Association of the Right Ventricle Cardiac Power Index with Glucose Metabolism and Prognosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients—PET/MRI Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population Characteristics
2.2. PET/CMR Imaging
2.3. Statistical Analysis
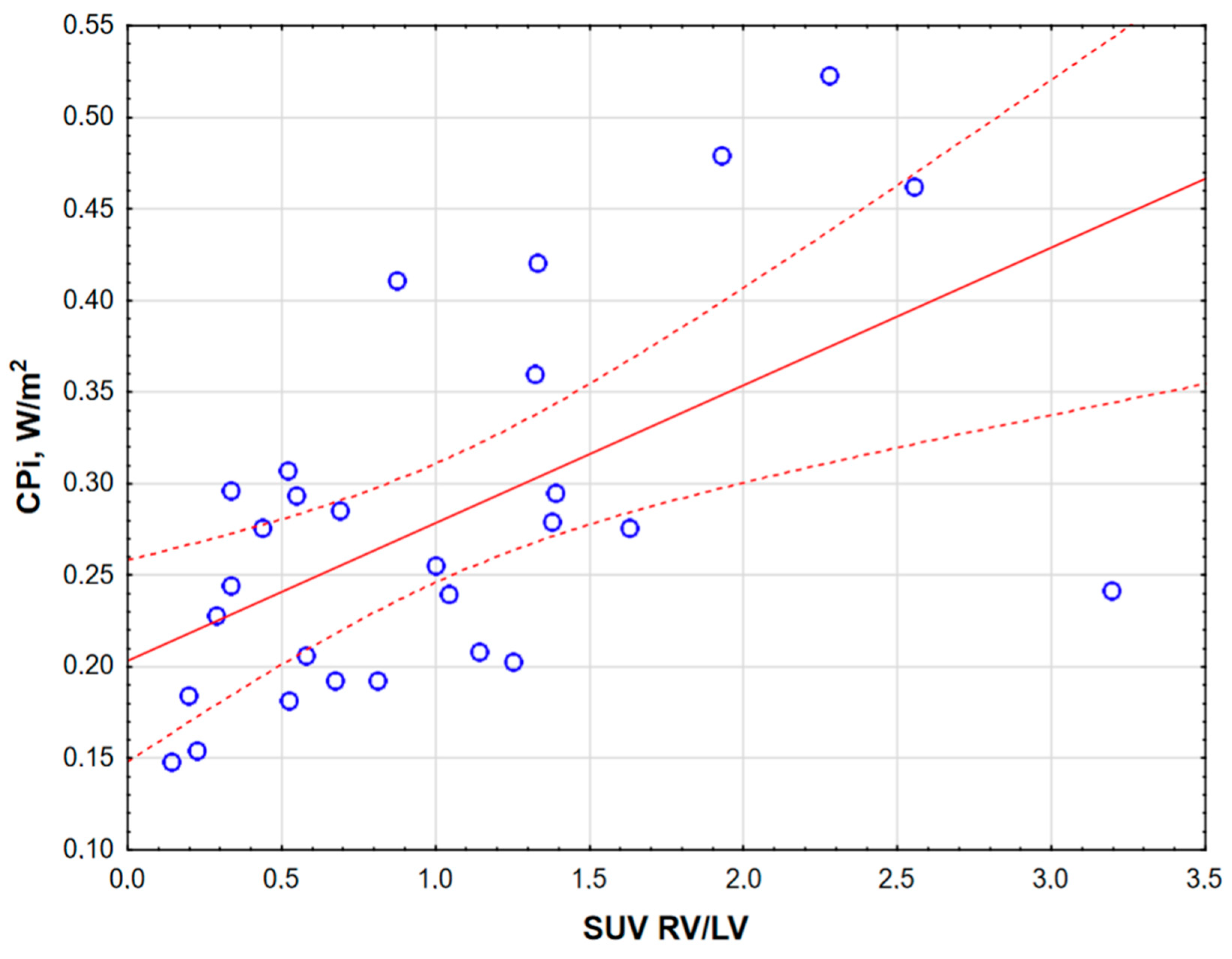
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
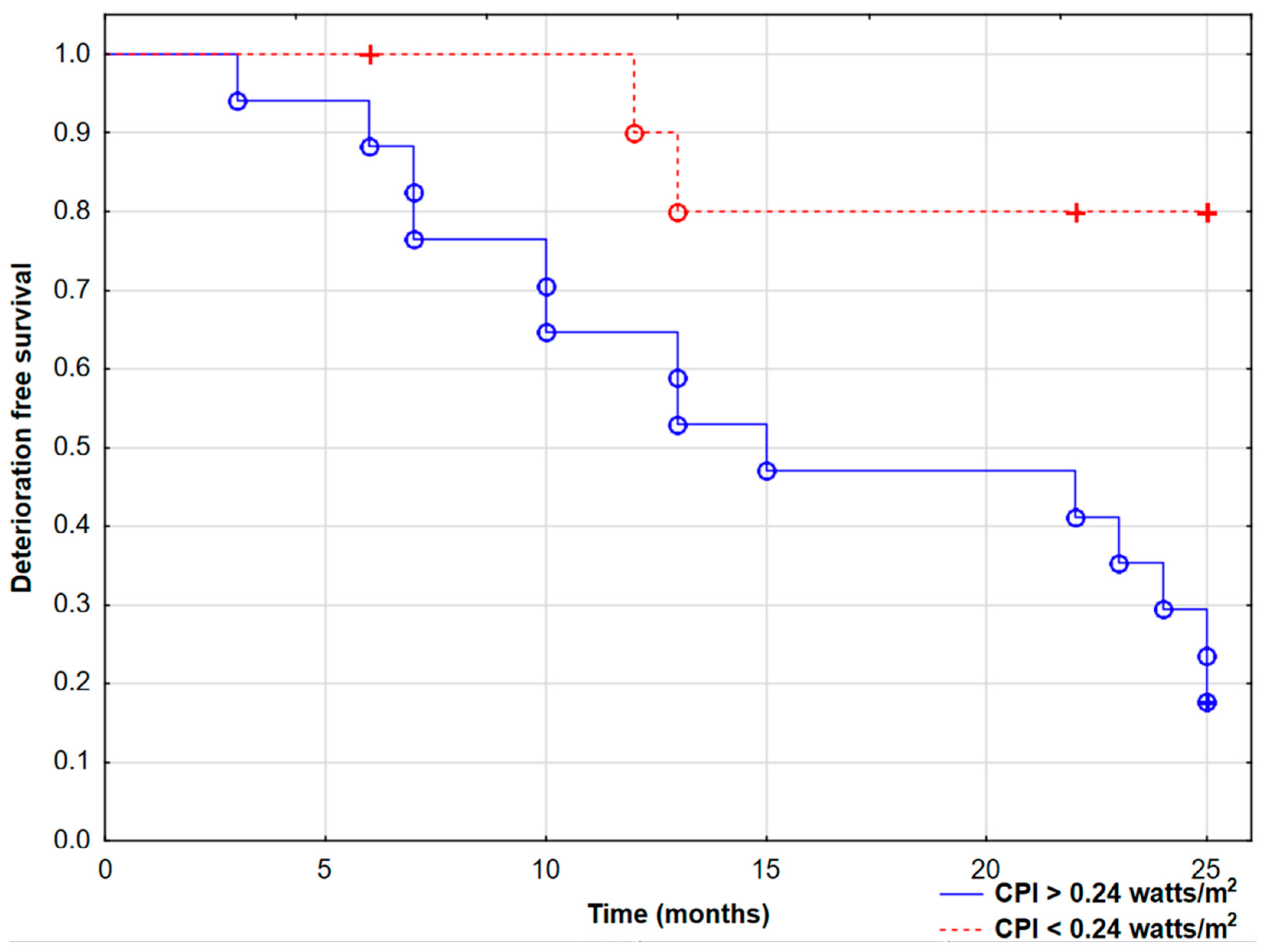
3.2. Follow-Up Visits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 18F-FDG | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose |
| CEP | composite endpoint |
| CI | cardiac index |
| CMR | cardiac magnetic resonance |
| CO | cardiac output |
| CPI | cardiac power index |
| CPO | cardiac power output |
| LV | left ventricle |
| mPAP | mean pulmonary artery pressure |
| PAH | pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PAWP | pulmonary artery wedge pressure |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PH | pulmonary hypertension |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| RHC | right heart catheterization |
| RV | right ventricle |
| RVEF | right ventricle ejection fraction |
| SUV | standardized uptake value |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WU | Wood’s unit |
References
- Fincke, R.; Hochman, J.S.; Lowe, A.M.; Menon, V.; Slater, J.N.; Webb, J.G.; LeJemtel, T.H.; Cotter, G.; SHOCK Investigators. Cardiac power is the strongest hemodynamic correlate of mortality in cardiogenic shock: A report from the SHOCK trial registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Cooke, G.; Wright, D.; Parsons, W.; Riley, R.; Marshall, P.; Tan, L.-B. Peak exercise cardiac power output; a direct indicator of cardiac function strongly predictive of prognosis in chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodin, J.L.; Mullens, W.; Dupont, M.; Wu, Y.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Tang, W.H.W. Prognostic role of cardiac power index in ambulatory patients with advanced heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, D.; Harada, T.; Obokata, M.; Kagami, K.; Sorimachi, H.; Yuasa, N.; Saito, Y.; Murakami, F.; Naito, A.; Kato, T.; et al. Pathophysiologic and prognostic importance of cardiac power output reserve in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 25, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hothi, S.; Tan, L.; Cotter, G. Resting cardiac power index and prediction of prognosis in heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Omote, K.; Iwano, H.