Development of Seizures Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Information
3.2. Hospital Outcomes
3.3. Comorbid Conditions
3.4. Comorbidity Predictive Factors
3.5. Type of TBI
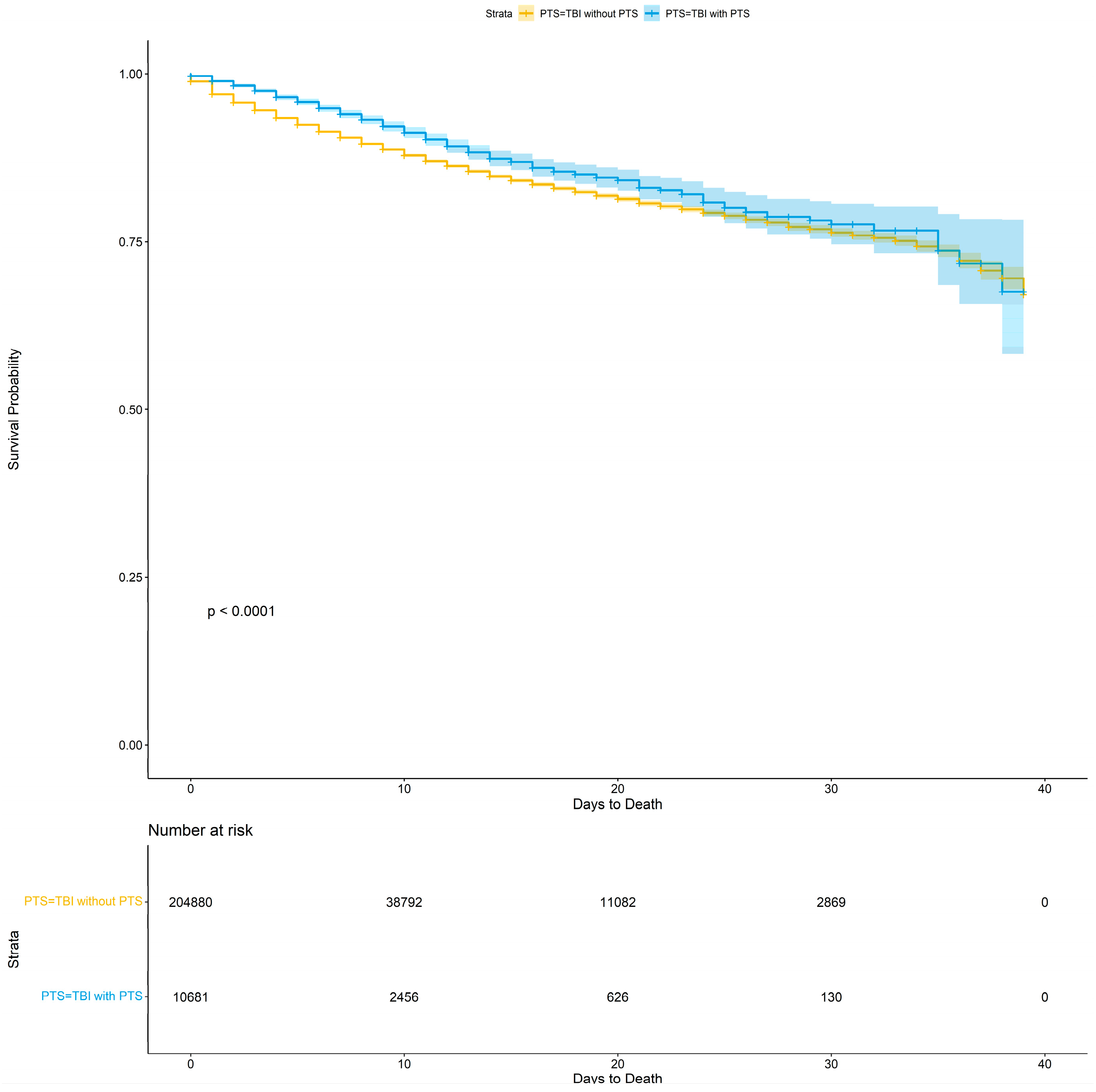
3.6. Mortality and Survival
3.7. Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Incidence and Demographics
4.2. Traumatic Brain Injury Subtypes
4.3. Mortality
4.4. Hospital Length of Stay (LOS)
4.5. Race and Socioeconomics
4.6. Complications
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Injury Prevention & Control: Traumatic Brain Injury & Concussion. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- CDC. Data & Statistics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/traumatic-brain-injury/data-research/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Faul, M.W.; Marlena, M.; Xu, L.; Coronado Victor, G. Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, 2002–2006; National Center for Injury Prevention and Control (U.S.), Division of Injury Response: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thurman, D.J.; Alverson, C.; Dunn, K.A.; Guerrero, J.; Sniezek, J.E. Traumatic brain injury in the United States: A public health perspective. J. Head. Trauma. Rehabil. 1999, 14, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verellen, R.M.; Cavazos, J.E. Post-traumatic epilepsy: An overview. Therapy 2010, 7, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowitz, D.; Grant, G. Frontiers in Neuroscience. In Translational Research in Traumatic Brain Injury; Laskowitz, D., Grant, G., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, J.; Gabbe, B.; Chen, Z.; Perucca, P.; Kwan, P.; O’Brien, T.J. Risk Factors and Prognosis of Early Posttraumatic Seizures in Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimian, S.; Kershenovich, A.; Miller, J.W.; Ojemann, J.G.; Hebb, A.O.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Ojemann, G.A. Long-term outcome of extratemporal resection in posttraumatic epilepsy. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Dagra, A.; Martinez, M.; Williams, E.; Lucke-Wold, B. Examining the role of astrogliosis and JNK signaling in post-traumatic epilepsy. Egypt. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Nguyen, L.; Turner, R.C.; Logsdon, A.F.; Chen, Y.-W.; Smith, K.E.; Huber, J.D.; Matsumoto, R.; Rosen, C.L.; Tucker, E.S. Traumatic brain injury and epilepsy: Underlying mechanisms leading to seizure. Seizure 2015, 33, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.; Lyketsos, C. Neuropsychiatric sequelae of traumatic brain injury. Psychosomatics 2000, 41, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.W.; Hart, Y.M.; Johnson, A.L.; Shorvon, S.D. National General Practice Study of Epilepsy: Newly diagnosed epileptic seizures in a general population. Lancet 1990, 336, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordington, S.; Manford, M. A review of seizures and epilepsy following traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiest, K.M.; Sauro, K.M.; Wiebe, S.; Patten, S.B.; Kwon, C.S.; Dykeman, J.; Pringsheim, T.; Lorenzetti, D.L.; Jetté, N. Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of international studies. Neurology 2017, 88, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Sander, J.W. The natural history of epilepsy: An epidemiological view. