Abstract
The problem of understanding and predicting tourist behavior in choosing their destinations is a long-standing one. The first step in the process is to understand users’ intention to visit a country, which may later translate into an actual visit. Would-be tourists may express their intention to visit a destination on social media. Being able to predict their intention may be useful for targeted promotion campaigns. In this paper, we propose an algorithm to predict visit (or revisit) intentions based on the texts in posts on social media. The algorithm relies on a neural network sentence-transformer architecture using optimized embedding and a logistic classifier. Employing two real labeled datasets from Twitter (now X) for training, the algorithm achieved 90% accuracy and balanced performances over the two classes (visit intention vs. no-visit intention). The algorithm was capable of predicting intentions to visit with high accuracy, even when fed with very imbalanced datasets, where the posts showing the intention to visit were an extremely small minority.
1. Introduction
Tourists typically make informed decisions before traveling to visit a country or a specific destination. Their final choice may depend on several reasons. For example, they may decide their destination based on local culture to gain insights into the rich history, traditions, and customs of the destination []. The cultural distance between the country of origin and the destination may also be a driving factor []. They may wish to explore historic landmarks and archeological sites to understand the destination’s past. They may be driven by the natural beauty of the destination, including the presence of unique landscapes, flora, and fauna []. Of course, they may also act based on the search for personal relaxation or recreation [], as well as to participate in an event [] or being moved by their personal nostalgia for the place []. In some cases, tourists may visit a country a second time or even become loyal visitors, choosing that country as their travel destination multiple times over the years. Tourists deciding to revisit a country have a special appeal, since it was shown in [] that loyal visitors are more likely to spread word-of-mouth advertising and offer a lower risk associated with their profitability. However, first-time visitors are reported in that paper to be less price-sensitive and spend more.
Entities in charge of promoting tourism have a significant interest in identifying would-be visitors. Such entities may be tourism ministries, national or regional tourism boards, chambers of commerce, private tourism companies, and event and conference organizers. There are several reasons for that interest. Identifying potential visitors allows tourism entities to tailor their marketing efforts to specific demographics, interests, and preferences. This targeted approach increases the chances of attracting the right audience for a destination. Knowing the characteristics and preferences of potential visitors may enable tourism organizations to create customized promotional campaigns, such as personalized advertising, special promotions, and tailored messages that resonate with the target audience. Furthermore, by understanding the demographics and geographic locations of potential visitors, tourism entities can allocate their resources more efficiently and even plan and develop the necessary infrastructure to accommodate the increased demand, e.g., by improving transportation networks, expanding accommodation options, and enhancing other essential services.
However, where can tourism-promoting agencies spot would-be visitors?
Social media is gaining an increasing role in tourism promotion [,,], acting as a modern and wide-ranging version of word-of-mouth (eWoM) mechanisms [,]. eWoM is particularly significant for tourism [,,]. Tourism promotion bodies may use social media to disseminate destination-related information. Social media is also a means through which past or prospective visitors express their opinions, influencing other would-be visitors. Travel blogs have arisen to reach a wide audience and share the blogger’s travel experiences []. Social media influencers may turn into real Internet celebrities whose endorsement may significantly increase the popularity of a destination []. The influence on would-be visitors may be quite remarkable. For millennials, it has been shown that sharing luxury travel experiences and benign envy toward the experience sharer stimulates consumers’ own intentions to visit the same destination [].
It is then a natural strategy for tourism promotion bodies to monitor social media and detect would-be visitors. This could be the first step towards opinion analysis tasks and more targeted promotional activities.
The literature has, so far, focused on identifying or checking the antecedents for visiting (or revisiting) a specific destination. Our purpose is, instead, to predict whether a specific prospective tourist manifests an intention to visit a destination. Detecting such an intention may be the first step in an organized strategy to transform that intention into a real visit. The information we exploit to perform that prediction is the text expressing prospective tourists’ opinions on social media. This is a further difference with respect to the literature where questionnaires (i.e., a structured tool rather than a freeform tool) are employed to elicit tourists’ attitudes. As far as the authors know, this is the first such attempt.
In this paper, we propose a sentence-transformer architecture to predict visit intention based on the text of posts on social media. We employ two datasets extracted from Twitter (now X) as the social media of choice and approach the problem as a classification task using logistic regression as a classifier. We show that we reach an average accuracy of 90%, with minimal deviations from that average performance figure.
Our original contributions are the following:
- We built two labeled datasets from social media containing opinions about Italy as a tourism destination;
- We applied machine learning techniques based on sentence transformers to predict visit intentions, considering both the cases where we have a largely imbalanced dataset and where the imbalance is mild, or nonexistent;
- We show the results of a preliminary explainability analysis to identify the most significant linguistic features that are associated with posts showing visit intentions.
2. Literature Review
The analysis of visit intentions as expressed on social media has gathered much attention in the literature. In this section, we review the literature, dividing it into two main streams: the papers examining the determinants of the intention to visit and those investigating the use of social media to express or trigger the intention to visit a destination. Much work has been devoted to analyzing either of two well-known investigation areas, which are the tourism destination image and the Product Country Image. The relevance of social media as a means to promote tourism by national tourism organizations was already established in []. However, as far as the authors know, there is no paper addressing the same research question as the one dealt with in this paper, i.e., predicting the intention to visit a destination based on the text posted on social media. It is to be noted that our intention is not to understand the determinants of the intention to visit a country but to understand whether a post on social media expresses such an intention or not.
As factors that delimit the scope of the literature analysis, we considered the country of origin, the status (currently visiting versus not), and the method of opinion sampling (in a structured way as those expressed in a survey or through an unstructured approach, as the posts freely submitted on a social media platform).
We can first consider the papers aiming to identify the determinants of the intention to visit (or revisit) a country.
A seminal paper is attributed to [], who built a structural equations model to describe travel intentions based on both paradigms of tourism destination image and Product Country Image.
In [], a survey was employed to find out whether social media content about Saudi Arabia influences the decision to revisit the country, also through the mediation of perceived value and perceived trust. The survey was distributed to tourists from all over the world who were visiting the town of Al-Ahas in Saudi Arabia. The method employed to assess the degree of influence was standard Structural Equation Modeling (SEM).
Satisfaction was considered to mediate the intention to revisit for British tourists currently visiting Spain or Turkey in []. The research methodology employed a self-administered questionnaire.
The impact of risk and uncertainty on the intention to visit was examined in []. The destination country of choice was Australia, and panels from South Korea, China, and Japan were interviewed through a structured questionnaire for that purpose. A similar study was conducted for Table Mountain National Park in South Africa []. The perception of risk was also found to be critical for the decision to attend mega-events [].
Instead, the influence of e-reputation, destination image, and social media marketing efforts on the intention to visit was examined in [] through the Stimulus–Organism–Response (SOR) approach. The data were collected again through a survey distributed to tourists in a specific location in India.
