Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) in education has become increasingly common in higher education, particularly in learning English as a second language (ESL). ChatGPT is a conversational AI model frequently used to support language acquisition by creating personalized, interactive learning experiences. This narrative review explored the impact of ChatGPT on ESL in higher education within the past three years. It employed a qualitative literature review using EBSCOhost, ERIC, and JSTOR databases. A total of 29 peer-reviewed articles published between 2023 and 2025 were selected for review. The Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles (SANRA) was applied as an assessment tool for quality and reliability. The results indicated that ChatGPT enhances learning outcomes in ESL by helping students improve their writing skills, grammar proficiency, and speaking fluency. Moreover, it fostered student engagement due to its personalized feedback and accessible learning resources. There were, however, concerns about plagiarism, factual errors, and dependency on AI tools. Although ChatGPT and similar models present promising opportunities and benefits in ESL education, there is a need for structured implementation and ethical guidance.
1. Introduction
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into educational practices has profoundly influenced students’ learning experiences across the globe [1]. Artificial technologies like ChatGPT have become very popular in education, especially in English as a Second Language (ESL) [2]. ChatGPT offers an interactive and personal learning experience, supporting learners’ language acquisition skills [2]. OpenAI developed ChatGPT, which uses language processing (NLP) algorithms [2]. ChatGPT helps learners engage with chat, correct grammar errors, and stimulate real-world language in their writing [3,4].
English communication skills have become essential for academic and professional success in the modern world [5]. Because of this, higher education institutions are exploring different pedagogical approaches to help learners develop better English language communication skills [5,6]. When instructors and students can effectively communicate with each other, especially using digital educational platforms, it can positively enhance engagement and motivation in higher education settings [7]. There are many challenges ESL learners face in higher education settings; they may have difficulty understanding complex sentences and have a lack of fluency in both writing and speaking skills [8]. Traditional lectures for ESL students depend on classroom lectures, peer and instructor interactions, and writing exercises, which are insufficient for all ESL learners [6]. Here, ChatGPT could be beneficial as it has features like a conversational interface, and it can generate human-like, contextually relevant text, which is incredibly helpful for ESL learners as they can learn to improve their writing skills independently with the help of immediate feedback [6].
A lack of research has been conducted on the applications of ChatGPT in the context of learning ESL [2]. Shaikh et al. [9] sought to assess the usability of ChatGPT for formal English language learning. The authors found that learners particularly appreciated the instant feedback on grammatical errors and sentence structure that the tool provides. Moreover, the interactive nature of ChatGPT encouraged learners to experiment more with the use of the language, which enhanced their confidence and willingness to communicate more in English [6]. Alsaedi [8] noted that the role of personalized and prompt feedback in developing ESL learners’ writing skills aligns with Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory, particularly the concept of the zone of proximal development (ZPD). The more ESL learners engage with ChatGPT and participate in meaningful language use, the more active learning and internalization of linguistic structures are promoted [2]. Du and Alm [10] utilized the self-determination theory to study how ChatGPT influences ESL learners’ motivation. They found that the personalized feedback mechanism of ChatGPT supports ESL learners’ autonomy, competence, and relatedness, which are fundamental components of intrinsic motivation [10]. When the learners noticed that their efforts were leading to improvements, their motivation to continue engaging with the language learning activities increased. This is a vital psychological aspect of language learning and is essential for ESL learners who can quickly feel overwhelmed by the linguistic demands of academic discourse [10].
Although ChatGPT has benefits in ESL learning environments, some studies pointed out challenges educators and students must navigate [8]. For example, Mohamed [6] conducted a qualitative study exploring the perceptions of ESL instructors about the integration of ChatGPT in their classrooms. The instructors expressed concerns about the reliability and accuracy of AI-generated content [6]. They noted grammatical inaccuracies, inappropriate vocabulary suggestions, and culturally insensitive language. Furthermore, the instructors were apprehensive about the potential for students to overly rely on ChatGPT, which undermines the development of independent language learning skills [6]. Other researchers have noted that educators are concerned about academic integrity with the integration of ChatGPT into ESL courses [2,11]. Lo et al. [2] found that some students will use the AI tool to generate entire essays without fully understanding the content or learning the academic writing skills the program should promote. To meet this challenge, plagiarism detection tools like Turnitin have begun incorporating AI-generated content detection features [12]. As AI technology evolves, it becomes increasingly difficult to distinguish between human and AI-generated content [2,12]. Researchers have emphasized the value of educating students on the ethical use of AI tools to promote a more balanced approach [13,14].