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIS. HCUP-US NIS Overview. Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- Cuccurullo, S.J. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, 4th ed.; Demos Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Annegers, J.F.; Hauser, W.A.; Coan, S.P.; Rocca, W.A. A population-based study of seizures after traumatic brain injuries. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasell, R.; Bayona, N.; Lippert, C.; Villamere, J.; Hellings, C. Post-traumatic seizure disorder following acquired brain injury. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, L.C. Epidemiology of posttraumatic epilepsy: A critical review. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caveness, W.F.; Walker, A.E.; Ascroft, P.B. Incidence of posttraumatic epilepsy in Korean veterans as compared with those from World War I and World War II. J. Neurosurg. 1962, 19, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.M.; Jabbari, B.; Vance, S.C.; Grafman, J.; Amin, D.; Dillon, J.D. Epilepsy after penetrating head injury. I. Clinical correlates: A report of the Vietnam Head Injury Study. Neurology 1985, 35, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, A.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Carr, K.; Maltenfort, M.; Emami, M.; Bell, R.; Moussouttas, M.; Yazbeck, M.; Rincon, F. The epidemiology, risk factors, and impact on hospital mortality of status epilepticus after subdural hematoma in the United States. Springerplus 2014, 3, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodobski, A.; Zink, B.J.; Szmydynger-Chodobska, J. Blood-brain barrier pathophysiology in traumatic brain injury. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Blood-brain barrier integrity and glial support: Mechanisms that can be targeted for novel therapeutic approaches in stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3624–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, F.; Nakagawa, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Dohgu, S. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction Amplifies the Development of Neuroinflammation: Understanding of Cellular Events in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells for Prevention and Treatment of BBB Dysfunction. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 661838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, P.; Dingledine, R.; Aronica, E.; Bernard, C.; Blümcke, I.; Boison, D.; Brodie, M.J.; Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forcelli, P.A.; et al. Commonalities in epileptogenic processes from different acute brain insults: Do they translate? Epilepsia 2018, 59, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.; Rappaport, Z.H. Epilepsy in chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir. 1993, 123, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, T.; Yamada, K.; Kuratsu, J. Seizures as a presenting symptom in neurosurgical patients: A retrospective single-institution analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.T.; Bi, W.L.; Abd-El-Barr, M.; Yan, S.C.; Tafel, I.J.; Dunn, I.F.; Gormley, W.B. The Neurocritical and Neurosurgical Care of Subdural Hematomas. Neurocrit. Care 2016, 24, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.C.; Bamford, J.M.; Heath, J.; Bradey, N.; Heatley, R.V. Multiple forms of epileptic attack secondary to a small chronic subdural haematoma. BMJ 1989, 299, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gilmore, E.J.; Gaspard, N.; Choi, H.A.; Cohen, E.; Burkart, K.M.; Chong, D.H.; Claassen, J.; Hirsch, L.J. Acute brain failure in severe sepsis: A prospective study in the medical intensive care unit utilizing continuous EEG monitoring. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernheimer, R.; O’Neal, S.; Kellogg, M. Analysis of EEG Use Utilizing the National Inpatient Sample (P3.263). Neurology 2018, 90, P3.263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilkman, D.M.W.; van Mook, W.; Mess, W.H.; van Kranen-Mastenbroek, V. The Use of Continuous EEG Monitoring in Intensive Care Units in The Netherlands: A National Survey. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 29, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilkman, D.M.; van Mook, W.N.; van Kranen-Mastenbroek, V.H. Continuous electroencephalographic-monitoring in the ICU: An overview of current strengths and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 30, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, K.L.; Nguyen, B.P.; Vatsaas, C.; Alger, A.; Brooks, K.; Agarwal, S.K. Socioeconomic Status Affects Outcomes after Severity-Stratified Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 235, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galovic, M.; Ferreira-Atuesta, C.; Abraira, L.; Döhler, N.; Sinka, L.; Brigo, F.; Bentes, C.; Zelano, J.; Koepp, M.J. Seizures and Epilepsy after Stroke: Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Management. Drugs Aging 2021, 38, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolk, K.; Lange, T.; Elwert, F.; Dreier, J.W.; Christensen, J. Traumatic brain injury, stroke, and epilepsy: A mediation study in a Danish nationwide cohort. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographics | Overall, N = 219,005 1 | TBI w/o PTS, N = 208,167 1 | TBI w/PTS, N = 10,838 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 61.75 (23.80) | 61.81 (23.96) | 60.62 (20.41) | <0.001 |
| Age Category | <0.001 | |||
| <55 | 69,400 (32%) | 65,819 (32%) | 3581 (33%) | |
| 55–74 | 64,585 (29%) | 60,472 (29%) | 4113 (38%) | |
| 75–89 | 67,889 (31%) | 65,132 (31%) | 2757 (25%) | |
| 90+ | 17,116 (7.8%) | 16,729 (8.0%) | 387 (3.6%) | |
| Gender | <0.001 | |||
| Female | 88,178 (40%) | 84,064 (40%) | 4114 (38%) | |
| Male | 130,764 (60%) | 124,040 (60%) | 6724 (62%) | |
| Race/Ethnicity | <0.001 | |||
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 7631 (3.5%) | 7386 (3.5%) | 245 (2.3%) | |
| Black | 22,512 (10%) | 20,978 (10%) | 1534 (14%) | |
| Hispanic | 24,818 (11%) | 23,699 (11%) | 1119 (10%) | |
| Native American | 1750 (0.8%) | 1611 (0.8%) | 139 (1.3%) | |
| Other | 7775 (3.6%) | 7437 (3.6%) | 338 (3.1%) | |
| White | 154,519 (71%) | 147,056 (71%) | 7463 (69%) | |
| Household income by zip code | <0.001 | |||
| 0–25th percentile | 60,418 (28%) | 57,175 (27%) | 3243 (30%) | |
| 26th to 50th percentile | 56,371 (26%) | 53,617 (26%) | 2754 (25%) | |
| 51st to 75th percentile | 53,778 (25%) | 51,133 (25%) | 2645 (24%) | |
| 76th to 100th percentile | 48,438 (22%) | 46,242 (22%) | 2196 (20%) | |
