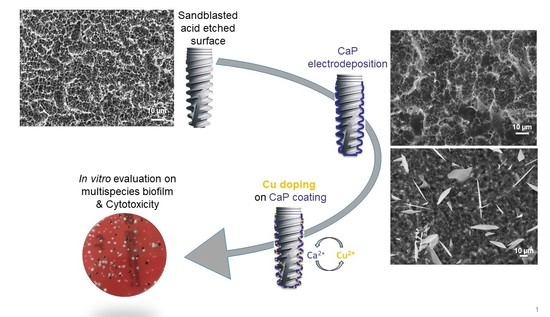
Antibacterial Electrodeposited Copper-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Dental Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Electrodeposition of Calcium Phosphate Coating
2.3. Ionic Exchange
2.4. Coating Characterization
2.5. In Vitro Biological Tests
2.5.1. Coupons under Assay
2.5.2. Tested Bacteria
2.5.3. Activity on Biofilms
| S. gordonii | CIP 105258T | 103/mL |
| A. naeslundii | CIP 103128T | 105/mL |
| P. micra | CIP 105294T | 106/mL |
| F. nucleatum | CIP 101130T | 107/mL |
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | CIP 52106T | 107/mL |
| P. intermedia | CIP 103607 | 107/mL |
| P. gingivalis | CIP 103683 | 107/mL |
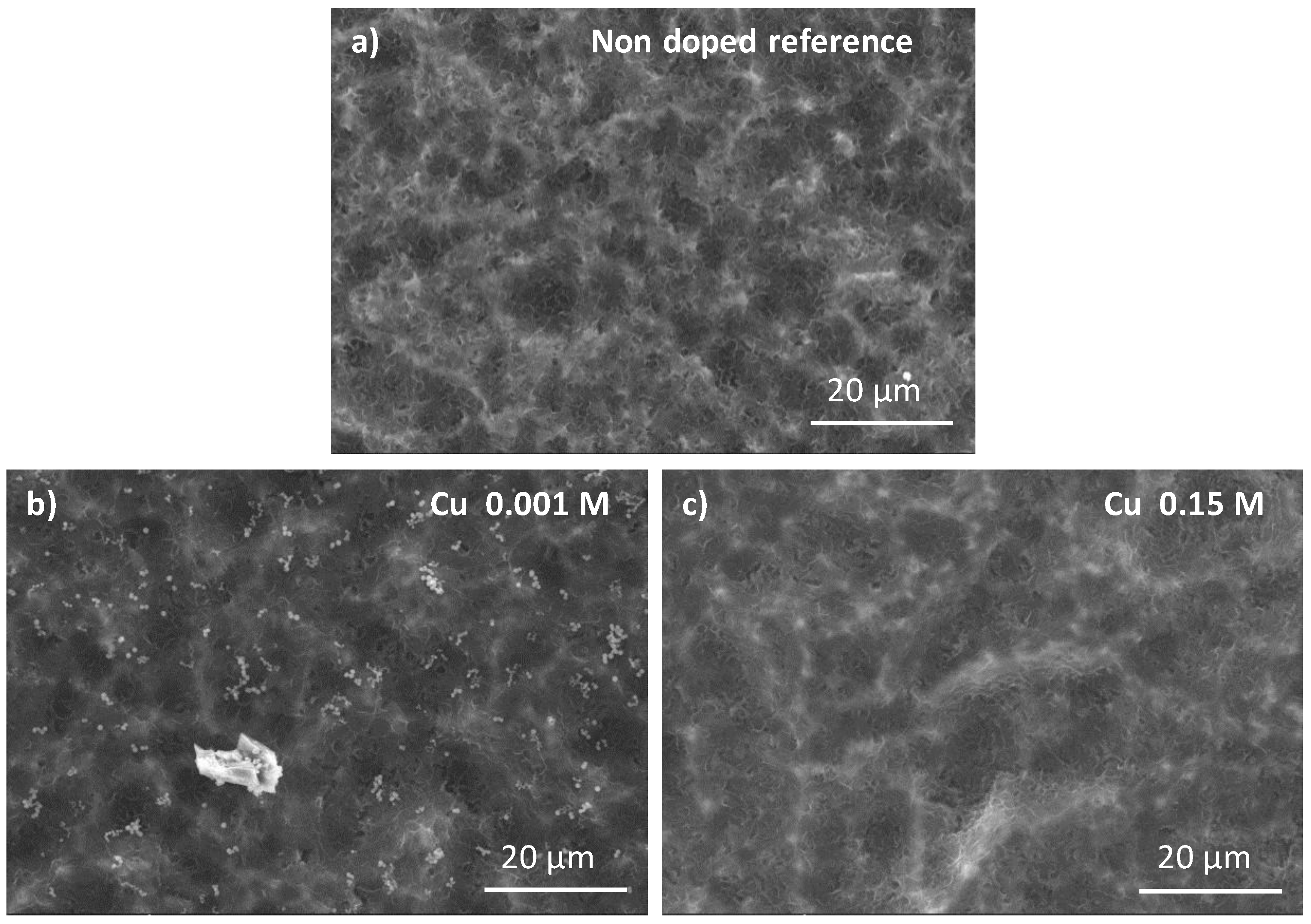
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
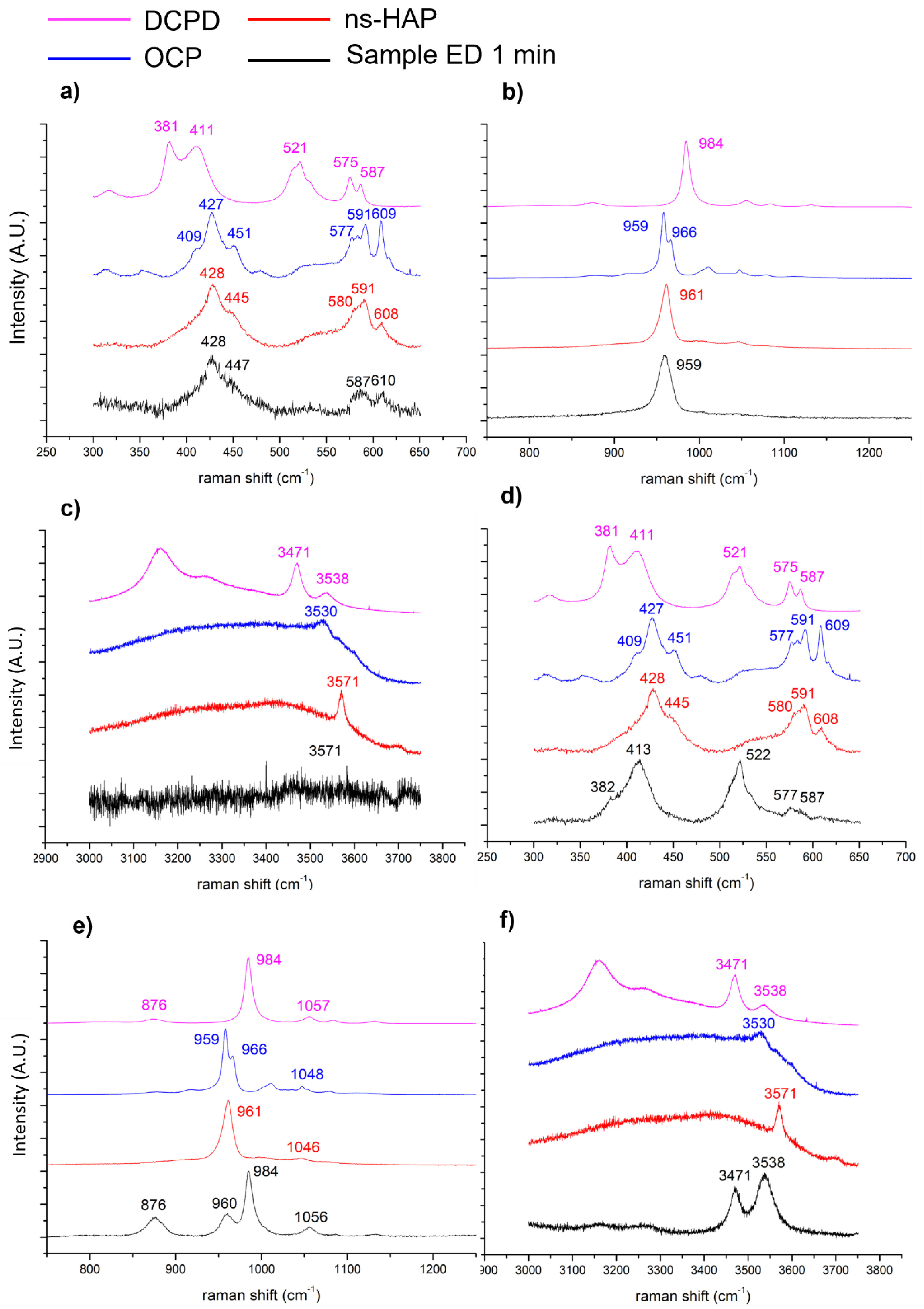
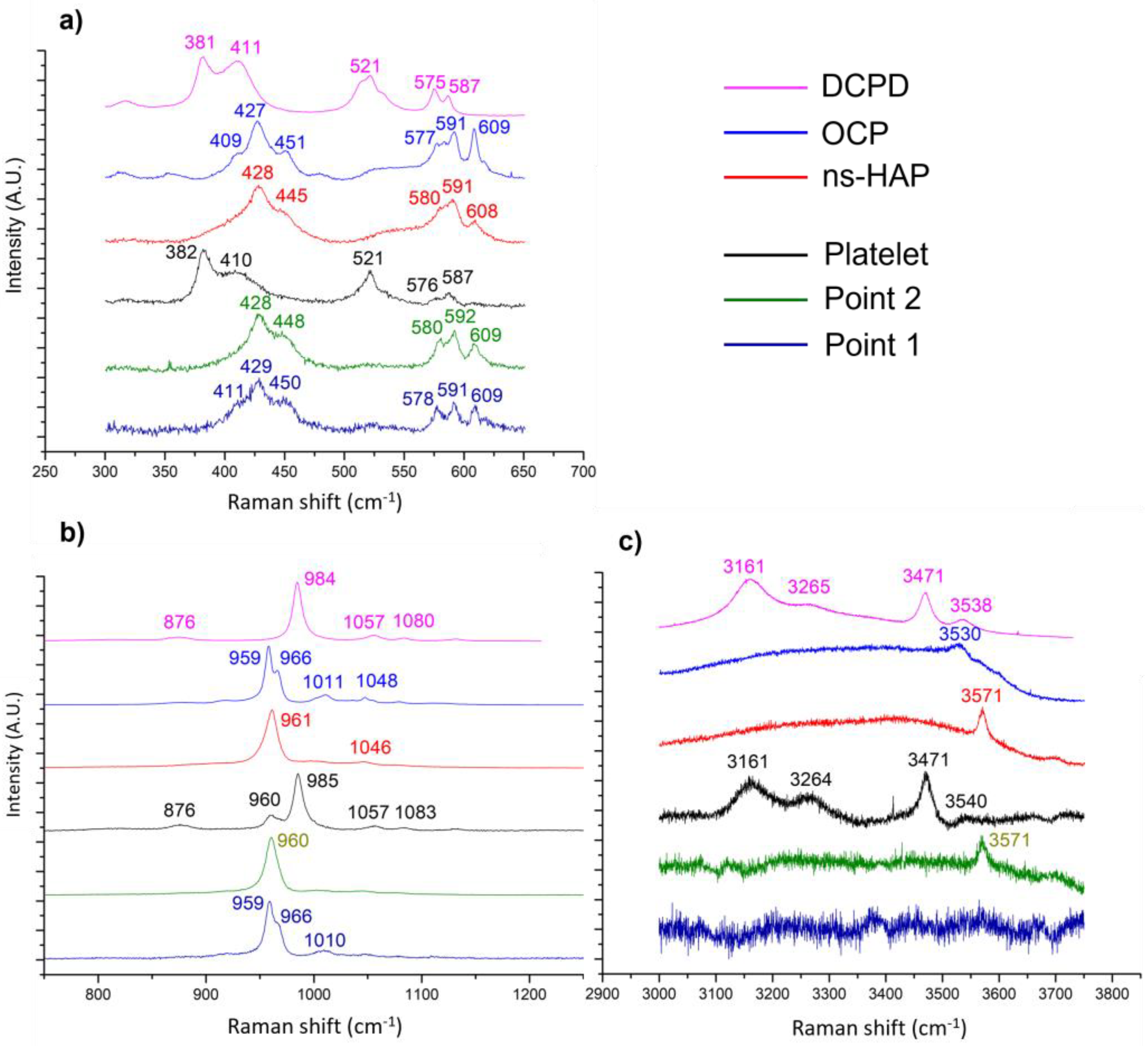
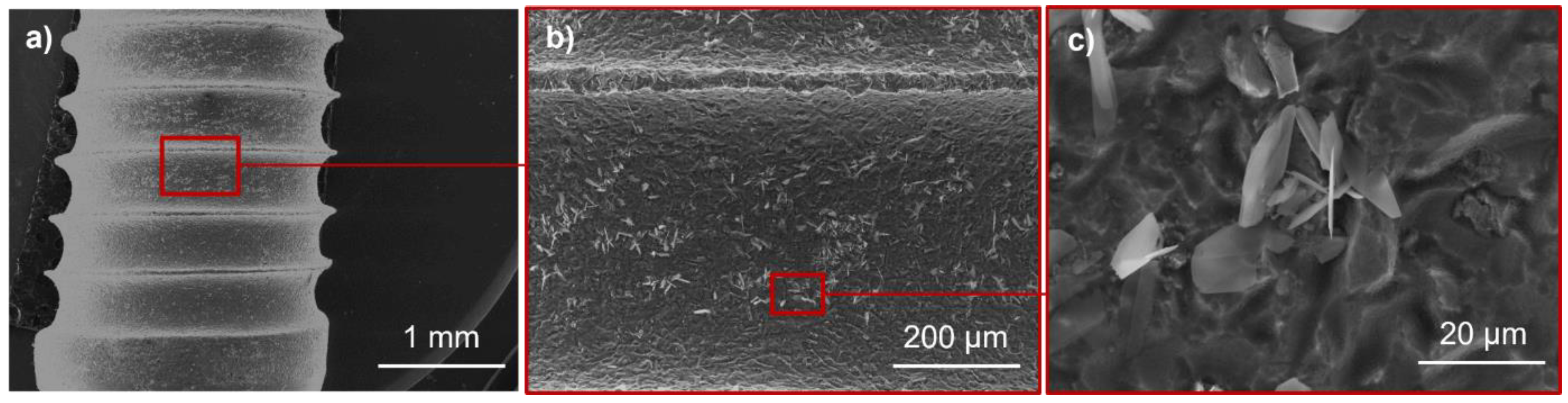
3.1. Influence of Electrodeposition Time
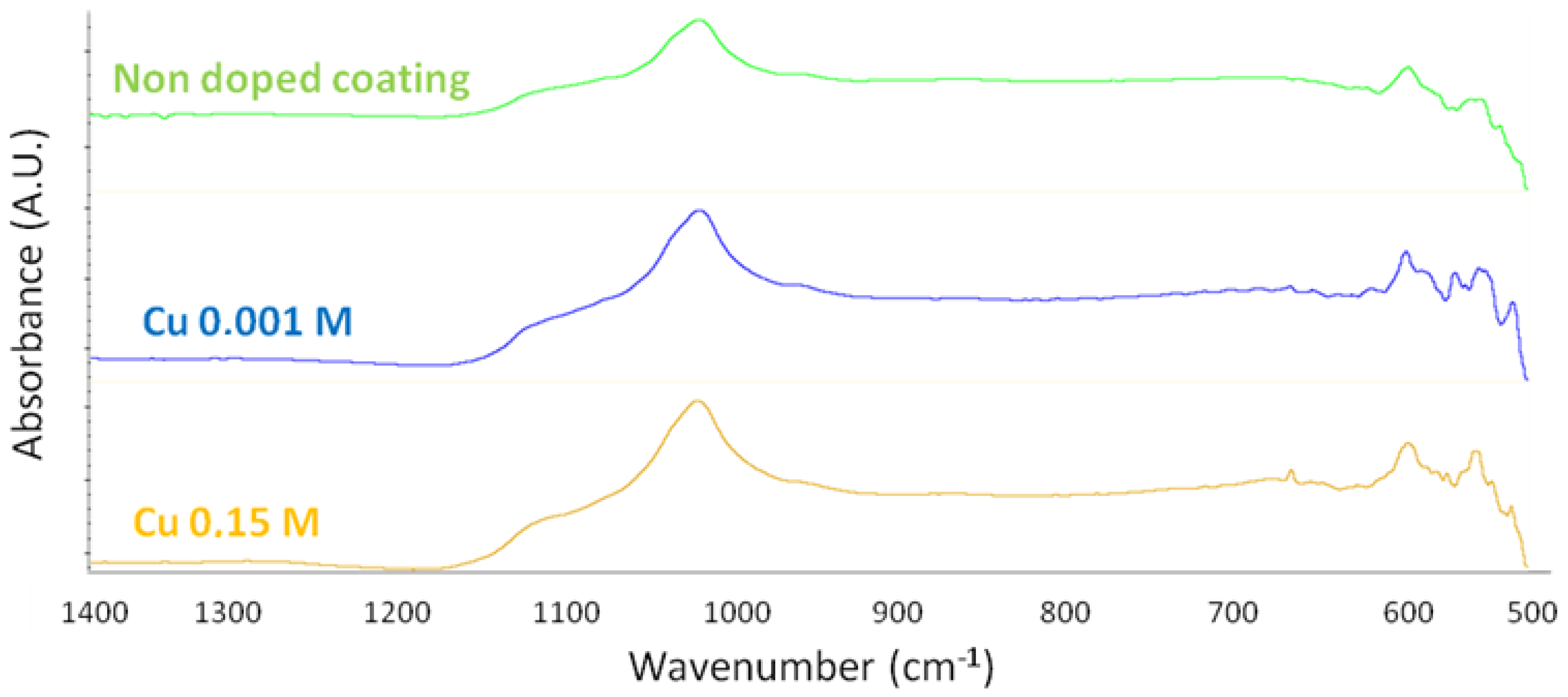
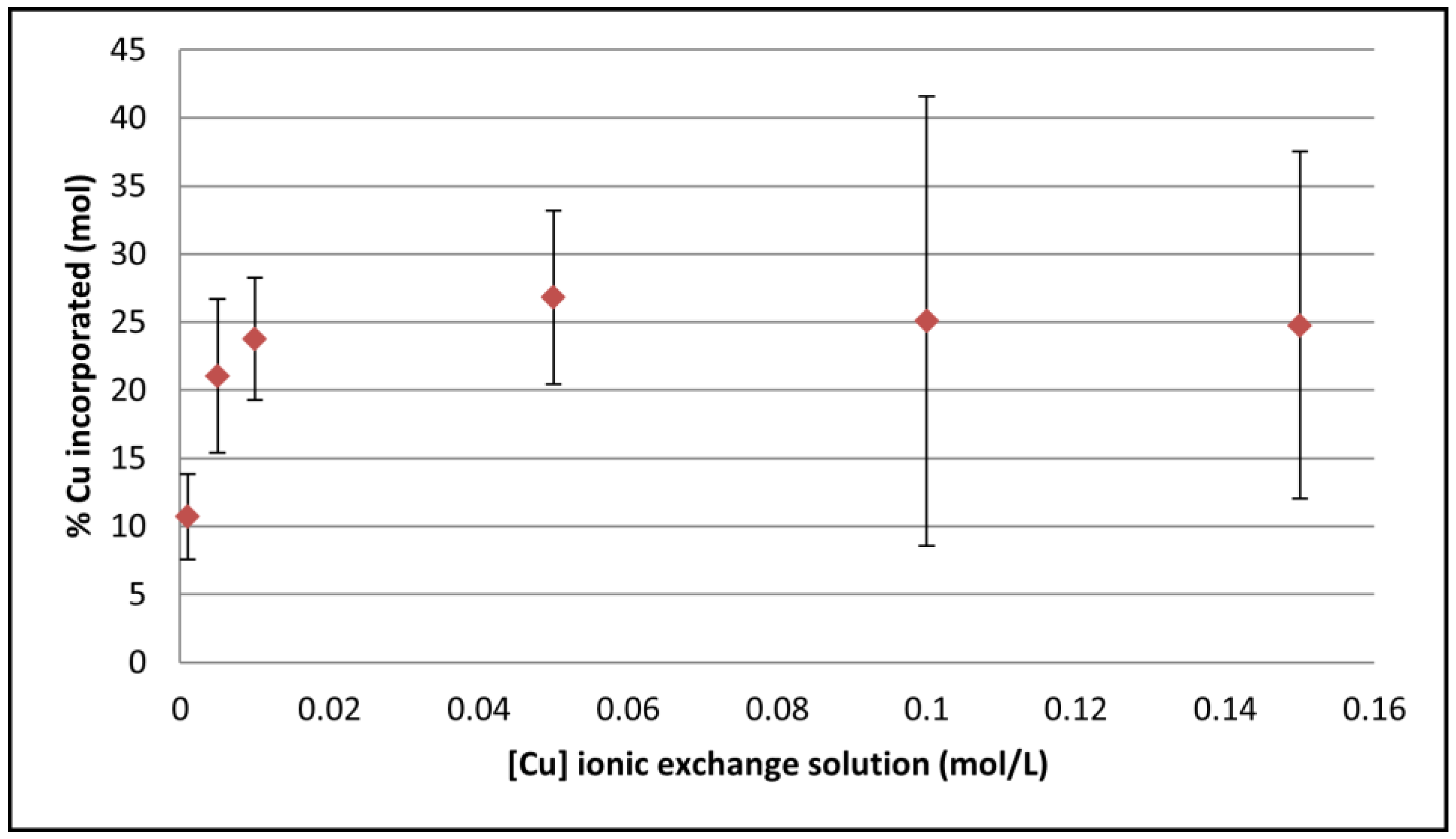
3.2. Cu-Doping of the CaP Coating
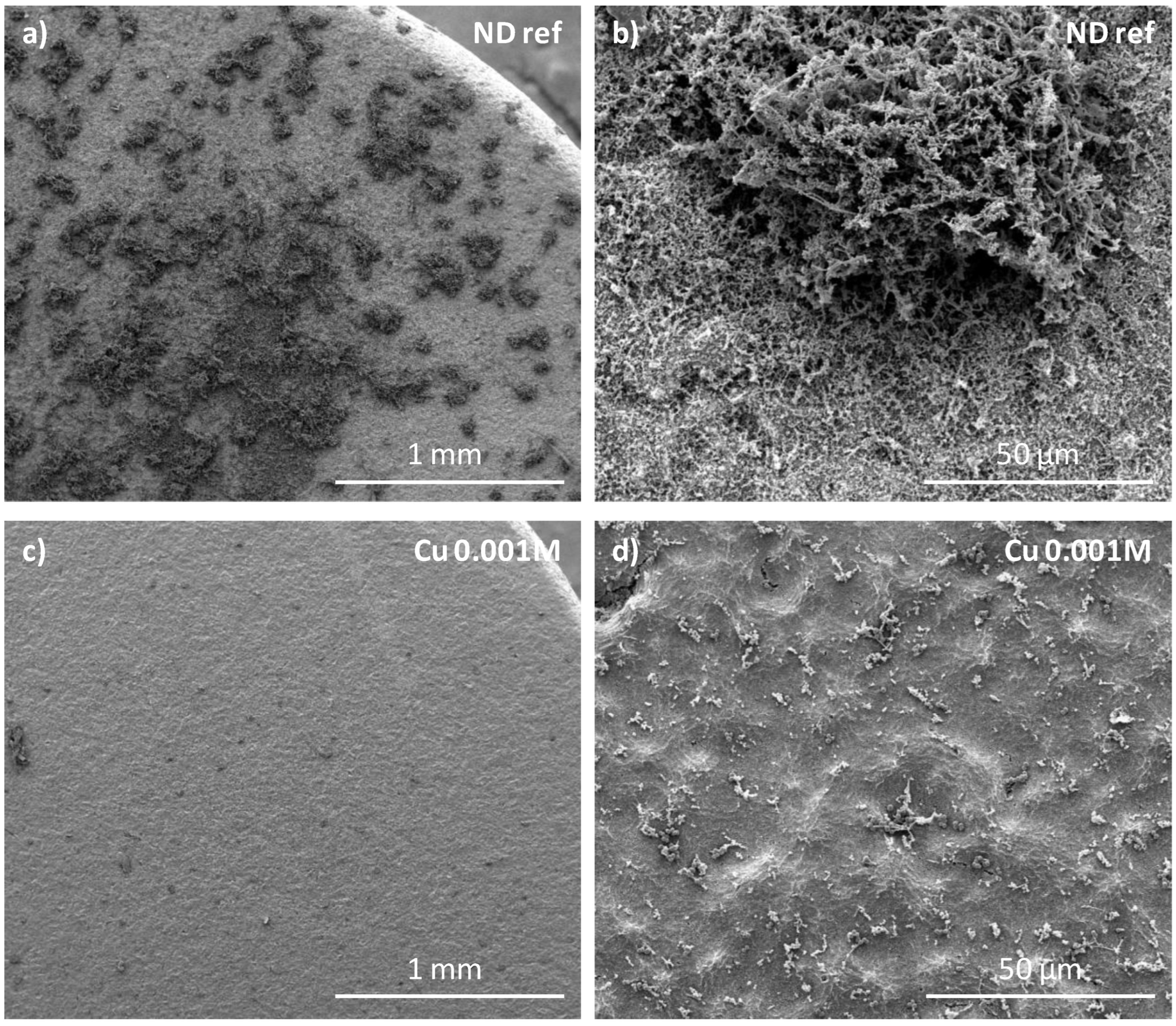
3.3. In Vitro Biological Properties
Antimicrobial Activity of Copper-Doped CaP Coating on Biofilm
4. Discussion
4.1. On the Formation of a Calcium-Phosphate-Electrodeposited Coating on Titanium Substrate
- Brushite (DCPD):
- 2.
- Octacalcium phosphate (OCP):
- 3.
- Non-stœchiometric apatite (ns-HAP):
- 4.
- Stoichiometric hydroxyapatite (HAP):
4.2. Cu-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coating and Their Related Microbiological Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pye, A.D.; Lockhart, D.E.A.; Dawson, M.P.; Murray, C.A.; Smith, A.J. A review of dental implants and infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 72, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathapachandran, J.; Suresh, N. Management of peri-implantitis. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzmann, N.U.; Berglundh, T. Definition and prevalence of peri-implant diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figurero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norowski, P.A.; Bumgardner, J.D. Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for peri-implantitis: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 88, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, S.; Spriano, S. Antibacterial titanium surfaces for medical implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waal, Y.C.; Raghoebar, G.M.; Meijer, H.J.; Winkel, E.G.; van Winkelhoff, A.J. Prognostic indicators for surgical periimplantitis treatment. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Quirynen, M. Risk indicators for peri-implantitis. A narrative review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 15–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, D.M.; Weinstein, B.F. Biofilm as a risk factor in implant treatment. Periodontology 2000 2019, 81, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, K.; Jung, R.E.; Molenberg, A.; Hammerle, C.H.F. Biofilm on Dental Implants: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 616–626. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt, A.; Renvert, S.; Dahlen, G. Microbial findings at failing implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1999, 10, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibli, J.A.; Melo, L.; Ferrari, D.S.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M.; Feres, M. Composition of supra- and subgingival biofilm of subjects with healthy and diseased implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meffert, R.M. Periodontitis vs. peri-implantitis: The same disease? The same treatment? Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1996, 7, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincón, M.V.; Gómez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Okada, S.; Yasuda, K.; Kawagoe, M.; Kajiya, M.; Tsuga, K. Microbial differences between active and remission peri-implantitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Varghese, S.S. Microbiological Profile in Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2022, 32, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitaille, N.; Reed, D.N.; Walters, J.D.; Kumar, P.S. Periodontal and peri-implant diseases: Identical or fraternal infections? Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2016, 31, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, A.; Maiden, M.F.J.; Lee, K.; Shulman, L.B.; Weber, H.P. Dental Implant Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, S213–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, G.E.; Aglietta, M.; Eick, S.; Sculean, A.; Lang, N.P.; Ramseier, C.A. Reversibility of experimental peri-implant mucositis compared with experimental gingivitis in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Daugela, P.; Faria de Almeida, R.; Saulacic, N. Surgical Non-Regenerative Treatments for Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Fretwurst, T.; Schwarz, F. Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional non-surgical and surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2021, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, F.; Keeve, P.L.; Ramanauskaite, A.; Schwarz, F.; Koo, K.T.; Sculean, A.; Romanos, G. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis—Consensus report of working group 4. Int. Dent. J. 2019, 69, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luengo, F.; Solonko, M.; Sanz-Esporrín, J.; Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Impact of the Surgical Treatment of Peri-Implantitis—A Prospective Case Series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, M. Base metal alloys used for dental restorations and implants. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 51, 603–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Antibacterial coatings on titanium implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 91, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigter, M.; Bezemer, J.; de Groot, K.; Layrolle, P. Incorporation of different antibiotics into carbonated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium implants, release and antibiotic efficacy. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsuwan, N.; Dwivedi, A.; Tancharoen, S.; Nasongkla, N. Development of dental implant coating with minocycline-loaded niosome for antibacterial application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanmard, F.; Croes, M.; Castilho, M.; Majed, A.; Steenbergen, M.J.; Lietaert, K.; Vogely, H.C.; van derWal, B.C.H.; Stapels, D.A.C.; Malda, J.; et al. Bactericidal coating to prevent early and delayed implant-related infections. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, E.J. Recent coating developments for combination devices in orthopedic and dental applications: A literature review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 112, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Weng, J.; Qu, S.; Feng, B.; Watari, F.; Ding, Y.; Leng, Y. Nano-Ag-loaded hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium surfaces by electrochemical deposition. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.C.; Lin, S.H.; Chien, C.S.; Kung, J.C.; Shih, C.J. In Vitro Bioactivity and Antibacterial Effects of a Silver-Containing Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Film on the Surface of Titanium Implants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, G.; Hardes, J.; Gosheger, G.; Stoeppeler, S.; Ahrens, H.; Blaske, F.; Wehe, C.; Karst, U.; Höll, S. Evaluation of osseous integration of PVD-silver-coated hip prostheses in a canine model. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 292406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.H.; Zhou, Z.B.; Yu, X.W. Coatings as the useful drug delivery system for the prevention of implant-related infections. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Nissan, B.; Choi, A.H.; Roest, R.; Latella, B.A.; Bendavid, A. Adhesion of hydroxyapatite on titanium medical implants. In Hydroxyapatite (Hap) for Biomedical Applications, 1st ed.; Mucalo, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, K.