Abstract
In 2023, we proposed the modified delay and Doppler profiler (mDDP) as an inter-carrier interference (ICI) countermeasure for underwater acoustic orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) mobile communications in a multipath environment. However, the performance improvement in the computer simulation and pool experiments was not significant. In a subsequent study, the accuracy of the channel transfer function (CTF), which is the input for the mDDP channel parameter estimation, was considered insufficient. Then a sequential ICI canceling mDDP was devised. This paper presents simulations of underwater OFDM communications using an iterative one- to three-step mDDP. The non-reflective pool experiment conditions are a two-wave multipath environment where the receiving transducer moves at a speed of 0.25 m/s and is subjected to a Doppler shift in the opposite direction. As NumCOL, the number of taps in the multitap equalizer which removes ICI, was increased, the bit error rate (BER) of 0.0526661 at NumCOL = 1 was significantly reduced by a factor of approximately 45 to a BER of 0.0011655 at NumCOL = 51 for the sequential ICI canceling mDDP.
1. Introduction
Underwater wireless communications are used in many applications to reduce cable costs and deployment time, such as harbor and shoreline monitoring, fish monitoring, and the monitoring of drilling sites such as oil wells and trenches []. The use of single-carrier transmission techniques has been the subject of study in the field of underwater acoustic communications [,,,,]. In radio frequency wireless communications, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technology, a type of multicarrier transmission, is frequently employed. OFDM technology has a long history, initially proposed in the 1950s [] and subjected to theoretical analysis in the 1960s []. In the 1970s, a methodology based on the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) was proposed and regarded as a promising avenue of inquiry []. OFDM was subsequently adopted for digital broadcasting in 1987 [] and continues to be employed in this capacity to the present day. To increase data bandwidth, OFDM-based wireless communication systems have received widespread attention for their high transmission rates and high spectrum efficiency, even for underwater applications. Since the Doppler shift occurs in underwater wireless communications due to the movement of equipment and vessels, signal processing is required to compensate for the Doppler shift. The performance of the OFDM system is seriously deteriorated by the inter-carrier interference (ICI) caused by the transmitter/receiver motion and ocean waves. Then, ICI mitigation in the OFDM system is required.
Instead of conventional fast Fourier transform (FFT), fractional fast Fourier transform (F-FFT) is utilized with adaptive way for ICI mitigation in paper []. However, if it assumes differential OFDM modulation, then high-order modulation such as 64QAM is difficult. In paper [], ICI self-cancellation is demonstrated by inactivating partial subcarriers and utilizing opposite polarity on two adjacent active subcarriers for ICI self-cancellation. Then, the effective subcarrier utilization in OFDM used to convoy information lowers. Another approach to mitigate ICI with an iterative receiver based on the turbo principle is also proposed in paper []. So far, our research team has proposed a time-domain signal processing algorithm for the OFDM Doppler compensation of the desired propagation path [,,]. But this approach cannot mitigate ICI caused by a multipath channel with a different Doppler shift.
In 2023, we proposed a modified delay and Doppler profiler (mDDP) as a frequency domain signal processer to combat ICI in underwater acoustic OFDM mobile communications in multipath environments [,]. However, the performance improvement in computer simulations and pool experiments was not remarkable. In a subsequent study, the accuracy of the channel transfer function (CTF), which is the input for the mDDP channel parameter estimation, was considered insufficient. In prior research [,], multitap ICI cancellation was performed by obtaining channel estimates from the scattered pilots (SPs) signal. However, this was an ICI cancellation for data carriers, and ICI cancellation for pilot signals was not performed. Therefore, this paper aims to further improve the BER by using a multistep mDDP, which denoises the SPs in the first-stage mDDP to cancel ICI-derived noise components, and then improves the accuracy of the input SPs in the second and subsequent stages of the mDDP. To further improve the accuracy of channel estimation, an mDDP was devised to sequentially cancel the ICI.
In this paper, the performance of underwater OFDM communications using an iterative one- to three-step mDDP are compared using computer simulation, assuming a two-wave multipath environment subject to the Doppler shift in the opposite direction as shown in Figure 1. Section 2 describes the system parameters of the underwater acoustic (UWA) OFDM modulation scheme used in underwater acoustic communication and the conventional Doppler shift cancellation scheme. Section 3 presents the details of the proposed UWA OFDM communication system using a multistep mDDP. In Section 4, computer simulation results are presented, and Section 5 presents the results of the simulations of the proposed method using the data obtained in the non-reflective pool experiment. Finally, in Section 6, the conclusions will be presented.
