Comparison of the Acute Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Breathing Exercise on the Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Biomechanical Properties of the Muscle in Healthy People
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Assessment
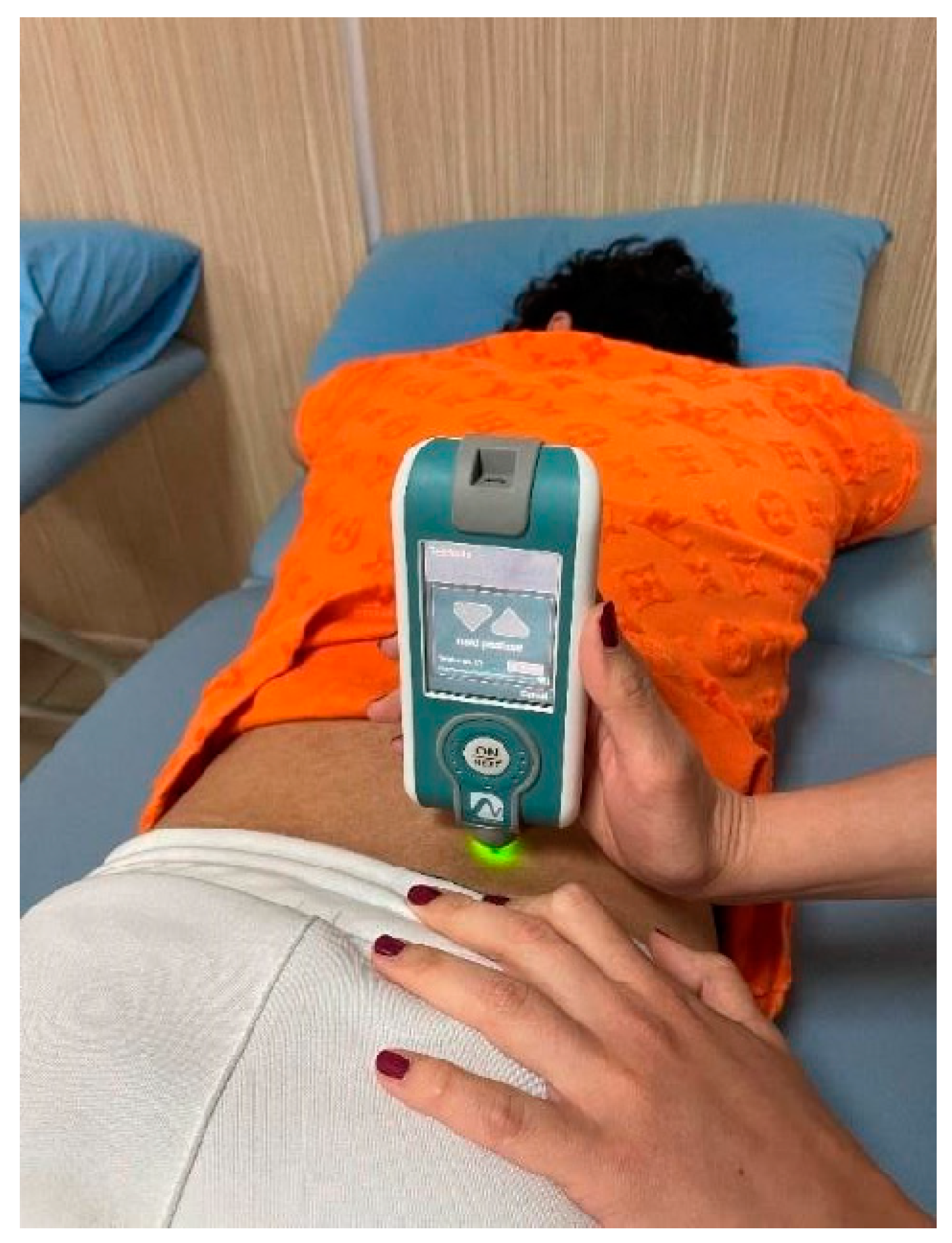
2.4.1. Vagus Nerve Stimulation
2.4.2. Deep Breathing Exercise
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Primary Outcome Measures
Analysis of the Autonomic Nervous System
- -
- High frequency (HF): It shows more parasympathetic activity.
- -
- leaseLow frequency (LF): It indicates more sympathetic activity.
- -
- RMSSD: It is the root mean square of consecutive R-wave peak to R-wave peak interval (RRI) differences. It reflects beat-to-beat variance in heart rate (HR), indicating parasympathetic activity.
- -
- Stress index: It indicates sympathetic activity.
- -
- SNS index: It indicates sympathetic activity.
- -
- PNS index: It indicates parasympathetic activity.
