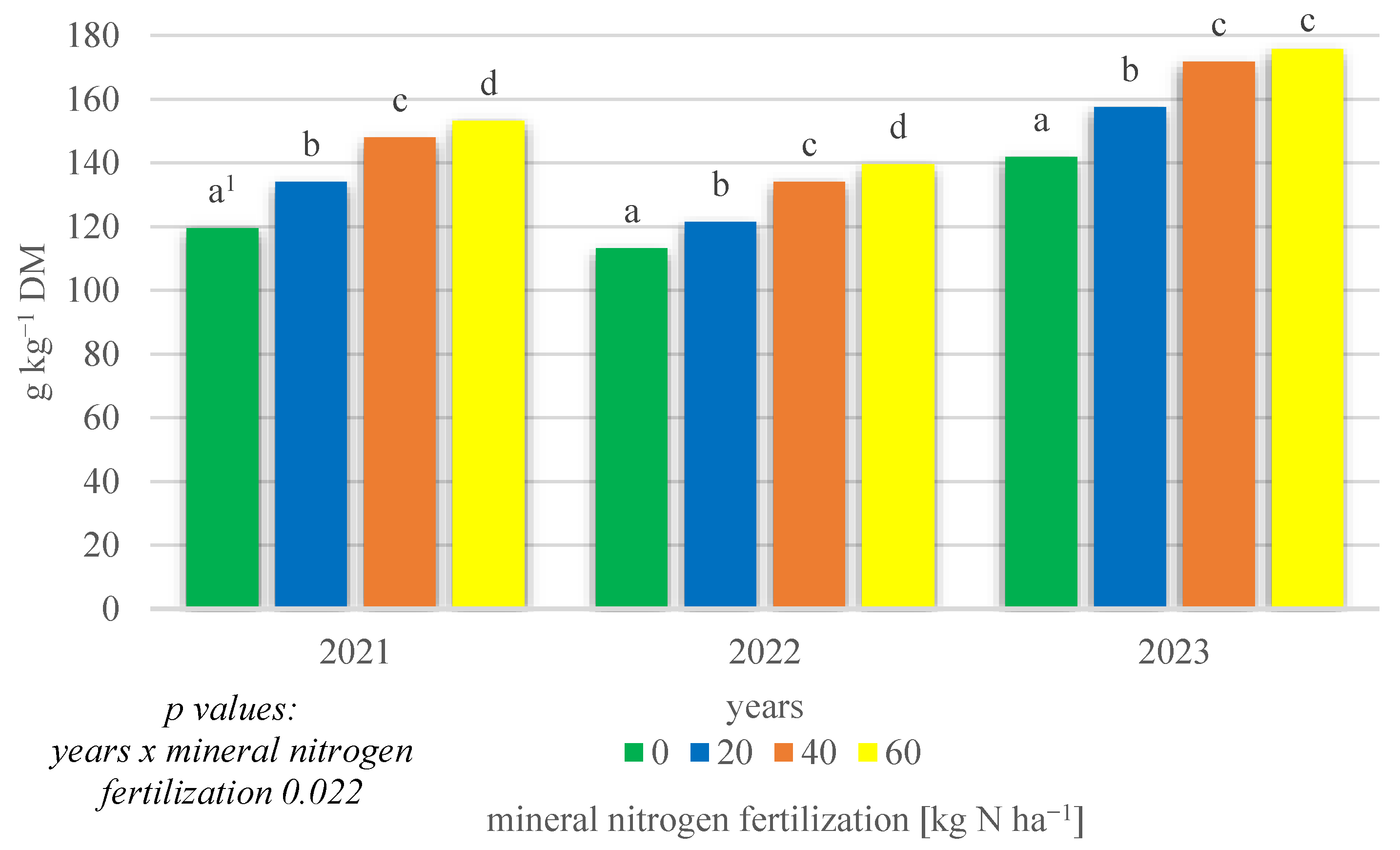Abstract
Intercropping of legumes and cereals can bring many benefits to agriculture, including an increase in yield and the quality of the crops obtained. In addition, it is possible to reduce mineral fertilization, which can have a positive impact on the environment. The aim of the field research conducted in 2021–2023 in central Poland was to evaluate the yields obtained, the content and yield of total protein and the value of land equivalent ratio in the intercropping of narrowleaf lupine with cereals at different seeding levels of components and variable mineral nitrogen fertilization. The following factors were tested: 1—share of components in the sowing: narrowleaf lupine (NL) 120 seeds m−2; spring barley (SB) 300 seeds m−2; M1—NL 30 + SB 225 seeds m−2; M2—NL 60 + SB 150 seeds m−2; M3—NL 90 + SB 75 seeds m−2; spring triticale (ST) 450 seeds m−2; M4—NL 30 + ST 340 seeds m−2; M5—NL 60 + ST 225 seeds m−2; M6—NL 90 + ST 115 seeds m−2; 2—mineral fertilization with nitrogen 0, 20, 40, 60 kg N ha−1. The most favorable results were obtained with mixtures containing 60 + 150 seeds m2 of narrowleaf lupine + spring barley and 90 + 115 seeds m−2 of narrowleaf lupine + spring triticale. In addition, the favorable results and the lack of significant differences at fertilization of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1 show the possibility of a limited dose of mineral nitrogen fertilization. Sowing narrowleaf lupine with spring barley at a ratio of 60 + 150 seeds m2 or with spring triticale at a ratio of 90 + 115 seeds m−2 and fertilizing with 40 kg N ha−1 can be recommended for agricultural practice. The proposed management technique ensures high yields of good quality and thus can be an interesting solution for sustainable cultivation and be successfully implemented on farms.
1. Introduction
Intercropping is a management technique in which two or more species are grown on the same area at the same time [1]. One of the most common intercropping practices is the cultivation of mixtures of legumes with cereals [2]. Such a crop can be used for grain feed, green fodder, silage or green manure [3]. Due to the global increase in demand for animal products [4], the need for feeds with high nutritional value continues to grow [5]. Cereals and legumes are important forage crops because of their nutritional value [6]. However, forage obtained solely from cereals is characterized by a relatively low protein content; therefore, the inclusion of legumes that contain high levels of protein significantly improves the quality of the forage obtained [7]. In addition to the higher quality of forage obtained from growing legumes with cereals, such cropping systems have higher yields and greater stability compared to monoculture, which is attributed to more efficient use of light, water and nutrients [2]. Higher yields are also often linked to better suppression of weeds [8] and diseases [9] by intercropping. According to Nelson et al. [10], sowing mixtures also mitigates the effects of water scarcity and drought on crop production. This is particularly important as climate change continues and periods of precipitation deficiency become more frequent [11]. An important benefit of including legumes in crops with cereals is their symbiosis with nodule bacteria that guarantees the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-available form [12]. Biologically bound nitrogen can be utilized by both the legume and the crops grown with them in mixture [13]. In addition, strong competition for soil nitrogen between legumes and cereals leads to an increase in atmospheric nitrogen fixation by legumes compared to single crops [14]. In addition, a benefit of intercropping legumes with cereals is their positive impact on soil quality. The reason for this is primarily due to the benefits of the legume component, whose cultivation is known for restoring soil fertility [15]. In addition to the mentioned increase in the pool of available nitrogen in the soil, legumes also have the ability to modify the pH of the rhizosphere and thus increase the availability of other nutrients. Also, the fact that legumes are deeply rooted can have a positive effect on soil structure [16]. Intercropping systems are also characterized by a greater diversity of roots and residues, which improves the energy supply of soil microbial biomass through the release of secretions such as amino acids and organic acids [17]. As a result, the effect of these residues on soil microbial biomass is more noticeable than in monoculture cultivation. The diversity of microbial community structure in the rhizosphere soil in an intercropping system is generally greater than in a monocropping system [18]. Thus, intercropping legumes with cereals can halt the downward trend of productivity in a continuous cereal–cereal system [19]. In order for the aforementioned benefits to be achieved to the highest possible degree, it is important to select the right plant species as well as the proportion of their sowing in order not to make the crop overly competitive [3]. Lupine is one of the main legumes grown in Europe [20] and can be a good alternative to soybeans due to its high protein content [21]. Lupine species additionally have high tolerance to various environmental stresses, excess nitrates, lime or salinity and therefore can be grown in many areas [22]. In contrast, lupine crops, like many legumes, are susceptible to weed infestation and yield variability due to water shortages [23]. The limitation of using lupins for feed purposes for many years has been due to the presence of antinutritional factors, mainly quinolizidine alkaloids. Alkaloids give the plants a bitter taste, thereby reducing their nutritional value, intake and digestibility [24]. The level of alkaloids is generally higher in the seeds of the plants than in the vegetative parts [25]. Additionally, modern lupine varieties contain very low levels of alkaloids [26]. Therefore, this plant can be successfully used as feed for livestock [3]. Triticale, on the other hand, can produce large amounts of biomass, is stable in yield and grows well under arid and semi-arid conditions, and it is suitable for most soil types [27]. In contrast, the quality of forage obtained from triticale is better than oats, but slightly worse than barley or corn [28]. Barley, on the other hand, can grow in unfavorable agroclimatic conditions [29] and marginal environments unsuitable for other cereals [30]. Potentially, therefore, the simultaneous cultivation of narrowleaf lupine with spring triticale or spring barley can allow farms to increase self-sufficiency in the production of green fodder with a relatively high protein content.
Nitrogen and water deficit are considered to be the main factors limiting crop yields [31]. Nitrogen, which is involved in physiological and metabolic activities of plants, is an important nutrient element in ecosystems and is an essential element for plant growth [32]. Improper use of nitrogen fertilizers not only increases environmental costs and pollution from agricultural production but also reduces nitrogen use efficiency [33]. Intercropping legumes with cereals can reduce the need for mineral fertilizers and thus lower production costs and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture [34]. Rational management of mineral fertilizers is additionally an important part of agriculture due to the fact that they are the main component of cost intensity in cultivation [35], and the global efficiency of nitrogen use from mineral fertilizers is only approximately 35% [36].