It is essential for educators to guide students on how to interact effectively with AI tools like ChatGPT [3,15]. Recent studies showed how ESL learners use ChatGPT for their language learning tasks, mainly writing and speaking [16,17]. Learners who regularly and actively interacted with ChatGPT improved their sentence complexity and lexical diversity [12]. However, researchers also found this was only true if the learners did not passively accept the tool’s suggestions [4]. When ChatGPT is used for structured, task-based activities, it promotes communication and critical thinking, and in that way, it can serve as a collaborative partner for ESL learning [18]. The authors found that ChatGPT assisted with collaborative writing tasks, particularly brainstorming ideas, drafting content, and revising drafts [18]. ChatGPT helped to reduce language-related communication barriers, particularly among those learners with lower English proficiency skills [3]. Still, the effectiveness of ChatGPT for improving language skills depends on various factors [18]. Prior experience in using AI tools, attitudes toward technology, and instructional context were all significant factors that affected the impact of ChatGPT on language learning [19]. Learners with higher digital literacy levels were, for example, better at forming more effective prompts and interpreting the feedback from ChatGPT [18]. That suggests that to successfully integrate ChatGPT into the ESL curricula, it is necessary to access the technology and train students to use it effectively [3].
The instructor’s role is also critical despite the increasingly widespread use of AI tools in ESL courses [5]. When teachers mediated ChatGPT interactions, it was more effective at promoting language development than when students used it independently [17,20]. Those teachers who provided students with guidance on the tool’s feedback and encouraged reflective practices found that their students’ writing quality improved more than the writing quality of students whose instructors who did not provide that kind of structure [17,20]. This shows a sociocultural perspective on language learning, meaning that human interaction is still essential in developing higher-order language skills [21]. The more effective pedagogy for integrating ChatGPT into ESL learning employs thoughtful planning and continuous evaluation [17,21]. ChatGPT is mainly for formative assessment, such as providing feedback on drafts or interactive grammar exercises [22]. Educators should maintain caution against overly relying on ChatGPT for summative assessments, given the potential to misuse AI-generated content [11]. Recent studies suggested that instructors incorporate discussions about AI literacy to help students learn to evaluate AI-generated text critically and use these kinds of tools responsibly [23,24].
Existing studies up to date demonstrate the potential of ChatGPT in enhancing ESL learning in higher education, but they also highlight the need for strategic, ethical implementation [17,22]. ChatGPT offers substantial benefits for ESL learners as it provides personalized, engaging language learning experiences [25,26]. The applications of this kind of AI tool offer benefits in various language skills, including writing, speaking, and grammar comprehension [4,9,16]. However, its effectiveness depends on how it is implemented, on the training that both learners and educators receive, and on the implementation of ethical standards of use [17,22]. If integrated into a well-structured pedagogical framework, ESL can support learners in their quest to develop the linguistic competence necessary for academic and professional success [17,22]. To address the critical aspects of ChatGPT use, the present study explored the following: (1) the impact of ChatGPT on ESL students’ writing proficiency and academic performance, (2) the perceptions and attitudes of ESL educators and students toward the use of ChatGPT as a pedagogical tool, and (3) the role of ChatGPT in enhancing ESL learners’ engagement, motivation, and self-directed learning in digital and hybrid environments.
2. Methodology
This narrative review explored EBSCOhost, ERIC, and JSTOR for studies on ChatGPT’s impact on ESL education in higher education, focusing on writing proficiency, language learning outcomes, engagement, and motivation. The search was refined to include peer-reviewed studies from 2023 to 2025.
2.1. Search Strategy
The Boolean operators used in the search strategy are outlined below (Table 1).

Table 1.
Keywords and Boolean Operators for Literature Search.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The studies were selected based on the criteria in Table 2, ensuring only the most relevant and recent research was included.

Table 2.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.
2.3. Review Process
Articles were initially screened by reviewing abstracts, introductions, and conclusions for relevance and adherence to inclusion criteria. The review adhered to the Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles (SANRA) guidelines [27] to maintain study quality. After applying selection criteria and eliminating duplicates, 29 studies were included. For transparency, the screening process was recorded using a PRISMA-ScR diagram [28].
3. Results
Screening Results
Out of 250 articles, only 29 met the inclusion criteria. Figure 1 outlines the selection process. The chosen studies employed diverse methodologies, including reviews and quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. Table 3 presents each article’s country/research site, purpose, approach, and key findings. Key themes were examined to assess their impact on online education, with a summary provided in Table 4.
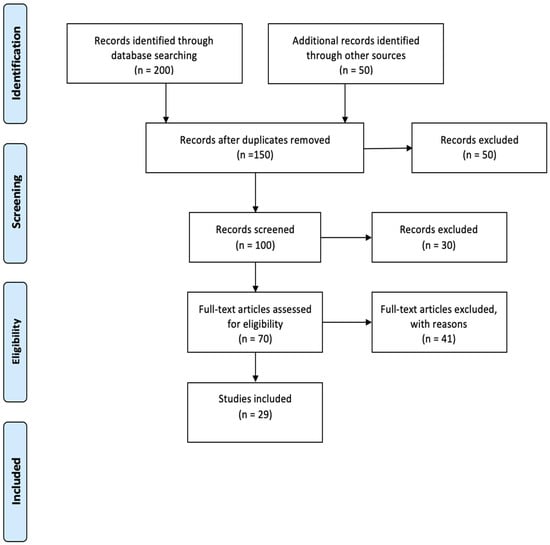
Figure 1.