| Rural/Urban | 0.2 | |||
| Rural | 13,916 (6.4%) | 13,259 (6.4%) | 657 (6.1%) | |
| Urban | 205,089 (94%) | 194,908 (94%) | 10,181 (94%) | |
| Payer | <0.001 | |||
| Medicaid | 30,938 (14%) | 28,827 (14%) | 2111 (19%) | |
| Medicare | 115,646 (53%) | 109,718 (53%) | 5928 (55%) | |
| Other | 11,243 (5.1%) | 10,778 (5.2%) | 465 (4.3%) | |
| Private insurance | 49,247 (22%) | 47,433 (23%) | 1814 (17%) | |
| Self-pay | 11,931 (5.4%) | 11,411 (5.5%) | 520 (4.8%) | |
| Time to Any First Procedure | 1.02 (3.05) | 1.01 (3.05) | 1.10 (3.04) | <0.001 |
| Length of Stay | 6.90 (10.94) | 6.87 (10.98) | 7.50 (9.99) | <0.001 |
| Total Charge | 98,184.45 (168,322.98) | 98,237.05 (169,873.87) | 97,174.11 (135,125.81) | <0.001 |
| Discharge Disposition | <0.001 | |||
| Adverse Discharge | 97,828 (45%) | 92,784 (45%) | 5044 (47%) | |
| Home Discharge with Care | 29,404 (13%) | 27,904 (13%) | 1500 (14%) | |
| Routine Discharge | 91,645 (42%) | 87,357 (42%) | 4288 (40%) | |
| Hospice | 16,735 (7.6%) | 15,960 (7.7%) | 775 (7.2%) | 0.049 |
| Severity of Injury | <0.001 | |||
| Extreme Loss of Function | 35,971 (16%) | 34,255 (16%) | 1716 (16%) | |
| Major Loss of Function | 59,142 (27%) | 55,901 (27%) | 3241 (30%) | |
| Minor Loss of Function | 43,397 (20%) | 41,804 (20%) | 1593 (15%) | |
| Moderate Loss of Function | 80,479 (37%) | 76,191 (37%) | 4288 (40%) | |
| Severe TBI | 3792 (1.7%) | 3651 (1.8%) | 141 (1.3%) | <0.001 |
| Mortality | 17,509 (8.0%) | 16,862 (8.1%) | 647 (6.0%) | <0.001 |
| Day of Death | 5.29 (8.90) | 5.22 (8.96) | 7.13 (7.13) | <0.001 |
| Elixhauser Comorbidity Index | <0.001 | |||
| ≤0 | 72,114 (33%) | 71,768 (34%) | 346 (3.2%) | |
| 1–2 | 6915 (3.2%) | 6726 (3.2%) | 189 (1.7%) | |
| 3–4 | 12,452 (5.7%) | 11,801 (5.7%) | 651 (6.0%) | |
| 5+ | 127,524 (58%) | 117,872 (57%) | 9652 (89%) | |
| Concussion | 16,401 (7.5%) | 15,904 (7.6%) | 497 (4.6%) | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Cerebral Edema | 882 (0.4%) | 856 (0.4%) | 26 (0.2%) | 0.008 |
| Diffuse Traumatic Brain Injury | 5919 (2.7%) | 5693 (2.7%) | 226 (2.1%) | <0.001 |
| Focal Traumatic Brain Injury | 18,369 (8.4%) | 17,481 (8.4%) | 888 (8.2%) | 0.2 |
| Epidural Hemorrhage | 8786 (4.0%) | 8417 (4.0%) | 369 (3.4%) | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Subdural hemorrhage | 105,554 (48%) | 99,357 (48%) | 6197 (57%) | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | 59,157 (27%) | 56,731 (27%) | 2426 (22%) | <0.001 |
| Other Specified Intracranial Injuries | 1155 (0.5%) | 1089 (0.5%) | 66 (0.6%) | 0.5 |
| Unspecified Intracranial Injury | 6603 (3.0%) | 6278 (3.0%) | 325 (3.0%) | >0.9 |
| Comorbidity | Overall, N = 219,005 1 | TBI w/o PTS, N = 208,167 1 | TBI w/PTS, N = 10,838 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congestive heart failure | 24,812 (11%) | 23,799 (11%) | 1013 (9.3%) | <0.001 |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 56,031 (26%) | 53,478 (26%) | 2553 (24%) | <0.001 |
| Valvular disease | 11,704 (5.3%) | 11,142 (5.4%) | 562 (5.2%) | 0.5 |
| Pulmonary circulation disorders | 5245 (2.4%) | 5014 (2.4%) | 231 (2.1%) | 0.066 |
| Peripheral vascular disorders | 12,192 (5.6%) | 11,622 (5.6%) | 570 (5.3%) | 0.2 |
| Hypertension (uncomplicated) | 89,900 (41%) | 85,006 (41%) | 4894 (45%) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (complicated) | 35,248 (16%) | 33,710 (16%) | 1538 (14%) | <0.001 |
