Expression of Immunoglobulin G4 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Endoscopic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of EoE and NOD Groups
3.2. Effectiveness of Treatment Modalities for EoE and NOD Groups
3.3. Baseline Characteristics of Endoscopic EoE Phenotypes
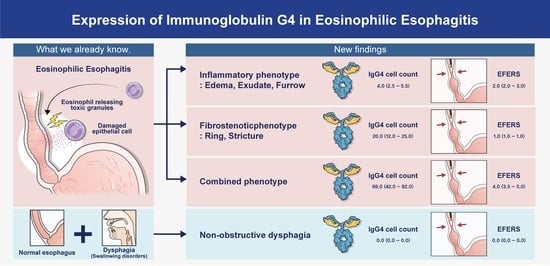
3.4. Serological and Pathological Differences among Endoscopic EoE Phenotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Collins, M.H.; Gupta, S.K.; Justinich, C.; Putnam, P.E.; Bonis, P.; Hassall, E.; Straumann, A.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: A systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1342–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 50, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Aldana, A.; Jaramillo-Santos, M.; Delgado, A.; Jaramillo, C.; Lúquez-Mindiola, A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Current concepts in diagnosis and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4598–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, G.T.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakala, V.; Lamb, C.A.; Haigh, C.; Stirling, R.W.; Attwood, S.E. The diagnosis of primary eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: Missed or misinterpreted? Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, F.; Fang, J.C.; Gleich, G.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Olalla, J.M.; Vinson, L.A.; Lowichik, A.; Chen, X.; Emerson, L.; Cox, K.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults is associated with IgG4 and not mediated by ige. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, A.E.; Stanzione, N.; Naini, B.V.; Garcia-Lloret, M.; Ghassemi, K.A.; Marcus, E.A.; Martin, M.G.; Wozniak, L.J. Esophageal IgG4: Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic correlations in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, M.Y.; LeSuer, W.E.; Horsley-Silva, J.L.; Putikova, A.; Buras, M.R.; Gibson, J.B.; Pyon, G.C.; Simmons, T.D.; Doyle, A.D.; Wright, B.L. Food-specific IgG4 is elevated throughout the upper gastrointestinal tract in eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, J.Y.; Lee, L.E.; Park, Y.B.; Lee, S.W. Comparison of the 2022 acr/eular classification criteria for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with previous criteria. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, itc65–itc80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, C.E.; Mingler, M.K.; Caldwell, J.M.; Collins, M.H.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Morris, D.W.; Mukkada, V.A.; Putnam, P.E.; Shoda, T.; Wen, T.; et al. Esophageal IgG4 levels correlate with histopathologic and transcriptomic features in eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2018, 73, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyk, M.; Strubchevska, K.; Kravchenko, Y.; Voroniak, D.; Cushman, J.; Giri, S. Eosinophilic esophagitis in the setting of prior caustic ingestion. Cureus 2023, 15, e35536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, W. Immunological mechanism of IgG4-related disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2020, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, P. IgG4-related oesophageal disease with cytomegalovirus infection: A case report. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.W.; Jeon, M.H.; Shin, H.D. IgG4-related disease with esophageal involvement. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2019, 13, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiorah, I.; Hussain, A.; Palese, C.; Azumi, N.; Benjamin, S.; Ozdemirli, M. IgG4-related disease involving the esophagus: A clinicopathological study. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-M.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, S.J.N.; Noh, M.-G.; Lee, T.-B.; Jung, Y.-W. Gastrointestinal aa amyloidosis following recurrent SARS-CoV-2 infection: A case report. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, M.B.; Chehade, M.; Brizuela, D.; Maydonovitch, C.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Riffle, M.E.; Achem, S.R.; Moawad, F.J. Early comparison of inflammatory vs. Fibrostenotic phenotype in eosinophilic esophagitis in a multicenter longitudinal study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, J.B.; Bolton, S.M.; Amsden, K.; Wershil, B.K.; Hirano, I.; Kagalwalla, A.F. Eosinophilic esophagitis reference score accurately identifies disease activity and treatment effects in children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Aderoju, A.; Woosley, J.T.; Sandler, R.S.; Shaheen, N.J. Variability in diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2300–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredenoord, A.J.; Patel, K.