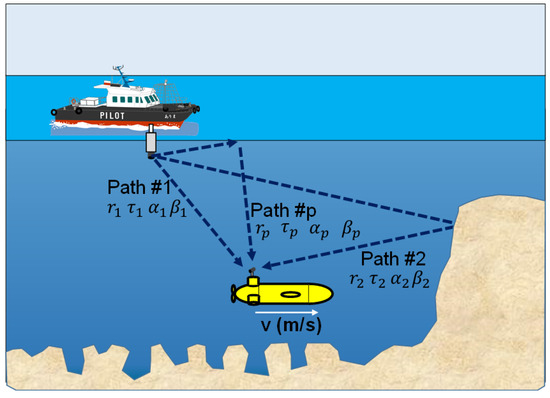
Figure 1.
UWA communication under multipath Doppler condition.
2. UWA OFDM Conventional Doppler Compensation Method
Figure 1 shows an example of an Np multipath environment in underwater acoustic communication. At the autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), Np overlapped, and Doppler-shifted and shrunk-or-expanded signals are received. The Path #p signal is characterized by complex attenuation , relative delay , normalized Doppler shift , and sampling clock error as explained in detail in []. Path #1 and Path #2 are affected by the backward Doppler shift when the receiving device moves. Therefore, as shown in Figure 2, the received signal is shrunk or expanded in underwater acoustic communication. In Figure 2, represents the moving speed of the receiver and index k corresponds to the OFDM symbol number. Then, we previously introduced resampling and de-rotation to the OFDM receiver as shown in Figure 3 []. The performance in the mobile reception is improved by detecting the desired path signal with high intensity and stretching the received signal in resample and de-rotation processing. However, if the Doppler shift of the second wave is different from the first wave, as in this case, the second wave is affected by the Doppler shift and generates ICI. In addition, channel estimation uses intermittently placed SPs to estimate the CTF for each carrier. In the conventional method, the channel estimation of the time and frequency directions are performed by applying a CTF interpolation filter in the time direction, as shown in the channel estimation block in Figure 3, followed by a CTF interpolation filter in the frequency direction. As shown in the channel estimation block in Figure 3, channel estimation was performed for each carrier within three symbols. In this method, carrier edge processing is required when performing CTF interpolation in the frequency direction, resulting in the degradation of the channel estimation accuracy at the carrier edges.
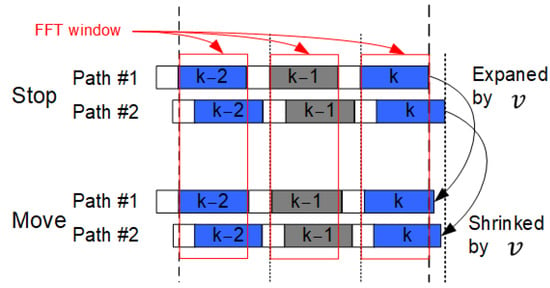
Figure 2.
OFDM signal after the shrink and expansion processing.
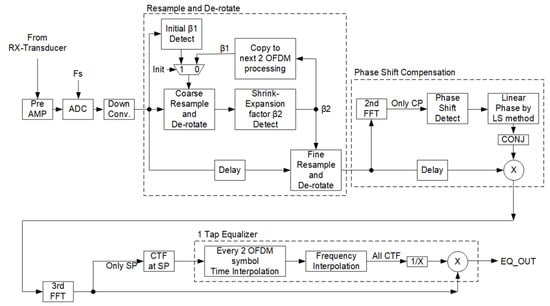
Figure 3.
Block diagram of previous receiver.
Detailed system parameters are listed in Table 1. The subcarrier spacing of the OFDM is 50 Hz, and the effective OFDM symbol duration is 20 ms with 2048 points IFFT/FFT as modulation/demodulation. Since the total number of subcarriers is 161, the OFDM signal bandwidth is roughly 8 kHz. Figure 4 shows the time–frequency subcarriers’ arrangement at the transmitter and receiver sides. To estimate CTF, two kinds of pilot signals are inserted. The blue circles are SPs which are inserted in every two rows and every two columns. The other yellow circles are continuous pilots (CPs) for tracking phase-change in the time domain every 12 rows. The modulated by 64QAM is sending data symbols of the subcarrier index at the kth OFDM symbol and is receiving data symbols of subcarrier index at the kth OFDM symbol.

Table 1.
UWA OFDM system parameters.
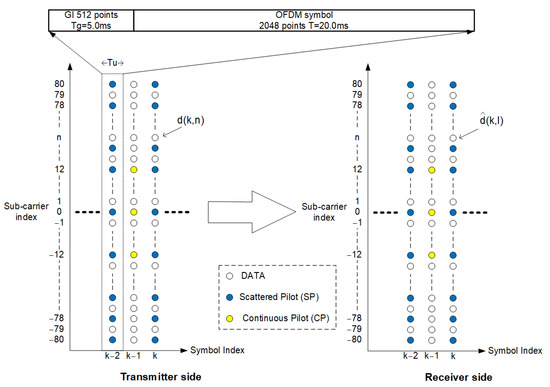
Figure 4.
