Abstract
Background: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) is a firmly established tool in oncology and is gaining importance in dermato-oncology. However, its use in advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is limited, with only a few case reports and a single study focused on vismodegib. This study evaluates the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in advanced BCC treated with sonidegib. Methods: We retrospectively assessed the clinical data of patients with advanced BCC who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT between January 2022 and January 2024. Inclusion criteria included histologically confirmed BCC, FDG-avid lesions on baseline PET/CT, and a minimum follow-up of 6 months. Metabolic response was assessed using the PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors (PERCIST). Results: Four patients with advanced BCC treated with sonidegib were included, presenting with a total of 10 hypermetabolic lesions at baseline PET/CT. The mean interval between baseline and follow-up scans was 8.7 ± 1.6 months. According to PERCIST, two patients achieved a complete metabolic response (CMR), while the other two had stable metabolic disease (SMD). Low baseline-standardized uptake values (i.e., SUVmax, SUVmean) and reduced total lesion glycolysis (TLG) were associated with CMR. No relapses were observed during follow-up. Conclusions: This study suggests that 18F-FDG PET/CT may help identify advanced BCC patients who are likely to benefit from sonidegib treatment. Further research is needed to fully explore the potential of PET/CT in this specific clinical context.
1. Introduction
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer worldwide, accounting for approximately 80% of all non-melanoma skin cancers. Originating from the basal cells in the lower part of the epidermis, BCC is typically characterized by slow growth and a low propensity for metastasis [1]. However, BCC can become advanced when it invades deeper tissues or becomes unresectable due to size, location, or patient comorbidities. Advanced BCC includes either metastatic BCC (mBCC) or locally advanced BCC (laBCC). Although precise estimates of the incidence of advanced BCC are difficult to obtain, it has been reported to constitute approximately 1–10% of all BCCs, with the occurrence of mBCC being even rarer, amounting to only 0.0028–0.5% [2]. Both laBCC and mBCC present significant clinical challenges [2]. Notably, laBCC is defined by its inability to be surgically excised with clear margins without substantial morbidity or by recurrent disease after multiple surgical attempts. Conversely, mBCC involves the spread of cancer cells to distant organs, including lymph nodes, lungs, and bones [3].
Managing advanced BCC requires a multidisciplinary approach, often involving dermatologists, oncologists, radiologists, and surgeons [4]. For advanced BCC, where surgery is not feasible, alternative treatment modalities are considered. Radiotherapy is a valuable option for patients who are not candidates for surgery due to medical comorbidities or when the BCC is located in a surgically challenging area. It is particularly effective in treating primary BCC and as adjuvant therapy post-surgery for residual disease. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in the pharmacological management of advanced BCC. Hedgehog pathway inhibitors (HPIs) have revolutionized the treatment landscape [5,6]. These drugs target the aberrant Hedgehog-signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in BCC pathogenesis. Vismodegib, the first HPI implemented for managing advanced BCC, has demonstrated efficacy in shrinking tumors and, in some cases, achieving complete remission. However, the use of HPIs is often limited by adverse effects, including muscle spasms, dysgeusia, and alopecia, which can impact patients’ quality of life [7]. In this context, identifying patients who are likely to benefit from molecularly targeted therapies is crucial for promptly switching non-responders to more effective alternative treatments. There is an unmet need for biological and imaging biomarkers suitable for prognostic stratification and response monitoring in patients with advanced BCC undergoing various therapeutic regimens.
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) has a well-established role in oncology and is gaining increasing importance in dermato-oncology [8,9]. However, its application in patients with advanced BCC remains anecdotal, limited to some published case reports, with the exception of a single study conducted on patients with advanced BCC treated with vismodegib [10]. The authors found that BCC lesions exhibited increased 18F-FDG uptake. Additionally, a reduction in tracer uptake on follow-up PET/CT scans was associated with a more favorable outcome. Despite these initial encouraging data, the potential of metabolic imaging in the field of BCC has not been further explored.
