Association between Psychological Distress and Possible, Probable, and Definite Sleep Bruxism—A Comparison of Approved Diagnostic Procedures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Sleep Bruxism Assessment
2.3. Assessment of Psychological Distress
2.4. Outcome Variables
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Agreement between Diagnostic Procedures
3.2. Group Comparison between SB Diagnosis and Psychological Distress
3.3. Correlational Analyses of Specific SB Parameters and Psychological Distress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, J.; Raphael, K.G.; Wetselaar, P.; Glaros, A.G.; Kato, T.; Santiago, V.; Winocur, E.; De Laat, A.; De Leeuw, R.; et al. International consensus on the assessment of bruxism: Report of a work in progress. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Winocur, E.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Paesani, D.; Lobbezoo, F. Epidemiology of bruxism in adults: A systematic review of the literature. J. Orofac. Pain 2013, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, G.; Duarte, J.; Pauletto, P.; Porporatti, A.L.; Stuginski-Barbosa, J.; Winocur, E.; Flores-Mir, C.; De Luca Canto, G. Bruxism: An umbrella review of systematic reviews. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 666–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluly, M.; Andersen, M.L.; Dal-Fabbro, C.; Garbuio, S.; Bittencourt, L.; de Siqueira, J.T.; Tufik, S. Polysomnographic study of the prevalence of sleep bruxism in a population sample. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 97S–103S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oporto, G.H.t.; Bornhardt, T.; Iturriaga, V.; Salazar, L.A. Genetic polymorphisms in the serotonergic system are associated with circadian manifestations of bruxism. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieckiewicz, M.; Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Mazur, G.; Danel, D.; Smardz, J.; Wojakowska, A.; Poreba, R.; Dratwa, M.; Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Winocur, E.; et al. Genetic basis of sleep bruxism and sleep apnea-response to a medical puzzle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeff, M.C.; Lobbezoo, F.; Wetselaar, P.; Aarab, G.; Koutris, M. Parkinson’s disease, temporomandibular disorders and bruxism: A pilot study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2018, 45, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynowicz, H.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Poreba, R.; Wojakowska, A.; Smardz, J.; Januszewska, L.; Markiewicz-Gorka, I.; Mazur, G.; Pawlas, K.; Gac, P. The Relationship between Sleep Bruxism Intensity and Renalase Concentration-An Enzyme Involved in Hypertension Development. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosztega, W.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Nowacki, D.; Michalek-Zrabkowska, M.; Poreba, R.; Wojakowska, A.; Kanclerska, J.; Mazur, G.; Martynowicz, H. Polysomnographic Assessment of Effects of Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption on Sleep Bruxism Intensity. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardz, J.; Martynowicz, H.; Wojakowska, A.; Michalek-Zrabkowska, M.; Mazur, G.; Wieckiewicz, M. Correlation between Sleep Bruxism, Stress, and Depression-A Polysomnographic Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polmann, H.; Reus, J.C.; Massignan, C.; Serra-Negra, J.M.; Dick, B.D.; Flores-Mir, C.; Lavigne, G.J.; De Luca Canto, G. Association between sleep bruxism and stress symptoms in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2021, 48, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saczuk, K.; Lapinska, B.; Wilmont, P.; Pawlak, L.