The variability in yield and quality of yields obtained from intercropping legumes with cereals in relation to soil and climatic conditions and the share and species of each component in the sowing [3] suggests the need for further field research in this research area. In addition, the high use of nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture and their negative impact on the environment highlights the need to develop field crop management techniques that reduce the use of mineral fertilizers without yield losses [16]. Therefore, field research was carried out with the aim of evaluating how different mutual sowing ratios of narrowleaf lupine with spring triticale or spring barley and different levels of mineral nitrogen fertilization affect the obtained dry matter yield, total protein content and total protein yield. The research hypothesis assumed that the appropriate share of components in sowing and optimized doses of mineral nitrogen fertilization would produce optimal yields of satisfactory quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology
Field research was conducted from 2021 to 2023 in central Poland in Ciechanów (52°52′54″ N 20°36′38″ E) in a temperate climate. The soil characteristics before the field experiment are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
The soil characteristics before the field experiment.
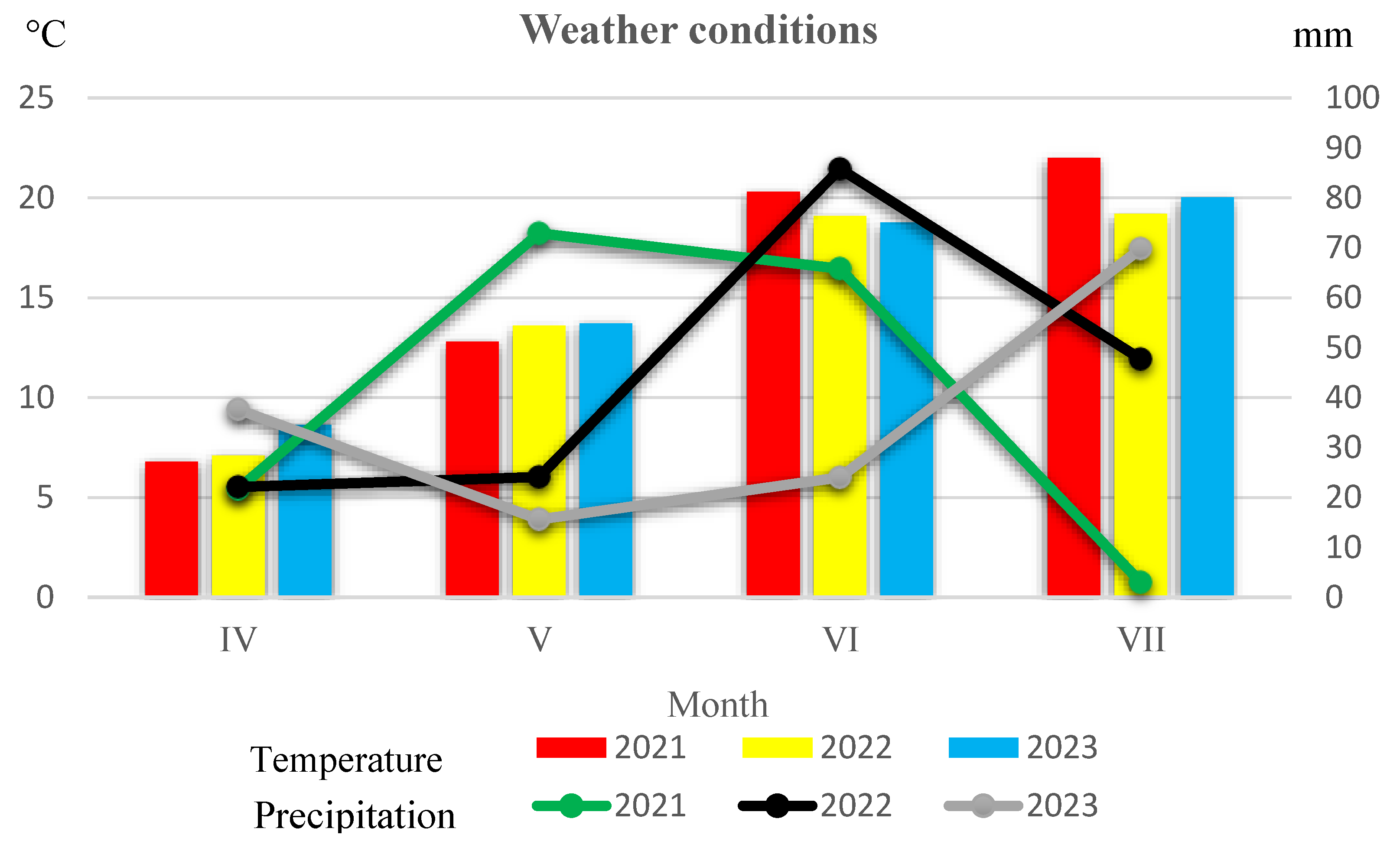
Weather conditions during the growing seasons of the three years of the experiment were obtained from the meteorological station of the Ignacy Mościcki University of Applied Sciences in Ciechanów. The weather conditions are shown in Figure 1.
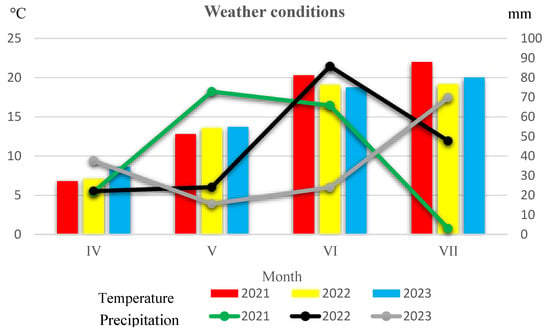
Figure 1.
Weather conditions during the growing seasons of field research according to the Ignacy Mościcki University of Applied Sciences in Ciechanów Meteorological Station.
2.2. Agrotechnological Practices
The field experiment was conducted in triplicate each year; the area of one experimental object was 20 m2 (4 × 5 m). Two factors of the experiment were tested: 1—the share of each component in sowing (Table 2); 2—mineral nitrogen fertilization: 0 kg N ha−1, 20 kg N ha−1, 40 kg N ha−1, 60 kg N ha−1.

Table 2.
The share of narrowleaf lupine, spring barley and spring triticale in sowing.
The forecrop in all years of research was oats. Pre-sowing fertilization was applied on all experimental objects at a rate of 35 kg P ha−1 and 100 kg K ha−1. For sowing, the low-alkaloid, sweet narrowleaf lupine variety Wars, the spring barley variety Farmer, and the spring triticale variety Milewo were used. Narrowleaf lupine seeds were inoculated with Bradyrhizobium lupini before sowing. The inoculant used contained 2 × 109 CTU ml−1. Inoculations were applied at a rate of 500 mL/1000 mL water 120 kg−1 narrowleaf lupine seeds. The sowing of seeds of narrowleaf lupine, spring triticale and spring barley according to factor 1 of the experiment was carried out in April each year. The seeding rate of individual plants in single sowings was based on variety recommendations. However, the intercropping was established according to the scheme of 25 + 75%, 50 + 50% and 75 + 25% of the respective components in the sowing. Sowing was carried out in two separate passes: in the first pass narrowleaf lupine was sown in the second pass spring triticale or spring barley. The row spacing was 20 cm. After sowing, harrowing was used to cover the seeds.
2.3. Data Collection
Crop harvesting was carried out at the flat green pod stage of narrowleaf lupine. The harvesting area was 1 m2 from each experimental object. After harvesting, narrowleaf lupine and cereal plants were separated, after which the yield obtained was determined. To determine the dry matter (DM) yield, the obtained samples were dried in an Ecocell 111 BMT (BMT Medical Technology, Brno, Czech Republic) dryer at 65 °C to a constant weight. The DM of the samples was ground to prepare them for chemical analysis. The obtained N content (Kjeldahl method) was multiplied by 6.25 to obtain the total protein content. Total protein yield was determined as the product of DM and total protein content. The land equivalent ratio (LER) was calculated as [37]:
where Y l and Y c are the yields of narrowleaf lupine and spring triticale/spring barley, respectively, in monoculture crops, and Y li and Y ci are the yields of narrowleaf lupine and spring triticale/spring barley, respectively, in intercropping.
LER = (Y li/Y l + Y ci/Y c),
2.4. Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, a three-way ANOVA was used to analyze the effects of the share of each component in sowing, mineral nitrogen fertilization, years of field research and interactions on the DM yield, content protein, protein yield and LER. The significance of sources of variability was tested using the Fisher–Snedecor F-test (p ≤ 0.05) and the differences between the compared averages were verified using Tukey’s HSD test (p ≤ 0.05). The strength of the relationships between DM yield, total content protein and total protein yield was assessed by calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficients. All the calculations were performed in Statistica, version 13.3 (Hamburg, Germany).
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Variance
The results of the analysis of variance of the obtained DM yield, total protein content, total protein yield and LER depending on the years of field research, share of each component in sowing, mineral nitrogen fertilization and interaction are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Analysis of variance of DM yield, total protein content, total protein yield and LER.
3.2. Dry Matter Yield
The field experiment demonstrated a significant effect of mixture components (p < 0.001) on the dry matter (DM) yield obtained (Table 4).

Table 4.
Dry matter yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to the share of seeds in sowing and mineral nitrogen fertilization (average of 2021–2023) (t ha−1).
