Abstract
Marine geological studies of Naples Bay are discussed and reviewed, focusing on the application of the seismo-stratigraphic concepts to a Late Quaternary volcanic area. The Naples Bay represents an active volcanic area in which the interactions between volcanic and sedimentary processes controlled a complex stratigraphic architecture during the Late Quaternary period. While the volcanic processes took place in correspondence with the activity of the Somma–Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei Ischia, and Procida volcanic complexes, the sedimentary processes were controlled by the fluvial processes in the Sarno-Sebeto coastal plain and by the tectonic uplift in correspondence with the Sorrento Peninsula’s structural high Key geophysical and stratigraphic studies of the three active volcanic complexes are revised and discussed. The seismo-stratigraphic concepts applied in the geological interpretation of seismic profiles of Naples Bay are reviewed and discussed: here, the classical concepts of seismic and sequence stratigraphy have been successfully applied, but only partly, due to the occurrence of several buried volcanoes and volcanic seismic units and tephra layers, calibrated by gravity cores.
1. Introduction
The seismic stratigraphy of Naples Bay is herein revised and discussed, starting from the old (1980–2000) seismo-stratigraphic data and proceeding towards the new (2000–2023) seismo-stratigraphic data. Focusing on case histories located in the Somma–Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Ischia and Procida offshore, the technological content of the seismo-stratigraphic data, if applied to the Naples Bay, is also taken into account, reviewing the basic seismic systems used in the acquisition of single-channel, multichannel, and magnetic data.
This introduction assesses reflection seismic overlays, diffraction, seismic sources, receivers, filters, move out, migration, and deconvolution processes, reporting which systems were deployed and which data were collected with them [1,2,3,4].
The Sparker is among the most important seismic sources for marine surveys and has been used extensively in Naples Bay, providing high-resolution seismic profiles useful in geological interpretation. It consists of an electrode array powered by a capacitor bank of a few hundred joules and has been widely employed as a source for studies of the continental shelf [1,2,3,4].
From 1998 to 2000, a large database of single-channel reflection seismic measurements has been recorded in the Naples and Pozzuoli Bays by the Parthenope University of Naples, using both the Multispot Extended Array Sparker (MEAS) [5] and the Surfboom. Both these systems are suitable for surveying the continental shelf and slope of Naples Bay [5].
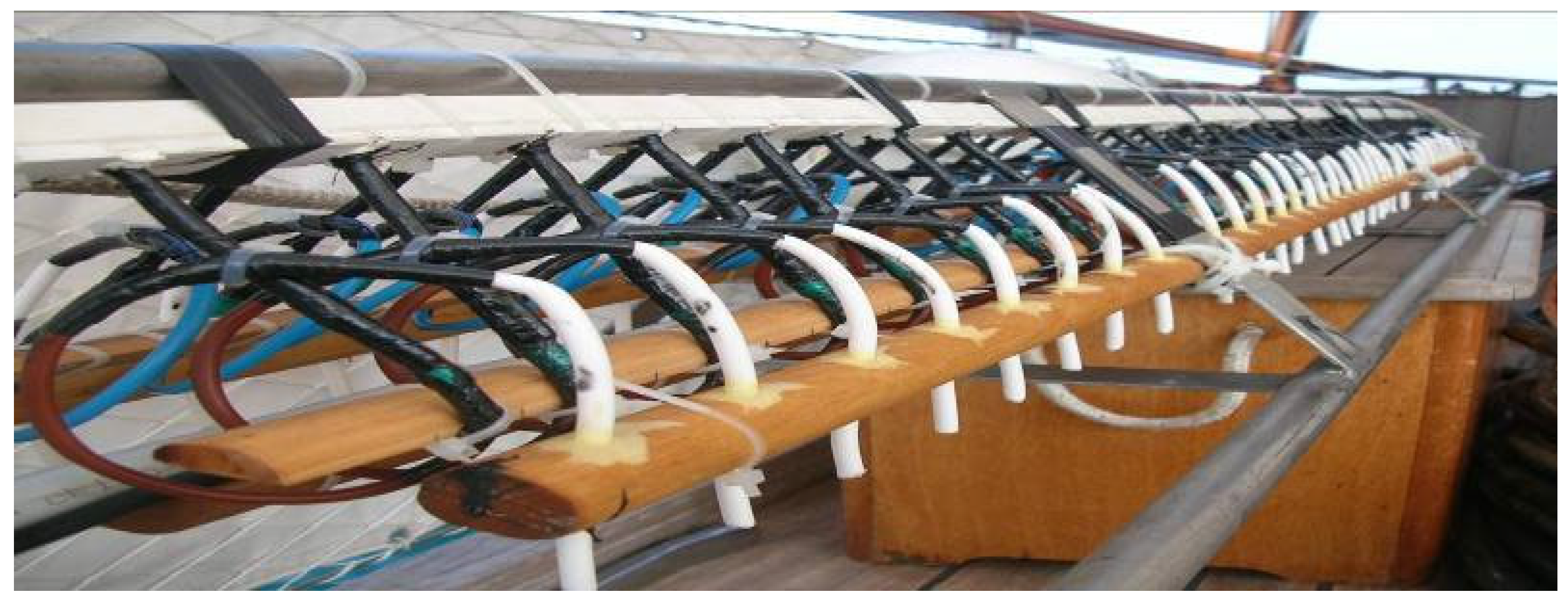
A further development of marine seismic technology in Naples Bay is the Sparker source SAM 96, employed in Antarctica expeditions from 2001 to the present (Figure 1) [6], which is characterized by a varying number of electrodes that can be arranged as “dual-in-line”.

Figure 1.
SAM 96: Sparker Array Multi-tip (96 electrodes), developed in the framework of the PNRA (Programma Nazionale Ricerche Antartide) [6].
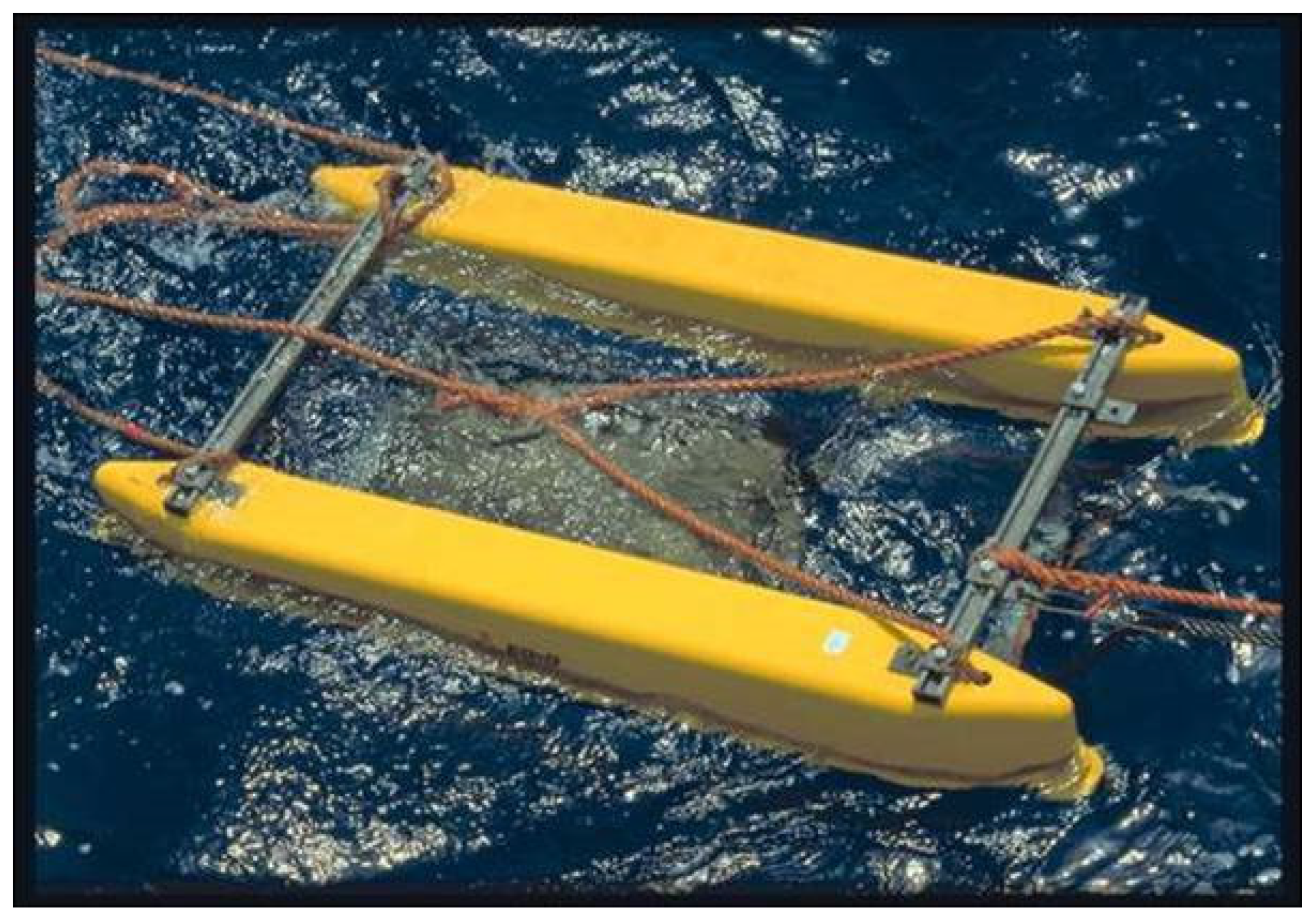
Boomers (EG&G Uniboom; Figure 2) with pulse lengths of 0.1–0.2 ms have been developed for reflection profiling in water depths of a few meters [7,8]. The Uniboom triggers a seismic wave capable of penetrating to significant depths below the seabed. The Uniboom is composed of an electrical coil magnetically coupled to a plate. It has only been subordinately used in Naples Bay, where the use of Sparker and Subbottom Chirp seismic sources has been preferred.

Figure 2.
The Uniboom seismic source.
The post-collapse evolution of the Phlegrean caldera is characterized by unrest and eruptions. The most recent evolution of the Phlegrean caldera has been characterized by short-term ground deformation (or bradyseism), culminating in unrest between 1969 and 1972 and between 1982 and 1984. After these bradyseismic crises, the Institute of Oceanology at the Istituto Universitario Navale (IUN) and the National Research Council (CNR ISMAR) in Naples, Italy, conducted high-resolution reflection seismic surveys in the Pozzuoli area [9,10,11,12,13,14]. These surveys were primarily single-channel, but occasionally multi-channel. Ranieri and Mirabile [9] studied the deep geological structure of the Campi Flegrei volcanic complex with the aim of improving knowledge on seismic technologies and seismic sources more appropriate for the study of volcanic margins. Additional geological and geophysical findings have been presented by Mirabile et al. [15] for the underwater volcanic region in Naples Bay.
D’Argenio et al. [10] applied Airgun technologies to the geological study of Naples Bay, providing interpreted seismic sections of the bay. Some structures are volcanic and their stratigraphic architecture has been reconstructed in detail [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Recently, Giordano et al. [23] have developed a new type of Sparker source that has been tested along seismic lines located in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in Naples harbor in order to provide specific seismic characteristics, which has included its use in shallow water depths and the recognition of the first sedimentary layers. The graphical interfaces have been provided by the D Seismic software (version 1), developed in the frame of the PNRA project [24,25,26]. This software allows for a real-time analysis of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) spectrum of the recorded seismic signals [23].
In this paper, a review of significant seismo-stratigraphic studies performed in Naples Bay is provided, referring to the key areas of the Somma–Vesuvius offshore, of Naples Bay, including the Gulf of Pozzuoli, and of the Ischia and Procida offshore, in order to construct significant stratigraphic correlations in the bay.