| Paralysis | 12,028 (5.5%) | 11,015 (5.3%) | 1013 (9.3%) | <0.001 |
| Other neurologic disorders | 54,002 (25%) | 43,164 (21%) | 10,838 (100%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 27,800 (13%) | 26,322 (13%) | 1478 (14%) | 0.002 |
| Diabetes (uncomplicated) | 23,391 (11%) | 22,285 (11%) | 1106 (10%) | 0.10 |
| Diabetes (complicated) | 24,469 (11%) | 23,302 (11%) | 1167 (11%) | 0.2 |
| Hypothyroidism | 27,147 (12%) | 25,752 (12%) | 1395 (13%) | 0.12 |
| Renal failure | 26,282 (12%) | 25,166 (12%) | 1116 (10%) | <0.001 |
| Liver disease | 9046 (4.1%) | 8422 (4.0%) | 624 (5.8%) | <0.001 |
| Peptic ulcer disease (excluding bleeding) | 757 (0.3%) | 723 (0.3%) | 34 (0.3%) | 0.6 |
| AIDS/HIV | 386 (0.2%) | 353 (0.2%) | 33 (0.3%) | 0.001 |
| Lymphoma | 1254 (0.6%) | 1194 (0.6%) | 60 (0.6%) | 0.8 |
| Metastatic cancer | 2571 (1.2%) | 2457 (1.2%) | 114 (1.1%) | 0.2 |
| Solid tumor without metastasis | 3071 (1.4%) | 2901 (1.4%) | 170 (1.6%) | 0.13 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis/collagen vascular diseases | 4497 (2.1%) | 4274 (2.1%) | 223 (2.1%) | >0.9 |
| Coagulopathy | 22,539 (10%) | 21,243 (10%) | 1296 (12%) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 12,162 (5.6%) | 11,588 (5.6%) | 574 (5.3%) | 0.2 |
| Weight loss | 15,293 (7.0%) | 14,549 (7.0%) | 744 (6.9%) | 0.6 |
| Fluid and electrolyte disorders | 66,947 (31%) | 63,172 (30%) | 3775 (35%) | <0.001 |
| Blood loss anemia | 1137 (0.5%) | 1073 (0.5%) | 64 (0.6%) | 0.3 |
| Deficiency anemias | 5292 (2.4%) | 4951 (2.4%) | 341 (3.1%) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol abuse | 32,401 (15%) | 30,083 (14%) | 2318 (21%) | <0.001 |
| Drug abuse | 12,947 (5.9%) | 12,083 (5.8%) | 864 (8.0%) | <0.001 |
| Psychoses | 3284 (1.5%) | 2930 (1.4%) | 354 (3.3%) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 27,610 (13%) | 25,838 (12%) | 1772 (16%) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | Odds Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congestive heart failure | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.92 | <0.001 |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.009 |
| Valvular disease | 1.10 | 1.06 | 1.14 | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary circulation disorders | 1.01 | 0.95 | 1.07 | 0.796 |
| Peripheral vascular disorders | 1.04 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 0.051 |
| Hypertension (uncomplicated) | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.491 |
| Hypertension (complicated) | 1.04 | 0.99 | 1.09 | 0.13 |
| Paralysis | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.04 | 0.55 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 1.03 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.037 |
| Diabetes (uncomplicated) | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes (complicated) | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| Hypothyroidism | 1.06 | 1.03 | 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Renal failure | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| Liver disease | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 0.599 |
| Peptic ulcer disease (excluding bleeding) | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.95 | 0.008 |