Statistically, the highest yields were obtained from mixtures M5 and M6, in which spring triticale was the cereal component. Compared to the narrowleaf lupine crop, the DM yields obtained were 66 and 64% higher, while for spring triticale they were 33 and 31% higher for the M5 and M6 mixtures, respectively. On objects where spring barley was the cereal component, the highest DM yields were obtained for mixtures M2 and M3. Compared to the narrowleaf lupine crop, the yields obtained were 41 and 37% higher, while compared to spring barley they were 33 and 28% higher for the M2 and M3 mixtures, respectively. In the experiment conducted, nitrogen fertilization also had a significant effect (p < 0.001) (Table 4). Statistically, the highest yields were obtained with fertilization of 60 and 40 kg N ha−1. Relative to control objects without mineral nitrogen fertilization, higher average yields were obtained by 60 and 59% for 60 and 40 kg N ha−1, respectively. A mixture × mineral nitrogen fertilization interaction was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) with respect to DM yield (Table 4). In the narrowleaf lupine crop, the highest DM yields were obtained with fertilization at 20 and 40 kg N ha−1. However, fertilization at 40 kg N ha−1 was not statistically different from the other fertilization levels. Also in triticale and spring barley, the highest DM yields were obtained at the two highest fertilization levels. DM yields in the cultivation of mixtures followed a similar pattern. The exception was the M6 mixture from which statistically the highest yields were obtained at a fertilization of 40 kg N ha−1.
Growing season conditions also significantly differentiated (p < 0.001) the DM yield obtained (Table 5).

Table 5.
Dry matter yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing in 2021–2023 (t ha−1).
The highest DM yields were obtained in 2021, were lower in 2022 and the lowest in 2023. Compared to 2021, the DM yields obtained in 2022 were lower by 11% and in 2023 by 41%. Significant integration of growing season conditions × mixture components was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) (Table 5). In 2021, the highest DM yields, not statistically different, were obtained from mixtures M2, M3, M5 and M6. On the other hand, in 2022 and 2023, the highest yields were obtained from mixtures M5 and M6.
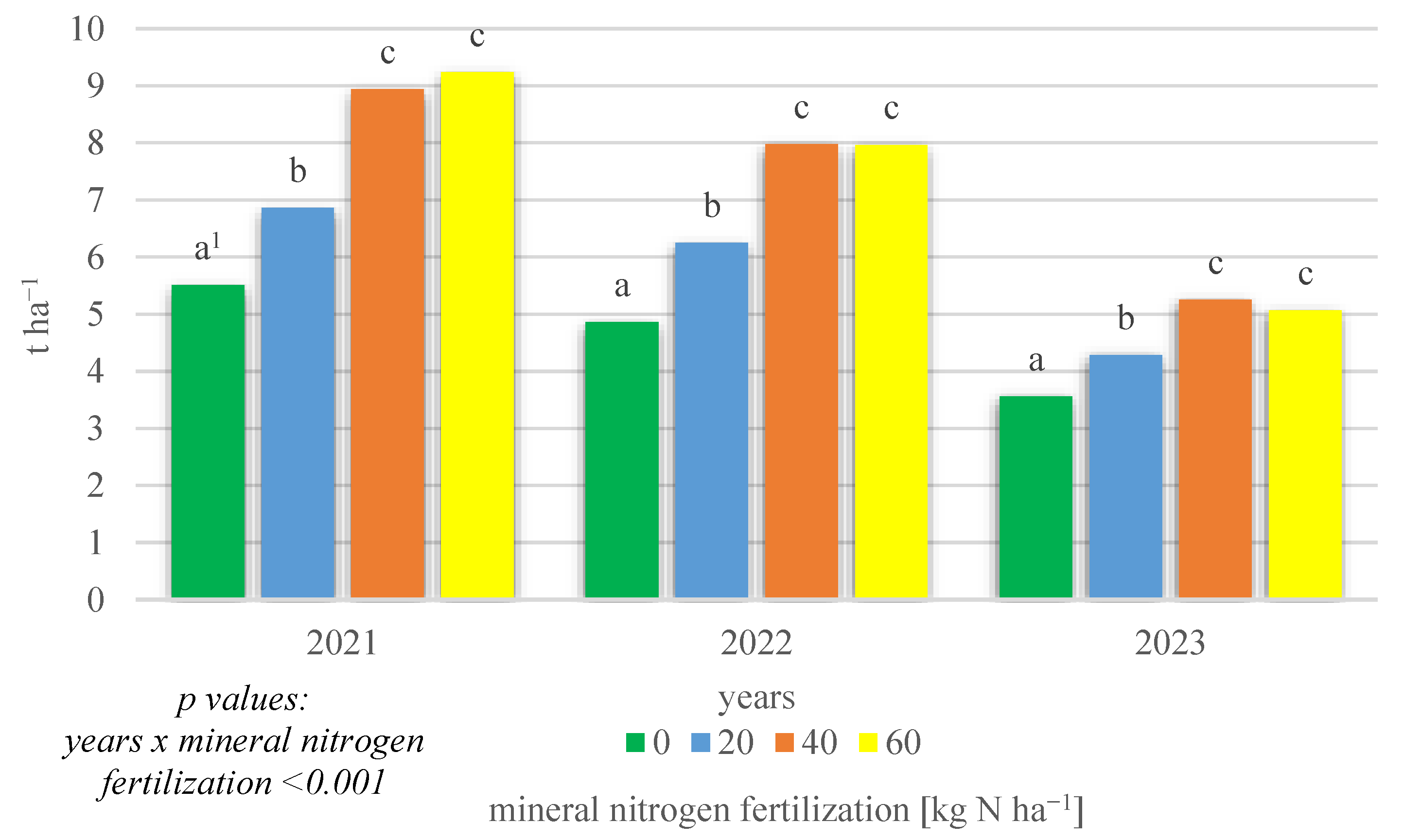
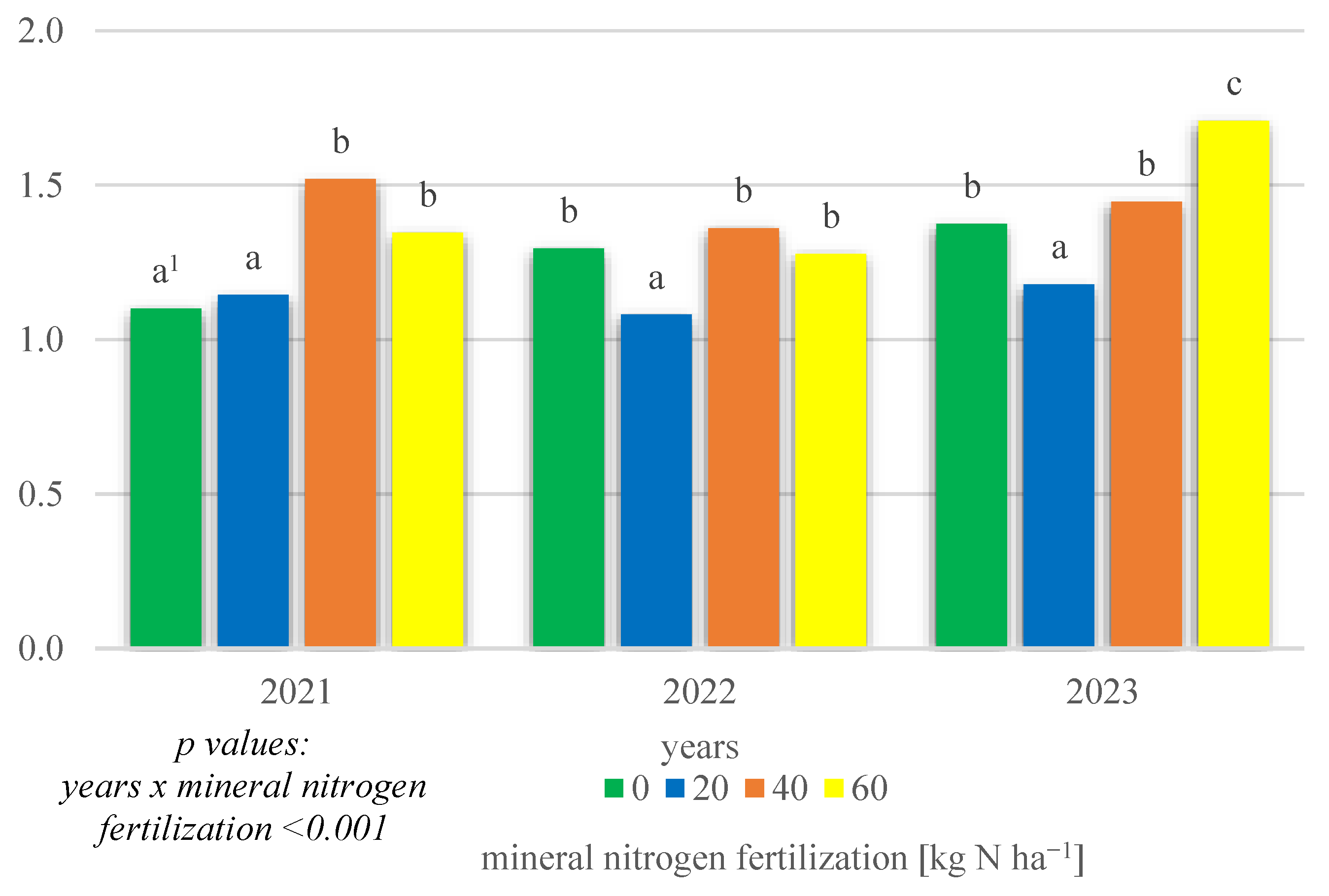
The field research also demonstrated a significant interaction of growing season conditions × mineral nitrogen fertilization (p < 0.001) (Figure 2).