The influence of food on the intention to revisit was examined in []. The sample was collected in Delhi, India, and was examined through SEM. The same aspect was investigated in [], where the impact of the food images of France, Italy, and Thailand was assessed through an online survey targeting online travel and food groups from Yahoo.com and MSN.com.
The image of the destination is also a relevant factor, as shown in [], where a SEM-based approach was employed to study its impact for American tourists traveling to Cuba. Four aspects that influence the perception of a tourism destination image were identified in []: experience, history and culture, leisure services, and tourist destination. Data employed in [] came from an online travel platform (Ctrip Travel, considered to be the largest in China). Again, the most relevant dimensions were identified in [], where posts from TripAdvisor and Mafengwo are analyzed. Sentiment analysis was carried out through VADER. A questionnaire-based survey was further employed to identify which attributes represent the image of a specific tourism destination.
A systematic literature review was conducted in [] to investigate the use and impact of user-generated photos.
Two constructs were examined in [] to predict the intention to visit a country: destination brand personality self-congruity and perceived risks derived from criminal activities. The data were collected in the USA and concerned the intention to visit Mexico (it was, therefore, a deviation from the other papers where the data collected concerned tourists from different countries). The method chosen for the analysis was, again, SEM.
The topics of interest in a tourism destination were determined by analyzing microblog social media in [], both on-site and after the trip.
A standard SEM model was employed in [] to investigate the effects of motivation, past experience, perceived constraint, and attitude on revisit intention for mainland Chinese tourists traveling to Hong Kong as their destination. Post-visit impressions were also examined in [] by collecting data from micro-forums, blogs, e-commerce platforms, and websites.
Of course, the characteristics of tourists may also play a role in their destination decisions, namely due to the presence of an emotional connection between tourists’ perceived self-image and the brand personality of destinations [].
We can now turn to the investigation of social media as a means to express or strengthen the intention to visit a destination.
As to the relevance of social media, it was found that word-of-mouth spread through social media is a significant factor in triggering the intention to visit [].
A specific analysis was carried out through questionnaires, considering Malaysia as the destination for medical tourism []. The role of social media (in comparison with other information sources) was found to be particularly relevant for attitudinal loyalty, i.e., the intention to visit coupled with past visits []. Again, the questionnaire tool was employed, targeting tourists from European countries. Social media was also found to be a mediating device for the influence of the subjective norm (i.e., the way the others perceive the tourist behaviors) on the intention to visit a destination []. The impact of social media on the effect that the destination image has on the intention to visit was also found to be significant in [], where questionnaires compiled from Malaysian tourists were examined for a very specific destination in Saudi Arabia. A specific investigation concerning the role of posts on Facebook in triggering visit intentions through benign envy was examined in []. A questionnaire-based survey, though restricted to Vietnamese nationals, was carried out in [] to determine the intention to visit as a function of the desire to visit, the destination image, envy, and the attitude towards visiting a travel destination. A SEM model was employed. Furthermore, the impact of user-generated content on the intention to revisit and word-of-mouth was analyzed in [] through questionnaires collected in a specific destination (the Gulangyu island). The sentiment towards a tourism destination image was also analyzed in [], employing nine measurement dimensions.
The opposite target was adopted in [], where factors for non-revisiting were investigated using sentiment analysis techniques to label reviews posted on social media and, subsequently, examine the factors leading to positive or negative sentiments.
The relationship between the information quality of social media and the intention to travel was investigated in []. The method of analysis was based on the Elaboration likelihood model framework and employed multiple linear regression to test the research hypotheses. The viewpoint adopted in [] is, however, different from ours: they study how the intention to travel of a social media user is influenced by other social media users through their posts (and the quality of the information they convey), while we considered whether a post by a social media user expresses their intention to travel.
Similarly, in [], the information posted on social media was used as a source of recommendations for tourist destinations, which are filtered and summarized by a BERT architecture. The same considerations put forward earlier apply to the target of the investigation, though a machine learning tool, rather than multiple linear regression, was employed.
Again, questionnaires were employed in [] to investigate the impact of social media on tourists’ destination decisions, where the SEM method was employed to analyze the questionnaires. The same considerations on the focus of the study and the method of choice done for the previous papers apply.
The impact of advertising (namely the types of destination advertising) through social media on tourists’ travel intentions was examined in [], where an experiment was carried out, and statistical hypothesis testing was adopted.
Tourists’ level of satisfaction, as well as the interaction with digital marketing channels, were investigated as the the antecedents of tourists’ behavioral intentions in their destination selection []. The method was, again, SEM, relying on a set of questionnaires.
Means of avoiding the negative impacts of social media-induced tourism were studied in [], where the leveraging of social media to encourage desirable traveler behaviors was also proposed. Social media were seen in this case as a tool to manage and exploit to obtain a desirable behavior, rather than a source of information.
A similar role for social media by influencers, who can actively influence the travel decisions of other social media users, was advocated in [], where a mediation model was built and tested through SEM.
The reasons for using social media to plan one’s travels were investigated in [], where technological convenience and perceived enjoyment were found to be the biggest motivations for using social media.
The attitude of the endorser, namely their facial expression (e.g., whether smiling or not), was also found to be a significant factor in the success of influence [].
The choice of sampling in a specific geographical location, however important it was, is a significant limitation of the studies conducted, with just a few exceptions.
With respect to the literature, our paper differs as follows. Our research question concerned detecting the intention to visit a destination rather than understanding the factors that influence that decision. Furthermore, we did not rely on questionnaires but drew on the potentially much larger data source represented by social media. The opinions we collected came from users that were not limited to a specific geographical area, unlike most literature. Questionnaires impose limitations due to the requirement of answering just the questions included in the questionnaire, while posts may include any opinion by the person posting it. Considering social media posts rather than questionnaires represents an improvement, since they widen the number of participants, their geographical origins, and their possibility of expression. Finally, we employed machine learning techniques rather than techniques based on a superimposed structured model like SEM. Structural Equation Models are linear by nature, while a machine learning approach allowed us to adopt intrinsically nonlinear relationships, hence offering a more flexible representation of reality. The papers employing machine learning in the literature survey do it for sentiment analysis, which is a task different from the one we were tackling here. This is the case of [] (which employs BERT) and [], which uses a selection of methods, including decision trees and Support Vector Machines. Latent Dirichlet allocation is employed in [] to identify the topics of interest, which, again, is a task different from what we investigated here.
Overall, we can conclude that the goal that we considered here has not been pursued yet in the literature, so a comparison of our results with the literature cannot be made. On the other hand, the methods attempted so far to elicit the opinion of potential visitors (which, again, is a different task than that dealt with here) rely on tools (like questionnaires) and methods (like SEM) that are intrinsically less flexible and less powerful than our machine learning approach based on social media posts.
