Abstract
Background: Breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) reduces the quality of life of patients and limits their activities of daily living. Even though resistance exercises seemed to be safe in BCRL patients, it was still controversial that resistance exercises improve lymphedema. Therefore, we sought to evaluate the effects of forearm-targeted resistance exercises on BCRL using segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). Methods: This study was a pilot-controlled randomized trial, with patients divided into the intervention and the control group. Both groups received 30 min of complete decongestive therapy (CDT) for 2 weeks. In addition, the intervention group received forearm strengthening training including warm-up and cool-down for an extra 20 min, and the control group received stretching exercises. 5 kHz impedance ratios were assessed by segmental BIA before and after treatments. Results: Among the eighteen patients enrolled, ten were assigned to the intervention group, and eight were in the control group. Only the 5 kHz impedance ratio in the forearm segment of the intervention group showed a statistically significant difference. The effect sizes of the groups were 0.71 for the intervention group and 0.93 in the between-group comparison. Conclusions: Forearm resistance exercises in patients with BCRL showed a significant decrease in extracellular fluid in the proximal forearm segment when using segmental BIA. Therefore, we suggest that resistance exercises targeting the forearm might be effective in treating lymphedema.
1. Introduction
Breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL), a common complication of breast cancer surgery, reduces the quality of life of patients and limits their activities of daily living [1]. In the past, it was known, as a principle, not to use the affected arm; however, a series of studies proved that remedial exercises, such as stretching exercises included in complete decongestive therapy (CDT), were effective. Based on these studies, remedial exercises along with CDT were widely performed [2]. Moreover, in recent studies, strengthening exercises, in addition to remedial exercises, improved the patient’s quality of life without increasing the risk of BCRL [3,4,5,6,7]. Some studies even suggest that resistance exercises and physical activity lower the risk of lymphedema [8,9]. Although resistance exercises appeared to be safe, it was still debatable whether they improved lymphedema in patients with BCRL.
Accordingly, various attempts have been made to show that resistance exercises combined with CDT are more useful than CDT alone with conventional manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) massage in patients with lymphedema. Some studies suggest that resistance exercise could reduce edema and have positive effects on the pathophysiology of BCRL [10]. However, most attempts have failed to demonstrate the superiority of resistance exercises over conventional rehabilitation treatment, owing to several reasons [5,11,12]. Furthermore, even in cases where positive effects have been observed, it has been noted that further research is needed on the methods, measurement techniques, and protocols of resistance exercises [10].
One of the reasons for the failure to show the superiority of strengthening exercises is the use of a similar method in previous studies. In many studies, resistance exercises targeting large muscles of the body that were usually used for conditioning exercises in patients with lymphedema were performed and were not associated with lymphedema sites in patients with breast cancer. Moreover, the parameters and evaluation tools used for outcome measures were also similar to those used in CDT studies [1,3,4,5,6,7,11]. Therefore, there was a need for exercises and evaluation tools for precise investigations of the resistance exercises.
Lymphedema was known to occur in the elbow and peripheral areas in patients with BCRL [12,13,14]. If the exercises target the forearm and the muscles around the elbow and not just the large muscles of the entire body, it is expected that changes not confirmed by existing measurement methods, such as arm volume measurement, or simple bioelectric spectroscopy, will be detected. Skeletal muscle pumping in the distal part, particularly through targeted forearm resistance exercises, may propel the lymphatic flow to drain toward the proximal part [15]. By directing lymphatic flow toward the proximal part, lymphedema around the elbow can be improved.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), which has been used for several years in recent BCRL research, is a method for measuring the impedance that changes with a difference in composition by flowing current through the body part to estimate the degree of edema. When evaluating BCRL with previously used multifrequency BIA (MFBIA), the entire upper extremity of one side, from the hand to the shoulder, has been evaluated as a single compartment. However, the lymph fluid is not drained equally in all sections of the upper extremity. Therefore, MFBIA may not sufficiently detect this difference compared with sub-limb segmental BIA [12,16,17,18,19]. Accordingly, there have been attempts to measure the impedance by dividing the upper limb into segments, which is known as sub-limb segmental BIA, and it has been shown to be useful in evaluating BCRL compared with MFBIA [20]. Using segmental BIA as the evaluation tool, the effect of the resistance exercises can be detected.
Therefore, in this study, we performed a different mode of resistance exercise targeting the forearm and verified the effects of resistance exercises using segmental BIA in a pilot randomized controlled trial (RCT). Through this, we aimed to examine the effects of applying resistance exercise to small muscle groups using sub-limb segmental BIA, which accounts for the differences in the degree of lymph fluid drainage. First, the single-frequency impedance ratio of segmental BIA was used to determine whether forearm resistance exercises affected the change in water distribution in the targeted area [19,21,22]. Second, we applied both the MFBIA and segmental BIA and compared their abilities to detect the effect of resistance exercises.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
From July 2020 to November 2020, patients with unilateral BCRL who visited the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine of a single center were included. Prior ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center, Korea (No. 2020-0447). The eligibility criteria were as follows: patients aged ≥18 years who had swelling in a single arm because of breast cancer with International Society of Lymphedema classification stage II; those who underwent breast cancer surgery and had at least two lymph nodes removed; those without evidence of cancer progression; and those without any other disqualification to limit exercise and treatment plans for at least 1 month after exercise. We defined a clinical diagnosis of lymphedema as a difference of 2 cm or >5% in the measured arm circumference [23,24]. We excluded patients who had bilateral breast cancer or trauma; those who had undergone surgery on upper extremities or the neck; and those who could not perform the proposed exercises at least 3 times a week. After the baseline measurement was performed, the patients were randomized into intervention and control groups. Patients were assigned to the two groups through computerized random allocation, which was conducted in an unpredictable manner and concealed from the research staff responsible for determining eligibility.