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Dellon, E.S.; Chehade, M.; Aceves, S.S.; Spergel, J.M.; Shumel, B.; Deniz, Y.; Rowe, P.J.; et al. Disease burden and unmet need in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, G.A.; Talley, N.J.; Romero, Y.; Arora, A.S.; Kryzer, L.A.; Smyrk, T.C.; Alexander, J.A. Prevalence and predictive factors of eosinophilic esophagitis in patients presenting with dysphagia: A prospective study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H. An overview of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Kim, H.P.; Sperry, S.L.; Rybnicek, D.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 577–585.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warners, M.J.; Oude Nijhuis, R.A.B.; de Wijkerslooth, L.R.H.; Smout, A.; Bredenoord, A.J. The natural course of eosinophilic esophagitis and long-term consequences of undiagnosed disease in a large cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Bussmann, C.; Kuchen, T.; Portmann, S.; Simon, H.U.; Straumann, A. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1230–1236.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Youn, Y.H.; Park, J.C.; Park, H. Reversibility of endoscopic features after treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidlich, S.; Nennstiel, S.; Jesinghaus, M.; Brockow, K.; Slotta-Huspenina, J.; Bajbouj, M.; Schmid, R.M.; Schlag, C. IgG4 is elevated in eosinophilic esophagitis but not in gastroesophageal reflux disease patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, K.; Kucharska, M.; Reszec, J.; Lebensztejn, D.M.; Daniluk, U. Immunohistochemical markers for eosinophilic esophagitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Hirano, I.; Chehade, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Spergel, J.M.; Aceves, S.; Sun, X.; et al. Dupilumab in adults and adolescents with eosinophilic esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racca, F.; Pellegatta, G.; Cataldo, G.; Vespa, E.; Carlani, E.; Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Messina, M.R.; Nappi, E.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. Type 2 inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis: From pathophysiology to therapeutic targets. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 815842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massironi, S.; Mulinacci, G.; Gallo, C.; Elvevi, A.; Danese, S.; Invernizzi, P.; Vespa, E. Mechanistic insights into eosinophilic esophagitis: Therapies targeting pathophysiological mechanisms. Cells 2023, 12, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Characteristics | EoE (n = 19) | NOD (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (IQR) | 41 (18–58) | 30.5 (19–46) | 0.173 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 18 (94.7) | 7 (58.3) | 0.014 |
| BMI, kg/m2 (IQR) | 23.5 (22.0–25.5) | 19.3 (18.3–21.1) | 0.002 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 6 (31.6) | 2 (16.7) | 0.509 |
| Alcohol, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 5 (41.7) | 0.484 |
| PPI, n (%) | 4 (21.1) | 2 (16.7) | 0.857 |
| NSAIDs, n (%) | 1 (5.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.826 |
| CCI, median (IQR) | 0 (0–1) | 0 (0–0) | 0.326 |
| Symptoms | |||
| Dysphagia, n (%) | 12 (63.2) | 8 (66.7) | 0.845 |
| Heartburn, n (%) | 4 (21.1) | 2 (16.7) | 0.767 |
| Dyspepsia, n (%) | 7 (36.8) | 7 (58.3) | 0.249 |
| Reflux, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 5 (41.7) | 0.381 |
| Food impaction, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (16.7) | 0.070 |
| Laboratory results (IQR) | |||
| Serum WBC, count/μL | 5720 (4965–6540) | 7015 (4952–8620) | 0.496 |
| Pathological results (IQR) | |||
| Eosinophil, cells/HPF | 91.5 (50.0–150.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.5) | <0.001 |
| IgG4, cells/HPF | 7.5 (3.5–22.5) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.003 |
| IgG, cells/HPF | 68.0 (42.0–101.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.004 |
| TRC positive, n (%) | 14 (73.68) | 4 (33.33) | 0.029 |
| EoE (n = 19) | NOD (n = 12) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of treatment | |||
| PPI, n (%) | 18 (94.7) | 11 (91.7) | 0.739 |
| Topical steroid, n (%) | 2 (10.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.253 |
| Diet therapy, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.056 |
| Pre-treatment (IQR) | |||
| Symptoms (NRS 0–10) | 3.0 (2.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.00–2.75) | 0.124 |
