Importance of Blood Glucose Measurement for Predicting the Prognosis of Long COVID: A Retrospective Study in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Definitions of Patients’ Groups with Long COVID
2.2. Evaluation of Patients’ Clinical Conditions
2.3. Laboratory Examinations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
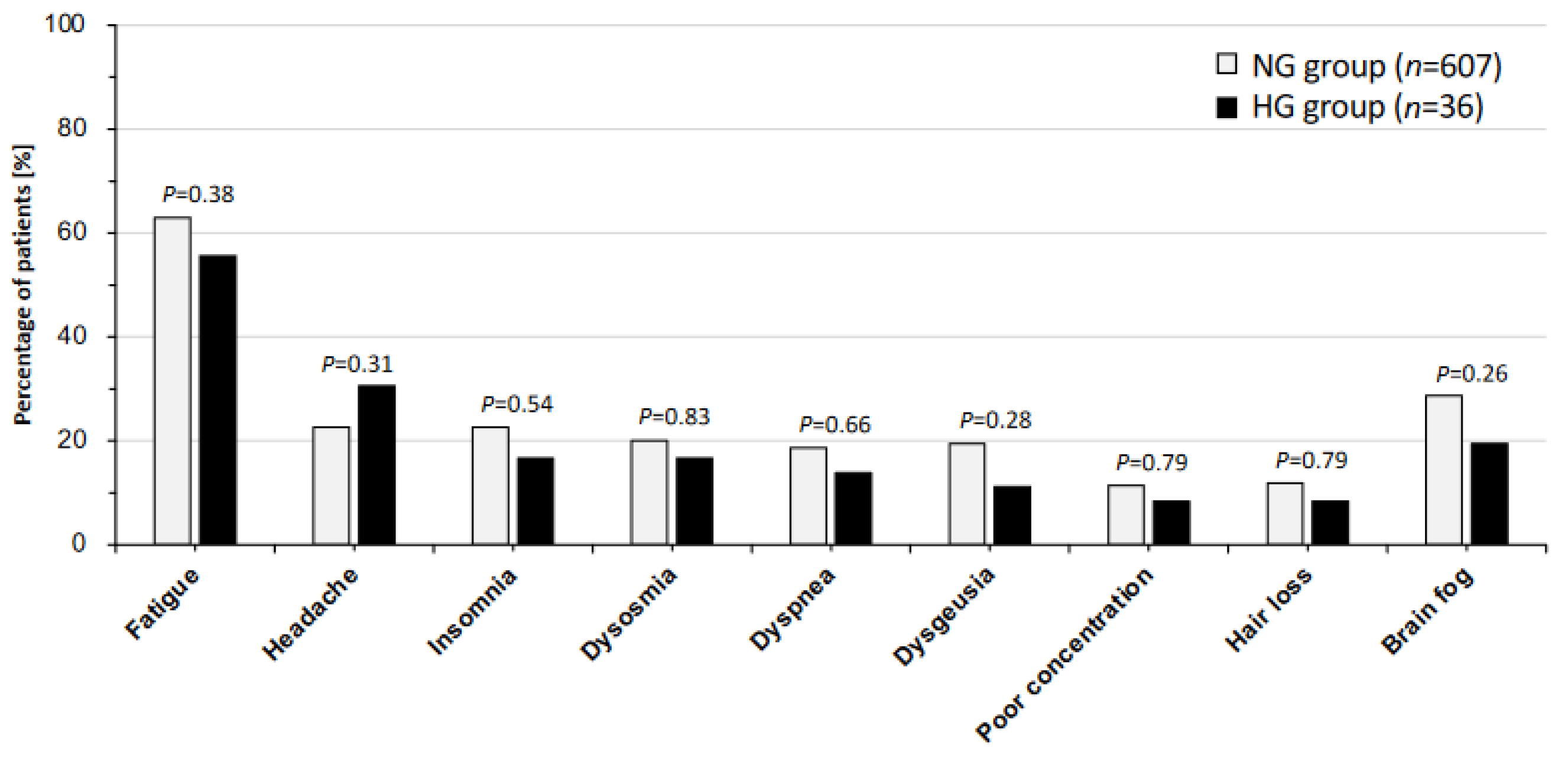
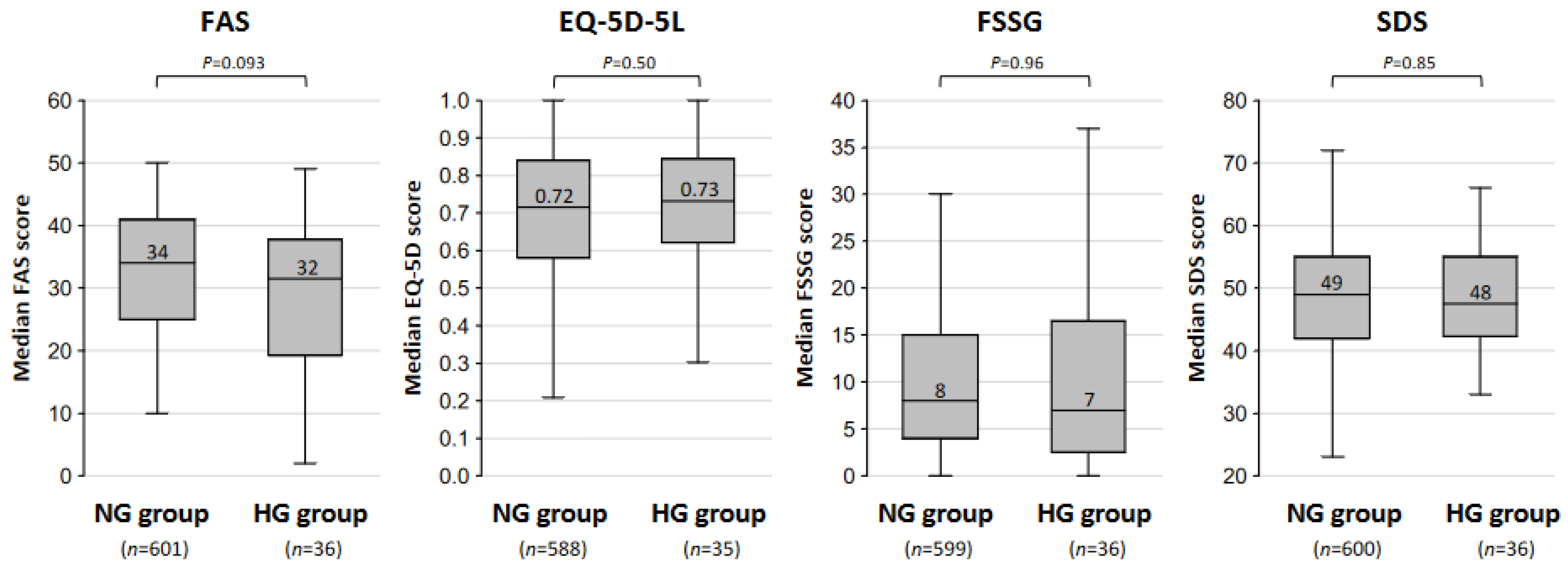
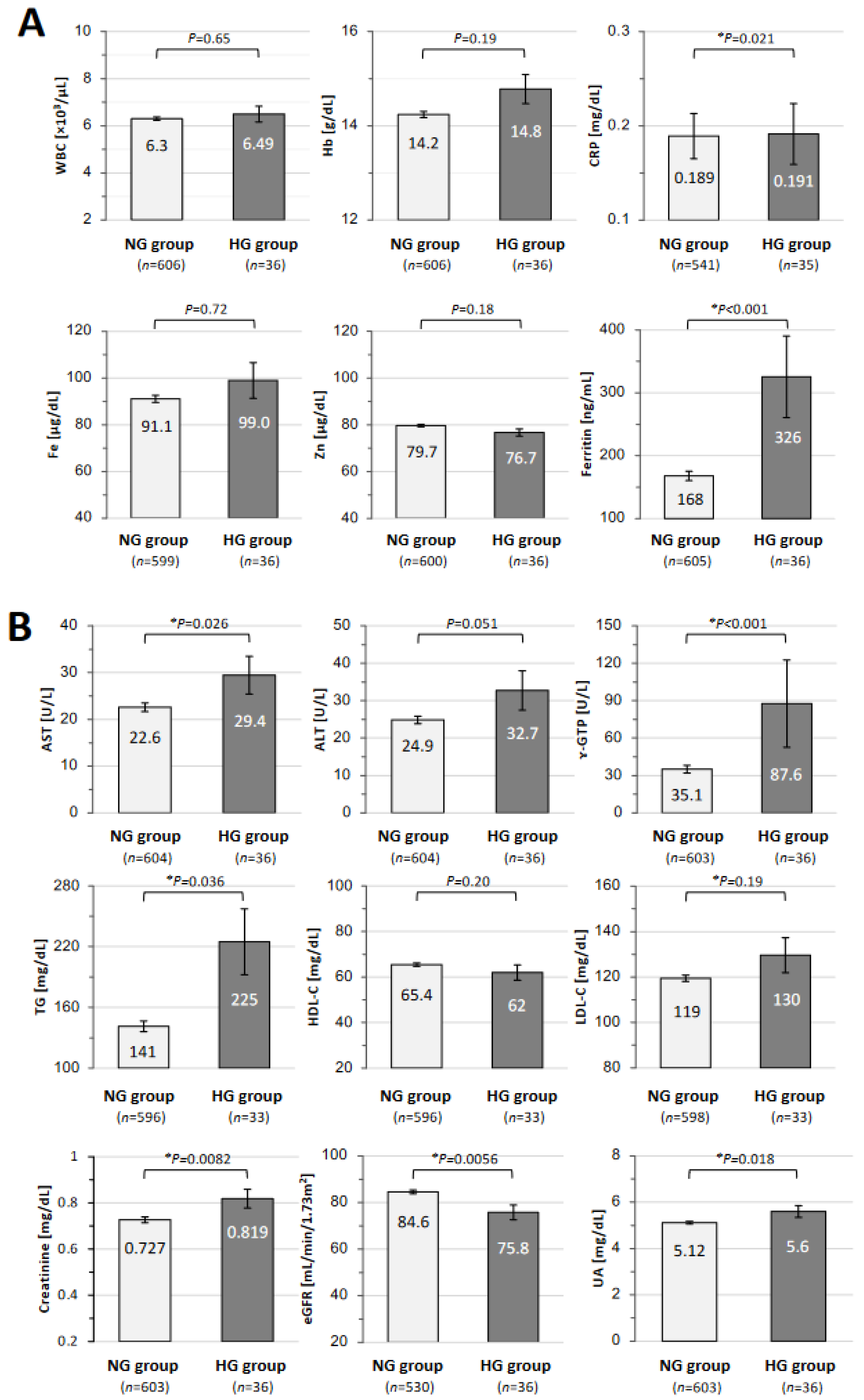
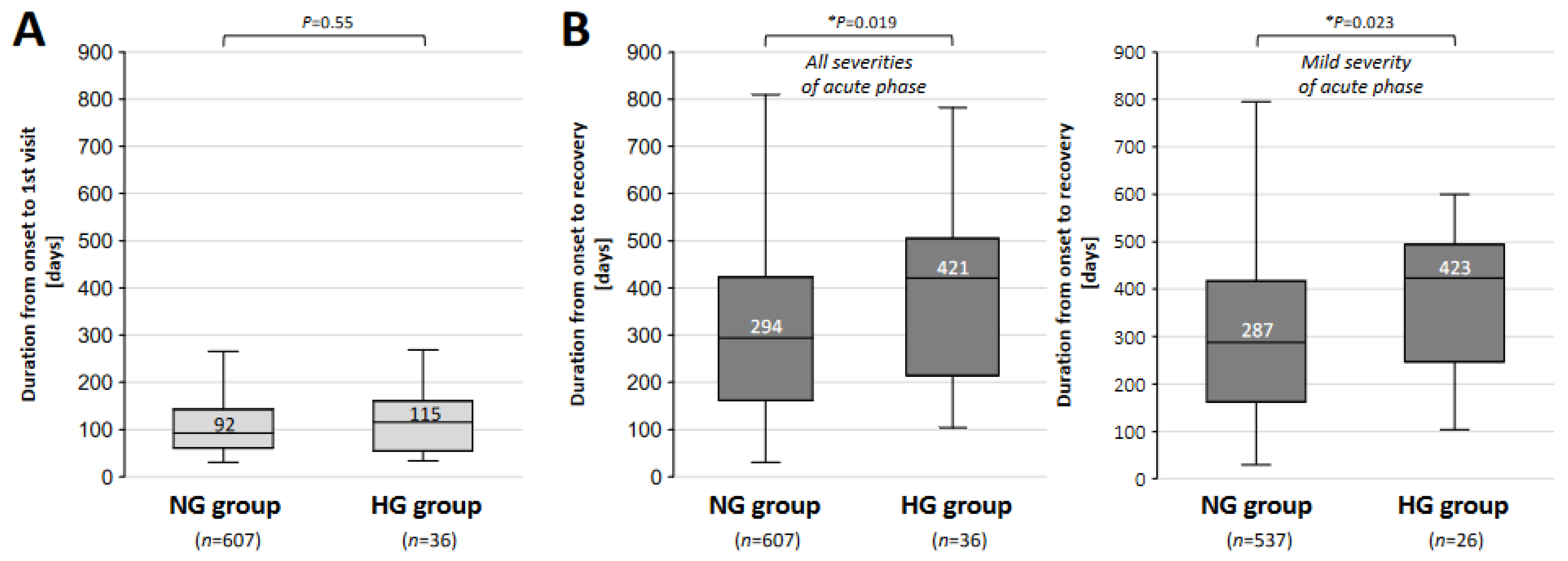
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Shrestha, L.B.; Foster, C.; Rawlinson, W.; Tedla, N.; Bull, R.A. Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants BA.1 to BA.5: Implications for immune escape and transmission. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveendran, A.V.; Jayadevan, R.; Sashidharan, S. Long COVID: An overview. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V.; WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballering, A.V.; van Zon, S.K.R.; Olde Hartman, T.C.; Rosmalen, J.G.M.; Lifelines Corona Research, I. Persistence of somatic symptoms after COVID-19 in the Netherlands: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2022, 400, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; Assaf, G.S.; McCorkell, L.; Wei, H.; Low, R.J.; Re’em, Y.; Redfield, S.; Austin, J.P.; Akrami, A. Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunada, N.; Nakano, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Tokumasu, K.; Honda, H.; Sakurada, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Omura, D.; Ochi, K.; et al. Characteristics of Sleep Disturbance in Patients with Long COVID: A Retrospective Observational Study in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Honda, H.; Sunada, N.; Tokumasu, K.; Sakurada, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Ochi, K.; Hagiya, H.; et al. Transitional Changes in Fatigue-Related Symptoms Due to Long COVID: A Single-Center Retrospective Observational Study in Japan. Medicina 2022, 58, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganami, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ogawa, Y. Adipose tissue inflammation and ectopic lipid accumulation. Endocr. J. 2012, 59, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobellis, G. COVID-19 and diabetes: Can DPP4 inhibition play a role? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chi, J.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y. Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Wood, J.; Jaycox, J.; Dhodapkar, R.M.; Lu, P.; Gehlhausen, J.R.; Tabachnikova, A.; Greene, K.; Tabacof, L.; Malik, A.A.; et al. Distinguishing features of Long COVID identified through immune profiling. Nature 2023, 623, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, M.; Iwasaki, A. The neurobiology of long COVID. Neuron 2022, 110, 3484–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siso-Almirall, A.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Conangla Ferrin, L.; Kostov, B.; Moragas Moreno, A.; Mestres, J.; Sellares, J.; Galindo, G.; Morera, R.; Basora, J.; et al. Long COVID-19: Proposed Primary Care Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Disease Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saand, A.R.; Flores, M.; Kewan, T.; Alqaisi, S.; Alwakeel, M.; Griffiths, L.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Burton, R.; Al-Jaghbeer, M.J.; et al. Does inpatient hyperglycemia predict a worse outcome in COVID-19 intensive care unit patients? J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes, A. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (Suppl. S1), S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumasu, K.; Ueda, K.; Honda, H.; Sunada, N.; Sakurada, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Obika, M.; et al. Application of Kampo Medicines for Treatment of General Fatigue Due to Long COVID. Medicina 2022, 58, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, T.; Tanaka, H.; Ishii, T. Bibliometric analysis of Kampo medicine hotspots and trends for the decade: 2013–2022. Medicine 2023, 102, e35897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.; Michielsen, H.; Van Heck, G.L.; Drent, M. Measuring fatigue in sarcoidosis: The Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS). Br. J. Health Psychol. 