2.2. Intervention
This study was a pilot randomized controlled trial. The intervention group performed a 20 min forearm resistance exercise in each session in addition to CDT for 2 weeks. Each session consisted of 5 min of warm-up and stretching; 10 min of resistance exercises, which mainly targeted the forearm, including wrist flexor exercises using elastic bands (Theraband, Akron, OH, USA) and forearm strengthening exercises using a gripper (Digi-Flex Hand Exerciser, Cando, White Plains, NY, USA), performed in sequence; and 5 min of cooldown. After fixing the elastic bands by stepping on them in the sitting position, the patients performed wrist flexion exercises with the forearm placed on their thighs. After marking the length at which sufficient tension was applied, repetitive exercises were performed at an intensity of 60% of one-repetition maximum (1 RM) during the first week and 80% of 1 RM during the second week, performed as many times as possible. Handgrip exercises were performed in the sitting position with full elbow extension, gradually increasing the intensity. The target score on the Borg scale was 12–16, representing moderate to high intensity. Each exercise was performed in 3 sets of 15 repetitions, and the patients alternately performed the exercises using both arms without a rest period. For the control group, experienced physical therapists performed CDT for 30 min with an additional 20 min of stretching exercises for 2 weeks, 5 times a week. Stretching exercises, combined with deep breathing, were composed of neck rotation, bending, shoulder shrugs, arm movements, wrist bending, and hand stretching. After the first education session, the patients of both groups performed all the exercise sessions under the supervision of the professional physical therapist. The exercises were performed while wearing a bandage or compression garment for both groups, if needed.
2.3. Outcome Measure
At the time of enrollment, anthropometric data (e.g., weight, body mass index [BMI], fat mass, and lean mass) and clinical characteristics (e.g., age and sex), and breast cancer-related features (e.g., cancer stage, number of lymph nodes removed, whether chemotherapy or radiotherapy was performed, and chemotherapy agents) were collected.
