QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality Based on Introgression Lines Population from G. hirsutum × G. tomentosum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Field Experiments
2.2. Collection of Fiber Quality Traits
2.3. Statistics of Phenotypic Data
2.4. Identification of SNP Markers
2.5. QTL Mapping
2.6. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Validation
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Statistical Analysis
3.2. Phenotypic Correlation Analysis
3.3. Phenotypic Variance Analysis
3.4. Genetic Map Construction
3.5. QTL Mapping of Fiber Quality Traits
3.6. Identification and Gene Expression Analysis of Candidate Genes Relating to Fiber Strength
4. Discussion
4.1. Population Dominance of Wild Species
4.2. Sources and Effects of Favorable Alleles
4.3. Distribution of QTL Clusters
4.4. Analysis of Co-Location QTL and Stable QTL
4.5. Candidate Gene Expression Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Tu, L.; Yuan, D.; Zhu, D.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Pei, L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; et al. Reference genome sequences of two cultivated allotetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, D.D.; Jenkins, J.N.; Deng, D.D.; McCarty, J.C.; Li, P.; Wu, J. Quantitative trait loci analysis of fiber quality traits using a random-mated recombinant inbred population in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gore, M.A.; Fang, D.D.; Poland, J.A.; Zhang, J.; Percy, R.G.; Cantrell, R.G.; Thyssen, G.; Lipka, A.E. Linkage Map Construction and Quantitative Trait Locus Analysis of Agronomic and Fiber Quality Traits in Cotton. Plant Genome 2015, 7, plantgenome2013.07.0023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Said, J.I.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, J. A comprehensive meta QTL analysis for fiber quality, yield, yield related and morphological traits, drought tolerance, and disease resistance in tetraploid cotton. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.H.; Wu, D.X.; Lu, X.J.; Tian, C.J.; Pan, Z.J.; Yang, H.; Wu, C. Research progress on QTL positioning of cotton fiber quality. Cotton Sci. 2017, 39, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Botstein, D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 1989, 121, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Song, G.; Yue, Z.; Cong, L.; Shang, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fan, G.; Wang, K.; Sun, F.; Yuan, Y.; Song, G.; Li, Q.; Ma, Z.; Lu, C.; Zou, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the cultivated cotton Gossypium arboreum. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, H.J.; Hu, Y.; Lu, G.; Yang, C.Q.; Chen, J.D.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, D.Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Gossypium barbadense genome sequence provides insight into the evolution of extra-long staple fiber and specialized metabolites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Nie, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Bai, J. Molecular diversity, genomic constitution, and QTL mapping of fiber quality by mapped SSRs in introgression lines derived from Gossypium hirsutum × G. darwinii Watt. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ding-Guo, L.I.; Nie, Y.C.; Lin, Z.X. QTL Mapping for Yield and Fiber Quality Traits Using Gossypium mustelinum Chromosome Segment Introgression Lines. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Cai, C.; Zhang, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, B. Construction of microsatellite-based linkage map and mapping of nectarilessness and hairiness genes in Gossypium tomentosum. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Rong, J.; Waghmare, V.N.; Chee, P.W.; May, O.L.; Wright, R.J.; Gannaway, J.R.; Paterson, A.H. QTL alleles for improved fiber quality from a wild Hawaiian cotton, Gossypium tomentosum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerio, A.A.; Shen, C.; Nie, Y.; Ahmed, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z. QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality and Yield Traits Based on Introgression Lines Derived from Gossypium hirsutum × G. tomentosum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.S. QTL Mapping for Yield and Fiber Quality Traits from the Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines of Gossypium tomentosum. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhen, H.; Hickford, J.G.H. Variation in a Newly Identified Caprine KRTAP Gene Is Associated with Raw Cashmere Fiber Weight in Longdong Cashmere Goats. Genes 2021, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.M.; Morris, R.M.; Vilgalys, R.; Labbé, J.; Schadt, C.W. Phylogenetic diversity of 200+ isolates of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Cenococcum geophilum associated with Populus trichocarpa soils in the Pacific Northwest, USA and comparison to globally distributed representatives. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0231367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, K.; Pang, C.; Wu, X.; Shi, R.; Sun, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. QTL Analysis of Five Silique-Related Traits in Brassica napus L. across Multiple Environments. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 766271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Jin, X.; Zhu, D.; Lin, Z. Uncovering SNP and indel variations of tetraploid cottons by SLAF-seq. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Hong, W.; Jiang, C.; Guan, N.; Ma, C.; Zeng, H.; et al. SLAF-seq: An efficient method of large-scale de novo SNP discovery and genotyping using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.; Xiao, X.; Gong, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; Peng, R.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y. Identification of Candidate Cotton Genes Associated with Fiber Length Through Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping and RNA-Sequencing Using a Chromosome Segment Substitution Line. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 796722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wan, X.; Li, H.; Pfeiffer, W.H.; Crouch, J.; Wan, J. Application of identified QTL-marker associations in rice quality improvement through a design-breeding approach. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellette, L.A.; Reid, R.W.; Blanchard, S.G.; Brouwer, C.R. LinkageMapView-rendering high-resolution linkage and QTL maps. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mccouch, S.; Cho, Y.; Yano, M.; Paul, E.; Blinstrub, M.; Morishima, H.; Mccouch, S.; Cho, Y.; Paul, E.; Morishima, H. Report on QTL nomenclature. In Rice Genetics Newsletter; Science Open: Berlin, Germany, 1997; Volume 14, pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, H.; Qiao, X.; Wei, L.; Rong, J.; May, O.L.; Paterson, A.H.; et al. A Genetic Map Between Gossypium hirsutum and the Brazilian Endemic G. mustelinum and Its Application to QTL Mapping. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.H.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Nie, H.S.; Zhao, N.; Hua, J.P. QTL controlling fiber quality traits under salt stress in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 661–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B. Genomic and epigenomic bases of transgressive segregation—New breeding paradigm for novel plant phenotypes. Plant Sci. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2019, 288, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooijen, J. JoinMap 4.0: Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage Maps in Experimental Population; Kyazma BV: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.M.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.N.; Gong, J.M. Cdi gene is required for pollen germination and tube growth in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Feng, T.; He, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, L. System Analysis of MIRNAs in Maize Internode Elongation. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, D.; Werck-Reichhart, D. A P450-centric view of plant evolution. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 66, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, M.; Undan, J.R.; Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Undan, J.Q.; Natsume, S.; Uemura, A.; Saitoh, H.; Matsumura, H.; et al. A cytochrome P450, OsDSS1, is involved in growth and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 88, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lee, M.M.; Schiefelbein, J.W. Regulation of the cell expansion gene RHD3 during Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Morrisoniii, W.H.; Ye, Z.H. The Arabidopsis RHD3 gene is required for cell wall biosynthesis and actin organization. Planta 2003, 217, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, J. The Origin of American Tetraploid Gossypium Species. Am. Nat. 1940, 74, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, V.G.; Meredith, W.R. New germplasm from crossing Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) with G. tomentosum. J. Hered. 1978, 69, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Awan, F.S.; Sadia, B.; Rana, R.M.; Khan, I.A. Genetic diversity studies among coloured cotton genotypes by using RAPD markers. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, D. Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.J. Characterization of Donor Chromosome Fragments from Gossypium barbadense L. in CCRI45 Background of Gossypium hirsutum L. and Identification of QTL Related to Fiber Yield and Quality Traits. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Guo, W.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T. Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci for fiber quality and yield trait by RIL approach in Upland cotton. Euphytica 2007, 155, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Dan, Y.Z.; LIANG, Y.; Gu, Y.J.; Zhang, B.C.; Li, J.W.; Gong, J.W.; Liu, A.Y.; Shang, H.G.; Wang, T. Evaluation of Yield and Fiber Quality Traits of Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines Population (BC5F3 and BC5F34) in Cotton. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2012, 13, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z. Structure, evolution, and comparative genomics of tetraploid cotton based on a high-density genetic linkage map. DNA Res. Int. J. Rapid Publ. Rep. Genes Genomes 2016, 23, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Mapping QTL for cotton fiber quality traits using simple sequence repeat markers, conserved intron-scanning primers, and transcript-derived fragments. Euphytica 2015, 201, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gong, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, A.; Lu, Q.; Shang, H.; Shi, Y.; Ge, Q.; et al. GWAS Analysis and QTL Identification of Fiber Quality Traits and Yield Components in Upland Cotton Using Enriched High-Density SNP Markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Teng, Z.; Zhai, T.; Fang, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K. Construction of genetic map and QTL analysis of fiber quality traits for Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 2015, 201, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Nie, X.; Shen, C.; You, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z. Population structure and genetic basis of the agronomic traits of upland cotton in China revealed by a genome-wide association study using high-density SNPs. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, L.; Magwanga, R.O.; Gong, W.; He, S.; Pan, Z.; Jia, Y.H.; Kirungu, J.N.; Du, X. QTL Mapping of Fiber Quality and Yield-Related Traits in an Intra-Specific Upland Cotton Using Genotype by Sequencing (GBS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 20441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Abduweli, A.; Cai, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, K.; Hua, J. Genetic Analysis and QTL Detection on Fiber Traits Using Two Recombinant Inbred Lines and Their Backcross Populations in Upland Cotton. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
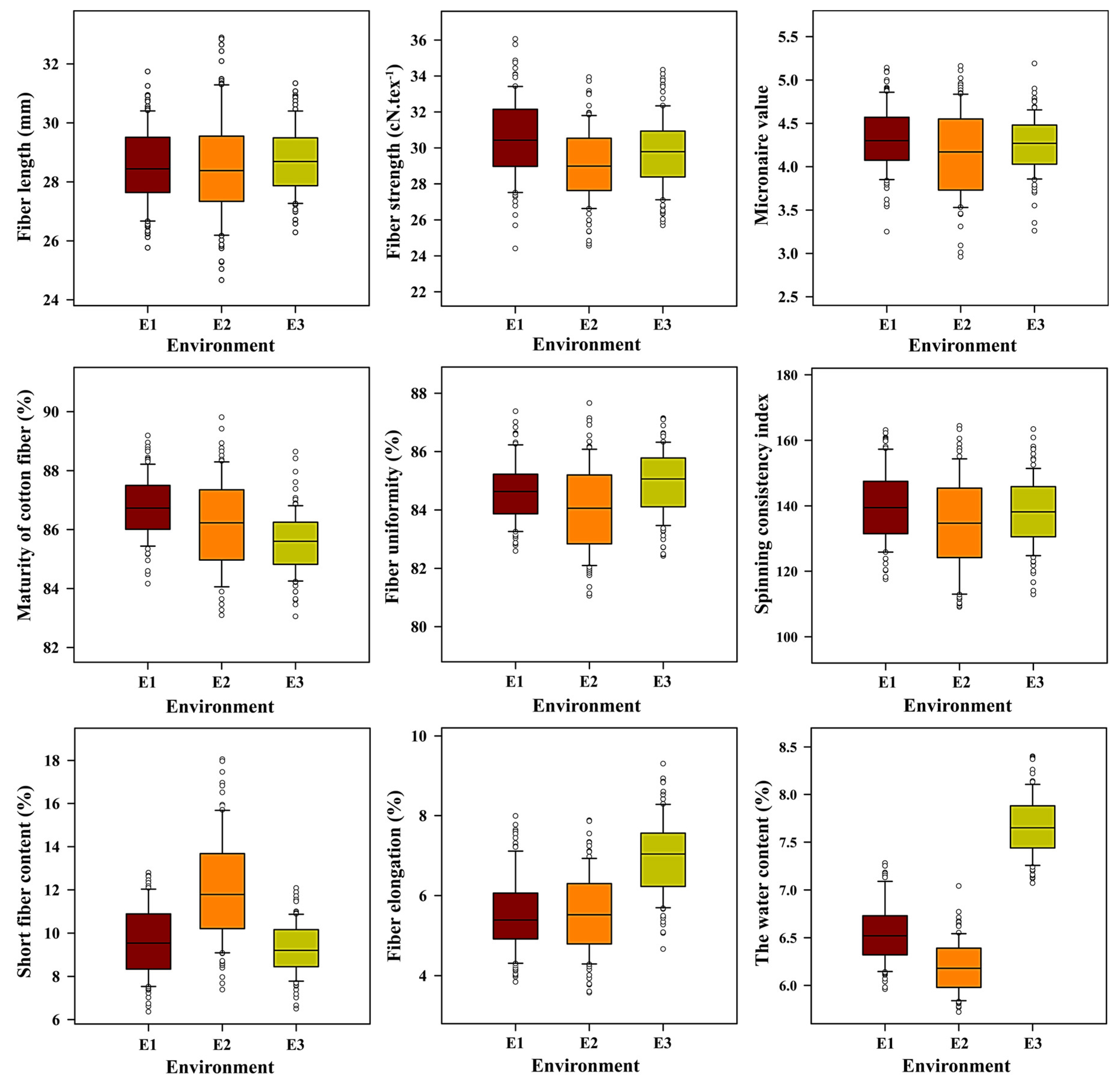
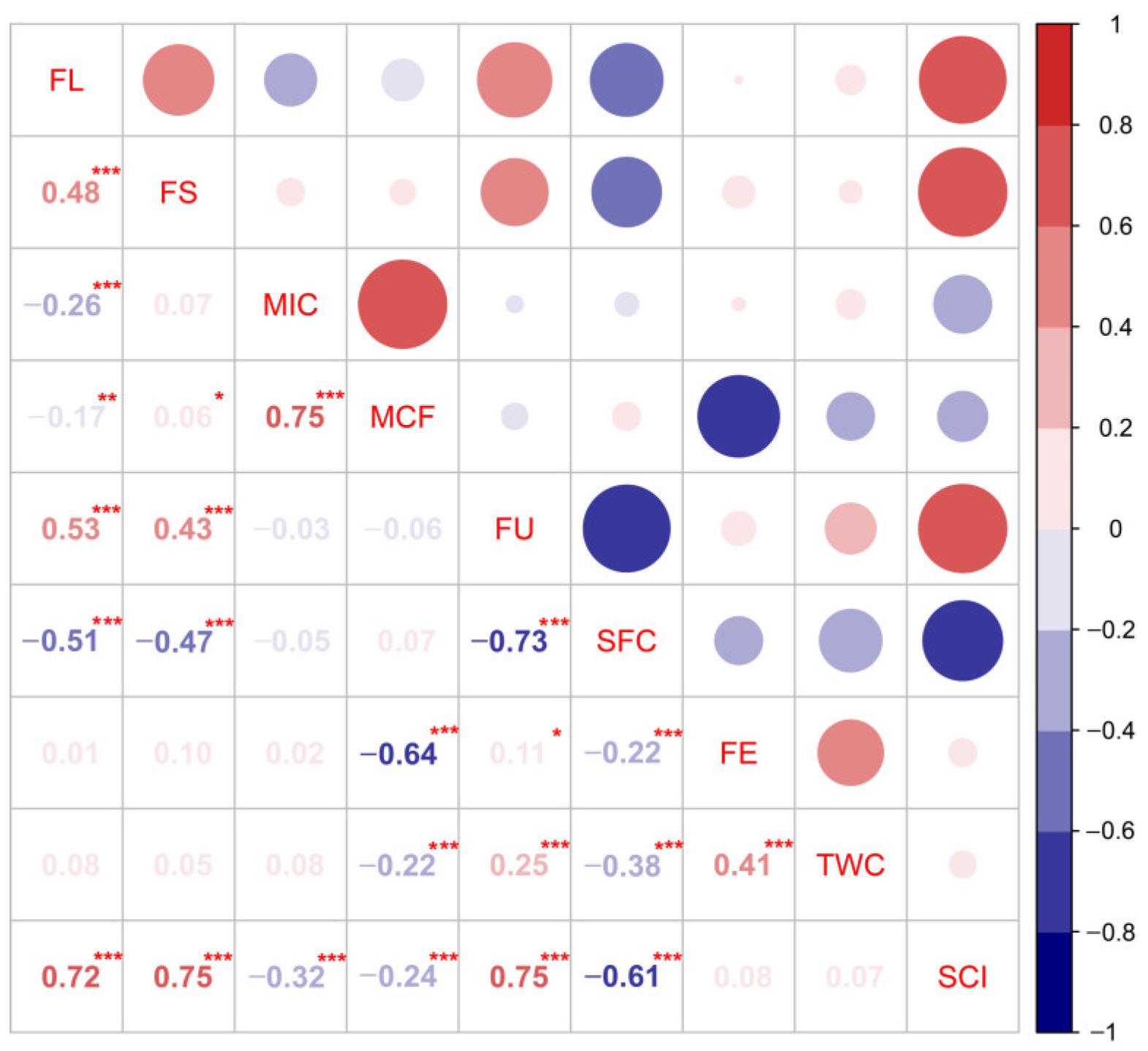



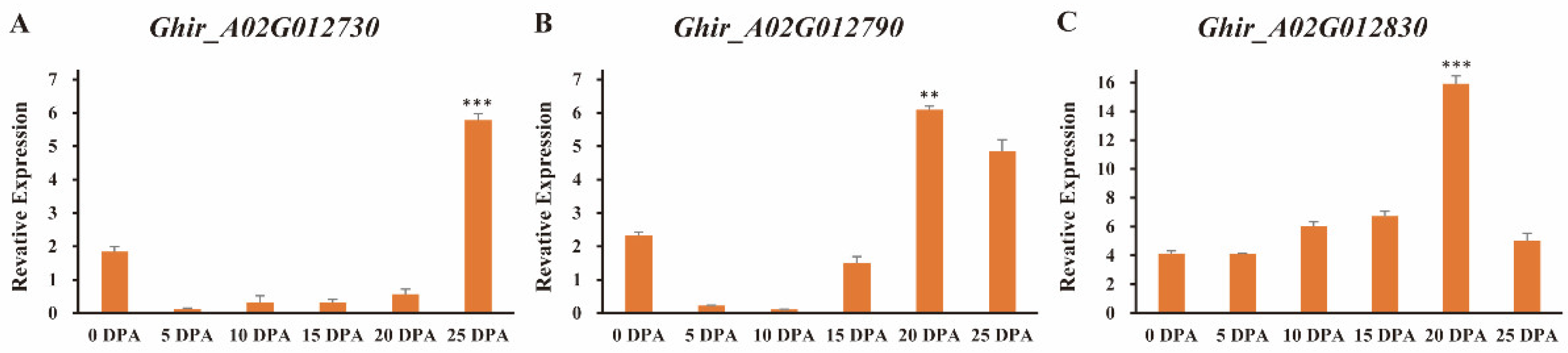
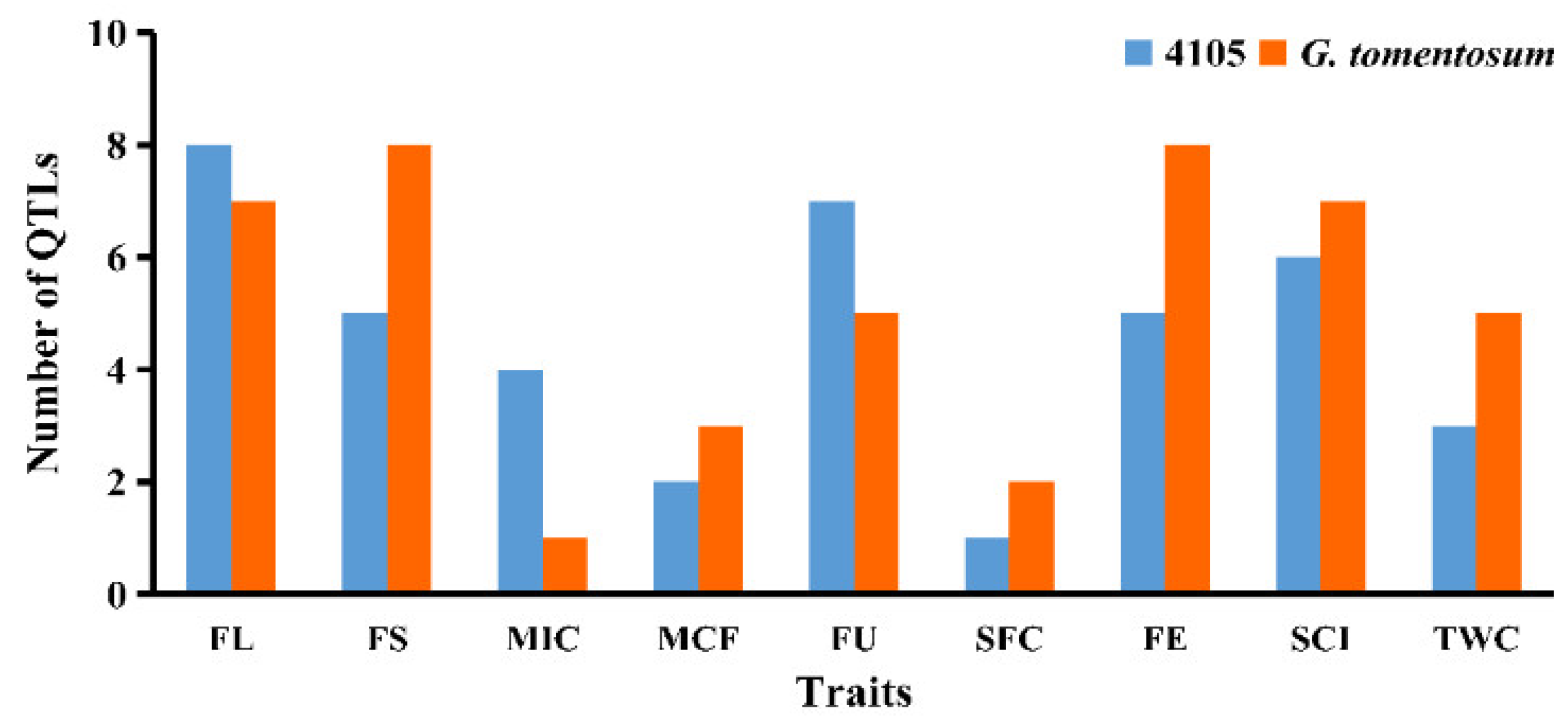
| Trait | Environment | 4105 Average | ILs Average | Max. | Min. | SD | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | H2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL (mm) | E1 | 29.21 | 28.49 | 31.74 | 25.76 | 1.33 | 4.66 | 0.13 | −0.62 | 61.48 |
| E2 | 29.03 | 28.56 | 32.89 | 24.66 | 1.80 | 6.29 | 0.31 | −0.12 | ||
| E3 | 27.69 | 28.73 | 31.34 | 26.20 | 1.10 | 3.83 | 0.23 | −0.39 | ||
| FS (cN.tex−1) | E1 | 30.20 | 30.56 | 36.06 | 24.4 | 2.21 | 7.24 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 61.4 |
| E2 | 28.25 | 29.08 | 33.94 | 24.55 | 2.04 | 7.02 | 0.06 | −0.31 | ||
| E3 | 29.73 | 29.77 | 34.34 | 25.69 | 1.96 | 6.60 | 0.14 | −0.33 | ||
| MIC | E1 | 4.50 | 4.32 | 5.14 | 3.25 | 0.37 | 8.69 | 0.00 | −0.18 | 55.56 |
| E2 | 3.34 | 4.15 | 5.16 | 2.96 | 0.49 | 11.82 | −0.14 | −0.56 | ||
| E3 | 4.75 | 4.25 | 5.19 | 3.26 | 0.33 | 7.68 | −0.18 | 0.58 | ||