2004, 9, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroiwa, T.; Ikeda, S.; Noto, S.; Igarashi, A.; Fukuda, T.; Saito, S.; Shimozuma, K. Comparison of Value Set Based on DCE and/or TTO Data: Scoring for EQ-5D-5L Health States in Japan. Value Health 2016, 19, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, M.; Shimoyama, Y.; Sugimoto, S.; Kawamura, O.; Maeda, M.; Minashi, K.; Kuribayashi, S.; Higuchi, T.; Zai, H.; Ino, K.; et al. Development and evaluation of FSSG: Frequency scale for the symptoms of GERD. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beau Lotto, R. Visual development: Experience puts the colour in life. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, R619–R621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y. Case Management of COVID-19 (Secondary Version). JMA J. 2021, 4, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, H.; Ito, H.; Ohashi, Y.; Akanuma, Y.; Yamada, N.; Japan Diabetes Complication Study, G. Obesity and type 2 diabetes in Japanese patients. Lancet 2003, 361, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimura, O. Insulin resistance and hypertension in Japanese. Hypertens. Res. 1996, 19 (Suppl. S1), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albai, O.; Braha, A.; Timar, B.; Sima, A.; Deaconu, L.; Timar, R. Assessment of the Negative Factors for the Clinical Outcome in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aon, M.; Alsaeedi, A.; Alzafiri, A.; Al-Shammari, A.; Taha, S.; Al-Shammari, O.; Tawakul, M.; Alshammari, J.; Alherz, N.; Alenezi, M.; et al. Stress Hyperglycemia Ratio as a Prognostic Marker in Diabetic Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida-Pititto, B.; Dualib, P.M.; Zajdenverg, L.; Dantas, J.R.; de Souza, F.D.; Rodacki, M.; Bertoluci, M.C.; Brazilian Diabetes Society Study, G. Severity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, A.V.; Misra, A. Post COVID-19 Syndrome (“Long COVID”) and Diabetes: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 102235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, Y.; Sunada, N.; Honda, H.; Tokumasu, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Hanayama, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Hagiya, H.; Otsuka, F. Serial Changes of Long COVID Symptoms and Clinical Utility of Serum Antibody Titers for Evaluation of Long COVID. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.; Golicki, D. EQ-5D-5L-based quality of life normative data for patients with self-reported diabetes in Poland. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamahara, J.; Honda, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Tokumasu, K.; Hanayama, Y.; Hagiya, H.; Obika, M.; Ueda, K.; Kishida, M.; Otsuka, F. Clinical Characteristics of Low Androgen Status in Males with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Med. Okayama 2021, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, H.; Hanayama, Y.; Obika, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Hamahara, J.; Kishida, M.; Hagiya, H.; Ogawa, H.; Kataoka, H.; Otsuka, F. Clinical Relevance of Blood Glucose and Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms to Depressive Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Med. Okayama 2020, 74, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S.; Cogswell, M.E. Diabetes and serum ferritin concentration among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomainen, T.P.; Nyyssonen, K.; Salonen, R.; Tervahauta, A.; Korpela, H.; Lakka, T.; Kaplan, G.A.; Salonen, J.T. Body iron stores are associated with serum insulin and blood glucose concentrations. Population study in 1013 eastern Finnish men. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Tokumasu, K.; Sunada, N.; Nakano, Y.; Honda, H.; Sakurada, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Hagiya, H.; Otsuka, F. Utility of Serum Ferritin for Predicting Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in Patients with Long COVID. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postic, C.; Girard, J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: Lessons from genetically engineered mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Takamura, T.; Ota, T.; Ando, H.; Akahori, H.; Kaji, K.; Sasaki, M.; Nakanuma, Y.; Miura, K.; Kaneko, S. Liver steatosis, but not fibrosis, is associated with insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Meng, X.F.; He, F.F.; Chen, S.; Su, H.; Xiong, J.; Gao, P.; Tian, X.J.; Liu, J.S.; Zhu, Z.H.; et al. High serum uric acid and increased risk of type 2 diabetes: A systemic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nagoshi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Oi, Y.; Yoshii, A.; Kimura, H.; Ito, K.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Tanaka, T.D.; Yoshimura, M. URAT1-selective inhibition ameliorates insulin resistance by attenuating diet-induced hepatic steatosis and brown adipose tissue whitening in mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 55, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emiroglu, C.; Dicle, M.; Yesiloglu, C.; Gorpelioglu, S.; Aypak, C. Association between newly diagnosed hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus, atherogenic index of plasma and obesity in post-COVID-19 syndrome patients. Endocrine 2024, 84, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Joseph, P.; Heerdt, P.M.; Cullinan, M.; Lutchmansingh, D.D.; Gulati, M.; Possick, J.D.; Systrom, D.M.; Waxman, A.B. Persistent Exertional Intolerance After COVID-19: Insights From Invasive Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Chest 2022, 161, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NG Group n = 607 (94.4%) | HG Group n = 36 (5.6%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casual blood glucose (mg/dL), mean ± SEM | 100.5 ± 0.5 | 178.9 ± 8.5 | * <0.001 |
| Patient’s profile | |||
| Male/Female (%) | 267 (44.0)/340 (56.0) | 24 (66.7)/12 (33.3) | * 0.009 |
| Age, median [IQR] | 41 [26, 50] | 55 [48, 59] | * <0.001 |
| BMI: median [IQR] | 22.2 [20.3, 25.7] | 25.2 [22.6, 30.2] | * <0.001 |
| SBP: median [IQR] | 122 [111, 135] | 138 [119, 148] | * <0.001 |
| DBP: median [IQR] | 72 [65, 81] | 81 [68, 93] | * 0.001 |
| Patients’ lifestyle | |||
| Smoking habit (%) | 195 (32.4)s | 14 (38.9) | 0.465 |
