3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.2. Preparation of Gel-Adhesive Glass Substrates and Bioink for 3D Bioprinting
2.3. 3D Cell Printing and Post-Processing of Printed Samples
2.4. RNA Analysis
2.5. Live/Dead Cell Analysis
2.6. Immunostaining
2.7. Microscopy Imaging
2.8. Patch Clamp Recordings
2.9. Calcium Imaging Recordings
3. Results
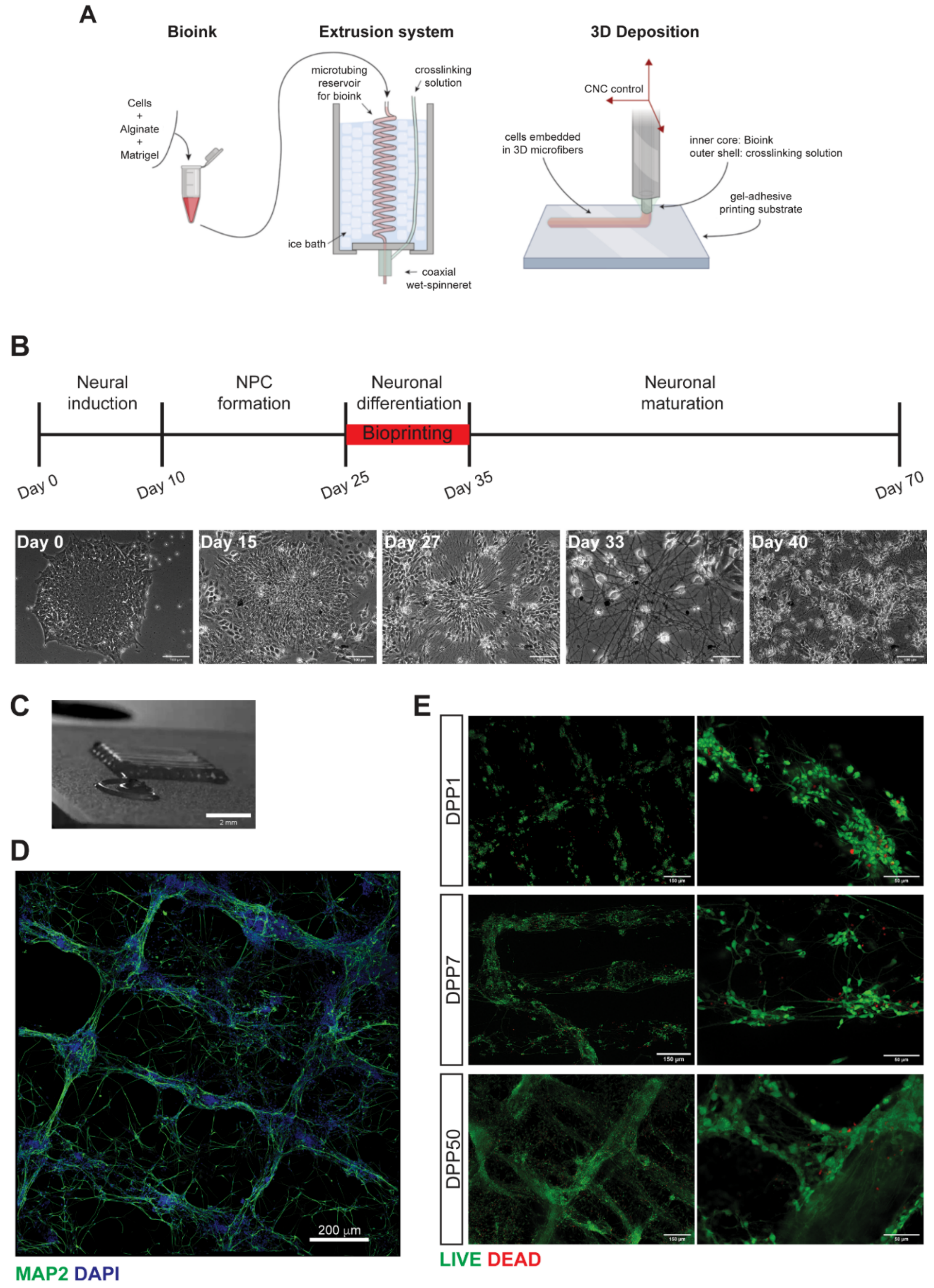
3.1. 3D Bioprinting of Differentiating Human iPSC-Derived Neurons and Glia
3.2. Characterization of 3D Bioprinted Neural Constructs
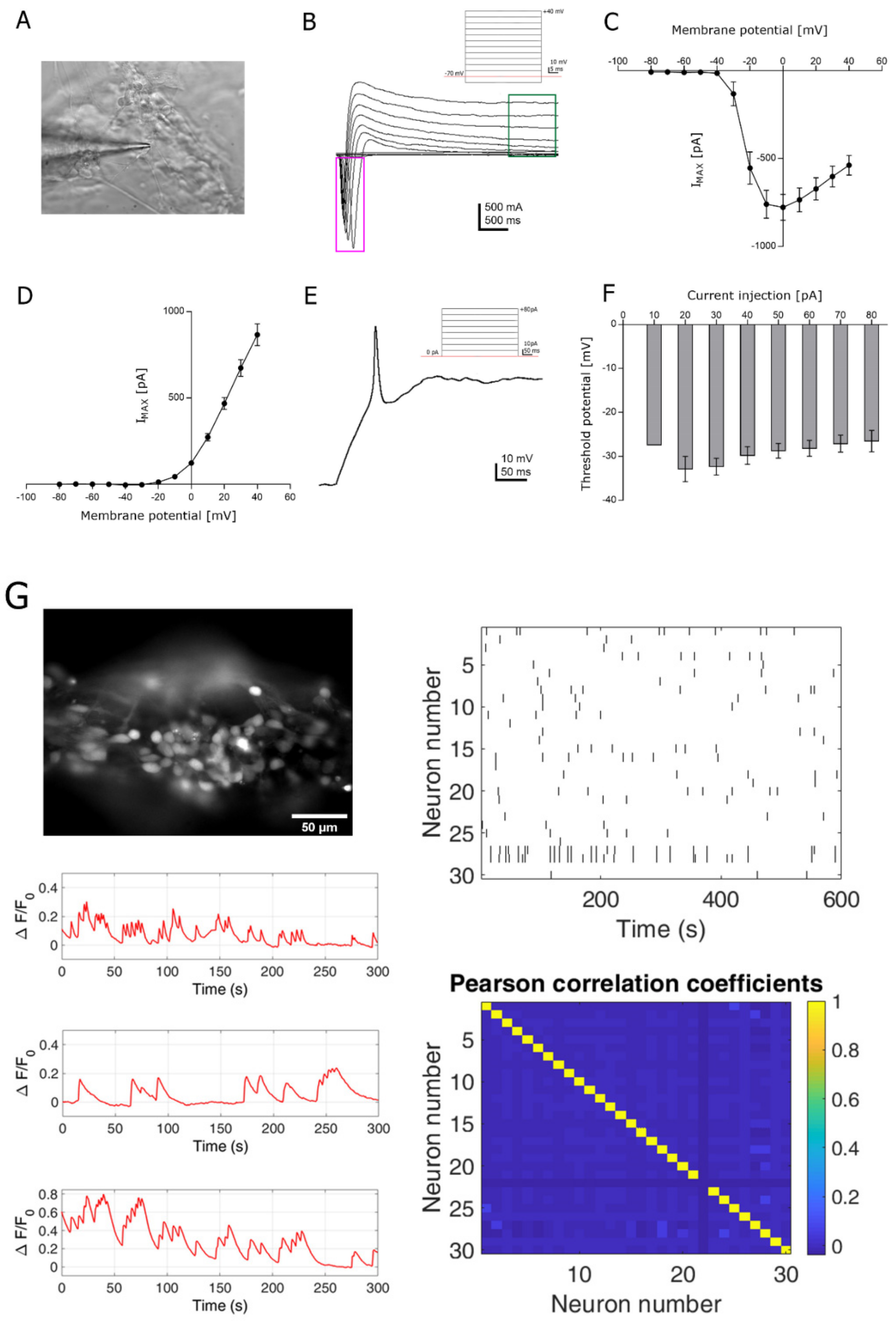
3.3. Functional Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, L.; Gruene, M.; Unger, C.; Chichkov, B. Laser assisted cell printing. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2013, 14, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Munguia-Lopez, J.G.; Flores-Torres, S.; Kort-Mascort, J.; Kinsella, J.M. Extrusion bioprinting of soft materials: An emerging technique for biological model fabrication. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 011310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.; Deiwick, A.; Franke, A.; Schwanke, K.; Haverich, A.; Zweigerdt, R.; Chichkov, B. Laser bioprinting of human induced pluripotent stem cells-the effect of printing and biomaterials on cell survival, pluripotency, and differentiation. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. 3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Constructs for In Situ Cell Proliferation and Successive Multilineage Differentiation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, J.A.; Mollica, P.A.; Johnson, G.D.; Ogle, R.C.; Bruno, R.D.; Sachs, P.C. Accessible bioprinting: Adaptation of a low-cost 3D-printer for precise cell placement and stem cell differentiation. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Hägg, D.A.; Forsman, A.; Ekholm, J.; Nimkingratana, P.; Brantsing, C.; Kalogeropoulos, T.; Zaunz, S.; Concaro, S.; Brittberg, M.; et al. Cartilage Tissue Engineering by the 3D Bioprinting of iPS Cells in a Nanocellulose/Alginate Bioink. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner-Jones, A.; Fyfe, C.; Cornelissen, D.-J.; Gardner, J.; King, J.; Courtney, A.; Shu, W. Bioprinting of human pluripotent stem cells and their directed differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells for the generation of mini-livers in 3D. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 044102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Qu, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.