Abstract
The olive tree is perfectly adapted to the Mediterranean region, where it represents high economic, social, and landscape importance, olive orchards being an important repository of biodiversity. The order Coleoptera encompasses families that provide important ecosystem services, such as pest limitation. The objective of this work was to compare the assemblage of families of Beetles between the olive grove and their surrounding semi-natural landscape in Trás-os-Montes. The ground beetles on four olive groves and their adjacent shrubland areas were sampled using pitfall traps near Mirandela (Northeastern Portugal) in May and June of 2015 and 2016. Anthicidae, Staphylinidae, and Scarabaeidae dominated the community. The richness of the families was significantly greater in the olive grove in both years of study. On the contrary, the overall diversity did not significantly differ. In both years, the complementarity between the areas was low, reflecting similar communities in terms of families. Predators were dominant in both habitats; therefore, the surrounding landscape could act as shelter and provide alternative resources to the community of Coleoptera inhabiting the olive grove during disturbances derived from agricultural management.
Keywords:
semi-natural; families; carnivores; herbivores; detritivores; fungivores; biological control 1. Introduction
The cultivation of the olive tree (Olea europaea L.) has great economic, social, and landscape relevance throughout the Mediterranean basin, it being an important repository of the edaphic fauna biodiversity [1,2,3]. The arthropod fauna inhabiting the soil of olive groves is highly diverse and has a significant influence on the maintenance of fundamental ecosystem services such as pest limitation [4,5]. Among soil invertebrates, the order Coleoptera stands out for its great taxonomic and functional diversity [6], occupying countless ecological niches [6,7,8]. Beetles feed on plants and animals so that the order encompasses herbivore and predatory species as well as frugivores, detritivores, and parasites [6,7,9,10]. Accordingly, the functional diversity of beetles is a key trait regarding their ecological role in agroecosystems [5,11,12].
A pool of families of Coleoptera, such as Carabidae, Staphylinidae, and Elateridae, is considered to include potential natural enemies against the main olive pests such as the olive fly, Bactrocera oleae (Rossi, 1790) (Diptera: Tephritidae) [1,5,12,13]. Moreover, since beetles are extremely sensitive to human alterations caused by the intensification of land uses, they are considered to be excellent bioindicators of agricultural practices [14].
The crop intensification of the olive grove agroecosystem [15] is a threat to this group’s diversity balance, resulting in reduced landscape complexity. In addition, agroecosystems maintain close links with the surrounding areas [16], adjacent semi-natural ones being considered key biodiversity repositories where ecological interactions such as predator–prey interactions are established. These dynamics are supported by the shelters and food sources available outside the crop [17].
The surrounding landscape of olive groves can be essential to increasing the diversity of beetles and enhancing the main ecosystem services including biological control [1]. However, the structure and ecology of the assemblage of beetles associated with the olive grove agroecosystem are not yet fully understood. In the case of beetles, the families are usually grouped according to feeding habits. For example, following Marinoni et al. [7], beetles can be subdivided into five trophic groups: herbivores, algivores, fungivores, detritivores, and carnivores. This high-taxonomical-rank functional approach could also help to shed light on the role of beetles as potential natural enemies, and the term trophic group is used here to group in the same class all of the species that use the same food source in the same way. This work aimed to assess the assemblage of families inhabiting the olive grove and adjacent Mediterranean shrublands and compare the diversity between both habitats in the region of Trás-os-Montes (Portugal). We hypothesize that the type of area (i.e., olive crops and Mediterranean shrublands) drives the total abundance and the richness and diversity of families of Coleoptera.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted in the “Terra Quente Transmontana” region near Mirandela (northeastern Portugal). According to the Köppen and Geiger classification, the region’s climate is Csa-type [18], characterized by a temperate climate with hot and dry summers and mild and humid winters, thus determining the typically Mediterranean vegetation and agriculture. The study area’s average annual precipitation and temperature are 776 mm and 13.8 °C [19], respectively, with the soils classified predominantly as Leptosols [20]. Four olive groves and their adjacent Mediterranean shrubland areas were selected. The characteristics of the olive crops are described in (Supplementary Table S1). The surrounding shrubland areas represent an important type of soil cover in the study area corresponding to a typical Mediterranean habitat. These areas are mainly characterized by an herbaceous stratum dominated by plants belonging to the Asterceae, Poaceae, and Fabaceae families, a stratum of shrubs dominated by Cistus ladanifer L., Cytisus sp., Lavandula sp., Rosmarinus officinalis L., Rubus ulmifolius Schott, and Crataegus monogyna Jacq, and an upper layer dominated by trees such as Quercus rotundifolia Lam., Quercus pyrenaica Willd., and Arbutus unedo L. [21].