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M. Relationship between Sleep Bruxism, Perceived Stress, and Coping Strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Schaefer, R.; Ommerborn, M.A.; Giraki, M.; Goertz, A.; Raab, W.H.; Franz, M. Maladaptive coping strategies in patients with bruxism compared to non-bruxing controls. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2007, 14, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polmann, H.; Domingos, F.L.; Melo, G.; Stuginski-Barbosa, J.; Guerra, E.; Porporatti, A.L.; Dick, B.D.; Flores-Mir, C.; De Luca Canto, G. Association between sleep bruxism and anxiety symptoms in adults: A systematic review. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Poggio, C.E.; Lobbezoo, F. Is bruxism a risk factor for dental implants? A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlmann, B.; Waldecker, M.; Leckel, M.; Bomicke, W.; Behnisch, R.; Rammelsberg, P.; Schmitter, M. Correlations between Sleep Bruxism and Temporomandibular Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Ahlberg, J.; Castroflorio, T.; Poggio, C.E.; Guarda-Nardini, L.; Lobbezoo, F. Diagnostic accuracy of portable instrumental devices to measure sleep bruxism: A systematic literature review of polysomnographic studies. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014, 41, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyano, K.; Tsukiyama, Y.; Ichiki, R.; Kuwata, T. Assessment of bruxism in the clinic. J. Oral Rehabil. 2008, 35, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Colonna, A.; Bracci, A.; Lobbezoo, F. Bruxism: A summary of current knowledge on aetiology, assessment and management. Oral Surg. 2020, 13, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Bargellini, A.; Debernardi, C.; Manfredini, D. Detection of sleep bruxism: Comparison between an electromyographic and electrocardiographic portable holter and polysomnography. J. Oral Rehabil. 2014, 41, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saczuk, K.; Lapinska, B.; Wilmont, P.; Pawlak, L.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M. The Bruxoff Device as a Screening Method for Sleep Bruxism in Dental Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Mikami, S.; Maeda, M.; Saito, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yachida, W.; Gotouda, A. Portable and wearable electromyographic devices for the assessment of sleep bruxism and awake bruxism: A literature review. Cranio 2023, 41, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompré, P.H.; Daigle-Landry, D.; Guitard, F.; Montplaisir, J.Y.; Lavigne, G.J. Identification of a sleep bruxism subgroup with a higher risk of pain. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, G.J.; Rompre, P.H.; Montplaisir, J.Y. Sleep bruxism: Validity of clinical research diagnostic criteria in a controlled polysomnographic study. J. Dent. Res. 1996, 75, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carra, M.C.; Huynh, N.; Lavigne, G.J. Diagnostic accuracy of sleep bruxism scoring in absence of audio-video recording: A pilot study. Sleep Breath 2015, 19, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommerborn, M.A.; Walentek, N.; Bergmann, N.; Franken, M.; Gotter, A.; Schafer, R. Validation of a new diagnostic method for quantification of sleep bruxism activity. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 4351–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emodi Perlman, A.; Lobbezoo, F.; Zar, A.; Friedman Rubin, P.; van Selms, M.K.; Winocur, E. Self-Reported bruxism and associated factors in Israeli adolescents. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoulaki, S.; Tortopidis, D.; Andreadis, D.; Koidis, P. Relationship between Sleep Bruxism and Stress Determined by Saliva Biomarkers. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluerasu, M.I.; Bocsan, I.C.; Buduru, S.; Pop, R.M.; Vesa, S.C.; Zaharia, A.; Negucioiu, M.; Iacob, S.M. The correlation between sleep bruxism, salivary cortisol, and psychological status in young, Caucasian healthy adults. Cranio 2021, 39, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Landi, N.; Fantoni, F.; Segu, M.; Bosco, M. Anxiety symptoms in clinically diagnosed bruxers. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Ciapparelli, A.; Dell’Osso, L.; Bosco, M. Mood disorders in subjects with bruxing behavior. J. Dent. 2005, 33, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletić, A.; Lazić, Z.; Todorović, A.; Đorđević, I.; Popović, D.; Lazić, V. Stress assessment in patients with clinically diagnosed sleep bruxism. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2018, 75, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraki, M.; Schneider, C.; Schafer, R.; Singh, P.; Franz, M.; Raab, W.H.; Ommerborn, M.A. Correlation between stress, stress-coping and current sleep bruxism. Head Face Med. 2010, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, D.; Arreghini, A.; Lombardo, L.; Visentin, A.; Cerea, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Siciliani, G. Assessment of Anxiety and Coping Features in Bruxers: A Portable Electromyographic and Electrocardiographic Study. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2016, 30, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlmann, B.; Bomicke, W.; Habibi, Y.; Rammelsberg, P.; Schmitter, M. Are there associations between sleep bruxism, chronic stress, and sleep quality? J. Dent. 2018, 74, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.R.; Sena, R.; de Freitas, A.M.; Silva, A.N.; Lamounier Júnior, E.A.; Soares, A.B. Neuro-behavioral pattern of sleep bruxism in wakefulness. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- John, M.T.; Hirsch, C.; Reiber, T.; Dworkin, S.F. Translating the research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders into German: Evaluation of content and process. J. Orofac. Pain 2006, 20, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, G.H. SCL-90®-S. Symptom-Checklist-90®-Standard–Manual; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen, T.; Myllymaa, K.; Hukkanen, T.; Toyras, J.; Sipila, K.; Myllymaa, S. Home Polysomnography Reveals a First-Night Effect in Patients With Low Sleep Bruxism Activity. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Haraldson, T.; Omar, R.; Kiliaridis, S.; Carlsson, G.E. A system for assessing the severity and progression of occlusal tooth wear. J. Oral Rehabil. 1993, 20, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundo, J.V.; Downey, R., III. Polysomnography. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 160, pp. 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, G.J.; Manzini, C.; Kato, T. Sleep bruxism. In Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine, 4th ed.; Kryger, M.H., Roth, T., Dement, W.C., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders, 3rd ed. text revision; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iber, C.; Anacoli-Israel, S.; Chesson, A.; Quan, S.F. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology, and Technical Specifications, 1st ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 1977, 33, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate—A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.; Miles, J.; Field, Z. Discovering Statistics Using R; Sage publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stuginski-Barbosa, J.; Porporatti, A.L.; Costa, Y.M.; Svensson, P.; Conti, P.C. Agreement of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders Criteria with polysomnography for sleep bruxism diagnosis: A preliminary study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castroflorio, T.; Bargellini, A.; Rossini, G.