2. Geological Setting
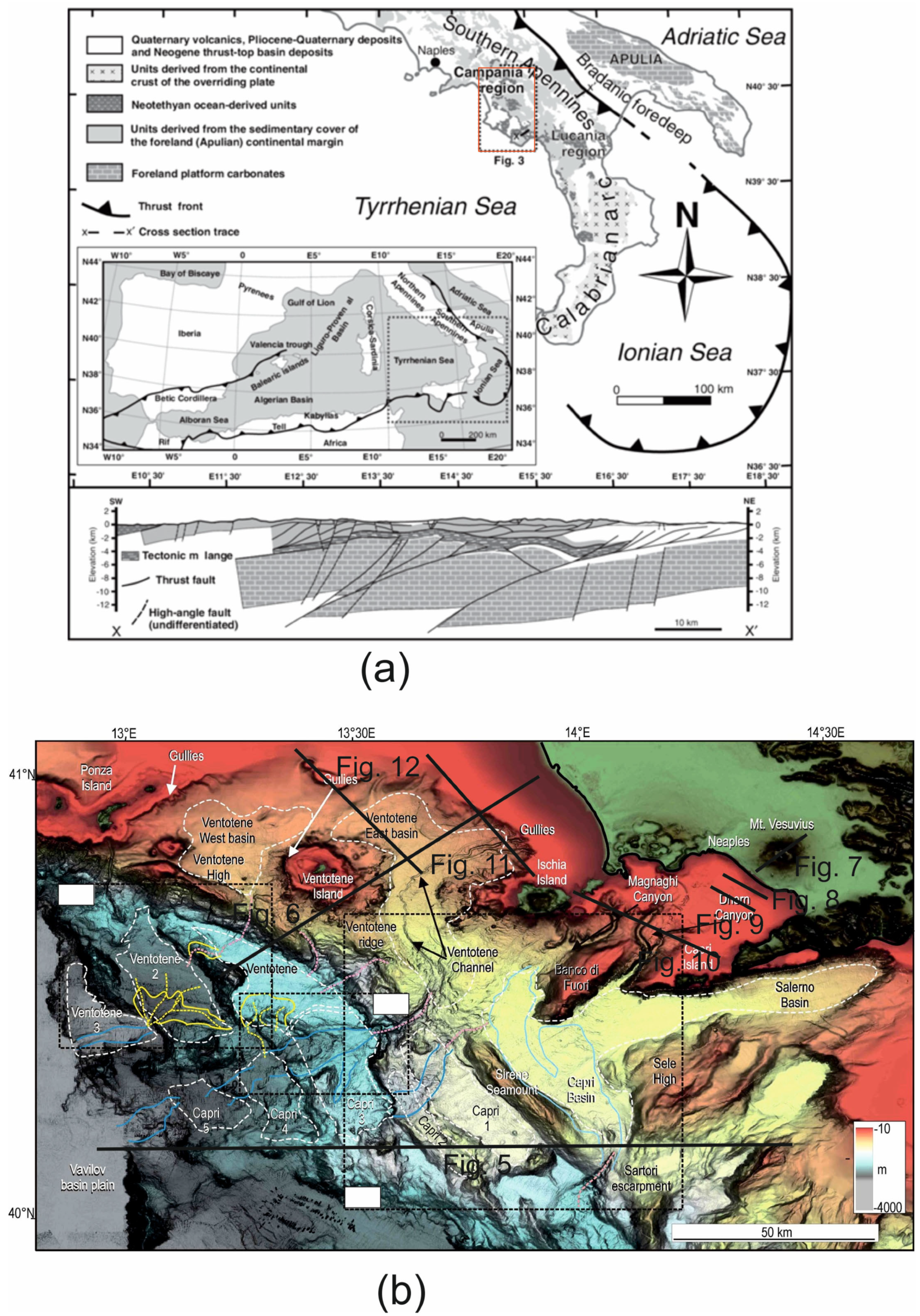
The Campania–Latium Tyrrhenian margin is distinguished from a continental slope, having a complex architecture. This slope bounds the Vavilov basin and is characterized by a southwards widening, proceeding from the Pontine Islands (20 km wide) to the Palinuro volcanic complex [27] (150 km wide; Figure 3b). A tectonic sketch map of the Southern Apennines shows the regional geological setting of the area [28] (Figure 3a). The Southern Apennines–Calabrian Arc system resulted from the convergence from the Upper Cretaceous to the Quaternary between the Corsica–Sardinia–Calabria block, of European origin, and the Apulian–Adriatic block, of African affinity [28] (Figure 3a). This process involved the subduction of the Neotethys oceanic lithosphere, originally interposed between the two paleo-continental margins.
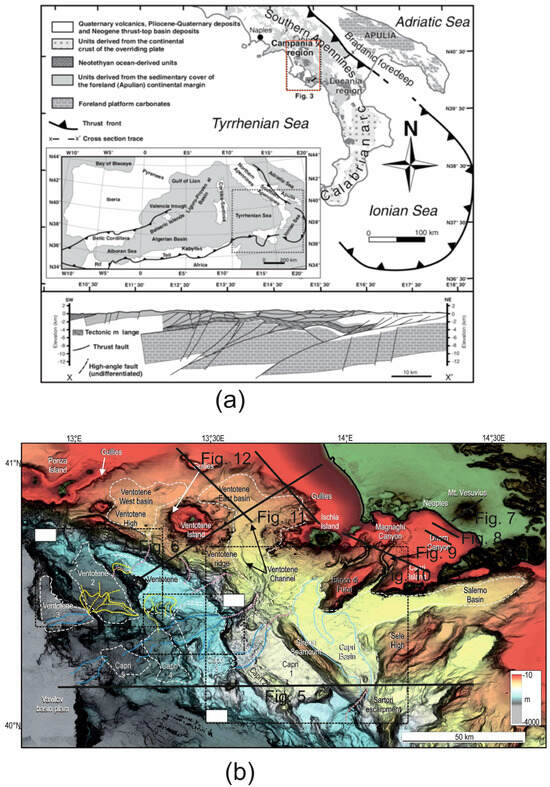
Figure 3.
(a) Tectonic sketch map of Southern Italy (modified after Ciarcia et al. [28]). (b) Shaded relief bathymetric map of the Latium–Campania continental margin (modified after Gamberi et al. [27]). The location of seismic profiles shown in this paper has also been reported. Blanked areas correspond to detailed figures not reported herein.
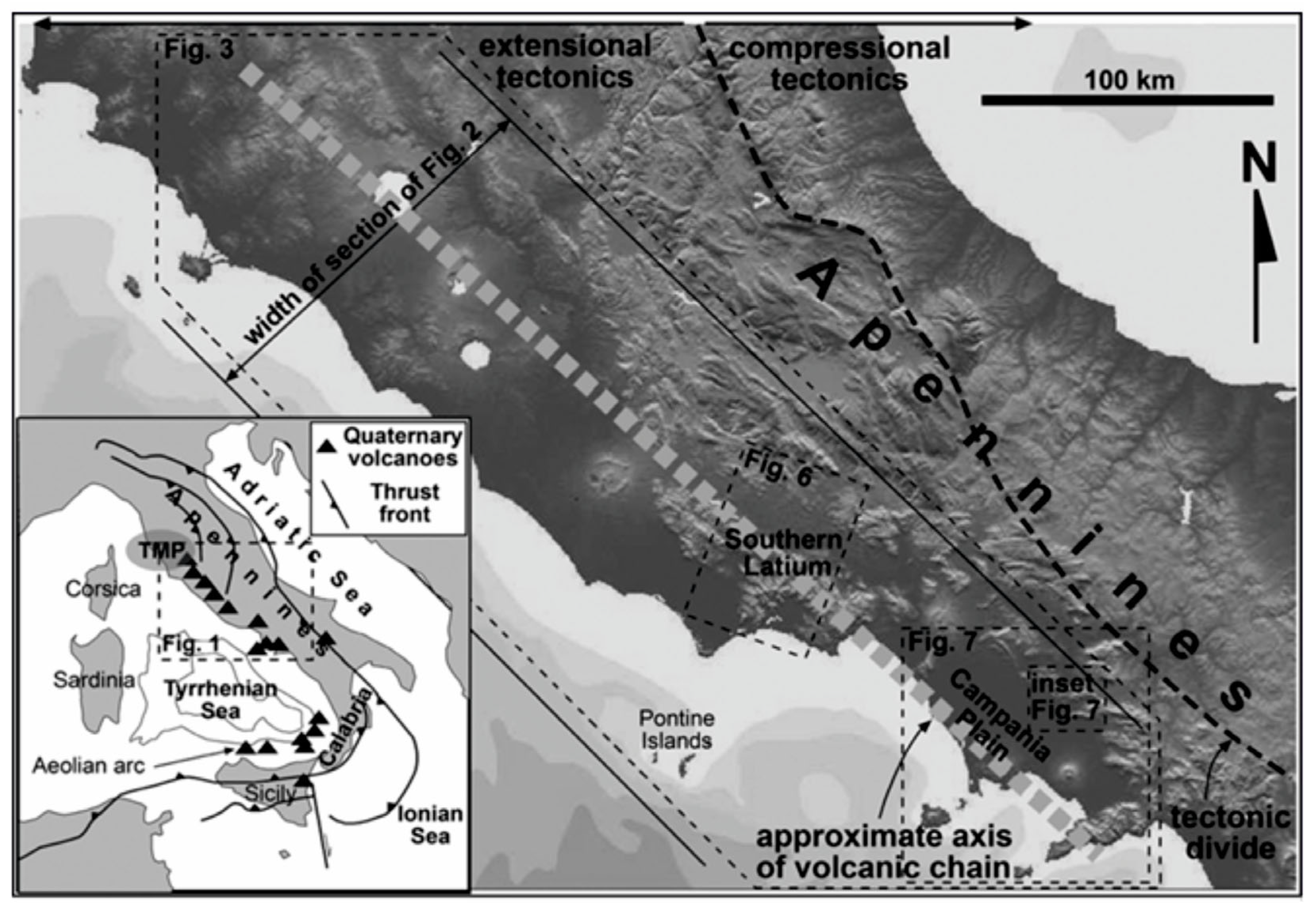
Transverse systems along the Tyrrhenian extensional margin of central and southern Italy have strongly controlled the volcanism [29] (Figure 4). Extensional processes have affected the Tyrrhenian margin of the Italian Peninsula since the Late Miocene period [30]. The relaxation occurred behind the eastward-migrating Apennine orogen and was largely controlled by the subduction of the oceanic lithosphere beneath the Calabrian Arc [30,31,32,33] (Figure 4). Along the Tyrrhenian margin of central Italy, active extensional tectonics migrated eastwards from the Tyrrhenian area (mainly during the Miocene–Pliocene) towards the Apennine divide, where the limit between the extensional and compressional domains is located [29,30,31,32,33] (Figure 4).
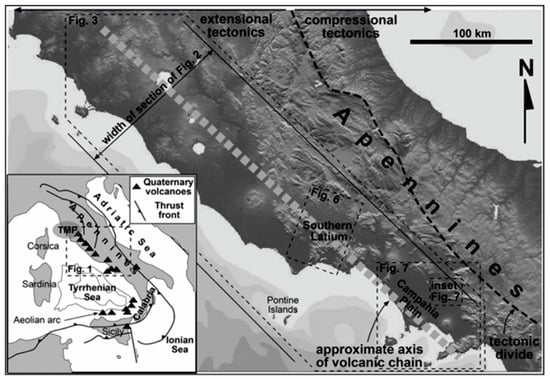
Figure 4.
Transverse system along the extensional margin of central and southern Italy (modified after Acocella and Funiciello [29]).