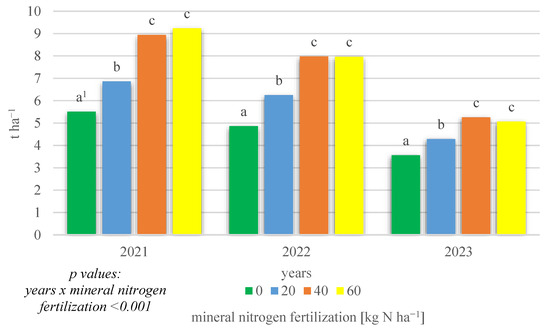
Figure 2.
Dry matter yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to mineral nitrogen fertilization in 2021–2023 (t ha−1). 1 Values in years for the interaction years × mineral nitrogen fertilization followed by the same small letter above the bar (a, b, c) do not differ significantly at p ≤ 0.05.
This shows that, in all years of the research conducted, the highest DM yields were obtained with fertilizations of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while the lowest yields were obtained with no mineral nitrogen fertilization.
3.3. Total Protein Content
The sown mixture significantly differentiated the total protein content (p < 0.001) of DM (Table 6).

Table 6.
Total protein content of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to the share of seeds in sowing and mineral nitrogen fertilization (average of 2021–2023) (g kg−1 DM).
The DM of narrowleaf lupine demonstrated the highest total protein content, while the DM of cereals was the lowest. However, the total protein content was significantly higher in the DM of spring barley compared to spring triticale. Thus, mixtures that included spring barley had higher DM total protein content. Among the mixtures, the highest total protein content was found in mixture M3. In terms of total protein content, the DM of narrowleaf lupine was 6% lower, while compared to the DM of spring barley it was 54% higher. The highest total protein content among mixtures that included spring triticale was obtained from mixture M6. The obtained content of total protein in the M6 mixture was lower than that obtained in narrowleaf lupine by 28%, while it was higher than that in spring triticale by 41%. Also, the amount of mineral nitrogen fertilization applied significantly affected the total protein content (p < 0.001) (Table 6). The highest total protein content was found when 40 and 60 kg N ha−1 were applied. Compared to objects where mineral nitrogen fertilization was not applied, total protein content was 21 and 25% higher for 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, respectively. A significant interaction of seeded mixture composition × mineral nitrogen fertilization was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) (Table 6). In the case of spring barley and spring triticale crops, the content of total protein increased significantly with successive increases in mineral nitrogen fertilization up to the statistically highest obtained at a fertilization of 60 kg N ha−1. On the other hand, in the narrowleaf lupine crop, the highest DM total protein content was found at a fertilization of 40 kg N ha−1, lower at 60 kg N ha−1, successively for fertilization of 20 and 0 kg N ha−1. When growing mixtures with spring barley in the M1 and M2 mixtures, the highest total protein content was found at a fertilization of 60 kg N ha−1, while in the M3 mixture it was found at 40 and 60 kg N ha−1. Mixtures in which spring triticale was the cereal component showed the highest total protein content in DM when fertilization was applied at 40 and 60 kg N ha−1.
Field research also demonstrated a significant effect of growing season conditions (p < 0.001) on DM total protein content (Table 7).

Table 7.
Total protein content of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing in 2021–2023 (g kg−1 DM).
The DM of crops harvested in 2023 had the highest total protein content, which was lower in 2021 and significantly lower in 2022. Compared to 2023, in 2021 the total protein content was 14% lower, while in 2022 it was 21% lower. A significant interaction of growing season conditions × share of components in the seeded mixture was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) (Table 7). The highest total protein content in all years of research was obtained in the DM of narrowleaf lupine, while the lowest was obtained in the DM of spring triticale. In the case of mixtures, a significant increase in total protein content was found in all years of field research with increasing the proportion of narrowleaf lupine sown.
A statistically significant interaction of growing season conditions x mineral nitrogen fertilization was also demonstrated (p = 0.022) (Figure 3). In 2021 and 2022, the highest total protein content was found at 60 kg N ha−1 fertilization. Reducing the amount of mineral nitrogen fertilization resulted in a statistically significant decrease in total protein content down to the lowest level obtained with no nitrogen fertilization. In 2023, the highest total protein content was found when fertilization was applied at 40 and 60 kg N ha−1. On the other hand, it was the lowest in the absence of nitrogen fertilization.
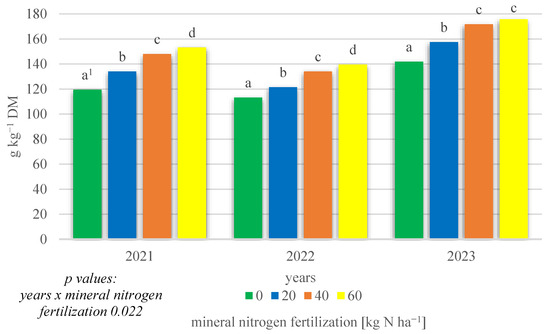
Figure 3.
Total protein content of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to mineral nitrogen fertilization in 2021–2023 (g kg−1 DM). 1 Values in years for the interaction years × mineral nitrogen fertilization followed by the same small letter above the bar (a, b, c, d) do not differ significantly at p ≤ 0.05.
3.4. Total Protein Yield
Total protein yield was statistically significantly influenced by the proportion of components (p < 0.001) sown on each object (Table 8).

Table 8.
Total protein yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing and mineral nitrogen fertilization (average of 2021–2023) (kg ha−1).
The lowest total protein yield was obtained on objects on which spring barley and spring triticale were sown. The highest total protein yield, on the other hand, was obtained when M2, M3 and M6 mixtures were sown. The obtained yield of total protein on these experimental objects was at the same statistical level. The cultivation of mixtures M2 and M3, in which spring barley was the cereal component yield of total protein, was 86 and 90% higher, respectively, compared to spring barley. On the other hand, in the M6 mixture, in which spring triticale was the cereal component, the total protein yield obtained was 75% higher compared to the objects in which spring triticale was the test crop. Also, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied significantly influenced the obtained yield of total protein (p < 0.001) (Table 8). Significantly, the highest yields of total protein were obtained at fertilization rates of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1. Compared to control objects with no N fertilization, the obtained values were 90 by 96% higher for fertilization rates of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, respectively. The field experiment also demonstrated a significant interaction of the share of components in the sown mixture × mineral nitrogen fertilization (p < 0.001) (Table 8). On objects where narrowleaf lupine was grown, the highest total protein yields were found at fertilization levels of 20 and 40 kg N ha−1. In contrast, in the other sowings tested, with the exception of the M1 and M6 mixtures, the highest yields of total protein that were not significantly different were obtained at fertilization levels of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1. In the M1 mixture, the highest total protein yields were obtained at a fertilization of 60 kg N ha−1, while in the M6 mixture they were obtained at a fertilization of 40 kg N ha−1.
Growing season conditions also significantly differentiated the total protein yield obtained (p < 0.001) (Table 9).

Table 9.
Total protein yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing in 2021–2023 (kg ha−1).
The highest protein yield was obtained in DM harvested in 2021, which was lower in 2022 and significantly lower in 2023. The total protein yield obtained in 2021 was higher than that in 2022 by 26%, while that obtained in 2023 was higher by 47%. A significant interaction of growing season conditions × seeded mixture components was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) (Table 9). In all years of the experiment, the lowest total protein yields were obtained from spring barley and spring triticale crops. In 2021, the highest total protein yields were obtained from the M2 and M3 mixtures. In the 2022 growing season, the highest total protein yields were recorded on objects where M2, M3 and M6 were grown. On the other hand, in 2023 the M5 and M6 mixtures showed the highest total protein yields.
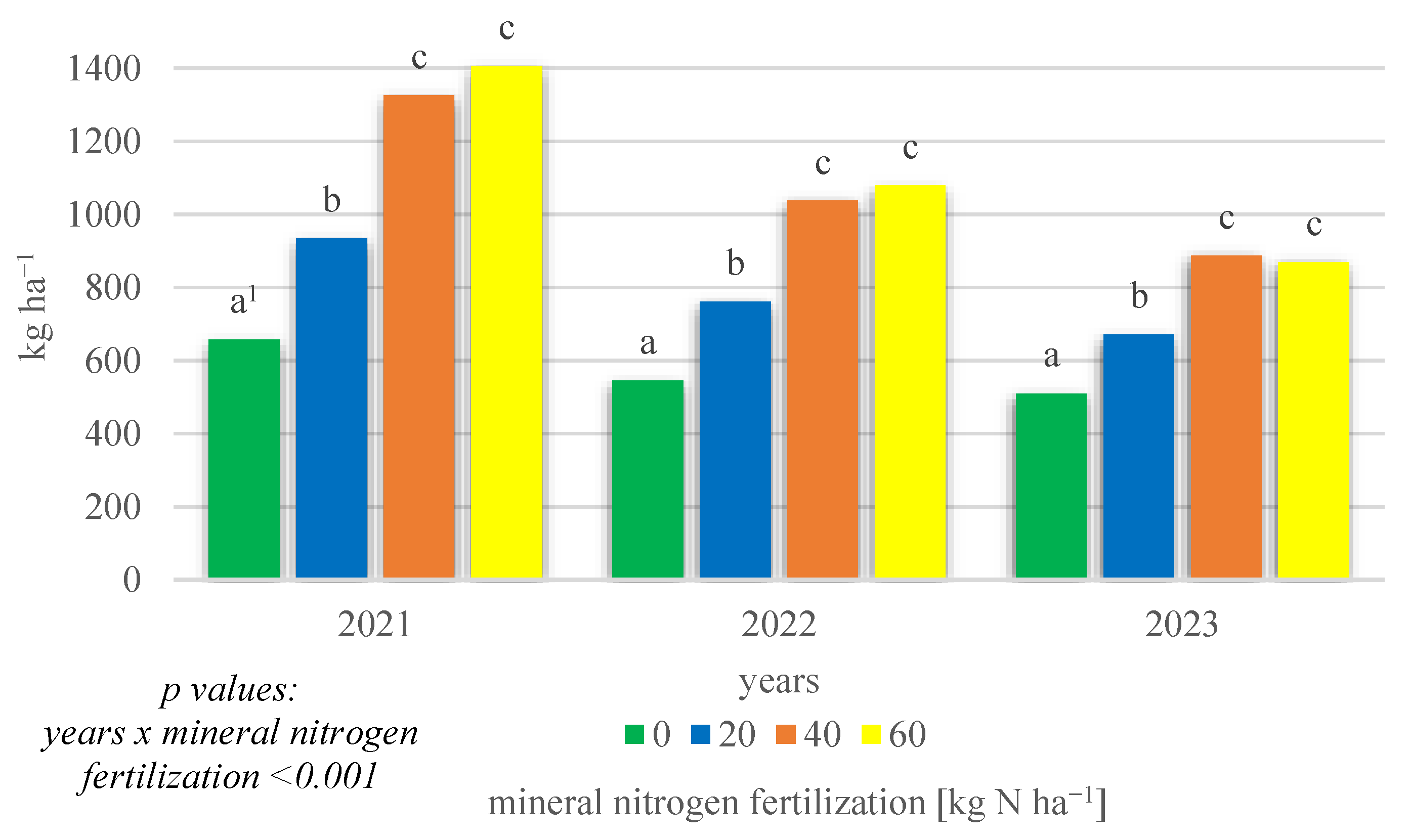
The field research also demonstrated a significant interaction of growing season conditions × mineral nitrogen fertilization (p < 0.001) affecting the total protein yield obtained (Figure 4). In all years of the research, significantly the highest total protein yields were obtained on objects where mineral fertilization was applied at 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while the lowest yields were obtained in the absence of mineral nitrogen fertilization.