Time–frequency representation of OFDM signal of transmitter and receiver.
Channel estimation uses intermittently placed SPs to estimate the CTF for each carrier. In the conventional method, channel estimation in the time and frequency directions is performed by applying a CTF interpolation filter in the time direction, as shown in the channel estimation block in Figure 3, followed by a CTF interpolation filter in the frequency direction. As shown in the channel estimation block in Figure 3, channel estimation was performed for each carrier within three symbols. In this method, carrier edge processing is required when performing CTF interpolation in the frequency direction, resulting in the degradation of channel estimation accuracy at the carrier edges.
3. Iterative Multistep mDDP-Based ICI Canceling UWA OFDM Communication System
Figure 5 shows the proposed iterative multistep mDDP-based OFDM receiver, which does not have resample and de-rotation. The received signal is amplified in the first stage pre-amplifier, and then converted to a digital signal with an analog to digital converter (ADC) with a sampling frequency of 102.4 kHz. Then, the ADC output is down-converted to a baseband signal. By applying the FFT processing, the frequency domain signal, which is composed of 161 vertical subcarriers as shown in Figure 4, can be obtained. Using the SP, channel multipath conditions are analyzed with mDDP. By defining CTF from sending the subcarrier index to receiving subcarrier index in time, index as , the inputs of mDDP are current time index ’s and two symbols ago ’s , where the subcarrier index of is only the SP positions. Since the transmitting SP values are predetermined, the inputs of the mDDP are easily calculated.
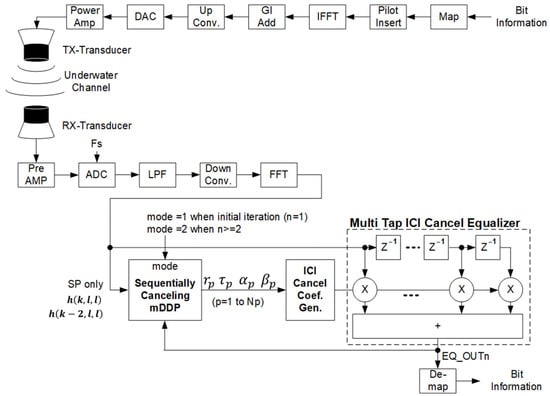
Figure 5.
Block diagram of proposed iterative multistep mDDP receiver.
Although the main focus of this proposal is on the two-step configuration, an -step mDDP is shown in the figure for simulation comparison. In this simulation, values of one to three steps were performed.
For each step, the OFDM receiver received a composite wave of the transmission path of the transmitter-derived signal, such as the reflected waves with different time delays, frequency differences, and power differences, as well as the noise component inside the receiver. The mDDP estimates a combination of multiple Doppler-shifted propagation paths and their parameters such as attenuation, relative delay, Doppler-shift, and sampling clock error as shown in Figure 6. The mDDP performs a more accurate channel estimation of the received signal by the following sequences.
- seq. 1.
- Calculate the channel estimate from the SPs after FFT and calculate the delay profile.
- seq. 2.
- The obtained delay profiles of two symbol indices k and k−2 are used to detect the OFDM head timing position, and the receiver sampling clock error is calculated by calculating the amount of signal shrinking or expanding from the difference between the two symbol head timing positions.
- seq. 3.
- After coarsely calculating the relative delay time from the delay profile, the attenuation and Doppler-shift , which are the parameters of the component waves in the received signal, are obtained. For specific derivation equations, is described in the mDDP in paper []’s Equations (12a) and (12b). Also, can be found in the mDDP in paper []’s Equations (13).
- seq. 4.
- A more accurate delay time is also detected in detail using the Newton method [,,].
- seq. 5.
- Remove the detected paths from the channel estimates, as well as the per-carrier ICI component.
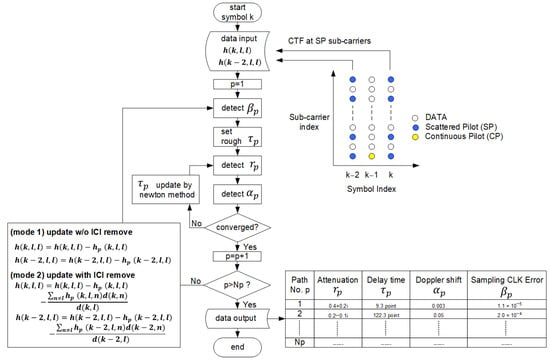
Figure 6.
Flowchart of iterative multistep modified delay and Doppler profiler.
