The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
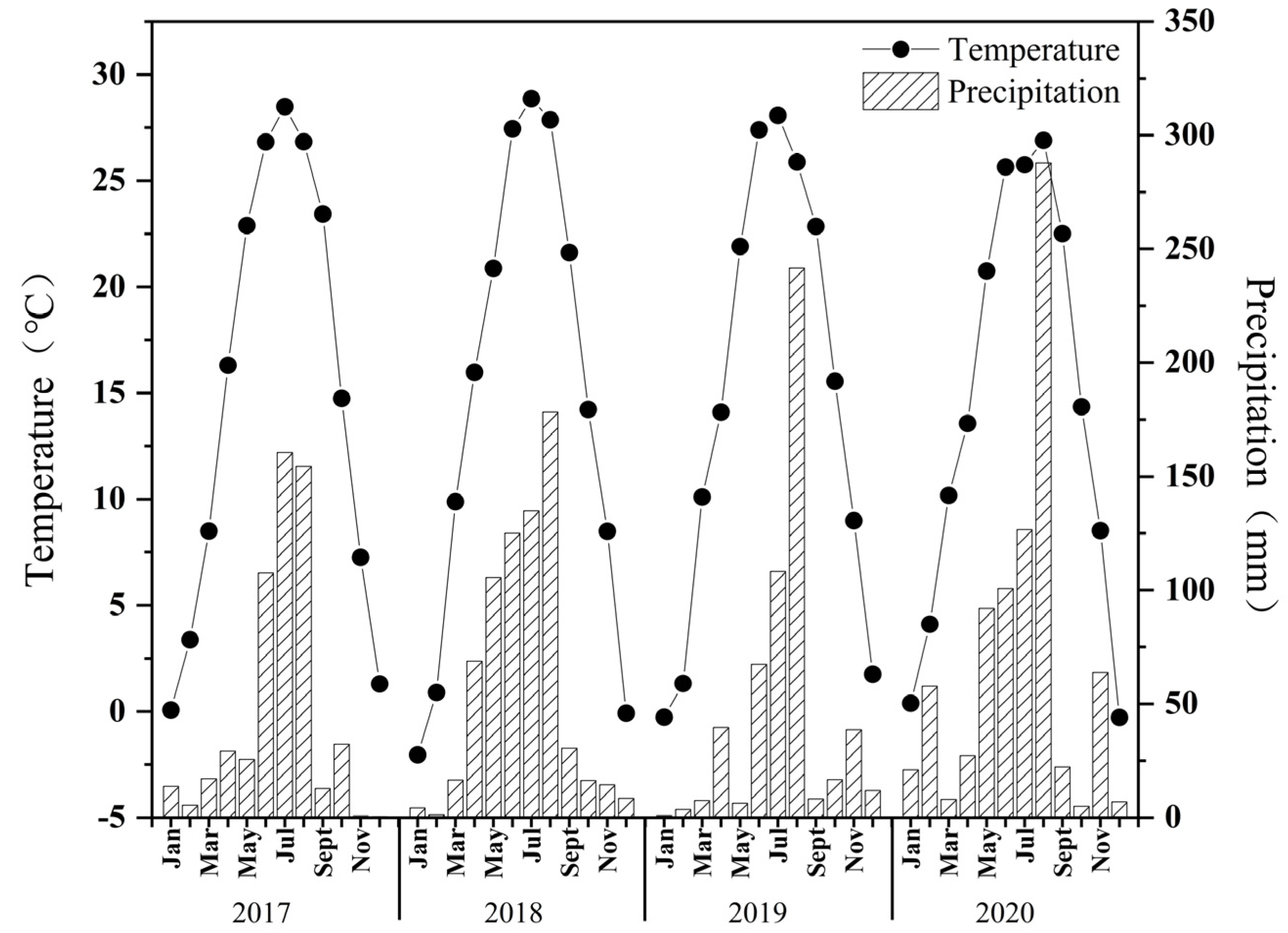
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Gas and Soil Sampling
2.3.1. Gas Sampling
2.3.2. Soil Sampling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
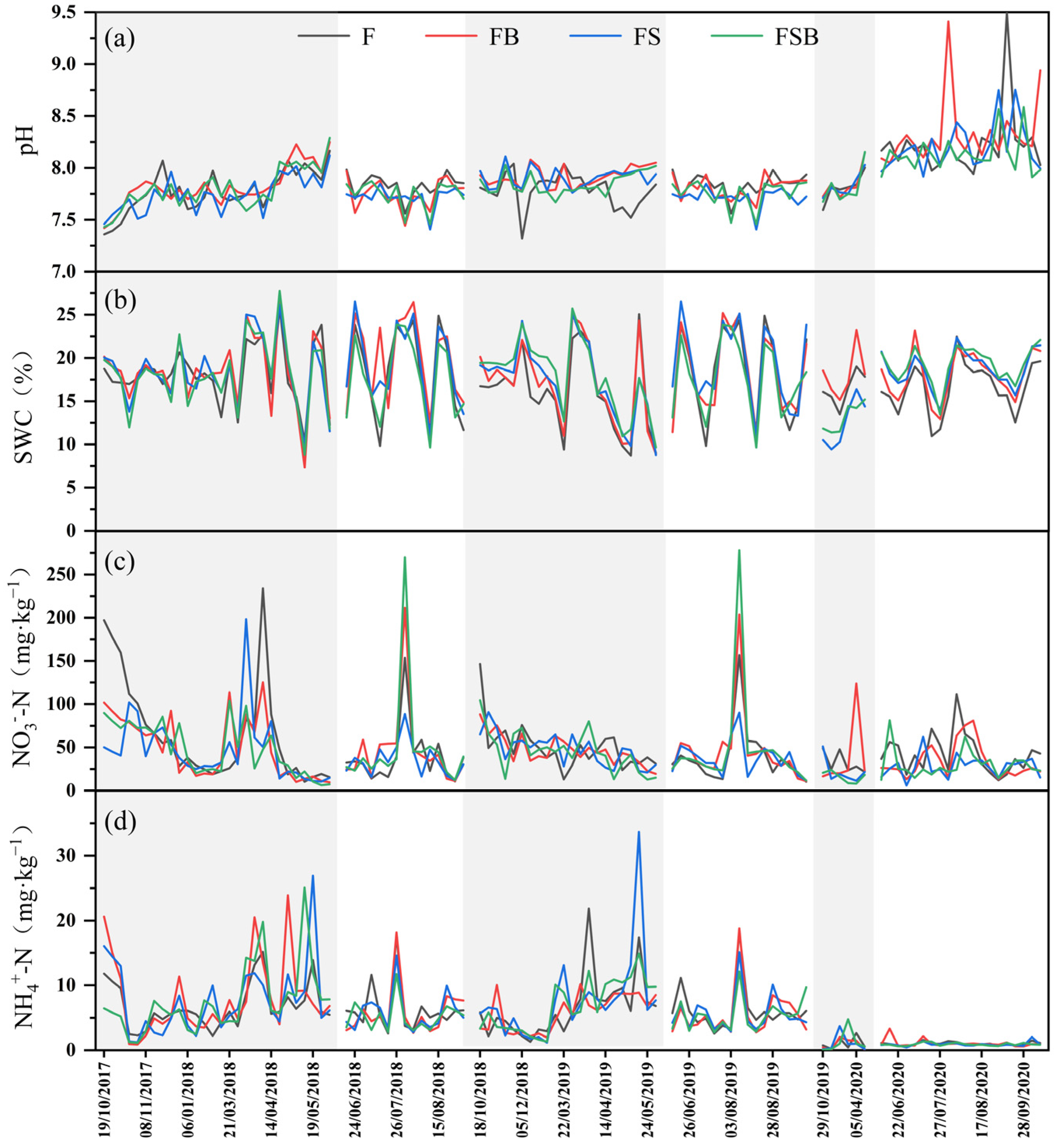
3.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
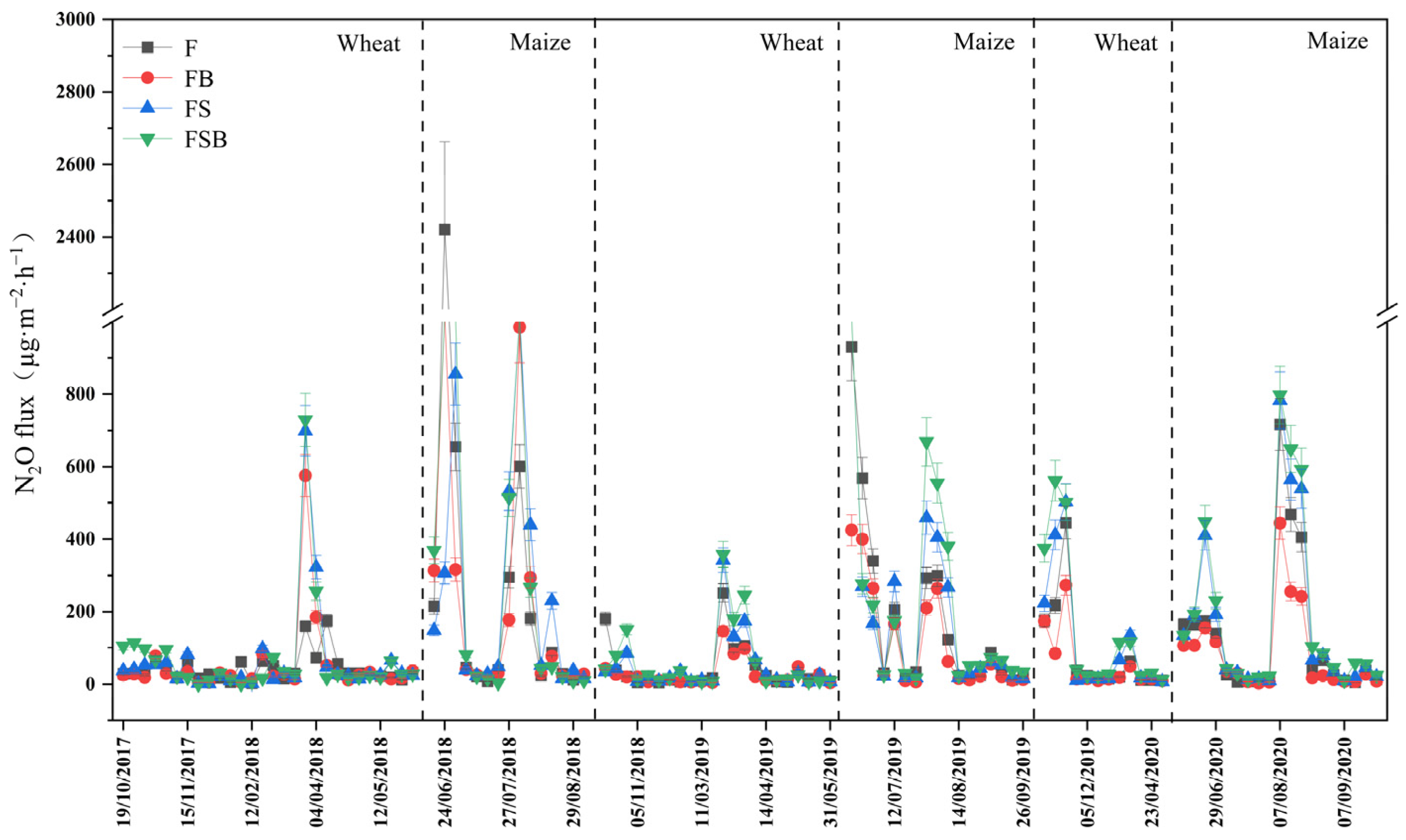
3.2. N2O Emissions
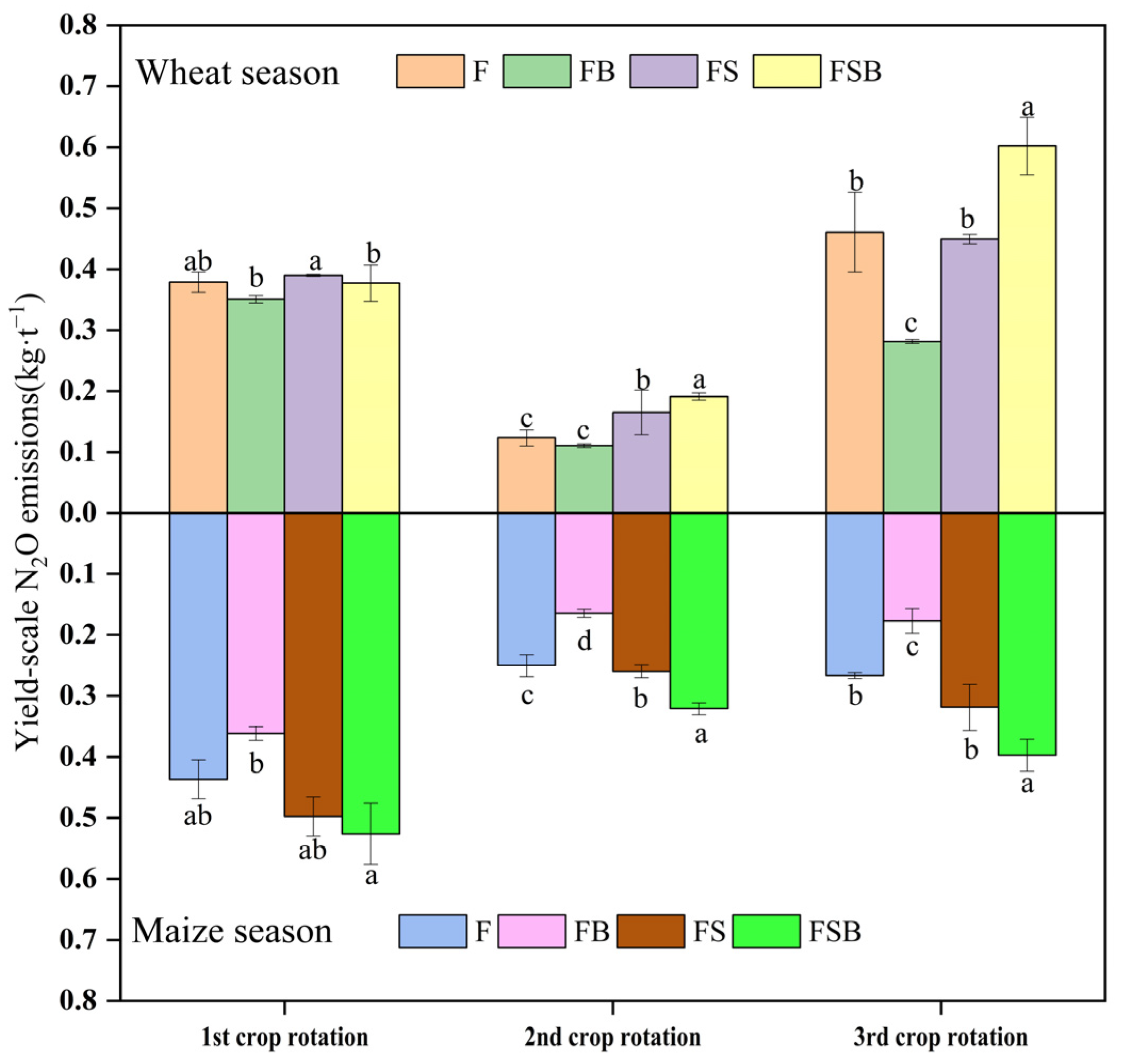
3.3. N2O Emission Factor
3.4. Correlations between N2O Emissions and Environmental Factors
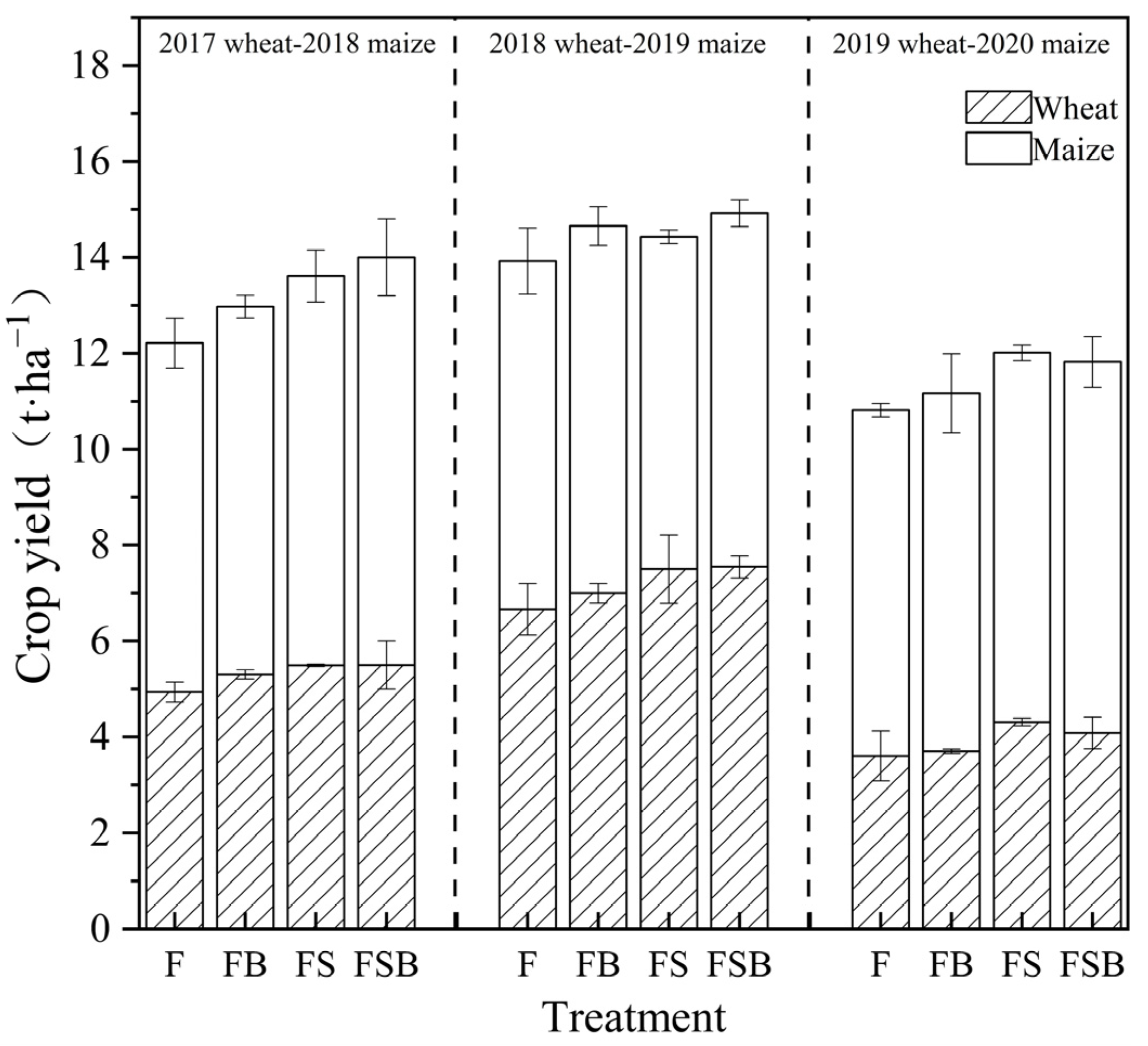
3.5. Crop Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Environmental Factors on N2O Emissions
4.2. Long-Term Effects of Continuous Application of Biochar and Straw on N2O Emissions
4.3. Effects of Biochar and Straw on Crop Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S. Fertilizer nitrogen and global warming—A review. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 89, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2013. In Climate Change 2013: The Phycial Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Lu, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Davidson, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Arneth, A.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P.; et al. Global soil nitrous oxide emissions since the preindustrial era estimated by an ensemble of terrestrial biosphere models: Magnitude, attribution, and uncertainty. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, M.F.; Abdullah, M.A.; Rizwan, M.; Haider, G.; Ali, M.A.; Zafar-ul-hye, M.; Abid, M. Different nitrogen and biochar sources’ application in an alkaline calcareous soil improved the maize yield and soil nitrogen retention. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Coulter, J.A.; Cai, L.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R. An overview on biochar production, its implications, and mechanisms of biochar-induced amelioration of soil and plant characteristics. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 107–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Ros, G.H.; de Vries, W. Impacts of agronomic measures on crop, soil, and environmental indicators: A review and synthesis of meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, E.; Six, J. Biochar does not mitigate field-scale N2O emissions in a Northern California vineyard: An assessment across two years. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.I.P.; Suddick, E.C.; Mansour, I.; Mukome, F.N.D.; Parikh, S.J.; Scow, K.; Six, J. Biochar alters nitrogen transformations but has minimal effects on nitrous oxide emissions in an organically managed lettuce mesocosm. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Arif, M.S.; Shahzad, S.M.; Farooq, T.H.; Ashraf, F.; Altaf, M.M.; Ahemd, W.; Tufail, M.A.; Ashraf, M. Does biochar accelerate the mitigation of greenhouse gaseous emissions from agricultural soil? —A global meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C. Long-term effects of biochar addition and straw return on N2O fluxes and the related functional gene abundances under wheat-maize rotation system in the North China Plain. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2019, 135, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, R.; Zhou, G.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Antagonistic interaction between biochar and nitrogen addition on soil greenhouse gas fluxes: A global synthesis. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntacyabukura, T.; Uwiringiyimana, E.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B.; Harerimana, B.; Nambajimana, J.D.; Nsabimana, G.; Nsengumuremyi, P. Effect of biochar and straw application on nitrous oxide and methane emissions from eutric regosols with different pH in Sichuan basin: A mesocosm study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Ying, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, P.; Teng, Y. Effects of biochar-based fertilizer on nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen losses via leaching and ammonia volatilization from an open vegetable field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65188–65199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayuela, M.L.; van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s role in mitigating soil nitrous oxide emissions: A review and meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Park, H.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Seo, B.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Yang, H.I.; Xu, X.; Tang, S.; Cheng, W.; Lim, S.S.; et al. Biochar-induced reduction of N2O emission from East Asian soils under aerobic conditions: Review and data analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; O’Connor, D.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Shen, Z.; Hou, D. Biochar aging: Mechanisms, physicochemical changes, assessment, and implications for field applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 54, 14797–14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, G.; Huang, X.; Cao, X.; Ye, A.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, C.; Zhang, R. Study on the physicochemical properties changes of field aging biochar and its effects on the immobilization mechanism for Cd2+ and Pb2+. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2022, 230, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Northup, B.K.; Rice, C.W.; Prasad, P.V.V. Biochar applications influence soil physical and chemical properties, microbial diversity, and crop productivity: A meta-analysis. Biochar 2022, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland-A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; He, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Lu, C.; Zheng, K.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Lou, S. Effect of straw retention on crop yield, soil properties, water use efficiency and greenhouse gas emission in China: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2019, 13, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.; Ju, X. Effect of fertilizer N rates and straw management on yield-scaled nitrous oxide emissions in a maize-wheat double cropping system. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Yan, G.; Zheng, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Straw return reduces yield-scaled N2O plus NO emissions from annual winter wheat-based cropping systems in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Sui, P.; Long, P.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Yan, P.; Shen, Y.; Dai, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Effects of different agricultural organic wastes on soil GHG emissions: During a 4-year field measurement in the North China Plain. Waste Manag. 2018, 81, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, W. The contrasting effects of biochar and straw on N2O emissions in the maize season in intensively farmed soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 29806–29819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Hansen, E.M.; Olesen, J.E.; Baral, K.R.; Petersen, S.O. Interactive effects of straw management, tillage, and a cover crop on nitrous oxide emissions and nitrate leaching from a sandy loam soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Bian, X. Evaluation of the agronomic impacts on yield-scaled N2O emission from wheat and maize fields in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Mu, Y. The influence of straw returning on N2O emissions from a maize-wheat field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wu, F.; Jia, Z.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Chang, S. Wheat straw and its biochar differently affect soil properties and field-based greenhouse gas emission in a Chernozemic soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L. The responses of soil N2O emissions to residue returning systems: A meta-analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, L.