The aim of this case series is to investigate the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with advanced BCC treated with sonidegib, a HPI recently introduced into clinical practice. This study particularly focuses on patient prognostic stratification and response monitoring.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
We carried out a retrospective analysis of clinical data from a cohort of patients with advanced BCC. This study included all patients who underwent an 18F-FDG PET/CT scan between January 2022 and January 2024 at our Nuclear Medicine Unit, as part of their diagnostic process. Participants were included based on the following criteria: (1) age over 18 years; (2) a histological confirmation of BCC; (3) a PET/CT scan performed before initiating the treatment regimen (PET-1) and subsequent follow-up to evaluate therapeutic response; (4) at least one FDG-positive lesion identified in the baseline PET/CT scan; (5) a minimum follow-up period of 6 months post-PET/CT, with complete and accessible medical records. The following criteria led to exclusion: (1) absence of FDG-positive lesions in the baseline PET scan; (2) lack of complete medical history or follow-up data.
This study retrospectively reviewed data collected during routine clinical practice, where the documentation for all patients under follow-up for BCC were examined. The data were anonymized and aggregated into an electronic database for further analysis. As the study utilized anonymized data obtained after patients had consented to follow-up and data collection, there was no requirement for individual informed consent. No experimental procedures, devices, or drugs were involved, and no funding was provided for this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. PET/CT Imaging Procedure
All patients underwent PET/CT scans with 18F-FDG in line with current imaging protocols [11]. The whole-body PET/CT was conducted from the vertex of cranium to the upper thighs, 60 min following an intravenous (i.v.) injection of 3.7 MBq/kg of 18F-FDG. The PET/CT examination utilized a digital Biograph Vision PET/CT system (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). The PET/CT scan acquisition protocol as well as the image reconstruction process have been thoroughly described in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Image Analysis
Two board-certified nuclear medicine physicians reviewed the images using Advantage 4.7 software (GE). Any area showing a tracer uptake higher than the background and not categorized as physiological was deemed potentially pathological. For each patient, sites and the number of pathological uptakes were annotated. Baseline PET/CT parameters included the number of FDG-avid lesions, mean and maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmean and SUVmax), total metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG). Lesions were segmented using a 42% SUVmax threshold, and TLG was calculated as MTV × SUVmean. The heterogeneity index (HI) was determined by dividing SUVmax by SUVmean [12].
2.4. Response Assessment and Follow-Up
PET/CT scans performed after therapy (PET-2) were compared to baseline scans (PET-1) and assessed using PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors (PERCIST) [13]. The lesion exhibiting the highest FDG uptake on both PET-1 and PET-2 was identified as the primary target. A complete metabolic response (CMR) was defined by the complete absence of all FDG-positive lesions compared to the baseline scan. For a partial metabolic response (PMR), there needed to be at least a 30% decrease in the peak standardized uptake value (SUV) adjusted for lean body mass (SULpeak) of the primary target lesion, while non-target lesions should not have shown any signs of progression. Stable metabolic disease (SMD) was defined as no change or progression, while progressive metabolic disease (PMD) was indicated by a 30% or more increase in the SULpeak of the target lesion or clear progression in non-target lesions.
2.5. Statistics
Continuous variables are reported as median, mean, and standard deviation (SD), whereas categorical data are presented as counts and percentages.
3. Results
From an initial search in our database, eight patients with BCC who underwent PET/CT were identified. However, four subjects were excluded because they had non-invasive forms and were treated with different therapies from HPI (radiotherapy, local therapy, surgery). The remaining four patients, with locally advanced BCC, treated with sonidegib (200 mg daily), were selected. Among the enrolled patients, three were male, and one was female. Of note, three out of four cases (75%) presented aggressive histotypes. The mean age was 81.2 ± 6.0.
The clinical and demographic characteristics of the selected patients are summarized in Table 1. Of note, two patients had not received BCC-specific therapy before sonidegib, while the remaining two had previously undergone loco-regional treatments.

Table 1.
The clinical and demographic characteristics of the selected patients.
3.1. Metabolic Characteristics of Lesions at Baseline
PET-1 revealed FDG-avid skin lesions in all patients. Overall, ten hypermetabolic lesions were detected; their metabolic quantitative features are reported in Table 2. The metabolic parameters resulted in (mean ± standard deviation, median): SUVmax: 9.4 ± 4.5, 7.8; SUVmean: 5.2 ± 3.2, 3.6; MTV (cc): 1.8 ± 1.7, 1.1; TLG (g/mL): 8.7 ± 6.5, 7.7.