By repeating the above process, from seq. 2 to seq. 5, for the number of path detection times Np, the signal components of each path of the composite wave components are detected. This path detection is used to perform ICI cancellation and data equalization. By performing data equalization once and using hard-decisioned data, the data portion can be treated as known information, and the ICI component removal using the data carrier can be applied to path detection iterations in two-step or higher channel estimation. When mDDP is applied for more than two steps, the above processing seq. 1 is performed sequentially, but since hard-determined data can be used, the CTF can be obtained with higher accuracy and the four parameters for each path, the relative delay time , attenuation , Doppler-shift , and sampling clock error , can be obtained.
The details of the iterative multistep mDDP are explained below using equations.
The FFT output of the OFDM demodulation generates the data symbol as expressed in Equation (1), which is referred from the original mDDP in paper []’s Equation (6) and the mDDP and DDP in papers [,,,].
where is the sending data symbol of the subcarrier index at the kth OFDM symbol, is additive noise that corresponds to the lth subcarrier in the kth OFDM symbol, and is the transfer function of the kth OFDM symbol with a sending subcarrier index to receiving subcarrier . is the number of subcarriers. The magnitude of the kth OFDM is at a maximum at and is getting smaller as is getting larger. Then, the range of the sum in Equation (1) can be decreased from to for approximation, where is the total number of sums. Assuming , Equation (1) can be shown as Equation (2) in matrix form. Non-diagonal components in the matrix correspond to ICI.
By neglecting the additive noise component, sending data symbol can be estimated from the receiver FFT outputs to as shown in Equation (3).
Equation (3) computation is implemented in a multitap ICI cancel equalizer in Figure 5. Once all values are available, ICI cancelling is possible.
can be expressed as Equations (4)–(6) according to the original mDDP in paper [].
where represents the normalized frequency offset of the pth path, represents the sampling clock error of the pth path and denotes relative delay time in sampling points.
Here, mDDP is applied repeatedly, but in the first mDDP, only the CTF of the SP position within one symbol is available for ICI cancellation, but in the second and subsequent mDDPs, the path information obtained in the first mDDP and the hard-decision results of the data carriers are used, and ICI cancellation can be performed. We defined the first mDDP as mode 1 and the second and subsequent mDDPs as mode 2.
From Equation (1), the inputs such as and of mDDP mode 1 in Figure 6 can be approximated as Equations (7) and (8), where the subcarrier index of is only the SP positions.
Also, mDDP mode 2 in Figure 6 can be shown as in Equations (9) and (10).
where can be calculated by Equations (4)–(6) using the parameters from the first mDDP. and can be obtained by the hard decision of multitap equalizer outputs. As explained above, the sequential ICI canceling mDDP is expected to improve the accuracy of the mDDP estimation parameters by improving the accuracy of the input signal. For details on the mDDP process for each step, the process described in seq. 1 to seq. 5 above is executed for the Np paths.
4. Computer Simulations
Figure 7 shows a computer simulation model assuming a reverse two-path multipath condition. Two transmitting transducers TX1 and TX2, 3.25 m apart, were used to model the multipath environment. A receiving transducer RX moves 0.75 m from 0.5 m from TX1 in the direction of TX2 with a speed of 0.25 m/s. The OFDM signal length is about 10.0 s with 400 OFDM symbols. The calculated 1st and 2nd received wave delay time and the desired (1st wave) to undesired (2nd wave) power ratio (DUR) are shown in Figure 8. The applied carrier to noise ratio (CNR) is 40 (dB). Figure 9 shows the time dependences of the measured bit error rate (BER) and the real value of the 64 QAM constellation of the conventional receiver and the two-steps of the sequential ICI canceling mDDP receiver with NumCOL = 1, 5, 11, 21 (the number of taps in the multitap equalizer). The "moving period" in the graph of time dependence of bit error rate represents the interval during which the RX transducer is moving. Figure 10 shows 64QAM constellations in the moving period for the same cases. As can be seen from these figures, in the two-steps of the sequential ICI canceling mDDP, the constellation disorder decreases and the BER value decreases dramatically as the value of NumCOL is increased.
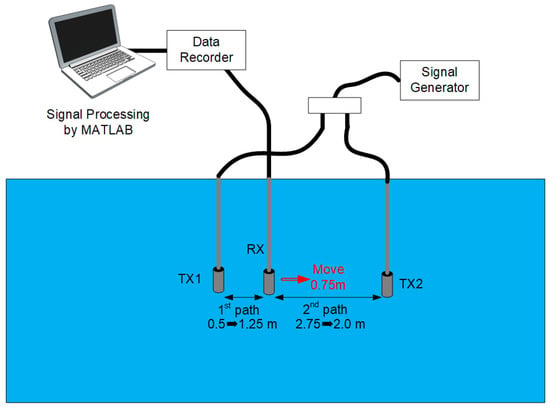
Figure 7.
