Abstract
The development of rural tourism plays an important role in promoting rural culture. By integrating 3833 household questionnaires from the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS) database with remote sensing data, we constructed an evaluation system to measure the level of rural culture. Then, we analyzed the impacts of rural tourism on rural culture from macro and micro perspectives. Our research results show the following: (1) Villages with developed rural tourism show a 85.9% increase in rural culture compared to those without tourism; (2) mechanism tests show that rural tourism promotes the rural culture by improving households’ risk-sharing behavior, human resources, and self-identification, leading to increases of 3.4%, 55% and 10.9%, respectively; (3) with micro-level (fieldwork survey) and macro-level analysis (remote sensing), we analyzed the various impacts of rural tourism on rural culture under different income levels, demographic structures, geographical locations and topographical conditions. The results show that at the micro level, the promotion effect of rural tourism on rural culture increases by 2.214% and 1.679% with the increase in per capita income and the proportion of women, respectively. For geographical location, macro-level data suggest that rural tourism in the east of China increases the rural culture by 3.416%. Moreover, in plain areas, both micro- and macro-level analysis indicated that rural tourism promotes rural culture by 2.323% and 4.607%, respectively. This is the first time rural culture has been evaluated on a large scale with two cross-validated approaches.
1. Introduction
Since the 1970s, rural tourism has played an important role in rural economic development [1]. Rural tourism has boosted rural economic growth [2], provided more employment opportunities, and improved recreational and cultural facilities [3], with a significant impact on rural socio-cultural activities. Tourism revenues reached USD 3.3 trillion in 2023, contributing 3% to the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP). In China, rural tourism has become a key approach to promote rural economic development, improve farmers’ living standards, and preserve rural culture [4]. In the first quarter of 2024, China’s GDP share of rural tourism income increased to 5.1%, which highlighted the development of urban and rural economies. However, rural tourism has also raised many problems, such as the cultural invasion, the rural societal collapse, and cultural shock at the reacting new urban environment. These problems have gradually diminished the core of rural culture [5], which could lead to the worsening of current situations in China during its transition period [6]. With the growth of rural tourism, a significant influx of industrial investment entered rural China, disrupting traditional land-based production. These industrial investments are a double-edged sword, as they have also improved the living standards of rural farmers [7]. Some experts claimed that rural tourism has undermined the foundations of traditional culture and caused certain crises in rural social relationships [3]. Therefore, this research focused on rural tourism in China as our research objective and provides valuable insights for other countries at similar stages of development.
The impact of rural tourism on rural socio-culture remains a controversial topic. Some scholars argued that the development of rural tourism has a negative impact on rural socio-cultural structures [8]. From a lifestyle perspective, rural tourism increases population density, raises the cost of living, disrupts traditional lifestyles, and exacerbates existing conflicts among different stakeholders. From a cultural perspective, rural tourism investments dominated by foreign investments may overlook or disrupt the social fabric and family values deeply embedded in local farming communities, which could gradually weaken rural social relationships [9]. In terms of local farmers’ participation, rural tourism manipulated by sources of external capital excludes indigenous people to join administration management [10]. A study of tourism development in the Dominican Republic found that local Dominicans were severely exploited by tourism, with many local residents deprived of “decent work” and relegated to lower social status [11]. On the other hand, some scholars stated that rural tourism contributed positively to rural socio-cultural development. Due to limited resources in rural areas, local tour operators formed a union to collectively address commercial challenges like competition, marketing, and management [12]. As a result, rural tourism stakeholders often choose to cooperate with each other for greater financial benefits [13]. Closed cooperation and social networking within local residents and the union are essential for the development of small-scale, community-based rural tourism [14]. Rural tourism can also promote cultural and heritage conservation in rural areas [15], strengthen social stability [16], and enhance community reputation and residents’ pride. There are two possible reasons for the controversy between the negative and positive aspects. First, the existing literature partially focuses on specific aspects such as women’s employment, rural heritage conservation, community participation, and socio-cultural relationships, but it fails to provide a comprehensive assessment of rural tourism and its impacts on local socio-culture aspects. The incomplete evaluations have led to inconsistent or even opposite research findings. To fill this gap, we introduced the concept of rural culture and constructed a rural culture construction index system to systematically analyze the influences of rural tourism on rural culture developments. The purpose of the research was to analyze the impacts of rural tourism to rural culture to two specific ends: (1) to evaluate whether the impact from rural tourism is positive or negative and (2) to explore the way in which rural tourism can influence rural culture.
We believe that rural economic conditions, including decent incomes, affordable housing, and proper rural infrastructures, determine the rural culture and rural morale. Negative economic impacts often impair the social collective responsibility, social ties, and foundation of rural culture, accelerating the loss of cultural awareness and confidence [17]. Conversely, positive economic development strengthens rural collective responsibility for individuals and promotes cultural growth. In recent years, rural tourism and its substantial benefits have emerged as an important driver of Chinese rural economic development to alleviate rural poverty and benefit rural revitalization. Rural tourism also serves as a magnet, attracting a significant influx of capital, talent, advanced technology, and management expertise to rural areas. This process has partially overcome the developing challenges posed by rural depopulation, ageing, and other issues [18] and laid a solid economic foundation for the construction of “new rural civilization”. Based on previous studies, we propose the following hypothesis.
H1.
Rural tourism has a significant positive impact on the construction of rural culture.
The existing research has failed to analyze the overall influences of rural tourism on rural socio-culture from a systematic theoretical perspective, so we applied the Stimulus–Organism–Response (S-O-R) theoretical model on the impact mechanism and explored how rural tourism affects rural culture. The S-O-R model, proposed by Mehrabian and Russell’s research [19], suggests that external stimuli trigger organismic responses, lead to rural cognitive changes, and subsequently predict human behaviors. Currently, the S-O-R theoretical framework has been widely applied to tourism design and tourism management [20]. With this model, Su and Swanson analyzed tourists’ environmental responsibility and argued that the social responsibilities in tour destination act as an external stimulus, which in turn promotes self-identification in the destinations and improved local environmental responsibilities [20]. Following this theoretical approach, we hypothesize that there are three ways for rural tourism to promote the construction of rural culture: improving the quantity and quality of human resources, strengthening villagers’ self-identification, and fostering villagers’ awareness of risk sharing. Rural residents are the primary contributors to rural tourism and the development of rural culture. Therefore, the impact of rural tourism on rural culture should support rural residents. The impacts from rural tourism may affect rural residents and their rural culture via three possible ways: First, rural tourism not only creates local employment opportunities and generates income for rural residents—thereby reducing population outflow and enhancing local education levels—but it also raises the standards for professional literacy, encouraging tourism operators to offer relevant training on cultural knowledge and skills to villagers [21]. As rural population quality is the foundation and the core of rural culture, improving the quantity and quality of human resource provides a solid foundation for rural cultural development [22]. Second, the development of rural tourism enhances villagers’ self-identification and then promotes the rural culture. The growth of rural tourism makes villagers realize that cultural resources can be turned into economic assets, which encourages the exploration, preservation, and transmission of local culture [23,24]. This helps villagers better understand the core content and value of local culture, thereby strengthening their cultural identification [25], which motivates the development of rural culture. Lastly, rural tourism increases villagers’ awareness of risk sharing, which further promotes rural culture. The rural tourism economic system with low working capital is fragile to natural or anthropogenic interferences and vulnerable to economic recession and policy instability. Risk sharing (community funds collectively raised by individual rural residents) as an informal social insurance mechanism is an important way for villagers to share risks, fostering a sense of community and reducing social stratification [26]. This also helps rural residents to promote rural culture. Based on the previous studies, we propose the following hypothesis.