| EREFS score (0–9) | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | <0.001 |
| Post-treatment (IQR) | |||
| Symptoms (NRS 0–10) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.126 |
| EREFS score (0–9) | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.002 |
| Response to treatment, n (%) | 17 (89.5) | 8 (66.7) | 0.035 |
| ΔEREFS score (0–9), (IQR) | −1.0 (−2.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.004 |
| Recurrence of symptoms, n (%) | 4 (21.1) | 1 (8.3) | 0.356 |
| Inflammatory Phenotype (n = 9) | Fibrostenotic Phenotype (n = 7) | Combined Phenotype (n = 3) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex, n (%) | 8 (88.9) | 7 (100) | 3 (100) | 0.391 |
| Age, years (IQR) | 42.78 (29–73) | 34.86 (18–44) | 47.33 (41–58) | 0.256 |
| BMI, kg/m2 (IQR) | 22.2 (20.8–23.7) | 24.2 (23.4–26.0) | 25.5 (23.8–27.4) | 0.087 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 3 (33.3) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (33.3) | 0.978 |
| Alcohol, n (%) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (14.3) | 3 (100.0) | 0.009 |
| PPI, n (%) | 3 (33.3) | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0.424 |
| NSAIDs, n (%) | 1 (11.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.574 |
| Endoscopic features | ||||
| Edema, n (%) | 4 (44.4) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (66.6) | |
| Ring, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (71.4) | 3 (100.0) | |
| Exudate, n (%) | 3 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Furrow, n (%) | 9 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (100.0) | |
| Stricture, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Pre-treatment EREFS (0–9), (IQR) | 2.0 (2.0–3.0) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 4.0 (3.5–5.0) | 0.034 |
| Post-treatment EREFS (0–9), (IQR) | 0.5 (0.0–1.0) | 1.0 (0.0–1.5) | 2.5 (2.0–3.0) | |
| ΔEREFS (0–9), (IQR) | −2.0 (−2.0–−2.0) | −1.0 (−1.0–0.5) | −1.0 (−2.0–0.0) | 0.005 |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Pre-treatment NRS score (0–10), (IQR) | 3.0 (3.0–4.0) | 2.0 (1.5–2.5) | 2.0 (1.5–3.0) | 0.086 |
| Post-treatment NRS score (0–10), (IQR) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.815 |
| Dysphagia, n (%) | 5 (55.6) | 6 (85.7%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0.175 |
| Heartburn, n (%) | 5 (55.6) | 1 (14.3%) | 2 (66.6%) | 0.131 |
| Reflux, n (%) | 3 (33.3%) | 1 (14.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.125 |
| Food impaction, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| Inflammatory Phenotype (n = 9) | Fibrostenotic Phenotype (n = 7) | Combined Phenotype (n = 3) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood test results (IQR) | ||||
| Serum WBC, count/μL | 5210 (4845–5965) | 6330 (5390–8405) | 5570 (5430–5925) | 0.453 |
| Serum eosinophil, count/μL | 295.4 (191.1–374.2) | 487.4 (220.0–585.0) | 200.0 (144.0–600.0) | 0.684 |
| Serum eosinophil, % | 5.1 (4.0–7.0) | 6.8 (4.1–8.7) | 3.6 (2.5–11.5) | 0.666 |
| Serum IgG4, mg/L | 111.5 (69.0–154.0) | 1010.0 (851.0–1280.0) | 570.0 (481.0–705.0) | 0.077 |
| Serum IgG, mg/L | 7313.5 (1191.1–13,436.0) | 13,864.0 (11,979.0–15,367.5) | 9854.0 (2482.0–12,751.0) | 0.140 |
| Serum IgE, KIU/L | 42.5 (12.4–72.1) | 92.0 (46.7–155.5) | 204.9 (86.7–323.0) | 0.915 |
| Pathologic results (IQR) | ||||
| Eosinophil, cells/HPF | 123.0 (86.5–150.0) | 50.0 (31.0–82.0) | 52.0 (51.0–101.0) | 0.055 |
| IgG4, cells/HPF | 4.0 (2.5–5.5) | 20.0 (12.0–25.0) | 69.0 (42.0–82.0) | 0.030 |
| IgG, cells/HPF | 50.0 (22.0–68.0) | 89.0 (72.0–113.0) | 85.0 (63.5–184.0) | 0.065 |
| TRC positive, n (%) | 4 (44.4) | 7 (100.0) | 3 (100.0) | 0.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-Y.; Nahm, J.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Youn, Y.-H.; Park, H. Expression of Immunoglobulin G4 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082175
Lee S-Y, Nahm J-H, Kim M-J, Kim Y, Kim J-H, Youn Y-H, Park H. Expression of Immunoglobulin G4 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(8):2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082175
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, See-Young, Ji-Hae Nahm, Min-Jae Kim, Yuna Kim, Jie-Hyun Kim, Young-Hoon Youn, and Hyojin Park. 2024. "Expression of Immunoglobulin G4 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 8: 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082175
APA StyleLee, S.-Y., Nahm, J.-H., Kim, M.-J., Kim, Y., Kim, J.-H., Youn, Y.-H., & Park, H. (2024). Expression of Immunoglobulin G4 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(8), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13082175