Table 2.
Metabolic parameters and response to HPI in the selected patients.
The HI resulted in (mean ± standard deviation, median): 1.8 ± 0.3, 1.9. In the study population, no significant inhomogeneity in the intralesional distribution of the radiopharmaceutical was found, suggesting a relative metabolic homogeneity of the BCC lesion.
3.2. Metabolic Response and Follow-Up
The mean interval between baseline (PET-1) and follow-up scan (PET-2) was 8.7 ± 1.6 months. According to PERCIST, two patients (pt. 1, pt. 2) achieved complete metabolic response, as shown in Figure 1. Conversely, the remaining two patients showed stable metabolic response (Figure 2).
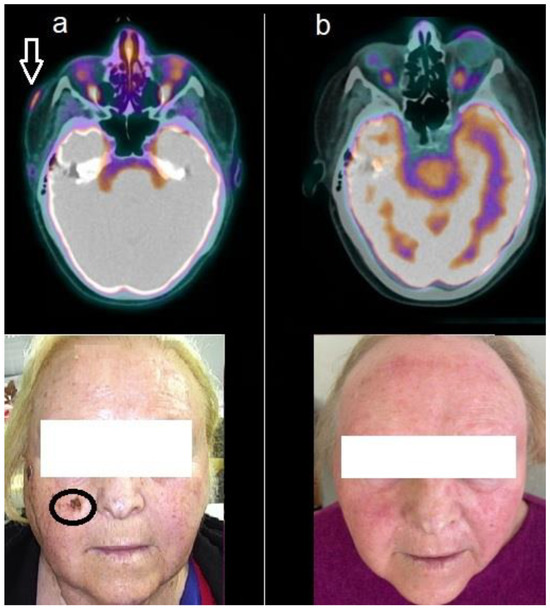
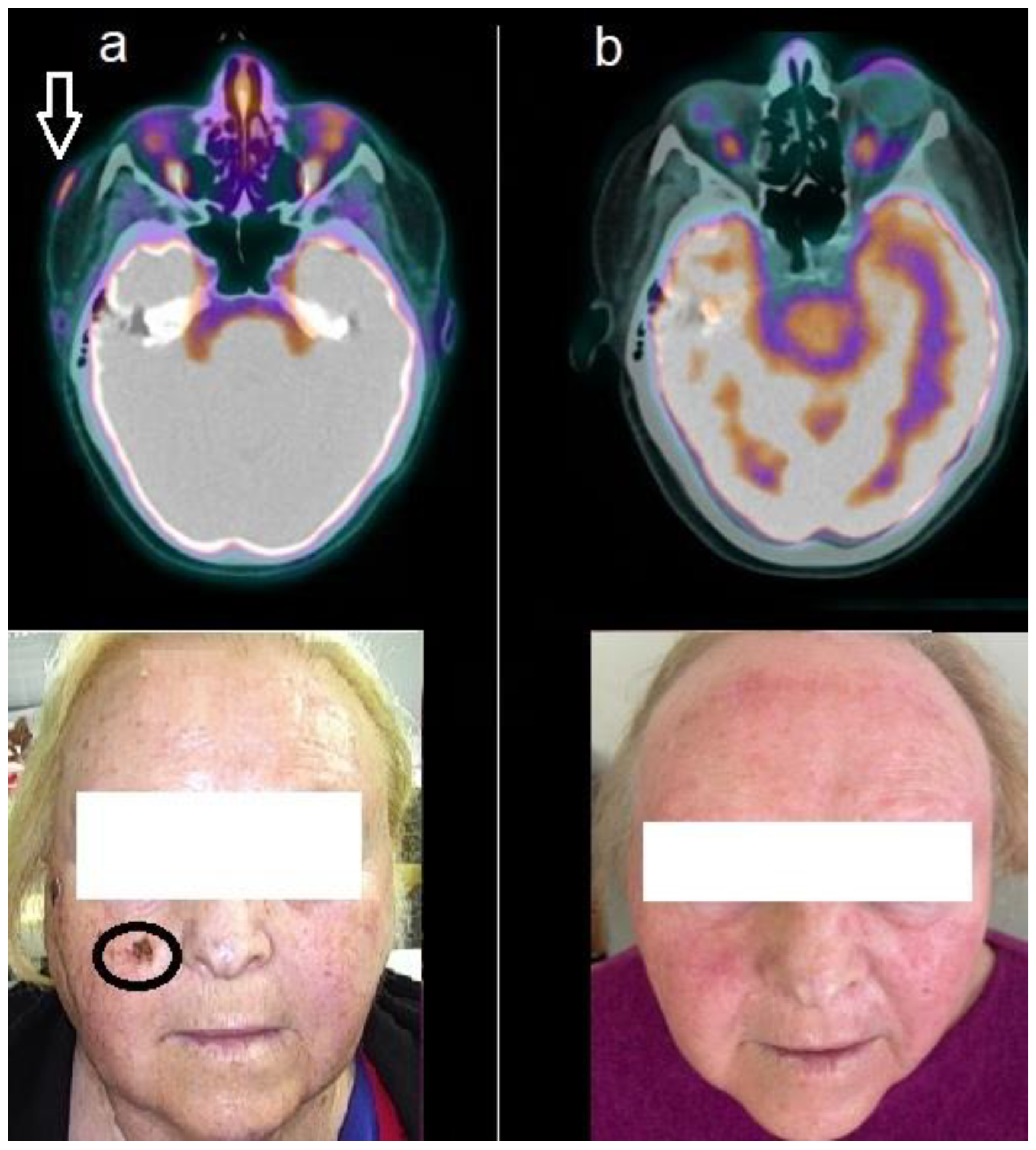
Figure 1.
Patient n. 1, a 74-year-old woman, affected by advanced BCC. (a) Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT showed increased tracer incorporation into the lesion of the right zygomatic region, as well evident in the fused axial (upper row, arrow) and at clinical examination (lower row, circle); (b) Follow-up PET/CT acquired after 8 months of HPI therapy, depicted complete metabolic response as evident in the axial images (upper row) and at clinical examination (lower row).
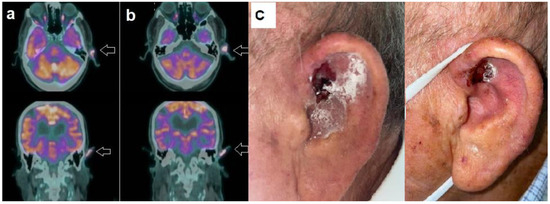
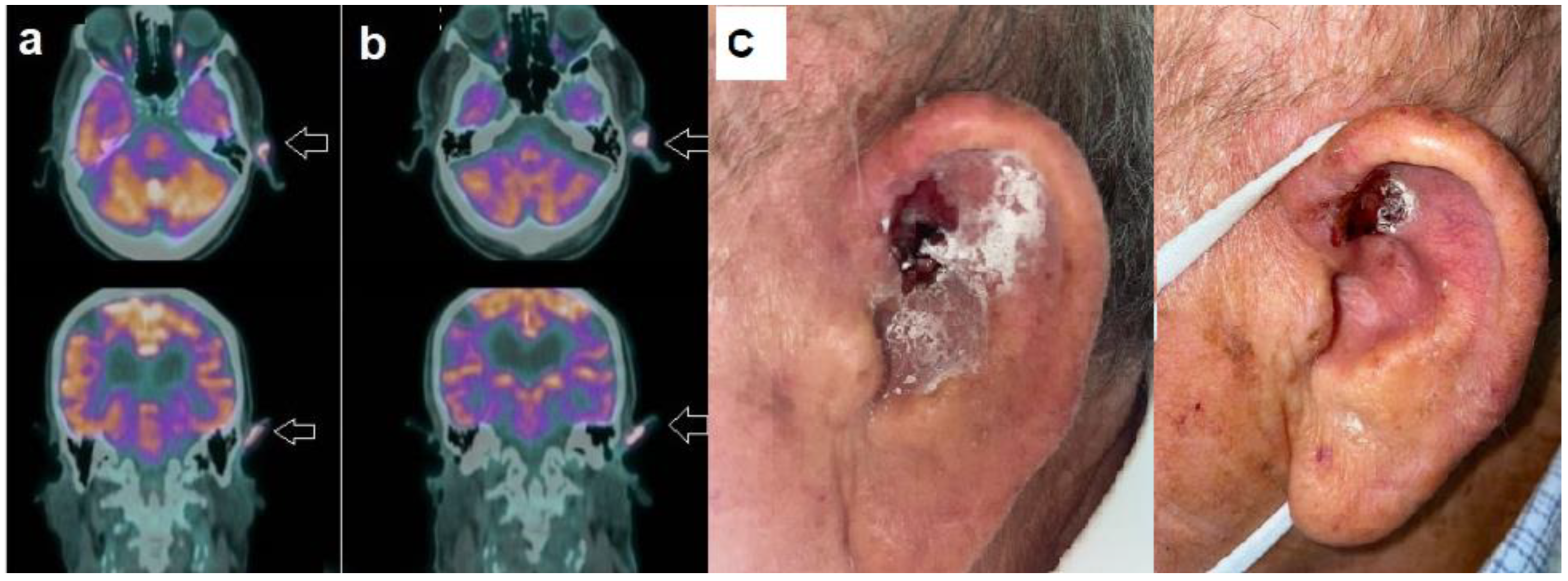
Figure 2.
Patient n. 3, an 89-year-old-male, affected by advanced BCC. (a) Baseline PET/CT showed increased tracer uptake in the left ear (arrow), as well evident in the axial (upper row) and coronal (lower row) image. (b) Follow-up PET/CT after 8 months of HPI therapy, demonstrating stable metabolic disease according to PERCIST; (c) Clinical examination at the time of PET-1 (left side) and of PET-2 (right side), consistent with substantially stable disease.
