How Far Will Climate Change Affect Future Food Security? An Inquiry into the Irrigated Rice System of Peninsular India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data and Sampling
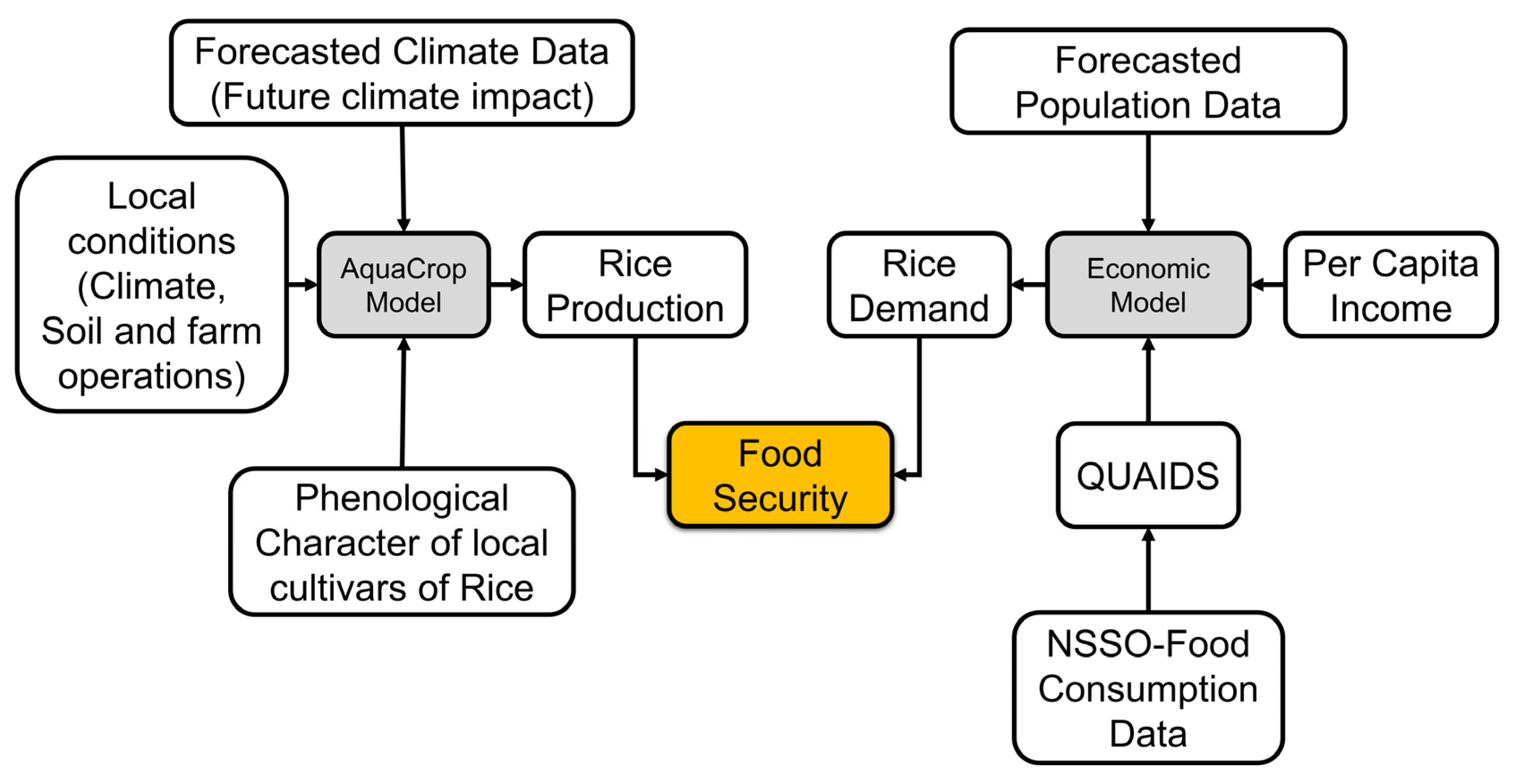
2.3. Food Security Assessment Framework
- (i)
- The technology is assumed to be constant during the study period;
- (ii)
- The cropping area is assumed to be constant during the study period;
- (iii)
- Except for climate, all the other factors (i.e., technology, input usage, etc.) that are associated with crop yield are assumed to be constant during the study period;
- (iv)
- Rice is being assumed as the primary food crop for the Cauvery delta region during the study period;
- (v)
- The consumption behavior and the real income of the consumer of the Cauvery delta zone are assumed to be constant during the study period;
- (vi)
- The contribution from the upper catchment to the delta’s irrigated rice would remain unaltered or constant in the future.