| AIDS/HIV | 1.23 | 1.05 | 1.44 | 0.011 |
| Lymphoma | 1.14 | 1.02 | 1.28 | 0.026 |
| Metastatic cancer | 0.96 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.376 |
| Solid tumor without metastasis | 1.12 | 1.05 | 1.20 | 0.001 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 0.99 | 0.93 | 1.05 | 0.702 |
| Coagulopathy | 1.04 | 1.01 | 1.07 | 0.005 |
| Obesity | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.002 |
| Weight loss | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.86 | <0.001 |
| Fluid and electrolyte disorders | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.94 | <0.001 |
| Blood loss anemia | 1.08 | 0.97 | 1.21 | 0.159 |
| Deficiency anemias | 1.02 | 0.97 | 1.07 | 0.544 |
| Alcohol abuse | 1.15 | 1.12 | 1.17 | <0.001 |
| Drug abuse | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 0.791 |
| Psychoses | 1.24 | 1.18 | 1.30 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.769 |
| Type of TBI | Odds Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concussion | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.74 | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Cerebral Edema | 0.52 | 0.35 | 0.75 | <0.001 |
| Diffuse Traumatic Brain Injury | –0.74 | 0.65 | 0.84 | <0.001 |
| Focal Traumatic Brain Injury | 0.97 | 0.90 | 1.03 | 0.319 |
| Epidural Hemorrhage | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.92 | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Subdural Hemorrhage | 1.38 | 1.32 | 1.43 | <0.001 |
| Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Other Specified Intracranial Injuries | 1.16 | 0.91 | 1.47 | 0.225 |
| Unspecified Intracranial Injury | 1.05 | 0.94 | 1.17 | 0.386 |
| Complication | Overall, N = 219,005 1 | TBI w/o PTS, N = 208,167 1 | TBI w/PTS, N = 10,838 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Complications | 96,110 (44%) | 91,050 (44%) | 5060 (47%) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory Failure | 35,501 (16%) | 33,837 (16%) | 1664 (15%) | 0.013 |
| Pulmonary Embolism | 1367 (0.6%) | 1304 (0.6%) | 63 (0.6%) | 0.6 |
| Pneumonia | 10,442 (4.8%) | 10,049 (4.8%) | 393 (3.6%) | <0.001 |
| Cardiac Arrest | 2904 (1.3%) | 2814 (1.4%) | 90 (0.8%) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 21,769 (9.9%) | 20,896 (10%) | 873 (8.1%) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 2397 (1.1%) | 2296 (1.1%) | 101 (0.9%) | 0.10 |
| Transfusion | 7531 (3.4%) | 7254 (3.5%) | 277 (2.6%) | <0.001 |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | 3844 (1.8%) | 3628 (1.7%) | 216 (2.0%) | 0.053 |
| Acute Kidney Disease | 20,336 (9.3%) | 19,495 (9.4%) | 841 (7.8%) | <0.001 |
| Urological Infections | 19,227 (8.8%) | 18,232 (8.8%) | 995 (9.2%) | 0.13 |
| Stroke | 3609 (1.6%) | 3354 (1.6%) | 255 (2.4%) | <0.001 |
| Delirium | 4739 (2.2%) | 4501 (2.2%) | 238 (2.2%) | 0.8 |
| Plegia and Paresis | 11,879 (5.4%) | 10,834 (5.2%) | 1045 (9.6%) | <0.001 |
| Osteomyelitis | 300 (0.1%) | 286 (0.1%) | 14 (0.1%) | 0.8 |
| Sepsis | 5637 (2.6%) | 5400 (2.6%) | 237 (2.2%) | 0.009 |
| Complication | Odds Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Complication | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 | <0.001 |
| Respiratory Failure | 0.95 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.063 |
| Pulmonary Embolism | 0.81 | 0.65 | 1.01 | 0.057 |