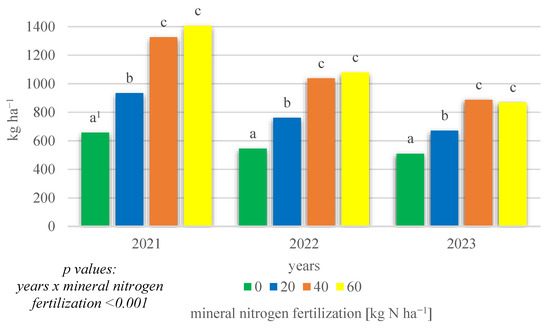
Figure 4.
Total protein yield of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to mineral nitrogen fertilization in 2021–2023 (kg ha−1). 1 Values in years for the interaction years × mineral nitrogen fertilization followed by the same small letter above the bar (a, b, c) do not differ significantly at p ≤ 0.05.
The correlation analysis demonstrated a highly significant effect (p < 0.001) of mixture yield as well as total protein content on the total protein yield obtained (Table 10).

Table 10.
Correlation coefficients between DM yield, total protein content and total protein yield.
However, the obtained correlation value was clearly higher for yield compared to total protein content. In contrast, the obtained negative correlation between total protein content and yield was not statistically significant (p = 0.248).
3.5. Land Equivalent Ratio (LER)
The LER value in the field research conducted was significantly differentiated by the proportion of components in the sown mixture (p < 0.001) (Table 11).

Table 11.
LER of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing and mineral nitrogen fertilization (average of 2021–2023).
The lowest LER values were obtained for mixtures M1 and M4, in which cereal sowing predominated. However, in the other mixtures (M2, M3, M5 and M6), the LER value was at the same highest statistical level. The LER value was 17 to 33% higher in these mixtures with respect to mixtures M1 and M4. The level of mineral N fertilization also significantly affected the LER value (p < 0.001) (Table 11). The highest LER values were obtained for mixtures fertilized with 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while they were significantly lower for the other N fertilization variants analyzed. The field research also demonstrated a significant interaction of the proportion of components in the mixture × N fertilization (p = 0.004) (Table 11). In the case of mixtures M1 and M4, in which the predominance of cereals was sown regardless of the nitrogen rate, the LER value was at the same level. In the M2 mixture, the highest LER was revealed at fertilization rates of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1. In addition, LER values for fertilization of 40, 20 and 0 kg N ha−1 were at the same statistical level. The highest LER in the seeded M3 mixture was revealed for a fertilization of 40 kg N ha−1. However, no significant differences were found between this fertilization level and 60 and 0 kg N ha−1. In addition, statistical analysis demonstrated the same statistical level of LER for fertilization of 60, 20 and 0 kg N ha−1. However, for the M5 and M6 mixtures, the highest LER values were demonstrated for objects fertilized with 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, and they were significantly lower for 0 and 20 kg N ha−1.
In the field research conducted, growing season conditions also significantly affected (p < 0.001) the LER value (Table 12).

Table 12.
LER of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according on the share of seeds in sowing in 2021–2023.
The significantly highest value was found in 2023, while significantly lower values were found in 2021 and 2022. Compared to 2023, the LER value in 2021 was lower by 10% and in 2022 by 12%. A significant interaction effect of growing season conditions × share of components in the seeded mixture was also demonstrated (p < 0.001) (Table 12). In 2021, the highest LER values statistically at the same level were demonstrated in all mixtures except M4. Thus, the M4 mixture had the lowest LER value; in addition, it was not significantly different from the M1 mixture. In 2022, the highest LER values were demonstrated in mixtures M2, M3, M5 and M6, while significantly lower values were demonstrated in mixtures M1 and M2. In addition, no statistically significant differences were found between mixtures M1, M2, M3 and M4, and in 2023 the highest LER value was demonstrated on objects where M6 and M5 mixtures were sown, significantly lower when M2, M3 and M4 mixtures were sown, and the lowest for the M1 mixture. In addition, the M1 and M4 mixtures, with a predominance of grain in the sown components, had the same statistical level.
The field experiment also demonstrated a significant interaction effect of growing season conditions × mineral N fertilization (p < 0.001) on LER values (Figure 5). In 2021, the highest LER was demonstrated on objects fertilized with 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while it was significantly lower at 0 and 20 kg N ha−1. In 2022, the highest LER was revealed on objects fertilized with 0, 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while it was significantly lower at 20 kg N ha−1. On the other hand, in 2023 the significantly highest LER was revealed on objects with fertilization at 60 kg N ha−1, and it was lower at N rates of 0 and 40 kg N ha−1 and significantly lower at a fertilization of 20 kg N ha−1.
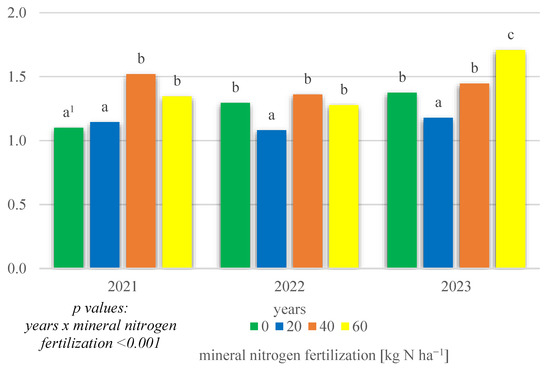
Figure 5.
LER of intercropping narrowleaf lupine with cereals according to mineral nitrogen fertilization in 2021–2023. 1 Values in years for the interaction years × mineral nitrogen fertilization followed by the same small letter above the bar (a, b, c) do not differ significantly at p ≤ 0.05.
4. Discussion
Growing mixtures of legumes with cereals is considered an effective way to improve forage yields [38]. Many scientific studies report higher yields compared to monoculture crops; however, the yields largely depend on the proportion of components in the sown mixtures [39]. Research by Wang et al. [40] demonstrated higher forage yields from 28.7 to 66.4% when the sowing ratio of oats to vetch was 50 + 50% compared to monocultures. On the other hand, Šarūnaitė et al. [34] demonstrated 9% higher biomass yields in a crop with an equal share of pea and oat components, and 13% higher when the share was 60 + 40%, respectively, compared to a pea crop. On the other hand, Sohail et al. [7], at a sowing rate of 70 + 30% for barley or oats + vetch, obtained higher biomass yields of 52 to 57% compared to the legume and comparable yields to the grain crop. The yield increases obtained for mixed crops compared to monocultures in our study are similar to those obtained by the cited authors. They amounted for mixtures of lupine with barley from 18 to 41% and mixtures with triticale from 40 to 66%. However, in contrast to the results presented by Baxevanos et al. [41], the obtained yields of mixed crops were also higher than those of cereal monocultures. The increase in yield of mixtures with respect to monocultures is attributed to greater efficiency in the use of resources during plant growth, such as water, nutrients and light [42]. This is supported by the results presented by Bouras et al. [43], in which higher water use was demonstrated by the biomass of legume–legume mixtures, especially under conditions of limited water availability. On the other hand, research by Umesh et al. [44] proved higher light interception and effective radiation utilization by mixtures of corn and sorghum with legumes compared to single crops. In turn, better nutrient utilization is linked to the root morphology of cereals and legumes [45]. Cereals are characterized by roots that are much finer and generally occupy the top layers of the soil compared to lupins with a tap root [46,47]. Thus, cereals can explore larger volumes of topsoil [48], forcing lupins to draw nutrients from deeper layers. Temporal resource requirements are also important. According to research by other authors [23,49,50], barley and triticale show high biomass production in the early growth stages, much earlier than peas or lupins. However, from the flowering stage onward the growth rate of lupine increased significantly, while that of triticale decreased significantly [23]. Thus, the significantly shifted period of maximum growth allows for complementarity of resource use over time.