BIA-related parameters were measured two times using BWA 2.0 (InBody Co., Ltd., Seoul, Republic of Korea) for MFBIA and Inbody M20 (InBody Co., Ltd., Seoul, Republic of Korea) for segmental BIA immediately before and after the treatment sessions. Handgrip, circumference, the EuroQol Visual Analog Scale (EQ-VAS), and EQ-5D-5L were also measured at the time of enrollment and after the last intervention. Handgrip strength was measured using a digital handheld dynamometer after BIA. After measuring twice, the average of the results was used.
2.4. Lymphedema Measurement
The circumference of the affected arm was measured in 4 cm intervals from just the distal part of the ulnar styloid process to the axillary fold, and volume was calculated by using Equation (1):
where R is the larger diameter of the limb (the limb circumference × 1/2π), r is the smaller diameter of the limb (the limb circumference × 1/2π), and h is the vertical distance between R and r. Measurement was performed softly while the patient was lying in the supine position using a measuring tape, without tissue indentation [24].
Volume of limbs = Σ (R2 + Rr + r2) πh/3
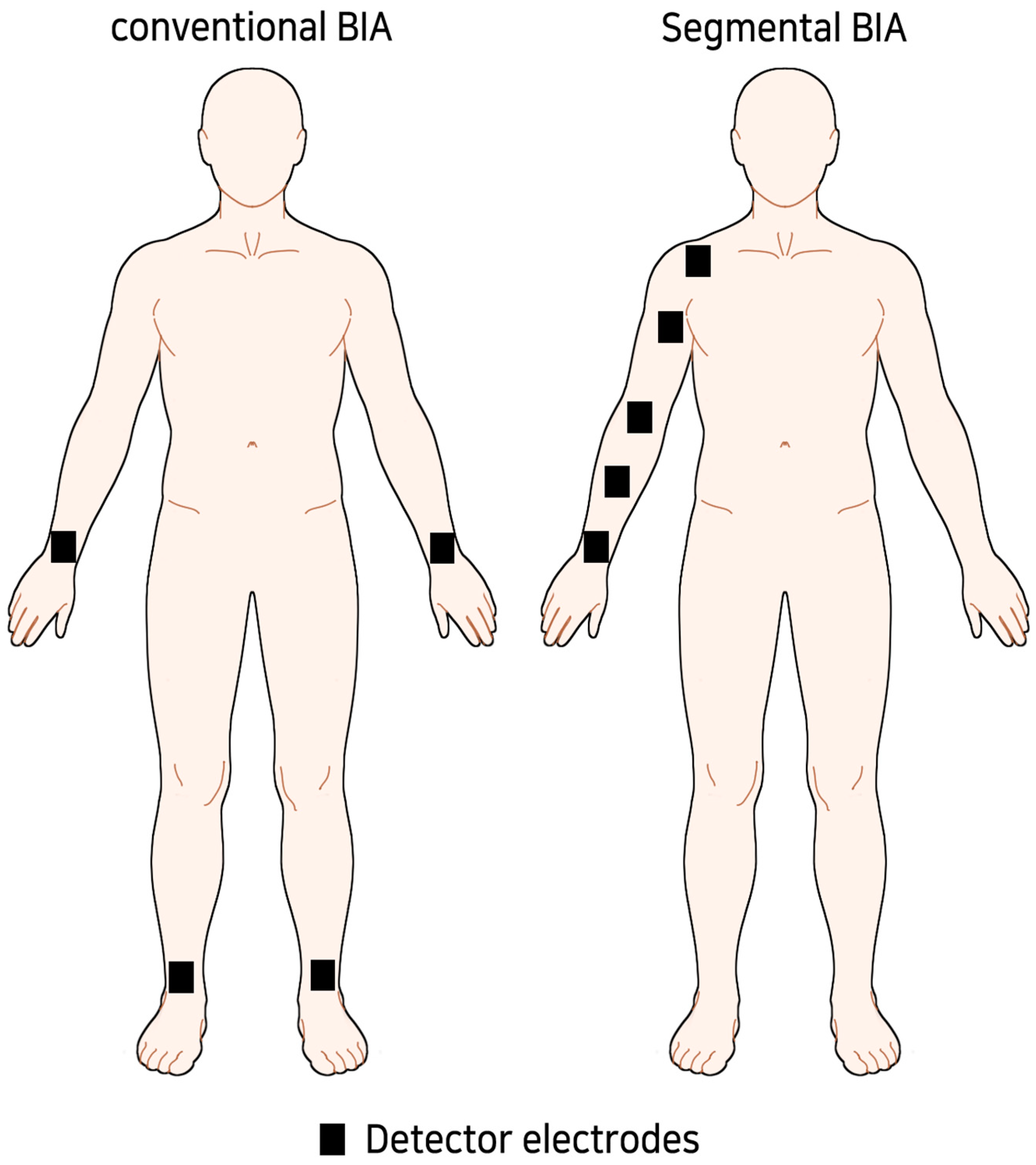
For BIA, the inspector tried to measure in a similar environment as possible. After resting for 5–10 min before measurement, extracellular water (ECW), total body water (TBW), ECW/TBW ratio, and arm body water (ABW) were measured using MFBIA, which were former parameters used for diagnosing BCRL and evaluating the effectiveness of CDT [25,26,27,28]. In the case of segmental BIA, the unilateral arm was divided into four sections based on the ulnar styloid, the midpoint of the ulnar styloid and lateral epicondyle, the lateral epicondyle, the midpoint of the lateral epicondyle and acromioclavicular (AC) joint, and the AC joint (Figure 1). We designated each segment as 1 to 4 from distal to proximal. Each segment was designed to be at least 10 cm in length.
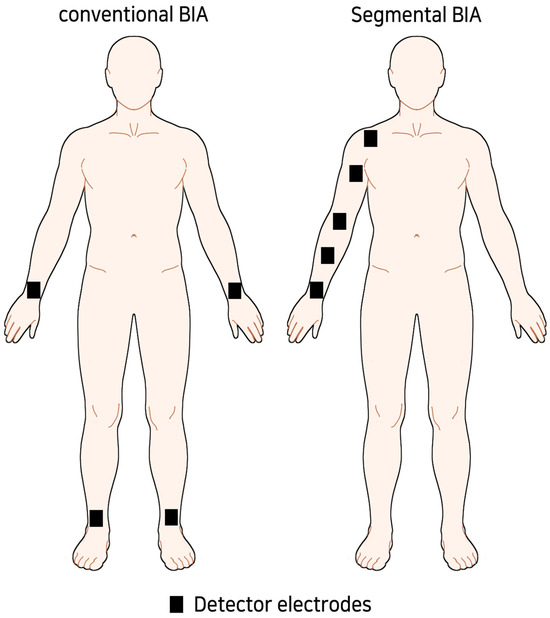
Figure 1.
