, E.M.K.; Töre, H.G.; Bayrak, A.; Güngör, D.; Coskun, M. MRI of central nervous system abnormalities in childhood leukemia. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 15, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Druss, J.G. Aural manifestations of leukemia. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1945, 42, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbrom, E.; Finch, S.C. The auditory manifestations of leukemia. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1958, 31, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shukla, G.K.; Dayal, D.; Gupta, K.R. Otological manifestations of leukemia. Jibiinkoka 1972, 44, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.; Bain, B.; Michaels, L.; Craven, E. Atypical Ph negative chronic myeloid leukemia presenting as sudden profound deaf- ness. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageris, B.; Or, R.; Hardan, I.; Polliack, A. Sudden onset deafness as a presenting manifestation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1993, 9, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genden, E.M.; Bahadori, R.S. Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss as a first symptom of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chim, C.S.; Woo, K.S. Deafness in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1997, 26, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.; Michaels, L.; Wells, D.G. Otolaryngological disturbances in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1977, 2, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shii, T.; Toriyama, M.; Takiguchi, T. Pathological findings in the cochlear duct due to endolymphatic hemorrhage. In Modern Perspectives in Otology; Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology; Karger Publishers: Berlin, Germany, 1983; Volume 31, pp. 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Politzer, A. Pathologische Veranderungen im bie leukaemischer Taubheit. Conger Intern. d’Otok Compt Rend 1885, 3, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Schuknecht, H.F.; Igarashi, M.; Chasin, W.D. Inner ear hem- orrhage in leukemia. A case report. Laryngoscope 1965, 75, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVenuta, F.; Moore, J.A. Involvement of the inner ear in acute stem cell leukemia. Report of two cases. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1972, 81, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, S.; Saito, H.; Morimoto, M.; Takahashi, K. Sudden deafness due to inner ear haemorrhage. Otologia 1975, 21 (Suppl. S2), 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Sando, I.; Egami, T. Inner ear hemorrhage and endolymphatic hydrops in a leukemic patient with sudden hearing loss. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1977, 86, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, T.; Kaga, K.; Kodama, A. Temporal bone pathology of a patient without hearing and caloric reaction, and with counter- rolling after chronic myelocytic leukemia. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1989, 108 (Suppl. S468), 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallpike, C.S.; Harrison, M.S. Clinical and pathological observa- tions on a case of leukemia with deafness and vertigo. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1950, 64, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, M.R.; Stein, R.S.; Dessypris, E.N. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia with hyperleukocytosis—The hyperviscosity syn- drome. Cancer 1985, 56, 2865–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagare, A.B.; Krajewski, K.M.; Hornick, J.L.; Zukotynski, K.; Kurra, V.; Jagannathan, J.P.; Ramaiya, N.H. MRI for evaluation of myeloid sarcoma in adults: A single-institution 10-year experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, S.K.B.; Redjal, N. Acute lymphocytic leukemia presenting as a single brain mass. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 33, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzolino, R.; Castro, V.; Gambacorta, V.; Tonon, E.; Cattaruzzi, E.; Orzan, E. A Case Report of Malignant Cerebellopontine Angle Lesion Highlighting the Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Challenge in the Case of Unilateral Progressive Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123483
Marzolino R, Castro V, Gambacorta V, Tonon E, Cattaruzzi E, Orzan E. A Case Report of Malignant Cerebellopontine Angle Lesion Highlighting the Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Challenge in the Case of Unilateral Progressive Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123483
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzolino, Riccardo, Veronica Castro, Valeria Gambacorta, Eleonora Tonon, Elisabetta Cattaruzzi, and Eva Orzan. 2024. "A Case Report of Malignant Cerebellopontine Angle Lesion Highlighting the Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Challenge in the Case of Unilateral Progressive Hearing Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123483
APA StyleMarzolino, R., Castro, V., Gambacorta, V., Tonon, E., Cattaruzzi, E., & Orzan, E. (2024). A Case Report of Malignant Cerebellopontine Angle Lesion Highlighting the Interdisciplinary Diagnostic Challenge in the Case of Unilateral Progressive Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123483