Mineral fertilization with nitrogen in many conducted studies led to an increase in the yield of legume–cereal mixtures [43,51,52,53]. An analogous relationship was obtained in the studies conducted. According to Salinas-Roco et al. [14], N fertilization in legume–cereal crops primarily benefits cereals by promoting increased photosynthesis and accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, resulting in better growth. Thus, cereals show high competition with legumes, especially in terms of soil nitrogen resources [54]. Increased competition from cereals forces legumes, in turn, to rely heavily on atmospheric nitrogen fixation to meet their needs [55]. The mutual competition for nitrogen between cereals and legumes has an additional agricultural benefit. Greater nitrogen uptake by cereals helps reduce nodule inhibition in legumes as a result of excess nitrogen in the soil [14]. On the other hand, with high levels of biological nitrogen fixation, up to 70% of the nitrogen can be transferred to the soil [56]. Therefore, this nitrogen can benefit crops grown in mixture with legumes [57,58]. However, field research demonstrated a lack of yield increase effect between nitrogen rates of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1, while narrowleaf lupine had higher yields at lower nitrogen fertilization rates. Also, studies by Salinas-Roco et al. [14] and Carton et al. [23] found no significant improvement in the DM yields of legumes and mixtures with cereals with increasing nitrogen fertilization. Such crop response can be explained by the fact that legumes, as a result of the efficient fixation of atmospheric nitrogen, compensate for the reduced availability of nitrogen from mineral fertilizers [59]. On the other hand, the higher DM yield of lupins when fertilized with 40 rather than 60 kg N ha−1 can also be linked to the formation of nodules and thus the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. Latati et al. [60] indicated a higher biomass of chickpea nodules at reduced soil nitrogen content; thus, excess nitrogen causes inhibition of nodule formation [61]. According to Tamiru et al. [62], legumes can fix up to 111 kg N ha−1 in a year. Thus, the effective fixation of atmospheric nitrogen can far exceed the amount of nitrogen supplied from mineral fertilizers, which can translate into the yield obtained. The availability of nutrients in the soil and the proper selection of crops to be grown in a mixture are linked to the quality of the resulting forage [63,64]. Legumes generally have a higher total protein content compared to cereals [65], which was also confirmed in the presented field experiment. Thus, with an increase in the sowing rate of narrowleaf lupine, an increase in the concentration of total protein in the obtained green mass was recorded. Also, other authors recorded an increase in the total protein content of mixtures in legumes compared to cereal crops [66,67,68]. The average increase in total protein content obtained in our study at 43% for mixtures with barley and 30% for mixtures with triticale was much higher than that reported by Soufan and Al-Suhaibani [69] at 10% with barley–pea mixtures. The increase in protein content in the biomass obtained can also be linked to increased nitrogen availability, as higher levels of available nitrogen result in better protein biosynthesis [70]. Similar to the studies conducted by Krga et al. [71] and Tamta et al. [72], an increase in the level of nitrogen fertilization resulted in an increase in the total protein content of the obtained yield. However, in the study conducted, the total protein content at 60 and 40 kg N ha−1 showed no significant differences. This may be due to the aforementioned compensation of the amount of available nitrogen due to the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen by legumes. According to Stagnari et al. [45], non-legumes can benefit from the additional nitrogen released into the soil by legumes. According to Li et al. [58], legumes can provide up to 15% of the nitrogen in cereals grown in mixtures. Also, Clark et al. [57] indicated that peas grown with barley contributed 19% of the nitrogen to the cereal plant after 70 days of cultivation. The total protein yield obtained depends on the total protein content of the biomass and the yields obtained. However, in both the authors’ earlier studies [39] and the one presented here, the yield of the obtained green matter shows a greater influence on the yield of total protein. An analogous relationship was also presented by Faligowska [12] in the case of lupine cultivation in monoculture. As a result, according to the findings of Wang et al. [64], the increase in yield of mixtures compared to monoculture crops resulted in an increase in total protein yield in our study, except for mixtures with a predominance of cereals in sowing. Baxevanos et al. [41], in their study of pea–oat mixtures, obtained a 27% increase in total protein yield compared to oat monoculture. On the other hand, Wang et al. [64] reported an increase in total protein yield in mixtures of vetch with oats by 52% in relation to oats and by 150% in the case of vetch. The average increases in total protein yield obtained in their study were higher, at 72% for mixtures with barley and 54% for mixtures with triticale, compared to cereal monoculture. In contrast, the increase in relation to narrowleaf lupine was much lower (6–18%). Similarly to the studies conducted by other authors [71,73,74], despite the significantly higher total protein content of narrowleaf lupine biomass, its low green matter yields resulted in low total protein yields.
Regarding LER, in many studies different authors showed values greater than 1 in the cultivation of different legume–cereal mixtures, indicating higher resource use efficiency of mixtures compared to monocultures [75,76,77]. Also in our study, LER values for all tested mixtures were higher than unity. In addition, the LER value decreased as the seeding rate of barley or triticale in the mixture increased. Similar observations were also made by Dhima et al. [78] in mixtures of faba bean with oats and Salinas-Roco et al. [14] with mixtures of faba bean or pea with wheat. In our study, higher LER values were obtained with fertilizations of 40 and 60 kg N ha−1 compared to those obtained with fertilizations of 0 and 20 kg N ha−1. On the other hand, the results obtained by other authors [51,55,79] demonstrated the opposite trend, where an increase in mineral nitrogen fertilization led to a decrease in LER value. However, the cited studies analyzed much higher nitrogen fertilization and compared it to no fertilization. According to Kamran et al. [80], in legumes it is important to pre-fertilize with low doses of nitrogen in order to ensure optimal nitrogen availability at the early stages of growth when atmospheric nitrogen fixation does not occur. This may explain the increase in LER obtained in our study at the proposed nitrogen fertilization levels.
Due to the climate changes observed in recent years, manifested by increasing temperatures and water shortages [11], it is important to analyze the yield of plants under varying weather conditions. In our own research, the lowest yields of mixtures of narrowleaf lupine with cereals were obtained in the year with the lowest precipitation during the growing season. Similar results were also obtained by Rad et al. [81] in their study of other legume–cereal mixtures. However, it is crucial to consider the different stages of plant development and the availability of water during this time [82]. According to research by Alghabari et al. [83], water deficits during the flowering period of spring barley can lead to yield losses of approximately 40%, while according to Anwaar et al. [84], water deficits during the reproductive stages of wheat lead to losses of 30%. On the other hand, in the case of legumes, various authors have observed higher yield losses occurring with water deficits at the flowering or pod beginning stages, for chickpea yield reductions of up to 90% [85], soybeans by 45% [86] or beans by 85% [87]. This may explain the lower yields of mixtures obtained in our study in a year with a higher total precipitation but a much lower total during the flowering period of the crops grown. In addition, it can be concluded that cereals tolerate water shortages better compared to legumes. According to Ding et al. [88], cereals maintain positive tissue turgor through osmotic regulation under even high water stresses, thereby maintaining stability in yield. Thus, cereals are more stable in yield under varying weather conditions [66]. Therefore, cereals, when grown with legumes, can act as a yield-stabilizing component, even during growing seasons with rainfall deficiency. In the study conducted, the total protein content of the obtained green forage was found to decrease with increasing precipitation during the growing season. Lower total protein content in the biomass of millet with legumes in a year with higher precipitation was also found by Giannoulis et al. [89] and Gill and Omokanye [90] with many other legume–cereal mixtures. Crops under drought stress increase root length and thus root biomass as a result, and they are able to absorb greater amounts of water and nutrients from the soil [91]. In addition, water shortages result in reduced plant height [92], reduced leaf number [93] and leaf area, which leads to lower total biomass [94]. Based on these statements, it can be assumed that the reduction in the biomass of the vegetative parts of the plants as a result of water shortage and the possible greater availability of nutrients for plant uptake dilution of components will be lower, which will translate into higher nutrient content, including total protein. According to the specified correlation, lower yields in years with limited rainfall translated into lower total protein yields, despite higher total protein contents. In contrast, similar to the studies of Yang et al. [51] and Lauriault et al. [5], the LER value was higher in years with less precipitation during the growing season. The higher LER in years with rainfall deficiency may be due to the higher yield reduction of legumes compared to cereals. Thus, higher productivity of mixtures and better resource utilization became more apparent in dry years [71].