2.2. Sampling of Arthropods
The sampling was conducted from May to June in 2015 (1 May to 20 June) and 2016 (1 May to 20 June) for seven weeks during the period of maximum arthropod activity in the olive grove, since, after the hot summers in the study area, as the temperature decreases, the arthropod abundance decreases as well [22]. In each olive grove and adjacent shrubland area, nine pitfall traps were installed, which were regularly distributed in the form of a 3 × 3 grid, spaced approximately 50 m apart to minimize interference. At each sampling point, a hole was dug in the soil with a width and depth sufficient to place a 200 mL plastic cup (70 mm in diameter at the top and 90 mm in height) with its edge leveled to the soil surface. Each trap was filled with 100 mL of a mixture of ethylene glycol, water, and detergent (2:2:1) as a preservative solution. The plastic covers fixed to the ground with wire were used to prevent flooding due to rainwater and the falling of medium/large-sized animals (e.g., rodents and small lizards), thus making the preservative solution impracticable and compromising the quality of the samples.
During the sampling periods, the traps were replaced weekly for seven consecutive weeks. Afterwards, the traps were transported to the Agrobiotechnology Laboratory of the Centro de Investigação de Montanha (CIMO, Portugal). The content of the traps was cleaned, and the individuals belonging to the beetles were sorted and preserved in 70% ethanol for subsequent identification. The identification of the families was conducted using a stereomicroscope and specific identification keys [10,23]. Finally, the identified families were assigned to trophic groups following Marinoni [24] and Marinoni et al. [7].
2.3. Data Analysis
The community structure of Coleoptera was assessed in terms of total abundance and the richness and diversity of the families. The data for each year of study (2015 and 2016) were treated independently to avoid bias due to interannual variability. All of the statistical analyses were performed in the R environment [25]. In terms of modelling, abundance was calculated as the number of individuals present in each sample (N), while richness (S) was calculated as the number of families present in each sample. The effect of the area type (olive grove or shrubland) and the effect of the sampling week were investigated using generalized estimating equations (GEE), an extension of the generalized linear models (GLMs) assuming an interchangeable correlation structure between the samples (a single correlation parameter, ρ) and the Poisson distribution due to count data [26,27].
A Venn diagram was built for each year of study, and a complementarity analysis [28] was used to compare the pools of families in both habitats (olive grove and adjacent shrubland areas) as:
where Sjk is the total combined richness, Sj indicates the total family richness of the first area, Sk indicates the total richness of the second area, and Vjk corresponds to the number of families in common between the two areas. The number of unique species Ujk to either inventory is:
and the complementarity is measured by Cjk as:
where Cjk measures the complementarity and ranges from 0 (when the lists of organisms are identical) to 1 (when the lists of organisms are completely different).
The ordination of families was assessed through canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) using the “cca” function of the “vegan” package [29] such that the data matrix was χ2-transformed and subjected to weighted linear regression on the drivers. Finally, the Simpson Index was calculated as a measure of diversity per sample. The Simpson index [30] reflects the probability that two individuals randomly captured in the community belong to the same species. The greater this probability, the lower the degree of diversity this community has. The index varies from 0 to 1, and the closer the value is to 1, the greater the probability that the individuals belong to the same species—that is, the greater the dominance and the lesser the diversity. The index was calculated for each year as:
where D is the Simpson index, ni indicates the density of each family, and N represents the total number of individuals in the sample. Subsequently, the index value was transformed as 1-D to facilitate its direct interpretation in terms of diversity.
3. Results
In total, 4.742 individuals were captured, of which 2.016 were registered in 2015 and 2.726 were registered in 2016 (Table 1). Over the two years of study, the Anthicidae, Staphylinidae, and Scarabaeidae families (1.074, 771, and 707 individuals, respectively) were the most abundant, whereas the Buprestidae, Cleridae, and Ripiphoridae families (a single individual captured from each family) were the least abundant (Table 1).

Table 1.
Abundance and Frequency (%) of Beetles Captured in Olive Groves (OG) and Adjacent Shrubland Areas (ASA) in the Mirandela Region (Northeast Portugal) in 2015 and 2016. TG Stands for Trophic Groups (H: Herbivores; C: Carnivores; F: Fungivores; D: Detritivores).