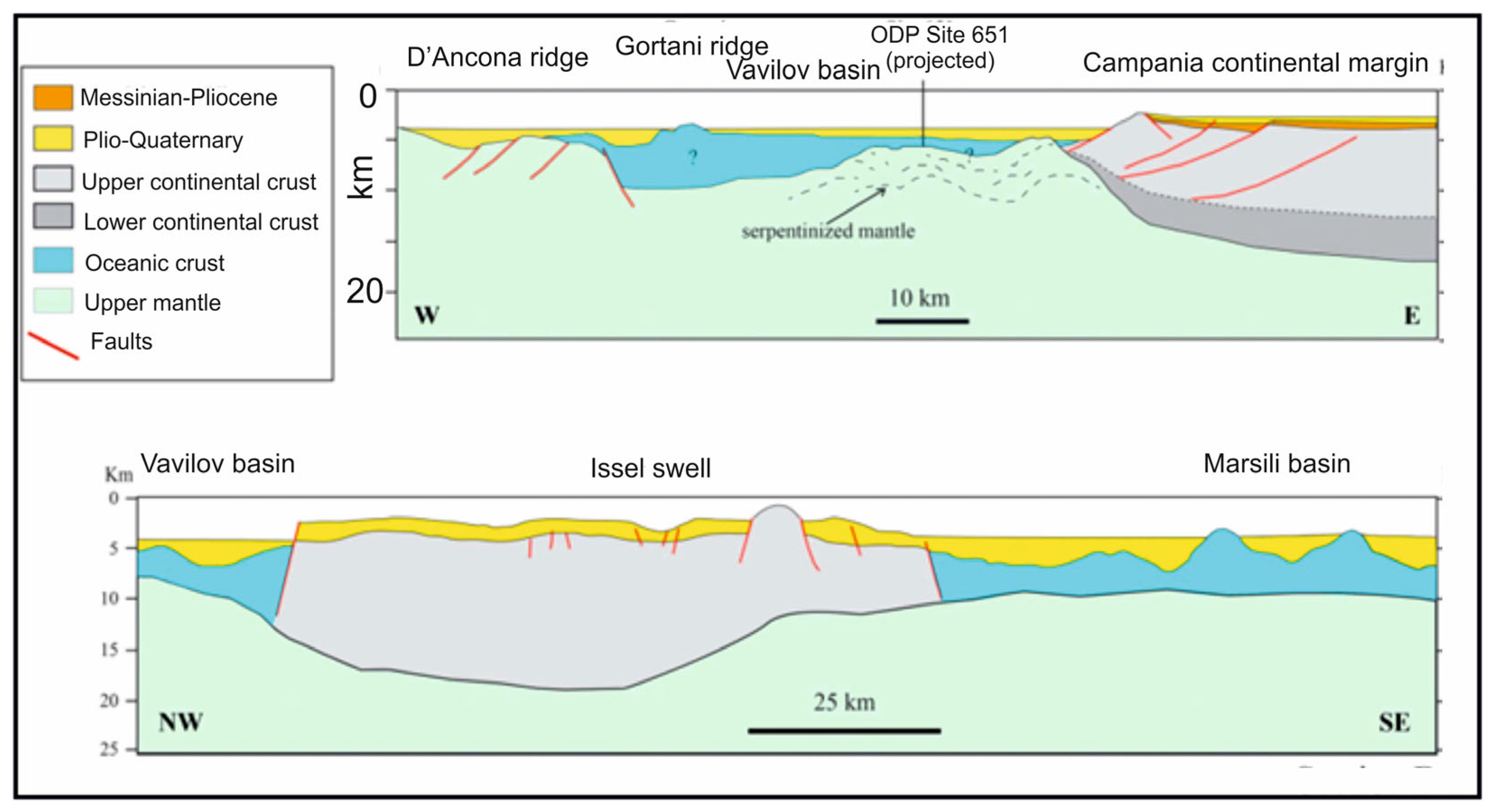
A key seismo-stratigraphic and regional geological study on the Campania Latium continental margin is that of Sartori et al. [34] (Figure 5). Figure 5 shows seismo-stratigraphic sections of the relationships between the Campania continental margin and the Marsili and Vavilov basins, where both continental and oceanic crust have been represented. The oceanic crust has been calibrated through ODP site 651. This sector is made up of horizontal, continuous Plio-Quaternary successions and covers an area with an asymmetrical basement. The sequences are composed of pelagic oozes and turbiditic deposits, the former becoming more and more prevalent (ODP Sites 650, 651). The Plio–Quaternary depocenters (more than 1.4 s twt) occur close to the Campania margin (Figure 5), hosted into half grabens and bounded by faults trending from N–S to NW–SE.
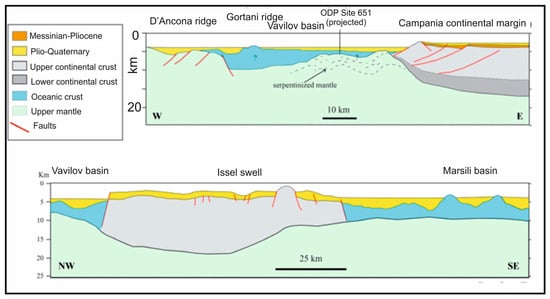
Figure 5.
Seismo-stratigraphic sections of the Campania continental margin, showing the relationships with the Vavilov and Marsili basins (modified after Sartori et al. [34]).
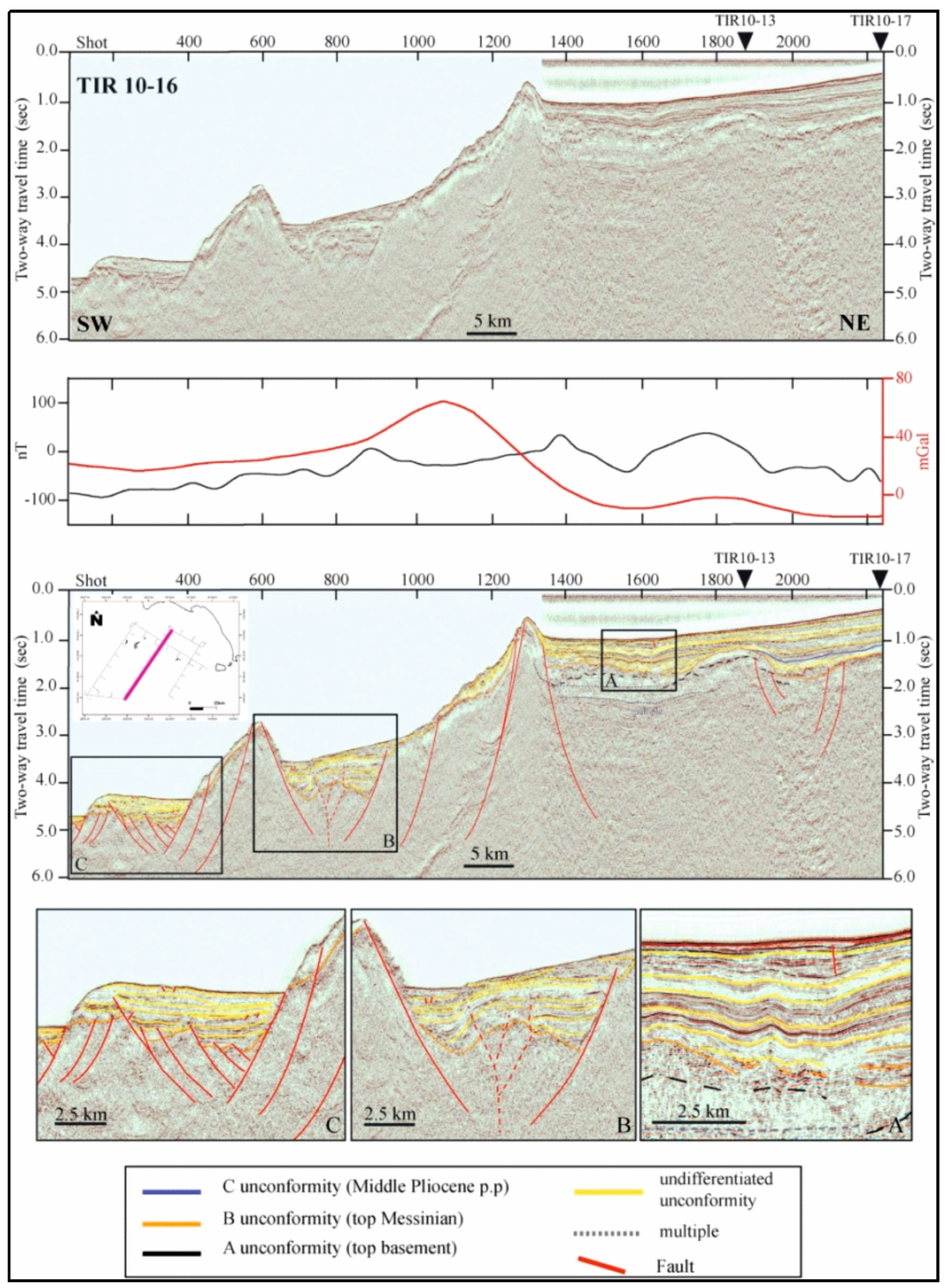
Another important seismo-stratigraphic study is that of Conti et al. [35], focusing on the tectono-stratigraphic evolution of the Campania continental margin (Figure 6). The seismic profile TIR10-16, trending from Ventotene to Ischia, displays the extension occurring on the Campania–Latium continental margin, as shown by the systems of normal faults trending NE–SW [35] (Figure 6).
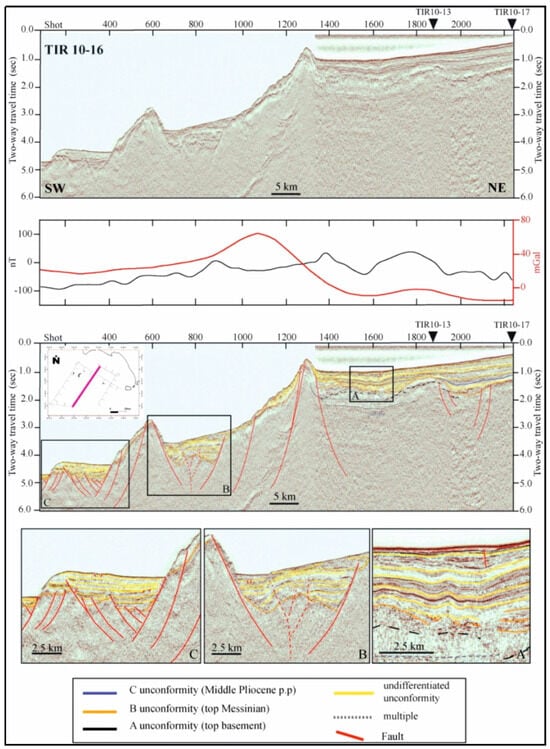
Figure 6.
Seismic section TIR 10–16 and corresponding geological interpretation (modified after Conti et al. [35]).
3. Applications of Seismic Stratigraphy
Seismo-stratigraphic concepts and methods have been applied to volcanic sequences [20,36,37,38,39,40]. The buried volcanoes of Ischia have been studied in detail based on seismo-stratigraphic methodologies integrated with the Kingdom software (version 2) [20]. Three serial geological sections, constructed based on seismic interpretation, have shown the geometric characteristics and the stratigraphic relationships between the volcanic and the sedimentary units in the northern Ischia offshore. The seismic units have been correlated with the volcanic units’ outcropping in the adjacent northern coastal belt of Ischia [20]. In particular, the V1 seismo-stratigraphic unit is genetically related to a buried volcano next to the Castello d’Ischia volcanic edifice, located in the northeastern Ischia offshore. The V2 seismo-stratigraphic unit is genetically related to a lava dome offshore of Mt. Vico, located in the northwestern Ischia offshore. The V3 seismo-stratigraphic unit is correlated with the Campanian Ignimbrite (39 ky B.P.) based on seismic facies, stratigraphic relationships, and correlation with the onshore geological units of Procida and Vivara [21]. Here, a transition from siliciclastic to bioclastic deposits has been highlighted [21]. The V4 seismo-stratigraphic unit has been correlated with the Sant’Anna lavas (22 ky B.P.). The V5 seismo-stratigraphic unit is genetically related to the Spiaggia degli Inglesi lava flows [22]. The V6 seismo-stratigraphic unit has been interpreted as a lava and scoria volcano, genetically related to the S. Pietro lavas, located eastwards of the Ischia harbor, where the S. Pietro lavas crop out. The V7 seismo-stratigraphic unit is a shallow buried volcano resembling a dome or a dyke, uplifting and deforming the surrounding sediments, and located offshore of Punta della Scrofa (northern Ischia).