In all cases, PET-based response was in agreement with clinical and dermatoscopic evaluation. After PET-2, all patients underwent regular follow-up through laboratory tests and clinical examination for the following 6 months. No patient relapsed or progressed during follow-up. All patients are still under HPI therapy.
3.3. Differences in Metabolic Parameters between CMR and SMD Patients
The analysis of metabolic parameters revealed that both patients who achieved a complete response after treatment with HPI (pt. 1, pt. 2) had lower SUVmax, SUVmean, and TLG values compared to the corresponding values in patients who exhibited stable disease (pt. 3, pt. 4). In contrast, the MTV and HI parameters were not sufficiently discriminative between patients with CMR and those with SMD after HPI. Specifically, patient n. 4 had a reduced disease volume (MTV: 1 cc) and a high uptake level (SUVmax: 16.9), achieving SMD after HPI.
4. Discussion
Our study is the first to specifically investigate the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in evaluating the therapeutic response of patients with advanced BCC treated with sonidegib. Our findings suggest that 18F-FDG PET/CT might help identify BCC patients likely to benefit from sonidegib treatment.
Nuclear medicine relies on the use of radiopharmaceuticals that target specific metabolic pathways or molecular markers. It is widely used to explore pathophysiological processes at both cellular and molecular levels [14,15,16]. Specifically, employing 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with advanced BCC may offer significant advancements in assessing the disease’s metabolic burden and treatment response. This molecular imaging technique provides a comprehensive view of tumor physiology, which is crucial for optimizing therapeutic strategies, especially in personalized and targeted treatment contexts. In our cohort, four patients with locally advanced BCC were analyzed using various quantitative parameters. It is worth noting that both SUVmax and SUVmean, as well as TLG, have shown potential in identifying BCC patients who are more likely to benefit from sonidegib. In this context, SUV plays a well-established role in oncology for characterizing tumor biological behavior, as higher SUV levels have been correlated with more aggressive lesions [17,18]. However, SUV has several limitations, as it only provides information on the most active portion of the tumor and does not account for the overall size of the lesion. Recently, PET-derived volumetric parameters have gained increasing importance as prognostic indicators. In particular, TLG, which combines SUVmean and MTV, as well as its changes after treatment, has been found to be particularly useful in this regard [19,20]. Our findings suggest that TLG might also have potential in the field of advanced BCC undergoing molecularly targeted therapies.