H2.
Rural tourism promotes rural culture by improving the quantity and quality of rural human resources, enhancing farmers’ identity sense, and promoting farmers’ awareness of risk sharing.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Areas
Our research covered 10 provinces or autonomous region in China: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, Anhui, Henan, Guizhou, Sichuan, Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. These provinces (and the autonomous region) have various socio-economic conditions, agricultural development, and geographical locations in China, which enhanced the representativeness and robustness of our analysis. Our survey data were from 50 counties (county-level cities) and 156 towns, and we collected 300 questionnaires on village development and more than 3800 questionnaires on the family and household. The government report showed that in 2019, the disposable income of rural residents per capita across the country reached RMB 17,131, marking a nominal increase of 6.9% compared to the previous year (2019), with an actual growth of 6.2% after accounting for price-level changes (https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-01/18/content_5580659.htm, accessed on 1 November 2024). The research dataset included both micro-level and macro-level sources. The micro-level questionnaire data come from the China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS), a national household survey. The CRRS data were collected by the Institute of Rural Development of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences in 2020 (http://rdi.cass.cn/dcsj/202306/t20230607_5643271.shtml, accessed on 1 November 2024). The comprehensive survey referred to various aspects of the rural economy, society, culture, politics, and farmers’ livelihoods and social welfare, the detailed data of which substantially supported our research on the micro level. The CRRS, with a combination of stratified and random sampling, recorded socio-economic developments, rural and agricultural conditions, geographical location, and interviewees’ information. Ten sample provinces were selected from the eastern, middle, western, and northeastern regions of China. First, all counties (cities and districts) in the involved provinces were grouped into five categories based on GDP per capita, and five counties (cities and districts) were selected from each sample province. Second, three towns were randomly selected from each selected county (city and district) using the same sampling method (Figure 1). Then, the administrative villages within each selected town were divided into two groups, i.e., “Good” and “Bad” based on economic conditions, and one village was randomly selected from each group. Finally, with the systematic sampling method, the surveyors randomly chose 12 to 14 households from the village household list and conducted face-to-face interviews with the same questionnaire template. (In-person interviews tended to involve persons with poor education who could not complete the questionnaires by themselves.) Our research only presented part of the questionnaire that referred to the relationship between local rural tourism and the development of rural culture and involved the relevant variables on rural tourism, rural culture, and control variables. After teasing out the missing and outlier values, we obtained available 3833 questionnaires on households.
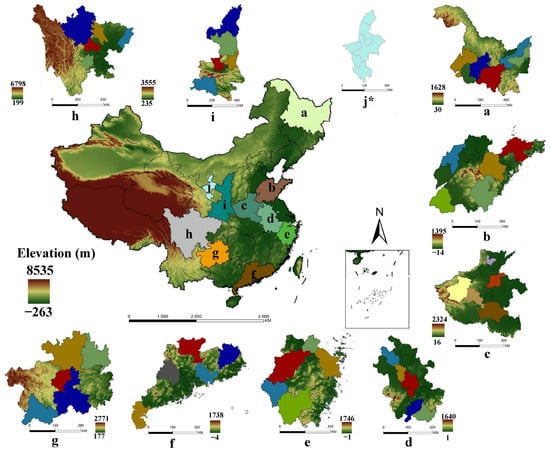
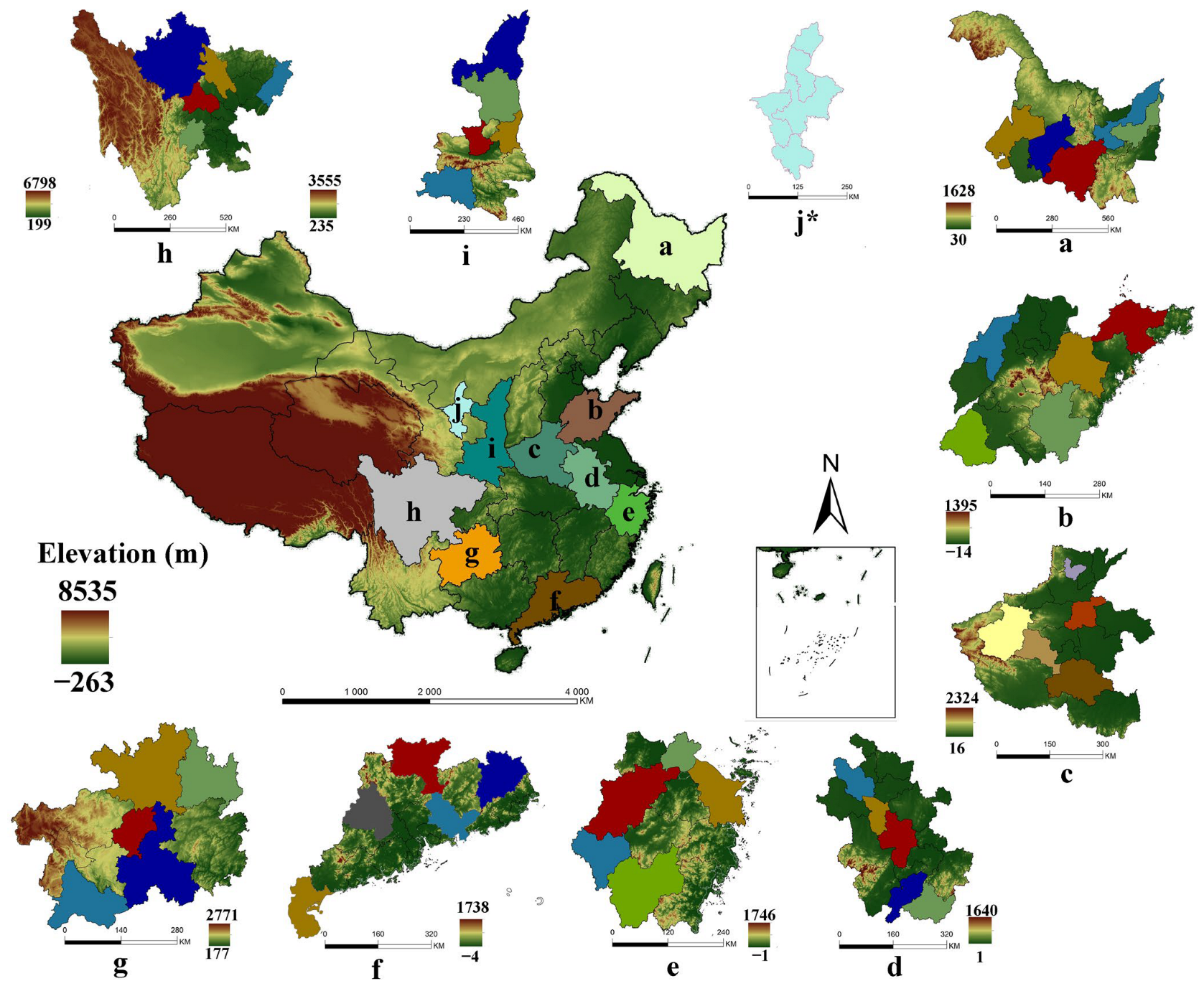
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of the selected provinces and cities. Notes: The colored areas were the selected provinces and selected cities. (a): Heilongjiang Province; (b): Shandong Province; (c): Henan Province; (d): Anhui Province; (e): Zhejiang Province; (f): Guangdong Province; (g): Guizhou Province; (h): Sichuan province; (i): Shaanxi Province; (j): Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. * All cities in Ningxia were selected.