Computer simulation model assuming reverse two-path multipath condition.
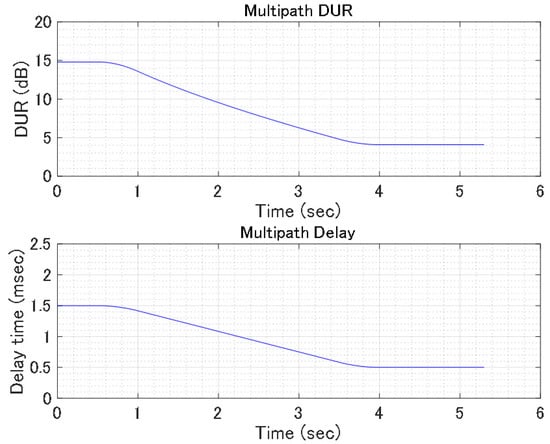
Figure 8.
Delay time and DUR in simulation.
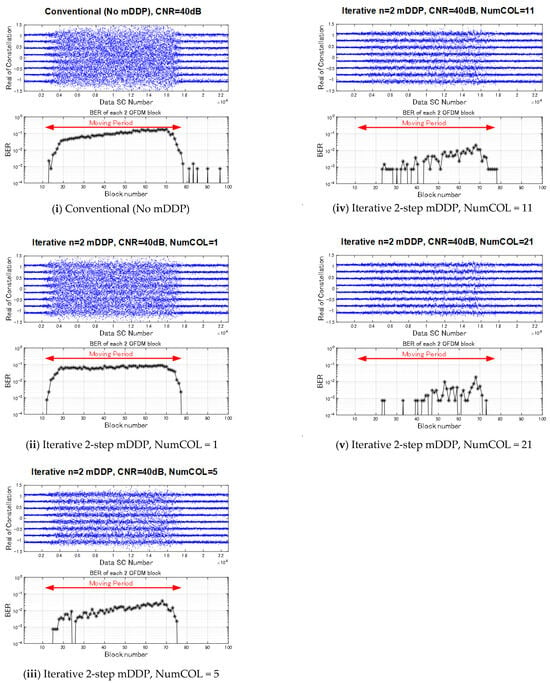
Figure 9.
Result of computer simulation assuming time dependencies of measured BER and constellation (real part of complex).
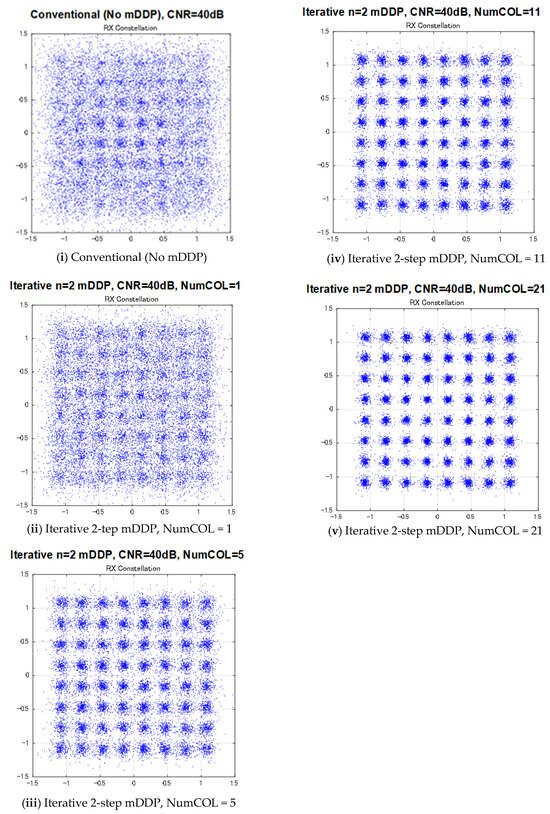
Figure 10.
Result of computer simulation assuming constellations in moving period.
Figure 11 summarizes simulated BER with changes in NumCOL for conventional and iterative one- to three-step mDDP. Increasing from one- to two-steps dramatically reduces the BER value but increasing to three-steps has no effect. There is a dependence of BER reduction on increasing NumCOL values, especially in two-step. The two-step mDDP scheme reduces ICI dramatically.