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Effects of straw returning levels on carbon footprint and net ecosystem economic benefits from rice-wheat rotation in central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H. Effects of straw incorporation methods on nitrous oxide and methane emissions from a wheat-rice rotation system. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bao, Y.; Lv, Q.; Tang, Q.; Nu, K. Simulation and influence factors of nitrous oxide (N2O) gases emission under different straw retention depths. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Che, Y.; Xiao, Y. Effects of rice straw incorporation and N fertilizer on ryegrass yield, soil quality, and greenhouse gas emissions from paddy soil. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.; Ma, C.; Tu, R.; Gao, H. Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from production, transportation and fertilization of synthetic nitrogen for wheat and maize in typical provinces of China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 707–713. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cong, H.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Meng, H.; Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Yuan, W.; Jia, J.; Xie, T.; Wu, Y. Distribution of crop straw resources and its industrial system and utilization path in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 132–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Shen, G.; Sun, M.; Cai, X.; Shang, G.; Chen, P. Effect of biochar on nitrous oxide emission and its potential mechanisms. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Cheng, G.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, M.; Feng, H.; Dyck, M.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Contrasting effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on net global warming potential in the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 205, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, Z. Biochar amendment reduced greenhouse gas intensities in the rice-wheat rotation system: Six-year field observation and meta-analysis. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, K.; Khan, H.; Zaman, M.; Muller, C.; Alam, S.S.; Fahad, S.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Alkahtani, J.; Saeed, B.; Saud, S.; et al. The effect of biochar and nitrogen inhibitor on ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions and wheat productivity. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Qiu, S.; Jin, L.; Wei, D.