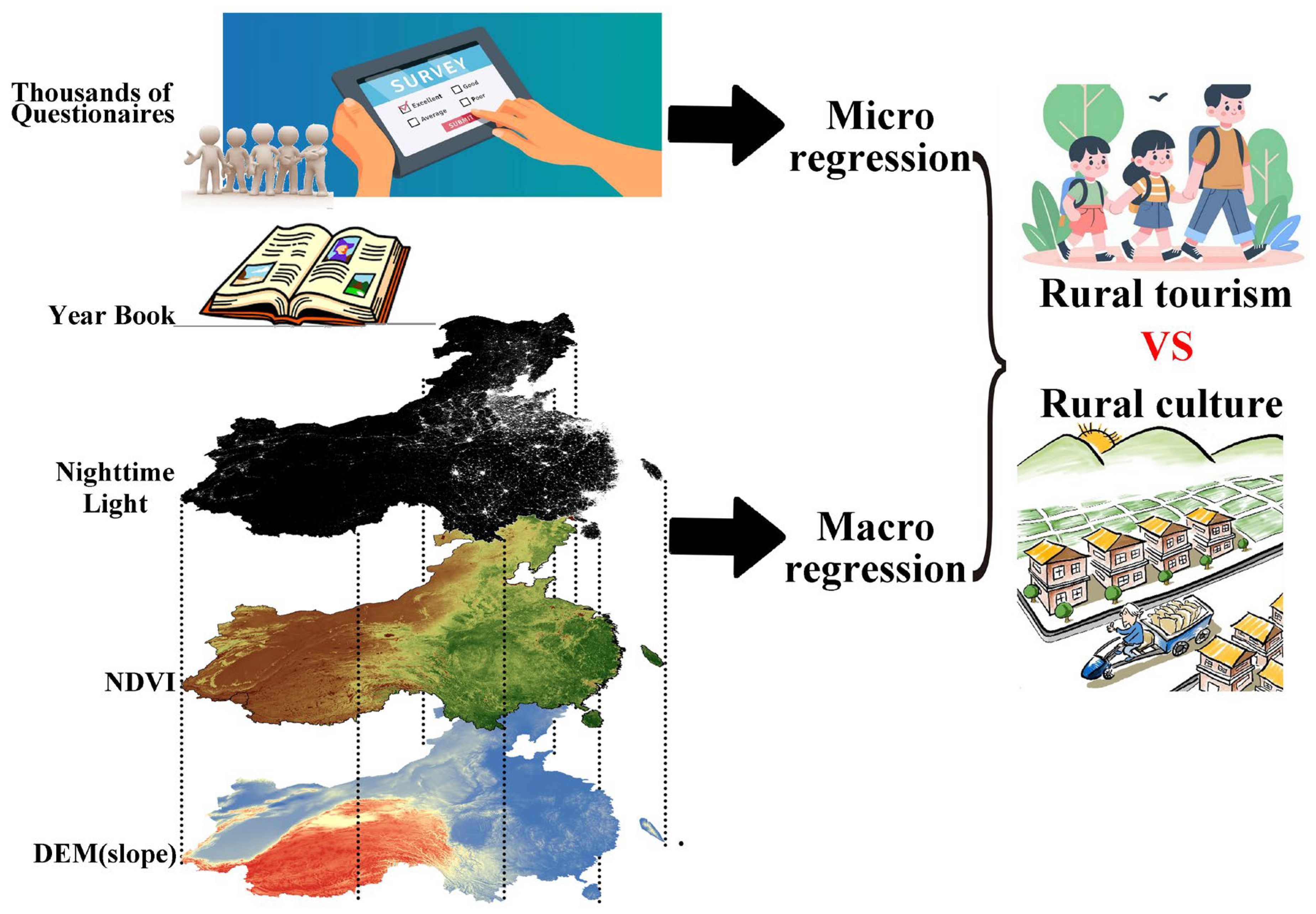
The macro-level remote sensing data primarily included elevation data, nighttime light data, land-use distribution layers, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), and the list of nationally recognized “civilized villages”. Elevation data were derived from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) digital elevation dataset with a spatial resolution of 90 m. The 2020 nighttime light data were derived from the NPP-VIIRS annual dataset with a spatial resolution of 500 m. The 2020 annual NDVI was derived from the MOD13Q1 product at a spatial resolution of 250 m. The list of “Civilized Villages” is updated annually and had been updated six times by 2020 (http://www.wenming.cn/wmsjk/cjdx_53740/qgwmczmd/202112/t20211227_6276649.shtml, accessed on 1 November 2024). We included all recognized civilized villages within our study areas. As our whole study did not involve layer stacking, there was no need to downscale any involved layers. Instead, we simply calculated the average value of each layer for each of the involved counties. These averages were used in the subsequent analysis.
