Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram (WISCA) to Support Empirical Antibiotic Therapy Decisions in Infected Ischemic Leg Ulcers—A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Ethics
2.4. Specimens and Microbiology
2.5. Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
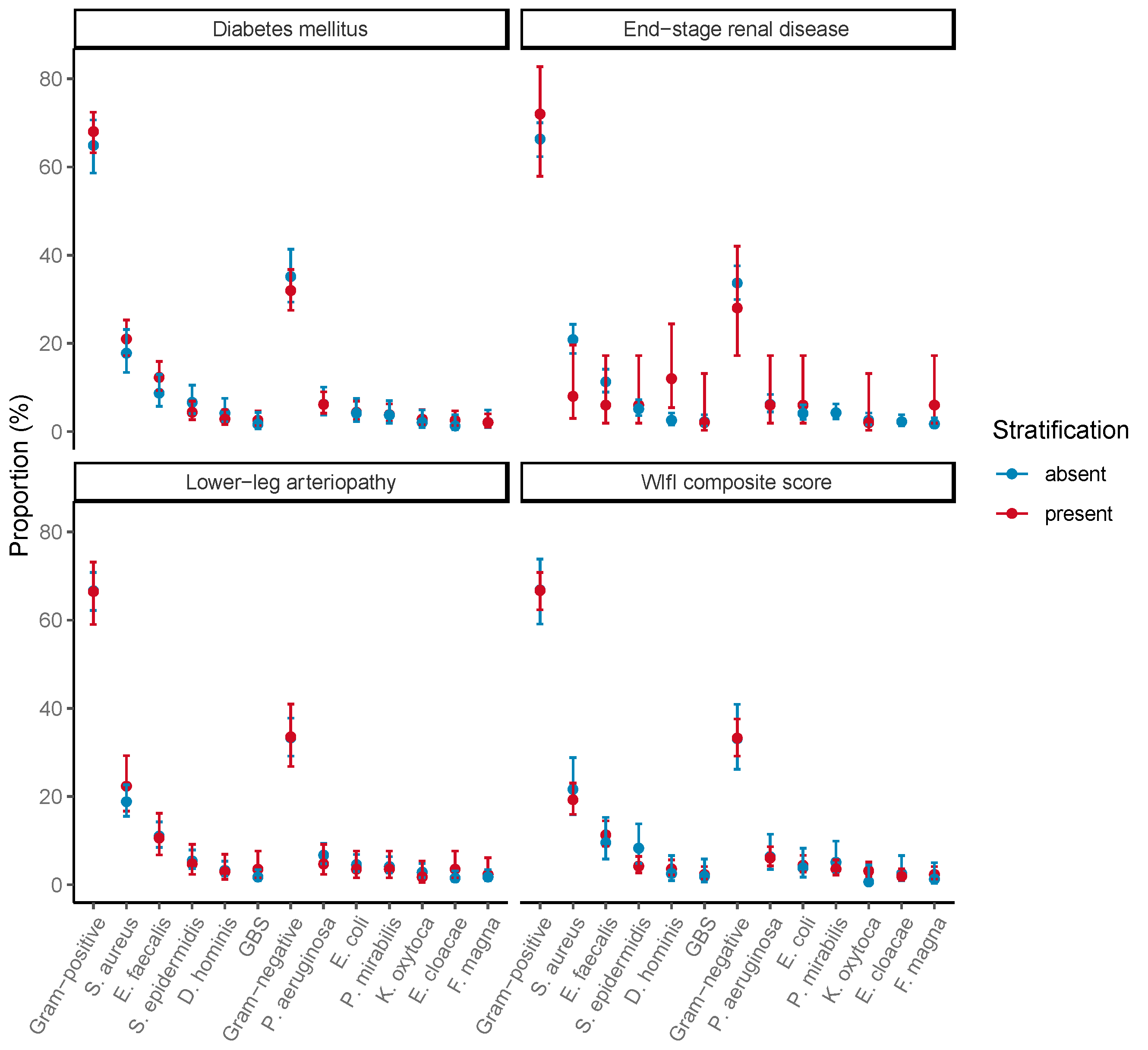
3.2. Pathogen Distribution
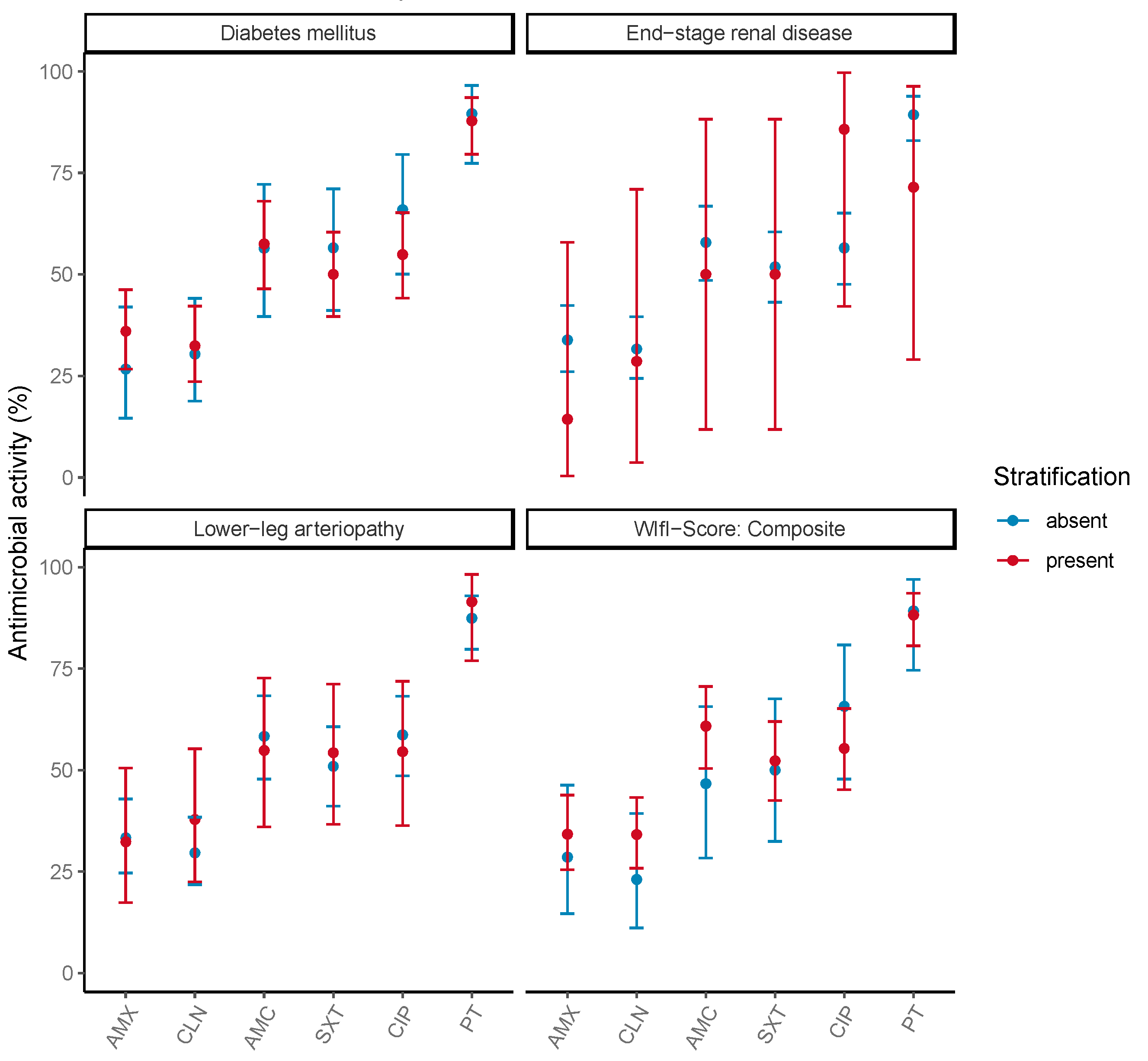
3.3. Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Murray, C.J.; Roth, G.A.; Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks Collaborators. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks, 1990–2022. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2350–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, H.; Unrath, M.; Freisinger, E.; Bunzemeier, H.; Meyborg, M.; Lüders, F.; Gebauer, K.; Roeder, N.; Berger, K.; Malyar, N.M. Peripheral Arterial Disease and Critical Limb Ischaemia: Still Poor Outcomes and Lack of Guideline Adherence. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, J.D.; McCallum, J.C.; Soden, P.A.; Guzman, R.J.; Wyers, M.C.; Hamdan, A.D.; Verhagen, H.J.; Schermerhorn, M.L. Predictive Ability of the Society for Vascular Surgery Wound, Ischemia, and Foot Infection (WIfI) Classification System after First-Time Lower Extremity Revascularizations. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, E.; Zamboni, M.; Sotgiu, G.; Saderi, L.; Federici, M.; Sangiorgi, G.M.; Puci, M.V.; Martelli, A.R.; Messina, T.; Frigatti, P.; et al. Sex-Related Differences and Factors Associated with Peri-Procedural and 1 Year Mortality in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia Patients from the CLIMATE Italian Registry. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.L., Sr.; Conte, M.S.; Armstrong, D.G.; Pomposelli, F.B.; Schanzer, A.; Sidawy, A.N.; Andros, G. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: Risk Stratification Based on Wound, Ischemia, and Foot Infection (WIfI). J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 59, 220–234.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboyans, V.; Ricco, J.-B.; Bartelink, M.-L.E.L.; Björck, M.; Brodmann, M.; Cohnert, T.; Collet, J.-P.; Czerny, M.; De Carlo, M.; Debus, S.; et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in Collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): Document Covering Atherosclerotic Disease of Extracranial Carotid and Vertebral, Mesenteric, Renal. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 763–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard-Herman, M.D.; Gornik, H.L.; Barrett, C.; Barshes, N.R.; Corriere, M.A.; Drachman, D.E.; Fleisher, L.A.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Hamburg, N.M.; Kinlay, S.; et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients with Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2017, 135, e726–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senneville, É.; Albalawi, Z.; van Asten, S.A.; Abbas, Z.G.; Allison, G.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Embil, J.M.; Lavery, L.A.; Alhasan, M.; Oz, O.; et al. IWGDF/IDSA Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes-Related Foot Infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, ciad527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, K.E.; Boeckh, S.; Stacey, H.J.; Jones, J.D. The Microbiology of Diabetic Foot Infections: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-X.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.-W.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.-Z.; Mai, L.-F.; Ren, M.; Yan, L. Empirical Antibiotic Treatment in Diabetic Foot Infection: A Study Focusing on the Culture and Antibiotic Sensitivity in a Population from Southern China. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2017, 16, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, C.; Ridgway, J.; Vekhter, B.; Brown, E.C.; Weber, S.G.; Robicsek, A. Demonstration of the Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram: An Empiric Prescribing Decision Aid. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salm, J.; Böhme, T.; Noory, E.; Beschorner, U.; Kramer, T.S.; Westermann, D.; Zeller, T. Arterial Leg Ulcers—Bacterial Patterns, Antimicrobial Resistance and Clinical Characteristics, a Retrospective Single-Centre Cohort, 2012–2021. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Lipsky, B.A.; Pecoraro, R.E.; Larson, S.A.; Hanley, M.E.; Ahroni, J.H. Outpatient Management of Uncomplicated Lower-Extremity Infections in Diabetic Patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; LeFrock, J.L.; Lew, D.P.; Mader, J.T.; Norden, C.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 885–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Gelone, S.P. FLUOROQUINOLONES. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 14, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.E.; Penning-van Bees, F.J.A.; Kasbergen, A.A.H.; De Smet, P.A.G.M.; Vulto, A.G.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H.C. Overanticoagulation Associated with Combined Use of Antibacterial Drugs and Acenocoumarol or Phenprocoumon Anticoagulants. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 88, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatipoglu, M.; Mutluoglu, M.; Turhan, V.; Uzun, G.; Lipsky, B.A.; Sevim, E.; Demiraslan, H.; Eryilmaz, E.; Ozuguz, C.; Memis, A.; et al. Causative Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance in Diabetic Foot Infections: A Prospective Multi-Center Study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Overall (N = 216) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean (SD) | 75.7 (10.6) |
| Sex | |
| Female (n (%)) | 76 (35.2) |
| Comorbidities (n (%)) | |
| Arterial hypertension | 194 (89.8) |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 163 (75.8) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 135 (62.8) |
| Nicotine consumption | 89 (41.4) |
| End-stage renal disease | 16 (7.4) |
| Intervened vessels (n (%)) | |
| Lower leg arteries 1 | 147 (68.1) |
| Femoropopliteal arteries | 111 (51.4) |
| External iliac artery | 18 (8.4) |
| Deep femoral artery | 19 (8.8) |
| Common iliac artery | 8 (3.7) |
| WIfI classification 2 (median (IQR)) | |
| Wound | 2.0 (2.0, 2.0) |
| Ischemia | 3.0 (1.8, 3.0) |
| Foot infection | 3.0 (3.0, 3.0) |
| Limb and survival outcomes | |
| Minor amputation | 67 (31.2) |
| Major amputation | 30 (14.0) |
| Periinterventional death 3 | 13 (6.0) |
| Systemic inflammation | 29 (13.6) |
| Wound localization (n (%)) | |
| Right | 110 (50.9) |
| Left | 106 (49.1) |
| Toes | 100 (46.3) |
| Foot | 87 (40.3) |
| Lower limb | 29 (13.4) |
| Laboratory parameters (mean (SD)) | |
| CRP 4 (mg/dL) | 6.8 (8.1) |
| WBC 5 (n/µL) | 15,453.2 (14,084.2) |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.7 (1.7) |
| Microbiology | |
| Polymicrobial (n (%)) | 154 (71.3) |
| N bacterial isolates (median (IQR)) | 2.0 (1.0, 4.0) |
| Pathogen (n = 635) | n | Percent (%) | 95% CI 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive | 424 | 66.8 | 63.0; 70.3 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 126 | 19.8 | 16.9; 23.1 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 69 | 10.9 | 8.7; 13.5 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 33 | 5.2 | 3.7; 7.2 |