5. Conclusions
Intercropping narrowleaf lupine with spring triticale or spring barley makes it possible to obtain fodder with satisfactory yield and quality results. The most favorable results were obtained from mixtures M2 and M5. In addition, the lack of clear differences between fertilization at 40 and 60 kg N ha−1 suggests that it is possible to use lower doses of mineral nitrogen fertilizers without a clear deterioration in the results obtained. Thus, it can be suggested for introduction in agricultural practice to sow narrowleaf lupine with spring barley at a ratio of 60 + 150 seeds m−2 or with spring triticale at a ratio of 90 + 115 seeds m−2 and fertilization of 40 kg N ha−1. The proposed intercropping management technique can produce satisfactory results in low-input crops with additional positive environmental effects. Very importantly, good cropping results were obtained, both in years with favorable weather conditions and those with less favorable ones, so intercropping of legumes and cereals can be a form of mitigation of unfavorable weather conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.G. and A.P.; methodology, R.G.; software, R.G.; validation, R.G and A.P.; formal analysis, R.G.; investigation, R.G.; resources, R.G.; data curation, R.G. and A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.G.; writing—review and editing, A.P.; visualization, R.G.; supervision, R.G.; project administration, R.G.; funding acquisition, R.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by a subvention for the development of lecturer Ignacy Mościcki University of Applied Sciences in Ciechanów PNW.611.5;1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pankou, C.; Lithourgidis, A.; Dordas, C. Effect of irrigation on intercropping systems of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with pea (Pisum sativum L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomph, T.; Dordas, C.; Baranger, A.; de Rijk, J.; Dong, B.; Evers, J.; Gu, C.; Li, L.; Simon, J.; Jensen, E.S.; et al. Designing intercrops for high yield, yield stability and efficient use of resources: Are there principles? Adv. Agron. 2020, 160, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Księżak, J.; Staniak, M.; Stalenga, J. Restoring the importance of cereal-grain legume mixtures in low-input farming systems. Agriculture 2023, 13, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Food Outlook—Biannual Report on Global Food Markets; Global Information and Early Warning System on Food and Agriculture: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lauriault, L.M.; Darapuneni, M.K.; Martinez, G.K. Pearl millet-cowpea forage mixture planting arrangement influences mixture yield and nutritive value in semiarid regions. Crops 2023, 3, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakeih, N.; Kayyal, H.; Larbi, A.; Habib, N. Forage yield and competition indices of triticale and barley mixed intercropping with common vetch and grasspea in the Mediterranean region. Jordan J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 6, 194. [Google Scholar]
- Sohail, S.; Ansar, M.; Skalicky, M.; Wasaya, A.; Soufan, W.; Ahmad Yasir, T.; El-Shehawi, A.M.; Brestic, M.; Sohidul Islam, M.; Ali Raza, M.; et al. Influence of tillage systems and cereals–legume mixture on fodder yield, quality and net returns under rainfed conditions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.; Sebastià, M.T.; Kirwan, L.; Finn, J.A.; Llurba, R.; Suter, M.; Collins, R.P.; Porqueddu, C.; Helgadóttir, A.; Baadshaug, O.H.; et al. Weed suppression greatly increased by plant diversity in intensively managed grasslands: A continental scale experiment. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 55, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, M.A. Diseases in intercropping systems. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.C.D.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Vadez, V.; Rötter, R.P.; Koch, M.; Whitbread, A.M. Can intercropping be an adaptation to drought? A model-based analysis for pearl millet—Cowpea. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2022, 208, 910–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, E.M.; Osman, H.S.; Gowayed, S.M.; Okasha, S.A.; Omara, A.E.D.; Sami, R.; Abd El-Monem, A.M.; Abd El-Razek, U.A. Minimizing the adversely impacts of water deficit and soil salinity on maize growth and productivity in response to the application of plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria and silica nanoparticles. Agronomy 2021, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faligowska, A. Response of new yellow lupin varieties to inoculation with Bradyrhizobium sp. Lupinus under Central European Conditions. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnalakshmi, K.; Yadav, V.; Tyagi, D.; Dhar, D.W.; Kannepalli, A.; Kumar, S. Significance of plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria in grain legumes: Growth promotion and crop production. Plants 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Roco, S.; Morales-González, A.; Espinoza, S.; Pérez-Díaz, R.; Carrasco, B.; del Pozo, A.; Cabeza, R.A. N2 fixation, N transfer, and Land Equivalent Ratio (LER) in grain legume–wheat intercropping: Impact of N supply and plant density. Plants 2024, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, Y.; Meena, R.S.; Kumar, S. Effect of INM on nodulation, yield, quality and available nutrient status in soil after harvest of greengram. Legume Res.-Int. J. 2016, 39, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, J.; Das, A.; Mitran, T.; Nath, C.; Meena, R.S.; Yadav, G.S.; Shivakumar, B.G.; Kumar, S.; Lal, R. Cereal+ legume intercropping: An option for improving productivity and sustaining soil health. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Meena, R., Das, A., Yadav, G., Lal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Sang, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, N. Response of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity and community in maize and soybean rhizosphere soil and roots to intercropping systems with different nitrogen application rates. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainard, L.D.; Koch, A.M.; Gordon, A.M.; Klironomos, J.N. Growth response of crops to soil microbial communities from conventional monocropping and tree-based intercropping systems. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, S. An agricultural pollutant: Chemical fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Miranda, C.; Trindade, H. Mediterranean lupines as an alternative protein source to soybean. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiewicz, K. Chemical composition of lupin (Lupinus spp.) as influenced by variety and tillage system. Agriculture 2022, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Bartkevics, V.; Starkute, V.; Krungleviciute, V.; Cizeikiene, D.; Zadeike, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Maknickiene, Z. Chemical composition and nutritional value of seeds of Lupinus luteus L., L. angustifolius L. and new hybrid lines of L. angustifolius L. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2016, 103, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carton, N.; Naudin, C.; Piva, G.; Corre-Hellou, G. Intercropping winter lupin and triticale increases weed suppression and total yield. Agriculture 2020, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.M.; Ganopoulos, I.; Madesis, P.; Mavromatis, A.; Mylona, P.; Nianiou-Obeidat, I.; Parissi, Z.; Polidoros, A.; Tani, E.; Vlachostergios, D. The Use of lupin as a source of protein in animal feeding: Genomic tools and breeding approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolko, B.; Clements, J.C.; Naganowska, B.; Nelson, M.N.; Yang, H. Lupinus. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalle, C.L.; Ravindran, V.; Ravindran, G. Nutritional value of white lupins (Lupinus albus) for broilers: Apparent metabolisable energy, apparent ileal amino acid digestibility and production performance. Animal 2012, 6, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elatty, S.A.A.; Nawar, A.I.; Salama, H.S.A.; Khattab, I.M.; Shaalan, A.M. The production of dual-purpose triticale in arid regions: Application of organic and inorganic treatments under water deficit conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, V.S.; Juskiw, P.E.; Aljarrah, M. Triticale as a forage. In Triticale; Eudes, F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czembor, E.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Pilarczyk, W.; Mańkowski, D.; Czembor, J.H. Simulating spring barley yield under moderate input management system in Poland. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.S.A.; El-Sobky, E.-S.E.A.; Farag, H.I.A.; Yasin, M.A.T.; Attia, A.; Rady, M.O.A.; Awad, M.F.; Mansour, E. Sowing date and genotype influence on yield and quality of dual-purpose barley in a Salt-Affected Arid Region. Agronomy 2021, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherif, O.; Seghouani, M.; Zemmouri, B.; Bouhenache, A.; Keskes, M.I.; Yacer-Nazih, R.; Ouaret, W.; Latati, M. Understanding the response of wheat-chickpea intercropping to nitrogen fertilization using agro-ecological competitive indices under contrasting pedoclimatic conditions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Pi, Y.; Long, D.; Duan, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Zhu, Y. Impact of organic and chemical nitrogen fertilizers on the crop yield and fertilizer use efficiency of soybean–maize intercropping systems. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.; Qin, W.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Environmental Assessment of Management Options for Nutrient Flows in the Food Chain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7260–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarūnaitė, L.; Toleikienė, M.; Arlauskienė, A.; Razbadauskienė, K.; Deveikytė, I.; Supronienė, S.; Semaškienė, R.; Kadžiulienė, Ž. Effects of pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars for mixed cropping with oats (Avena sativa L.) on yield and competition indices in an organic production system. Plants 2022, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.M.; Rubio, G.; Häner, L.L.; Delgado, J.A.; Lucho-Constantino, C.A.; Islas-Valdez, S.; Pellet, D. Emerging and established technologies to increase nitrogen use efficiency of cereals. Agronomy 2016, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Oyebiyi, F.; Raun, W.R. World cereal nitrogen use efficiency trends: Review and current knowledge. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, R.; Willey, R. The concept of a ‘land equivalent ratio’ and advantages in yields from intercropping. Exp. Agric. 1980, 16, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Q.; Qin, A.Z.; Gan, Y.T.; Yu, A.Z. Higher yield and lower carbon emission by intercropping maize with rape, pea, and wheat in arid irrigation areas. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płaza, A.; Górski, R. The effect of field pea grown in mixtures with spring triticale on the content of total protein and amino acids. Crop Pasture Sci. 2024, 75, CP23153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Hu, Y.G.; Zang, H.D. Sowing ratio determines forage yields and economic benefits of oat and common vetch intercropping. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxevanos, D.; Tsialtas, I.T.; Vlachostergios, D.Ν.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Dordas, C.; Lithourgidis, A. Cultivar competitiveness in pea-oat intercrops under Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.W.; Dang, K.; Lv, S.M.; Zhao, G.; Tian, L.X.; Luo, Y.; Feng, B.L. Interspecific root interactions and water-use efficiency of intercropped proso millet and mung bean. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 115, 126034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, F.-Z.; Hadjout, S.; Haddad, B.; Malek, A.; Aitmoumene, S.; Gueboub, F.; Metrah, L.; Zemmouri, B.; Kherif, O.; Rebouh, N.-Y.; et al. The effect of nitrogen supply on water and nitrogen use efficiency by wheat–chickpea intercropping system under rain-fed mediterranean conditions. Agriculture 2023, 13, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, M.R.; Angadi, S.; Begna, S.; Gowda, P.; Lauriault, L.; Hagevoort, R.; Darapuneni, M. Intercropping and species interactions on physiological and light use characteristics of forage cereals-legumes combinations in semi-arid regions. Field Crops Res. 2023, 290, 108755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnari, F.; Maggio, A.; Galieni, A.; Pisante, M. Multiple benefits of legumes for agriculture sustainability: An overview. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Masoni, A.; Ercoli, L.; Arduini, I. Above-and below-ground competition between barley, wheat, lupin and vetch in a cereal and legume intercropping system. Grass Forage Sci. 2009, 64, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiche, O.; Kummer, N.A.; Heilmeier, H. Interspecific root interactions between white lupin and barley enhance the uptake of rare earth elements (REEs) and nutrients in shoots of barley. Plant Soil 2016, 402, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Ambus, P.; Jensen, E.S. Temporal and spatial distribution of roots and competition for nitrogen in pea–barley intercrops—A field study employing 32 P technique. Plant Soil 2001, 236, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.K.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Ambus, P.; Jensen, E.S. Biomass production, symbiotic nitrogen fixation and inorganic N use in dual and tri-component annual intercrops. Plant Soil 2005, 266, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellostas, N.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Andersen, M.K.; Jensen, E.S. Early interference dynamics in intercrops of pea, barley and oilseed rape. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2003, 21, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Fan, Z.; Chai, Q. Agronomic and economic benefits of pea/maize intercropping systems in relation to N fertilizer and maize density. Agronomy 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanick, B.; Mahapatra, B.S.; Datta, D.; Dey, P.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, A.; Paramanik, B.; Awasthi, N. An innovative approach to improve oil production and quality of mustard (Brassica juncea L.) with multi-nutrient-rich polyhalite. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpunar-Krok, E.; Wondołowska-Grabowska, A.; Bobrecka-Jamro, D.; Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Kotecki, A.; Kozak, M. Effect of nitrogen fertilisation and inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum on the fatty acid profile of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) Seeds. Agronomy 2021, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Carlsson, G.; Englund, J.-E.; Flöhr, A.; Pelzer, E.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Makowski, D.; Jensen, E.S. Grain legume-cereal intercropping enhances the use of soil-derived and biologically fixed nitrogen in temperate agroecosystems. A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 118, 126077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowden, R.J.; Shah, A.N.; Lehmann, L.M.; Kiær, L.P.; Henriksen, C.B.; Ghaley, B.B. Nitrogen fertilizer effects on pea–barley intercrop productivity compared to sole crops in Denmark. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Liu, X.J.; Tong, C.C.; Wu, Y. A Study of root system characteristics and carbon and nitrogen metabolism of alfalfa and four grass forages in monoculture or intercropped. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2019, 28, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.; Tilman, D. Comparative analysis of environmental impacts of agricultural production systems, agricultural input efficiency, and food choice. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Ran, W.; Zhang, R.P.; Sun, S.B.; Xu, G.H. Facilitated legume nodulation, phosphate uptake and nitrogen transfer by arbuscular inoculation in an upland rice and mung bean intercropping system. Plant Soil 2009, 315, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudin, C.; Corre-Hellou, G.; Pineau, S.; Crozat, Y.; Jeuffroy, M.H. The effect of various dynamics of N availability on winter pea-wheat intercrops: Crop growth, N partitioning and symbiotic N2 fixation. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latati, M.; Dokukin, P.; Aouiche, A.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Takouachet, R.; Hafnaoui, E.; Hamdani, F.Z.; Bacha, F.; Ounane, S.M. Species interactions improve above-ground biomass and land use efficiency in intercropped wheat and chickpea under low soil inputs. Agronomy 2019, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, L.; Zheng, Y. Interactive influences of intercropping by nitrogen on flavonoid exudation and nodulation in faba bean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiru, M.; Alkhtib, A.; Belachew, B.; Demeke, S.; Worku, Z.; Wamatu, J.; Burton, E. Oat–field pea intercropping for sustainable oat production: Effect on yield, nutritive value and environmental impact. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankou, C.; Lithourgidis, A.; Menexes, G.; Dordas, C. Importance of selection of cultivars in wheat–pea intercropping systems for high productivity. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Ni, W.; Feng, Q.; Lan, J. Effect of seeding options on interspecific competition in oat (Avena sativa L.)–common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) forage crops. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghpour, A.; Jahanzad, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Hosseini, M.B.; Hashemi, M. Forage yield, quality and economic benefit of intercropped barley and annual medic in semi-arid conditions: Additive series. Field Crops Res. 2013, 148, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, M.; Monti, M.; Calvi, A.; Lo Presti, E.; Pellicanò, A.; Preiti, G. Forage potential of cereal/legume intercrops: Agronomic performances, yield, quality forage and LER in two harvesting times in a mediterranean environment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begna, S.; Angadi, S.; Mesbah, A.; Umesh, R.M.; Stamm, M. Forage yield and quality of winter canola–pea mixed cropping system. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, P.T.; Bai, Y.; Dong, Y.; Shi, H.; Soe Htet, M.N.; Samoon, H.A.; Zhang, R.; Tanveer, S.K.; Hai, J. Influence of different harvesting stages and cereals–legume mixture on forage biomass yield, nutritional compositions, and quality under Loess Plateau Region. Plants 2022, 11, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufan, W.; Al-Suhaibani, N.A. Optimizing yield and quality of silage and hay for pea–barley mixtures ratio under irrigated arid environments. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjun, R.H.; Kumar, R.; Meena, R.K.; Ginwal, D. Yield and chemical composition of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) fodder as affected by tillage practices and nitrogen management. Indian J. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 35, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krga, I.; Simić, A.; Dželetović, Ž.; Babić, S.; Katanski, S.; Nikolić, S.R.; Damnjanović, J. Biomass and protein yields of field peas and oats intercrop affected by sowing norms and nitrogen fertilizer at two different stages of growth. Agriculture 2021, 11, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamta, A.; Kumar, R.; Ram, H.; Meena, R.K.; Meena, V.K.; Yadav, M.R.; Subrahmanya, D.J. Productivity and profitability of legume-cereal forages under different planting ratio and nitrogen fertilization. Legume Res. 2019, 42, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, A.; Asik, F. The effect of mixture rates and cutting stages on some yield and quality characters of pea (Pisum sativum L.) + oat (Avena sativa L.) mixture. Turk. J. Field Crops 2012, 17, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kocer, A.; Albayrak, S. Determination of forage yield and quality of pea (Pisum sativum L.) mixtures with oat and barley. Turk. J. Field Crops 2012, 17, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Boutagayout, A.; Belmalha, S.; Nassiri, L.; El Alami, N.; Jiang, Y.; Lahlali, R.; Bouiamrine, E.H. Weed competition, land equivalent ratio and yield potential of faba bean (Vicia faba L.)-cereals (Triticum aestivum L. and/or Avena sativa L.) intercropping under low-input conditions in Meknes Region, Morocco. Vegetos 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurgi, N.; Tana, T.; Dechassa, N.; Tesso, B.; Alemayehu, Y. Effect of spatial arrangement of faba bean variety intercropping with maize on yield and yield components of the crops. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.; Pellicanò, A.; Santonoceto, C.; Preiti, G.; Pristeri, A. Yield components and nitrogen use in cereal-pea intercrops in Mediterranean environment. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhima, K.V.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Keco, R.X.; Dima, A.K.; Paschalidis, K.A.; Gatsis, T.D. Forage yield and competition indices of faba bean intercropped with oat. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampana, S.; Arduini, I.; Andreuccetti, V.; Mariotti, M. Fine-tuning N fertilization for forage and grain production of barley–field bean intercropping in Mediterranean environments. Agronomy 2022, 12, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Yan, Z.; Jia, Q.; Chang, S.; Ahmad, I.; Ghani, M.U.; Hou, F. Irrigation and nitrogen fertilization influence on alfalfa yield, nutritive value, and resource use efficiency in an arid environment. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, S.V.; Valadabadi, S.A.R.; Pouryousef, M.; Saifzadeh, S.; Zakrin, H.R.; Mastinu, A. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of Sorghum bicolor L. under intercropping with legumes and different weed control methods. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, J.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Boraiah, K.M.; Meena, K.K.; Pradhan, A.; Prasad, P.V.V. The adaptation and tolerance of major cereals and legumes to important abiotic stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghabari, F.; Ihsan, M. Effects of drought stress on growth, grain filling duration, yield and quality attributes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Bangladesh J. Bot. 2018, 47, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwaar, H.A.; Perveen, R.; Mansha, M.Z.; Abid, M.; Sarwar, Z.M.; Aatif, H.M.; ud din Umar, U.; Sajid, M.; Aslam, H.M.U.; Alam, M.M.; et al. Assessment of grain yield indices in response to drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Turner, N.C.; Du, Y.L.; Colmer, T.D.; Siddique, K.H.M. Pattern of water use and seed yield under terminal drought in chickpea genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Hicks, D.; Naeve, S. Predicting the Last Irrigation for Corn and Soybeans in Central Minnesota. Minnesota Crop News, 2018. Available online: https://blog-crop-news.extension.umn.edu/2018/08/predicting-last-irrigation-for-corn-and.html (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Zare, M.; Nejad, M.G.; Bazrafshan, F. Influence of drought stress on some traits in five mung bean (Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek) genotypes. Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2012, 3, 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; Schoenau, J.; Si, B. Water footprint for pulse, cereal, and oilseed crops in Saskatchewan, Canada. Water 2018, 10, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulis, K.D.; Bartzialis, D.; Skoufogianni, E.; Gintsioudis, I.; Danalatos, N.G. Could a legume–switchgrass sod-seeding system increase forage productivity? Plants 2022, 11, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, K.S.; Omokanye, A.T. Potential of spring barley, oat and triticale intercrops with field peas for forage production, nutrition quality and beef cattle diet. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Abdi, G.; Saleem, M.H.; Ali, B.; Ullah, S.; Shah, W.; Mumtaz, S.; Yasin, G.; Muresan, C.C.; Marc, R.A. Plants’ physio-biochemical and phyto-hormonal responses to alleviate the adverse effects of drought stress: A Comprehensive review. Plants 2022, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Bagavathiannan, M.; Wang, H.; Sharpe, S.M.; Meng, W.; Yu, J. Osmopriming with polyethylene glycol (Peg) for abiotic stress tolerance in germinating crop seeds: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Kamran, M.; Ding, R.; Meng, X.; Wang, H.; Ahmad, I.; Fahad, S.; Han, Q. Exogenous melatonin confers drought stress by promoting plant growth, photosynthetic capacity and antioxidant defense system of maize seedlings. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Islam, H.M.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ongoma, V.; Khan, R.; Mallick, J. Water resources pollution associated with risks of heavy metals from Vatukoula Goldmine Region, Fiji. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).