2.2. Structure of the Indicator System
2.2.1. Micro-Level Indicator System
With the deepening of the development of the market economy, a large amount of industrial capital has begun to pour into the countryside, and while this capital improves the material living standards of the peasants, it also changes the traditional land-based production mode, which to some extent affects the foundation of traditional culture, and in the context of this era, the construction of folkways culture is of great significance. From the basis of the development of folkways culture, we can see that folkways culture is essentially a cultural form developed on the basis of a specific field environment. Existing research on the construction of the indicator system of rural culture focuses more on social security, cultural hardware facilities, the development of rural education, ideological and moral construction, and other aspects. For example, the indicator system for the construction of rural culture was constructed in terms of the level of social security, the development of public culture, the quality of rural education, the construction of ideology and morality, the construction of culture and education, the development of public culture, and the inheritance of excellent culture [27]. Taken together, these studies have laid an important research foundation for us to learn from, especially the importance attached to the aspect of public culture. It should be noted that rural culture cannot be separated from the interaction and communication among villagers, especially including neighborhood relationships, social trust, and social security, which are the specific embodiment of rural culture construction that should be focused upon, and existing studies have neglected this point. In addition, with the development of digital economy, digital infrastructure construction plays an important role in facilitating farmers’ communication, promoting farmers’ learning of external knowledge and culture, and participation in village affairs, etc., and should be considered as part of the indicator system of rural culture, which has been neglected in existing studies. In addition, unlike existing studies, in our research, we tried to quantify the indicators with micro-survey data, which are closer to the actual situation of rural culture construction than macro-data such as statistical yearbooks. Therefore, we constructed a system of indicators of rural culture from five aspects: public culture, neighborhood relations, social trust, social security, and modernity. Among them, we mainly measured public culture by five indicators: the proportion of party members, the proportion of cultural expenditure, the number of years of villagers’ education, the proportion of public welfare expenditure, and the proportion of farm households’ holiday welfare expenditure. Neighborhood relationships are mainly measured by the fact that rural culture has a kind of upward and good spirit and rural atmosphere built with excellent local culture as the core [28]. This was measured by three indicators: neighborhood disputes, neighborhood assistance, and human expenditure. Social trust is also an important part of the development of rural culture, which was measured in this part by three indicators: the degree of trust between neighbors, the degree of trust in village cadres, and the degree of trust in township cadres. We also measured social security by the presence of criminal cases and the percentage of social security expenditure. It should be noted that the strong vitality of rural culture is due to the fact that the construction of rural culture can keep pace with the times [29]. In the context of the Internet, the construction of rural culture is strengthened by the vehicle of digital elements, which enables it to keep up with the times. We measured this by mobile phone and Internet penetration. Finally, we referred to Zhang et al.’s research through the entropy value method on the comprehensive calculation of the micro-level indicator system of rural civilization [30]. A detailed description of the variables in the micro-level indicator system for rural culture is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Development of a micro-level indicator system for rural civilization and rural tourism.
2.2.2. Macro-Level Indicator System
Although our field survey provided detailed demographic information about villagers, the stratified sampling cannot cover all individuals in our study areas. While the remote sensing imagery can comprehensively cover the entire study area and provide a broad overview for the research objectives, unfortunately, remote sensing data cannot capture psychological perceptions at the household level. Given the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches, we compared the results with remote sensing and field surveys and drew our conclusions based on both. The collection of remote sensing data included the following: the number of “civilized villages”, vegetation density, nighttime light, and geographic slope. The number of “civilized villages” in each county corresponds to the rural culture in that county, where the higher rural culture in a county, the higher the number of “civilized villages”. Rural tourism is closely linked to a good ecological environment, so we used the averaged Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) of each county in 2020 as an indicator, where the higher the average vegetation index, the more developed the rural tourism in that county. The economic development of a county can be reflected by the nighttime light index, where a county with brighter nighttime is more economically developed. The geographic slope in a county reflects its topography, where flatter land can be more economically friendly to building processes. In addition, the latitude and longitude coordinates of a county reflect its geographical position, and we defined them as “northness” and “eastness”. Gender ratios for each county can also be found in the Yearbook (Figure 2). The micro research was an individual-level analysis where 3384 interviewees joined the research, while the macro research was a county-level analysis where 50 counties were involved. The details of the macro-level indicator system for rural culture and rural tourism are shown in Table A1 in Appendix A.
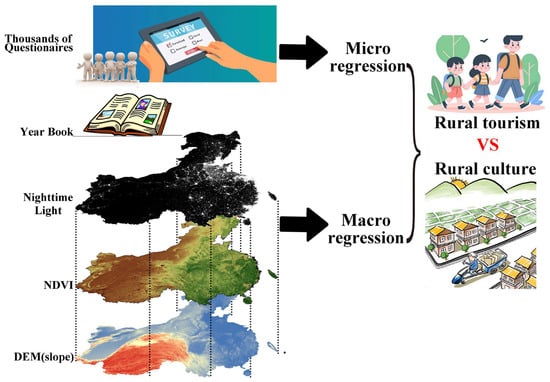
Figure 2.
Data collection from micro and macro sources and data processing.
2.3. The Relationship Between Rural Tourism and Rural Culture
We established a regression model to analyze the relationship between rural culture (dependent variables) and rural tourism (dependent variables) on a micro level (Equation (1)).
where Rural Culturej represents the culture level in the village j and is a composite indicator constructed from the previous section using the entropy value method; Rural Culturej indicates whether rural tourism exists on household i in the village j (value is 1 if it exists and otherwise 0); Xj represents relevant control variables; , , , and are the coefficients and error term, respectively.
To further explore the mechanism through which rural tourism affects rural culture on the micro level (three possible candidates: the quantity and quality of rural human resources, enhancing farmers’ identity sense, and promoting farmers’ awareness of risk sharing), a moderation effect model was used, based on the theoretical analysis presented earlier. The specific model is as follows (Equation (2)):
where Regulatoryj is the moderating variable in village j, and Rural tourismj × Regulatoryj is the interaction term between rural tourism and the moderating variable, which is used to assess the specific effect of the moderating variable on the influence of rural tourism on rural culture. is relevant control variable; , , , , and are are the coefficients and error term, respectively. If the is positive, it indicates that the moderating variable enhances the effect of rural culture; if negative, it suggests inhibition.
In addition, a multiple linear regression model was established to compare and analyze the influencing factors of rural tourism on rural culture on both micro and macro levels. The computing ratio can quantify the direction and magnitude of the influence, reveal the causal relationship between rural tourism and rural culture, and provide a solid support for empirical research. The specific model is as follows (Equation (3)):
where Rural culturej/Rural tourismj is the ratio between rural culture and rural tourism in village j using micro and macro approaches; Factorsj represents a set of influencing factors such as per capita income, gender ratio, and geographical terrain; is relevant control variable; , , , , and are the coefficients and error term, respectively. The heteroscedasticity of all regressions were tested. If the results met the significant level (p < 0.05), which indicated the existence of heteroscedasticity, robust estimations were conducted in the regression.