PRISMA-ScR Diagram Illustrating the Study Selection Process.

Table 3.
Summary of Studies Included in the Review.

Table 4.
Overview of Key Themes in ESL Learning with ChatGPT Integration.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of ChatGPT on ESL Students’ Writing Proficiency and Academic Performance
The research showed that ChatGPT helps improve students’ proficiency and academic performance when incorporated with ESL writing instruction [4,9]. ESL students benefited from ChatGPT in many ways. It helped improve sentence structure, grammatical accuracy, vocabulary use, and overall text coherence [9,24]. Research also indicated that students want to use ChatGPT as a writing aid because they feel satisfied with the interaction and results. That suggests the tool helps them stay motivated and actively engaged with their learning experience [9,11]. Moreover, ChatGPT helped students by giving instant feedback, and it could revise their writing numerous times, thereby reducing their writing anxiety and boosting their academic performance [10,17].
4.1.1. Improvements in Writing Proficiency
One of the most critical skills for ESL learners is their writing ability, especially in higher educational settings, as students must write a considerable amount of academic text [17]. Diasamidze and Tedoradze [17] stated that students who use ChatGPT in their writing assignments improve their sentence construction proficiency. They also demonstrated improvements in grammar accuracy. The AI helped students with instant feedback, allowing them to find errors and refine their assignments more effectively. Additionally, Polakova and Ivenz [13] found that students using AI-generated suggestions showed improvements in argument coherence and logical flow in their essays. It was suggested that ChatGPT is an effective scaffolding tool that helps ESL learners develop more vigorous writing habits with structured guidance and corrections [13].
Mahapatra [22] also found that students who engaged repeatedly with ChatGPT’s feedback could provide clearer argumentation, better paragraph transitions, and fewer grammar errors. This emphasizes the value of iterative writing and revision in ESL learners and suggests that ChatGPT can complement traditional teaching methods by allowing students to work independently and make corrections without requiring teacher feedback [8,17,22]. Diasamidze and Tedoradze [17] and Wu [24] examined how ChatGPT can help enhance word choice, lexical diversity, and syntactic complexity when used by ESL learners. They found that students who regularly used the AI tool to draft their content could expand their range and utilize more advanced sentence structures in their essays. It was apparent that AI-generated responses can support the development of higher-order language skills, which is critical for ESL students aiming for academic success [17,24].
4.1.2. Impact on Academic Performance
ChatGPT has also been found to help students boost their academic performance because it helps them generate well-structured academic papers and research assignments [9,17]. Specifically, Mahapatra [22] found that students who had integrated ChatGPT into their writing process produced more comprehensive and well-structured arguments in their essays, which helped them to improve their academic achievement. The specific feature of the AI tool that helped the most was its immediate feedback, which helped students make necessary revisions and submit higher-quality assignments with fewer errors and improved clarity [13,17]. Alsaedi [8] and Werdiningsih et al. [15] found that students using ChatGPT to plan their essays and self-edit them had greater confidence when completing their writing assignments. This consequently led to improvements in academic performance. In addition, Alsaedi [8], Diasamidze and Tedoradze [17], and Wu [24] found that students greatly benefited from using ChatGPT regularly, especially for writing tasks like thesis statements. It helped them support their arguments with logically arranged events, allowing learners to evaluate the outcomes of their writing tasks. The studies discussed above reveal that AI-assisted writing aids will enable learners to improve their critical thinking ideas by refining their writing.
Although studies revealed the positive impacts of ChatGPT on writing tasks, they also noted specific concerns [8,15]. Alsaedi [8], Du [10], and Werdiningsih et al. [15] argued that students’ over-reliance on AI writing tools like ChatGPT could negatively affect their thinking skills, leading to dependency on AI to create content rather than develop their skills. Alsaedi [8] and Du [10] emphasized that while ChatGPT enhances ESL learning, educators must implement strategies to prevent over-reliance and support independent thinking. These AI tools have clear benefits, but they need to be implemented in a structured way to emphasize their ethical use [8,17].