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A.; Manfredini, D. Agreement between clinical and portable EMG/ECG diagnosis of sleep bruxism. J. Oral Rehabil. 2015, 42, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayar, G.R.; Tutuncu, R.; Acikel, C. Psychopathological profile of patients with different forms of bruxism. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlberg, J.; Lobbezoo, F.; Ahlberg, K.; Manfredini, D.; Hublin, C.; Sinisalo, J.; Kononen, M.; Savolainen, A. Self-reported bruxism mirrors anxiety and stress in adults. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e7–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhou, N.; Wu, L. A preliminary study on potential association between psychopathological status and rhythmic masticatory muscle activity of young patients with sleep bruxism in Tianjin China. Sleep Med. 2018, 51, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, D.; Lobbezoo, F. Role of psychosocial factors in the etiology of bruxism. J. Orofac. Pain 2009, 23, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, K.; Ikawa, T.; Shigeta, Y.; Shigemoto, S.; Ogawa, T. Evaluation of sleep bruxism with a novel designed occlusal splint. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2017, 61, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casett, E.; Reus, J.C.; Stuginski-Barbosa, J.; Porporatti, A.L.; Carra, M.C.; Peres, M.A.; de Luca Canto, G.; Manfredini, D. Validity of different tools to assess sleep bruxism: A meta-analysis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diagnostic Procedure | Method | Outcome | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-report | Single question “Do you grind your teeth during sleep?” in the screening | SB self-report (screening) (y/n) | Possible SB |
| Clinical examination | Based on ICSD-3 TR: Inspection of teeth Anamnestic interview | SB self-report (interview) (y/n) SB external report (y/n) Tiredness/stiffness (y/n) Masseter hypertrophy (y/n) Number of teeth with abnormal attrition | Probable SB |
| Examination of masseter muscle | |||
| PSG | Analysis of physiological sleep data including muscle activity of masseter muscle | SB index Number of episodes with grinding sounds index | Definite SB |
| Diagnostic sheet and software | Fully automated, computer-based analysis of wear on the diagnostic sheet | Pixelscore | - |
| Psychometric self-evaluation | SCL-90-S | GSI | - |
| Diagnostic Procedure | SB n (%) | Non-SB n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Self-report | 21 (46.67%) | 24 (53.33%) |
| Clinical examination | 20 (44.44%) | 25 (55.56%) |
| PSG | 10 (22.22%) | 35 (77.78%) |
| Diagnostic sheet and software | 17 (37.78%) | 28 (62.22%) |
| SB Diagnosis Based upon PSG | ||||
| SB (n = 10) | Non-SB (n = 35) | |||
| Specific Parameter | M | SD | M | SD |
| SB index | 8.40 | 4.56 | 2.40 | 0.96 |
| Episodes with grinding sounds index | 3.61 | 4.77 | 0.26 | 0.37 |
| SB Diagnosis Based upon Clinical Examination | ||||
| SB (n = 20) n (%) | Non-SB (n = 25) n (%) | |||
| SB self-report (interview): | ||||
| Yes (n = 15) | 15 (75.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | ||
| No (n = 30) | 5 (25.00%) | 25 (100.00%) | ||
| SB third-party report: | ||||
| Yes (n = 14) | 14 (70.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | ||
| No (n = 31) | 6 (30.00%) | 25 (100.00%) | ||
| Feeling of tiredness/stiffness: | ||||
| Yes (n = 15) | 13 (65.00%) | 2 (8.00%) | ||
| No (n = 30) | 7 (35.00%) | 23 (92.00%) | ||
| Masseter hypertrophy: | ||||
| Yes (n = 14) | 10 (50.00%) | 4 (16.00%) | ||
| No (n = 31) | 10 (50.0%) | 21 (84.00%) | ||
| M | SD | M | SD | |
| Number of teeth with abnormal attrition | 7.90 | 6.68 | 6.00 | 5.40 |