Planke et al. [36] have highlighted that the seismic units of volcano stratigraphy consist of landward flows, lava deltas, inner flows, inner SDR (Seaward Dipping Reflectors), outer high, and outer SDR. A five-stage volcano stratigraphic model has been proposed for a rifted continental margin, including initial explosive volcanism with the formation of basaltic complexes poorly imaged on seismic data, effusive subaerial volcanism forming the inner flows, lava deltas and landward flows’ seismic units, continuing effusive subaerial volcanism forming the inner SDR at the narrowing rift, explosive shallow marine volcanism including the outer high, and deep marine volcanism forming the outer SDR [36]. Jerram et al. [37] have provided a volcano stratigraphic framework identifying a set of lava sequences, including tabular simple flows, compound-braided flows, and subaqueously deposited hyaloclastite facies. Abdelmalak et al. [38] have applied the volcano stratigraphic model of Planke et al. [36], recording the early encroachment of flood basalt into the basin and the buildup of a lava delta system. Bischoff et al. [39] proposed the classification of buried volcanoes into three main geomorphic categories, including the small-volume clusters, craters, and cones, the wide, composite, shield, and caldera volcanoes, and the voluminous lava fields. Martì et al. [40] have reviewed the volcano-stratigraphic concepts, highlighting that different types of volcanic unconformities exist. The first type of volcanic unconformities (‘minor unconformities’) appear between successive eruptions that are separated by phases of quiescence, or even between different pulses of the same eruption, and are not associated with varying dynamics of the volcanic system. The second type of volcanic unconformities (“moderate unconformities”) are formed during the erosional processes of previous volcanic deposits, during the deposition of reworked materials and the formation of paleosoil separating different volcanic deposits. The third type of volcanic unconformities (“major unconformities”) individuates during the construction of a stratovolcano and involves sector failures, caldera collapses, and changes in the clustering of the volcanic cones.
4. Results
4.1. Seismic Stratigraphy of the Somma–Vesuvius Offshore
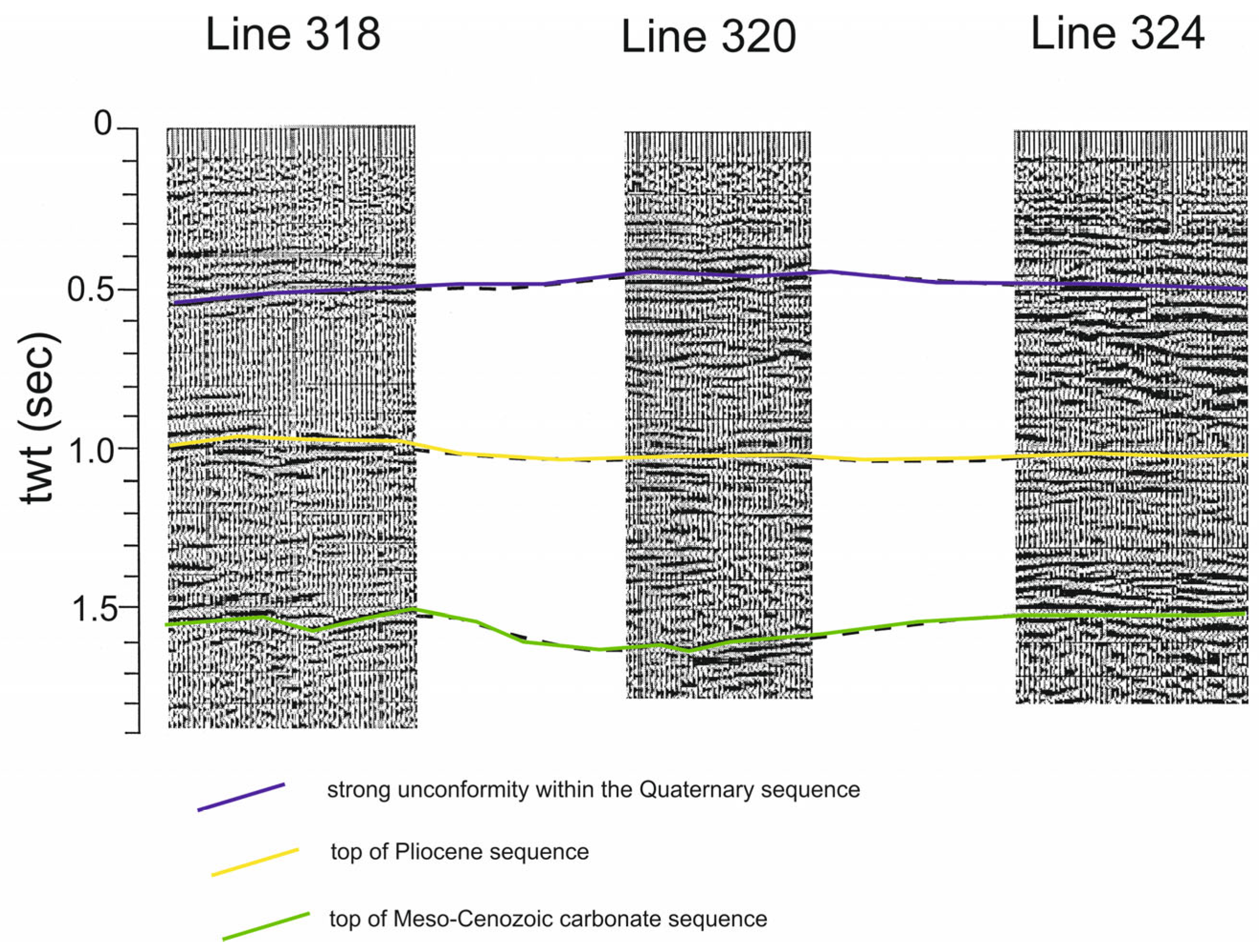
The seismic stratigraphy offshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex, as studied by several authors, is herein revised [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. Gravimetric data have been used to complement seismo-stratigraphic knowledge [50]. Bruno et al. [49] have shown the seismo-stratigraphic setting of the Mesozoic carbonate basement onshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex to be based on multichannel seismic profiles. Three important seismic reflectors have been recognized, corresponding with the top of the Meso-Cenozoic carbonate sequence, the top of Pliocene deposits, and a strong unconformity within the Quaternary deposits, respectively (Figure 7) [49].
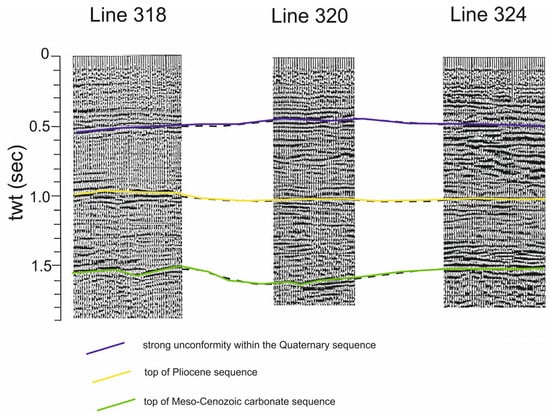
Figure 7.
Sketch diagram showing significant seismic horizons onshore the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex (modified after Bruno et al. [49]).
Three representative examples of the reflective subsurface image from the area are shown in Figure 7 at 0.5 s, 1 s, and 1.5 s, for two-way time. The three horizons can be traced within the two other sequences, as well. The Trecase 1 well has calibrated the third horizon at 1.5 s, concurrent with the top of the carbonate determined down the well. The low seismic data quality on line 316 does not permit a certain reciprocity of the other two upper reflectors with the post-Mesozoic stratigraphy. The reflector at around 1 s, with two-way time, is relevant to the top of the Pliocene sequence beneath the Quaternary sediments. The uppermost horizon, at about 0.5 s, stands for a strong unconformity within the Quaternary deposits. The general structure of the carbonate basement is more composite than a monoclinalic structure, dipping towards the northwest. In general, the carbonates deepen towards Naples Bay and towards the center of the Campania Plain. They are downthrown by regional faults, controlling a horst and graben-like structure, and reach a maximum depth of approximately 2600 m in the Acerra graben, located in the Campania Plain [49].
Bruno and Rapolla [43] have integrated their previous results through a seismic profile recorded within the Avellino caldera, at the southwestern edge of the Great Cone of Vesuvius. An important seismic horizon suggests an SW lateral collapse was undergone by the volcano, probably between 35 and 11 ky B.P. Buried craters, dykes, and pyroclastic deposits were discovered on the eastern side of the volcanic complex. The existence of NW–SE striking faults that cut across Vesuvius has been substantiated, and probably played a major role in the genesis of the volcano. Ring faults were found mainly in the northeastern and southeastern sectors of the volcano. These faults appeared on the seismic data as a low signal-to-noise area qualified by high lateral heterogeneity and the existence of numerous fractures due to the stress field created by the volcano collapse [43].
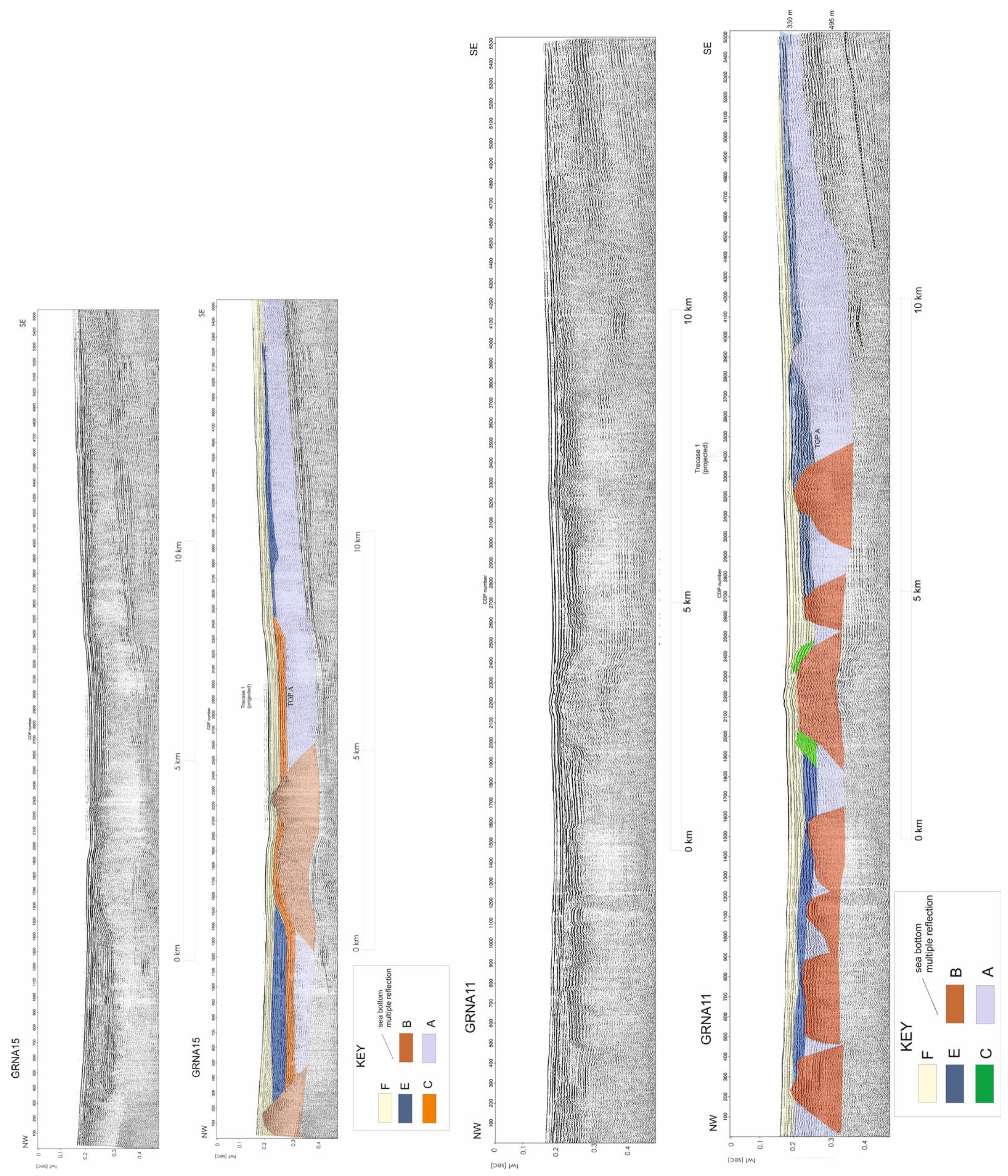
Aiello [41] has recently proposed an up-to-date seismo-stratigraphic setting offshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcano. Figure 8 shows the main seismo-stratigraphic results. The seismic profiles are located on the continental shelf of the Bay of Naples offshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex and have been recorded through a Watergun seismic source.