| Alcohol drinking (%) | 207 (34.4) | 19 (52.8) | * 0.031 |
| Clinical condition in acute phase of COVID-19 | |||
| Hospital admission (%) | 92 (15.2) | 8 (22.2) | 0.242 |
| O2 and/or steroid therapy (%) | 47 (7.7) | 7 (19.4) | * 0.024 |
| Mild condition (%) | 537 (88.5) | 26 (72.2) | * 0.008 |
| Moderate-to-severe condition (%) | 70 (11.5) | 10 (27.8) | |
| COVID-19 vaccination status | |||
| <2 doses (%) | 240 (39.9) | 9 (25.0) | 0.081 |
| ≥2 doses (%) | 361 (60.1) | 27 (75.0) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yokoyama, S.; Honda, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Tokumasu, K.; Nakano, Y.; Sakurada, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Sunada, N.; Hasegawa, T.; Takase, R.; et al. Importance of Blood Glucose Measurement for Predicting the Prognosis of Long COVID: A Retrospective Study in Japan. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144099
Yokoyama S, Honda H, Otsuka Y, Tokumasu K, Nakano Y, Sakurada Y, Matsuda Y, Sunada N, Hasegawa T, Takase R, et al. Importance of Blood Glucose Measurement for Predicting the Prognosis of Long COVID: A Retrospective Study in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(14):4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144099
Chicago/Turabian StyleYokoyama, Sho, Hiroyuki Honda, Yuki Otsuka, Kazuki Tokumasu, Yasuhiro Nakano, Yasue Sakurada, Yui Matsuda, Naruhiko Sunada, Toru Hasegawa, Ryosuke Takase, and et al. 2024. "Importance of Blood Glucose Measurement for Predicting the Prognosis of Long COVID: A Retrospective Study in Japan" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 14: 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144099
APA StyleYokoyama, S., Honda, H., Otsuka, Y., Tokumasu, K., Nakano, Y., Sakurada, Y., Matsuda, Y., Sunada, N., Hasegawa, T., Takase, R., Omura, D., Soejima, Y., Ueda, K., Kishida, M., & Otsuka, F. (2024). Importance of Blood Glucose Measurement for Predicting the Prognosis of Long COVID: A Retrospective Study in Japan. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(14), 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144099