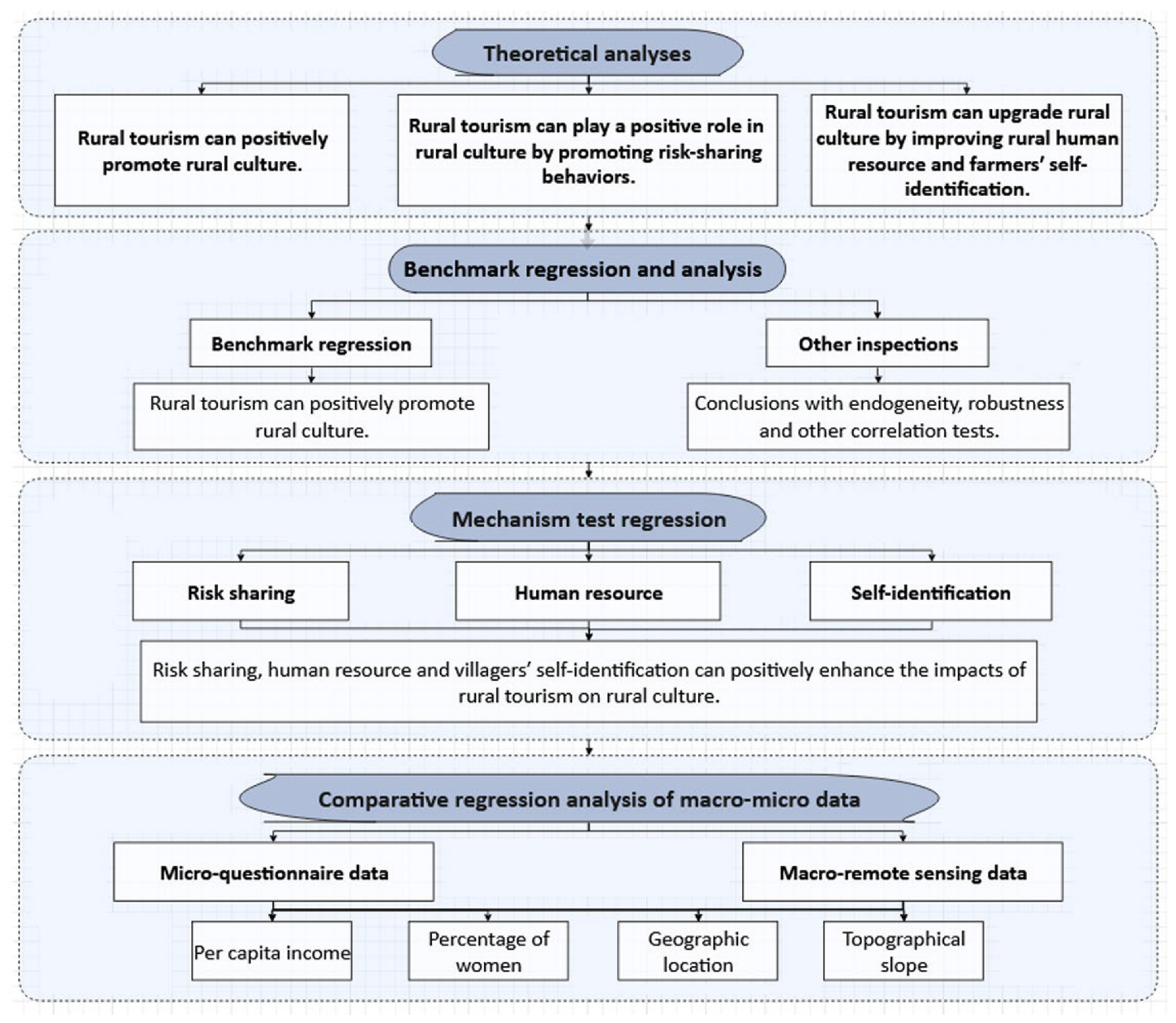
To examine the impact of rural tourism on rural culture, we chose the following models, collected questionnaires and spatial data, established multiple regressions, and compared the results via micro-level analysis and macro-level analysis (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
The workflow of the research.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Regression Analysis
At the micro level, the rural tourism data indicated that 32.3% of the villages in the study area have developed rural tourism (Table 2). At the macro level, the standard error of rural culture is 2.011, reflecting a significant difference in the level of rural culture between different villages. In addition, 47.9% of the villages have developed rural tourism, a higher percentage compared to the micro-level data (Table 2). For the control variables on the individual household level, it is generally assumed that being married compared to being unmarried leads to greater family and social responsibility, which are good for the development of rural culture. Household heads who are members of the Communist Party of China had a positive impact on the local rural culture. At the household level, it is generally accepted that families with a member holding a village cadre position have a higher level of ethical standards than ordinary households because village cadres should play an exemplary role among rural residents. For villages, a lower proportion of poor households, a lower proportion of the seniors, a higher proportion of the religious, and shorter distances to county hall are positive for the development of rural culture. To avoid possible multicollinearity problems, the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) was calculated (Table A2 in Appendix A). Our results demonstrated that all VIF values were below 2, suggesting that there was no multicollinearity among the key variables in our study.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for variables.
Heteroscedasticity may lead to biased and invalid statistical inferences. Before starting regression, we used the Breusch–Pagan (BP) test to diagnosis heteroscedasticity (Table 3). The regression p-values were all less than 0.05, indicating the presence of heteroscedasticity in the data (Table 3). Consequently, we further employed robust standard errors for the regression analysis. Compared to the villages with limited rural tourism (Table 3), rural culture in villages with advanced rural tourism was strengthened by 85.9%, confirming Hypothesis 1, which states that rural tourism positively promotes the development of rural culture. Additionally, the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) value was introduced to assess the degree of model fit. The one with the smallest AIC value, Model 3, was the best model, where the model included all variables (Table 3).

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics for variables.
To avoid potential interruptions from reverse causality, omitted variable bias, and sample self-selection, we selected industrial wastewater discharge as an instrumental variable to address reverse causality concerns (Table A3 in Appendix A). In addition, to ensure the robustness of our research conclusions, we applied propensity score matching [31] and conducted robustness checks using alternative explanatory variables (Table A4 and Table A5 in Appendix A). The results from various perspectives all showed that the development of rural tourism evidently supported rural culture.
3.2. Regression to Explore Three Drivers to Increase Rural Culture
Rural tourism has a significant positive effect on the rural culture via risk sharing, human resource, and residents’ self-identification to achieve the impacts. Rural tourism increased rural culture by 56.3%. The interaction of the three pairs (rural tourism and risk sharing, rural tourism and human resource, and rural tourism and peasants’ self-identification) increased rural culture by 3.4%, 55%, and 10.9%, respectively (Table 4).

Table 4.
Mechanical testing to explore which drivers brought positive effects on rural culture.