Concept image of sub-limb segmental BIA.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Due to the small sample size, nonparametric tests were used for data analysis. Descriptive statistics for the characteristics of the patients were presented as means (standard deviations) and ranges. The Mann–Whitney test was used to compare the baseline characteristics between the two groups. To confirm the effects of treatment, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for comparison within each group, and the Mann–Whitney test was used for comparison between groups. Effect sizes for the 5 kHz impedance ratio of the segmental BIA were calculated using Cohen’s d.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Patients
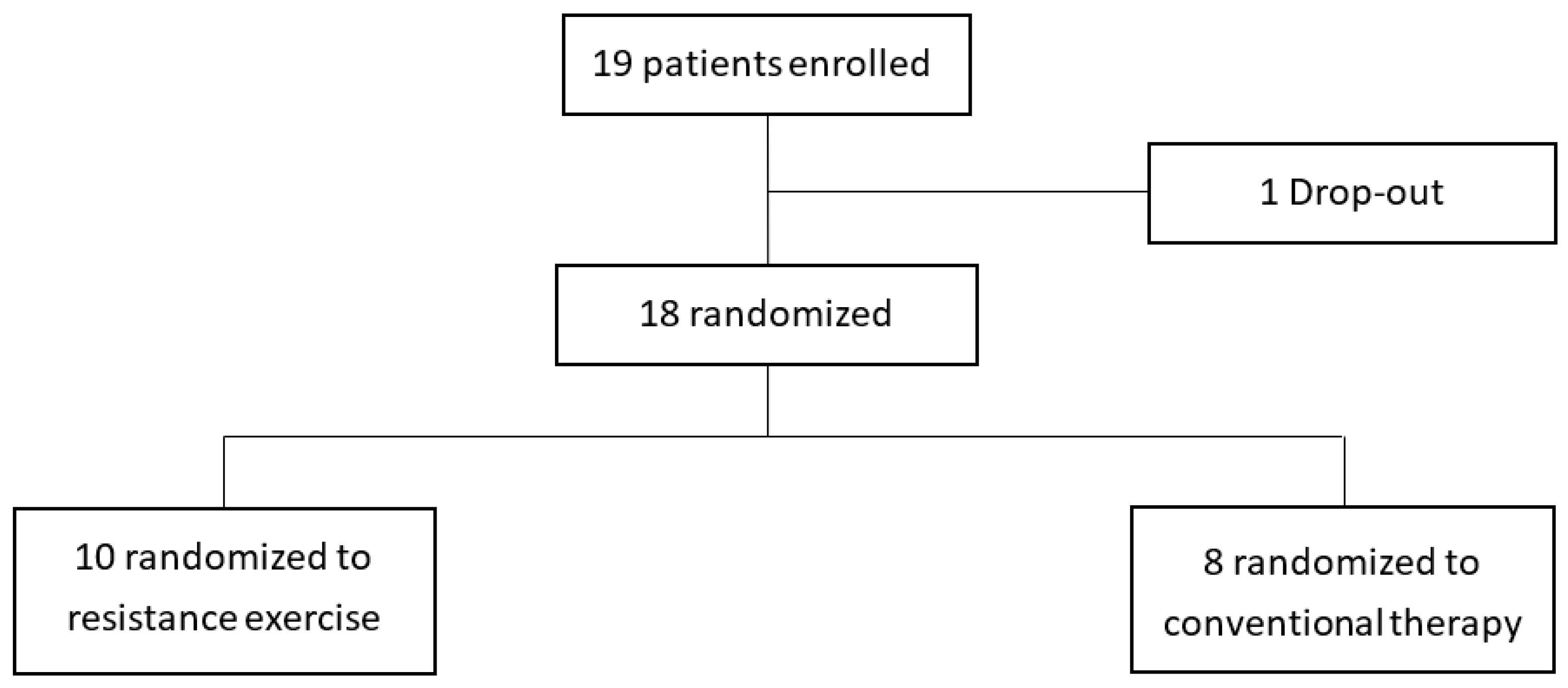
Among the patients who visited the outpatient clinic from July 2020 to November 2020, 19 patients who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled. One of them did not come to the hospital for treatment and was dropped out. Ten were assigned to the intervention group, and eight were assigned to the control group (Figure 2). In Table 1, the weight of the control group was 64.8 ± 6.3 kg, which was slightly higher than that of the intervention group (52.6 ± 4.7 kg). Of the 10 sessions, the intervention group attended an average of 8.2 ± 1.1 times, and the control group attended 7.9 ± 0.6 times, showing no significant difference. No adverse events were reported during the exercise sessions in both groups.
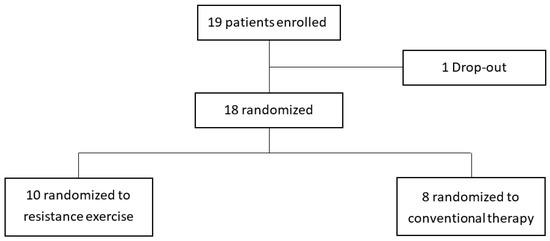
Figure 2.
Enrollment of the study population.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the patients.
3.2. Parameters of MFBIA
In Table 2, the ECW/TBW ratio, ECW, and ABW of the affected arm were evaluated within each group. They tended to decrease after the intervention, except for the ECW/TBW ratio, in the control group. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of MFBIA parameters.

Table 2.
Parameters from MFBIA.