- -
- PNN50: It refers to the division of the number of normal to normal R-R (NN) intervals differing by >50 ms from the preceding interval (NN50) by the total number of NN intervals. It indicates parasympathetic activity [10].
Analysis of the Structural Features of the Muscles
2.5.2. Secondary Outcome Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, R.K.; Acharya, A.; Nepal, O. Autonomic Influence on Heart Rate for Deep Breathing and Valsalva Maneuver in Healthy Subjects. JNMA J. Nepal. Med. Assoc. 2018, 56, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, A.D.; Albu-Soda, A.; Aziz, Q. Vagus nerve stimulation in clinical practice. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnon, V.; Dutheil, F.; Vallet, G.T. Benefits from one session of deep and slow breathing on vagal tone and anxiety in young and older adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, B.; Haleagrahara, N.; Bhat, R.; Kulur, A.B.; Avabratha, S.; Adhikary, P. Increase in the heart rate variability with deep breathing in diabetic patients after 12-month exercise training. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2010, 220, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.F.; Albusoda, A.; Farmer, A.D.; Aziz, Q. The anatomical basis for transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation. J. Anat. 2020, 236, 588–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.A.; Mary, D.A.; Witte, K.K.; Greenwood, J.P.; Deuchars, S.A.; Deuchars, J. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation in healthy humans reduces sympathetic nerve activity. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.-M.; Xiao, J.; Ren, F.-F.; Chen, Z.-S.; Li, C.-R.; Bai, Z.-M.; Rukšenas, O. Acute effect of breathing exercises on muscle tension and executive function under psychological stress. Front. Physiol. 2023, 25, 1155134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampusch, S.; Kaniusas, E.; Széles, J.C. Modulation of Muscle Tone and Sympathovagal Balance in Cervical Dystonia Using Percutaneous Stimulation of the Auricular Vagus Nerve. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.K.; Henry, I.C.; Mietus, J.E.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Khalsa, G.; Benson, H.; Goldberger, A.L. Heartrate Dynamics during three forms of meditation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2004, 95, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An overview of heart rate variability metrics and norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, N.R. The Effect of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Pain and Quality of Life in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Master’s Thesis, Bahçeşehir University Institute of Health Sciences, Istanbul, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Lu, Z.; He, W.; Huang, B.; Jiang, H. Autonomic modulation by electrical stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system: An emerging intervention for cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2016, 34, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billman, G.E. The LF/HF ratio does not accurately measure cardiac sympatho-vagal balance. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, D.; Azizi, B.; Sima, S.; Tavakoli, K.; Mohammadi, N.S.H.; Vahabie, A.-H.; Akbarzadeh-Sherbaf, K.; Vasheghani-Farahani, A. A systematic review of the effects of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in healthy subjects. Clin. Auton. Res. 2023, 33, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferstl, M.; Teckentrup, V.; Lin, W.M.; Kräutlein, F.; Kühnel, A.; Klaus, J.; Walter, M.; Kroemer, N.B. Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation boosts mood recovery after effort exertion. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 3029–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.E.; Huebschmann, N.A.; Iverson, G.L. Safety and tolerability of an innovative virtual reality-based deep breathing exercise in concussion rehabilitation: A pilot study. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2021, 24, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Couck, M.; Caers, R.; Musch, L.; Fliegauf, J.; Giangreco, A.; Gidron, Y. How breathing can help you make better decisions: Two studies on the effects of breathing patterns on heart rate variability and decision-making in business cases. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 139, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.K.; Andersen, S.S.; Andersen, S.S.; Liboriussen, C.H.; Kristensen, S.; Jochumsen, M. Modulating Heart Rate Variability through Deep Breathing Exercises and Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Study in Healthy Participants and in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Sensors 2022, 22, 7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerath, R.; Edry, J.W.; Barnes, V.A.; Jerath, V. Physiology of long pranayamic breathing: Neural respiratory elements may provide a mechanism that explains how slow deep breathing shifts the autonomic nervous system. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konakoğlu, G.; Özden, A.V.; Solmaz, H.; Bildik, C. The effect of auricular vagus nerve stimulation on electroencephalography and electromyography measurements in healthy persons. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1215757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Hahm, S.-C.; Oh, H.-K.; Jung, K.-S.; Cho, H.-Y. Effects of lumbar lordosis assistive support on craniovertebral angle and mechanical properties of the upper trapezius muscle in subjects with forward head posture. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.E. Influential factors of masticatory performance in older adults: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roatta, S.; Passatore, M. Autonomic effects on skeletal muscle. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 250–253. [Google Scholar]

| Gender | VNS | DB | Total | Pearson Chi-Square | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % İntragroup | n | % İntragroup | n | % İntergroup | |||
| Male | 5 | 16.67 | 15 | 50.00 | 20 | 33.33 | 7.500 | 0.006 |
| Female | 25 | 83.33 | 15 | 50.00 | 40 | 66.67 | ||
| Total | 30 | 100 | 30 | 100 | 60 | 100 | ||
| N = 60 | DB N = 30 | VNS N = 30 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Z/t | p | Mean ± SD | Z/t | p | |
| Height (cm) | 171.97 ± 9.34 | −0.074 | 0.941 | 171.70 ± 8.17 | −0.074 | 0.941 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.60 ± 12.54 | −0.429 | 0.668 | 68.40 ± 13.22 | −0.429 | 0.668 |
| Age | 24.70 ± 4.50 | −2.859 | 0.004 | 31.27 ± 8.23 | −2.859 | 0.004 |
| DB | VNS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Z/t | p | Mean ± SD | Z/t | p | ||
| Perceived stress scale | 1st measurement | 27.20 ± 7.29 | 3.892 | 0.001 ** | 26.10 ± 8.31 | 2.443 | 0.021 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 25.97 ± 7.26 | 24.80 ± 7.81 | |||||
| Pulse | 1st measurement | 78.53 ± 9.73 | 4.556 | 0.000 ** | 79.53 ± 9.90 | 6.009 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 74.00 ± 9.74 | 73.50 ± 8.11 | |||||
| Systolic pressure | 1st measurement | 118.23 ± 11.31 | 5.245 | 0.000 ** | 119.73 ± 13.74 | 6.394 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 112.33 ± 12.47 | 112.37 ± 13.76 | |||||
| Diastolic pressure | 1st measurement | 73.40 ± 10.03 | 3.267 | 0.003 ** | 76.00 ± 12.03 | 4.906 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 70.13 ± 10.08 | 70.50 ± 13.57 | |||||
| SNS index | 1st measurement | 0.24 ± 1.01 | 6.041 | 0.000 ** | 0.74 ± 0.95 | 7.75 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | −0.48 ± 1.16 | 0.02 ± 0.79 | |||||
| PNS index | 1st measurement | 0.35 ± 1.32 | −4.33 | 0.000 * | −0.46 ± 1.13 | −4.76 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 9.34 ± 17.59 | 0.55 ± 1.74 | |||||
| RMSSD | 1st measurement | 53.94 ± 30.71 | −4.78 | 0.000 * | 47.03 ± 34.88 | −4.73 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 232.60 ± 421.98 | 75.83 ± 59.47 | |||||
| Stress index | 1st measurement | 8.25 ± 3.07 | 8.519 | 0.000 ** | 9.39 ± 3.65 | −4.58 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 4.79 ± 2.22 | 6.61 ± 2.65 | |||||
| PNN50 | 1st measurement | 21.70 ± 13.31 | −6.23 | 0.000 ** | 13.23 ± 15.54 | −3.96 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 40.01 ± 21.46 | 20.63 ± 16.84 | |||||
| LF/HF | 1st measurement | 1.37 ± 1.62 | −1.29 | 0.199 | 2.56 ± 2.44 | −0.83 | 0.405 |
| 2nd measurement | 1.14 ± 0.62 | 2.60 ± 2.39 | |||||
| Stiffness-trapezius muscle | 1st measurement | 267.18 ± 33.88 | 5.784 | 0.000 ** | 259.43 ± 44.90 | −4.38 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 249.70 ± 31.19 | 244.45 ± 43.59 | |||||
| Stiffness-erector spinae muscle | 1st measurement | 235.53 ± 87.88 | −4.54 | 0.000* | 192.15 ± 46.10 | −3.67 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 235.53 ± 87.88 | 185.92 ± 43.91 | |||||