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A. Calcium phosphate coatings for medical implants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 1998, 212, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, C.; Bertrand, G.; Rey, C.; Benhamou, O.; Combes, C. Calcium phosphate coatings elaborated by the soaking process on titanium dental implants: Surface preparation, processing and physical-chemical characterization. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, e25–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drevet, R.; Benhayoune, H. Electrodeposition of Calcium Phosphate Coatings on Metallic Substrates for Bone Implant Applications: A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N. Electrocrystallization of Calcium Phosphates. Isr. J. Chem. 2008, 48, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drouet, C.; Gomez-Morales, J.; Iafisco, M.; Sarda, S. Calcium Phosphate Surface Tailoring Technologies for Drug Delivering and Tissue Engineering. In Surface Tailoring of Inorganic Materials for Biomedical Applications; Rimondini, L., Bianchi, C.L., Vernè, E., Eds.; Bentham eBooks: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2012; pp. 43–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf-Brandstetter, C.; Oswald, S.; Bierbaum, S.; Wiesmann, H.P.; Scharnweber, D. Influence of pulse ratio on codeposition of copper species with calcium phosphate coatings on titanium by means of electrochemically assisted deposition: Influence of Pulse Ratio on Codeposition of Cu(I) Species with CPP. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, F.; Khireddine, H.; Touati, A.; Sidane, D.; Yala, S.; Oudadesse, H. Electrochemical depositions of fluorohydroxyapatite doped by Cu2+, Zn2+, Ag+ on stainless steel substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7021–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Nakai, M.; Niinomi, M.; Nakano, T. Antibacterial Cu-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coating on Pure Titanium. Mater. Trans. 