Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Histopathological Examination of Heart Tissue
2.4. TGF-β1 Immunoexpression
2.5. Measurement of Plasma TGF-β, Pro-BNP, Troponin T
2.6. Heart Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Evaluation of Lipid Peroxidation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
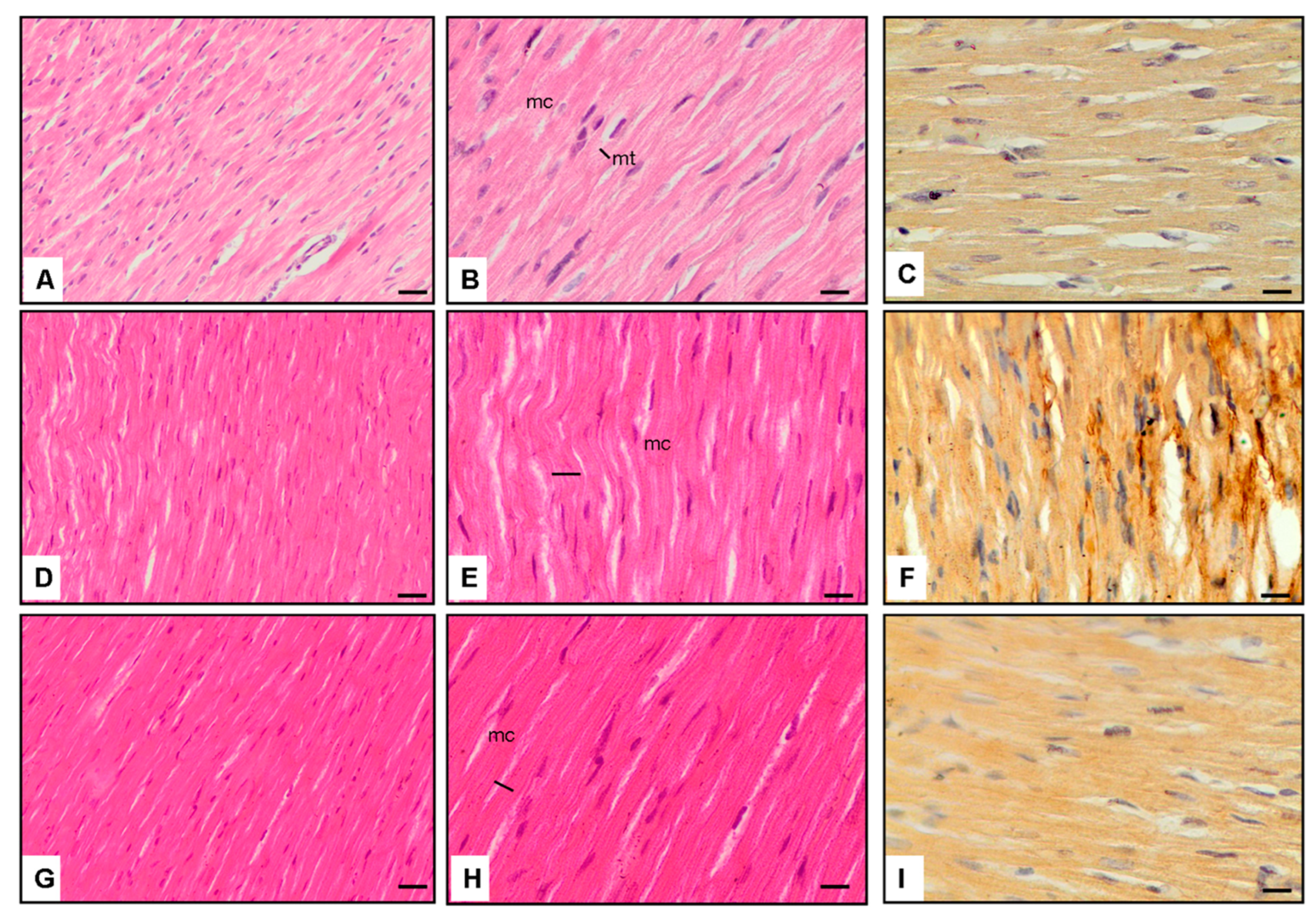
3.1. Cardiac Morphology
3.1.1. Cardiac Muscle Cell Thickness
3.1.2. Left Ventricular Thickness
3.1.3. Right Ventricular Thickness
3.1.4. Interventricular Septum Thickness
3.1.5. Immunoexpression of TGF-β1
3.1.6. Blood Glucose Levels
3.2. Plasma Biomarkers
3.3. Cardiac Biomarkers
3.4. Microscopic Observations
3.5. Interpretation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, G.; Hill, M.A.; Sowers, J.R. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: An update of mechanisms contributing to this clinical entity. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Xie, Z. Chapter 7-Treatment of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy through Upregulating Autophagy by Stimulating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. In Autophagy: Cancer, Other Pathologies, Inflammation, Immunity, Infection, and Aging; Hayat, M.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Piek, A.; de Boer, R.A.; Silljé, H.H. The fibrosis-cell death axis in heart failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2016, 21, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boudina, S.; Abel, E.D. Diabetic cardiomyopathy, causes and effects. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brahma, M.; Ghosal, S.; Maruthi, M.; Suresh, K.K. Chapter Fourteen-Endocytosis of LXRs: Signaling in liver and disease. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Mani, I., Singh, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 194, pp. 347–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kralik, P.M.; Epstein, P.N. Causes and characteristics of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2006, 3, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytas, D.Z.; Stougiannos, P.N.; Zairis, M.N.; Foussas, S.G.; Pyrgakis, V.N.; Kyriazis, I.A. Diabetic myocardial disease: Pathophysiology, early diagnosis and therapeutic options. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2009, 23, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; DeMarco, V.G.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorincz, C.; Karpati, E.; Szporny, L.; Szasz, K.; Kisfaludy, L. Alkaloid esters. Ger. Offen. 2253750. Chem. Abstr. 1973, 79, 42726. [Google Scholar]
- Szobor, A.; Klein, M. Ethyl apovincaminate therapy in neurovascular diseases. Arzneimittelforschung 1976, 26, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patyar, S.; Prakash, A.; Modi, M.; Medhi, B. Role of Vinpocetine in cerebrovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L. Anti-inflammatory effects of Vinpocetine in atherosclerosis and ischemic stroke: A review of the literature. Molecules 2015, 20, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, S.; Erdogan, M.A.; Armagan, G.; Sevgili, E.; Dagcı, T. Erratum to: Vinpocetine and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Attenuate Manganese-Induced Toxicity in NE-4C Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 175, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Rybalkin, S.D.; Pi, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Munzel, T.; Beavo, J.A.; Berk, B.C.; Yan, C. Upregulation of phosphodiesterase 1A1 expression is associated with the development of nitrate tolerance. Circulation 2001, 104, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Knight, W.E.; Guo, S.; Li, J.D.; Knight, P.A.; Yan, C. Vinpocetine suppresses pathological vascular remodeling by inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Li, J.D.; Yan, C. Vinpocetine attenuates lipid accumulation and atherosclerosis formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, X. Neuregulin-1, a potential therapeutic target for cardiac repair. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 945206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cardiovascular disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dobaczewski, M.; Chen, W.; Frangogiannis, N. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.-I.; Xu, X.; Aizawa, T.; Lim, J.H.; Jono, H.; Kwon, D.-S.; Abe, J.-i.; Berk, B.C.; Li, J.-D.; Yan, C. Vinpocetine inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent inflammation via an IKK-dependent but PDE-independent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9795–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, C.; Pintor-Chocano, A.; Carrasco, S.; Sanz, A.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D. Paricalcitol Has a Potent Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Rat Endothelial Denudation-Induced Intimal Hyperplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K.; Fan, F.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Inhibitory effects of vinpocetine on the progression of atherosclerosis are mediated by Akt/NF-κB dependent mechanisms in apoE-/- mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kannel, W.B.; Hjortland, M.; Castelli, W.P. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure; the Framingham study. Am. J. Cardiol. 1974, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penpargkul, S.; Fein, F.; Sonnenblick, E.H.; Scheuer, J. Depressed cardiac sarcoplasmic reticular function from diabetic rats. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1981, 13, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Pan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xiong, D. The protective role of neuregulin-1: A potential therapy for sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 788, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochais, F.; Fischmeister, R. Acute cardiac effects of neuregulin-1/ErbB signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 88, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, M.; Lal, H.; Ahmad, F.; Sawyer, D.; Hill, M. Chronic Neuregulin-1β Treatment Mitigates the Progression of Postmyocardial Infarction Heart Failure in the Setting of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Suppressing Myocardial Apoptosis, Fibrosis, and Key Oxidant-Producing Enzymes. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Zhong, H.; Bosch-Marcé, M.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Wang, L.; Wei, C.; Trush, M.; Semenza, G. Complete loss of ischaemic preconditioning-induced cardioprotection in mice with partial deficiency of HIF-1 alpha. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Qi, G. Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha on hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaie, M.; El-Hussieny, M.; Abdel-Hakeem, E.; Fawzy, M.; Rahman, E.; Shehata, S. Phosphodiesterase inhibitor, Vinpocetine, guards against doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity via modulation of HIF/VEGF and cGMP/cAMP/SIRT signaling pathways. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 09603271221136209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Y.; Kang, L.; Song, L. Role of Biomarkers of Myocardial Injury to Predict Adverse Outcomes in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2024, 17, e010243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Ghorbani, A.; Alavi, M.S.; Forouhi, N.; Rajabian, A.; Boroumand-Noughabi, S.; Sahebkar, A.; Eid, A.H. Cardioprotective effect of Sanguisorba minor against isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1305816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, J.; Chase, P.; Pinto, J. Troponin through the looking-glass: Emerging roles beyond regulation of striated muscle contraction. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1461–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youyou, Z.; Yalei, Y.; Jie, Z.; Chuhuai, G.; Liang, L.; Liang, R. Molecular biomarkers of cantharidin-induced cardiotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats: Troponin T, vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia inducible factor-1α. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belen, E.; Canbolat, I.P.; Yigittürk, G.; Cetinarslan, O.; Akdeniz, C.S.; Karaca, M.; Sonmez, M.; Erbas, O. Cardio-protective effect of dapagliflozin against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 4403–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Ueda, A.; Ikeda, M.; Hirota, M. Estimation of brain natriuretic peptide values from N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels and other factors. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.P.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhou, Q.M.; Xiong, J.; Dong, Y.R.; Yan, C. Higenamine protects ischemia/reperfusion induced cardiac injury and myocyte apoptosis through activation of beta2-AR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 104, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnen, P.; Petrov, V.; Fagard, R. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by transforming growth factor-beta(1). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 71, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.L.; Cai, Y.; Oikawa, M.; Thomas, T.; Dostmann, W.R.; Zaccolo, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Yan, C. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A: A key regulator of cardiac fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix remodeling in the heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Knight, W.; Yan, C. Roles of PDE1 in Pathological Cardiac Remodeling and Dysfunction. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwar, N.; Samidurai, A.; Movsesian, M.; Das, A.; Kukreja, R. PDE1 Inhibition Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Toxicity in Primary Mouse Cardiomyocytes. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 817.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.; Nour-Eldine, W.; Saliba, Y.; Dagher-Hamalian, C.; Hachem, P.; Abou-Khalil, P.; Mika, D.; Varin, A.; Hayek, M.; Pereira, L.; et al. Cardiac phosphodiesterases are differentially increased in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 2021, 283, 119857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Li, J.D.; Yan, C. An update on Vinpocetine: New discoveries and clinical implications. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosenkranz, S. TGF-beta1 and angiotensin networking in cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, K.; Connelly, K.; Kelly, D.; Zhang, Y.; Prior, D.; Martin, J.; Cox, A.; Thai, K.; Feneley, M.; Tsoporis, J.; et al. Functional, structural and molecular aspects of diastolic heart failure in the diabetic (mRen-2)27 rat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 76, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fein, F.; Cho, S.; Zola, B.; Miller, B.; Factor Bando, Y.K.; Murohara, T. Diabetes-related heart failure. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 576–583. [Google Scholar]