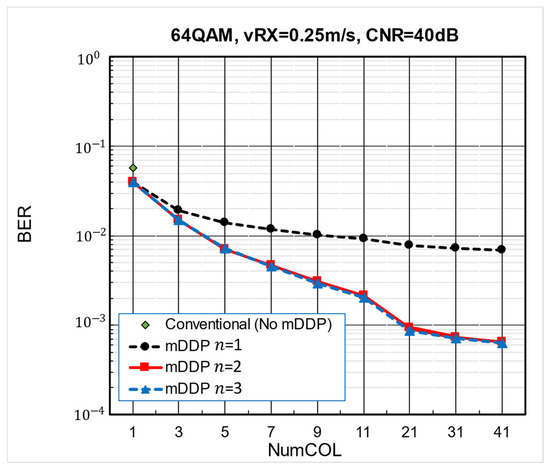
Figure 11.
Comparison of simulated BER.
The graphs of SNR vs. BER for the conventional method and iterative multistep mDDP with a NumCOL value of 21 are shown in Figure 12. When CNR is large, the effect of the iterative two-step mDDP can be seen clearly; when CNR is less than 20 dB, the difference between one-step mDDP and iterative two-step mDDP is small, but some BER improvement can be expected. As for the iterative three-step mDDP, the difference between it and the two-step mDDP is very small in the CNR vs. BER graph.
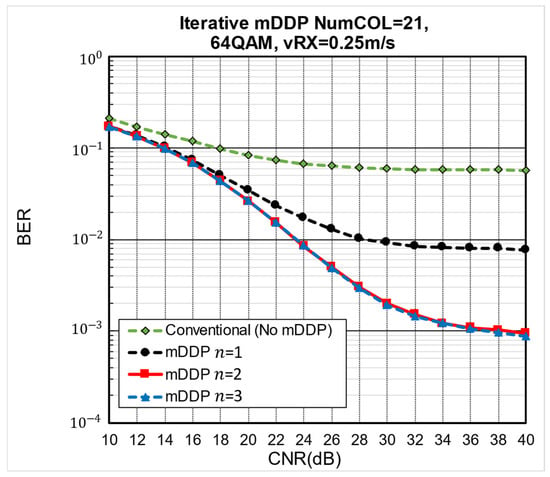
Figure 12.
BER vs. CNR of conventional and iterative mDDP on NumCOL = 21.
5. Pool Experiment
We conducted a non-reflective pool experiment to validate our proposed method. Figure 13 shows a pool experiment assuming a reverse two-path multipath condition. This pool’s dimensions are 5.0 m by 2.5 m and the depth is 2.5 m. Two transmitting transducers TX1 and TX2, about 3.2 m apart, are used to model the multipath environment. While TX1 and TX2 send signals at the same power, a receiving transducer RX moves 0.75 m from 0.5 m from TX1 in the direction of TX2 with a speed of 0.25 m/s. All transducers were installed at the same depth, 1.8 m.
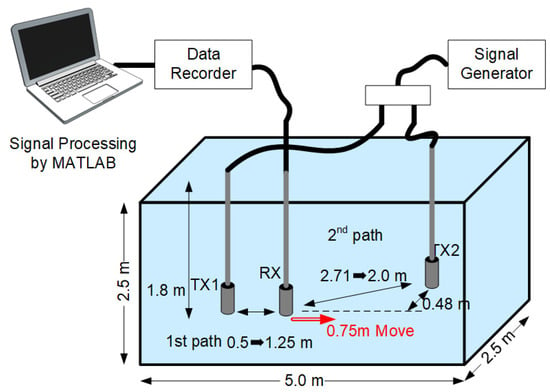
Figure 13.
Non-reflective pool experiment environment.
Using time domain signals obtained through the RX transducer in the non-reflective pool environment, BER measurements were made using the computer simulations of the conventional and proposed methods. Figure 14 shows the spectrum of the received advance signal of the RX transducer. An 8 kHz bandwidth between 20 kHz and 28 kHz with a center frequency of 24 kHz can be seen in the received spectrum. The reason why the power spectrum is rising steadily to the right is due to the frequency characteristics of the transducer used. A low pass filter was inserted to flatten the power spectrum in order to cancel the frequency response of the receiving transducer when the received signal is used in a computer simulation.
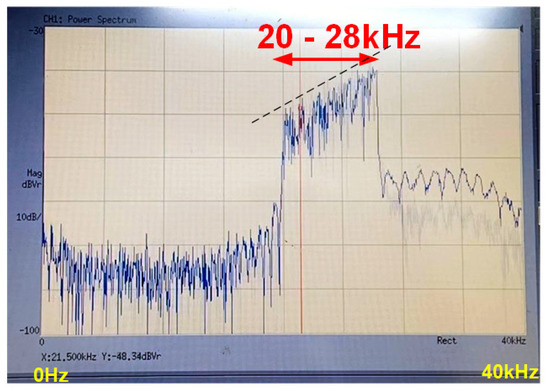
Figure 14.
The received spectrum on RX transducer.