3. Dataset
In order to predict the visit intention as expressed on social media, we considered Twitter (now X) as the social media of choice. We extracted a large number of tweets using words related to tourism to filter out unrelated tweets. We focused on Italy as a country with a very large tourist base. We employed Twitter’s API to retrieve the tweets of interest [,], following the approach in []. The query we used for the search was Italy AND (visit OR holiday OR travel OR trip). We retrieved two datasets at different times using the same query. The two datasets differed largely in size and were labeled by different groups of examiners. The intent was to explore the performance of our method when fed with diverse inputs. In the following, we refer to those datasets as (the smaller one) and (the larger one). After collecting the data using Twitter’s API, we removed the duplicates (there were 169 in and 23 in ). The text of each tweet was subsequently retrieved and labeled as either showing the intention to visit the country or not. Manual labeling was adopted. Each tweet was submitted to a couple of independent examiners (different for the two datasets). In the case of contrasting labels, the decision was reached by consensus. Consensus was built by a discussion between the two examiners. In the case of persisting differences, an expert adjudicator was called to decide. Cross-verification, where each examiner examines the labels provided by the other examiners, was therefore not needed as the examiners discussed the cases of contrasting labeling. The percentage of cases where consensus building was needed lay below 5% in both datasets. The accuracy of the process relied on the use of a couple of examiners, which reduced the risk of mislabeling. In fact, if we identify the probability of mislabeling for the single examiners as and , the probability of obtaining a correct decision without resorting to consensus building was , and the probability of straightforward error was (i.e., when both examiners err), which is quite lower than the individual probabilities of error. We referred to the group showing the intention to visit as the Visit class. Hence, the tweets concerning tourism but with no visit intentions were marked as the NoVisit class. We stress the fact that we did not have any information about whether the people who posted the tweet actually visited Italy. We acted based on the text only and identified the sheer intention to visit.
The datasets’ size and composition are shown in Table 1. As can be seen, we have two datasets of quite different sizes, and , with being roughly seven times as large as . The two datasets are made of completely different tweets, i.e., there is no overlapping. Furthermore, they exhibit quite different levels of balance. The composition of is largely imbalanced, with the Visit class representing just 4.2% of the total. Instead, , though not perfectly balanced, exhibits a mild imbalance, again with the Visit class being the smaller one, representing 37.3% of the total.

Table 1.
Dataset composition.
Since an imbalanced dataset may lead to misleading results, we employed rebalancing techniques for the dataset , which is heavily imbalanced. We refrained from using rebalancing techniques for the dataset , since it is just mildly imbalanced.
For the dataset , we employed downsampling to achieve a balanced dataset. Downsampling, as all rebalancing actions, aims at removing or mitigating the bias due to the larger presence of the majority class. Though downsampling could introduce bias of its own if done incorrectly, here, we employed random downsampling for the majority class. Specifically, we employed simple random sampling without replacement, where the size of the subsample obtained after downsampling is fixed, and each possible subsample has the same probability of being extracted [], thus preserving the original distribution. Since we were applying sampling to a single class (the majority one), class-proportional techniques to preserve the original probability distribution, as in [], were not needed. It has been shown, e.g., in [], that downsampling helps manage the skewness due to the majority class and achieves better classifier performance. In order to exploit the minority class (Visit instances) as much as possible, we kept all the Visit instances and randomly sampled an equal number of NoVisit instances. Since the number of Visit instances was 230, we collected 230 NoVisit instances and ended up with a dataset made of 460 tweets (230 per class). However, in order to fully exploit our imbalanced dataset, we employed cross-validation []. Cross-validation involves dividing the available data into multiple folds (subsets), using one of these folds as a testing set, and training the model on the remaining folds. This process is repeated multiple times, each time using a different fold as the testing set. Finally, the results from each testing step are averaged to produce a more robust estimate of the model’s performance. As to the number of folds employed in cross-validation, most textbooks and libraries adopt a default value of 10. However, a recent experiment highlighted that the differences in performance due to the number of folds are quite limited, and the optimal number of folds lies between 10 and 20 [], but depends on the overall size of the dataset. We opted for the higher end of the range and chose to use 20 folds. It is to be noted that the use of cross-validation practically removes the loss of information that is typically associated with downsampling, as the construction of several training datasets ends up exploiting all the instances in the dataset. Since we had 4601 NoVisit tweets for , we partitioned them into 20 groups of 230 tweets each to match the number of Visit tweets. This left a single tweet out, so we practically exploited the entire original dataset to its full extent. We selected each of those 20 groups, in turn, to couple them with the single group of Visit tweets, making 20 balanced datasets of 460 tweets each. Each balanced dataset was made of the unique group of 230 Visit tweets and one of the 20 groups of 230 NoVisit tweets. We carried out a 20-fold cross-validation, expecting something less than a 20-fold improvement in the variance, as all folds had half of their data in common, namely the Visit tweets. We ran our classification algorithm for each derived balanced dataset, randomly splitting the dataset into two portions, devoted, respectively, to training and testing according to the fixed proportions 80% and 20%, respectively.
As for the dataset , the imbalance was not so large as to call for rebalancing. In addition, the dataset was quite large. Hence, we employed it as it was, without any rebalancing or cross-validation.
4. Method
In this section, we describe the method we employed to identify the presence of a visit intention in posts on social media.
The task of distinguishing between Visit and NoVisit instances was modeled as a binary classification task. For the sake of avoiding confusion, we do not use the term positive for the Visit class (and, similarly, the term negative for the NoVisit class), since we will later use those terms in the contrastive approach that is embedded in SetFit. We did not distinguish whether the visit was actually a revisit, as we did not have information about the previous behavior of the people submitting the post. Revisit intentions were then labeled as visit intentions nonetheless, regardless of the fact that the would-be tourist had already visited the country. We stress, once again, that our purpose was not to predict whether the social media user would actually visit the country but rather to predict whether that user was showing the intention to visit the country in their post. In the absence of true, validated data about the social media user’s identity and a tracking system that links that user to their travel behavior (e.g., tracking their entry into a country or their purchase of tickets), predicting users’ actual visits could not be validated, and we were limited to predicting intentions.
In the following, we describe the methodology we employed to analyze the two datasets. As already mentioned, the two datasets exhibited quite a different degree of imbalance. For that reason, we employed different algorithms. Dataset needed a thorough rebalancing activity, while that was not the case for . First, we describe the methodology for . What follows refers exclusively to , until we explicitly turn to .