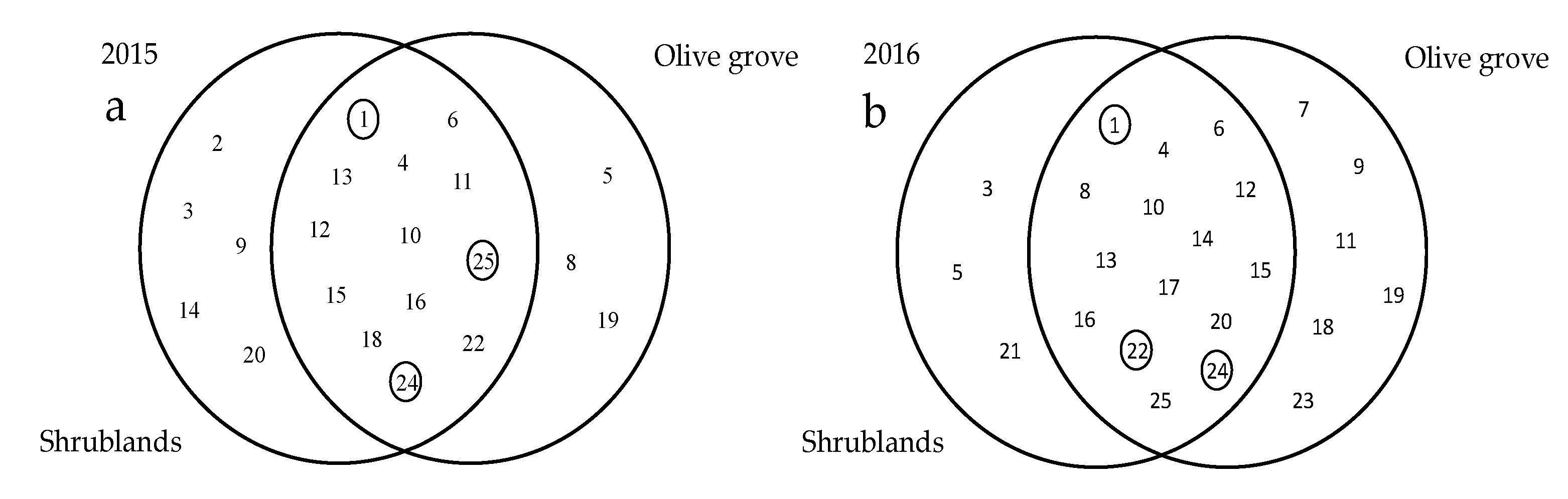
In total, 25 families were recorded (Table 1). In 2015, the Buprestidae, Cantharidae, Cucujidae, Malachiidae, and Ptinidae families were exclusive families of the shrubland areas, whereas Cerambycidae, Coccinellidae, and Phalacridae were exclusive families of the olive groves (Figure 1). In 2016, Cantharidae, Cerambycidae, and Ripiphoridae were found exclusively in the shrubland areas, whereas Cleridae, Cucujidae, Elateridae, Oedemeridae, Phalacridae, and Silphidae were exclusively found in the olive groves (Figure 1).
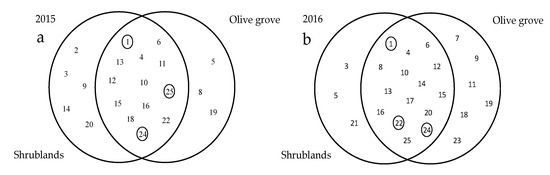
Figure 1.
Complementarity of Coleoptera families in the Mirandela region (Northeast Portugal) in (a) 2015 and (b) 2016. Circles inside the Venn diagrams indicate the most abundant families. Numbers inside the Venn diagrams correspond to the families indicated in Table 1.
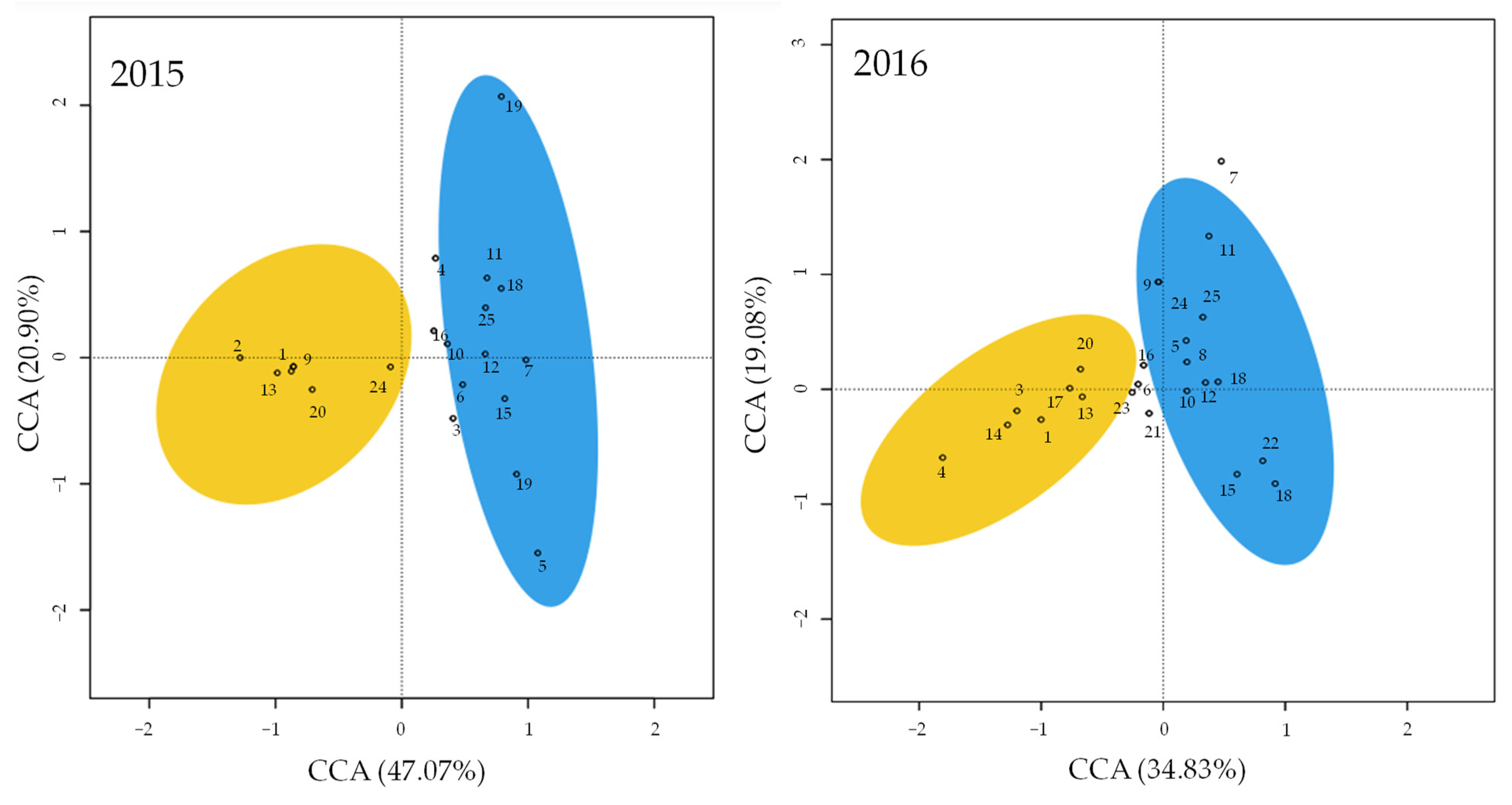
The complementarity between the areas was 0.17 in both years of study (Figure 1). The CCA explained 68% and 54% of the variation in 2015 (χ2 = 0.89, d.f. = 7, p < 0.01) and 2016 (χ2 = 0.76, d.f. = 7, p < 0.01), respectively, and the two habitats (i.e., the olive grove and surrounding shrubland areas) were separated by the first axis (Figure 2).