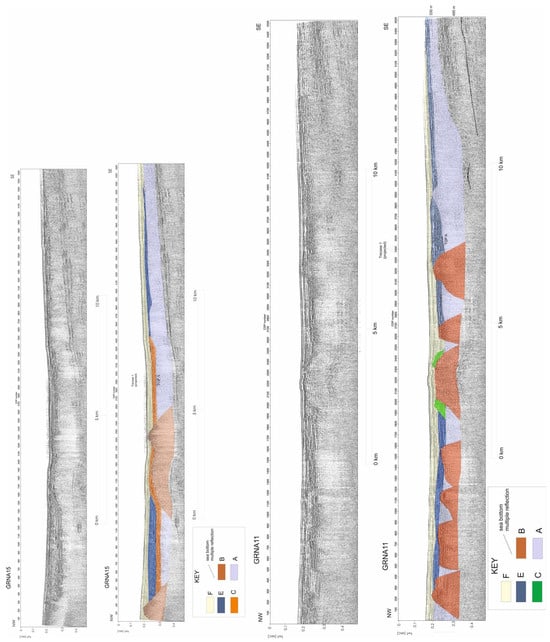
Figure 8.
Seismo-stratigraphic setting of the Somma–Vesuvius offshore (modified after Aiello [41] and reinterpreted here as part of the current study). G: PDC older than the AD 79 deposits (detected on other seismic lines and shown in Aiello [41]). F: Highstand System Tract. E: Debris flow genetically related to Somma–Vesuvius. C: Lowstand System Tract. D: NYT (Neapolitan Yellow Tuff deposits; detected on other seismic lines as shown in Aiello [41]). B: Buried tuff rings (cryptodomes in the previous literature). A: Campanian Ignimbrite.
The seismic units previously recognized offshore of Somma–Vesuvius have been reviewed and compared with the seismic units recognized in this paper in a sketch table (Table 1). Previous studies on the submarine structure of the Somma–Vesuvius volcano have reported on the occurrence of buried volcanic structures and thick volcanic seismic units, genetically related with the eruptive events of the Somma–Vesuvius volcano (Table 1) [42,46,47,51].

Table 1.
Revision of the seismic units offshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex.
In particular, Milia et al. [42] have recognized different seismic units in the Somma–Vesuvius offshore based on the interpretation of Sparker seismic profiles (Table 1). These authors have considered two possible explanations for the buried mounds. The first hypothesis is that these buried mounds are hummocks in a debris flow, produced during the Mt. Somma collapse, creating the breached crater. The second account is that they are cryptodomes, rising upwards and warping the horizontal layers of the lowstand marine deposits. The cryptodomes are represented by intrusions triggering the uprising of the overlying sediments, whose comprehension is important for the volcanic hazard assessment.
A three-dimensional reconstruction of the volcanic structures located offshore of the Torre del Greco town (Vesuvius area) has been carried out [51]. In particular, the seismic units include the Holocene mud wedge, overlying the underlying volcanic structures; the Late Pleistocene marine and coastal deposits, characterized by parallel to sub-parallel seismic reflectors, with lateral terminations of onlap on the flanks of the volcanic domes; the BV unit, a wide volcanic vent located offshore of the volcano; the B unit, corresponding with the mound-shaped, isolated, and buried volcanic structures located near the top of the CI seismic unit; and the Campanian Ignimbrite (CI) seismic unit, showing a complex palaeo topography, with some palaeo-terraced surfaces located at its top, controlled by normal faults with a little throw (Table 1).
Several seismic units have been reported on the submarine slopes of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex (Table 1) [47], mainly represented by the highstand and transgressive deposits (PGLM) overlying a regional unconformity, corresponding with the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM; 19 ky B.P.). Fluid vents (FV) and mound-shaped cryptodomes (V1-V6) have also been distinguished (Table 1). Four volcanic vents, located offshore of the Somma–Vesuvius volcanic complex, have been emplaced after the LGM, while a fifth vent was emplaced during more recent times, suggesting the reactivation of volcanic activity during historical times.
4.2. Seismic Stratigraphy of Naples Bay
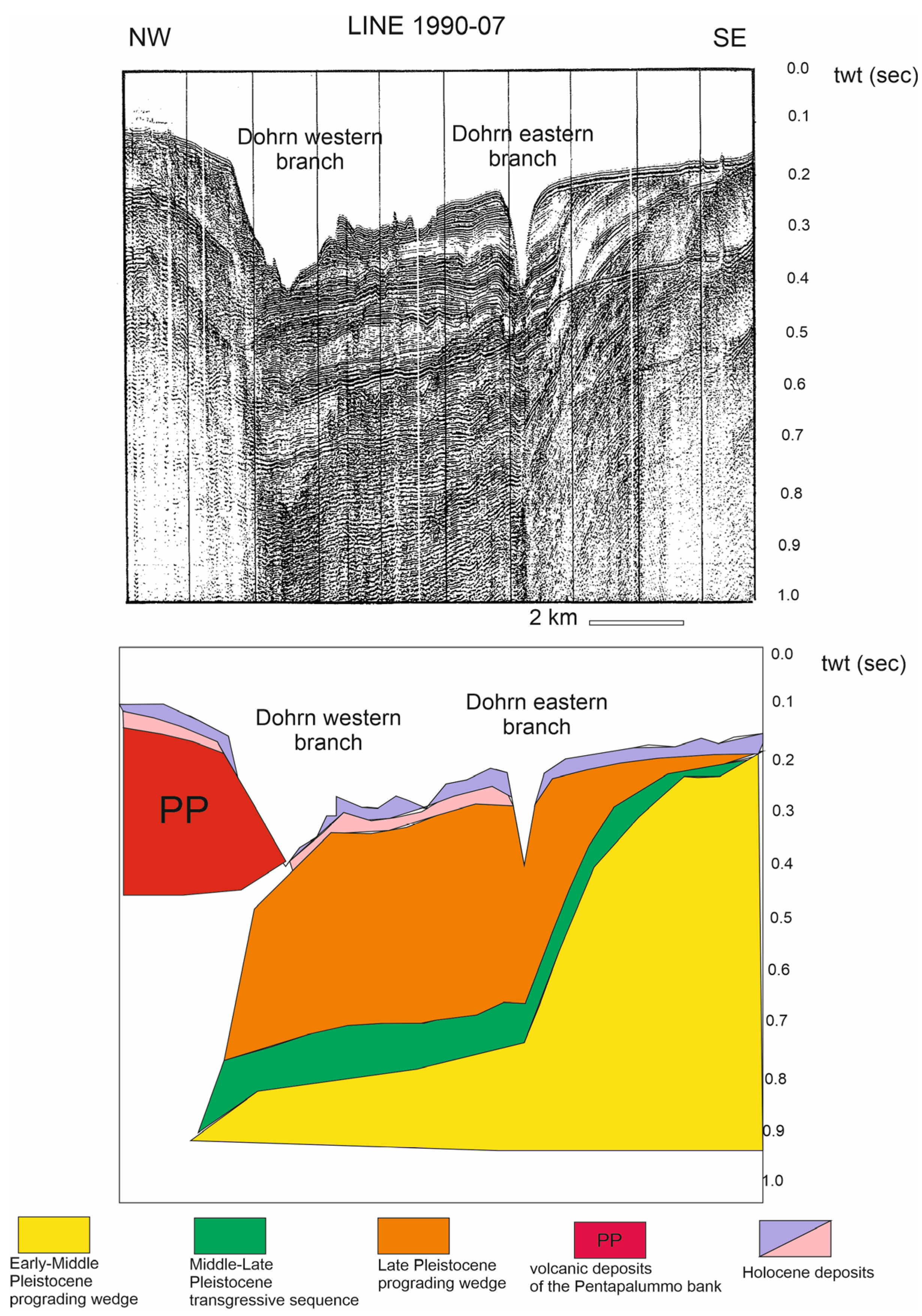
One of the key papers on the seismic stratigraphy of Naples Bay is that of Fusi et al. [52], whose seismic sections have been recently revised by Aiello and Caccavale [46]. Figure 9 shows one of the most significant seismic sections of the Sparker database of Fusi et al. [52], as reassessed by Aiello and Caccavale [46], which is located in the central sector of Naples Bay, corresponding to the Dohrn canyon (Dohrn western branch and Dohrn eastern branch). In particular, this seismic profile shows that the Dohrn eastern branch was completely incised in the Late Pleistocene prograding wedge. The upper part of the wedge on the canyon’s southeastern flank is being eroded away. This implies that the origin of this canyon has been controlled by both the sedimentary processes and by the volcanic ones (Figure 9).
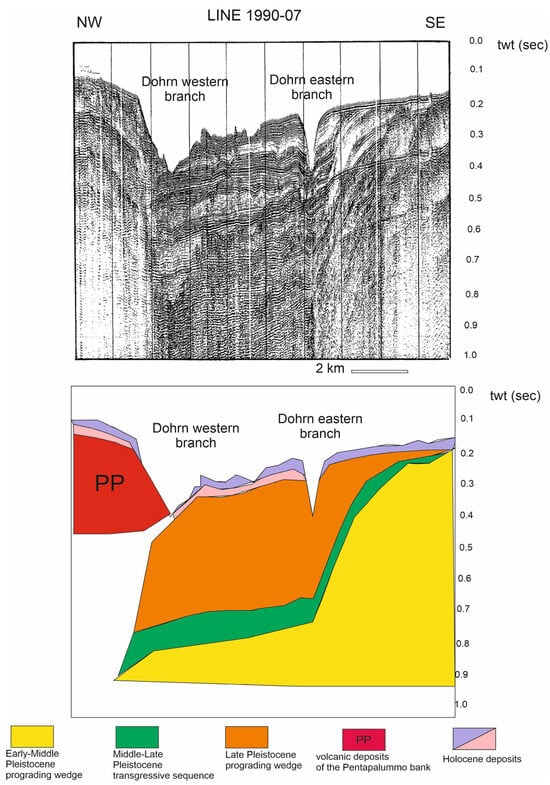
Figure 9.
Sparker profile 1990-07 and corresponding geological interpretation (modified after Fusi et al. [52] and Aiello and Caccavale [46] and reinterpreted here as part of the current study).