3.3. Comparison Between Micro-Level and Macro-Level Analyses
The regression results from the micro and macro data showed differences in the effects of GDP, gender, and geographical location (Table 5). At the micro level, GDP is measured by the “income per capita” data from the survey. The results indicated that for each unit increase in per capita income, the positive effect of rural tourism on rural culture increased by 2.214% (β = 2.214; p < 0.01). At the macro level, GDP is measured by the “average nighttime light index”, but this result is not statistically significant. At the micro level, the positive impact of rural tourism on the rural culture increased by 1.679% (β = 1.679; p < 0.01) as the proportion of women increased. However, at the macro level, the data indicated that the proportion of women had no significant effect (p > 0.10). For geographical location, micro-level data supported that whether a village is located in the eastern or central region does not significantly affect the impact of rural tourism on rural culture (p > 0.10). However, in the west, rural culture in the villages with tourism development were 7.869% (p < 0.01) higher than those without tourism development. In contrast, macro-level data suggested that rural tourism development in eastern villages improved the construction of rural culture by 3.416% (p < 0.10), while it had no significant effect in western villages (p > 0.10). Both micro- and macro-level data provide consistent conclusions on the slope of the terrain (Table 4). When villages are situated in plains, both micro- and macro-level results indicate that rural tourism contributes to the enhancement of rural culture by 2.323% (p < 0.10) and 4.607% (p < 0.10), respectively. However, when villages are located in mountainous areas, rural tourism hinders the development of rural culture. Both models met the significance level (p < 0.0001), and the macro model was better than the micro model, and its whose AIC model was a little smaller than the micro one (Table 5).

Table 5.
Comparison of β coefficients of micro and macro regression results.
4. Discussion
4.1. Three Drivers Motivating Rural Culture
4.1.1. Risk Sharing
Rural tourism can promote the development of rural culture by encouraging farmers’ risk-sharing behavior (Table 3). In villages with rural tourism, villagers often participate in tourism by providing land, capital, or labor for the development. However, rural tourism is vulnerable and sensitive to natural factors such as natural disasters, seasonality, and socio-economic interference, including tourism industry boom and the propagation of social media [22]. To mitigate potential losses, villagers raise money and start collective funds to share both profits and risks [32]. This behavior fosters a collaborative and supportive social environment, which significantly contributes to the development of rural culture. These findings are supported by Kou and Xue’s research [33].
4.1.2. Human Resource
Rural tourism can enhance rural culture by increasing both the quantity and quality of human resource in the villages (Table 3). Previous research confirmed that rural tourism and its substantial profits, as a strong magnet, encouraged citizens (who used to be villagers) to not only reflow from the urban areas but also to start their own rural businesses [34] that attract external labor with high education levels, which can promote the quantity of the rural population. In addition, rural tourism has established higher demands for the profession and management skills of villagers employed in the sector, necessitating a continuous evolution in the quality of human resources to maintain the competitiveness of local tourism [26]. As both the quantity and quality of human resources in rural areas improve, local rural culture also gets better. This conclusion is consistent with the findings of Gocer et al.’s research analyzing the relationship between tourism and rural heritage community resilience in Behram, Turkey [35]. Meanwhile, rural tourism promotes local employment and income diversification—providing an alternative source of income beyond agriculture—and helps to break the isolation of rural communities. The presence of tourists and tourism workers serve as a navigator for improving the behavior of villagers, which indirectly motivates rural culture [36].
4.1.3. Self-Identification
Rural tourism promotes the development of rural culture by enhancing villagers’ sense of identification (Table 3). The growth of rural tourism encourages local villagers to invest resources such as housing, land, and skills into the tourism industry, transforming their role from passive workers to active shareholders [3]. Nelson et al. [25] also had a similar finding, and they claimed that substantial changes in villages can trace back to urbanization and technological advancement. Moreover, rural tourism and its profits bring villagers greater exposure to and appreciation of rural culture. The villagers become participants and beneficiaries of rural tourism, which strengthens their cultural identity [32]. Those enhanced identities motivate villagers to engage in public cultural activities, contributing to the preservation and promotion of traditional culture [37], which in turn fosters rural culture.
4.2. Comparison Between Questionnaire and Remote Sensing Analysis
The micro-level data indicated that higher per capita income is associated with a greater impact of rural tourism on rural culture. In contrast, at the macro level, the results were not statistically significant. The contradictions arose from the use of two different data sources. The macro-level data utilized the nighttime light index to represent income levels, which primarily reflects the development of the manufacturing and service industries while excluding agriculture, which generates less nighttime illumination. The micro-level survey data gathered the actual income of the surveyed rural households, providing an unbiased representation of real rural life. For gender ratio, the micro-level survey data show that a higher proportion of women increased the impact of rural tourism on rural culture, while the macro-level remote sensing data show no significant effect. The highly likely cause of the difference that the macro-level remote sensing data used the regional sex ratio from the 2020 Chinese Yearbook, which may differ from the actual gender distribution in the selected villages and households. From our fieldwork observations, women’s social roles make them well organized, and they are willing to join the development of rural culture. Compared to men, women show a greater preference for public cultural activities and communal meals. They are also more supportive of initiatives aimed at preserving agricultural culture and documenting local histories, all of which contribute significantly to rural culture [18]. In addition, women have a natural affinity and vested interest in activities related to environmental cleanliness and ecological viability, which are often part of fine-tuned activities in rural cultures [38]. At the micro level, the survey data suggested rural tourism had no significant effect on rural culture if the villages were situated in the east of China, while rural tourism played a positive role on rural culture if the villages were located in the west of China. Conversely, the macro-level results suggest that rural tourism in eastern regions contributes positively to rural culture, while the data for western regions are not significant. We believe that the macro-level data results are more in line with real conditions. In the economically developed eastern regions, public cultural facilities are relatively complete and meet the needs of different age groups and social strata, so rural tourism can easily promote rural culture. However, in less economically developed regions, especially in the central and western areas that have only recently alleviated poverty, public cultural infrastructures and facilities remain underdeveloped [39]. Rural tourism struggles to improve rural culture in these regions, which highlights the strengths of macro-level data covering larger areas.
Both the macro- and micro-level data show similar results regarding the slope of the terrain. Villages located on plains showed significantly strengthened positive effects of rural tourism on rural culture, while mountainous areas inhibited this effect. We speculate that rural systems are strongly influenced by natural conditions and resources, leading to significant regional differences. Plains typically feature expansive, flat terrain with larger, more concentrated villages, which facilitates communication among residents and enhances access to public services and cultural activities [13]. In contrast, villages in hilly or mountainous areas are often arranged in a linear pattern along rivers or valleys, with small, dispersed settlements. In some villages, the slope of the terrain impacts the level of tourism, which in turn influences the rural culture. Rugged terrain, poor transport links, and vulnerability to natural disasters pose significant challenges for rural tourism and rural culture. Due to a remote location and low economic incomes, it is difficult to raise funds in such villages. Underdeveloped public services such as education, healthcare, and elderly care slow down the development of rural tourism and the promotion of public culture [40]. The consistency between the CRRS data and macro-level GIS data further validates the rationality of this analysis.