| Dermabacter hominis | 21 | 3.3 | 2.2; 5.0 |
| GBS 2 | 14 | 2.2 | 1.3; 3.7 |
| Gram-negative | 211 | 33.2 | 29.7; 37.0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 39 | 6.1 | 4.5; 8.3 |
| Escherichia coli | 27 | 4.3 | 2.9; 6.1 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 25 | 3.9 | 2.7; 5.8 |
| Klebsiella oxycota | 16 | 2.5 | 1.5; 4.1 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 13 | 2.0 | 1.2; 3.5 |
| Obligate anaerobic | |||
| Finegoldia magna | 13 | 2.0 | 1.2; 3.3 |
| Antibiotic | N Covered Patients 1 | N Patients 2 | Percent (%) | 95% CI 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMX | 21 | 97 | 21.6 | 13.9; 31.2 |
| CLN | 33 | 119 | 27.7 | 29.9; 36.7 |
| AMC | 41 | 81 | 50.6 | 39.3; 61.9 |
| SXT | 52 | 98 | 53.1 | 42.7; 63.2 |
| CIP | 51 | 92 | 55.4 | 44.7; 65.8 |
| PT | 85 | 103 | 82.5 | 73.8; 89.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salm, J.; Ikker, F.; Noory, E.; Beschorner, U.; Kramer, T.S.; Westermann, D.; Zeller, T. Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram (WISCA) to Support Empirical Antibiotic Therapy Decisions in Infected Ischemic Leg Ulcers—A Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206219
Salm J, Ikker F, Noory E, Beschorner U, Kramer TS, Westermann D, Zeller T. Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram (WISCA) to Support Empirical Antibiotic Therapy Decisions in Infected Ischemic Leg Ulcers—A Feasibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(20):6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206219
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalm, Jonas, Franziska Ikker, Elias Noory, Ulrich Beschorner, Tobias Siegfried Kramer, Dirk Westermann, and Thomas Zeller. 2024. "Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram (WISCA) to Support Empirical Antibiotic Therapy Decisions in Infected Ischemic Leg Ulcers—A Feasibility Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 20: 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206219
APA StyleSalm, J., Ikker, F., Noory, E., Beschorner, U., Kramer, T. S., Westermann, D., & Zeller, T. (2024). Weighted-Incidence Syndromic Combination Antibiogram (WISCA) to Support Empirical Antibiotic Therapy Decisions in Infected Ischemic Leg Ulcers—A Feasibility Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(20), 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206219