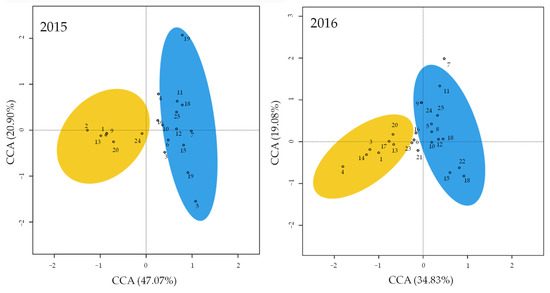
Figure 2.
Ordination plot (canonical correspondence analysis CCA) for the complete pool of Coleoptera families found in the olive groves (blue) and shrubland (yellow) in Trás-os-Montes (Portugal) in 2015 and 2016. Ellipses represent the standard deviation. The numbers within the panels correspond to the numbers of the families in Table 1.
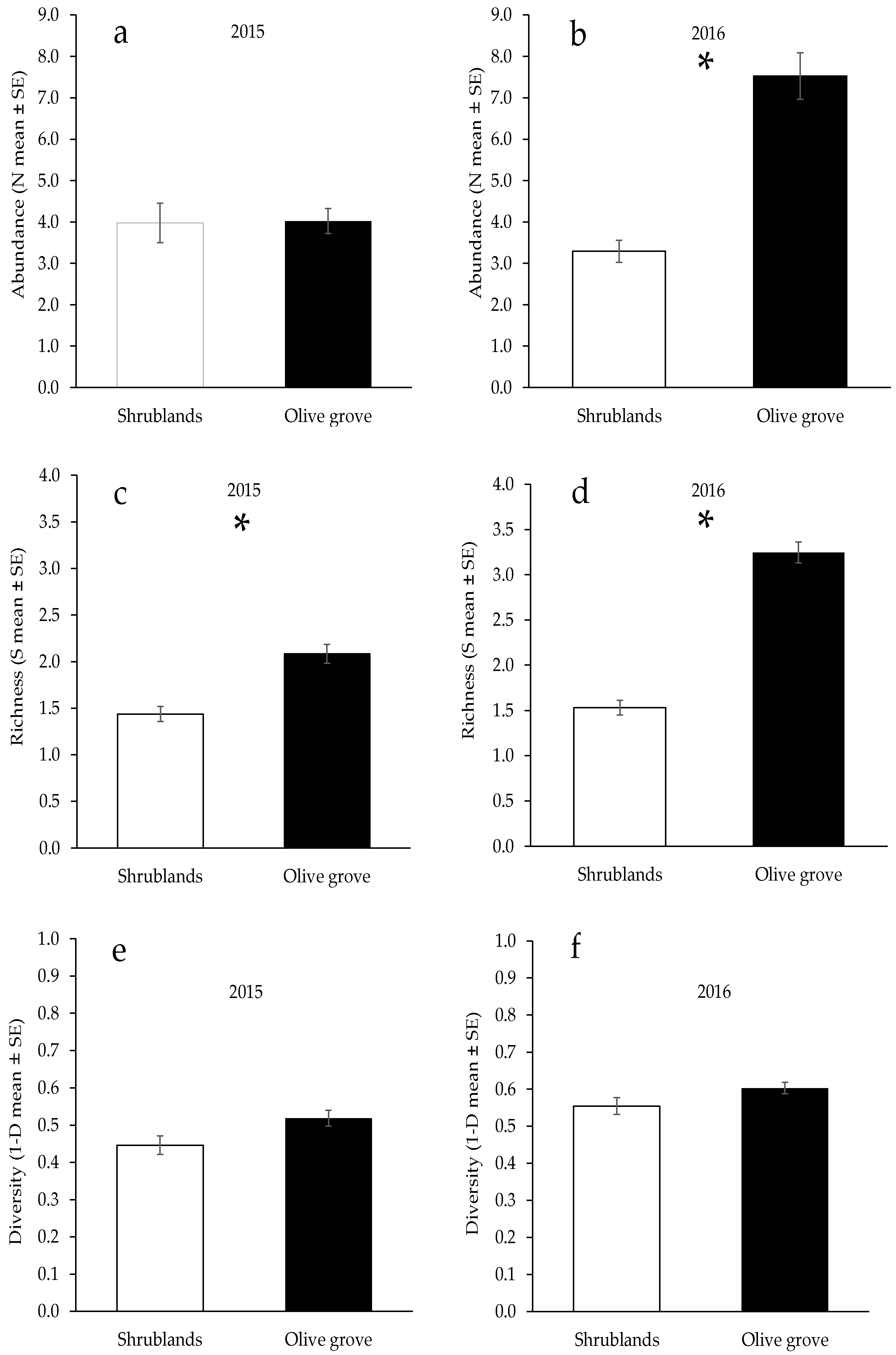
The abundance of beetles in the olive grove was significantly higher than that in the shrubland area only in 2016 (Table 2, Figure 3), whereas the week of sampling significantly influenced the number of individuals captured only in 2015 (Table 2). In both years of study, the richness of the families (S) in the olive grove areas was significantly greater than that in the adjacent shrubland areas (Table 2, Figure 3). The Simpson index was not significantly different between the study areas (Table 2, Figure 3).

Table 2.