As described in Section 3, the size of each training/testing dataset in the dataset was not very large by machine learning standards: each fold was made of 460 tweets, which we further subdivided into a training portion (made of 368 tweets) and a testing one (made of 92 tweets). Nowadays, datasets in excess of hundreds of terabytes may be available []. The small-dataset problem is well known in machine learning. The capability of machine learning algorithms to recognize patterns is related to the size of the dataset: the smaller the dataset, the less accurate the algorithm []. However, good results may also be obtained with datasets as small as hundreds of instances []. The set of techniques to deal with small datasets in machine learning falls under the name of few-shot learning [,], where examples falling in the categories of few-shot learning exhibit a number of instances per class ranging from tens of instances to slightly beyond one thousand (see Table 3 in []).
The scarcity of labeled data made this dataset prone to be categorized as a case of few-shot learning []. For this reason, we resorted to the SetFit method presented in [], which should allow us to obtain good accuracy even in the presence of a small number of labeled instances in our training dataset. SetFit relies on sentence transformers and falls into the class of few-shot learning methods, which aim to achieve good classification performances.
A graphical description of the flow of operation in SetFit is shown in Figure 1. It is based on two phases. In the first phase, a sentence transformer is fine-tuned after being fed with sentence pairs under a contrastive approach. In the second phase, a text classification head is trained using the data output in the first phase as training data. We now describe the steps composing these two phases in Figure 1 in detail.
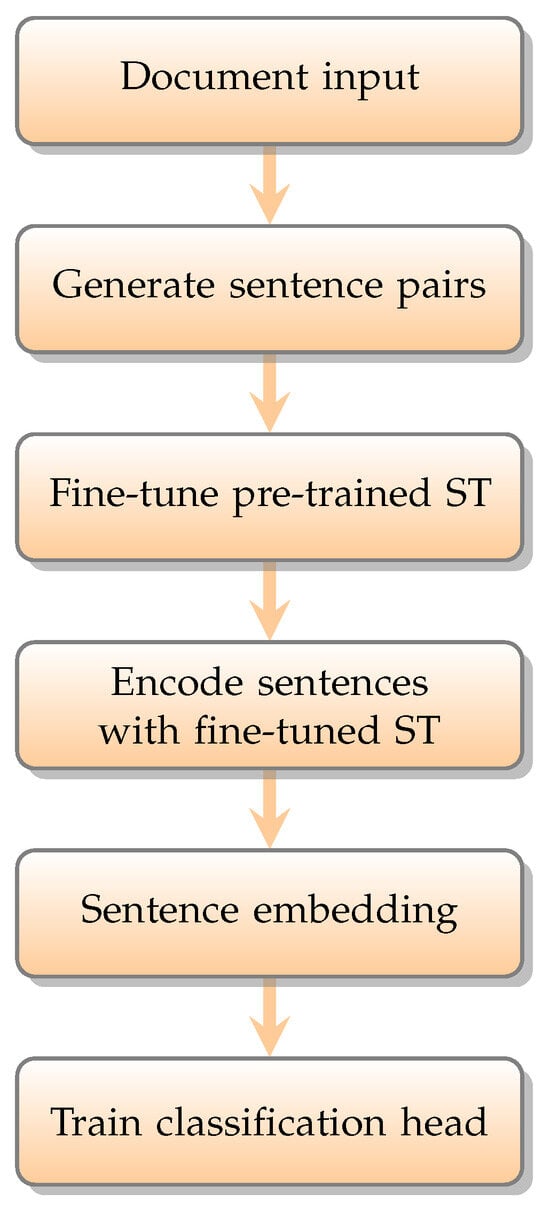
Figure 1.
SetFit flow diagram.
The first step, as described in Figure 1, is represented by feeding the algorithm with our documents. In our case, the dataset described in Section 3 was fed as a csv file, where each row contained a tweet and its label.
In the second step in Figure 1, we generated the pairs of positive and negative sentences. As we will describe hereafter, our method employed a Siamese configuration. Hence, we had to feed the model with pairs of labeled tweets rather than directly with Visit and NoVisit instances. For that purpose, we randomly picked pairs of tweets and labeled them. Labeling was performed using a contrastive criterion, i.e., we labeled pairs from the same class (e.g., two tweets both in the Visit class) as positive and pairs from different classes (e.g., one tweet belonging in the Visit class and the other in the NoVisit) as negative. It is to be noted that labeling now applies to pairs of tweets rather than single tweets. This contrastive fine-tuning approach allowed us to obtain a much larger training set. As shown in [], we obtained a roughly quadratic increase in the number of training instances. We now describe the sentence-pair generating process in more detail.
Formally, we had a dataset of n tweets , and their respective labels , , with {Visit, NoVisit}. For each fold, we generated a set of 460 tweets, perfectly balanced between the Visit class and the NoVisit class (i.e., 230 instances for each class). We recall that the Visit instances were always the same, while a subdivision into twenty folds was made for the much larger NoVisit class. By stratified sampling (so as to maintain the balance), we extracted the training and testing datasets according to the 80/20 proportions, which led us to have a training dataset made of 368 tweets and a testing dataset made of 92 tweets. From the dataset, we randomly picked R same-class pairs and R different-class pairs. If the number of tweets in the Visit class is v and that in the NoVisit class is , the number of potential same-class pairs is , where the first term represents all the pairs that we can form by coupling two Visit instances (which can be obtained as the number of combinations of v instances two by two, i.e., ), and the second term refers, instead, to the NoVisit instances. For the training dataset, since we must have a balanced dataset, in the end, we needed after downsampling from the original dataset of 4831 instances (we recall, once again, that downsampling actually refers to the NoVisit class only). The number of potential same-class pairs was then . On the other hand, the number of potential different-class pairs was , where we coupled each Visit instance with each NoVisit instance. This formula is simply the cardinality of the Cartesian product of the set of Visit instances by the set of NoVisit instances. Again, in the case at hand, , so we had . We marked the same-class (positive) pairs with bit 1 and different-class (negative) pairs with bit 0. For both classes, we had two sets of pairs (positive and negative). For the class Visit, after adding the bit showing class concordance, we had the sets of triplets , where Visit, and , where Visit. Similarly, for the class NoVisit, we had , where NoVisit, and , where NoVisit. We generated the fine-tuning dataset by aggregating the positive and negative triplets across the two classes .
The third step in Figure 1 consists of fine-tuning a sentence transformer. Sentence transformers are derived from pre-trained transformer models that use Siamese and triplet network structures to obtain semantically meaningful sentence embeddings []. By semantically meaningful, it is intended that the vector representation of two semantically similar words are close to each other in the vector space. In a Siamese (triplet) neural network, identical algorithms are applied to two (three) input vectors along two (three) parallel paths, with their outputs being compared at the end [,]. The sentence transformer we used is a modification of the BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model [], namely paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2 (see the model on the Hugging Face repository at https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers/paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2 (accessed on 29 September 2024)). Fine-tuning the model was accomplished by feeding our Siamese configuration with the pairs of positive and negative instances. The semantic similarity was evaluated through the cosine similarity between the embedding vector representation of those tweets. Fine-tuning was carried out by minimizing the cosine similarity (which plays the role of loss function) between the vectors representing positive pairs and maximizing it for negative pairs, as in []. This optimization (minimization and maximization) task was accomplished through the AdamW optimizer []. This optimizer has been shown in [] to yield models that generalize much better than Adam and to compete with the stochastic gradient descent optimizer while training much faster. The fine-tuned model was then used to encode the sentences (step 4 in Figure 1) and obtain a single sentence embedding per training sample (step 5 in Figure 1).