| SB Diagnosis Based upon Diagnostic Sheet | ||||
| SB (n = 17) | Non-SB (n = 18) | |||
| M | SD | M | SD | |
| Pixelscore | 1274.23 | 735.72 | 168.69 | 139.00 |
| Diagnosis Based upon PSG | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnoses Based upon Other Procedures | SB (n = 10) n (%) | Non-SB (n = 35) n (%) | Statistics |
| Self-report: | |||
| SB (n = 21) | 7 (70.00%) | 14 (40.00%) | κ = 0.22 |
| non-SB (n = 24) | 3 (30.00%) | 21 (60.00%) | |
| Clinical examination: | |||
| SB (n = 20) | 7 (70.00%) | 13 (37.14%) | κ = 0.24 |
| non-SB (n = 25) | 3 (30.00%) | 22 (62.86%) | |
| Diagnostic sheet and software: | |||
| SB (n = 17) | 10 (100.00%) | 7 (20.00%) | κ = 0.64 |
| non-SB (n = 28) | 0 (0.00%) | 28 (80.00%) | |
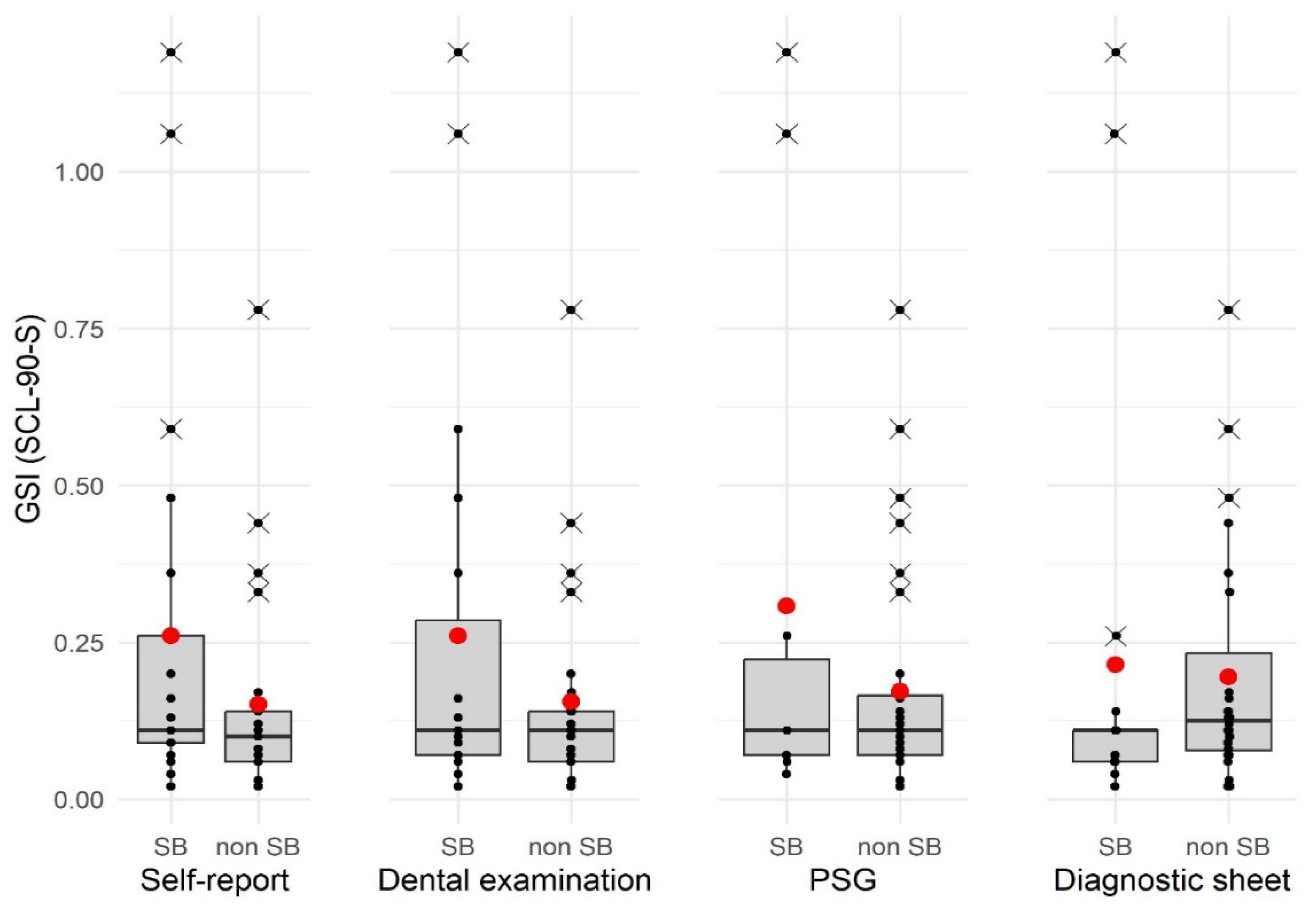
| GSI (SCL-90-S) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis SB | M | SD | Median | Statistics | p † |
| Self-report: | W = 190.50 | ||||
| Yes (n = 21) | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.400 | |
| No (n = 24) | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.10 | ||
| Clinical examination: | W = 215.00 | 0.572 | |||
| yes (n = 20) | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.11 | ||
| No (n = 25) | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.11 | ||
| PSG: | W = 172.00 | ||||
| Yes (n = 10) | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.945 | |
| No (n = 35) | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.11 | ||
| Diagnostic sheet and software: | W = 293.00 | 0.400 | |||
| yes (n = 17) | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.11 | ||
| No (n = 28) | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.12 | ||
| GSI (SCL-90-S) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | rb | rs | p † |
| Self-report: | |||
| SB self-report (screening)/Diagnosis of SB | 0.27 | - | - |
| Clinical examination: | |||
| Diagnosis of SB | 0.26 | - | - |
| SB self-report (interview) | 0.44 | - | - |
| SB third-party report | 0.20 | - | - |
| Feeling of tiredness/stiffness | 0.24 | - | - |
| Masseter hypertrophy | 0.12 | - | - |
| Number of teeth with attrition | - | 0.22 | 0.580 |
| PSG: | |||
| Diagnosis of SB | 0.31 | - | - |
| SB index | - | 0.05 | 0.715 |
| Episodes with grinding sounds index | - | −0.06 | 0.715 |
| Diagnostic sheet: | |||
| Diagnosis of SB | 0.05 | - | - |
| Pixelscore | - | −0.11 | 0.715 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walentek, N.P.; Schäfer, R.; Bergmann, N.; Franken, M.; Ommerborn, M.A. Association between Psychological Distress and Possible, Probable, and Definite Sleep Bruxism—A Comparison of Approved Diagnostic Procedures. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020638
Walentek NP, Schäfer R, Bergmann N, Franken M, Ommerborn MA. Association between Psychological Distress and Possible, Probable, and Definite Sleep Bruxism—A Comparison of Approved Diagnostic Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(2):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020638
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalentek, Nicole Pascale, Ralf Schäfer, Nora Bergmann, Michael Franken, and Michelle Alicia Ommerborn. 2024. "Association between Psychological Distress and Possible, Probable, and Definite Sleep Bruxism—A Comparison of Approved Diagnostic Procedures" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 2: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020638
APA StyleWalentek, N. P., Schäfer, R., Bergmann, N., Franken, M., & Ommerborn, M. A. (2024). Association between Psychological Distress and Possible, Probable, and Definite Sleep Bruxism—A Comparison of Approved Diagnostic Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(2), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020638