- Algeciras, L.; Palanca, A.; Maestro, D.; RuizdelRio, J.; Villar, A. Epigenetic alterations of TGFβ and its main canonical signaling mediators in the context of cardiac fibrosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2021, 159, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, F.S.; Cho, S.; Zola, B.E.; Miller, B.; Factor, S.M. Cardiac pathology in the hypertensive diabetic rat. Biventricular damage with right ventricular predominance. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 134, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Litwin, S.; Raya, T.; Anderson, P.; Daugherty, S.; Goldman, S. Abnormal cardiac function in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Changes in active and passive properties of the left ventricle. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M. Evaluation of Cardioprotective Role of Vinpocetine in Isoproterenol-induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 9, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhuang, T.; Pi, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Tomlinson, B.; Chan, P.; et al. Endothelial Forkhead Box Transcription Factor P1 Regulates Pathological Cardiac Remodeling through Transforming Growth Factor-β1–Endothelin-1 Signal Pathway. Circulation 2019, 140, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Normal Control (Group-1) | Diabetes and Saline Treatment (Group-2) | Diabetes and Vinpocetine (5 mg/kg) Treatment (Group-3) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac muscle cell thickness (% of control) | 100 a | 119.2 ± 2.3 b | 108.5 ± 1.1 c | <0.01 |
| Left ventricle Cardiac muscle cell thickness (µm) | 28.1 ± 0.5 a | 33.7 ± 1.6 b | 29.8 ± 0.7 a | <0.01 |
| Left ventricle thickness (mm) | 3.12 ± 0.3 a | 3.85 ± 0.2 b | 3.41 ± 0.09 c | <0.01 |
| Right ventricle thickness (mm) | 0.95 ± 0.08 a | 1.16 ± 0.1 b | 1.04 ± 0.06 a | <0.01 |
| Interventricular septum thickness (mm) | 2.23 ± 0.1 a | 2.69 ± 0.2 b | 2.25 ± 0.3 a | <0.01 |
| Normal Control (Group-1) | Diabetes and Saline Treatment (Group-2) | Diabetes and Vinpocetine (5 mg/kg) Treatment (Group-3) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunoexpression TGF-β1 percent (%) | 1.2 ± 0.3 a | 15.7 ± 2.8 b | 4.9 ± 1.6 a | <0.001 |
| Blood glucose (mg/dL) | 75.4 ± 2.3 a | 420.8 ± 6.9 b | 401.6 ± 8.9 b | <0.01 |
| Plasma TGF-Beta (ng/mL) | 17.4 ± 1.8 a | 72.5 ± 4.4 b | 39.6 ± 2.1 c | <0.001 |
| Plasma MDA (nM) | 73.6 ± 5.2 a | 349.1 ± 7.6 b | 158.1 ± 6.5 c | <0.001 |
| Cardiac HIF-1alpha (pg/mg) | 7.3 ± 0.1 a | 2.8 ± 0.3 b | 4.2 ± 0.1 c | <0.01 |
| Cardiac neuregulin-1β (pg/mg) | 32.8 ± 1.7 a | 20.6 ± 0.8 b | 25.3 ± 2.2 b | <0.01 |
| Plasma Pro-BNP (pg/mL) | 3.6 ± 0.8 a | 9.8 ± 0.5 b | 6.06 ± 0.3 b | <0.01 |
| Plasma Troponin T (pg/mL) | 0.72 ± 0.2 a | 2.1 ± 0.09 b | 1.5 ± 0.1 b | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erciyes, D.; Bora, E.S.; Tekindal, M.A.; Erbaş, O. Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164637
Erciyes D, Bora ES, Tekindal MA, Erbaş O. Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164637
Chicago/Turabian StyleErciyes, Demet, Ejder Saylav Bora, Mustafa Agah Tekindal, and Oytun Erbaş. 2024. "Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164637
APA StyleErciyes, D., Bora, E. S., Tekindal, M. A., & Erbaş, O. (2024). Demonstration of the Protective Effect of Vinpocetine in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164637