4.1.3. The Role of AI-Assisted Feedback in Academic Success
ChatGPT helps students by providing instant feedback on sentence structure, grammatical errors, and overall clarity [2,3]. Traditional classroom feedback is associated with delayed feedback, sometimes by days or weeks, but ChatGPT helps learners obtain real-time feedback [2,3]. Mahapatra [22] and Selim [33] found that students who use ChatGPT for feedback on multiple drafts can independently produce their revisions, leading to an overall improvement in their academic outcomes compared to learners who depend only on instructor feedback. ChatGPT allows students to explore various sentence structures, using different vocabulary and new writing styles, ultimately leading to more polished and sophisticated academic texts [20,22]. Lin [25] and Polakova and Ivenz [13] stated that students who use ChatGPT to obtain feedback are more self-aware of their weaknesses and work to improve their writing. However, despite the engaging features of ChatGPT, it has its limitations, including the risk of over-reliance and reduced critical thinking among learners [25], as well as concerns about accuracy and ethical considerations in AI-generated content [6]. Werdiningsih et al. [15] found that AI-generated content sometimes does not align with academic integrity standards; students should be trained to use AI ethically and maintain the code of ethics in their institutions. Moreover, over-editing could lead to a rise in the use of AI suggestions, leading to a lack of personal touch and originality [4,15]. Educators should incorporate AI-assisted feedback with traditional academic instruction to facilitate student learning while adhering to academic honesty [6,33].
4.2. Perceptions and Attitudes of ESL Educators and Students Toward the Use of ChatGPT as a Pedagogical Tool
Incorporating ChatGPT into ESL instruction has elicited a range of perspectives among educators and students [6,14]. Some educators welcome AI’s benefits in designing course curricula while others have expressed significant concerns about students’ academic integrity and ChatGPT’s adverse effects that could hinder students’ critical thinking [14,15]. Students perceived ChatGPT positively as a learning aid, especially for self-planned learning [18,19]. Some students, however, reported a lack of personal suggestions, which could be a barrier to learning a language [14,15]. The section below describes in more detail the results of empirical studies exploring the perspectives of both educators and students.
4.2.1. Educators’ Perceptions of ChatGPT in ESL Instruction
ChatGPT helps educators organize course content, grade student assignments, and prepare classroom material [4]. According to Mohamed [6], EFL faculty members acknowledged that ChatGPT’s rapid and accurate responses to students’ inquiries help with content development and enrich the traditional classroom approach. Similarly, Lo et al. [2] reported that ChatGPT helped educators hone their skills for lesson planning. ChatGPT was used to create sample exercises for students and offered suggestions for essay assignments [4]. Educators noted this helped save them a significant amount of time. They had more time to engage directly with students to give them individualized suggestions to improve their academic content [6]. Van Horn [3] stated that providing individual feedback is challenging for educators in a large classroom because of the high number of students. ChatGPT facilitates automatic assessments, significantly reducing the time spent grading assignments and quizzes [2]. Although ChatGPT has these benefits as a writing tool, Liang and Wu [23] reported that ESL instructors are concerned that students who depend heavily on ChatGPT may fail to develop independent writing skills and coherent, compelling arguments. Although ChatGPT helps to produce grammatically correct texts, it cannot facilitate a deep cognitive process that requires constructing logical arguments and critical analyses [23].
Similarly, Liang and Wu [23] emphasized that many students use ChatGPT to generate content without knowing or verifying the accuracy of the information provided. Students who regularly used ChatGPT showed a gradual decline in reasoning skills compared to those without AI-generated assistance [23]. Tram et al. [4] also noted that guiding students in using ChatGPT ethically remains one of the biggest challenges for educators, particularly in preventing over-reliance on AI-generated content.
Despite these concerns, many learners view ChatGPT as a valuable tool. A recent study from Van Horn [3], 56% (n = 67) of 120 respondents expressed a positive outlook on using ChatGPT for EFL learning. However, ESL instructors have expressed concerns about academic integrity. Li et al. [26] found that ESL instructors were concerned that students using ChatGPT had an increased risk of dishonesty, particularly in writing assignments and take-home exams. Both Diasamidze [17] and Alsaedi [8] emphasized that instructors have more difficulty assessing students’ language proficiency when students use ChatGPT without proper attribution. To solve this issue, some institutions now use AI-detection tools and require assignments to go through process-based submissions, where students must submit their assignment draft before the final version [22]. Altering the assessment methods could be helpful. One suggestion is to assign students in-class writing tasks and evaluations, which could help to ensure that learners are at ease and engage in authentic language learning [14,22].
4.2.2. Students’ Perceptions and Experiences with ChatGPT in ESL Learning
Most students acknowledged that ChatGPT is widely used and find it invaluable for improving writing proficiency and grammar skills [14,17]. Teng [14] and Nguyen et al. [4] found that ESL students had used ChatGPT for writing assignments, reporting that ChatGPT helped them to make confident adjustments in their academic writing. The studies mentioned that the learners like ChatGPT, which gives them immediate feedback, especially when instructors are too busy to provide rapid input or real-time instruction [14,32]. Similarly, Xiao and Zhi [18] noted that lexical variety and syntactical accuracy were significantly improved in those students who were engaged with ChatGPT-assisted writing exercises. The study emphasized that ChatGPT is an accessible self-editing tool that effectively identifies grammatical errors and helps refine sentence structure without relying solely on instructor feedback [18].