3.3. Parameters of Segmental BIA
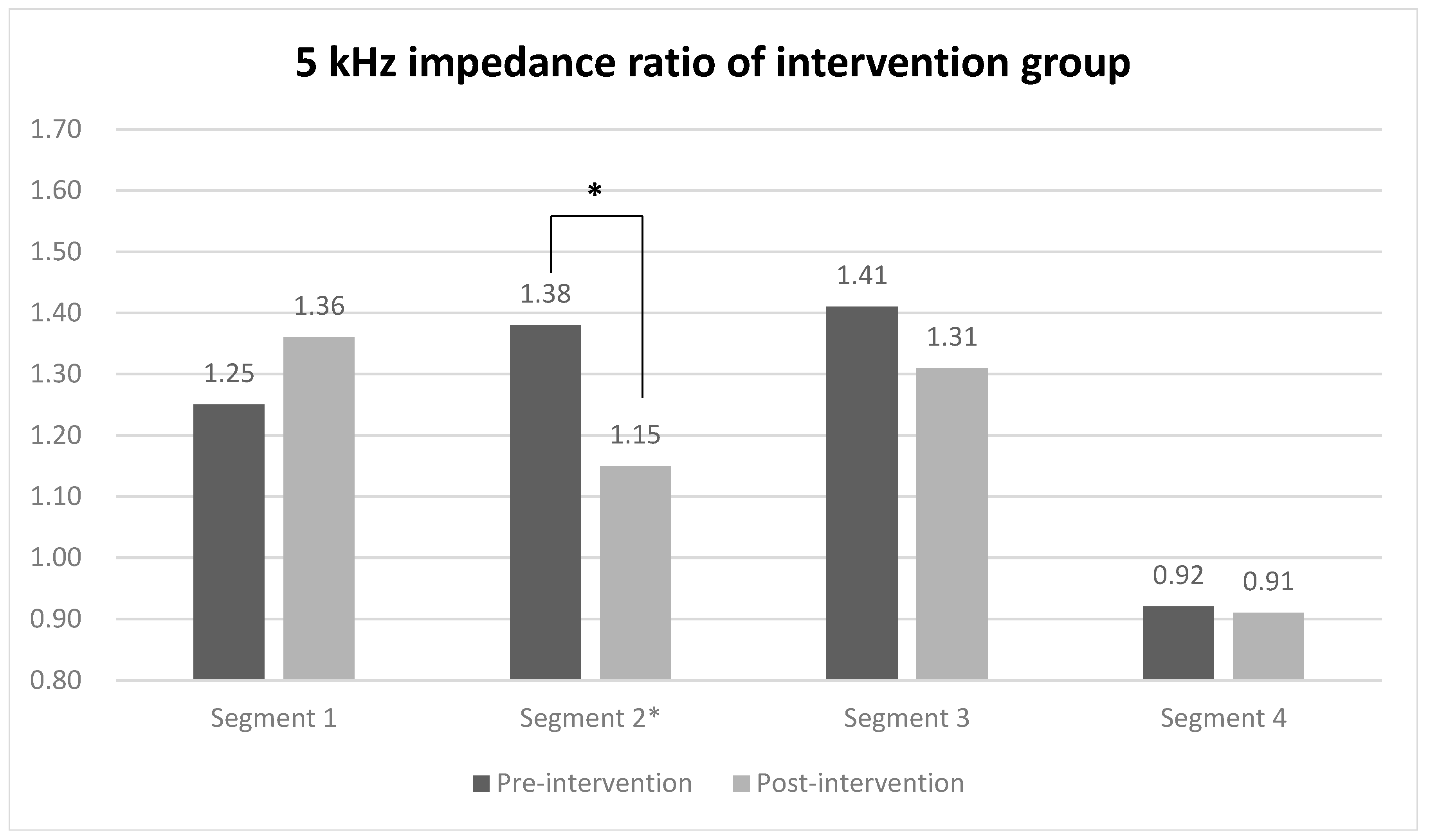
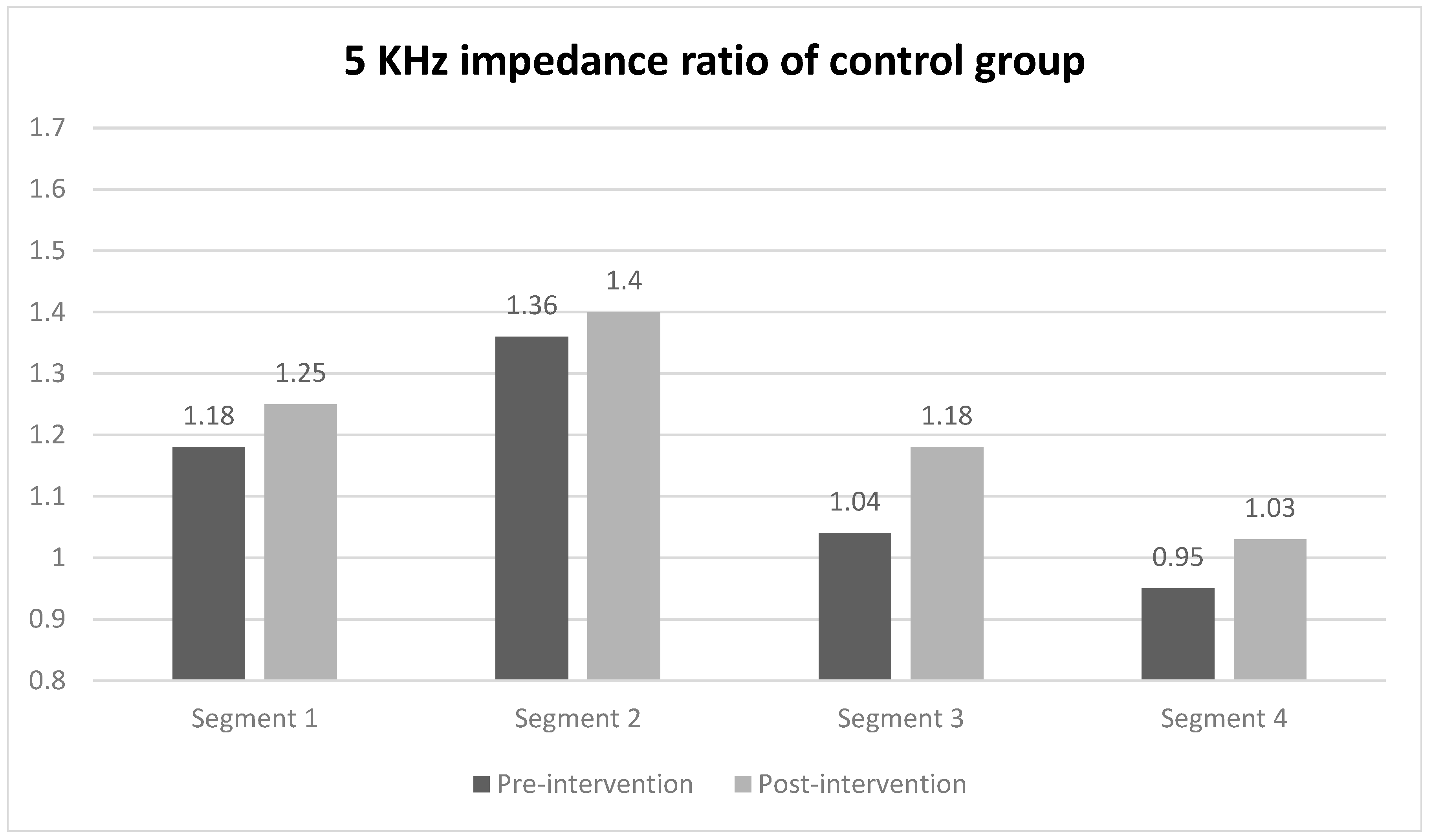
When evaluating the 5 kHz impedance ratio of each segment using segmental BIA for comparing between groups, a statistically significant difference was observed only in segment 2 (midpoint of the ulnar styloid and the lateral epicondyle to the lateral epicondyle) of the intervention group, with values of 1.38 before the intervention and 1.15 after the intervention (Figure 3). In contrast, the impedance ratios of all segments in the control group did not show statistically significant changes before and after the intervention. The effect sizes of the groups were 0.71 for the intervention group and 0.93 in the between-group comparison (Table 3).
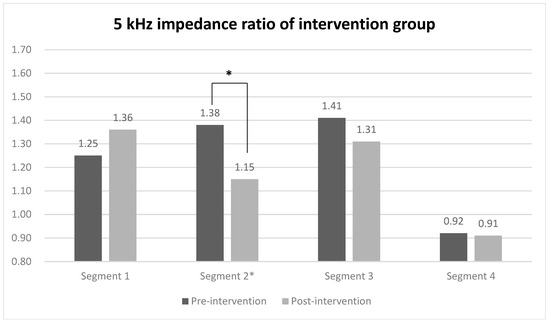
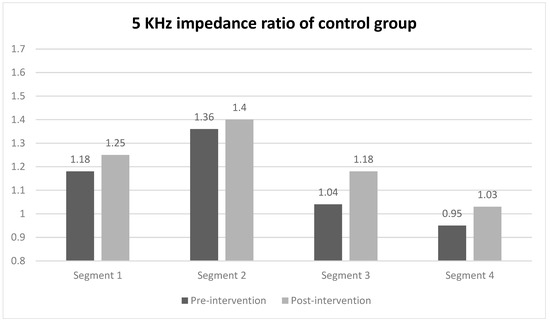
Figure 3.
5 kHz impedance ratio of each segment in intervention and control group. Values are presented as median or as indicated. * Wilcoxon signed-rank test.

Table 3.
5 kHz impedance ratio of each segment by segmental BIA.
3.4. Other Outcomes
In both groups, the volume of the affected limb significantly changed after the sessions. Additionally, the evaluated handgrip strength, EQ-VAS, and EQ-5D-5L showed no significant difference in both groups (Table 4).

Table 4.
Volume of the affected limb, strength, and EQ-VAS, 5D-5L.
4. Discussion
This study was a pilot RCT that evaluated the effects of forearm resistance exercises in patients with BCRL using segmental BIA. Previously, some studies had attempted to verify the effects of additionally performing resistance exercises. However, they failed to show the superiority of resistance exercises over conventional MLD or other treatment options, only proving their safety [4,8,11]. Recent studies have reported that resistance