Predictors Factors of Uncontrolled Masked Hypertension (MUCH) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
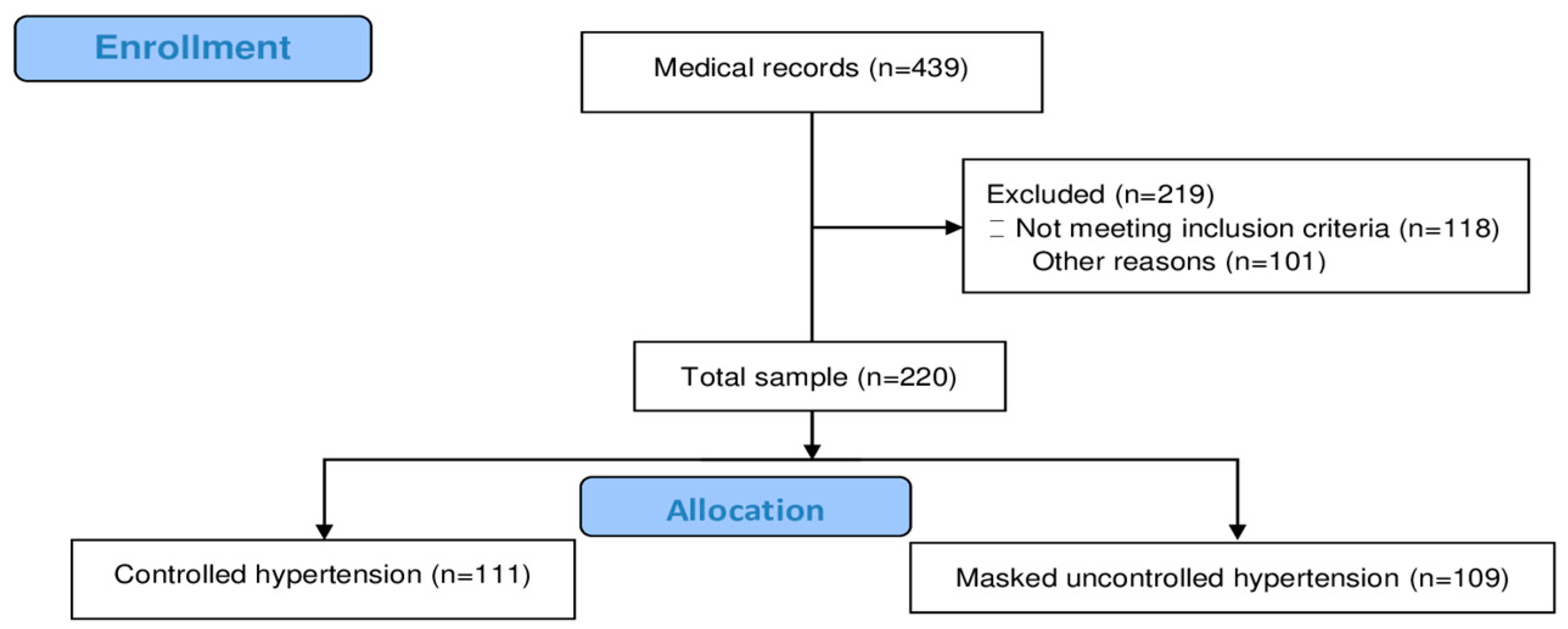
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.5. Classification of Participants
2.6. Phenotypical Categorization of Participants
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Predictor Factors
4.2. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, R.; Pappas, M.K.; Sinha, A.D. Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Guo, L.; Kong, B.; Shuai, W.; Huang, H. Nomogram Based on Clinical Features at a Single Outpatient Visit to Predict Masked Hypertension and Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension: A Study of Diagnostic Accuracy. Medicine 2022, 101, e32144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Kashfi, K.; Ghasemi, A. The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Citation. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 18, e102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.T.; Urbina, E.M.; Brady, T.M.; Baker-Smith, C.; Daniels, S.R.; Hayman, L.L.; Mitsnefes, M.; Tran, A.; Zachariah, J.P. Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in the Young Committee of the American Heart Association Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; Council on Hypertension; and Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Children and Adolescents: 2022 Update: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2022, 79, e114–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, G.; Nagy, S.; El-gengehe, A.; Abdel Aal, A.; Hamid, M.A. Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension: Prevalence and Predictors. Egypt. Heart J. 2018, 70, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallion, J.-M.; Clerson, P.; Bobrie, G.; Genes, N.; Vaisse, B.; Chatellier, G. Predictive Factors for Masked Hypertension within a Population of Controlled Hypertensives. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoni, D. Masked Hypertension: How to Identify and When to Treat? High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2016, 23, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupisti, A.; Bruno, R.M.; Puntoni, A.; Varricchio, E.; Giglio, E.; Meniconi, O.; Zullo, C.; Barsotti, M.; Egidi, M.F.; Ghiadoni, L. Blood Pressure Phenotype Reproducibility in CKD Outpatients: A Clinical Practice Report. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R. Albuminuria and Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccina, F.; Borrelli, P.; Pierdomenico, A.M.; Pizzicannella, J.; Guagnano, M.T.; Cuccurullo, C.; Di Nicola, M.; Renda, G.; Trubiani, O.; Cipollone, F.; et al. Prediction of Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension Detected by Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palla, M.; Saber, H.; Konda, S.; Briasoulis, A. Masked Hypertension and Cardiovascular Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Integr. Blood Press. Control. 2018, 11, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Algharably, E.A.E.; et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: Endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 1874–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.; Drawz, P. Masked Hypertension in CKD: Increased Prevalence and Risk for Cardiovascular and Renal Events. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, E.; Errayes, A.; Habas, E.; Alfitori, G.; Habas, A.; Farfar, K.; Rayani, A.; Habas, A.; Elzouki, A.-N. Masked Phenomenon: Renal and Cardiovascular Complications; Review and Updates. Blood Press. 2024, 33, 2383234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, P.E.; Alper, A.B.; Anderson, A.H.; Brecklin, C.S.; Charleston, J.; Chen, J.; Deo, R.; Fischer, M.J.; He, J.; Hsu, C.; et al. Masked Hypertension and Elevated Nighttime Blood Pressure in CKD: Prevalence and Association with Target Organ Damage. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa Filho, V.C.; de Quadros, T.M.B.; de Souza, E.A.; Gordia, A.P.; de Campos, W. A utilização do critério da Organização Mundial de Saúde para classificação do estado nutricional em crianças. Mot. Rev. Educ. Física UNESP 2010, 16, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, S.; Arima, H.; Arima, S.; Asayama, K.; Dohi, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Horio, T.; Hoshide, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimitsu, T.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1235–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, R.; Brunström, M.; Burnier, M.; Grassi, G.; Januszewicz, A.; Muiesan, M.L.; Tsioufis, K.; de Pinho, R.M.; Albini, F.L.; Boivin, J.-M.; et al. 2024 European Society of Hypertension Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 126, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Gao, C.; Chu, H.; Fan, W.; Bai, Y.; Yang, J. Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banegas, J.R.; Ruilope, L.M.; de la Sierra, A.; de la Cruz, J.J.; Gorostidi, M.; Segura, J.; Martell, N.; García-Puig, J.; Deanfield, J.; Williams, B. High Prevalence of Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in People with Treated Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3304–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, P.; Kan, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, H. Association of Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases in Treated Hypertensive Patients. Arch. Med Sci. 2020, 16, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccina, F.; Pierdomenico, A.M.; Cuccurullo, C.; Pizzicannella, J.; Madonna, R.; Trubiani, O.; Cipollone, F.; Pierdomenico, S.D. Prognostic Value of Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension Defined by Different Ambulatory Blood Pressure Criteria. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.; Judd, E.K.; Zhang, B.; Dudenbostel, T.; Carey, R.M.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension Is Accompanied by Increased Out-of-Clinic Aldosterone Secretion. Hypertension 2021, 77, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andalib, A.; Akhtari, S.; Rigal, R.; Curnew, G.; Leclerc, J.-M.; Vaillancourt, M.; Tardif, J.-C. Determinants of Masked Hypertension in Hypertensive Patients Treated in a Primary Care Setting. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierdomenico, S.D.; Lapenna, D.; Di Tommaso, R.; Di Carlo, S.; Esposito, A.L.; Di Mascio, R.; Ballone, E.; Cuccurullo, F.; Mezzetti, A. Blood Pressure Variability and Cardiovascular Risk in Treated Hypertensive Patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 2006, 19, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, J.; Ng, D.; Flynn, J.T.; Mitsnefes, M.; Poffenbarger, T.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.; Chronic Kidney Disease in Children Study Group. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Patterns in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Hypertension 2012, 60, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, S.; Sarac, E.; Tran, H. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Resistant Hypertension. J Clin. Hypertens. 2012, 14, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, E.; Lee, B.J.; Wei, J.; Weir, M.R. Hypertension in CKD: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.-H.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Kang, Y.-Y.; Guo, Q.-H.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Huang, J.-F.; Huang, Q.-F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.-J.; Dou, Y.; et al. The Prevalence of Masked Hypertension and Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in Relation to Overweight and Obesity in a Nationwide Registry in China. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Petiot, E.; Metzger, M.; Faucon, A.-L.; Boffa, J.-J.; Haymann, J.-P.; Thervet, E.; Houillier, P.; Geri, G.; Stengel, B.; Vrtovsnik, F.; et al. Extracellular Fluid Volume Is an Independent Determinant of Uncontrolled and Resistant Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease: A NephroTest Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, R.J.H.; Houben, A.J.H.M.; Kooman, J.P.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M.; Dagnelie, P.C.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; Kroon, A.A.; Leunissen, K.M.L.; van der Sande, F.M.; Schaper, N.C.; et al. Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction Is Associated with Albuminuria: The Maastricht Study. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Bundy, J.D.; Charleston, J.; Cohen, D.; Cohen, J.; Drawz, P.E.; Ghazi, L.; Horowitz, E.; Lash, J.P.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Ambulatory BP Monitoring in CKD: A Report from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2609–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiejunaite, J.; Flamant, M.; Arnoult, F.; Lahens, A.; Tabibzadeh, N.; Boutten, A.; Rouzet, F.; Vrtovsnik, F.; Vidal-Petiot, E.; de Pinho, N.A. Predictors of Daytime Blood Pressure, Nighttime Blood Pressure, and Nocturnal Dipping in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.S.; Thijs, L.; Li, Y.; Hansen, T.W.; Boggia, J.; Liu, Y.; Asayama, K.; Björklund-Bodegård, K.; Ohkubo, T.; Jeppesen, J.; et al. Masked Hypertension in Diabetes Mellitus: Treatment Implications for Clinical Practice. Hypertension 2013, 61, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, X.; Brisson, C.; Gilbert-Ouimet, M.; Duchaine, C.S.; Dalens, V.; Talbot, D.; Milot, A. Masked Hypertension Incidence and Risk Factors in a Prospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Shin, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, W.S.; Park, S.; Rhee, S.J.; Lee, E.M.; Ihm, S.H.; et al. Clinical Features and Predictors of Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension from the Korean Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Registry. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All (n = 220) | CH (n = 111) | MUCH (n = 109) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62 (49–73) | 63 (51–76) | 61 (48–70) | 0.11 |