Our study was the first research to explore rural management using the Geographic Information System (GIS) and questionnaires in China. GIS and remote sensing covered the entire study area (10 provinces) and provided regular updates on geographic information (such as terrain slope) and economic (such as nighttime light levels) information [41,42]. The questionnaire reflected the interviewees’ psychological conditions and cultural values [43]. The results of each can partly (though not fully) reveal the relationship between rural tourism and rural culture, so we combined both approaches to present the relationship comprehensively.
4.3. Limitation and Future Studies
Our two hypotheses were verified, but there are still some limitations that we can improve in our further studies. Firstly, we can collect more questionnaires for each village. Although our database collected 3383 household questionnaires from 10 provinces, the number of available questionnaires for each village ranged from 12 to 14 due to time and resource constraints. In particular, for villages with large populations, this sample size may not adequately reflect the local tourism and cultural situations. We plan to increase the number of interviewees, especially in some populous villages. We will also add the number of cultural institutions into our indicator system, which could reflect local frequencies of culture activities in each village. Secondly, the effects of rural tourism may influence not only rural culture but also urban culture. We will conduct analyses on the spatial spillover effect of rural tourism and evaluate whether it can effectively impact urban life using both macro and micro approaches. Lastly, we intend to extend our study areas. The results and conclusions of the current study only focus on China. We plan to cooperate with other universities and conduct similar surveys in other Asian countries like Singapore, Indonesia, and Malaysia. Then, we could summarize the commonalities of the relationship between rural tourism and rural culture in Asian countries.
5. Conclusions
This study was based on the S-O-R model and explored the impact of rural tourism on rural culture through both micro-level and macro-level analyses. With the systematic theoretical framework, we constructed an indicator system for rural culture, with its foundation, core, and contemporary characteristics. Based on this framework, we examined the mechanisms of how rural tourism influences rural culture. Our results suggested that, on average, villages with rural tourism experience an 85.9% increase in rural culture compared to those without tourism. Given the potential endogeneity and robustness issues of the results, we employed instrumental variable methods and propensity score matching. These consistent results also demonstrated that rural tourism promotes rural cultures. To verify how rural tourism contributes to rural culture, we applied the S-O-R model framework and empirically tested three mechanism channels: risk sharing, human resources, and residents’ self-identification. The interaction between rural tourism and these three mechanisms enhances rural culture development by 3.4%, 55%, and 10.9%, respectively. We analyzed and compared the micro-level survey data and the macro-level remote sensing data. At the micro level, for every unit increase in per capita income and the proportion of women, the contribution of rural tourism to rural culture increases by 2.214% and 1.679%, respectively, while no significant impact was observed at the macro level. This highlights that micro-level data precisely capture household income and other characteristics. At the macro level, the remote sensing data suggested that rural tourism in villages located in the east of China increases rural culture by 3.416%, a conclusion that was more reliable. Macro-level analysis using remote sensing was effective for addressing spatial problems. Both micro- and macro-level data provided consistent results regarding the slope of the terrain. When villages are located on plains, rural tourism increases rural culture by 2.323% and 4.607%, respectively. However, in mountainous areas, rural tourism hinders rural culture.
Our dataset covers 10 provinces and autonomous regions in China, including Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shandong, Anhui, Henan, Heilongjiang, Guizhou, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. The data were collected from 50 counties (county-level cities), and the number of available questionnaires reached 3833. We used a cross-validation method combining remote sensing and survey data (CRRS) to reveal the relationship between rural tourism and rural culture. The combination of these two methods enabled mutual validation, which increased the accuracy and reliability of the research results. In further studies, we plan to increase sample size for each village (especially for the populous villages), explore the spatial spillover effects of rural tourism on urban life, and summarize the commonalities in Asian countries by conducting similar surveys in other countries. We will continue to use the cross-validation method (GIS and questionnaires), which integrates spatial-scale data with household-level data and is the first of its kind in the field. We suggest that more researchers conduct rural studies by using GIS and questionnaire survey in the future to provide a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of rural culture and rural development.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed significantly to this work. Conceptualization, H.L., Y.W. and Y.C.; methodology, Y.W., Y.C. and H.L.; formal analysis, Y.W. and W.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C. and I.-C.C.; writing—review and editing, H.L., Y.W. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers who gave us practical and helpful suggestions and comments on our research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Construction of a macro-level indicator system for rural culture and rural tourism.
Table A1.
Construction of a macro-level indicator system for rural culture and rural tourism.
| Objective Level | Specific Measurement Indicators | Indicator Meaning | Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural culture | Number of “civilized villages” | Represents the culture of the county | + |
| Rural tourism | NDVI | Represents the tourism strength of the county | + |
| Slope | Represents the topography of the county | − | |
| Luminosity index | Represents the economic development of the county | + | |
| Longitude | Represents the eastness of the county | + | |
| Latitude | Represents the northness of the county | + |
+ and − indicate positive and negative effects, respectively.

Table A2.
Robustness tests: changing estimation methods.
Table A2.
Robustness tests: changing estimation methods.
| Variable | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| Rural tourism | 1.06 | 0.94 |
| Risk sharing | 1.05 | 0.95 |
| Human resource | 1.11 | 0.90 |
| Self-identification | 1.08 | 0.93 |
| Marriage status | 1.01 | 0.9877 |
| Religious belief | 1.03 | 0.98 |
| Cadre | 1.06 | 0.95 |
| Senior people ratio | 1.01 | 0.99 |
| Poverty-stricken village | 1.11 | 0.90 |
| Distance to government | 1.22 | 0.82 |

Table A3.
Endogeneity test.
Table A3.
Endogeneity test.
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Phase II | |
| Rural tourism | 0.658 ** | |
| (0.305) | ||
| IV_Isd | 0.051 *** | |
| (0.019) | ||
| Cons | 0.020 * | 0.086 *** |
| (0.010) | (0.012) | |
| Sample size | 3833 | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | 6.905 *** | |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F statistic | 16.900 | |
| Hansen J | 0.000 | |
Note: *, **, and *** denote 10%, 5%, and 1% significance levels, respectively. Values in the parentheses are the standard errors.

Table A4.
Robustness tests: changing estimation methods.
Table A4.
Robustness tests: changing estimation methods.
| Matching Methods | Processing Group | Control Group | ATT | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Near neighbor matching (1:1) | 0.1179 | 0.1238 | −0.0059 *** | 0.0046 |
| Near neighbor matching (1:4) | 0.1179 | 0.1210 | −0.0031 *** | 0.0032 |
| Radius caliper matching | 0.1179 | 0.1239 | −0.0060 *** | 0.0047 |
| Kernel matching | 0.1179 | 0.1240 | −0.0061 *** | 0.0049 |
Note: *** denote 1% significance levels, respectively. Values in the parentheses are the standard errors.