| MCF (%) | E1 | 86.93 | 86.77 | 89.19 | 84.16 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.00 | −0.22 | 54.3 |
| E2 | 84.27 | 86.27 | 89.81 | 83.27 | 0.01 | 1.68 | 0.08 | −0.59 | ||
| E3 | 86.96 | 85.59 | 88.64 | 83.05 | 0.01 | 1.19 | 0.19 | 0.53 | ||
| FU (%) | E1 | 85.61 | 84.67 | 87.38 | 82.59 | 1.03 | 1.22 | 0.36 | −0.21 | 22.62 |
| E2 | 87.72 | 84.03 | 87.66 | 81.07 | 1.46 | 1.73 | 0.21 | −0.58 | ||
| E3 | 85.67 | 84.93 | 87.14 | 82.42 | 1.13 | 1.33 | −0.13 | −0.44 | ||
| SFC (%) | E1 | 8.51 | 9.56 | 12.79 | 6.36 | 1.56 | 16.37 | 0.13 | −0.86 | 17.95 |
| E2 | 8.24 | 11.88 | 17.53 | 7.38 | 2.26 | 19.06 | 0.44 | −0.23 | ||
| E3 | 7.12 | 9.31 | 12.08 | 6.50 | 1.16 | 12.43 | 0.02 | −0.28 | ||
| FE (%) | E1 | 5.95 | 5.57 | 7.99 | 3.84 | 0.97 | 17.35 | 0.51 | −0.26 | 74.29 |
| E2 | 5.62 | 5.55 | 7.88 | 3.57 | 0.99 | 17.79 | 0.17 | −0.49 | ||
| E3 | 7.17 | 6.90 | 9.18 | 4.66 | 0.91 | 13.23 | 0.02 | −0.3 | ||
| SCI | E1 | 142.82 | 140.33 | 163.11 | 117.5 | 11.05 | 7.87 | 0.17 | −0.58 | 57.08 |
| E2 | 156.28 | 134.81 | 164.35 | 109.08 | 13.68 | 10.15 | 0.00 | −0.68 | ||
| E3 | 135.05 | 138.19 | 163.43 | 112.91 | 10.71 | 7.75 | −0.08 | −0.38 | ||
| TWC (%) | E1 | 6.22 | 6.54 | 7.28 | 5.96 | 0.31 | 4.74 | 0.48 | −0.15 | 40 |
| E2 | 6.11 | 6.20 | 7.04 | 5.72 | 0.26 | 4.25 | 0.41 | −0.08 | ||
| E3 | 6.71 | 7.67 | 8.40 | 7.07 | 0.32 | 4.13 | 0.22 | −0.52 |
| Source | Genotype (df = 106) | Environment (df = 2) | Genotype × Environment (df = 206) | Error (df = 103) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL | 5.258 *** | 4.367 * | 2.040 ** | 0.823 |
| FS | 3.438 *** | 15.849 *** | 1.388 * | 2.772 |
| MIC | 4.261 *** | 10.946 *** | 1.763 *** | 0.08 |
| MCF | 3.456 *** | 60.282 *** | 1.380 * | 0.873 |
| FU | 1.959 *** | 24.028 *** | 1.498 * | 1.227 |
| SFC | 0.268 | 3.477 * | 0.277 | 56.097 |
| FE | 3.107 *** | 131.828 *** | 0.803 ** | 0.771 |
| SCI | 2.367 *** | 3.802 * | 1.038 * | 142.465 |
| TWC | 1.05 | 551.562 *** | 0.639 * | 0.168 |
| Chromosome | Size of Physical Distance (Mb) | Length of Introgressed Segments in Genome (Mb) | Number of SNP Markers | Average Marker Distance (Mb) | Max Interval (Mb) | Percentage of Genome Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 99.88 | 38 | 317 | 0.31 | 16.91 | 38.04 |
| A02 | 83.45 | 34 | 99 | 0.84 | 28.19 | 40.74 |
| A03 | 100.26 | 22 | 65 | 1.49 | 17.33 | 21.94 |
| A04 | 62.91 | 13 | 30 | 2.12 | 23.27 | 20.66 |
| A05 | 82.05 | 29 | 81 | 1.11 | 26.61 | 35.35 |
| A06 | 103.17 | 24 | 82 | 1.25 | 46.03 | 23.26 |
| A07 | 78.25 | 24 | 95 | 0.78 | 29.57 | 30.67 |
| A08 | 103.63 | 39 | 108 | 0.94 | 14.27 | 37.64 |
| A09 | 75.00 | 30 | 158 | 0.45 | 10.99 | 40.00 |
| A10 | 100.87 | 29 | 83 | 1.21 | 21.00 | 28.75 |
| A11 | 93.32 | 19 | 55 | 1.71 | 36.06 | 20.36 |
| A12 | 87.48 | 40 | 108 | 0.81 | 8.56 | 45.72 |
| A13 | 79.96 | 62 | 535 | 0.14 | 4.76 | 77.54 |
| At-total | 1150.23 | 403 | 1816 | |||
| Average | 88.48 | 31.00 | 139.69 | 1.01 | 23.23 | 35.44 |
| D01 | 61.46 | 15 | 39 | 1.55 | 22.78 | 24.41 |
| D02 | 67.28 | 34 | 245 | 0.27 | 8.99 | 50.53 |
| D03 | 46.69 | 9 | 24 | 1.86 | 22.18 | 19.28 |
| D04 | 51.45 | 22 | 79 | 0.64 | 17.27 | 42.76 |
| D05 | 61.93 | 21 | 65 | 0.84 | 9.97 | 33.91 |
| D06 | 64.29 | 38 | 384 | 0.16 | 5.40 | 59.10 |
| D07 | 55.31 | 32 | 178 | 0.29 | 4.99 | 57.85 |
| D08 | 65.89 | 14 | 58 | 1.14 | 35.71 | 21.25 |