-S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Lai, C.S.E.; Zanella, F.; et al. Deterministically patterned biomimetic human iPSC-derived hepatic model via rapid 3D bioprinting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, P.; Miller, K.L.; Stupin, J.; Koroleva-Maharajh, A.; Hairabedian, A.; Chen, S. Scanningless and continuous 3D bioprinting of human tissues with decellularized extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 2019, 194, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.S.; Fukunishi, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.Y.; Nashed, A.; Blazeski, A.; Di Silvestre, D.; Vricella, L.; Conte, J.; Tung, L.; et al. Biomaterial-Free Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Cardiac Tissue using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, L.; Barnard, A.; Gil, C.-H.; Lin, Y.; Grant, M.B.; Yoder, M.C.; Prasain, N.; Moldovan, N.I. iPSC-Derived Vascular Cell Spheroids as Building Blocks for Scaffold-Free Biofabrication. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkio, A.; Koch, L.; Koivusalo, L.; Deiwick, A.; Miettinen, S.; Chichkov, B.; Skottman, H. Human stem cell based corneal tissue mimicking structures using laser-assisted 3D bioprinting and functional bioinks. Biomaterials 2018, 171, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, D.; Truong, V.; Neitzke, C.C.; Guo, S.-Z.; Walsh, P.J.; Monat, J.R.; Meng, F.; Park, S.H.; Dutton, J.R.; Parr, A.M.; et al. 3D Printed Stem-Cell Derived Neural Progenitors Generate Spinal Cord Scaffolds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Vega, L.; Rosas Gómez, A.D.; Abelseth, E.; Abelseth, L.; Allisson da Silva, V.; Willerth, S. 3D Bioprinting Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Tissues Using a Novel Lab-on-a-Printer Technology. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellin, M.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H.; Mummery, C.L. Induced pluripotent stem cells: The new patient? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosi, C.; Costantini, M.; Barbetta, A.; Dentini, M. Microfluidic Bioprinting of Heterogeneous 3D Tissue Constructs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1612, 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi, J.; De Santis, R.; de Turris, V.; Morlando, M.; Laneve, P.; Calvo, A.; Caliendo, V.; Chiò, A.; Rosa, A.; Bozzoni, I. ALS mutant FUS proteins are recruited into stress granules in induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) derived motoneurons. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Kirwan, P.; Livesey, F.J. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to cerebral cortex neurons and neural networks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Zhang, T.; Lin, S.; Parada, G.A.; Zhao, X. Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, G.; Moroni, M.; Soloperto, A.; Aletti, G.; Naldi, G.; Vassalli, M.; Nieus, T.; Difato, F. Fast wide-volume functional imaging of engineered in vitro brain tissues. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, I.; Fièvre, S.; Telley, L.; Oberst, P.; Bariselli, S.; Frangeul, L.; Baumann, N.; McMahon, J.J.; Klingler, E.; Bocchi, R.; et al. Progenitor Hyperpolarization Regulates the Sequential Generation of Neuronal Subtypes in the Developing Neocortex. Cell 2018, 174, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeno, E.G.Z.; Cimarosti, H.; Bithell, A. 2D versus 3D human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cultures for neurodegenerative disease modelling. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.-A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelava, I.; Lancaster, M.A. Dishing out mini-brains: Current progress and future prospects in brain organoid research. Dev. Biol. 2016, 420, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salaris, F.; Rosa, A. Construction of 3D in vitro models by bioprinting human pluripotent stem cells: Challenges and opportunities. Brain Res. 2019, 1723, 146393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelseth, E.; Abelseth, L.; De la Vega, L.; Beyer, S.T.; Wadsworth, S.J.; Willerth, S.M. 3D Printing of Neural Tissues Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using a Fibrin-Based Bioink. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Lozano, R.; Chen, Y.; Kapsa, R.M.; Zhou, Q.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. Functional 3D Neural Mini-Tissues from Printed Gel-Based Bioink and Human Neural Stem Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salaris, F.; Colosi, C.; Brighi, C.; Soloperto, A.; de Turris, V.; Benedetti, M.C.; Ghirga, S.; Rosito, M.; Di Angelantonio, S.; Rosa, A. 3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101595
Salaris F, Colosi C, Brighi C, Soloperto A, de Turris V, Benedetti MC, Ghirga S, Rosito M, Di Angelantonio S, Rosa A. 3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101595
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalaris, Federico, Cristina Colosi, Carlo Brighi, Alessandro Soloperto, Valeria de Turris, Maria Cristina Benedetti, Silvia Ghirga, Maria Rosito, Silvia Di Angelantonio, and Alessandro Rosa. 2019. "3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101595
APA StyleSalaris, F., Colosi, C., Brighi, C., Soloperto, A., de Turris, V., Benedetti, M. C., Ghirga, S., Rosito, M., Di Angelantonio, S., & Rosa, A. (2019). 3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101595