| Gender M (%) | 100 (45) | 45 (40.5) | 55 (50.5) | 0.17 |
| Race Nº (%) | ||||
| White | 170 (77) | 88 (79.3) | 82 (75.2) | 0.57 |
| Non-white | 50 (23) | 23 (20.7) | 27 (24.8) | |
| Diabetes Y (%) | 53 (24) | 28 (25.2) | 25 (22.9) | 0.81 |
| Dyslipidemia Y (%) | 168 (76) | 92 (82.9) | 76 (69.7) | 0.03 |
| No. of antihypertensives | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 0.69 |
| No. of Antihypertensives Classes | ||||
| 01 Class | 41 (19) | 16 (14.4) | 25 (22.9) | 0.4 |
| 02 Classes | 48 (22) | 27 (24.3) | 21 (19.3) | |
| 03 Classes | 51 (23) | 27 (24.3) | 24 (22.0) | |
| 04 or more Classes | 80 (36) | 41 (36.9) | 39 (35.8) | |
| AH Resistant n (%) | 91 (41) | 41 (36.9) | 50 (54.9) | 0.22 |
| Class of medication | ||||
| ACEI/ARB | 156 (71) | 86 (77.5) | 70 (64.2) | 0.04 |
| CCB | 126 (57) | 62 (55.9) | 64 (58.7) | 0.77 |
| BB | 116 (53) | 59 (53.2) | 57 (52.3) | 1 |
| Thiazide | 110 (50) | 60 (54.1) | 50 (45.9) | 0.28 |
| Office BP (mmHg) | ||||
| SBP | 126 (117–131) | 125 (113–131) | 127 (120–131) | 0.06 |
| DBP | 74 (66–79) | 72 (64–87) | 75 (67–82) | <0.01 |
| ABPM (mmHg) | ||||
| 24 h SBP | 126 (116–136) | 117 (111–123) | 137 (131–175) | <0.01 |
| 24 h DBP | 75 (68–82) | 69 (65–74) | 82 (76–88) | <0.01 |
| SBP awake | 122 (±14.82) | 118 (±8.90) | 140 (±10.95) | <0.01 |
| DBP awake | 77 (±10.57) | 63 (±6.62) | 75 (±9.51) | <0.01 |
| SBP sleep | 122 (±16.67) | 111 (±9.81) | 133 (±14.73) | <0.01 |
| DBP sleep | 69 (±10.32) | 63 (±6.62) | 75 (±9.51) | <0.01 |
| ND Absent (%) | 156 (71) | 75 (67.6) | 81 (74.3) | 0.34 |
| All (n = 220) | CH (n = 111) | MUCH (n = 109) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 27 (24–32) | 28 (25–34) | 26 (23–29) | <0.01 |
| Waist (cm) | ||||
| M | 101 (93–111) | 103 (94–113) | 101 (93–109) | 0.33 |
| F | 99 (±14.20) | 102 (±13.83) | 95 (±13.83) | <0.01 |
| Hip (cm) | ||||
| M | 103 (96–110) | 105 (96–112) | 103 (97–109) | 0.27 |
| F | 106 (98–115) | 109 (98–118) | 103 (98–111) | 0.03 |
| WHR | ||||
| M | 0,98 (±0.05) | 0.98 (±0.06) | 0.98 (±0.05) | 0.78 |
| F | 0,93 (0.88–0.97) | 0.94 (0.90–0.97) | 0.92 (0.85–0.97) | 0.12 |
| All (n = 220) | CH (n = 111) | MUCH (n = 109) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.65 (1.28–2.26) | 1.57 (1.24–2.03) | 1.75 (1.37–2.50) | 0.07 |
| GFR (CKD-EPI) | 35 (26–49) | 37 (27–51) | 32 (25–49) | 0.23 |
| Albuminuria | 121 (26–535) | 69 (13–316) | 275 (41–1,109) | <0.01 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 172 (142–199) | 175 (137–201) | 171 (148–197) | 0.78 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 96 (71–120) | 96 (72–118) | 96 (68–121) | 0.87 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 47 (37–59) | 47 (39–59) | 46 (36–58) | 0.46 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 132 (93–194) | 132 (98–184) | 142 (89–205) | 0.87 |