| D09 | 51.00 | 12 | 41 | 1.23 | 31.77 | 23.53 |
| D10 | 63.37 | 19 | 101 | 0.61 | 14.97 | 29.98 |
| D11 | 66.09 | 13 | 42 | 1.60 | 34.50 | 19.67 |
| D12 | 59.11 | 12 | 30 | 1.82 | 26.46 | 20.30 |
| D13 | 60.53 | 21 | 55 | 1.07 | 11.46 | 34.69 |
| Dt-total | 774.40 | 262 | 1341 | |||
| Average | 59.57 | 20.15 | 103.15 | 1.01 | 18.96 | 33.64 |
| Total | 1924.63 | 665 | 3157 |
| Trait | Environment | Chromosome | Position (Mb) | QTL | LOD | PVE (%) | Add | Source of Favorable Alleles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL | E1 | A01 | 33.83 | qFL-A01-1 | 6.32 | 10.24 | −0.57 | 4015 |
| E3 | A03 | 5.28 | qFL-A03-1 | 4.02 | 6.04 | −0.73 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A05 | 4.58 | qFL-A05-1 | 3.38 | 5.11 | −0.34 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A05 | 60.15 | qFL-A05-2 | 5.05 | 7.76 | 0.63 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A06 | 32.34 | qFL-A06-1 | 3.41 | 5.06 | 0.57 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A08 | 83.82 | qFL-A08-1 | 7.19 | 11.89 | −0.82 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A08 | 7.97 | qFL-A08-2 | 3.22 | 4.74 | −0.41 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A10 | 20.72 | qFL-A10-1 | 8.56 | 14.23 | 0.52 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | D02 | 3.37 | qFL-D02-1 | 9.45 | 16.46 | −0.61 | 4105 | |
| E2 | D02 | 1.50 | qFL-D02-2 | 4.48 | 14.91 | −0.72 | 4105 | |
| E3 | D02 | 21.93 | qFL-D02-3 | 8.95 | 15.02 | 0.50 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | D04 | 37.79 | qFL-D04-1 | 6.59 | 10.75 | 0.78 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | D06 | 52.24 | qFL-D06-1 | 4.05 | 6.32 | −0.42 | 4015 | |
| E3 | D08 | 28.80 | qFL-D08-1 | 4.65 | 7.08 | 1.74 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D08 | 33.59 | qFL-D08-2 | 3.08 | 4.53 | 0.99 | G. tomentosum | |
| FS | E1 | A02 | 81.75 | qFS-A02-1 | 5.51 | 9.80 | 1.04 | G. tomentosum |
| E2 | A02 | 81.75 | qFS-A02-2 | 7.59 | 16.71 | 1.21 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A03 | 95.37 | qFS-A03-1 | 3.02 | 7.23 | 0.57 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | A10 | 40.14 | qFS-A10-1 | 4.89 | 10.10 | 1.65 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A13 | 26.20 | qFS-A13-1 | 8.70 | 16.67 | −4.09 | 4015 | |
| E2 | A13 | 78.98 | qFS-A13-2 | 3.84 | 7.74 | −0.76 | 4015 | |
| E1 | D07 | 26.27 | qFS-D07-1 | 3.75 | 6.41 | −1.05 | 4015 | |
| E1 | D08 | 30.65 | qFS-D08-1 | 3.33 | 5.64 | 0.72 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D08 | 30.85 | qFS-D08-2 | 5.26 | 10.97 | 4.10 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D08 | 32.26 | qFS-D08-3 | 3.40 | 8.20 | −1.31 | 4015 | |
| E3 | D08 | 42.32 | qFS-D08-4 | 6.11 | 15.66 | −1.14 | 4015 | |
| E1 | D09 | 46.21 | qFS-D09-1 | 7.98 | 15.02 | 1.81 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D11 | 16.80 | qFS-D11-1 | 3.45 | 8.33 | 1.05 | G. tomentosum | |
| MIC | E1 | A03 | 90.56 | qMIC-A03-1 | 4.32 | 10.08 | 0.26 | G. tomentosum |
| E1 | A04 | 59.45 | qMIC-A04-1 | 5.12 | 12.17 | −0.22 | 4015 | |
| E1 | A07 | 50.02 | qMIC-A07-1 | 5.13 | 12.19 | −0.33 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A08 | 69.93 | qMIC-A08-1 | 3.37 | 11.38 | −0.11 | 4015 | |
| E3 | D01 | 42.61 | qMIC-D01-1 | 3.71 | 12.62 | −0.14 | 4105 | |