For the signals sent out from TX1 and TX2, we used the 400 OFDM symbols (about 10.0 s) used in the computer simulation presented in Table 1. Figure 15 shows the BER for approximately 3 s during which the RX transducer is being moved out of approximately 10 s of signal transmission from TX1 and TX2. In Figure 15, the word “Moving” is shown in red in the graph of the time dependence of the bit error rate when the RX transducer is moving. It can be seen that the BER is degraded for NumCOL = 1 for the iterative mDDP of the proposed method compared to the BER of the conventional method, but as the value of NumCOL is increased, the BER improves. At NumCOL = 51, the error rate is a factor of approximately 45 of the conventional method. Figure 16 is a graph of NumCOL vs. BER for the non-reflective pool experiment. The one-step mDDP shows that BER saturates at NumCOL = 31, but the iterative two-step mDDP shows that BER improves even when NumCOL is 31 or higher. This may be due to the fact that the effect of ICI becomes smaller as the carriers subject to ICI cancellation move further away.
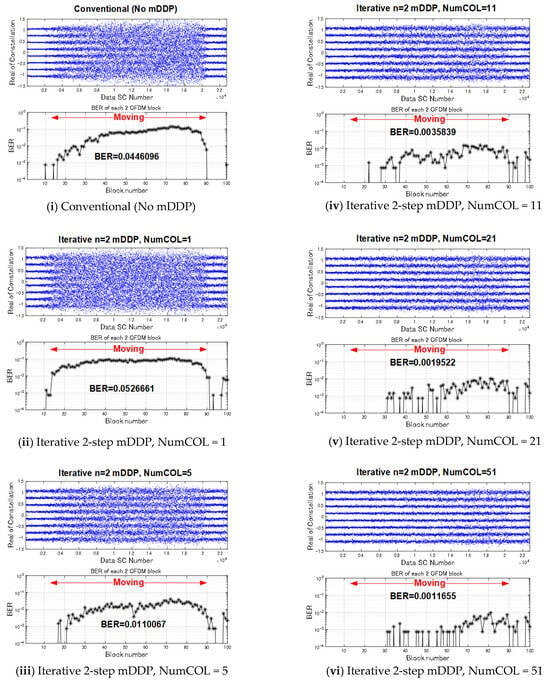
Figure 15.
Results of pool experiment environment time dependencies of measured BER and constellation (real part of complex).
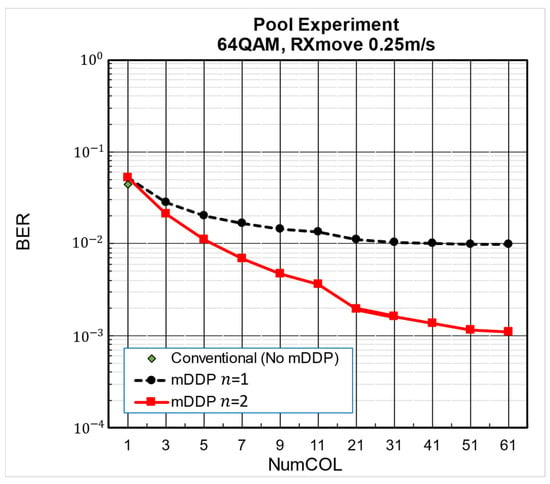
Figure 16.
BER comparison of non-reflective pool experiment.
One of the reasons for the slight degradation of BER compared to the two-wave multipath environment subjected to the Doppler shift created in the simulation is the non-reflective pool environment, but signal reflection from the pool surface is considered to exist because the experiment is conducted with the transducer suspended above the water surface. Therefore, the possibility of a two or more-wave multipath environment and noise superimposition from the acoustic device of the signal receiver are also possible.
6. Conclusions
Basically, the modified delay and Doppler profiler (mDDP), which estimates not only attenuation, relative delay, and the Doppler shift, but also the sampling clock shift of each multipath component, combined with an ICI canceling multitap equalizer reduces inter-carrier interference between OFDM subcarriers. With the one-step mDDP, the BER reduction was limited by the degradation of the estimation accuracy of those parameters, but with the iterative two-step mDDP, dramatic ICI cancellation can be achieved.
In the non-reflective pool experiment of a two-wave multipath environment where the receiving transducer moves at a speed of 0.25 m/s and is subject to the backward Doppler shift, increasing NumCOL, the number of taps in the multitap equalizer that removes ICI, the BER of 0.0526661 at NumCOL = 1 was reduced by a sequential ICI-canceling mDDP, the BER at NumCOL = 51 was significantly reduced by about a factor of 45 to 0.0011655.