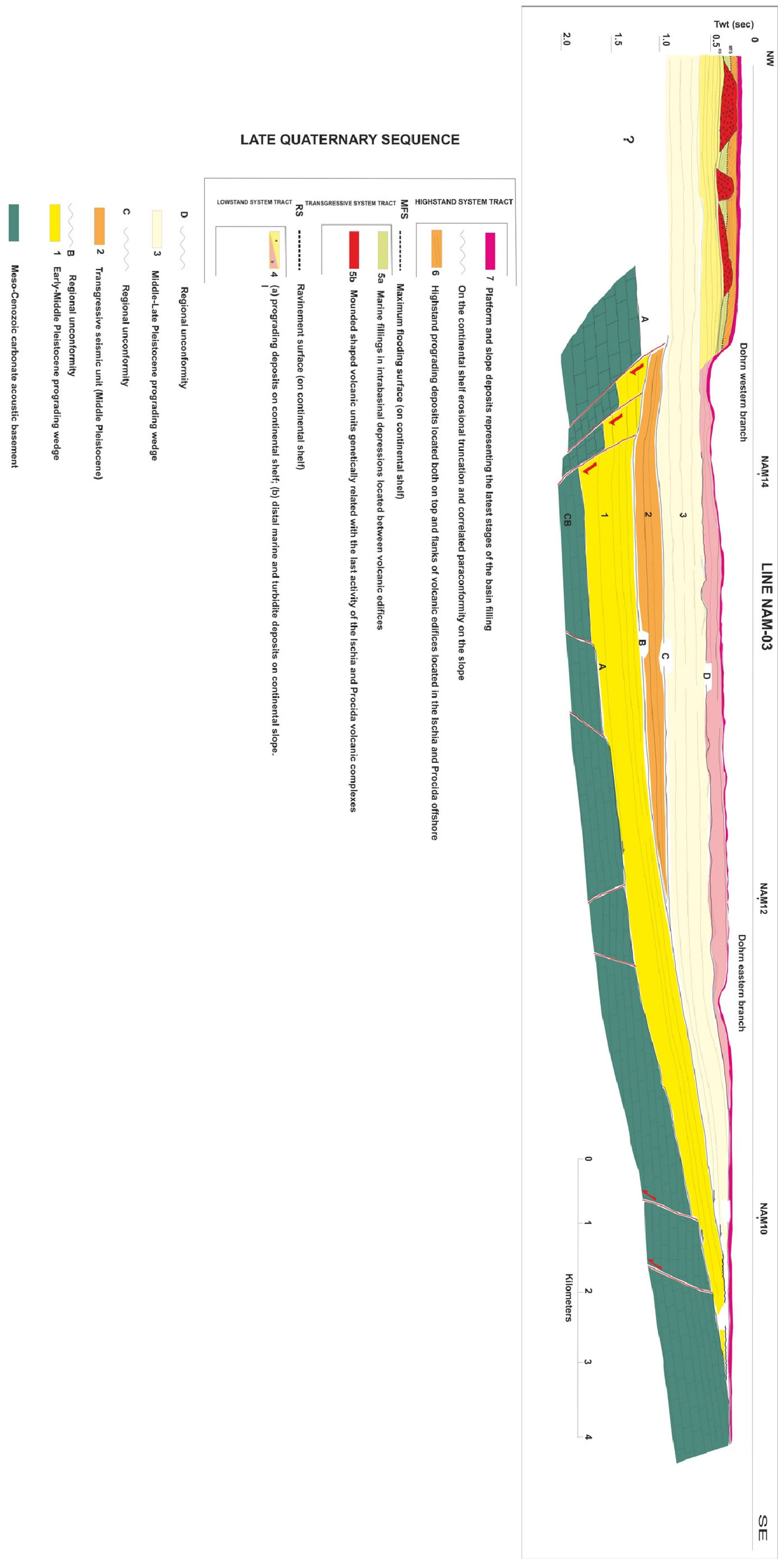
The key seismic section showing the stratigraphy of Naples Bay has been reinterpreted, aimed at showing a complete seismo-stratigraphic setting of the area [10] (Figure 10). The seismic profile of Figure 10 is located in Naples Bay from offshore of the Ischia and Procida Islands and offshore of the Sorrento Peninsula [10]. The carbonate acoustic basement is characterized by a NW-dipping monoclinalic structure and is genetically related to the Meso-Cenozoic carbonate unit outcropping in the adjacent coastal belt in correspondence with the Sorrento Peninsula and Capri Island. The deepest seismic unit is represented by a NW-dipping prograding wedge, with eroded topsets and preserved clinoforms, Early–Middle Pleistocene in age (Figure 10). The B unconformity bounds the seismic unit 1 in its upper part and represents an erosional truncation extending from the continental shelf to the upper slope. On the northwestern flank of the basin, the unconformity is down-thrown by normal faults with a little vertical throw, while on the southeastern one it rises along the NW-dipping monoclinalic structure composed of the carbonate basement and seismic unit 1 (Figure 10).
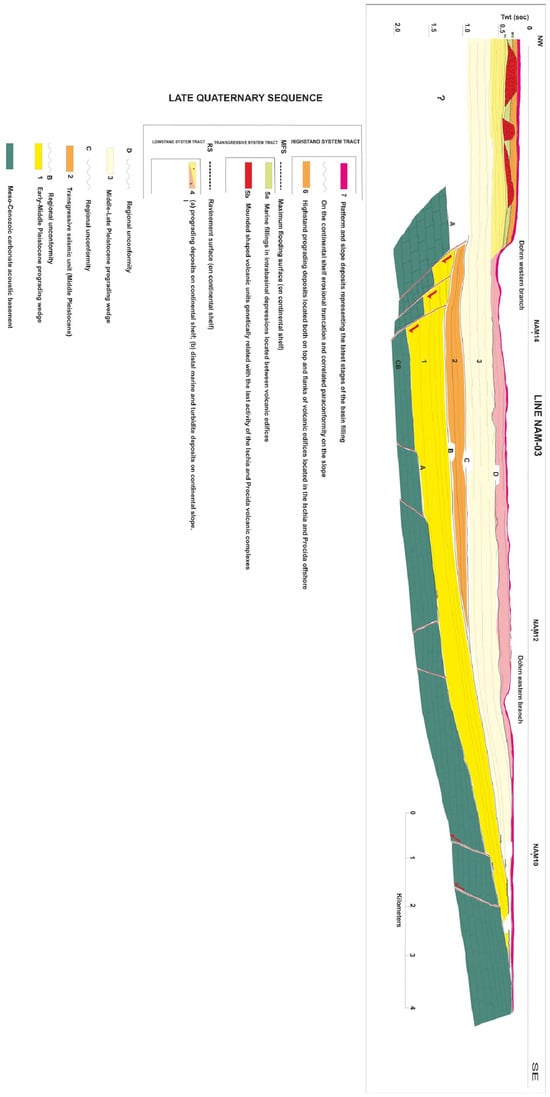
Figure 10.
Geological interpretation of the NAM3 multichannel profile (modified after D’Argenio et al. [10] and reinterpreted here as part of the current study).
Seismic unit 2 is wedge-shaped and shows a progressive onlap of the seismic reflectors on the B unconformity. The stratigraphic relationships with the adjacent seismic units and the overall seawards shifting of the coastal and marine facies suggest its deposition during a transgressive phase younger than the B unconformity. The wedging of seismic unit 2 highlights its synsedimentary nature and that it was deposited during active tectonic phases of the adjacent mainland (Figure 10). The C unconformity bounds seismic unit 2 in its upper part and is characterized by an erosional to non-depositional hiatus ranging in age from the Late Pleistocene to the Holocene.
Seismic unit 3 is a shelf and slope sequence characterized by sigmoidal/oblique to parallel reflectors (Figure 10). It is widespread in the western sector of the bay and is older than the emplacement of the Campanian Ignimbrite seismic unit (39 ky B.P.). The entry points of the prograding wedge indicate feeding sources located in correspondence with the Sarno river mouth. The Dohrn and Magnaghi canyons are carved deeply into the unit, displaying relict morphologies located at the Dohrn eastern head and suggesting its deposition during lowstand phases of the Middle–Late Pleistocene era. The D unconformity is located at the top of seismic unit 3 and at the base of the Late Quaternary depositional sequence. It corresponds to an erosional unconformity, probably subaerial, as shown by the occurrence of palaeochannels (Figure 10).
The Late Quaternary depositional sequence is composed of lowstand, transgressive, and highstand system tracts (Figure 10).
The lowstand system tract is composed of two kinds of deposits, namely the prograding deposits on the continental shelf (4a in Figure 10) and the distal marine and turbidite deposits on the continental slope (4b in Figure 10). Prograding deposits are cut by the seismic section perpendicular to their direction of progradation, and they may appear as sub-horizontal reflectors. On the slope, distal marine facies and gravitational reworked sediments alternating with chaotic and acoustically transparent intervals lie in paraconformity on the underlying seismic units. In its upper part, the lowstand system tract is bounded by a ravinement surface (Figure 10).
The transgressive system tract constitutes volcanic bodies, mound-shaped (5a in Figure 10), and marine fillings deposited in intrabasinal depressions located between the volcanic edifices (5b in Figure 10). It is bounded upwards by the maximum flooding surface.
The highstand system tract is represented by highstand prograding deposits located both on top and on the flanks of volcanic edifices and by gravitational reworked sediments and turbidite deposits, representing the latest stages of basin filling (Figure 10).
4.3. Seismic Stratigraphy of the Ischia Offshore
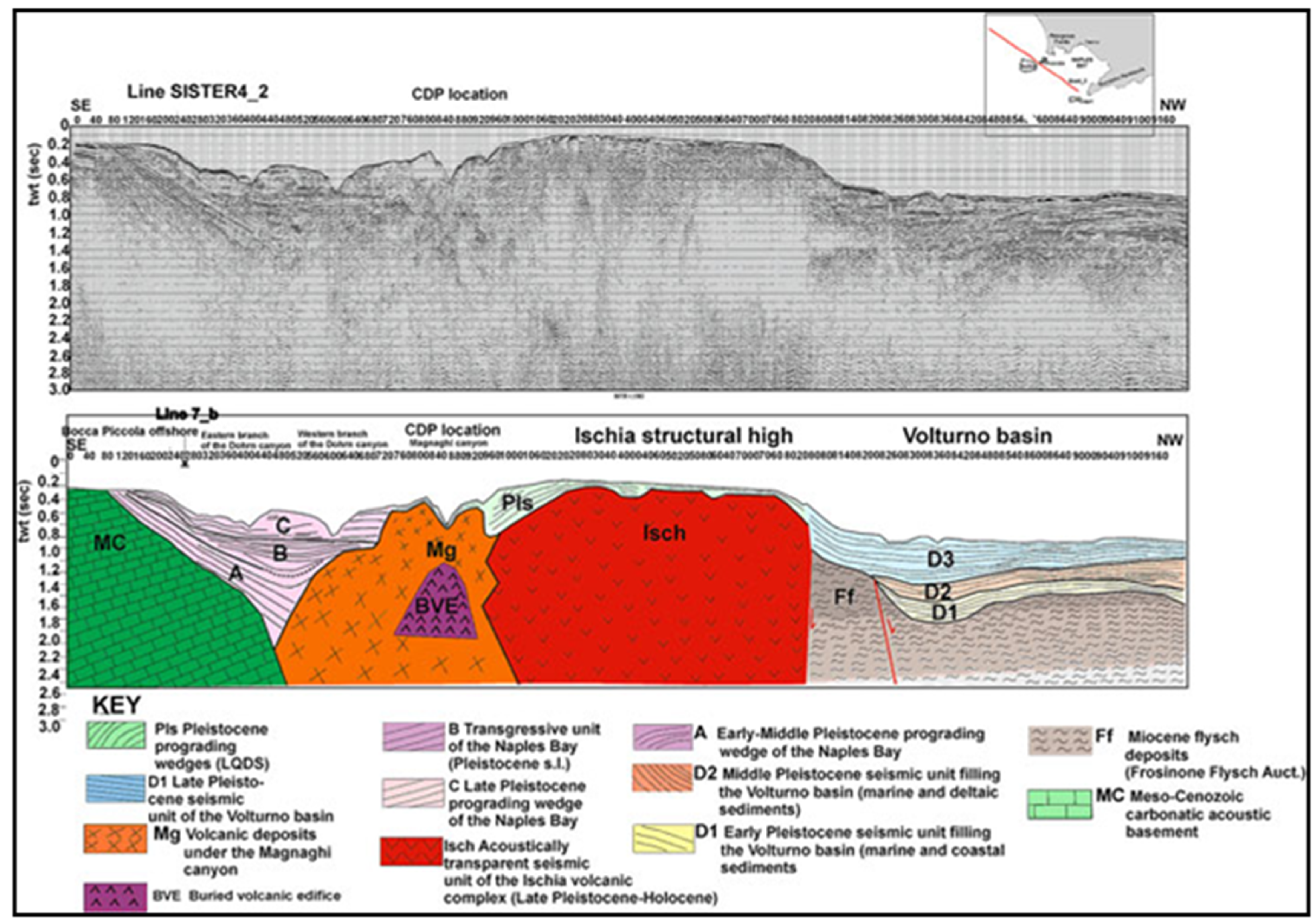
Key seismo-stratigraphic studies on the Ischia volcanic complex are those of Bruno et al. [53], Aiello et al. [54], Aiello et al. [55], Aiello [56], Aiello and Caccavale [21], and Milia et al. [20]. All these studies have highlighted that the occurrence of isolated volcanic bodies renders the sequence stratigraphic approach particularly challenging for the geological interpretation of seismic profiles. The volcanic bodies of Ischia have been successfully mapped using the software Kingdom (version 2) [20]. Bruno et al. [53] have reported E–W and NE–SW volcanic ridges following the regional faults, NE–SW trending. Submerged volcanoes are cut by fault scarps that balance, with a strong vertical component, Holocene marine and volcaniclastic deposits. Aiello et al. [54] have highlighted submarine gravitational instabilities occurring in the northwestern off-shore of the island as resulting from widespread debris avalanches, often interlayered in the stratigraphic succession. Aiello et al. [55] have established the general seismo-stratigraphic setting of the Ischia off-shore, correlating onshore volcanic stratigraphy with the seismic stratigraphy of the offshore sectors of Punta Imperatore, Grotta del Mavone, Punta del Chiarito, S. Angelo, Barano, and Maronti. Figure 11 shows the seismo-stratigraphic setting of the Ischia structural high in the regional framework of the Bay of Naples.