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Amanai, S.; Yoshida, K.; Kato, T.; Kurosawa, K.; Nagai, T.; et al. Cardiac Power Output Is Independently and Incrementally Associated With Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Wong, I.M.H.; Ho, C.B.; Chiang, M.C.S.; Fong, Y.H.; Lee, P.H.; So, T.C.; Yeung, Y.K.; Leung, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; et al. Cardiac power output ratio: Novel survival predictor after percutaneous ventricular assist device in cardiogenic shock. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 3674–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupi-Herrera, E.; Sandoval, J.; Figueroa, J.; Carrillo, A.; Aguirre, R.; Santos-Martínez, L.E.; Pulido, T. Left and right ventricular power: Outputs are the strongest hemodynamic correlates to allow identification of acute responders to vasodilator treatment in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2011, 81, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sert, S.; Asarcikli, L.D.; Esen, A.; Ösken, A.; Şimşek, B.; Yağmur, A.; Güngör, B.; Yildirimtürk, Ö. Right Ventricular Cardiac Power Output as a Mortality Predictor in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Sak. Med. J. 2021, 11, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Dekemp, R.; Pena, E.; Davies, R.A.; Stewart, D.J.; Chandy, G.; Contreras-Dominguez, V.; Dennie, C.; Mc Ardle, B.; Mc Klein, R.; et al. Shifts in myocardial fatty acid and glucose metabolism in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A potential mechanism for a maladaptive right ventricular response. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczyk, R.; Szumowski, P.; Nekolla, S.G.; Blaszczak, P.; A Malek, L.; Milosz-Wieczorek, B.; Misko, J.; Jurgilewicz, D.; Hladunski, M.; Knapp, M.; et al. Prognostic role of PET/MRI hybrid imaging in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart 2021, 107, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczyk, R.; Szumowski, P.; Nekolla, S.G.; Malek, Ł.A.; Blaszczak, P.; Sobkowicz, B.; Myśliwiec, J.; Kamiński, K.A. What is the meaning of late gadolinium enhancement at right ventricular insertion points in pulmonary arterial hypertension? Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 16806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczyk, R.; Szumowski, P.; Nekolla, S.G.; Malek, L.A.; Blaszczak, P.; Hladunski, M.; Sobkowicz, B.; Mysliwiec, J.; Kaminski, K.A. The impact of specific pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy on cardiac fluorodeoxyglucose distribution in PET/MRI hybrid imaging–follow-up study. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, O.; Aslan, G.; Demirozu, Z.T.; Yenigun, C.D.; Yazicioglu, N. Evaluation of Resting Cardiac Power Output as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzi, G.; Benza, R.L.; Argiento, P.; Casu, G.; Corda, M.; Correale, M.; D’Alto, M.; Galgano, G.; Garascia, A.; Ghio, S.; et al. Gaps in evidence in the treatment of prevalent patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension at intermediate risk: An expert consensus. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2024, 157, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Xiong, C.-M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ni, X.-H.; Liu, Z.-H.; Fang, W.; et al. The Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG Uptake Ratio Between the Right and Left Ventricles in Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 40, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Xiong, C.-M.; He, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Ni, X.-H.; Fang, W.; Liu, Z.-H. The ratio of (18)F-FDG activity uptake between the right and left ventricle in patients with pulmonary hypertension correlates with the right ventricular function. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, K.; Dalmer, A.; Vanderpool, R.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Naeije, R.; Roller, F.; Seeger, W.; Wilhelm, J.; Gall, H.; Richter, M.J. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Right Ventricular Strain Analysis for Assessment of Coupling and Diastolic Function in Pulmonary Hypertension. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12 Pt 1, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakasis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Giannakoulas, G.; Rosenkranz, S.; Fragakis, N. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on pulmonary arterial wedge pressure. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 124, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baseline | Follow-Up | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 20 * | 20 | |
| Clinical endpoint (deaths) | 16 (4) | ||
| Age, years | 47.9 ± 15.1 | 49.3 ± 15.2 | 0.01 |
| Sex (females), % (n) | 75 (15) | 70 (14) | |
| 6 min walking test distance, m | 404 (87.8) | 412 ± 77 | 0.15 |
| World Health Organization class | 2.1 (0.7) | 2.3 (0.7) | 0.76 |
| BNP, pg/mL | 90.8 [46–282] | 114 [77–245] | 0.14 |
| PAH etiology | |||
| Idiopathic or heritable PAH, % (n) | 60 (12) | 60 (12) | |
| Connective-tissue-disease-related PAH, % (n) | 15 (3) | 15 (3) | |
| Congenital-heart-disease-related PAH, % (n) | 25 (5) | 25 (5) | |
| PAH-specific therapy | |||
| Phosphodiesteraze type 5 inhibitors, % (n) | 40 (8) | 10 (2) | |
| Endothelin receptor antagonists, % (n) | 15 (3) | 15 (3) | |
| Prostacyclins, % (n) | 20 (5) | 65 (13) | |
| Phosphodiesteraze type 5 inhibitors + endothelin receptor antagonists, % (n) | 20 (4) | 10 (2) | |
| Hemodynamics | |||
| Systolic pulmonary artery pressure, mm Hg | 82.2 (29.2) | 72.2 (24.2) | 0.44 |