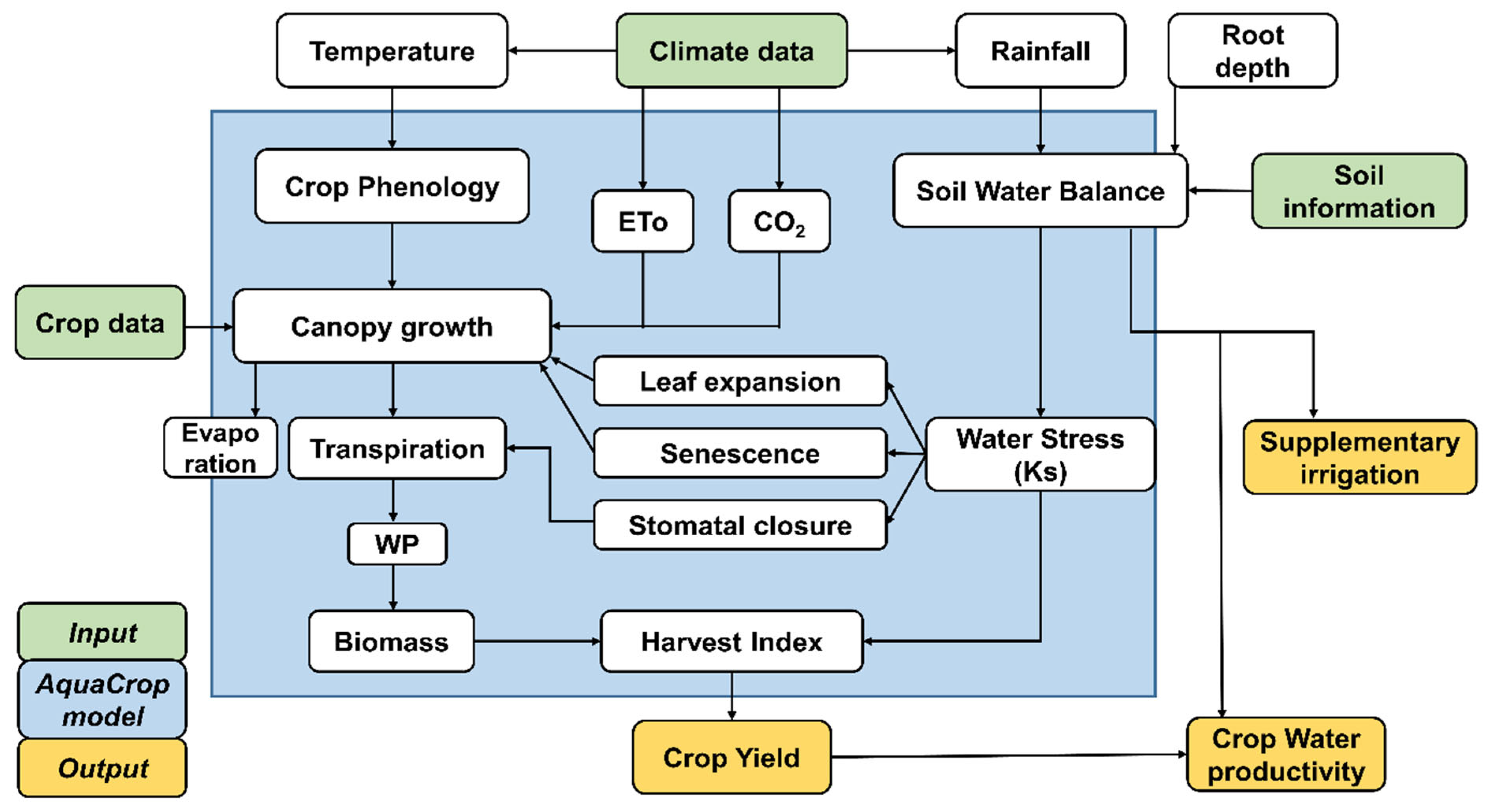
2.3.1. Projections on Supply of Rice through AquaCrop Modeling
2.3.2. Projections on Demand for Rice through the Demand Model
- (i)
- Own-price elasticity
- (ii)
- Cross-price elasticity
- (iii)
- Income elasticity
3. Results
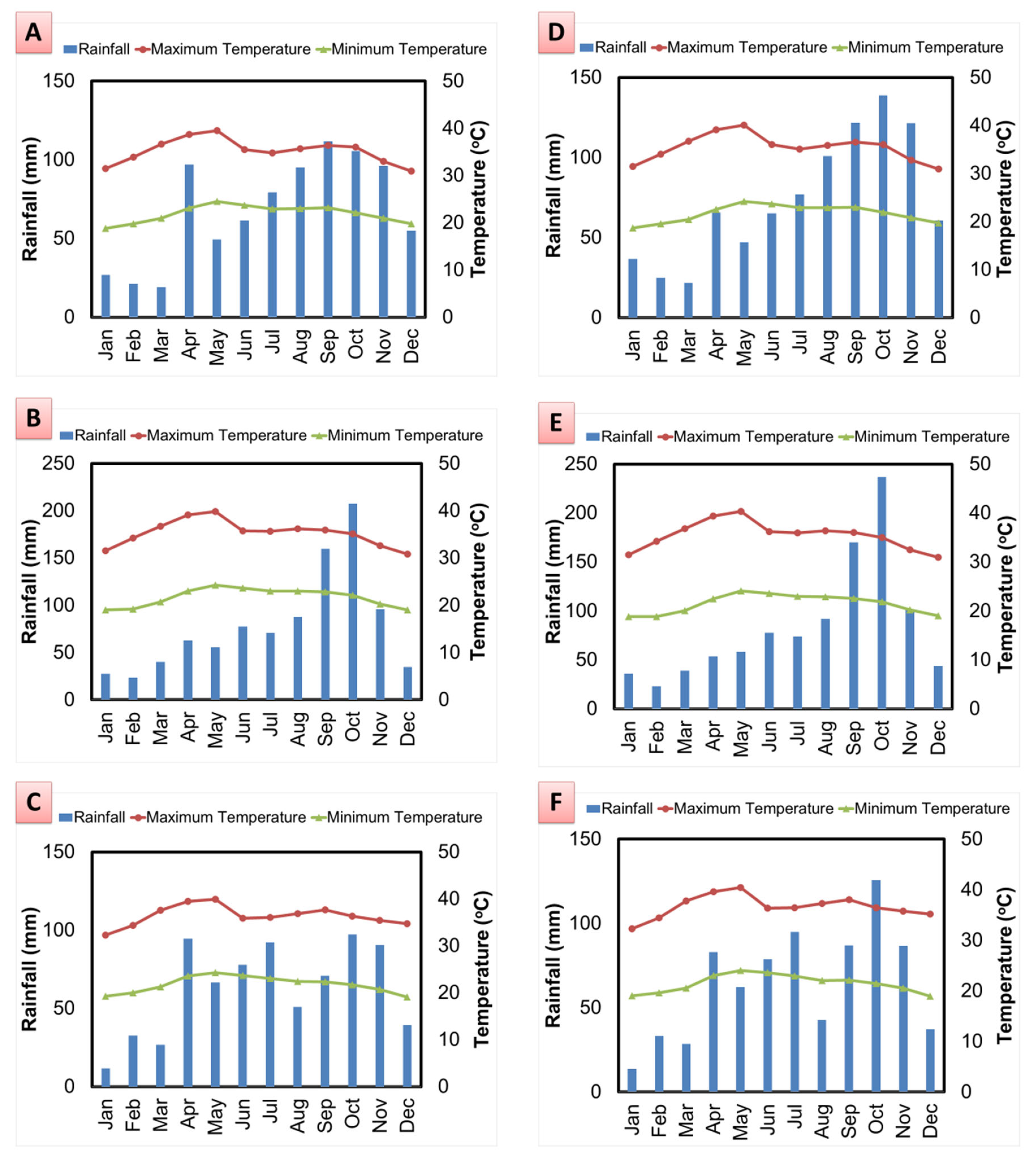
3.1. Characteristics of the Projected Climate Data
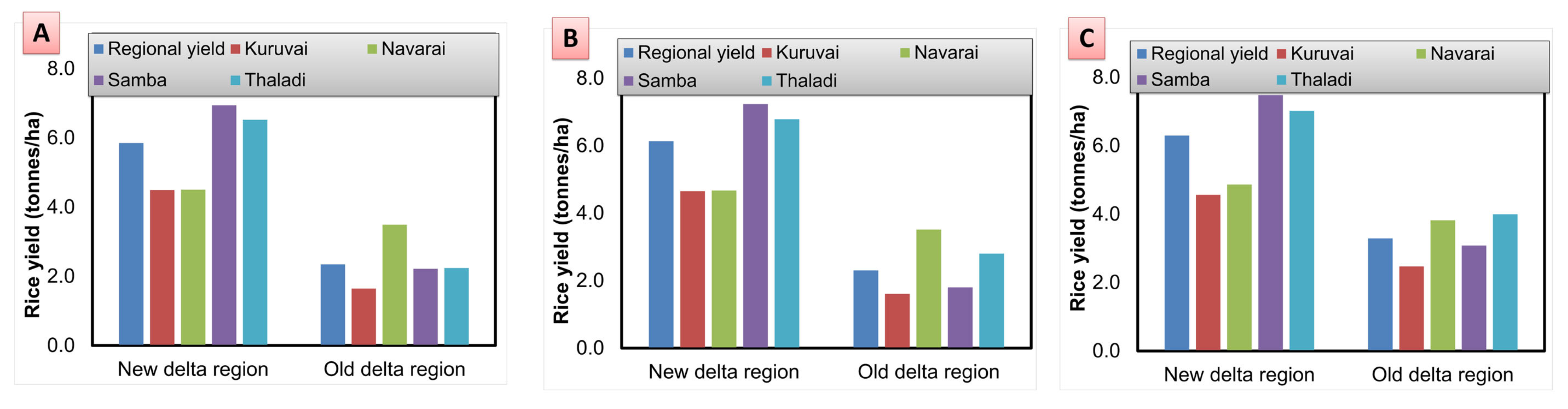
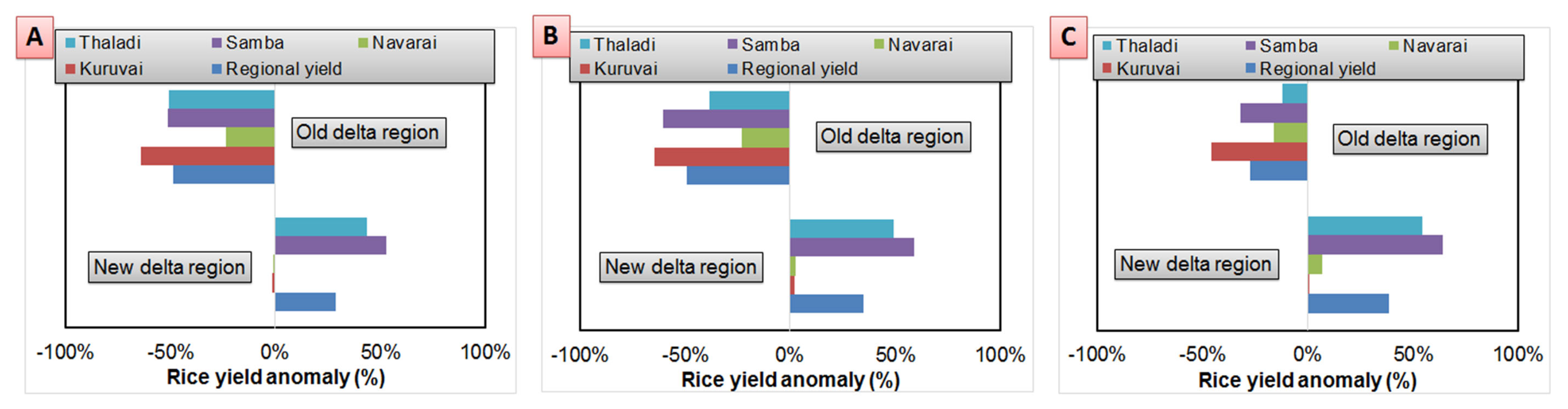
3.2. Projections on Rice Production
3.3. Projections of Demand for Rice
3.4. Projections on Food Security through the Rice Supply–Demand Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, A.; Erenstein, O. Assessing Farmer Use of Climate Change Adaptation Practices and Impacts on Food Security and Poverty in Pakistan. Clim. Risk Manag. 2017, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.P.; Perryman, A.H.; Osborne, T.M. Modelling Impacts of Climate Change on Global Food Security. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.W. Food Security under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.; Von Braun, J. Climate Change Impacts on Global Food Security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Clark, H.; Dong, H.; Elsiddig, E.A.; Haberl, H.; Harper, R.; House, J.; Jafari, M.; Masera, O.; Mbow, C. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU). In Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. IPCC Working Group III Contribution to AR5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aryal, J.P.; Sapkota, T.B.; Khurana, R.; Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Rahut, D.B.; Jat, M.L. Climate Change and Agriculture in South Asia: Adaptation Options in Smallholder Production Systems. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 5045–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schauberger, B.; Archontoulis, S.; Arneth, A.; Balkovic, J.; Ciais, P.; Deryng, D.; Elliott, J.; Folberth, C.; Khabarov, N.; Müller, C. Consistent Negative Response of US Crops to High Temperatures in Observations and Crop Models. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemma, M.; Alemie, A.; Habtu, S.; Lemma, C. Analyzing the Impacts of on Onset, Length of Growing Period and Dry Spell Length on Chickpea Production in Adaa District (East Showa Zone) of Ethiopia. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2016, 7, 349. [Google Scholar]
- Barnwal, P.; Kotani, K. Climatic Impacts across Agricultural Crop Yield Distributions: An Application of Quantile Regression on Rice Crops in Andhra Pradesh, India. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 87, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, F. How Do Droughts Impact Household Food Consumption and Nutritional Intake? A Study of Rural India. World Dev. 2019, 122, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Haneishi, Y.; Okello, S.E.; Asea, G.; Tsuboi, T.; Takagaki, M.; Kikuchi, M. Rice Green Revolution and Climatic Change in East Africa: An Approach from the Technical Efficiency of Rainfed Rice Farmers in Uganda. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palazzo, A.; Vervoort, J.M.; Mason-D’Croz, D.; Rutting, L.; Havlík, P.; Islam, S.; Bayala, J.; Valin, H.; Kadi Kadi, H.A.; Thornton, P.; et al. Linking Regional Stakeholder Scenarios and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: Quantified West African Food and Climate Futures in a Global Context. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 45, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutten, M.; Van Dijk, M.; Van Rooij, W.; Hilderink, H. Land Use Dynamics, Climate Change, and Food Security in Vietnam: A Global-to-Local Modeling Approach. World Dev. 2014, 59, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Simulated Responses of Global Rice Trade to Variations in Yield under Climate Change: Evidence from Main Rice-Producing Countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 124690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Krey, V.; Riahi, K.; Bertram, C.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Bosetti, V.; Callen, J.; Després, J.; Doelman, J.; et al. A Multi-Model Assessment of Food Security Implications of Climate Change Mitigation. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soora, N.K.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Saxena, R.; Rani, S.; Jain, S.; Chauhan, N. An Assessment of Regional Vulnerability of Rice to Climate Change in India. Clim. Chang. 2013, 118, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, K.; Robinson, S.; Cattaneo, A. Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security: Impacts and the Potential for Adaptation and Mitigation. In Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmelev, S.E.; Salnikov, V.; Turulina, G.; Polyakova, S.; Tazhibayeva, T.; Schnitzler, T.; Shmeleva, I.A. Climate Change and Food Security: The Impact of Some Key Variables on Wheat Yield in Kazakhstan. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogo, B.K.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R. Climate Change and Variability in Kenya: A Review of Impacts on Agriculture and Food Security. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J.; Tubiello, F.N. Global Food Security under Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19703–19708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.W.; Lee, W.-K.; Son, Y. An Assessment of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation in South Asian Agriculture. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2017, 9, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlstein, I.; Portmann, R.W.; Daniel, J.S.; Solomon, S.; Knutti, R. Perceptible Changes in Regional Precipitation in a Future Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L05701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeswaran, R. Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation in the Agriculture Sector of Sri Lanka: What We Learnt and Way Forward. In Climate Change Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, C.; Wang, R.Y.; Chen, X.; Lian, Y. Drying Tendency Dominating the Global Grain Production Area. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 16, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhogyel, N.; Kumar, L. Climate Change and Potential Impacts on Agriculture in Bhutan: A Discussion of Pertinent Issues. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, S.K.; Sharma, D. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Yield of Major Crops in the Banas River Basin, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.K.; Surampalli, R.Y. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources in India. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birthal, P.S.; Khan, T.; Negi, D.S.; Agarwal, S. Impact of Climate Change on Yields of Major Food Crops in India: Implications for Food Security. Agric. Econ. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Mu, J. Water Management and Crop Production for Food Security in China: A Review. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Sensarma, S.R. Climate Change and Food Security in India: Adaptation Strategies and Major Challenges. In Sustainable Solutions for Food Security: Combating Climate Change by Adaptation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, R.K.; Singh, R.; Gupta, A.; Srinivasan, G.; Rathore, L.S. Impact of Climate Change on Indian Agriculture: A Review. Clim. Chang. 2006, 78, 445–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, S.K.; Singh, G.B.; Rai, M. Decline in Crop Productivity in Haryana and Punjab: Myth or Reality; Indian Council of Agricultural Research: New Delhi, India, 1998; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, A.; Chan, C.; Kumar, P.; Halbrendt, J.; Sipes, B. Potential of Conservation Agriculture (CA) for Climate Change Adaptation and Food Security under Rainfed Uplands of India: A Transdisciplinary Approach. Agric. Syst. 2017, 163, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Hunger Index. Global Hunger Index-Peer-Reviewed Annual Publication Designed to Comprehensively Measure and Track Hunger at the Global, Regional, and Country Levels. 2019. Available online: https://www.globalhungerindex.org/india.html (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Maclean, J.L.; Dawe, D.C.; Hettel, G.P. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; ISBN 0851996361. [Google Scholar]
- Seck, P.A.; Diagne, A.; Mohanty, S.; Wopereis, M.C.S. Crops That Feed the World 7: Rice. Food Secur. 2012, 4, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.A.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, E.J.; Horstmann, N.; Park, H.; Veasna, T.; Vanndy, L.; Pros, K.; et al. Assessing Rice Productivity and Adaptation Strategies for Southeast Asia under Climate Change through Multi-Scale Crop Modeling. Agric. Syst. 2016, 143, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Hayashi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M. Global Warming, Rice Production, and Water Use in China: Developing a Probabilistic Assessment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseng, S.; Ewert, F.; Rosenzweig, C.; Jones, J.W.; Hatfield, J.L.; Ruane, A.C.; Boote, K.J.; Thorbur, P.J.; Rötter, R.P.; Cammarano, D.; et al. Uncertainty in Simulating Wheat Yields under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manivasagam, V.S.; Nagarajan, R. Rainfall and Crop Modeling-Based Water Stress Assessment for Rainfed Maize Cultivation in Peninsular India. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdermid, S.; Gowtham, R.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Vellingiri, G.; Arunachalam, L. The Impacts of Climate Change on Tamil Nadu Rainfed Maize Production: A Multi-Model Approach to Identify Sensitivities and Uncertainties. Curr. Sci. 2016, 110, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Ruane, A.C.; Müller, C.; Arneth, A.; Boote, K.J.; Folberth, C.; Glotter, M.; Khabarov, N.; et al. Assessing Agricultural Risks of Climate Change in the 21st Century in a Global Gridded Crop Model Intercomparison. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3268–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manivasagam, V.S.; Rozenstein, O. Practices for Upscaling Crop Simulation Models from Field Scale to Large Regions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Wang, J.; Ullah, A.; Ishtiaque, A.; Javed, T.; Nurgazina, Z. The Impact of Climate Change on the Economic Perspectives of Crop Farming in Pakistan: Using the Ricardian Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.L.; Bo, Y.S.; Fahad, S. Economic Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture Using Ricardian Approach: A Case of Northwest Vietnam. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros Silva, W.K.; de Freitas, G.P.; Coelho Junior, L.M.; de Almeida Pinto, P.A.L.; Abrahão, R. Effects of Climate Change on Sugarcane Production in the State of Paraíba (Brazil): A Panel Data Approach (1990–2015). Clim. Chang. 2019, 154, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntukula, R.; Goyari, P. The Impact of Climate Change on Maize Yields and Its Variability in Telangana, India: A Panel Approach Study. J. Public Aff. 2020, 20, e2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanmehr, S.; Rastegari Henneberry, S.; Sabouhi Sabouni, M.; Shahnoushi Foroushani, N. Drought, Climate Change, and Dryland Wheat Yield Response: An Econometric Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samiappan, S.; Hariharasubramanian, A.; Venkataraman, P.; Jan, H.; Narasimhan, B. Impact of Regional Climate Model Projected Changes on Rice Yield over Southern India. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2838–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of India. Crop Production Statistics, Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India. 2022. Available online: https://aps.dac.gov.in/APY/Public_Report1.aspx (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Government of India. GOI Census 2011. Available online: https://censusindia.gov.in/census.website/ (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Raes, D.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop—The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: I. Concepts and Underlying Principles. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, T.C.; Heng, L.; Steduto, P.; Rojas-Lara, B.; Raes, D.; Fereres, E. Aquacrop-The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: III. Parameterization and Testing for Maize. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, D.; Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop—The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: II. Main Algorithms and Software Description. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanitha, K. Physiological Comparison of Surface and Sub Surface Drip System in Aerobic Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kanimoli, S. Assessment of Diazotrophic Diversity and Development of Suitable Microbial Consortia for Enhanced Nitrogen Fixation in Lowland, SRI and Aerobic Rice. Ph.D. Thesis, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, E.; Martin, G.J.; Suburayalu, E.; Mohan, R. Aerobic Rice: Water Saving Rice Production Technology. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 49, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kandamoorthy, S.; Govindarasu, R. Genetic Analysis in Very Early Rice under Two Culture Systems in the Coastal Region of Cauvery Delta Zone. Indian Soc. Coast. Agric. Res. 2011, 1, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneshwari, R. Developing Molecular Methods for Testing Seed Genetic Purity of Major Paddy Varieties in Tamil Nadu. Ph.D. Thesis, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Manivasagam, V.S.; Nagarajan, R. Assessing the Supplementary Irrigation for Improving Crop Productivity in Water Stress Region Using Spatial Hydrological Model. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaddar, A.; Mohibbe Azam, M.; Singaravadivel, K.; Venkatachalapathy, N.; Swain, B.B.; Mishra, P. Post-harvest Management and Value Addition of Rice and Its By-Products. In The Future Rice Strategy for India; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpa, R.; Sassikumar, D.; Iyyanar, K.; Suresh, R.; Manimaran, R. Study of Physicochemical, Cooking and Nutritional Properties of Promising Rice Varieties of Tamil Nadu. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2019, 10, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A.; Muellbauer, J. An Almost Ideal Demand System. Am. Econ. Rev. 1980, 70, 312–326. [Google Scholar]
- Geethalakshmi, V.; Lakshmanan, A.; Rajalakshmi, D.; Jagannathan, R.; Sridhar, G.; Ramaraj, A.P.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Gurusamy, L.; Anbhazhagan, R. Climate Change Impact Assessment and Adaptation Strategies to Sustain Rice Production in Cauvery Basin of Tamil Nadu. Curr. Sci. 2011, 101, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, S.; Jeyaprakash, P.; Amudha, K.; Pushpam, R.; Rajeswari, S.; Manonmani, S.; Ravichandran, V.; Soundararajan, R.P.; Ramanathan, A.; Ganesamurthy, K. Rice CR1009 Sub 1(IET 22187)—A New Flood Tolerant Rice Variety. Electron. J. Plant Breed. 2019, 10, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, M.K.; Manivasagam, V.S.; Nikoo, M.R.; Saravanane, P.; Narayanan, A.; Manalil, S. Rainfall Variability and Rice Sustainability: An Evaluation Study of Two Distinct Rice-Growing Ecosystems. Land 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
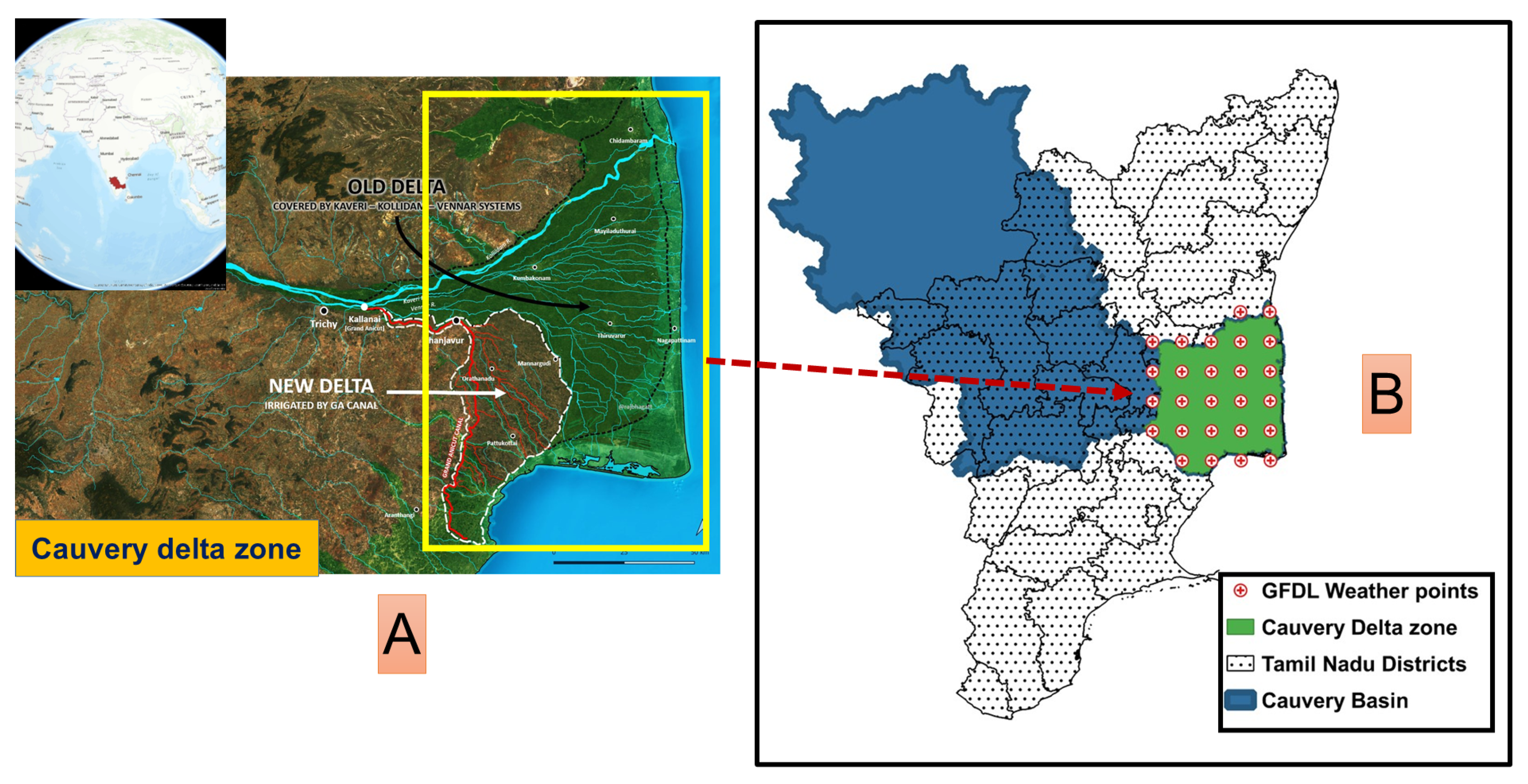
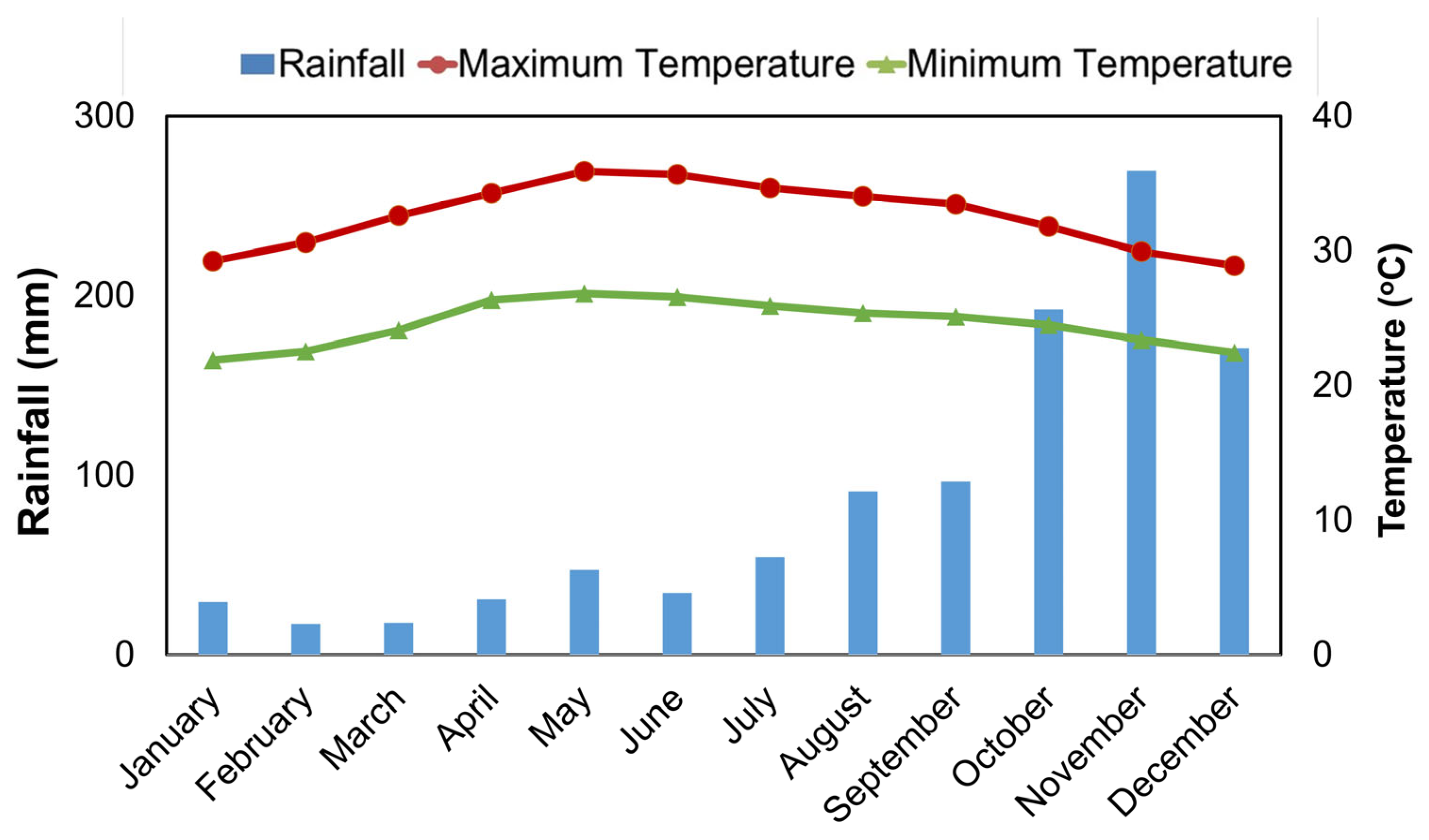
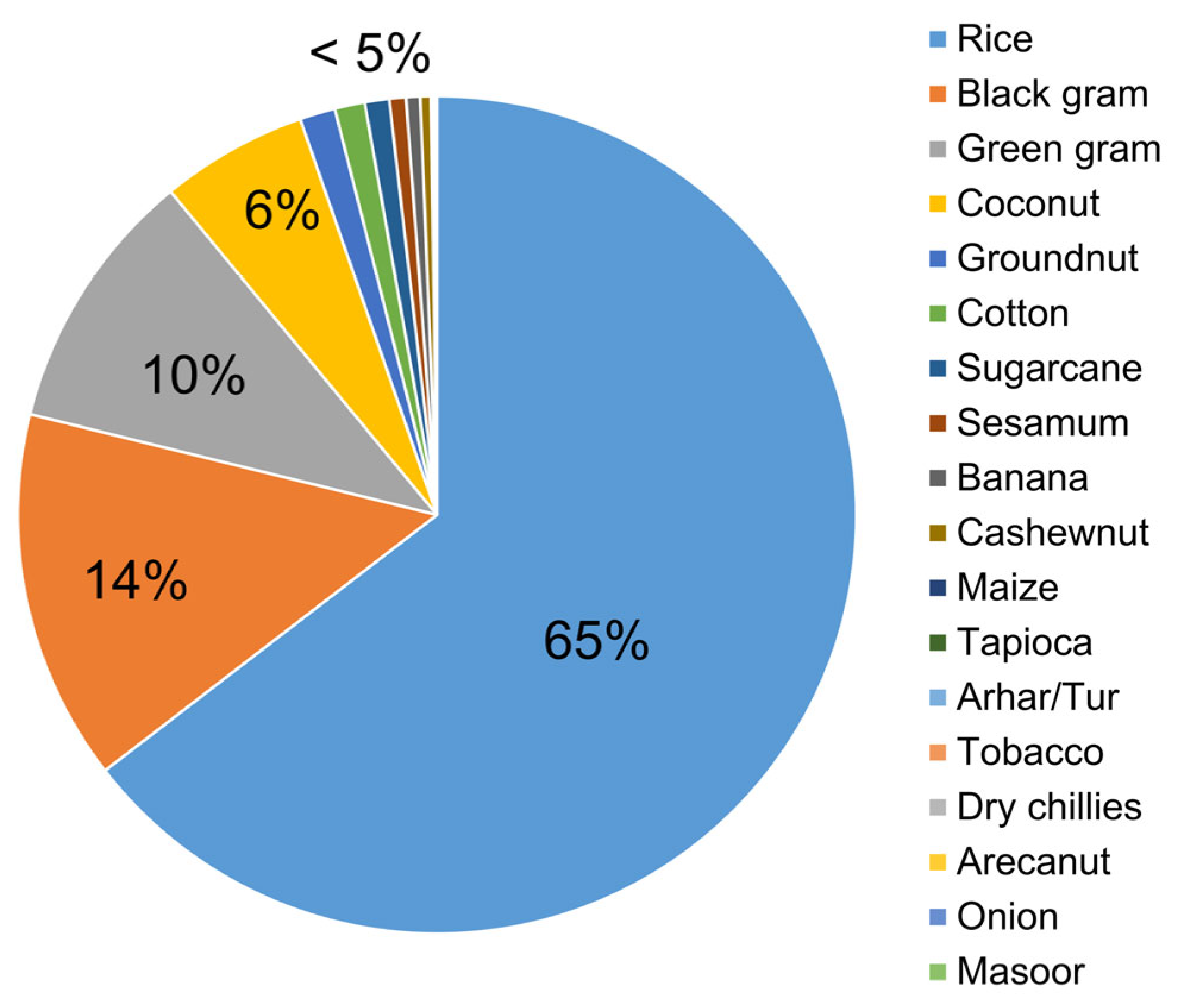
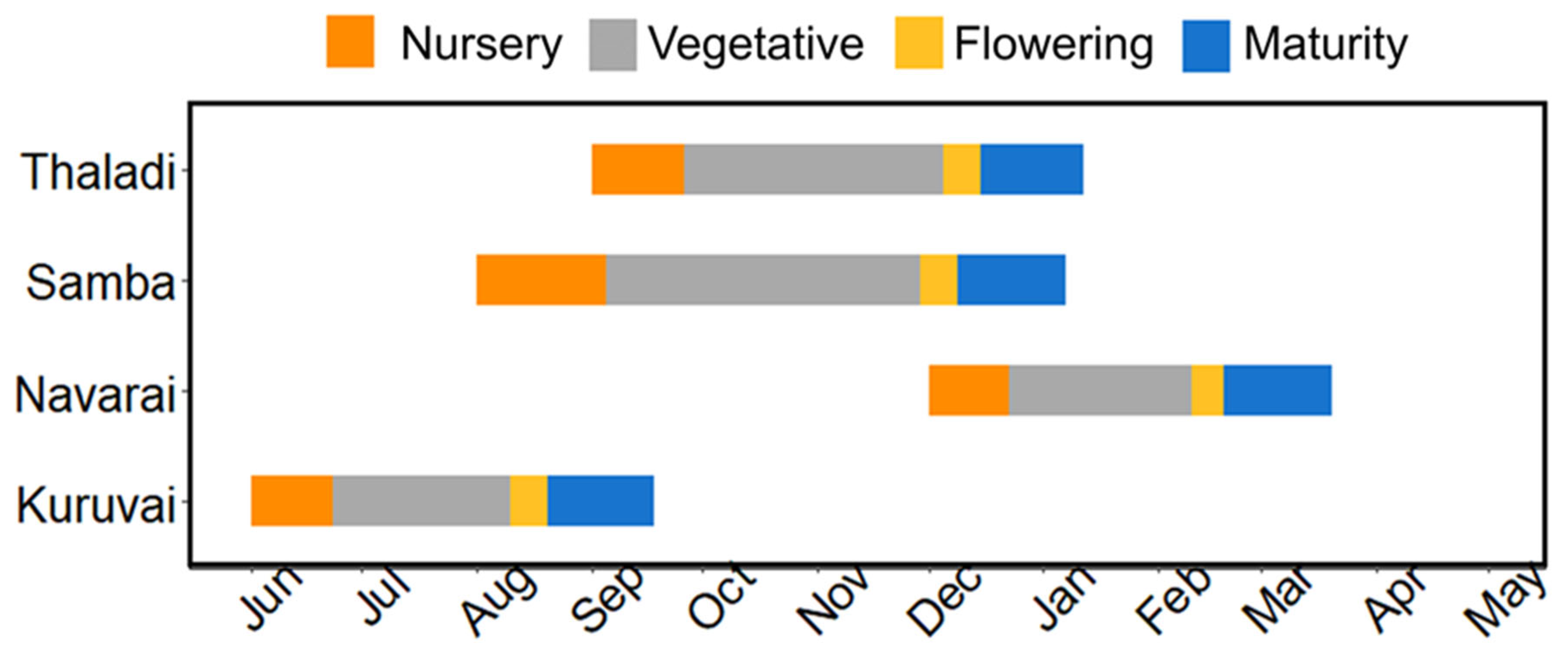

| Period | Rice Cultivated Area (Million ha) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Kuruvai | Samba | Thaladi | |
| 1989–1998 | 0.074 | 0.370 | 0.353 |
| 1999–2008 | 0.076 | 0.327 | 0.064 |
| 2009–2018 | 0.086 | 0.333 | 0.079 |
| Particulars | Unit | CR1009D | CR1009T | ADT38 | ADT43 | ASD16 | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial canopy cover | % | 2.5 | 4.95 | 7.5 | 9.9 | 9.9 | [56] |
| Plant density | plants per ha | 500,000 | 330,000 | 500,000 | 660,000 | 660,000 | [56,57,58] |
| Maximum canopy cover (CCx) | % | 80 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 80 | [56] |
| Reference harvest index (HIo) | % | 41 | 41 | 42 | 40 | 35 | [56,59] |
| From transplanting to recovered transplant | Days | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | [60] |
| From transplanting to maximum canopy cover | Days | 65 | 62 | 39 | 30 | 32 | [60] |
| From transplanting to starting senescence | Days | 120 | 100 | 90 | 70 | 75 | [60] |
| From transplanting to maturity | Days | 150 | 125 | 110 | 88 | 93 | [60] |
| Maximum effective rooting depth | Meter | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | [58] |
| Cultivar | Season | Basin |
|---|---|---|
| ADT43 | Kuruvai | Old delta |
| ASD16 | Kuruvai/Navarai | Old/New delta |
| CR1009 | Samba | Old/New delta |
| ADT38 | Thaladi | Old/New delta |
| Season | Date of Sowing | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Sowing Window | 2nd Sowing Window | 3rd Sowing Window | |
| Kuruvai | 27 June 2021 | 7 July 2021 | 17 July 2021 |
| Samba (Transplanted) | 9 September 2021 | 19 September 2021 | 29 September 2021 |
| Samba (Direct sown) | 5 August 2021 | 15 August 2021 | 25 August 2021 |
| Thaladi | 30 September 2021 | 10 October 2021 | 20 October 2021 |
| Navarai | 26 December 2021 | 6 January 2022 | 16 January 2022 |