| Pneumonia | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.79 | <0.001 |
| Cardiac Arrest | 0.62 | 0.50 | 0.77 | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.69 | <0.001 |
| Myocardial Infarction | 0.81 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.046 |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | 1.04 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 0.628 |
| Acute Kidney Disease | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.78 | <0.001 |
| Urological Infection | 1.03 | 0.97 | 1.09 | 0.407 |
| Stroke | 1.37 | 1.20 | 1.56 | <0.001 |
| Delirium | 1.05 | 0.93 | 1.19 | 0.438 |
| Encephalopathy | 1.30 | 1.23 | 1.37 | <0.001 |
| Plegia and paresis | 1.26 | 1.19 | 1.34 | <0.001 |
| Osteomyelitis | 0.77 | 0.47 | 1.26 | 0.295 |
| Sepsis | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.89 | <0.001 |
| Demographic Variables | Odds Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age < 50 | 1.00 | |||
| Age 55–74 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.87 | <0.001 |
| Age 75–89 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.47 | <0.001 |
| Age 90+ | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Female | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.05 | 0.568 |
| White | 1.00 | |||
| Black | 1.29 | 1.22 | 1.36 | <0.001 |
| Hispanic | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.033 |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.80 | <0.001 |
| Native American | 1.40 | 1.18 | 1.66 | <0.001 |
| Other | 0.89 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0.04 |
| Elixhauser ≤ 0 | 1.00 | |||
| Elixhauser 1–2 | 7.67 | 6.46 | 9.10 | <0.001 |
| Elixhauser 3–4 | 13.68 | 12.05 | 15.52 | <0.001 |
| Elixhauser 5+ | 24.98 | 22.47 | 27.76 | <0.001 |
| Minor Loss of Function | 1.00 | |||
| Moderate Loss of Function | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.81 | <0.001 |
| Major Loss of Function | 0.60 | 0.56 | 0.63 | <0.001 |
| Extreme Loss of Function | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.44 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moran, M.; Lajeunesse, B.; Kotzur, T.; Momtaz, D.A.; Smerin, D.L.; Lafuente, M.F.; Azari Jafari, A.; Mirmoeeni, S.; Garcia, C.; Martinez, P.; et al. Development of Seizures Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185399
Moran M, Lajeunesse B, Kotzur T, Momtaz DA, Smerin DL, Lafuente MF, Azari Jafari A, Mirmoeeni S, Garcia C, Martinez P, et al. Development of Seizures Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(18):5399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoran, Margaret, Brooke Lajeunesse, Travis Kotzur, David Arian Momtaz, Daniel Li Smerin, Molly Frances Lafuente, Amirhossein Azari Jafari, Seyyedmohammadsadeq Mirmoeeni, Carlos Garcia, Paola Martinez, and et al. 2024. "Development of Seizures Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 18: 5399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185399
APA StyleMoran, M., Lajeunesse, B., Kotzur, T., Momtaz, D. A., Smerin, D. L., Lafuente, M. F., Azari Jafari, A., Mirmoeeni, S., Garcia, C., Martinez, P., Chen, K., & Seifi, A. (2024). Development of Seizures Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(18), 5399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185399