Although students appreciated ChatGPT’s ability to provide instant feedback, some students reported difficulty with AI-generated instruction to improve their quality of writing [5]. Abusahyon et al. [5] and Sallam et al. [19] discussed grammar skills in AI-driven learning and feedback, noting that AI tools provide grammar explanations and interactive lessons to support ESL students. ESL students who lacked reading skills could not interpret ChatGPT’s feedback, which was often negatively affected by their original use of incorrect words and inconsistencies in sentence structure. The issue was particularly relevant for those who lack a foundation in grammar skills; they needed extra help from educators to understand AI-generated corrections [4,14]. Additionally, Van Horn [3] highlighted that sometimes ChatGPT may create misleading content, and students may, therefore, require assistance from instructors to ensure accurate language choice. These findings suggest that ChatGPT should be used as a supplementary writing tool but not as a writing tutor, emphasizing the necessity of human oversight in AI-assisted learning [3].
4.2.3. Institutional Strategies for Effective AI Integration and Balancing AI Assistance with Human Feedback
Recognizing ChatGPT’s challenges and ethical risks is essential [11,15,26] Educational institutions need to, therefore, implement structured AI literacy programs to help guide their educators and students in responsible AI usage [23,24]. Lo et al. [2] and Liang and Wu [23] suggested that AI workshops could be integrated into ESL curricula to ensure that students learn the basics of critically evaluating AI-generated content and that students and educators can differentiate between AI-assisted and original writing. Many universities are setting rules to track how students use AI in their work, focusing on ethical use and its impact on writing and thinking [2,23]. These straightforward guidelines promote the ethical use of AI tools like ChatGPT. Educators are also utilizing blended AI–human instruction models to help ensure that ChatGPT does not replace the students’ development of critical thinking and writing skills [23]. Teng [14] suggested instructors should use ChatGPT only as a prewriting and brainstorming tool. That should be followed by peer review sessions and instructor-led discussions, which will help reinforce the development of critical analysis and independent learning skills. Chandrasekera et al. [30] also recommend using AI selectively for lower-stakes assignments, such as grammar exercises and writing drafts. Final submissions, the author noted, should be student-generated with minimal AI influence.
4.2.4. The Future of AI in ESL Education
The future of ChatGPT in ESL education involves how institutions balance AI-driven learning with traditional teaching models [10]. Students recognized that AI-driven learning has potential benefits [13,24,33]. Still, their concerns about ethical issues of academic integrity, AI dependency, and plagiarism must be addressed as part of a structured integration process [15]. Future research could help explore this issue by utilizing longitudinal studies to assess ChatGPT’s effects on student writing proficiency, engagement, and independent language learning [2,30]. This will help ensure that AI remains an effective tool without replacing human instruction.
4.3. The Role of ChatGPT in Enhancing ESL Learners’ Engagement, Motivation, and Self-Directed Learning in Digital and Hybrid Environments
While ChatGPT use has become more widespread in ESL education, particularly in digital and hybrid platforms, to foster writing proficiency, it can also improve motivation, engagement, and self-directed learning (SDL) [25,26]. The many features that students find most helpful, such as real-time interaction, personalized feedback, and adaptive learning experiences, are also beneficial in keeping them engaged with the material [4,25]. AI’s effectiveness in this regard, however, depends on how students use the tools and their ability to integrate them with their structured learning tasks [24]. The following sections discuss ChatGPT’s role in helping with this.
4.3.1. Enhancing Engagement in ESL Learning
Student engagement is a critical element of language learning. Studies show that ESL learners use AI tools like ChatGPT more than traditional pedagogical approaches [8,17]. Li [26] found that students using ChatGPT to generate interactive language practice exercises established more vigorous habitual learning routines than they might otherwise have in non-AI-assisted classrooms. ChatGPT’s real-time response feature helped encourage spontaneous language use and allowed students to think more critically about sentence formation and grammatical accuracy [4]. Students engaging with ChatGPT for structured classroom discussion participated more actively, particularly in digital learning environments [3]. Educators noted that the integration of ChatGPT resulted in more student-led discussions in which learners posed more questions, tested vocabulary, and formulated their responses dynamically [3].
Additionally, real-life simulations and activities can foster higher-order thinking while establishing a community among AI learners [25]. This integrates unique human abilities with AI systems to encourage critical thinking, social interactions, and community building [23]. Adaptive AI challenges, like context-based writing tasks, real-life conversation simulations, and AI-generated quizzes, effectively created a more engaging learning environment that motivated students to continue practicing their skills [3,11].
Deep et al. [31] highlighted that students’ motivation and engagement are influenced by using gamification in the classroom. Their study found that ESL students do better using gamification techniques like leaderboards, point systems, and interactive feedback. Students also increased classroom participation and could study longer than in traditional classrooms if gamified features were used. This suggests that language learning could be enhanced if educational institutions use gamified AI features, such as real-time changes and reward systems [9,31]. Another notable study by Li et al. [26] confirmed that if the students customize the ChatGPT exercise, they tend to stay engaged longer. These findings reveal that students participate more in the learning process when using AI, which is also associated with better engagement and motivation [6,13].