| G1 (13) | G2 (17) | G3a (51) | G3b (55) | G4 (70) | G5 (14) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUCH Phenotype n (%) | 7 (53.8) | 5 (29.4) | 25 (49) | 26 (47.3) | 37 (52.9) | 9 (64.3) | 0.48 |
| Absent ND n (%) | 7 (53.8) | 11 (64.7) | 30 (58.8) | 41 (74.5) | 54 (77.1) | 13 (92.9) | 0.05 |
| Clinic | |||||||
| SBP | 127 | 126 | 126 | 125 | 126 | 125 | 0.99 |
| DBP | 74 | 77 | 72 | 73 | 71 | 75 | 0.19 |
| ABPM | |||||||
| 24 h SBP | 126 (±10.22) | 121 (±9.95) | 127 (±13.11) | 125 (±16.29) | 128 (±15.13) | 134 (±18.00) | 0.17 |
| 24 h DBP | 76 (±5.70) | 76 (±6.74) | 76 (±9.98) | 74 (±10.67) | 74 (±10.91) | 79 (±10.75) | 0.45 |
| Daytime SBP | 129 (±10.41) | 123 (±9.84) | 130 (±13.20) | 126 (±16.62) | 129 (±15.34) | 134 (±17.92) | 0.37 |
| Daytime DBP | 78.84 (±6.09) | 79 (±7.31) | 78 (±10.50) | 76 (±10.97) | 75 (±11.36) | 80 (±11.84) | 0.58 |
| Night SBP | 119 (±12.04) | 115 (±12.79) | 121 (±15.28) | 118 (±17.53) | 124 (±16.25) | 136 (±20.04) | <0.01 |
| Night DBP | 68 (±6.91) | 70 (±6.97) | 69 (±10.25) | 67 (±10.89) | 69 (±10.73) | 77 (±9.33) | 0.04 |
| No. Medications | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3.5 | 0.04 |
| Resistant AH No. (%) | 3 (23.1) | 10 (58.8) | 15 (29.4) | 25 (45.5) | 30 (42.9) | 8 (57.1) | 0.11 |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MUCH Phenotype n (%) | 18 (34) | 33 (47.1) | 49 (65.3) | <0.01 |
| Absent DN n (%) | 34 (64.2) | 52 (74.3) | 58 (77.3) | 0.24 |
| Clinic | ||||
| SBP | 124 (116–131) | 126 (117–130) | 127 (120–132) | 0.35 |
| DBP | 73 (66–78) | 73 (65–79) | 74 (67–81) | 0.55 |
| ABPM | ||||
| 24 h SBP | 123 (±12.23) | 125 (±14.51) | 132 (±15.55) | <0.01 |
| 24 h DBP | 72 (±11.06) | 75 (±8.99) | 78 (±10.18) | <0.01 |
| Daytime SBP | 125 (±13.17) | 126 (±14.69) | 134 (±15.21) | <0.01 |
| Daytime DBP | 74 (±11.96) | 76 (±9.33) | 79 (±10.54) | 0.01 |
| Night SBP | 117 (±11.99) | 120 (±15.68) | 129 (±18.88) | <0.01 |
| Night DBP | 65 (±9.68) | 69 (±9.36) | 73 (±10.66) | <0.01 |
| No. Medications | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 0.19 |
| AH Resistant No. (%) | 16 (30.2) | 29 (41.4) | 39 (52.0) | 0.04 |
| Odds Ratio | IC 95% | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI <25 Kg/m2 | 2.21 | 1.08–4.52 | 0.03 |
| DBP ≥ 75 mmHg | 1.93 | 1.03–3.64 | 0.04 |
| Albuminuria ≥ 300 mg | 3.26 | 1.71–6.19 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Junior, R.S.; Silva, G.F.; Drager, L.F.; Pio-Abreu, A. Predictors Factors of Uncontrolled Masked Hypertension (MUCH) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082663
Junior RS, Silva GF, Drager LF, Pio-Abreu A. Predictors Factors of Uncontrolled Masked Hypertension (MUCH) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082663
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunior, Roberto Santos, Gabriel Fernandes Silva, Luciano Ferreira Drager, and Andrea Pio-Abreu. 2025. "Predictors Factors of Uncontrolled Masked Hypertension (MUCH) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082663
APA StyleJunior, R. S., Silva, G. F., Drager, L. F., & Pio-Abreu, A. (2025). Predictors Factors of Uncontrolled Masked Hypertension (MUCH) in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082663