exercise shows significant effects on reducing pain or edema in patients with BCRL, but they also recommend further studies using various resistance exercise modes and evaluation tools [10,29]. Considering the lymph drainage system, it seemed that previous evaluation tools were inadequate to catch the efficacy of resistance exercises, particularly those focused on a specific segment. In this study, we attempted to prove it from two perspectives. First, we performed forearm-targeted resistance exercises based on the locations in which lymphedema frequently occurred. Second, we applied segmental BIA. Through this, we could compensate for the difficulty in detecting the composition change or specifically confirming the changes in focal edema [20]. The results of this pilot RCT with the medium intergroup effect size and large within-group effect size of the 5 kHz impedance ratio in segment 2 indicated that it would be useful to imitate this study with a larger sample size.
As mentioned above, lymphedema is known to occur in the forearm and surrounding areas [12,13,14]. Furthermore, there is usually little fat tissue with a relatively large muscle portion, which is advantageous for determining the effectiveness of resistance exercises. Hence, the forearm may be one of the most suitable body parts for proving the effectiveness of resistance exercises. It is also possible that muscle contraction through forearm resistance exercises improved subfascial lymph drainage and demonstrated more effective lymph drainage [13,30]. In other words, resistance exercises that generate counterpressure between the muscle and a compression garment or skin could create similar effects to MLD. Therefore, resistance exercises targeting the forearm with CDT could be effective in improving lymphedema, particularly in patients with BCRL.