2021, 62, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Mao, H.; Li, T.; Zhao, R.; Yan, Y.; Pang, X. Osteoblastic cell responses and antibacterial efficacy of Cu/Zn co-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings on pure titanium using electrodeposition method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17076–17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Mamat, B.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, N.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Ma, C.; Zang, F.; Wang, Y. Multi-metal ions doped hydroxyapatite coatings via electrochemical methods for antibacterial and osteogenesis. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 43, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, B.; Giertsen, E.; Schüpbach, P.; Shapiro, S. Validation of an in vitro Biofilm Model of Supragingival Plaque. J. Dent. Res. 2001, 80, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aal, E.A.; Dietrich, D.; Steinhaeuser, S.; Wielage, B. Electrocrystallization of nanocrystallite calcium phosphate coatings on titanium substrate at different current densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 5895–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumelié, N.; Benhayoune, H.; Rousse-Bertrand, C.; Bouthors, S.; Perchet, A.; Wortham, L.; Douglade, J.; Laurent-Maquin, D.; Balossier, G. Characterization of electrodeposited calcium phosphate coatings by complementary scanning electron microscopy and scanning-transmission electron microscopy associated to X-ray microanalysis. Thin Solid Film. 2005, 492, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.; Giertsen, E.; Guggenheim, B. An in vitro Oral Biofilm Model for Comparing the Efficacy of Antimicrobial Mouthrinses. Caries Res. 2002, 36, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnheer, T.; Gmur, R.; Shapiro, S.; Guggenheim, B. Mass Transport of Macromolecules within an In Vitro Model of Supragingival Plaque. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gmur, R.; Guggenheim, B. Antigenic Heterogeneity of Bacteroides intermedius as Recognized by Monoclonal Antibodies. Infect. Immun. 