After obtaining the optimal encoding, we could use the embedding that was now associated with the tweets as features for the classifier. Specifically, the components of each embedding vector, together with the associated label, were fed as input to the classifier. As a classifier, we employed logistic regression, adopting the same choice as in []. The logistic classifier returned a probability value for each of the two classes. We chose the higher-probability class as the output of our classifier.
After this long description of the method employed for the dataset , we can now describe the much simpler procedure for the dataset . We did not need rebalancing. We did not need cross-validation. We did not need to adopt a few-shots learning approach. For , we just coded each tweet through the same sentence transformer employed for , without any fine-tuning, and then fed those embeddings to the logistic classifier.
5. Results
In this section, we show the results of our classification task to predict the intention to visit a tourism destination, Italy in our case.
We employed the following well-established performance metrics:
- Accuracy;
- Precision;
- Recall;
- F1.
In order to precisely define these metrics, we now associate the term Positive with Visit and Negative with NoVisit, so that, e.g., True Positives (TPs) will represent the Visit instances that were correctly classified as such, while False Negatives (FNs) will represent the Visit instances that were incorrectly classified as NoVisit ones. The labels assigned to the instances by the human experts mentioned in Section 3 were considered as the ground truth.
Accuracy is defined as the percentage of correctly classified instances:
Precision is the percentage of truly Visit instances over all the instances that have been classified as Visit ones:
Recall is the percentage of Visit instances that have been correctly classified as Visit, i.e., is the accuracy over the Visit class:
Finally, F1 is the harmonic mean of precision and recall:
We first report the results for the dataset and then for the dataset .
As stated in Section 3, for the dataset , we adopted a cross-validation approach to make full use of our data. Since we obtained 20 training and testing datasets, we carried out a 20-fold cross-validation. For each fold, we computed all four performance metrics introduced earlier: accuracy, precision, recall, and F1. We iterated network training through ten epochs.
In Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5, we report the values of all four performance metrics for epochs 1, 2, 5, and 10, respectively.

Table 2.
Performance metrics: one epoch.

Table 3.
Performance metrics: two epochs.

Table 4.
Performance metrics: five epochs.

Table 5.
Performance metrics: 10 epochs.
The average accuracy is over 90% up to five epochs and goes slightly below (89.4%) for ten epochs. The minimum accuracy achieved over the 20 folds is 85%. The coefficient of variation (ratio of standard deviation to average value) for accuracy is never larger than 3.5%. Hence, the accuracy is very high and pretty stable across the folds. We obtain similar performances by looking at other metrics. The average precision is not lower than 86.7%, with a peak of 90% at epoch 1. The standard deviation is a bit larger, but always around 5%. We obtain higher values for the recall metrics, which exhibit an average value significantly higher than 90% and a coefficient of variation around 3%. As can be seen, all the metrics exhibit a very low standard deviation across the 20 folds. Hence, the performance of our algorithm appears very stable and reliable. Though the performance metrics exhibit very close value, recall is always found to be larger than precision: the algorithm is slightly generous in assigning instances to the Visit class, allowing us to capture more Visit instances at the risk of including some NoVisit instances in the Visit class.
Recall is found to be higher (on average) than precision on all epochs. The algorithm is definitely cleverer at recognizing posts showing the intention to visit than rejecting posts that do not show that intention. In a real scenario, where negatives largely outnumber positives (with roughly a 20:1 ratio in some datasets like , as can seen in Table 1), this behavior can lead to quite a higher number of false positives than false negatives and make the algorithm err on the more tolerant side, labeling as positive more posts than what would be right.
We can see how the estimated accuracy changes with the number of epochs. In Figure 2, we have plotted the accuracy with three-sigma error bars vs. the number of epochs. Under the Gaussian assumption for the distribution of the sampling accuracy, the three-sigma interval ensures that accuracy values fall into this interval with 99.7% probability []. Hence, the three-sigma interval can be considered a safe bracket for the accuracy values we can obtain for out-of-sample data. We can see that the average accuracy degrades by a tiny amount (1.8%), probably highlighting a slight overfitting. In order to provide a quantitative indication of the degree of overfitting, we compare the accuracy we have obtained on the training and testing datasets, respectively. The presence of overfitting is due to the ML model parameters being too fit for the training dataset at the expense of the capability of generalizing and obtaining good accuracy on the testing dataset. For that reason, we considered the following overfitting metric, where the accuracy gap is normalized to the average accuracy over the testing and training datasets:
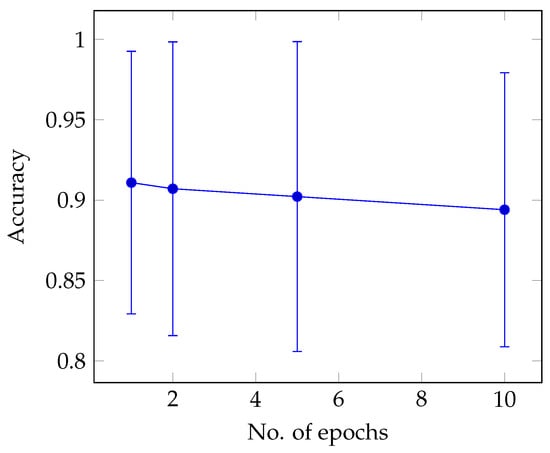
Figure 2.
Three-sigma accuracy vs. number of epochs.
We obtained , i.e., the accuracy gap was slightly larger than 2%, which can be considered quite a low value. Going back to Figure 2, the estimation interval width is quite steady, with a 3- roughly around ± 0.09 (i.e., roughly 10% of the average accuracy).
We can achieve a better understanding of the way our algorithm errs and where it may be improved by looking at the confusion matrix. We focused on the two extreme cases, i.e., the best-accuracy fold (which was 9 in epoch 1) and the worst-accuracy fold (which was 14 in epoch 1). We report the two confusion matrices in Table 6 and Table 7, respectively. The number of total instances is 92, i.e., 20% of the total dataset made of 460 instances. As can be seen, our algorithm is quite balanced, with type I errors (i.e., mistaking no-intention posts for intention ones or false positives) slightly prevailing in the best-performing fold and the reverse happening for the worst-performing fold (where false negatives slightly prevail). Of course, as already hinted, these values refer to our balanced dataset and would change in the presence of an imbalanced scenario that may occur in the actual application of the algorithm.