| Diastolic pulmonary artery pressure, mm Hg | 33.8 (14.3) | 28.2 (13.9) | 0.33 |
| Mean pulmonary artery pressure, mm Hg | 50.5 (18.3) | 42.8 (18.6) | 0.03 |
| Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, mm Hg | 10.6 (2.5) | 9.73 (3) | 0.26 |
| Pulmonary vascular resistance, Wood’s units | 8.9 (5.7) | 7.3 (4.7) | 0.04 |
| Cardiac index, L/min/m2 | 2.5 (0.4) | 2.9 (0.4) | 0.04 |
| Right atrium pressure, mm Hg | 8.6 (3.6) | 8.1 (5.3) | 0.64 |
| Right ventricle parameters (CMR) | |||
| RV ejection fraction, % | 45.1 (9.6) | 52.4 (12.9) | 0.01 |
| RV EDV/BSA, mL/m2 | 113.2 (24.5) | 106 (27) | 0.27 |
| RV ESV/BSA, mL/m2 | 62.7 (22.7) | 50 (11) | 0.10 |
| RV mass/BSA, g/m2 | 39.9 (13.9) | 39.2 (14.6) | 0.50 |
| RV compacted myocardium thickness, mm | 5.7 (1.5) | 5.2 (1.3) | 0.56 |
| Pulmonary arterial compliance, mL/mm Hg | 2.4 (1.8) | 3.2 (2.4) | 0.04 |
| Right ventricle stroke work index, g·m·m2/beat | 20.6 (8.4) | 18.2 (7.5) | 0.44 |
| SUVRV/LV ratio | 0.9 [0.4–1.4] | 0.6 [0.4–1.1] | 0.19 |
| RV CPO, W | 0.50 ± 0.15 | 0.47 ± 0.18 | 0.27 |
| RV CPI, W/m2 | 0.28 ± 0.09 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazimierczyk, R.; Szumowski, P.; Nekolla, S.G.; Malek, L.A.; Blaszczak, P.; Sobkowicz, B.; Mysliwiec, J.; Benza, R.L.; Kaminski, K.A. Association of the Right Ventricle Cardiac Power Index with Glucose Metabolism and Prognosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients—PET/MRI Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041062
Kazimierczyk R, Szumowski P, Nekolla SG, Malek LA, Blaszczak P, Sobkowicz B, Mysliwiec J, Benza RL, Kaminski KA. Association of the Right Ventricle Cardiac Power Index with Glucose Metabolism and Prognosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients—PET/MRI Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(4):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazimierczyk, Remigiusz, Piotr Szumowski, Stephan G. Nekolla, Lukasz A. Malek, Piotr Blaszczak, Bozena Sobkowicz, Janusz Mysliwiec, Raymond L. Benza, and Karol A. Kaminski. 2025. "Association of the Right Ventricle Cardiac Power Index with Glucose Metabolism and Prognosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients—PET/MRI Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 4: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041062
APA StyleKazimierczyk, R., Szumowski, P., Nekolla, S. G., Malek, L. A., Blaszczak, P., Sobkowicz, B., Mysliwiec, J., Benza, R. L., & Kaminski, K. A. (2025). Association of the Right Ventricle Cardiac Power Index with Glucose Metabolism and Prognosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients—PET/MRI Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14041062