Summary Statistics for the Models Developed to Assess the Effect of the Area (Olive Grove vs. Adjacent Shrubland Area) and the Week of Sampling on the Diversity of Families of Coleoptera in the Mirandela Region (Northeast Portugal) in 2015 and 2016. DV: Dependent Variable. IV: Independent Variable. SI: Simpson Index. df: Degrees of Freedom.
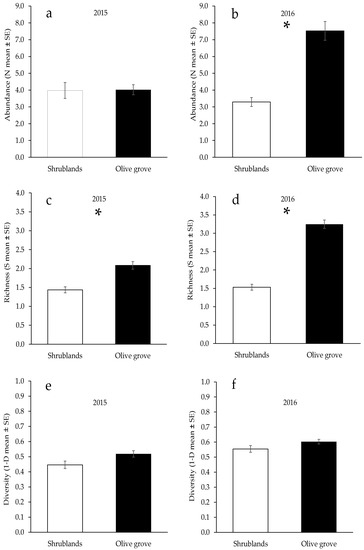
Figure 3.
Comparison of the samples of Coleoptera (GEEs) between the two studied habitats (olive grove and adjacent shrublands) in the Mirandela region (Northeast Portugal) in 2015 and 2016. (a,b): Total abundance; (c,d): Richness of families; (e,f): Simpson index for families. Asterisk (*) indicates significant differences between habitats (α < 0.01).
4. Discussion
In this study, the diversity of the order Coleoptera in olive groves and their corresponding areas of adjacent Mediterranean shrubland was evaluated over two years. The sampling was conducted for seven weeks in the spring. Although this could be a short sampling period, during this time-lapse, the abundance of arthropods maximizes, and the data better reflect the differences among the plots (see [22]).