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; He, P.; Wang, L.; Christie, P.; Zhou, W. Quantifying soil N pools and N2O emissions after application of chemical fertilizer and straw to a typical chernozem soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liang, X.; He, S.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, G. Biochar slows gross nitrification and gasses N emission via lower autotrophic nitrification in paddy soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Jiang, S.; Cao, C.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, J. Combined effects of straw returning and chemical N fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions and yield from paddy fields in Northwest Hubei province. China J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 20, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Sheng, F.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Effects of long-term no tillage and straw return on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields from a rice-wheat system in central China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Soil pH as the chief modifier for regional nitrous oxide emissions: New evidence and implications for global estimates and mitigation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aamer, M.; Shaaban, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Ma, Q.; Munir, H.; Rasheed, A.; Li, X.; Li, P.; et al. N2O emissions mitigation in acidic soil following biochar application under different moisture regimes. J. Plant Nutr. Soil. Sci. 2020, 20, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, H.; Fan, M.; Chen, H.; Guo, D.; Cao, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biochar effects on crop yields and nitrogen loss depending on fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Rahaman, M.A.; Yang, Z. Inhibited effect of biochar application on N2O emissions is amount and time-dependent by regulating denitrification in a wheat-maize rotation system in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G. Effects of biochar and straw on soil N2O emission from a wheat maize rotation system. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1569–1580. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Troy, S.M.; Lawlor, P.G.; O’ Flynn, C.J.; Healy, M.C. Impact of biochar addition to soil on greenhouse gas emissions following pig manure application. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2013, 60, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Morris, S.; Macdonald, L.M.; Rust, J.; Petty, S.; Joseph, S.; Rose, T. Biochar improves diary pasture yields by alleviating P and K constraints with no influence on soil respiration or N2O emissions. Biochar 2019, 1, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, D.; He, T.; Yoo, G.