4.3.2. ChatGPT’s Role in Sustaining Motivation
Language anxiety is widespread among ESL students, so they hesitate to participate in speaking practices: “Foreign language anxiety rendered students unwilling to communicate in English” [29]. ChatGPT, however, helps ESL learners without judgment since they are not talking with a human, which alleviates language anxiety. Research shows that AI tools create a “low-anxiety environment” that encourages students to participate more in language activities [9]. Lo [2] discussed research that found that using a ChatGPT extension called Voice Master helped boost student confidence and speaking skills. However, the author noted that technical issues presented problems for students when using ChatGPT in this capacity, stating that AI tools’ impact remains under-researched. Similarly, Lo [2] observed that AI-mediated writing helps ESL learners become more confident in writing academic texts. Features like immediate feedback help learners take risks in their learning process, reinforcing positive learning behavior among students [6]. AI tools like ChatGPT are also crucial in assisting students to set and achieve language learning goals [26]. Research suggests that ChatGPT supports learners in establishing learning objectives, creating personalized learning plans, and tracking progress throughout their learning journey [26]. Moreover, ChatGPT has progress-tracking features that help learners check their performance and adjust their learning strategies. Students who use ChatGPT’s tracking features improve their language learning experiences and develop personalized approaches to enhance their language skills [26]. This finding suggests that AI-powered goal-setting features benefit learners by improving motivation and ensuring consistent language learning.
4.3.3. ChatGPT and Self-Directed Learning in ESL Education
Self-directed learning (SDL) is essential for ESL students, especially in digital and hybrid learning environments [26]. Research suggests that ChatGPT could be an encouraging tool for developing SDL skills among ESL learners [26]. Li et al. [26] found that over 89% of students using ChatGPT reported that they can direct their language learning progress, which kept them engaged and motivated. Moreover, students who used ChatGPT for tasks like summarizing, paraphrasing, and learning grammar rules demonstrated more retention of vocabulary and grammar structures [3]. This suggests that AI-assisted SDL uses improve the acquisition and retention of more profound language skills [3]. Another issue for self-directed learning is time management [26]. ChatGPT has features that help organize study schedules; students can set reminders for their assignment due dates and track their progress [25,26]. Nguyen [4] discusses how ChatGPT serves as a writing assistance tool, potentially aiding students in maintaining more structured practice routines. Furthermore, Van Horn [3] found that task competition rates also increase when ChatGPT is used to review materials. This indicates that AI-driven scheduling tools provide the structure that helps learners stay on track with their learning goals [25].
4.3.4. Addressing Challenges in AI-Assisted Learning
While ChatGPT has numerous potential benefits, it is not without its challenges [3]. One of the main concerns is that students will rely on AI-generated responses too much [4]. Some students who regularly used ChatGPT for grammar corrections and sentence structuring became reliant on AI-generated feedback, which sometimes reduced their engagement in independent proofreading and critical language analysis [23]. This emphasizes balancing AI-assisted writing with independent language analysis and development. Another concern is the accuracy of AI-generated responses [18]. Some AI-generated explanations either contained errors or could not explain the cultural and contextual nuance the content needed [8,10]. That can easily lead to misunderstandings in language usage. To meet this challenge, students must be adequately trained in AI literacy. They must learn to critically evaluate AI-generated feedback instead of simply accepting it uncritically [10,18,23].
The findings of these reviewed studies overwhelmingly indicate that ChatGPT has the potential to significantly enhance ESL engagement, motivation, and self-directed learning, particularly within digital and hybrid course settings, but its use must be implemented carefully [9,15]. AI-driven tools can provide interactive, adaptive, and goal-oriented learning experiences, improving student participation, motivation, and engagement [24,33]. However, educators must train learners in the responsible use of AI to ensure that it complements human instruction rather than replacing it and undermining students’ ability to think critically about language use [15,33]. If institutions and educators implement structured AI use and learning strategies, ESL learners can improve their engagement and independent learning to foster long-term language proficiency [5,26,33].
5. Limitations of the Current Review
One of the limitations of the current review is that it focused on more recent studies, which do not provide insights into the long-term effects of AI-assisted ESL learning. Understanding whether AI-driven learning leads to sustained language proficiency or if its use is limited to only temporary gains is essential. Moreover, the focus on digital and hybrid environments leaves out the effectiveness, or lack thereof, of AI-assisted learning strategies in traditional classrooms. Comparative studies help evaluate its role in the face-to-face classroom. Another significant limitation of the current review is that it lacks focus on individual learning differences. How students interact with AI is affected by their digital literacy, cognitive styles, and initial proficiency levels. While some learners may struggle with AI-generated feedback, others can use it more strategically. Research is needed to explore how AI can be adapted to diverse learning styles. Finally, the review also does not deeply engage with contrasting theoretical perspectives across the literature, which could further enrich the analysis. Finally, broader ethical concerns such as AI bias, fairness in assessment, and long-term impacts on learning processes have only been briefly noted and remain underexplored. These are topics that require further investigation.