The 25 families identified represent 23.58% of the Iberian coleopteran diversity at this taxonomic level [31]. In general, both the abundance and richness of the families of beetles were greater in the olive groves. Although the significantly higher abundance of beetles in 2016 could be solely due to interannual variation, the greater richness of the families was consistent over the two years of study. The CCA separated both habitats; however, the identification of the community of beetles at the family level prevents a clear separation regarding the feeding habits [32]. The complementarity of the families between the two areas was relatively low in both years, indicating an overlap of the assemblages between the olive groves and the adjacent shrub areas. On the other hand, a separation into herbivores and non-herbivores (i.e., carnivores, fungivores, and detritivores) allowed for a different point of view of the community structure. In this sense, there was a dominance of non-herbivorous beetles. Their higher abundance may be related to the complexity of the landscape and may also be a result of the sampling method, since pitfall traps capture mostly carnivores, fungivores, and detritivores [24]. Among the families considered exclusively herbivorous, Curculionidae was abundant in the two years of study. In the olive groves this family is linked to the olive bark beetle, Phloeotribus scarabaeoides Bern, 1788, and other phytophagous bark beetles [33].
The Anthicidae family was dominant in the adjacent shrubland areas compared to the olive groves. Marinoni and Ganho [34] attribute the dominance of a group to the availability of food. Anthicidae beetles are cosmopolitan and predatory, occurring in halophilic, forest, coastal, floricultural, and riverine areas [35]. The species of this family usually inhabit leaves, flowers, rocks, trunks, or debris and are associated with ants, feeding on the eggs of Lepidoptera, first instar larvae, other insect pupae, small dead invertebrates, and pollen [36,37,38]. Carpio et al. [39] found that bare soil areas favored the presence of Anthicidae. In contrast, our results suggest that the adjacent shrubland may favor this family due to the greater plant complexity and the large rocky structures found in these areas compared to the olive grove.
The selected groves are conducted under Organic Production or Integrated Pest Management, in which the vegetation cover is maintained between the rows of the plantation and the soil is not tilled. Álvarez et al. [40] found that a spontaneous vegetation cover is a source of food and ecological niches for different arthropods. In the case of ground beetles, this may explain the higher abundance of Tenebrionidae and Scarabaeidae in the olive grove areas compared to that in the shrubland areas in both years of study (see [33,41]).
Most species of Tenebrionidae feed on decaying plants or animal matter and soil-inhabiting larvae, although they can also feed on roots and seeds, live in forest areas and eat fungi, or even act as facultative predators [7,42]. On the other hand, the Scarabaeidae family provides important soil services such as nutrient recycling. The species of Scarabaeidae are ecological indicators of environmental changes regulating the populations of other arthropods [43,44]. Our results in the olive grove areas support those reported by other authors who observed the Tenebrionidae, Scarabaeidae, Carabidae, and Staphylinidae families as being particularly associated with systems with a vegetation cover at the ground level [7,12,45].
Carabidae and Staphylinidae are commonly reported in olive groves, where their presence is relevant regarding the limitation of pests such as the olive fly, Bactrocera oleae [5,10,24]. The presence of these families in the adjacent shrublands suggests that the heterogeneity of the landscape surrounding the olive groves could contribute to their conservation, as the temperature and soil moisture are factors that regulate their distribution [46]. This is consistent with the work of Taboada et al. [47] and Madeira et al. [16], who found adjacent areas of complex structures housing predatory species beneficial to cultivated areas.
Preserved ecosystems have a greater complexity in terms of ecological niches and a higher abundance of non-herbivorous beetles [34,48,49]. Subsequently, this could result in a greater contribution to biological control (e.g., Carabidae and Staphylinidae). Although high-rank taxonomic studies may help in characterizing the community of soil-inhabiting beetles in olive groves and adjacent landscapes, species-based studies are mandatory to shed light on the effect of environmental variables on the spatiotemporal patterns of the assemblage.