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Fan, J. Wheat straw-derived biochar amendment stimulated N2O emissions from rice paddy soils by regulating the amoA genes of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuer-Gatius, J.; Shanskiy, M.; Soosaar, K.; Astover, A.; Raave, H. High-temperature hay biochar application into soil increases N2O fluxes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bi, Z.; Xiong, Z. Dynamic responses of nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen use efficiency to nitrogen and biochar amendment in an intensified vegetable field in southeastern China. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Z.; He, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, T.; Xing, G. Successive straw biochar amendments reduce nitrous oxide emissions but do not improve the net ecosystem economic benefit in an alkaline sandy loam under a wheat-maize cropping system. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 868–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, Z. Field-aged biochar stimulated N2O production from greenhouse vegetable production soils by nitrification and denitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Kammann, C.I.; Schmidt, H.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Nitrate capture and slow release in biochar amended compost and soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Müller, C.; Jansen-Willems, A.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; Niu, Y.; Ding, W. Field-aged biochar decreased N2O emissions by reducing autotrophic nitrification in a sandy loam soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Wu, J. Response of N2O emissions to biochar amendment on a tea field soil in subtropical central China: A three-year field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 318, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shan, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yan, X. Variable responses of nitrification and denitrification in a paddy soil to long-term biochar amendment and short-term biochar addition. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Fan, F.; Liao, Y. Long-term effect of biochar application on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions in a rice paddy cropping system: A four-year case study in south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Gao, M.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Lv, S.; Luo, M. Effect of straw residues in combination with reduced fertilization rate on greenhouse gas emissions from a vegetable field. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 4694–4704. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Song, K.; Zhu, X.; Shen, W.; Xu, H. Dynamic interactions of nitrogen fertilizer and straw application on greenhouse gas emissions and sequestration of soil carbon and nitrogen: A 13-year field study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 325, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, T.; Schlatter, N.; Baumgarten, A.; Bechini, L.; Krüger, J.; Grignani, C.; Zavattaro, L.; Costamagna, C.; Spiegel, H. Effect of crop residue incorporation on soil organic carbon and greenhouse gas emissions in European agricultural soils. Soil. Use Manag. 2014, 30, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wang, B.; Gu, Z.; Tao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhu, L.; Meng, Y. Effects of different straw returning modes on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, M.; Hui, D.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Lu, C.; Sheng, J.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y.; et al. Straw incorporation influences soil organic carbon sequestration, greenhouse gas emission, and crop yields in a Chinese rice (Oryza sativa L.)-wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cropping system. Soil. Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Q.; Wang, C.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ping, F.; Thies, J.; Wu, W. Biochar amendment pyrolysed with rice straw increases rice production and mitigates methane emission over successive three years. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. After-effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on crop growth, yield, and soil properties in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)-maize (Zea mays L.) rotations: A four-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Omidvar, N.; Gallart, M.; Kämper, W.; Tahmasbian, I.; Farrar, M.B.; Singh, K.; Zhou, G.; Muqadass, B.; Xu, C.; et al. Combined effects of biochar and fertilizer applications on yield: A review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N. The Effect of Biochar Application on Soil Carbon and Grain Yield in High Yield Farmland of the North China Plain. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Bejing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Dong, F.; Li, J.; Duan, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Li, F. Effects of maize straw-derived biochar application on soil temperature, water conditions and growth of winter wheat. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2019, 70, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Wan, Y.; Xie, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, W. Biochar derived from corn straw affected availability and distribution of soil nutrients and cotton yield. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e189924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Shan, J.; Xia, Y.; Lin, J.; Yan, X. A 2-year study on the effect of biochar on methane and nitrous oxide emissions in an intensive rice-wheat cropping system. Biochar 2019, 1, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lv, J.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.; Xi, H.; Kou, C.; He, Z.; Shen, A. Long-term decomposed straw return positively affects the soil microbial community. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 128, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hu, M.; Shi, J.; Tian, X. Improving long-term crop productivity and soil quality through integrated straw-return and tillage strategies. Agron. J. 2021, 114, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Meng, F.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Hu, Z. Ecological impacts of winter wheat and summer maize straw incorporation in Huantai County, Shandong Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 4157–4168. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, W.; Wei, Y.; Hu, K. Effects of straw return and regional factors on spatio-temporal variability of soil organic matter in a high-yielding area of northern China. Soil. Tillage Res. 2015, 145, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiao, X.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Jiang, H.; Mahmoud, A. Effects of biochar on water quality and rice productivity under straw returning condition in a rice-wheat rotation region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 2019–2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | 1.81% | 0.84% | 1.07% |
| FB | 1.62% | 0.467% | 0.474% |
| FS | 2.38% | 1.14% | 1.60% |
| FSB | 2.57% | 1.52% | 2.05% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Peng, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, C. The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13112091
Gao S, Peng Q, Liu X, Xu C. The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment. Agriculture. 2023; 13(11):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13112091
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Shangjie, Qin Peng, Xingren Liu, and Chunying Xu. 2023. "The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment" Agriculture 13, no. 11: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13112091
APA StyleGao, S., Peng, Q., Liu, X., & Xu, C. (2023). The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment. Agriculture, 13(11), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13112091