In this study, the 5 kHz impedance ratio using segmental BIA significantly improved in the proximal forearm section. It showed a medium effect size in the intervention group and a large effect size in the between-group comparison. In previous studies validating resistance exercise, some used bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) to measure total body water. However, this approach only measures total volume and classifies the entire limb as a single segment, which presents a limitation in distinguishing specific components, such as lymphedema and muscle mass, in the desired area [9]. This may result in the relative growth of muscle mass, masking the effects of the exercise. Therefore, sub-limb segment analysis using specific impedance ratios is presumed to be more useful from certain perspectives. The proximal forearm was the actual targeted area of the resistance exercises performed, and the resistance exercises performed mainly on a specific area were effective in improving interstitial fluid discharge in the relevant area. This finding was consistent with those of previous studies that indicated that lymphedema seemed not to have a uniform distribution and might be mainly occurring around the elbow in relation to the lymphatic drainage system along the forearm [12,13,14]. Considering these findings, segmental BIA could be a useful monitoring tool for patients with BCRL when performing resistance exercises.
ECW and ABW tended to decrease in both groups, but MFBIA parameters yielded no significant results. Given that both groups performed CDT, these results differed from previous studies that found a statistically significant change in MFBIA parameters after CDT in patients with BCRL [1,3]. We assumed that this was because of the small number of enrolled patients and MFBIA’s relatively low sensitivity compared with segmental BIA. If the exercise is performed by targeting the forearm and the study is carried out with a large number of patients, we can expect that MFBIA will also aid in proving the effect of forearm-targeted resistance exercises.
Handgrip strength did not change significantly. Handgrip strength in the intervention group did not improve significantly when compared with the control group. Forearm muscles are usually composed of type 1 muscle fiber, and we assumed that 2 weeks of exercises seemed to be relatively short for functional change, considering that at least 4 weeks of exercises were performed in other studies [3,31]. However, as shown in Table 4, although not statistically significant, there was an overall increasing trend compared to before the intervention. This suggests that in a large population study, the results could be statistically significant. Further studies with a longer exercise schedule are required.
Study Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, as a pilot study, the number of enrolled patients was small; therefore, further study with a larger study population is required. Second, it was possible that incomplete data were derived because of the instability of the equipment used. Third, because the parameters of MFBIA were not statistically significant in the within-group comparisons, we could not perform the comparisons between the groups. Fourth, since the weight difference between the two groups was statistically significant, the results could be biased, considering that weight could affect lymphedema. Finally, because of the relatively short intervention period, only the time point immediately after 2 weeks of exercises was evaluated; therefore, the long-term outcomes could not be evaluated. Follow-up studies are needed to determine whether the effect of exercises continues and examine the effect of resistance exercises focusing on partial segments on the prognosis of BCRL.
5. Conclusions
Forearm resistance exercises in patients with BCRL showed a significant decrease in extracellular fluid in the proximal forearm segment when using segmental BIA. Therefore, resistance exercises targeting the forearm might be effective in treating lymphedema with appropriate use of segmental BIA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.C.S. and J.Y.J.; data curation, H.C.; formal analysis, W.C.S. and S.A.K.; investigation, W.C.S.; methodology, S.A.K. and A.H.K.; validation, H.C.; writing—original draft, W.C.S.; writing—review and editing, J.Y.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the InBody Co., Ltd. (No. 2020OM0255). These funding sources were not involved in the study design, data collection, management, analysis, interpretation of the data, or writing of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (No. 2020-0447, dated 25 March 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the physicians and physical therapists in Asan Medical Center who agreed to participate in the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Singh, B.; DiSipio, T.; Peake, J.; Hayes, S.C. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Exercise for Those with Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 302–315.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasinski, B.B.; Thrift, K.M.; Squire, D.; Austin, M.K.; Smith, K.M.; Wanchai, A.; Green, J.M.; Stewart, B.R.; Cormier, J.N.; Armer, J.M. A Systematic Review of the Evidence for Complete Decongestive Therapy in the Treatment of Lymphedema From 2004 to 2011. PM R 2012, 4, 580–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilani, M.; Hasenoehrl, T.; Neubauer, M.; Crevenna, R. Resistance exercise and secondary lymphedema in breast cancer survivors—A systematic review. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuiver, M.M.; ten Tusscher, M.R.; Agasi-Idenburg, C.S.; Lucas, C.; Aaronson, N.K.; Bossuyt, P.M. Conservative interventions for preventing clinically detectable upper-limb lymphoedema in patients who are at risk of developing lymphoedema after breast cancer therapy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormie, P.; Pumpa, K.; Galvão, D.A.; Turner, E.; Spry, N.; Saunders, C.; Zissiadis, Y.; Newton, R.U. Is it safe and efficacious for women with lymphedema secondary to breast cancer to lift heavy weights during exercise: A randomised controlled trial. J. Cancer Surviv. 2013, 7, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Ahmed, R.L.; Troxel, A.; Cheville, A.; Smith, R.; Lewis-Grant, L.; Bryan, C.J.; Williams-Smith, C.T.; Greene, Q.P. Weight Lifting in Women with Breast-Cancer-Related Lymphedema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Ahmed, R.L.; Troxel, A.B.; Cheville, A.; Lewis-Grant, L.; Smith, R.; Bryan, C.J.; Williams-Smith, C.T.; Chittams, J. Weight lifting for women at risk for breast cancer-related lymphedema: A randomized trial. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2010, 304, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskett, E.D.; Dean, J.A.; Oliveri, J.M.; Harrop, J.P. Cancer-related lymphedema risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and impact: A review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3726–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Y.X.; Wang, T.T.; Chen, K.X.; Shang, S.M. Breast cancer-related lymphoedema and resistance exercise: An evidence-based review of guidelines, consensus statements and systematic reviews. J. Clin. Nurs. 2023, 32, 2208–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenoehrl, T.; Palma, S.; Ramazanova, D.; Kölbl, H.; Dorner, T.E.; Keilani, M.; Crevenna, R. Resistance exercise and breast cancer–related lymphedema—A systematic review update and meta-analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 3593–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markes, M.; Brockow, T.; Resch, K.L. Exercise for women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.J.; Dylke, E.S.; Ward, L.C.; Kilbreath, S.L. Segmental impedance thresholds for early detection of unilateral upper limb swelling. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2015, 13, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Stanton, A.W.B.; Mellor, R.H.; Peters, A.M.; Levick, J.R.; Mortimer, P.S. Regional distribution of epifascial swelling and epifascial lymph drainage rate constants in breast cancer-related lymphedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2005, 3, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerniec, S.A.; Ward, L.C.; Lee, M.-J.; Refshauge, K.M.; Beith, J.; Kilbreath, S.L. Segmental measurement of breast cancer-related arm lymphoedema using perometry and bioimpedance spectroscopy. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewski, W.L. Contractility patterns of human leg lymphatics in various stages of obstructive lymphedema. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stanton, A.W.; Svensson, W.E.; Mellor, R.H.; Peters, A.M.; Levick, J.R.; Mortimer, P.S. Differences in lymph drainage between swollen and non-swollen regions in arms with breast-cancer-related lymphoedema. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, N.L.; Pfalzer, L.A.; Levy, E.; McGarvey, C.; Springer, B.; Gerber, L.H.; Soballe, P. Segmental limb volume change as a predictor of the onset of lymphedema in women with early breast cancer. PM R 2011, 3, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlit, S.; Brade, J.; Tuschy, B.; Foeldi, E.; Walz-Eschenlohr, U.; Leweling, H.; Suetterlin, M. Whole-body versus Segmental Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Patients with Edema of the Upper Limb After Breast Cancer Treatment. Anticancer. Res. 2013, 33, 3403–3406. [Google Scholar]
- Czerniec, S.A.; Ward, L.C.; Meerkin, J.D.; Kilbreath, S.L. Assessment of segmental arm soft tissue composition in breast cancer-related lymphedema: A pilot study using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and bioimpedance spectroscopy. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2015, 13, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, B.J.; Dylke, E.S.; Ward, L.C.; Kilbreath, S.L. Segmental Bioimpedance Informs Diagnosis of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2017, 15, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.L.; Rosenthall, L.; Towers, A.; Hodgson, P.; Shay, C.A.; Tidhar, D.; Vigano, A.; Kilgour, R.D. Determining the precision of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and bioelectric impedance spectroscopy in the assessment of breast cancer-related lymphedema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2013, 11, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorup, C.; Zerahn, B.; Hendel, H.W. Assessment of volume measurement of breast cancer-related lymphedema by three methods: Circumference measurement, water displacement, and dual energy X-Ray absorptiometry. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2010, 8, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheville, A.L.; McGarvey, C.L.; Petrek, J.A.; Russo, S.; Thiadens, S.R.; Taylor, M.; Petrek, J.A.; Russo, S.A.; Taylor, M.E. The grading of lymphedema in oncology clinical trials. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2003, 13, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.R.; Hugi, M.R.; Olivotto, I.A.; Levine, M. Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment of breast cancer: 11. Lymphedema. CMAJ 2001, 164, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terada, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Sawaki, M.; Hattori, M.; Naomi, G.; Kotani, H.; Adachi, Y.; Iwase, M.; Kataoka, A.; Sugino, K.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes and objective assessments with arm measurement and bioimpedance analysis for lymphedema among breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Yu, X. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Fluid Overload in Southern Chinese Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Jeon, J.Y.; Yun, G.J.; Yang, S.; Kwon, S.; Seo, Y.J. Reference values of bioelectrical impedance analysis for detecting breast cancer-related lymphedema. Medicine 2018, 97, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Jeon, J.Y.; Sung, I.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Do, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Prediction of Treatment Outcome with Bioimpedance Measurements in Breast Cancer Related Lymphedema Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, M.; Basoglu, C.; Korkmaz, M.D.; Yildirim, M.A.; Ones, K. Effectiveness of Combined Complex Decongestive Therapy and Resistance Exercises in the Treatment of Lymphedema Associated with Breast Cancer and the Effect of Pain on Treatment Response. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2021, 19, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, C.C.; Ryan, M.; Villa, G.; Di Summa, P.; Cherubino, M.; Boccardo, F. Rationale for Study of the Deep Subfascial Lymphatic Vessels During Lymphoscintigraphy for the Diagnosis of Peripheral Lymphedema. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.S.; Ringqvist, M.; Schmidt, E.M. Fiber type composition of monkey forearm muscle. Anat. Rec. 1985, 211, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).