We particularly focused on the HI, which measures metabolic heterogeneity within the lesion [21]. This index helps assess tumor heterogeneity, a crucial factor in understanding tumor aggressiveness, predicting treatment response, and guiding personalized therapy. In a recently published systematic review [22], the HI showed variable levels of correlation with pathological characteristics and the prediction of tumor staging across a wide range of cancers (breast, head and neck, esophagus, etc.) Although promising results were obtained for predicting treatment failure and tumor relapse, there is no consensus on how HI should be calculated, and its role in oncology remains unclear. In our cohort of patients, no significant heterogeneity was observed in the radiopharmaceutical distribution within the lesions, suggesting that BCC might have less biological variability compared to other tumor types, potentially leading to a more uniform treatment response. Nonetheless, further research is needed to determine whether HI has a significant prognostic role in BCC.
Regarding the use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in evaluating treatment response, the only similar published study, by Thacker et al., assessed response to vismodegib using PET/CT [10]. They found that a 33% reduction in total SUVmax during treatment correlated with longer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to those who did not achieve this reduction. Notably, they applied both PERCIST and EORTC (European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer) criteria for response assessment.
Both the PERCIST and EORTC criteria aim to standardize tumor response assessment using PET/CT, but they differ in approach [23,24,25,26]. The EORTC criteria, being older, use the mean SUV of the tumor for evaluation and classify responses into categories such as complete metabolic response, partial metabolic response, stable metabolic disease, and progressive metabolic disease. However, EORTC criteria are less stringent about scanning conditions, which can introduce variability. PERCIST, a newer set of guidelines, focuses on SUVpeak within a small tumor volume and emphasizes consistent scanning conditions, such as fasting blood glucose levels and post-injection timing, to ensure reliable measurements. This specificity helps reduce variability and enhances the precision of metabolic response assessment. In our cohort, we applied PERCIST due to its more detailed and standardized approach compared to the broader EORTC criteria [27]. Our findings demonstrated that the PERCIST aligned with clinical evaluations. Although the follow-up period was limited, no relapse or progression was observed in the 6 months following the second PET/CT scan, suggesting that PET/CT-detected metabolic changes may be indicative of a durable clinical response.
Additionally, considering the timing of PET/CT evaluations after initiating sonidegib therapy is important. Given that the action of HPIs is generally slow, as observed by Thacker et al., who reported a median response time of 183 days, we conducted evaluations with an 8-month follow-up [28].
The main limitations of this study are represented by the small sample size, which constrains the generalizability of the results, the single-center characteristic, and the relatively short study duration. In addition, in our cohort of patients, following a multidisciplinary consensus meeting, ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT was identified as the preferred imaging approach for evaluating patients with advanced BCC at baseline and after HPI. Consequently, as contrast-enhanced CT was not routinely performed, response evaluation according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) was not available and should be the subject of further investigation.
Advanced BCC is rare, and clinical experiences with sonidegib are often based on small cohorts. In a recent single-center study of 19 patients, 15 (78.9%) experienced a benefit, although no correlation was found between clinicopathological and treatment characteristics [29]. Another issue is determining when to discontinue HPI treatment. A recent multicenter study of 68 BCC patients treated with vismodegib suggested that discontinuing HPI therapy after achieving a complete clinical response may improve disease-free survival [30]. However, this has not yet been thoroughly investigated in patients receiving sonidegib. Further research is needed to explore the role of PET/CT in decisions about discontinuing HPI therapy.
It should be underlined that the use of PET/CT in BCC cannot be considered routine, also taking into account the cost/benefit balance. These tumors are primarily located in the head/neck region and rarely tend to metastasize. In our center, we have reserved the use of PET/CT for patients with advanced BCC with the aim of acquiring prognostic information and monitoring the response to a recently implemented therapy, allowing for a whole-body assessment to identify potential sites of distant progression as well as to detect the metabolic correlations of any adverse reaction. 18F-FDG PET/CT shows promise in managing advanced BCC by providing accurate assessments of the disease’s metabolic burden and treatment response, which can help optimize therapeutic strategies. The potential applications of PET/CT in oncology, especially in dermato-oncology, remain underexplored. Advances in radiopharmaceuticals, such as Fibroblast Activation Protein ligands, and the development of ‘long axial field-of-view’ PET/CT scanners with extraordinary sensitivity could revolutionize its use in both oncological and non-oncological fields [31,32]. Additionally, radiomics, which involves extracting reproducible quantitative data from morphological and functional images, is yielding promising results for developing predictive models of oncological outcomes [33].