5. Conclusions
Olive groves provide habitats to communities of beetles, supporting a greater abundance and richness of families compared to the adjacent shrubland area in Trás-os-Montes. Furthermore, the adjacent semi-natural areas could house relevant beetle diversity, indirectly contributing to the natural limitation of pests in neighboring agroecosystems such as the olive grove. Species-level studies on diversity and its relationship with the environmental variables, feeding habits, and population dynamics of beetles are still needed to understand the extent to which key species and guilds may exert efficient pest suppression in the olive grove agroecosystem. For example, mark-release-recapture experiments in different seasons would provide information on the migration patterns of beetles between olive groves and adjacent shrublands, whereas functional response assays can allow for the assessment of the potential efficiency of pest suppression exerted by key species.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture12060771/s1, Table S1: Main characteristics of the selected olive groves and their adjacent shrublands.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B.-M. and S.A.P.S.; methodology, J.B.-M., J.A.P., K.L.K. and S.A.P.S.; formal analysis, J.B.-M. and K.L.K.; data curation, J.B.-M. and K.L.K.; writing K.L.K., J.B.-M., S.A.P.S. and J.A.P.; supervision, J.B.-M., J.A.P., S.A.P.S. and D.T.; funding acquisition, J.A.P. and S.A.P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT, Portugal), by financial support from national funds to the project “OLIVESIM–Managing ecosystem services in olive groves using advanced landscape agent-based models” (Ref. PTDC/ASP-PLA/30003/2017), and by financial support from the national funds FCT/MCTES to CIMO (UIDB/00690/2020) and LA SusTEC (LA/P/0007/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Santos, S.A.; Cabanas, J.E.; Pereira, J.A. Abundance and diversity of soil arthropods in olive grove ecosystem Portugal: Effect of pitfall trap type. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2007, 43, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Chapuis, E.; Tavoillot, J.; Mateille, T. Plant-parasitic nematodes associated with olive tree (Olea europaea L.) with a focus on the Mediterranean Basin: A review. C. R. Biol. 2014, 337, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO-Organização Das Nações Unidas Para a Alimentação e a Agricultura. FAOSTAT. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Gonçalves, M.F.; Pereira, J.A. Abundância e diversidade de artrópodes do solo no olival ecossistema. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis, A.M.; Pereira, J.A.; Pimenta, M.C.; Oliveira, J.; Benhadi–Marín, J.; Santos, S.A.P. Suppression of Bactrocera oleae Diptera: Tephritidae pupae by soil arthropods in the olive grove. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 140, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, P.; Smith, A.B.T.; Douglas, H.; Gimmel, M.L.; Brunke, A.J.; Kanda, K. Biodiversity of Coleoptera. In Insect Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Foottit, R.C., Adler, P.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 337–417. [Google Scholar]
- Marinoni, R.C.; Ganho, N.G.; Monné, M.L.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Hábitos Alimentares em Coleoptera Insecta, 1st ed.; Holos Editora Ltda: Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, 2001; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Jordan, G.J.; Baker, T.P.; Balmer, J.M.; Wardlaw, T.; Baker, S.C. Living near the edge: Being close to mature forest increases the rate of succession in beetle communities. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplehorn, C.A.; Johnson, N.F. Estudo dos Insetos, 2nd ed.; Cengage Learning: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; p. 776. [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, M.M.; Daane, K.M.; Sime, K.R.; Nelson, E.H. Mortality of olive fruit fly pupae in California. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daane, K.M.; Johnson, M.W. Olive fruit fly: Managing an ancient pest in modern times. Ann. Ver. Entomol. 2010, 55, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, A.C.C.; Oliveira, O.C.C.; Silva, R.A.; Albuquerque, P.M.C.; Rebêlo, J.M.M.; Viana, J.H.; Siqueira, G.M. Abundance and diversity of beetles Insecta: Coleoptera in land use and management systems. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2020, 44, e0190183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NG, K.; Mclntyre, S.; Macfadyen, S.; Barton, P.S.; Driscoll, D.A.; Lindenmayer, D.B. Dynamic effects of ground-layer plant communities on beetles in a fragmented farming landscape. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 2131–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Rossi, J.P.; Decaëns, T.; Aubert, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Bureau, F.; Margerie, P.; Mora, P. Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P. O Olival em Portugal Dinâmicas, Tecnologias e Relação Com o Desenvolvimento Rural; Editora Rainho & Neves: Lisboa, Portugal, 2014; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Madeira, F.; Tscharntke, T.; Elek, Z.; Kormann, U.G.; Pons, X.; Rösch, V.; Batáry, P. Spillover of arthropods from cropland to protected calcareous grassland–the neighbouring habitat matters. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 235, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchi, M.S.; Bocci, G.; Petacchi, R.; Entling, M.H. Effects of local and landscape factors on spiders and olive fruit flies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. Updated world map of the Koppen–Geiger climate classification. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. Worldclim 2: New 1–km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRB I.W.G. World reference base for soil resources 2014. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Report; FAO: Budapest, Hungary, 2014; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Benhadi–Marín, J.; Pereira, J.A.; Sousa, J.P.; Santos, S.A.P. Distribution of the spider community in the olive grove agroecosystem Portugal: Potential bioindicators. Agric. For. Entomol. 2020, 22, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, F.; Lozano, C.; Garcia, P.; Peña, A.; Tinaut, A.; Pascual, F.; Campos, M. Use of arthropods for the evaluation of the olive-orchard management regimes. Agric. For. Entomol. 2004, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harde, K.W.; Severa, F. Guía de Campo de Los Coleópteros de Europa; Omega: Madrid, Spain, 1984; p. 332. [Google Scholar]