| Stiffness- gastrocnemius muscle | 1st measurement | 262.80 ± 53.84 | 3.466 | 0.000 ** | 236.68 ± 38.18 | 5.163 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 249.10 ± 50.39 | 227.13 ± 39.87 | |||||
| Stiffness-biceps brachii muscle | 1st measurement | 243.65 ± 36.29 | −4.78 | 0.000 * | 229.68 ± 31.29 | −4.63 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 230.60 ± 37.59 | 216.18 ± 23.66 | |||||
| Stiffness-masseter muscle | 1st measurement | 328.25 ± 88.46 | 3.444 | 0.000 ** | 362.68 ± 61.49 | 3.533 | 0.001 ** |
| 2ndmeasurement | 313.47 ± 76.18 | 343.65 ± 57.96 | |||||
| Relaxation-trapezius muscle | 1st measurement | 18.37 ± 1.94 | −3.97 | 0.000 * | 18.66 ± 1.99 | −4.47 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 19.09 ± 1.98 | 19.69 ± 2.02 | |||||
| Relaxation-erector spinae muscle | 1st measurement | 22.98 ± 5.22 | −4.57 | 0.000 * | 26.53 ± 3.98 | −4.25 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 24.23 ± 4.42 | 27.05 ± 3.89 | |||||
| Relaxation-gastrocnemius muscle | 1st measurement | 19.04 ± 4.05 | −2.24 | 0.014 * | 22.46 ± 3.56 | −5.71 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 19.57 ± 3.93 | 23.63 ± 3.59 | |||||
| Relaxation-biceps brachii muscle | 1st measurement | 19.60 ± 1.75 | −4.92 | 0.000 * | 20.84 ± 2.26 | −4.1 | 0.000 * |
| 2nd measurement | 20.60 ± 1.36 | 21.72 ± 1.79 | |||||
| Relaxation-masseter muscle | 1st measurement | 15.84 ± 2.90 | −1.53 | 0.138 | 15.67 ± 2.73 | −4.98 | 0.000 ** |
| 2nd measurement | 16.18 ± 2.70 | 16.39 ± 2.70 | |||||
| DB | VNS | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |||
| Perceived stress scale | −1.23 ± 1.74 | −1.30 ± 2.91 | −0.663 | 0.510 |
| Pulse | −4.53 ± 5.45 | −6.03 ± 5.49 | −1.729 | 0.089 |
| Diastolic pressure | −3.27 ± 5.48 | −5.50 ± 6.14 | −1.281 | 0.205 |
| Systolic pressure | −5.90 ± 6.16 | −7.37 ± 6.31 | −0.097 | 0.923 |
| RMSSD | 178.67 ± 413.87 | 28.79 ± 36.28 | −2.221 | 0.030 |
| Stress index | −3.45 ± 2.22 | −2.77 ± 2.63 | −2.417 | 0.019 |
| PNN50 | 18.31 ± 16.10 | 7.40 ± 9.14 | −2.518 | 0.015 |
| LF/HF | −0.23 ± 1.60 | 0.04 ± 2.29 | −1.555 | 0.125 |
| SNS index | −0.73 ± 0.66 | −0.71 ± 0.50 | −1.136 | 0.893 |
| PNS index | 8.99 ± 17.25 | 1.008 ± 1.08 | −1.129 | 0.264 |
| Stiffness-trapezius muscle | −17.48 ± 16.55 | −14.98 ± 17.23 | −0.672 | 0.504 |
| Stiffness-erector spinae muscle | −26.72 ± 48.77 | −6.23 ± 9.05 | −0.785 | 0.435 |
| Stiffness-gastrocnemius muscle | −13.70 ± 21.65 | −9.55 ± 10.13 | −1.065 | 0.291 |
| Stiffness-biceps brachii muscle | −13.05 ± 9.12 | −13.50 ± 19.42 | −0.422 | 0.675 |
| Stiffness-masseter muscle | −14.78 ± 23.51 | −19.03 ± 29.51 | −0.801 | 0.426 |
| Relaxation-trapezius muscle | 0.73 ± 1.00 | 1.03 ± 1.26 | −0.949 | 0.347 |
| Relaxation-erector spinae muscle | 1.25 ± 1.49 | 0.52 ± 0.58 | −1.616 | 0.111 |
| Relaxation-gastrocnemius muscle | 0.53 ± 1.30 | 1.17 ± 1.13 | −2.346 | 0.010 |
| Relaxation-biceps brachii muscle | 0.99 ± 1.11 | 0.88 ± 1.11 | −0.057 | 0.955 |
| Relaxation-masseter muscle | 0.34 ± 1.23 | 0.72 ± 0.79 | −0.418 | 0.678 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ertürk, Ç.; Özden, A.V. Comparison of the Acute Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Breathing Exercise on the Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Biomechanical Properties of the Muscle in Healthy People. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041046
Ertürk Ç, Özden AV. Comparison of the Acute Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Breathing Exercise on the Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Biomechanical Properties of the Muscle in Healthy People. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041046
Chicago/Turabian StyleErtürk, Çağıl, and Ali Veysel Özden. 2025. "Comparison of the Acute Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Breathing Exercise on the Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Biomechanical Properties of the Muscle in Healthy People" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041046
APA StyleErtürk, Ç., & Özden, A. V. (2025). Comparison of the Acute Effects of Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation and Deep Breathing Exercise on the Autonomic Nervous System Activity and Biomechanical Properties of the Muscle in Healthy People. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041046