| Scenario | Season | Type of Sowing | Sowing Date | Cultivar | Soil | Basin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 27 June 2021 | ADT43 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S2 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 7 July 2021 | ADT43 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S3 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 17 July 2021 | ADT43 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S4 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 27 June 2021 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S5 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 7 July 2021 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S6 | Kuruvai | Transplanted | 17 July 2021 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S7 | Samba | Transplanted | 9 September 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S8 | Samba | Transplanted | 19 September 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S9 | Samba | Transplanted | 29 September 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S10 | Samba | Transplanted | 9 September 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S11 | Samba | Transplanted | 19 September 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S12 | Samba | Transplanted | 29 September 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S13 | Samba | Direct sown | 5 August 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S14 | Samba | Direct sown | 15 August 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S15 | Samba | Direct sown | 25 August 2021 | CR1009 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S16 | Samba | Direct sown | 5 August 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S17 | Samba | Direct sown | 15 August 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S18 | Samba | Direct sown | 25 August 2021 | CR1009 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S19 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 30 September 2021 | ADT38 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S20 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 10 October 2021 | ADT38 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S21 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 20 October 2021 | ADT38 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S22 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 30 September 2021 | ADT38 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S23 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 10 October 2021 | ADT38 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S24 | Thaladi | Transplanted | 20 October 2021 | ADT38 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S25 | Navarai | Transplanted | 26 December 2021 | ASD16 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S26 | Navarai | Transplanted | 6 January 2022 | ASD16 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S27 | Navarai | Transplanted | 16 January 2022 | ASD16 | Paddy soil | Old delta |
| S28 | Navarai | Transplanted | 26 December 2021 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S29 | Navarai | Transplanted | 6 January 2022 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| S30 | Navarai | Transplanted | 16 January 2022 | ASD16 | Sandy loam | New delta |
| Particulars | New Delta | Old Delta |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | ||
| Annual rainfall (mm) | 1022 | 1067 |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 33 | 33 |
| Projected | ||
| Decade I (2021–2030) | ||