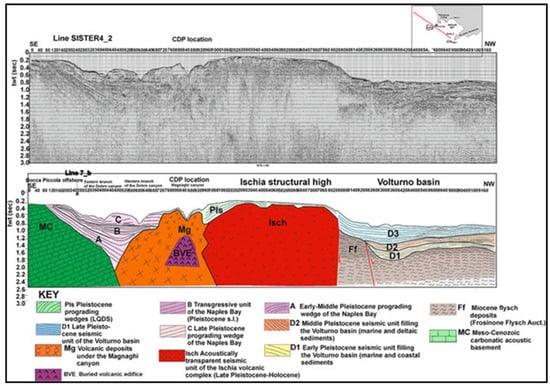
Figure 11.
Geological interpretation of the SISTER4_2 multichannel profile (modified after Aiello et al. [13] and reinterpreted here as part of the current study). Volcanic structures: Mg (Magnaghi canyon), BVE (Buried Volcanic Edifice), Isch (Ischia structural high).
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Marine geological studies on Naples Bay have been revised, focusing on the application of seismo-stratigraphic concepts to a Late Quaternary volcanic area, and in particular, to the Somma–Vesuvius, central Naples Bay and Ischia offshore areas.
The seismo-stratigraphic method has been fully applied in central Naples Bay, where four regional unconformities (A, B, C, and D in Figure 10), separating incomplete depositional sequences in the Naples basin filling, have been recognized (Figure 10). The only complete depositional sequence is the Late Quaternary one.
In the Somma–Vesuvius offshore area, the seismic profiles have recorded a low seismic unit (CI), corresponding to the 39 ky old Campanian Ignimbrite and another seismic unit (B), located seawards, that is located below the LST deposits and is overlain by the HST deposits (Figure 8) [41]. B is associated with cryptodomes. If lowstand deposits lie on the B unit, the B unit should have emerged at the moment of LST deposition. A cryptodome is, by definition, a subsurface structure.
In proximal regions, the lowstand deposits are overlaid by a chaotic seismic unit, explained as pyroclastic flow deposits (PF) [41]. The lowstand deposits, which have parallel and continuous seismic reflectors, lie above the Campanian Ignimbrite. Due to its seismic facies and stratigraphic relationships, the lowstand unit has been explained as the sediments that were put in the falling and as lowstand of the sea level. A local uplift has occurred in recent times, as commanded by the cryptodome intrusion, and can be observed in the seafloor deformation. These events have been troubled by the eruption of the NYT unit (15 ky B.P.) in the Naples offshore area, representing a main volcano–tectonic case in the Naples area.
A close linkage of the Somma–Vesuvius seismo-stratigraphic data with the Quaternary volcanism of the Campania continental margin is suggested. Offshore of the Vesuvius volcano, seven seismic units are known, in particular the G, the F, the E, the D, the C, the B, and the A units (Figure 8) [41]. These units, corresponding to PDC older than the 79 A.D. eruption (G), to the Highstand System Tract (F), to a debris flow genetically related to Somma–Vesuvius (E), to the Lowstand System Tract (C) D: to the NYT deposits (D), to the buried tuff rings (B, cryptodomes in the previous literature), and to the Campanian Ignimbrite (A), respectively, are associated with the Quaternary volcanism of the Campania continental margin [11,12,30,48].
The transverse extensional systems occurring on the Tyrrhenian extensional margin of central and southern Italy have strongly influenced the distribution of volcanism [28,29]. This is demonstrated by the structural maps showing the main fault systems and the Plio-Quaternary volcanoes and confirmed by the location of volcanic edifices along the margin (Vulsini, Sabatini, Colli Albani, Roccamonfina, and volcanoes of the Neapolitan district) [29]. Moreover, this has been confirmed by regional seismo-stratigraphic evidence on the continental margin. The seismic profiles TIR 10–16 (Figure 6) and TIR10-14 have shown the extension on the Campania–Latium margin as controlled by NE–SW trending normal faults [35], and a strike-slip component, locally occurring, suggests transverse systems.
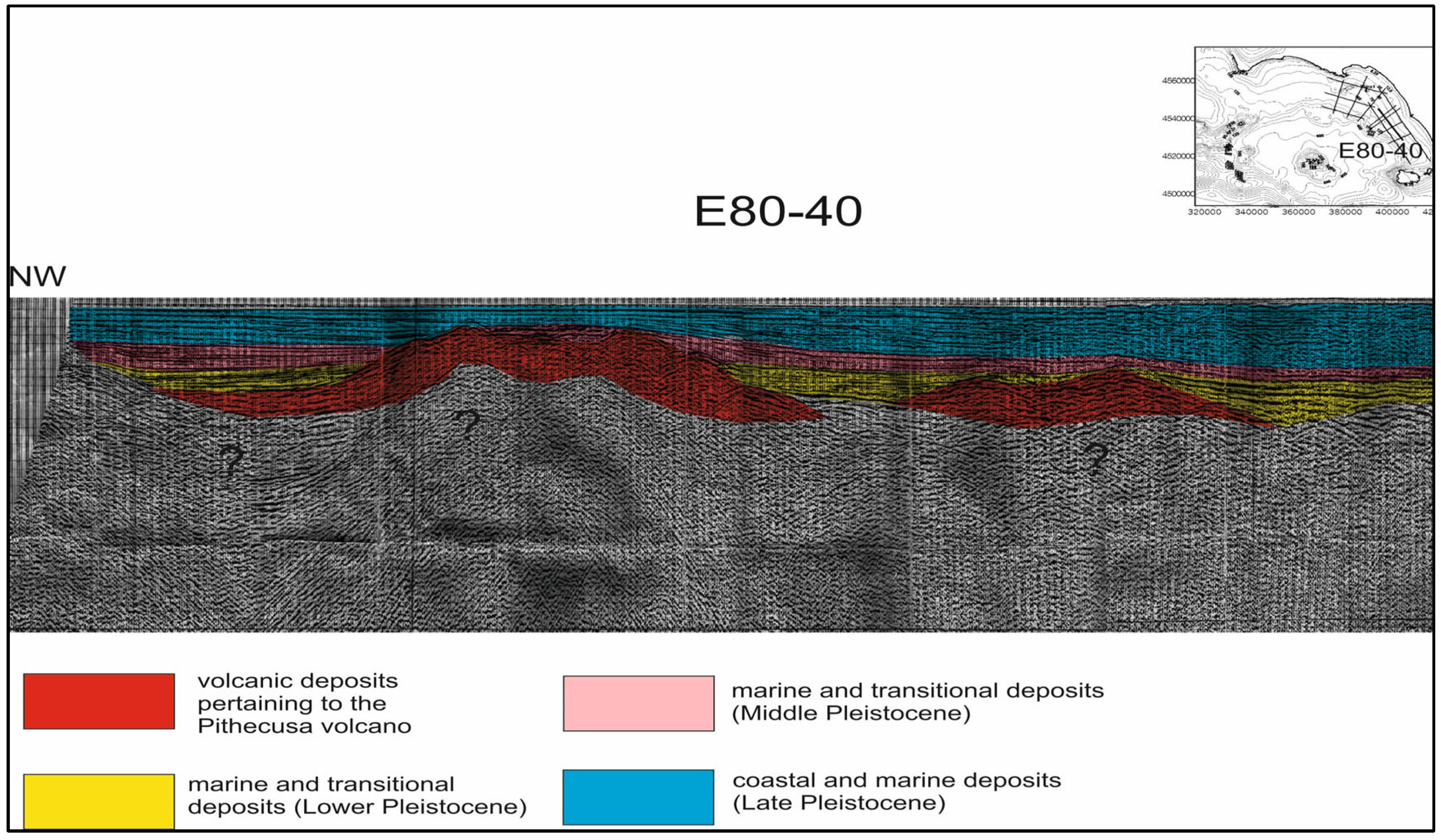
Important buried volcanic structures occur on the Campania continental margin. Apart the buried volcanoes shown in the Somma–Vesuvius offshore area (Figure 8), central Naples Bay (Figure 9 and Figure 10), and Ischia (Figure 11), another important volcanic edifice, namely the Pithecusa volcano, has been detected at the Volturno river mouth based on seismic interpretation (Figure 12). Its emplacement is genetically related to the eruptive phases of the Neapolitan volcanoes (Figure 12). In its upper part, the volcanic edifice is eroded by a regional unconformity and its northeastern slope is down thrown by a normal fault, marking the passage to a seismo-stratigraphic unit correlated to the Frosinone Flysch (Figure 12). This unit appears clearly on the northeastern side of the buried volcanic edifice, where it is down-thrown by normal faults. The western side of the volcano, as well as the seismic unit genetically related to the flysch deposits, are overlain by a thick seismic unit, genetically related to Early Pleistocene marine and coastal deposits (Figure 12).
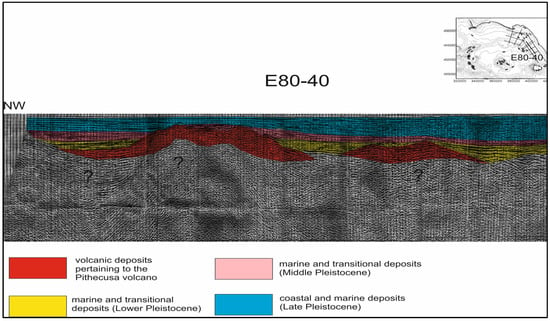
Figure 12.
Seismo-stratigraphic setting of the Pithecusa volcano on the Campania continental margin (Volturno river mouth).