- Marinoni, R.C. Os grupos tróficos em Coleoptera. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2001, 18, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R–project.org/ (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Gail, M., Krickeberg, K., Samet, J.M., Tsiatis, A., Wong, W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 574. [Google Scholar]
- Pekár, S.; Brabec, M. Generalized estimating equations: A pragmatic and flexible approach to the marginal GLM modelling of correlated data in the behavioural sciences. Ethology 2018, 124, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; et al. Package ‘Vegan’. Community Ecology Package, 2019. Version 2.5–6. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso–Zarazaga, M.A. Orden Coleoptera. Rev. IDE@–SEA 2015, 55, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, R.L.; Andreazze, R.; Almeida, H.T.A.; Pinheiro, M.P.G. Riqueza de famílias e hábitos alimentares em Coleoptera capturados na fazenda da EMPARN-Jiqui, Parnamirim/RN. EntomoBrasilis 2010, 3, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M. Diversidade de artrópodes associados à oliveira (Olea europaea L.), no Algarve. Ecol. Rev. Online Soc. Port. Ecol. 2014, 7, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Marinoni, R.C.; Ganho, N.G.A. diversidade diferencial beta de Coleoptera Insecta em uma paisagem antropizada do Bioma Araucária. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2006, 50, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, J.; Bolaño, J.A.S. Catálogo comentado de los Anthicidae y Aderidae Coleoptera de la provincia de Badajoz Extremadura, España. Bol. SEA 2014, 54, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, C.S.; Galvão, J.C.C.; Picanço, M.C.; Cecon, P.R.; Pereira, P.R.G. Incidência de insetos fitófagos e de predadores no milho e no feijão cultivados em sistema exclusivo e consorciado. Cienc. Rural 2003, 33, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Audino, L.D.; Nogueira, J.M.; da Silva, P.G.; Neske, M.Z.; Ramos, A.H.B.; Moares, L.D.M.; Borba, M.F.S. Identificação dos Coleópteros (Insecta: Coleoptera) das Regiões de Palmas (município de Bagé) e Santa Barbinha (Município de Caçapava do Sul, RS); Embrapa Pecuária Sul: Bagé, Brazil, 2007; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, F.L.; Picanço, M.C.; de Sena Fernandes, M.E.; Xavier, V.M.; Martins, J.C.; da Silva, V.F. Controle biológico natural de pragas e interações ecológicas com predadores e parasitóides em feijoeiro. Biosci. J. 2010, 26, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Carpio, A.J.; Castro, J.; Tortosa, F.S. Arthropod biodiversity in olive groves under two soil management systems: Presence versus absence of herbaceous cover crop. Agric. For. Entomol. 2018, 21, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, H.A.; Muñoz, R.J.; Morente, M.; Campos, M.; Ruano, F. Ground cover presence in organic olive orchards affects the interaction of natural enemies against Prays oleae, promoting an effective egg predation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 315, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotes, B.; Campos, M.; Pascual, F.; García, P.A.; Ruano, F. Comparing taxonomic levels of epigeal insects under different farming systems in Andalusian olive agroecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, S. Ecology and Conservation of tenebrionid beetles in Mediterranean coastal areas. In Insect Ecology and Conservation; Fattori, S., Ed.; Research Signpost: Trivandrum, India, 2008; pp. 165–297. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, E.; Spector, S.; Louzada, J.; Larsen, T.; Amezquita, S.; Favila, M.E. Ecological functions and ecosystem services provided by Scarabaeinae dung beetles. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 14, 1461–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, A.; Araújo, R.B.; da Silva, L.; de Souza, M.D.; da Silva Júnior, J.G.; Machado, M.P.; Martinovski, P.P. Ocorrência de escarabeíneos coleoptera: Scarabaeidae, Scarabaeinae em 2 tipos de armadilhas iscadas com etanol em área de transição Cerrado sensu stricto, Pantanal, Mato Grosso. Biodiversidade 2017, 16, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pompeo, P.N.; Oliveira Filho, L.C.I.; Klauberg Filho, O.; Mafra, Á.L.; Baretta, C.R.D.M.; Baretta, D. Diversidade de Coleoptera Arthropoda: Insecta e atributos edáficos em sistemas de uso do solo no Planalto Catarinense. Sci. Agrar. 2016, 171, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlet, J.; Costa, E.C.; Boscardin, J.; Machado, D.N.; Pedron, L. Fauna de Coleoptera edáfica em eucalipto sob diferentes sistemas de controle químico da Matocompetição. Floresta Ambient. 2015, 22, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, A.; Kotze, D.J.; Salgado, J.; Tárrega, R. The value of semi–natural grasslands for the conservation of carabid beetles in long–term managed forested landscapes. J. Insect Conserv. 2011, 15, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganho, N.G.; Marinoni, R.C. Fauna de Coleoptera no Parque Estadual de Vila Velha, Ponta Grossa, Paraná, Brasil: Abundância e riqueza das famílias capturadas através de armadilhas malaise. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2003, 20, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, M.; Fontaneto, D. Biodiversity of ground beetles Coleoptera: Carabidae in different habitats of the Italian Polowland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).