Table A5.
Robustness Tests: replacement Variables.
Table A5.
Robustness Tests: replacement Variables.
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Rural Culture | Rural Culture | |
| Rural tourism | 0.190 *** | |
| (0.060) | ||
| Percentage of forest cover | 0.019 *** | |
| (0.006) | ||
| Cons | 12.194 *** | 11.617 *** |
| (0.447) | (0.440) | |
| AIC value | 5241.63 | 6510.1825 |
| Regression p-value | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Chi2 | 474.31 | 441.73 |
| Prob > Chi2 | p < 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
| Sample size | 3833 | 3833 |
Note: *** denote 1% significance levels, respectively. Values in the parentheses are the standard errors. The heteroscedasticities were detected (p < 0.05), and robust estimations were conducted in both regressions.
References
- Su, B. Rural tourism in China. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 1438–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.M.; Wall, G.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Livelihood sustainability in a rural tourism destination—Hetu Town, Anhui Province, China. Tour. Manag. 2019, 71, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalina, P.D.; Dupre, K.; Wang, Y. Rural tourism: A systematic literature review on definitions and challenges. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Filieri, R. Resident-tourist value co-creation: The role of residents’ perceived tourism impacts and life satisfaction. Tour. Manag. 2017, 61, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q. Research on the Changes in Cultural Landscape of Tourist-Type Traditional Chinese Villages from the Perspective of Cultural Memory: Taking Anzhen Village in Chongqing as an Example. Land 2023, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Woods, M.; Fois, F. Rural decline or restructuring? Implications for sustainability transitions in rural China. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, B. Revitalizing traditional villages through rural tourism: A case study of Yuanjia Village, Shaanxi Province, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 63, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xie, S.; Knight, D.W.; Teng, S.; Liu, C. Tourism-induced landscape change along China’s rural-urban fringe: A case study of Zhangjiazha. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2020, 25, 914–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaiwa, J.E. Enclave tourism and its socio-economic impacts in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutberlet, J. Rural Development and Social Exclusion: A case study of sustainability and distributive issues in Brazil. Aust. Geogr. 1999, 30, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, A.L. Tropical Blues: Tourism and Social Exclusion in the Dominican Republic. Lat. Am. Perspect. 2008, 35, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.; Zhou, Y. Community, governments and external capitals in China’s rural cultural tourism: A comparative study of two adjacent villages. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, N.; Mahmood, T. Historical and Systemic Overview of Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA): A Cultural Landscape. J. Hist. Stud. 2021, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Iorio, M.; Corsale, A. Community-based tourism and networking: Viscri, Romania. J. Sustain. Tour. 2013, 22, 234–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May-Chiun, L.; Peter, S.; Azlan, M.A. Rural tourism and destination image: Community perception in tourism planning. Macrotheme Rev. 2013, 2, 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.B.; Yoon, Y.S. Developing sustainable rural tourism evaluation indicators. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 13, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.I.; Fan, F.U. The impact of Population Changes on Cultural Landscape of Traditional Villages. Art Des. 2015, 2, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Z. Cultural heritage as rural economic development: Batik production amongst China’s Miao population. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 81, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environment Psychology; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Swanson, S.R. The effect of destination social responsibility on tourist environmentally responsible behavior: Compared analysis of first-time and repeat tourists. Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.; Cheyne, J. Residents’ attitudes to proposed tourism development. Ann. Tour. Res. 2000, 27, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F. Joint development of cultural heritage protection and tourism: The case of Mount Lushan cultural landscape heritage site. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, A.; Lowengart, O.; Milman, A. Rural tourism in Israel: Service quality and orientation. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.; Jolliffe, L. Cultural rural tourism: Evidence from Canada. Ann. Tour. Res. 2003, 30, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.S.; Tuan, D.B.; Nathan, A.G.; Devon, W.; Hayden, C.; Watson, J.T.; Xin, A. Definitions, measures, and uses of rurality: A systematic review of the empirical and quantitative literature. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 82, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasstrøm, M.; Normann, R. The role of local government in rural communities: Culture-based development strategies. Local Gov. Stud. 2019, 45, 848–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Advancements, Dynamics, and Future Directions in Rural Environmental Governance Research in China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.; Karahalios, K.; Sandvig, C. The network in the garden: Designing social media for rural life. Am. Behav. Sci. 2010, 53, 1367–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K. New lives, New Landscapes. Landscape, Heritage and Rural Revitalisation: Whose Cultural Values? Built Herit. 2019, 3, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Y. Assessing rural revitalization potential through rural transformation degree and sustainability: A quantitative study of 460 case villages in Lingbao, China. Habitat Int. 2024, 153, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.B. Multivariate matching methods that are equal percent bias reducing, II: Maximums on bias reduction for fixed sample sizes. Biometrics 1976, 32, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T. The Spatial Perception and Spatial Feature of Rural Cultural Landscape in the Context of Rural Tourism. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Xue, X. The influence of rural tourism landscape perception on tourists’ revisit intentions—A case study in Nangou village, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Hassan, S. Investment and Tourism: Insights from the literature. Int. J. Econ. Perspect. 2016, 10, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocer, O.; Boyacıoğlu, D.; Karahan, E.E.; Shrestha, P. Cultural tourism and rural community resilience: A framework and its application. J. Rural. Stud. 2024, 107, 1032387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Tourism and gender equality: An Asian perspective. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 85, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Henneberry, S.R.; Ni, J.; Radmehr, R.; Wei, C. Socio-cultural roots of rural settlement dispersion in Sichuan Basin: The perspective of Chinese lineage. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijijayanti, T.; Agustina, Y.; Winarno, A.; Istanti, L.; Dharma, B. Rural Tourism: A Local Economic Development. Australas. Account. Bus. Financ. J. 2020, 14, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xu, H. Cultural Integration and Rural Tourism Development: A Scoping Literature Review. Tour. Hosp. 2023, 4, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yue, K.; Zhang, X. Ignored Opinions: Villager-Satisfaction-Based Evaluation Method of Tourism Village Development—A Case Study of Two Villages in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Speer, J.H.; Thapa, I. Analyzing Resilience in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem after the 1988 Wildfire in the Western US Using Remote Sensing and Soil Database. Land 2022, 11, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sindín, X.S.; Chen, T.H.K.; Prishchepov, A.V. Are night-time lights a good proxy of economic activity in rural areas in middle and low-income countries? Examining the empirical evidence from Colombia. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.; Kastenholz, E.; Lane, B. Challenges for collecting questionnaire-based onsite survey data in a niche tourism market context: The case of wine tourism in rural areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).