5. Conclusions
Our findings indicate that 18F-FDG PET/CT might be utilized to assess treatment response in patients with locally advanced BCC undergoing sonidegib therapy. A baseline evaluation of the disease’s metabolic characteristics may help identify patients who are more likely to benefit from targeted therapy with HPI. Further research is required to better define the role of metabolic imaging in this clinical setting, considering recent advancements in radiopharmacy and PET technology.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm13175087/s1, Supplemental Data S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.P. and L.F.; methodology, I.P., L.F. and O.B.; writing—original draft preparation, I.P. and L.F.; writing—review and editing, L.F., O.B. and I.P.; supervision, C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because every single clinical case was discussed by a panel of experts during the periodical meeting held in Terracina Hospital.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish their anonymized imaging.
Data Availability Statement
Original data are available from the corresponding authors for reasonable motivations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Murgia, G.; Denaro, N.; Boggio, F.; Nazzaro, G.; Benzecry, V.; Bortoluzzi, P.; Passoni, E.; Garrone, O.; Marzano, A. Basosquamous Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2023, 12, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, J.T.; Corner, C.; Dziewulski, P.; Fife, K.; Ross, G.L.; Varma, S.; Harwood, C.A. Challenges and New Horizons in the Management of Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma: A UK Perspective. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stătescu, L.; Trandafir, L.M.; Țarcă, E.; Moscalu, M.; Leon Constantin, M.M.; Butnariu, L.I.; Trandafirescu, M.F.; Tîrnovanu, M.C.; Heredea, R.; Pătrașcu, A.V.; et al. Advancing Cancer Research: Current Knowledge on Cutaneous Neoplasia. IJMS 2023, 24, 11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usheva, S.; Vassilev, I.; Jelev, G.; Sedloev, T.; Dimitrov, I.; Terziev, I.; Boyadzhieva, M.; Milusheva, Y.; Troyanova, P. Surgical Management of Giant Skin Tumor—A Case Report. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthétique 2024, 69, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.A.; Aldahan, A.S.; Hughes, O.B.; Shah, V.V.; Strasswimmer, J. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis of Interventional Studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trane, L.; Salvati, L.; Silvestri, F.; Venturi, F.; Zuccaro, B.; Perillo, G.; De Giorgi, V. The Importance of Caregivers for Patients with Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Hedgehog-Pathway Inhibitors: An Observational Prospective Study. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2024, 34, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulic, A.; Migden, M.R.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Garbe, C.; Gesierich, A.; Lao, C.D.; Miller, C.; Mortier, L.; Murrell, D.F.; For the ERIVANCE BCC Investigators; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Vismodegib in Patients with Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma: Final Update of the Pivotal ERIVANCE BCC Study. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathekge, M.M.; Ankrah, A.O.; Lawal, I.; Vorster, M. Monitoring Response to Therapy. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 48, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, L.J.; Pomper, M.G. The Evolution of Imaging in Cancer: Current State and Future Challenges. Semin. Oncol. 2011, 38, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, C.A.; Weiss, G.J.; Tibes, R.; Blaydorn, L.; Downhour, M.; White, E.; Baldwin, J.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Korn, R.L. 18-FDG PET/CT Assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma with Vismodegib. Cancer Med. 2012, 1, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM Procedure Guidelines for Tumour Imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Gu, B.; Li, N.; Pan, H.; Chen, W.; Qiao, Y.; Song, S.; Liu, X. Prognostic Value of Heterogeneity Index Derived from Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 862473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, W.L. From RECIST to PERCIST: Navigating the Landscape of Tumor Response Assessment. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 3656–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.P.; Pomper, M.G. Molecular Imaging in Oncology: Current Impact and Future Directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Biancone, L.; Petruzziello, C.; Schillaci, O. Tc-99m HMPAO-Labeled Leukocyte Scintigraphy with Hybrid SPECT/CT Detects Perianal Fistulas in Crohn Disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 31, 541–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbán, C.J.; Galbán, S.; Van Dort, M.E.; Luker, G.D.; Bhojani, M.S.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B.D. Applications of Molecular Imaging. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 95, pp. 237–298. ISBN 978-0-12-385071-3. [Google Scholar]