Table 6.
Confusion matrix for best-accuracy fold in epoch 1 (V: Visit and NV: NoVisit).

Table 7.
Confusion matrix for worst-accuracy fold in epoch 1 (V: Visit and NV: NoVisit).
We can now examine the results for the dataset . In Table 8, we show the confusion matrix. As stated in Section 4, for the dataset , we did not need to resort to rebalancing and cross-validation. Hence, there is no across-fold analysis. The overall accuracy is 90.2%, while the per-class accuracy values are, respectively, 89% for the Visit class and 91% for the NoVisit class. As can be seen, the performances of the two classes are very close, and the bias towards the majority class is extremely limited without resorting to rebalancing. If we look at the other performance metrics as we did for , we obtain a precision of 85.4% and a recall of 89%. Again, the two metrics are rather close, but recall is higher than precision. This result confirms what we observed for : the algorithm tends to include more instances than necessary in the Visit classes. Furthermore, the performance appears quite aligned for both the small, heavily imbalanced dataset and the larger, mildly imbalanced dataset .

Table 8.
Confusion matrix for the dataset (V: Visit and NV: NoVisit).
Finally, we analyzed the linguistic features that were associated with the user’s intentions. First, we analyzed two sample tweets to examine how the sentence elements contribute to the algorithm’s decision in a concrete case. We then considered the top features across the whole dataset. We first considered two sample tweets labeled, respectively, as Visit and NoVisit and correctly classified by our classifier. For both, we carried out an explainability analysis by adopting the LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation) method [], using the words in the tweets as features (see [] for a recent survey of explainability methods for transformers). The LIME method provides a surrogate linear model, where the weights in the regression equation represent the relative importance of the associated features (each feature acts as a regressor in the linear model) in leading to the classifier’s decisions. In Figure 3, we see that the major features justifying the label Visit mention Italy and the verb wanna shows a voluntary action. On the other hand, the major features for the NoVisit tweet in Figure 4 are, again, Italy and want as the major positive features, while the think verb and the personal noun Daniel appear as the major negative features leading to the overall negative intention. In both cases, the use of verbs appear as a major element in explaining the classifier’s decisions.
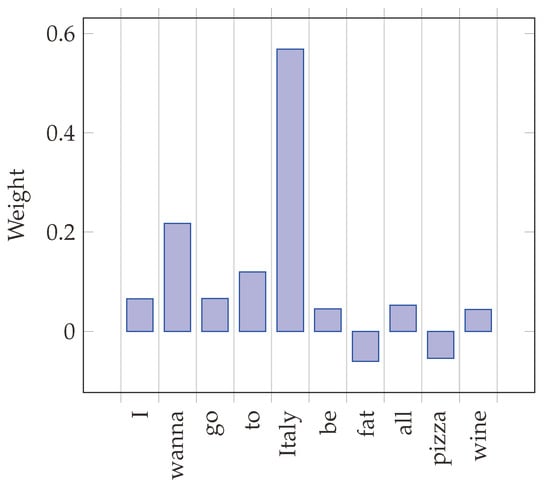
Figure 3.
Feature weights for the tweet I just wanna go to Italy and be a fat ass and eat all the pasta, pizza and drink wine, correctly labeled as Visit.
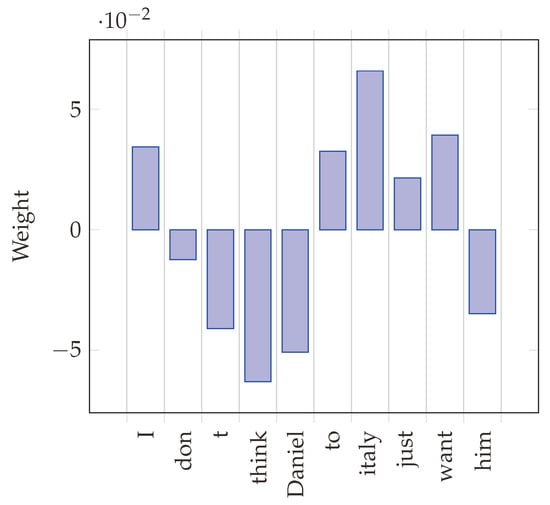
Figure 4.
Feature weights for the tweet At this point I do not think Daniel will come back to italy anytime soon and I’m sad I just want them back here, correctly labeled as NoVisit.
In Figure 5, we see, instead, the ten features with the highest average weight, considering all the tweets. All the terms have been pre-converted to lowercase. We see two terms, travel and visit, that form the object of the intention expressed in the tweet. We see, again, the voluntary verb wanna and the motion verb go, associated with the motion preposition to. A specific destination appears (Taormina). The picture is completed by the reference to the user itself (myself) and watercolour, related to the landscape sometimes associated with the destination.
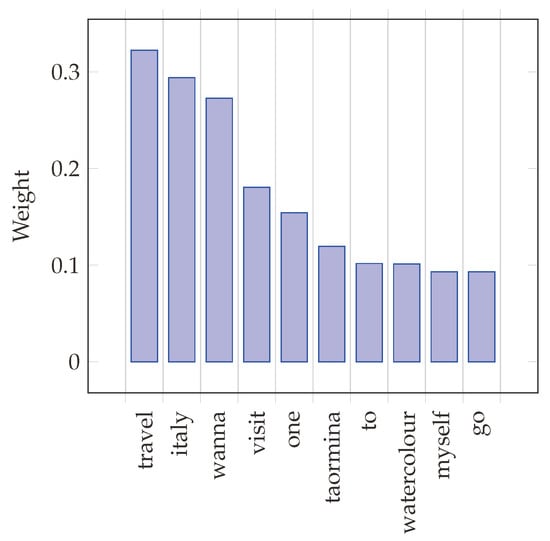
Figure 5.
Top 10 feature weights (across all the tweets).
6. Conclusions
As far as the authors know, the problem of predicting visit intentions from the texts of posts on social media has not been tackled before. We have modeled that problem as a classification task here and proposed a logistic regression classifier based on sentence transformers to carry out the classification task.
The results show that we can achieve a high classification accuracy (roughly 90%). We erred on the plus side, adding to the score of posts showing the intention to visit posts that do not actually show that intention. However, we can consider this to be the least harmful of the two types of error. We can envisage the output of the classification as triggering a targeted communication effort to strengthen the intention to visit and transform it into a real visit to the intended destination. Though we do not know additional information about the social media participants, they can be reached through the same social media where they expressed their interest in a country or a specific destination and push marketing information about the places of their interest, proposing special offers and discounts for travel and accommodation. With this aim in sight, being more generous in classification would mean widening the audience of our communication campaign, even if some of those we reach may not be interested. Erring on the other side, i.e., not including social media users who actually intend to visit the destination in our communication campaign, would instead mean excessively restricting our communication audience and failing to reach otherwise valuable customers.