| MCF | E2 | A02 | 41.92 | qMCF-A02-1 | 8.78 | 16.17 | 0.03 | G. tomentosum |
| E1 | A03 | 89.63 | qMCF-A03-1 | 3.64 | 11.25 | 0.01 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A05 | 35.08 | qMCF-A05-1 | 3.22 | 5.22 | −0.01 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A08 | 52.24 | qMCF-A08-1 | 6.49 | 11.32 | 0.00 | - | |
| E1 | D02 | 10.92 | qMCF-D02-1 | 3.32 | 10.18 | −0.01 | 4015 | |
| E2 | D02 | 3.37 | qMCF-D02-2 | 3.20 | 10.30 | 0.01 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D05 | 51.40 | qMCF-D05-1 | 4.36 | 7.27 | 0.00 | - | |
| E3 | D07 | 8.74 | qMCF-D07-1 | 4.07 | 6.74 | 0.00 | - | |
| E3 | D07 | 21.28 | qMCF-D07-2 | 3.48 | 5.72 | 0.00 | - | |
| FU | E3 | A03 | 27.53 | qFU-A03-1 | 6.77 | 10.86 | −0.72 | 4015 |
| E1 | A05 | 44.26 | qFU-A05-1 | 3.75 | 7.34 | 0.92 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A05 | 2.79 | qFU-A05-2 | 3.54 | 5.24 | −0.26 | 4105 | |
| E3 | A05 | 78.57 | qFU-A05-3 | 8.93 | 15.03 | 0.90 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A06 | 19.81 | qFU-A06-1 | 8.98 | 19.92 | −0.64 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A07 | 20.64 | qFU-A07-1 | 4.86 | 7.46 | −0.34 | 4015 | |
| E2 | A08 | 88.37 | qFU-A08-1 | 3.13 | 8.04 | 0.50 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D08 | 50.42 | qFU-D08-1 | 6.64 | 18.56 | −0.77 | 4105 | |
| E1 | D10 | 10.63 | qFU-D10-1 | 3.49 | 6.82 | −0.36 | 4105 | |
| E3 | D11 | 16.80 | qFU-D11-1 | 6.51 | 10.41 | 0.64 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | D12 | 6.53 | qFU-D12-1 | 5.43 | 11.03 | 0.63 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D13 | 41.37 | qFU-D13-1 | 5.90 | 9.27 | −0.76 | 4015 | |
| SFC | E1 | A13 | 59.98 | qSFC-A13-1 | 5.46 | 20.21 | 0.87 | G. tomentosum |
| E2 | D04 | 50.11 | qSFC-D04-1 | 4.13 | 18.17 | 1.01 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D07 | 53.59 | qSFC-D07-1 | 3.84 | 15.25 | −0.48 | 4015 | |
| FE | E2 | A03 | 63.06 | qFE-A03-1 | 3.55 | 8.33 | 0.49 | G. tomentosum |
| E1 | A04 | 57.88 | qFE-A04-1 | 4.82 | 10.09 | 0.52 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A04 | 10.54 | qFE-A04-2 | 3.26 | 6.32 | 0.28 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | A05 | 48.90 | qFE-A05-1 | 3.24 | 7.55 | 1.51 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A07 | 23.81 | qFE-A07-1 | 4.56 | 9.48 | −0.32 | 4015 | |
| E1 | A07 | 71.27 | qFE-A07-2 | 6.39 | 13.86 | −1.01 | 4105 | |
| E2 | A07 | 61.62 | qFE-A07-3 | 3.41 | 7.97 | −0.37 | 4105 | |
| E3 | A07 | 40.54 | qFE-A07-4 | 3.75 | 7.34 | 0.54 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A11 | 93.03 | qFE-A11-1 | 3.27 | 6.60 | 1.37 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D04 | 47.00 | qFE-D04-1 | 4.56 | 10.94 | −0.36 | 4015 | |
| E3 | D07 | 8.93 | qFE-D07-1 | 5.60 | 11.43 | −0.38 | 4015 | |
| E3 | D07 | 21.28 | qFE-D07-2 | 7.71 | 16.50 | 0.74 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D10 | 1.74 | qFE-D10-1 | 5.47 | 13.41 | 0.42 | G. tomentosum | |
| SCI | E3 | A01 | 20.34 | qSCI-A01-1 | 3.91 | 6.33 | 2.82 | G. tomentosum |
| E1 | A02 | 81.75 | qSCI-A02-1 | 8.30 | 20.92 | 6.84 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | A02 | 81.75 | qSCI-A02-2 | 3.74 | 14.78 | 6.66 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | A02 | 82.67 | qSCI-A02-3 | 6.65 | 11.45 | −4.07 | 4105 | |
| E3 | A04 | 30.63 | qSCI-A04-1 | 3.57 | 5.74 | −3.25 | 4015 | |