6. Suggestions for Future Research
One topic that needs more research is long-term retention among learners in AI-assisted ESL courses. It is essential to understand if students can retain the skills they learn even if they no longer have continuous AI support. AI technologies are evolving rapidly in the modern world, and future research should focus on longitudinal studies to better understand the impact of AI tools like ChatGPT on language acquisition and academic performance. Along those lines, future research should explore the intersection of AI tools with other instructional methods, including task-based learning and content and language-integrated learning (CLIL), to best understand the value of optimizing ChatGPT and similar applications in ESL education. This helps address how AI can complement in-person ESL instruction, providing adaptive tools while maintaining teacher-led interactions. Understanding this is vital to developing personalized AI models to cater to diverse learners whose proficiency levels and learning speeds vary significantly. Another area for more investigation is how AI can play a role in formal assessments to ensure fair and unbiased evaluations. Moreover, it is critical to focus on AI literacy programs, plagiarism policies, and ethical guidelines that can help promote the responsible use of AI in ESL education while still maintaining student autonomy and academic integrity.
7. Conclusions
Artificial intelligence is becoming ubiquitous in educational contexts, and its role in ESL education is rapidly evolving. This review has explored the impact of ChatGPT on student writing proficiency, academic performance, engagement, and motivation. Moreover, it examined student and educator perceptions of this popular AI tool. The findings demonstrate that ChatGPT has the potential to enhance writing accuracy, coherence, and sentence structure as it provides instant feedback and revision support. However, this review has also found significant concerns about over-reliance on AI, diminished independent thinking skills, and academic integrity risks. Additionally, educators and students hold diverse perspectives on the role that ChatGPT should play in ESL instruction. Students appreciate AI tools’ personalized and interactive learning, while educators are concerned about how AI-generated content affects originality and critical thinking. Educational institutions are attempting to implement AI literacy programs, highlighting the need for training in AI’s ethical and responsible use in ESL instruction.
While student engagement and motivation are significantly influenced by AI-driven gamification, goal-setting, and interactive exercise, AI dependency remains challenging, emphasizing the importance of human oversight in digital and hybrid learning environments. Through its analysis, the review fulfilled its first objective by demonstrating that ChatGPT significantly contributes to improvements in ESL students’ writing proficiency and academic performance. Across multiple studies, students showed enhanced grammar, vocabulary use, and coherence in their academic writing when supported by AI-generated feedback. In relation to the second objective, the review identified a range of perspectives among both educators and students regarding ChatGPT. While students valued the immediacy and personalization of AI assistance, educators expressed cautious optimism due to concerns about over-reliance, authenticity, and critical thinking. This diversity of views underscores the complexity of integrating AI tools into pedagogical practice. The third objective was also achieved, as the review revealed that ChatGPT plays a substantial role in promoting engagement, motivation, and self-directed learning—particularly in online and hybrid environments. The presence of interactive and adaptive features allowed learners to feel more autonomous and confident, while also reinforcing learning routines and goal-setting behaviors. That is why future research must explore longitudinal studies focused on long-term AI-assisted learning outcomes, appropriate ethical frameworks, and finding the right balance between AI and human instruction. The latter involves utilizing AI to enhance rather than replace human educators as a sustainable, more effective model for ESL learning. Integrating AI strategically into pedagogical frameworks can help educators maximize its benefits while ensuring students learn critical thinking skills as they engage in active and autonomous learning and maintain the academic integrity essential to language learning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.D.D. and M.S.R.; methodology, P.D.D.; software, P.D.D.; validation, P.D.D., N.M. and N.G.; formal analysis, P.D.D. and N.G.; investigation, P.D.D.; resources, P.D.D., N.M. and M.S.R.; data curation, N.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.D.D.; writing—review and editing, N.M., N.G. and M.S.R.; visualization, P.D.D. and N.G.; supervision, N.M. and M.S.R.; project administration, P.D.D., N.M. and M.S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xu, Q. Action research plan: A methodology to examine the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on the cognitive abilities of university students. Discov. Educ. 2024, 3, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.K.; Yu, P.L.H.; Xu, S.; Ng, D.T.K.; Jong, M.S.Y. Exploring the application of ChatGPT in ESL/EFL education and related research issues: A systematic review of empirical studies. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Horn, K.R. ChatGPT in English Language Learning: Exploring Perceptions and Promoting Autonomy in a University EFL Context. TESL-EJ 2024, 28, n1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tram, N.H.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, C.D. ChatGPT as a tool for self-learning English among EFL learners: A multi-methods study. System 2024, 127, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuSahyon, A.S.E.; Alzyoud, A.; Alshorman, O.; Al-Absi, B. AI-driven Technology and Chatbots as Tools for Enhancing English Language Learning in the Context of Second Language Acquisition: A Review Study. Int. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M. Exploring the potential of an AI-based Chatbot (ChatGPT) in enhancing English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teaching: Perceptions of EFL Faculty Members. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 3195–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, P.D.; Chen, Y.; Ghosh, N.; Rahaman, M.S. The Influence of Student–Instructor Communication Methods on Student Engagement and Motivation in Higher Education Online Courses During and After the COVID-19 Pandemic. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, N. ChatGPT and EFL/ESL Writing: A Systematic Review of Advantages and Challenges. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2024, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Yayilgan, S.Y.; Klimova, B.; Pikhart, M. Assessing the Usability of ChatGPT for Formal English Language Learning. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 1937–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Alm, A. The Impact of ChatGPT on English for Academic Purposes (EAP) Students’ Language Learning Experience: A Self-Determination Theory Perspective. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekturova, M.; Tulepova, S.; Zhaitapova, A. Predicting Kazakhstani TEFL students’ continuance intention towards using ChatGPT in academic writing. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, A. Exploring the Role of AI-Driven Dynamic Writing Platforms in Improving EFL Learners’ Writing Skills and Fostering Their Motivation [Internet]. 2025. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-5788599/v1 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Polakova, P.; Ivenz, P. The impact of ChatGPT feedback on the development of EFL students’ writing skills. Cogent Educ. 2024, 11, 2410101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.F. “ChatGPT is the companion, not enemies”: EFL learners’ perceptions and experiences in using ChatGPT for feedback in writing. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdiningsih, I.; Marzuki; Rusdin, D. Balancing AI and authenticity: EFL students’ experiences with ChatGPT in academic writing. Cogent Arts Humanit. 2024, 11, 2392388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalem, M.S. EFL Students’ Perception and Attitude towards the Use of ChatGPT to Promote English Speaking Skills in the Saudi Context. Arab World Engl. J. 2024, 15, 73–84. Available online: https://awej.org/efl-students-perception-and-attitude-towards-the-use-of-chatgpt-to-promote-english-speaking-skills-in-the-saudi-context/ (accessed on 1 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Diasamidze, L.; Tedoradze, T. The Eurasia Proceedings of Educational & Social Sciences (EPESS) The Eurasia Proceedings of Educational Enhancing ESL Students’ Writing Skills through Natural Language Processing Model Chat GPT. Eurasia Proc. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2024, 35, 230–238. Available online: www.isres.org (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Xiao, Y.; Zhi, Y. An Exploratory Study of EFL Learners’ Use of ChatGPT for Language Learning Tasks: Experience and Perceptions. Languages 2023, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.; Elsayed, W.; Al-Shorbagy, M.; Barakat, M.; El Khatib, S.; Ghach, W.; Alwan, N.; Hallit, S.; Malaeb, D. ChatGPT usage and attitudes are driven by perceptions of usefulness, ease of use, risks, and psycho-social impact: A study among university students in the UAE. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1414758. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2024.1414758/full (accessed on 1 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, C. Measuring EFL learners’ use of ChatGPT in informal digital learning of English based on the technology acceptance model. Innov. Lang. Learn. Teach. 2024, 18, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L. Artificial intelligence in language instruction: Impact on English learning achievement, L2 motivation, and self-regulated learning. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1261955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S. Impact of ChatGPT on ESL students’ academic writing skills: A mixed methods intervention study. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wu, Y. Exploring the use of ChatGPT to foster EFL learners’ critical thinking skills from a post-humanist perspective. Think. Ski. Creat. 2024, 54, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Study on the Impact of Utilizing ChatGPT and Other AI Tools for Feedback in EAP Writing Classrooms on the Discursive Writing Performance of English Major Students. Trans. Soc. Sci. Educ. Humanit. Res. 2024, 4, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X. Exploring the Role of ChatGPT as a Facilitator for Motivating Self-Directed Learning Among Adult Learners. Adult Learn. 2024, 35, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Bonk, C.J. Exploring the Utility of ChatGPT for Self-Directed Online Language Learning. Online Learn. J. 2024, 28, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S. The predictive effects of foreign language anxiety and boredom on willingness to communicate among Chinese struggling EFL learners. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekera, T.; Hosseini, Z.; Perera, U.; Bazhaw Hyscher, A. Generative artificial intelligence tools for diverse learning styles in design education. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, P.D.; Ghosh, N.; Gaither, C.; Koptelov, A.V. Gamification Techniques and the Impact on Motivation, Engagement, and Learning Outcomes in ESL Students. RAIS J. Soc. Sci. 2024, 8, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.H.B.; Ngoc, H.H.B.; Dan, T.C. Efl Students’ Perceptions and Practices of Using ChatGPT for Developing English Argumentative Essay Writing Skills. Eur. J. Altern. Educ. Stud. 2024, 9, 168–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.S.M. The Transformative Impact of AI-Powered Tools on Academic Writing: Perspectives of EFL University Students. Int. J. Engl. Linguist. 2024, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).