- Berghmans, T.; Dusart, M.; Paesmans, M.; Hossein-Foucher, C.; Buvat, I.; Castaigne, C.; Scherpereel, A.; Mascaux, C.; Moreau, M.; Roelandts, M.; et al. Primary Tumor Standardized Uptake Value (SUVmax) Measured on Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography (FDG-PET) Is of Prognostic Value for Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (MA) by the European Lung Cancer Working Party for the IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surov, A.; Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A. Associations Between PET Parameters and Expression of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraez, I.; Bento, L.; Daumal, J.; Repetto, A.; Del Campo, R.; Perez, S.; Ramos, R.; Ibarra, J.; Mestre, F.; Bargay, J.; et al. Total Lesion Glycolysis Improves Tumor Burden Evaluation and Risk Assessment at Diagnosis in Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.; Lin, X.; Yin, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, L. Prognostic Value of MTV and TLG of 18 F-FDG PET in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Park, J.-Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.J.; Moon, S.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Cheon, G.J.; Chung, H.H. Preoperative [18F]FDG PET/CT Tumour Heterogeneity Index in Patients with Uterine Leiomyosarcoma: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinfosse, P.; Hatt, M.; Visvikis, D.; Hustinx, R. Heterogeneity Analysis of 18F-FDG PET Imaging in Oncology: Clinical Indications and Perspectives. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2018, 6, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Liu, C.; Gu, B.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Pan, H.; Yao, Z.; Wang, M.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Early Prediction of Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Prognosis: Comparison of PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors and European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Criteria in Breast Cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2020, 41, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.D.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H. Comparison of the Morphologic Criteria (RECIST) and Metabolic Criteria (EORTC and PERCIST) in Tumor Response Assessments: A Pooled Analysis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinker, K.; Riedl, C.; Weber, W.A. Evaluating Tumor Response with FDG PET: Updates on PERCIST, Comparison with EORTC Criteria and Clues to Future Developments. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasnon, C.; Quak, E.; Le Roux, P.-Y.; Robin, P.; Hofman, M.S.; Bourhis, D.; Callahan, J.; Binns, D.S.; Desmonts, C.; Salaun, P.-Y.; et al. EORTC PET Response Criteria Are More Influenced by Reconstruction Inconsistencies than PERCIST but Both Benefit from the EARL Harmonization Program. EJNMMI Phys. 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Ling, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, B.; Gong, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, H. Comparison of RECIST, EORTC Criteria and PERCIST for Evaluation of Early Response to Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Song, R.; Xie, J. Sonidegib: Mechanism of Action, Pharmacology, and Clinical Utility for Advanced Basal Cell Carcinomas. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallone, G.; Carbone, A.; Sperati, F.; Frascione, P.; Eibenschutz, L. Clinical Determinants of Clinical Response to Sonidegib in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Monocenter Experience. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, S.; Romanò, R.; Marceglia, S.; De Giorgi, V.; Peris, K.; Sollena, P.; Piccerillo, A.; Moro, R.; Gualdi, G.; Ascierto, P.A.; et al. Hedgehog Inhibitors Beyond Clinical Complete Response in Basal Cell Carcinoma: Should I Stop or Should I Go? Oncologist 2024, 29, e699–e707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Wan, Z.; Fan, D.; Huang, Z. Malignant Melanoma of the External Auditory Canal on 68 Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 48, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A.; Evangelista, L.; Schillaci, O. Long Axial Field-of-View PET/CT Devices: Are We Ready for the Technological Revolution? Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2022, 19, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrane, K.; Meur, C.L.; Thuillier, P.; Berthou, C.; Uguen, A.; Deandreis, D.; Bourhis, D.; Bourbonne, V.; Abgral, R. Review on Radiomic Analysis in 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography for Prediction of Melanoma Outcomes. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).