There are several possible uses of the information that we can extract from social media about the intentions of people to visit a specific destination (we considered Italy, i.e., a country, as a case study, but the methodology can easily be applied to more specific destinations, such as towns or even monuments or cultural institutions). For example, tourism boards and private companies wishing to promote a tourist destination could target the social media users who expressed the intention to visit, build a list of potential targets for marketing campaigns made of those users’ usernames, and then use them as recipients of promotion campaign messages. Addressing people who have already expressed their intention to visit would certainly increase the conversion rate of the promotion campaign. Another possibility would be to use the explainability analysis to extract some features that may be more interesting for the would-be visitor (since they have been a major driving force for the ML model to make the classification decision) and use them as leverage to build more attention-grabbing campaigns.
As a limitation, we must admit that intentions, as identified by labelers, may be misinterpreted and may not transform into actual visits. In practical terms, that would mean that a promotion campaign based on the ML model’s output would miss its target and would address people who are not interested in visiting the country. A more accurate identification of intentions would require, however, sidelining posts with other information. For example, a more accurate determination of the ground truth would call for the analysis of the subsequent behavior, e.g., examining whether a post has been followed by an actual visit. However, the latter would require tracking the user, which is not possible unless you have access to personal information concerning purchasing behavior. This would be accurate only if we are able to match the poster’s identity across platforms (i.e., the social media platform with the e-commerce platform used to purchase travel tickets or accommodation). A promotion campaign based on the social media username only would certainly be less effective, since it could not use additional information to target the potential visitor more specifically and customize the offer. An interesting line of research would be to draw an integrated sales and media strategy that would induce the social media user to release more information about themselves, e.g., through a more controlled registration process, and ease the transmission of information between the social media platform and the sales channel.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N. and G.M.; methodology, M.N. and P.F.; software, P.F.; validation, P.F.; formal analysis, M.N.; investigation, P.F.; resources, M.N. and P.F.; data curation, P.F.; writing—original draft preparation, P.F.; writing—review and editing, M.N.; visualization, P.F.; supervision, M.N.; project administration, G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
An anonymous version of the data employed in this paper is available from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| eWoM | Electronic word-of-mouth |
| LIME | Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation |
| ML | Machine learning |
| SOR | Stimulus–Organism–Response |
| VADER | Valence-Aware Dictionary and sEntiment Reasoner |
References
- Timothy, D.J. Contemporary cultural heritage and tourism: Development issues and emerging trends. Public Archaeol. 2014, 13, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.I.; Lee, J.A.; Soutar, G.N. Tourists’ intention to visit a country: The impact of cultural distance. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, C. Nature, beauty and tourism. In Philosophical Issues in Tourism; Channel view Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2009; pp. 154–170. [Google Scholar]
- Csirmaz, É.; Pető, K. International trends in recreational and wellness tourism. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 32, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, P.; Lamont, M.; Scherrer, P.; Kennelly, M. Reframing mass participation events as active leisure: Implications for tourism and leisure research. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 39, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.A. Tourism experiences as the remedy to nostalgia: Conceptualizing the nostalgia and tourism nexus. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrick, J.F. Are loyal visitors desired visitors? Tour. Manag. 2004, 25, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Gerritsen, R. What do we know about social media in tourism? A review. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2014, 10, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T. Role of social media in tourism: A literature review. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gebreel, O.S.S.; Shuayb, A. Contribution of social media platforms in tourism promotion. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Educ. Commun. Econ. 2022, 1, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, A.M. The word-of-mouth phenomenon in the social media era. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2014, 56, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, A.J.; Kitchen, P.J. Word of mouth and social media. J. Mark. Commun. 2014, 20, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, A.; Croy, G.; Mair, J. Social media in destination choice: Distinctive electronic word-of-mouth dimensions. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2013, 30, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfakhimi, S.; Duncan, T.; Coetzee, W.J. Electronic word of mouth in tourism and hospitality consumer behaviour: State of the art. Tour. Rev. 2020, 75, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Menendez, A.; Correia, M.B.; Matos, N.; Adap, C. Understanding online consumer behavior and eWOM strategies for sustainable business management in the tourism industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Shang, R.A.; Li, M.J. The effects of perceived relevance of travel blogs’ content on the behavioral intention to visit a tourist destination. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 30, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pratt, S. Social media influencers as endorsers to promote travel destinations: An application of self-congruence theory to the Chinese Generation Y. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2018, 35, 958–972. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wu, L.; Li, X. Social media envy: How experience sharing on social networking sites drives millennials’ aspirational tourism consumption. J. Travel Res. 2019, 58, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankov, U.; Lazic, L.; Dragicevic, V. The extent of use of basic Facebook user-generated content by the national tourism organizations in Europe. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, J.; Heslop, L.; O’Reilly, N.; Luk, P. Destination in a country image context. Ann. Tour. Res. 2008, 35, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, E.A.; Hassan, T.H.; Abdelmoaty, M.A.; Salem, A.E.; Saleh, M.I.; Helal, M.Y.; Abuelnasr, M.S.; Mohamoud, Y.A.; Abdou, A.H.; Radwan, S.H.; et al. Exploration or Exploitation of a Neighborhood Destination: The Role of Social Media Content on the Perceived Value and Trust and Revisit Intention among World Cup Football Fans. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M. Repeaters’ behavior at two distinct destinations. Ann. Tour. Res. 2001, 28, 784–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintal, V.A.; Lee, J.A.; Soutar, G.N. Risk, uncertainty and the theory of planned behavior: A tourism example. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R. Visitor perceptions of crime-safety and attitudes towards risk: The case of Table Mountain National Park, Cape Town. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.X.; Gibson, H.J.; Zhang, J.J. Perceptions of risk and travel intentions: The case of China and the Beijing Olympic Games. J. Sport Tour. 2009, 14, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baber, R.; Baber, P. Influence of social media marketing efforts, e-reputation and destination image on intention to visit among tourists: Application of SOR model. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2022, 6, 2298–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Galati, A.; Sharma, S. Explore, eat and revisit: Does local food consumption value influence the destination’s food image? Br. Food J. 2023, 125, 4639–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Karim, S.; Chi, C.G.Q. Culinary tourism as a destination attraction: An empirical examination of destinations’ food image. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2010, 19, 531–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulagain, S.; Wiitala, J.; Fu, X. The impact of country image and destination image on US tourists’ travel intention. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Liu, S. Urban tourism destination image perception based on LDA integrating social network and emotion analysis: The example of Wuhan. Sustainability 2021, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, S. A cross-cultural anatomy of destination image: An application of mixed-methods of UGC and survey. Tour. Manag. 2023, 98, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Hsu, C.H. Research on user-generated photos in tourism and hospitality: A systematic review and way forward. Tour. Manag. 