| Annual rainfall (mm) | 817 | 881 |
| Change in rainfall (%) | 20 | 17 |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 35 | 35 |
| Change in temperature (°C) | 2 | 2 |
| Decade II (2031–2040) | ||
| Annual rainfall (mm) | 944 | 1005 |
| Change in rainfall (%) | 8 | 6 |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 35 | 35 |
| Change in temperature (°C) | 2 | 2 |
| Decade III (2041–2050) | ||
| Annual rainfall (mm) | 751 | 773 |
| Change in rainfall (%) | 26 | 27 |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 36 | 37 |
| Change in temperature (°C) | 3 | 4 |
| Particulars | Decade I (2021–2030) | Decade II (2031–2040) | Decade III (2041–2050) |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Delta | |||
| Yield (tonnes/ha) | 5.85 | 6.14 | 6.30 |
| Area (million ha) | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 |
| Production (million tonnes) | 0.520 | 0.545 | 0.560 |
| Old Delta | |||
| Yield (tonnes/ha) | 2.35 | 2.31 | 3.29 |
| Area (million ha) | 0.419 | 0.419 | 0.419 |
| Production (million tonnes) | 0.983 | 0.966 | 1.38 |
| Cauvery Delta Zone | |||
| Area (million ha) | 0.508 | 0.508 | 0.508 |
| Production (million tonnes) | 1.50 | 1.51 | 1.94 |
| Particulars | Value |
|---|---|
| MPC (in Kg) | 9.72 |
| MPCE (in INR) | 137.05 |
| Expenditure elasticity | 0.82 |
| Expenditure share (%) | 22.08 |
| Marginal expenditure share (%) | 18.08 |
| Period | Population (Million) | Elasticity | Demand (Million Tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decade I (2021–2030) | 9.69 | 0.82 | 0.609 |
| Decade II (2031–2040) | 10.33 | 0.82 | 0.774 |
| Decade III (2041–2050) | 10.78 | 0.82 | 0.933 |
| Period | Future Rice Production (Million Tonnes) | Future White Rice Availability for Consumption * (Million Tonnes) | Future Rice Demand (Million Tonnes) | Rice Supply and Demand Difference (Million Tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decade I (2021–2030) | 1.50 | 1.01 | 0.609 | 0.392 |
| Decade II (2031–2040) | 1.51 | 1.06 | 0.774 | 0.232 |
| Decade III (2041–2050) | 1.94 | 1.30 | 0.933 | 0.358 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arivelarasan, T.; Manivasagam, V.S.; Geethalakshmi, V.; Bhuvaneswari, K.; Natarajan, K.; Balasubramanian, M.; Gowtham, R.; Muthurajan, R. How Far Will Climate Change Affect Future Food Security? An Inquiry into the Irrigated Rice System of Peninsular India. Agriculture 2023, 13, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030551
Arivelarasan T, Manivasagam VS, Geethalakshmi V, Bhuvaneswari K, Natarajan K, Balasubramanian M, Gowtham R, Muthurajan R. How Far Will Climate Change Affect Future Food Security? An Inquiry into the Irrigated Rice System of Peninsular India. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030551
Chicago/Turabian StyleArivelarasan, Tamilarasu, V. S. Manivasagam, Vellingiri Geethalakshmi, Kulanthaivel Bhuvaneswari, Kiruthika Natarajan, Mohan Balasubramanian, Ramasamy Gowtham, and Raveendran Muthurajan. 2023. "How Far Will Climate Change Affect Future Food Security? An Inquiry into the Irrigated Rice System of Peninsular India" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030551
APA StyleArivelarasan, T., Manivasagam, V. S., Geethalakshmi, V., Bhuvaneswari, K., Natarajan, K., Balasubramanian, M., Gowtham, R., & Muthurajan, R. (2023). How Far Will Climate Change Affect Future Food Security? An Inquiry into the Irrigated Rice System of Peninsular India. Agriculture, 13(3), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030551