| E3 | A04 | 62.70 | qSCI-A04-2 | 3.17 | 5.04 | 3.18 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A05 | 86.26 | qSCI-A05-1 | 4.18 | 9.59 | 4.71 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | A08 | 63.85 | qSCI-A08-1 | 3.49 | 7.88 | −8.15 | 4105 | |
| E2 | A12 | 46.99 | qSCI-A12-1 | 3.31 | 12.96 | −5.63 | 4105 | |
| E1 | A13 | 21.67 | qSCI-A13-1 | 3.58 | 8.11 | −18.14 | 4105 | |
| E3 | D08 | 29.17 | qSCI-D08-1 | 3.23 | 5.15 | 4.86 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D11 | 16.80 | qSCI-D11-1 | 8.88 | 16.09 | 7.29 | G. tomentosum | |
| E3 | D13 | 41.37 | qSCI-D13-1 | 6.24 | 10.64 | −7.50 | 4015 | |
| TWC | E3 | A06 | 31.94 | qTWC-A06-1 | 3.07 | 12.89 | 0.20 | G. tomentosum |
| E1 | A09 | 51.56 | qTWC-A09-1 | 3.22 | 8.29 | 0.19 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | A12 | 74.65 | qTWC-A12-1 | 4.99 | 12.00 | −0.11 | 4105 | |
| E1 | A13 | 1.76 | qTWC-A13-1 | 3.44 | 8.90 | −0.13 | 4105 | |
| E1 | A13 | 68.49 | qTWC-A13-2 | 4.46 | 11.79 | 0.13 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D04 | 0.35 | qTWC-D04-1 | 3.80 | 8.92 | 0.09 | G. tomentosum | |
| E1 | D08 | 3.82 | qTWC-D08-1 | 5.71 | 15.54 | 0.21 | G. tomentosum | |
| E2 | D10 | 8.18 | qTWC-D10-1 | 4.86 | 11.65 | −0.10 | 4105 |
| QTL Clusters | Chromosome Position Range (Mb) | QTL Number | QTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A02-cluster | 81.75–82.67 | 5 | qFS-A02-1, qFS-A02-2 |
| qSCI-A02-1, qSCI-A02-2 | |||
| qSCI-A02-3 | |||
| A03-cluster | 89.63–95.37 | 3 | qMCF-A03-1, qMIC-A03-1 |
| qFS-A03-1 | |||
| A04-cluster | 57.88–62.70 | 3 | qFE-A04-1, qMIC-A04-1 |
| qSCI-A04-2 | |||
| D02-cluster | 1.50–10.92 | 4 | qFL-D02-1, qFL-D02-2 |
| qMCF-D02-1, qMCF-D02-2 | |||
| D07-cluster | 21.28–26.27 | 3 | qMCF-D07-2, qFE-D07-2 |
| qFS-D07-1 | |||
| D08-cluster | 28.79–33.59 | 6 | qFL-D08-1, qFL-D08-2 |
| qSCI-D08-1, qFS-D08-1 | |||
| qFS-D08-2, qFS-D08-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Guo, C.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Shen, C.; Chao, L.; Shui, G.; You, C.; Xu, J.; Lin, Z.; et al. QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality Based on Introgression Lines Population from G. hirsutum × G. tomentosum. Agriculture 2023, 13, 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030579
Chang X, Guo C, Pan Z, Wu Y, Shen C, Chao L, Shui G, You C, Xu J, Lin Z, et al. QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality Based on Introgression Lines Population from G. hirsutum × G. tomentosum. Agriculture. 2023; 13(3):579. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030579
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xinyi, Chunping Guo, Zhenyuan Pan, Yuanlong Wu, Chao Shen, Lei Chao, Guangling Shui, Chunyuan You, Jianwei Xu, Zhongxu Lin, and et al. 2023. "QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality Based on Introgression Lines Population from G. hirsutum × G. tomentosum" Agriculture 13, no. 3: 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030579
APA StyleChang, X., Guo, C., Pan, Z., Wu, Y., Shen, C., Chao, L., Shui, G., You, C., Xu, J., Lin, Z., & Nie, X. (2023). QTL Mapping for Fiber Quality Based on Introgression Lines Population from G. hirsutum × G. tomentosum. Agriculture, 13(3), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13030579