Although the simulations in this paper were performed assuming a two-wave multipath Doppler-shift environment, DDP and mDDP have achievements in analyses for multipaths that are larger than the current assumed environment by setting the number of detected paths Np, to a large value, such as 16. The marine experiment is also planned at the end of 2024.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.W.; methodology, T.W.; software, S.O.; validation, S.K., S.O., R.S. and T.W.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, S.K. and T.W.; resources, S.K., R.S. and T.W.; data curation, S.K. and S.O.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.; writing—review and editing, R.S. and T.W.; visualization, S.O. and R.S.; supervision, T.W.; project administration, T.W.; funding acquisition, T.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data contained in this article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank OKI Com Echoes, Inc. of Numazu City, Shizuoka Prefecture, for making the use of their non-reflective pool convenient for the underwater acoustic OFDM communication pool experiment. We would especially like to thank Hiromasa Yamada, a researcher at OKI Com Echoes, Inc. and other people at OKI Com Echoes for their assistance in the program development, equipment setup, and data collection of the pool experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Suguru Kuniyoshi and Rie Saotome were employed by the company Magna Design Net, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Heidemann, J.; Stojanovic, M.; Zorzi, M. Underwater sensor networks: Applications, advances and challenges. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, A.; Yauchi, S. An Acoustic Communication System for Subsea Robot. In Proceedings of the OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 September 1989; pp. 765–770. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Herold, D.; Catipovic, J. The design and performance of a compact underwater acoustic network node. In Proceedings of the OCEANS’94, Brest, France, 13–16 September 1994; Volume 463, pp. III/467–III/471. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, L.; Johnson, M.; Frye, D. High-rate acoustic communications for ocean observatories-performance testing over a 3000 m vertical path. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2000 MTS/IEEE Conference and Exhibition, Providence, RI, USA, 11–14 September 2000; Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37158). Volume 1442, pp. 1443–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Kebkal, K.G.; Kebkal, A.G.; Bannasch, R. Performance of S2C acoustic modem in horizontal underwater acoustic channels. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference & Exhibition on Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies and Results, Crete, Greece, 25–29 June 2007; pp. 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Ochi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Shimura, T. Measurement of Absorption Loss at 80 kHz Band for Wideband Underwater Acoustic Communication. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.W. Synthesis of band-limited orthogonal signals for multichannel data transmission. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1966, 45, 1775–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Gibby, R. A Theoretical Study of Performance of an Orthogonal Multiplexing Data Transmission Scheme. IEEE Trans. Commun. Technol. 1968, 16, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.; Ebert, P. Data Transmission by Frequency-Division Multiplexing Using the Discrete Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Commun. Technol. 1971, 19, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alard, M.; Lassalle, F. Principles of modulation and channel coding for digital broadcasting for mobile receivers. EBU Rev. 1987, 224, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, L. Adaptive F-FFT Demodulation for ICI Mitigation in Differential Underwater Acoustic OFDM Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 7–11 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, L. Index modulated OFDM with ICI self-cancellation in underwater acoustic communications. In Proceedings of the 2014 48th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2014; pp. 338–342. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, S.; Huang, J.; Berger, C.R.; Willett, P. Progressive Inter-Carrier Interference Equalization for OFDM Transmission Over Time-Varying Underwater Acoustic Channels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Wada, T.; Yamada, H.; Nakagawa, S. An underwater acoustic OFDM communication system with robust Doppler compensation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2017, 17, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hoq, M.A.; Oshiro, S.; Wada, T. Two steps Doppler compensation Algorithm from moving AUV to AUV/Mother Ship for OFDM-based UWA communication system. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2020, 20, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro, S.; Muller, Y.; Yamada, H.; Wada, T. An UWA OFDM Communication System with Improved Doppler compensation and Initial Synchronization. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2022, Hampton Roads, Hampton Roads, VA, USA, 17–20 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro, S.; Akioya, C.; Yamada, H.; Wada, T. A Prototype ICI Canceling Underwater OFDM Communication System for Multi-Path Doppler Channel. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2023—MTS/IEEE U.S. Gulf Coast, Biloxi, MS, USA, 25–28 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Akioya, C.; Oshiro, S.; Yamada, H.; Wada, T. A Modified Delay and Doppler Profiler based ICI Canceling OFDM Receiver for Underwater Multi-path Doppler Channel. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2023, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Itami, M.; Itoh, K.; Aghvami, H. ICI Cancellation Technique based on Estimating Delay and Doppler Profile in OFDM Reception. J. Inst. Image Inf. Telev. Eng. 2002, 56, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Fujii, M.; Itami, M.; Itoh, K. MMSE ICI Canceller for OFDM Mobile Reception. J. Inst. Image Inf. Telev. Eng. 2004, 58, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, A.; Nakamura, M.; Fujii, M.; Itami, M.; Itoh, K.; Ohta, H. A study on improving performance of an OFDM ICI canceller. J. Inst. Image Inf. Telev. Eng. 2005, 59, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).