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jones, E.J.W. Marine Geophysics, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 1–474. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, E.A. Seismic Velocity Analysis and the Convolutional Model, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 1–290. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, R.H. Underwater Explosions; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 1–490. [Google Scholar]
- Knott, S.T.; Hersey, J.B. Interpretation of high-resolution echo-sounding techniques and their use in bathymetry, marine geophysics and biology. Deep Sea Res. 1956, 4, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabile, L.; Fevola, F.; Galeotti, F.; Ranieri, G.; Tangaro, G. Sismica monocanale ad alta risoluzione con sorgente multi spot di tipo sparker: Applicazione ai dati di tecniche di deconvoluzione. In Proceedings of the 10th GNGTS Congress, Rome, Italy, 18–21 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, N.; Ferrari, M.; Giordano, F.; Giordano, R.; Ivaldi, R.; Sbrana, A. SAM-source and D-seismic system: The Use in Marine Geological Mapping CARG and PNRA Projects. In Proceedings of the 27th IAS Meeting of Sedimentologists, Alghero, Italy, 18–20 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton, H.E.; Hayward, G.G. The boomer sonar source for seismic profiling. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 68, 3033–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkin, P.G.; Davis, A. For seismic profiling in very shallow water, a novel receiver. Sea Technol. 1993, 34, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ranieri, G.; Mirabile, L. Ricerca ed applicazione di metodi geofisici al rilievo sperimentale della struttura medio-profonda dell’area flegrea con uso di sorgenti sismiche watergun. Ann. Ist. Univ. Navale Napoli 1991, 57, 149–186. [Google Scholar]
- D’Argenio, B.; Aiello, G.; de Alteriis, G.; Milia, A.; Sacchi, M.; Tonielli, R.; Angelino, A.; Budillon, F.; Chiocci, F.L.; Conforti, A.; et al. Digital Elevation Model of the Naples Bay and Adjacent Area (Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy); Atlante di Cartografia Geologica, “Mapping Geology in Italy”; APAT: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Angelino, A.; D’Argenio, B.; Marsella, E.; Ruggieri, S.; Siniscalchi, A. Buried volcanic structures in the Gulf of Naples (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy) resulting from high resolution magnetic survey and seismic profiling. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Cicchella, A.G.; Di Fiore, V.; Marsella, E. New seismo-stratigraphic data of the Volturno Basin (Northern Campania, Tyrrhenian margin, Southern Italy): Implications for tectono-stratigraphy of the Campania and Latium sedimentary basins. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Marsella, E.; Cicchella, A.G.; Di Fiore, V. New insights on morpho-structures and seismic stratigraphy of the Campania continental margin based on deep multichannel profiles. Rend. Lince-Sci. Fis. Nat. 2011, 22, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Cicchella, A.G. Dati sismostratigrafici sul margine continentale della Campania tra Ischia, Capri ed il bacino del Volturno (Tirreno meridionale, Italia) in base al processing sismico ed all’interpretazione geologica di profili sismici a riflessione multicanale. Quad. Geofis. 2019, 149, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mirabile, L.; De Marinis, E.; Frattini, M. The Phlegrean fields beneath the sea: The underwater volcanic district of Naples, Italy. Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl. 2000, 41, 159–186. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Angelino, A.; Marsella, E.; Ruggieri, S.; Siniscalchi, A. Carta magnetica di alta risoluzione del Golfo di Napoli (Tirreno meridionale). Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2004, 123, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Secomandi, M.; Paoletti, V.; Aiello, G.; Fedi, M.; Marsella, E.; Ruggieri, S.; D’Argenio, B.; Rapolla, A. Analysis of the magnetic anomaly field of the volcanic district of the Bay of Naples, Italy. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2003, 24, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrino, G.; Cerutti, G.; Corrado, G.; De Maria, P.; Riccardi, U. Gravity studies on active Italian volcanoes: A comparison between absolute and relative gravimetry. Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl. 1998, 40, 497–510. [Google Scholar]
- Fedi, M.; Quarta, T. Wavelet analysis for the regional-residual and local separation of potential field anomalies. Geophys. Prospect. 1998, 46, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A.; Aiello, G.; Iannace, P.; Torrente, M.M. Complex stratigraphic relationships between volcanic features and sedimentary deposits in a submarine environment: The northern offshore Holocene Ischia volcanic field (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2021, 419, 107379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Caccavale, M. From Siliciclastic to Bioclastic Deposits in the Gulf of Naples: New Highlights from Offshore Ischia and Procida–Pozzuoli Based on Sedimentological and Seismo-Stratigraphic Data. Quaternary 2021, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G. New insights on the late Quaternary geologic evolution of the Ischia Island coastal belt based on high-resolution seismic profiles. Ital. J. Geosci. 2018, 137, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; De Luca, L.; Giordano, P. Design and implementation of a marine seismic source by electrical discharge. Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl. 2020, 61, 589–606. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, F.; Giordano, R.; Corradi, N. D-Seismic: A very flexible low cost hardware/software system for acquisition, real time and post processing of seismic data of Ross Sea (Antartica 2002 expedition). In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum Seville 2002, Seville, Spain, 16–20 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, F.; Giordano, R.; Corradi, N.; Nicotra, G.; Ortosecco, I.; Pittà, A. Improving “S/N” in reflection seismic marine records by mean SAM96 (Sparker array multitip) and D-Seismic (hardware—Software system for seismic data acquisition and processing). In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Noise Control, EURONOISE 2003, Naples, Italy, 19–21 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, N.; Giordano, F.; Giordano, R. The application of a very high resolution hardware and software (D-Seismic) system for the loss of seismic data for the study of the Ross Sea sedimentary. In Proceedings of the AIOL, Genova, Italy, 14–18 September 2004; Volume 17, pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gamberi, F.; Della Valle, G.; Marani, M.P.; Mercorella, A.; Distefano, S.; Di Stefano, A. Tectonic controls on sedimentary system along the continental slope of the central and southeastern Tyrrhenian Sea. Ital. J. Geosci. 2019, 138, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarcia, S.; Vitale, S.; Di Staso, A.; Iannace, A.; Mazzoli, S.; Torre, M. Stratigraphy and tectonics of an Internal Unit of the southern Apennines: Implications for the geodynamic evolution of the peri-Tyrrhenian mountain belt. Terra Nova 2012, 21, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acocella, V.; Funiciello, R. Transverse systems along the extensional Tyrrhenian margin of central Italy and their influence on volcanism. Tectonics 2006, 25, TC2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Faccenna, C.; Goff, B.; Mattei, M.; Rossetti, F.; Brunet, C.; Storti, F.; Funiciello, R.; Cadet, J.P.; d’Agostino, N.; et al. Midcrustal shear zones in postorogenic extension: Example from the northern Tyrrhenian Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 12123–12160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, A.; Ryan, W.B.F. Extension in the Tyrrhenian Sea and shortening in the Apennines as result of arc migration driven by sinking of the lithosphere. Tectonics 1986, 5, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.; Patacca, E.; Scandone, P. Segmentation and configuration of subducted lithosphere in Italy: An important control on thrust-belt and foredeep-basin evolution. Geology 1987, 15, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacca, E.; Sartori, R.; Scandone, P. Tyrrhenian basin and Apenninic arcs: Kinematic relations since Late Tortonian times. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1990, 45, 425–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, R.; Torelli, L.; Zitellini, N.; Carrara, G.; Magaldi, M.; Mussoni, P. Crustal features along a W–E Tyrrhenian transect from Sardinia to Campania margins (Central Mediterranean). Tectonophysics 2004, 383, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Bigi, S.; Cuffaro, M.; Doglioni, C.; Scrocca, D.; Muccini, F.; Cocchi, L.; Ligi, M.; Bortoluzzi, G. Transfer zones in an oblique back-arc basin setting: Insights from the Latium-Campania segmented margin (Tyrrhenian Sea). Tectonics 2017, 36, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planke, S.P.A.; Symonds, E.; Avelstad, J.; Skogseid, J. Seismic volcanostratigraphy of large-volume basaltic extrusive complexes on rifted margins. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerram, D.A.; Single, R.T.; Hobbs, R.W.; Nelson, C.E. Understanding the offshore flood basalt sequence using onshore volcanic facies analogues: An example from the Faroe–Shetland basin. Geol. Mag. 2009, 146, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalak, M.M.; Planke, S.; Faleide, J.I.; Jerram, D.A.; Zastrozhnov, D.; Eide, S.; Myklebust, R. The development of volcanic sequences at rifted margins: New insights from the structure and morphology of the Vøring Escarpment, mid-Norwegian Margin. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 5212–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, A.; Planke, S.; Holford, S.; Nicol, A. Seismic Geomorphology, Architecture and Stratigraphy of Volcanoes Buried in Sedimentary Basins. In Updates in Volcanology—Transdisciplinary Nature of Volcano Science; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, J.; Groppelli, G.; Brum da Silveira, A. Volcanic stratigraphy: A review. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 357, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G. Submarine Stratigraphy of the Eastern Bay of Naples: New Seismo-Stratigraphic Data and Implications for the Somma-Vesuvius and Campi Flegrei Volcanic Activity. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A.; Mirabile, L.; Torrente, M.M.; Dvorak, J.J. Volcanism offshore of Vesuvius volcano in Naples Bay. Bull. Volcanol. 1998, 59, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, P.P.G.; Rapolla, A. Study of sub-surface structure of Somma-Vesuvius (Italy) by seismic reflection data: Implications for Campanian volcanism. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 1999, 92, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A.; Torrente, M.M.; Bellucci, F. A possible link between faulting, cryptodomes and lateral collapses at Vesuvius Volcano (Italy). Glob. Planet Change 2012, 90–91, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Insinga, D.D.; Milia, A.; Molisso, F.; Raspini, A.; Torrente, M.M.; Conforti, A. Stratigraphic signature of the Vesuvius 79 AD event off the Sarno prodelta system, Naples Bay. Mar. Geol. 2005, 222–223, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Caccavale, M. The Coastal Areas of the Bay of Naples: The Sedimentary Dynamics and Geological Evolution of the Naples Canyons. Geosciences 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, S.; Sacchi, M.; Tamburrino, S.; Ventura, G. Fluid Vents, Flank Instability, and Seafloor Processes along the Submarine Slopes of the Somma-Vesuvius Volcano, Eastern Tyrrhenian Margin. Geosciences 2018, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milia, A.; Torrente, M.M. Space-time evolution of an active volcanic field in an extensional region: The example of the Campania margin (eastern Tyrrhenian Sea). In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism, 1st ed.; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 297–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, P.P.; Cippitelli, G.; Rapolla, A. Seismic study of the Mesozoic carbonate basement around Mt. Somma—Vesuvius, Italy. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 84, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, N.; Ricci, T.; Baron, L.; Shakas, A.; Berrino, G. The 3-D structure of the Somma-Vesuvius volcanic complex (Italy) inferred from new and historic gravimetric data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Marsella, E.; Ruggieri, S. Three-dimensional magneto-seismic reconstruction of the ‘Torre del Greco’ submerged volcanic structure (Naples Bay, Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): Implications for Vesuvius’s marine geophysics and volcanology. Near Surf. Geophys. 2010, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, N.; Mirabile, L.; Camerlenghi, A.; Ranieri, G. Marine geophysical survey of the Gulf of Naples (Italy): Relationship between submarine volcanic activity and sedimentation. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1991, 47, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, P.P.G.; de Alteriis, G.; Florio, G. The western undersea section of the Ischia volcanic complex (Italy, Tyrrhenian sea). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 57-1–57-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Marsella, E.; Passaro, S. Submarine instability processes on the continental slopes off the Campania region (Southern Tyrrhenian sea, Italy): The case history of Ischia island (Naples Bay). Boll. Geof. Teor. Appl. 2009, 50, 193–207. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Marsella, E.; Passaro, S. Stratigraphic and structural setting of the Ischia volcanic complex (Naples Bay, Southern Italy) revealed by submarine seismic reflection data. Rend. Lince-Sci. Fis. Nat. 2012, 23, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G. New sedimentological and coastal and marine geological data on the Quaternary marine deposits of the Ischia Island (Gulf of Naples, Southern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Geomarine Lett. 2020, 40, 593–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).