2023, 96, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Milán, O.; Castillo-Ortiz, I. Destination brand personality self-congruity and crime perceptions: Effects on travel intentions. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2023, 28, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Ni, L.M. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Hsu, C.H. Effects of travel motivation, past experience, perceived constraint, and attitude on revisit intention. J. Travel Res. 2009, 48, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, P. Unexpected surprise: Emotion analysis and aspect based sentiment analysis (ABSA) of user generated comments to study behavioral intentions of tourists. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2023, 45, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.; Benckendorff, P.; Moscardo, G. Linking travel motivation, tourist self-image and destination brand personality. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2007, 22, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.P.; Lim, W.M.; Jain, T. Electronic word of mouth on social networking sites: What inspires travelers to engage in opinion seeking, opinion passing, and opinion giving? Tour. Recreat. Res. 2022, 49, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cham, T.H.; Lim, Y.M.; Sia, B.C.; Cheah, J.H.; Ting, H. Medical tourism destination image and its relationship with the intention to revisit: A study of Chinese medical tourists in Malaysia. J. China Tour. Res. 2021, 17, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Santana, A.; Moreno-Gil, S. New trends in information search and their influence on destination loyalty: Digital destinations and relationship marketing. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2017, 6, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Seok, H.; Nam, Y. The moderating effect of social media use on sustainable rural tourism: A theory of planned behavior model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gasawneh, J.A.; Al-Adamat, A.M. The relationship between perceived destination image, social media interaction and travel intentions relating to Neom city. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 2020, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, K.; Malik, M.Y.; Pitafi, A.H.; Kanwal, S.; Latif, Z. If you travel, I travel: Testing a model of when and how travel-related content exposure on Facebook triggers the intention to visit a tourist destination. Sage Open 2020, 10, 2158244020925511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Tong, S. The impact of user-generated content on intention to select a travel destination. J. Mark. Anal. 2023, 11, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheung, L.T.; Lovett, J.; Duan, X.; Pei, Q.; Liang, D. Understanding the influence of user-generated content on tourist loyalty behavior in a cultural World Heritage Site. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2023, 48, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Yao, X. Research on the evaluation of tourism destination image based on user generated content. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems, Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.R.; Chen, M.Y.; Chen, L.S.; Tseng, S.C. Why customers don’t revisit in tourism and hospitality industry? IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146588–146606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, J. Effects of social media tourism information quality on destination travel intention: Mediation effect of self-congruity and trust. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1049149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudholi, D.H.; Zahra, A.; Rani, S.; Huda, S.N.; Paputungan, I.V.; Zukhri, Z. BERT-based tourism named entity recognition: Making use of social media for travel recommendations. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelson, S.A.; Bruce, E.; Egala, S.B.; Amoah, J.; Bashiru Jibril, A. Driving forces of social media and its impact on tourists’ destination decisions: A uses and gratification theory. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2024, 10, 2318878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhao, Y. Impact of destination advertising on tourists’ visit intention: The influence of self-congruence, self-confidence, and destination reputation. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2024, 31, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armutcu, B.; Tan, A.; Amponsah, M.; Parida, S.; Ramkissoon, H. Tourist behaviour: The role of digital marketing and social media. Acta Psychol. 2023, 240, 104025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, L.A.; Tussyadiah, I.; Scarles, C. Exploring behaviors of social media-induced tourists and the use of behavioral interventions as salient destination response strategy. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2023, 27, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusra, Y.; Vilzati, V.; Eliana, E.; Ariffin, A.A.M.; Susanto, P. Stimulating visit intention using social media influencer: Mediating role of enjoyment. Indones. J. Bus. Entrep. 2023, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakshi; Tandon, U.; Ertz, M.; Bansal, H. Social vacation: Proposition of a model to understand tourists’ usage of social media for travel planning. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101438. [Google Scholar]
- Schoner-Schatz, L.; Hofmann, V.; Stokburger-Sauer, N.E. Destination’s social media communication and emotions: An investigation of visit intentions, word-of-mouth and travelers’ facially expressed emotions. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 22, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, J. twitteR: R Based Twitter Client; R Package Version 1.1.9; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, M.W.; Heiss, A.; Briatte, F. rtweet: Collecting Twitter Data; R Package Version 1.0.2; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mastroeni, L.; Naldi, M.; Vellucci, P. Wind energy: Influencing the dynamics of the public opinion formation through the retweet network. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 194, 122748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillé, Y.; Wilhelm, M. Probability sampling designs: Principles for choice of design and balancing. Stat. Sci. 2017, 32, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötsch, J.; Malkusch, S.; Ultsch, A. Optimal distribution-preserving downsampling of large biomedical data sets (opdisDownsampling). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Mittal, S. Sampling approaches for imbalanced data classification problem in machine learning. In Proceedings of the ICRIC 2019: Recent Innovations in Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Berrar, D. Cross-Validation. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Ranganathan, S., Gribskov, M., Nakai, K., Schönbach, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedele, O. Determining the optimal number of folds to use in a K-fold cross-validation: A neural network classification experiment. Res. Math. 2023, 10, 2201015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jarrah, O.Y.; Yoo, P.D.; Muhaidat, S.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Taha, K. Efficient machine learning for big data: A review. Big Data Res. 2015, 2, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Kokol, M.; Zagoranski, S. Machine learning on small size samples: A synthetic knowledge synthesis. Sci. Prog. 2022, 105, 00368504211029777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, D.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, C.C. Evaluation of a decided sample size in machine learning applications. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnami, A.; Lee, M. Learning from few examples: A summary of approaches to few-shot learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.04291. [Google Scholar]
- Jadon, S. An overview of deep learning architectures in few-shot learning domain. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.06365. [Google Scholar]
- Tunstall, L.; Reimers, N.; Jo, U.E.S.; Bates, L.; Korat, D.; Wasserblat, M.; Pereg, O. Efficient few-shot learning without prompts. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 3982–3992. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D. Siamese neural networks: An overview. Artif. Neural Netw. 2021, 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer, E.; Ailon, N. Deep metric learning using triplet network. In Proceedings of the Similarity-Based Pattern Recognition: Third International Workshop, SIMBAD 2015, Copenhagen, Denmark, 12–14 October 2015; pp. 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Liu, M.; Cutkosky, A.; Orabona, F. Understanding adamw through proximal methods and scale-freeness. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Fixing weight decay regularization in Adam. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1711.0510v2. [Google Scholar]
- Pukelsheim, F. The three sigma rule. Am. Stat. 1994, 48, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreau, D.; Luxburg, U. Explaining the explainer: A first theoretical analysis of LIME. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; PMLR: Birmingham, UK, 2020; pp. 1287–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Fantozzi, P.; Naldi, M. The Explainability of Transformers: Current Status and Directions. Computers 2024, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).