1983, 42, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Souda, S.S.M.; Ibrahim, N.; Perio, P.; Ibrahim, H.; Pigasse-Hénocq, C.; Roques, C.; Nepveu, F. Powerful Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Properties of Cassia roxburghii DC. Leaves Cultivated in Egypt in Relation to Their Anti-Infectious Activities. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2015, 21, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rey, C.; Marsan, O.; Combes, C.; Drouet, C.; Grossin, D.; Sarda, S. Characterization of calcium phosphates using vibrational spectroscopies, Chapter 8. In Advances in Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials; Ben-Nissan, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 229–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Eliyahu, M. Electrochemical processes of nucleation and growth of hydroxyapatite on titanium supported by real-time electrochemical atomic force microscopy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 80, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevet, R.; Velard, F.; Potiron, S.; Laurent-Maquin, D.; Benhayoune, H. In vitro dissolution and corrosion study of calcium phosphate coatings elaborated by pulsed electrodeposition current on Ti6Al4V substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokabber, T.; Lu, L.Q.; van Rijn, P.; Vakis, A.I.; Pei, Y.T. Crystal growth mechanism of calcium phosphate coatings on titanium by electrochemical deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, X.Y. Principles of Mimicking and Engineering the Self-organized Structure of Hard Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41286–41293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eliaz, N.; Sridhar, T.M. Electrocrystallization of Hydroxyapatite and Its Dependence on Solution Conditions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, M.; Tadier, S.; Meille, S.; Chevalier, J. Resorption of calcium phosphate materials: Considerations on the in vitro evaluation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 38, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Ma, X.; Guan, S. Formation mechanism of Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite coating on Mg–Zn–Ca alloy for orthopaedic implant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Leng, Y. Theoretical analysis of calcium phosphate precipitation in simulated body fluid. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Kopelovitch, W.; Burstein, L.; Kobayashi, E.; Hanawa, T. Electrochemical processes of nucleation and growth of calcium phosphate on titanium supported by real-time quartz crystal microbalance measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 89, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Mao, H.; Yan, Y.; Pang, X. Antibacterial efficacy, corrosion resistance, and cytotoxicity studies of copper-substituted carbonated hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boanini, E.; Gazzano, M.; Bigi, A. Ionic substitutions in calcium phosphates synthesized at low temperature. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazalbou, S.; Eichert, D.; Ranz, X.; Drouet, C.; Combes, C.; Harmand, M.F.; Rey, C. Ion exchanges in apatites for biomedical application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drouet, C.; Carayon, M.T.; Combes, C.; Rey, C. Surface enrichment of biomimetic apatites with biologically-active ions Mg2+ and Sr2+: A preamble to the activation of bone repair materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wired Chemist. Metallic, Covalent and Ionic Radii. Available online: http://www.wiredchemist.com/chemistry/data/metallic-radii (accessed on 15 June 2018).





| Tested Strains | Reference | Subculturing Media | Incubation Conditions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | Streptococcus gordonii | CIP 105258T | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis |
| Actinomyces naeslundii | CIP 103128T | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis | |
| Parvimonas micra | CIP 105294T | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | Fusobacterium nucleatum | CIP 101130T | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis |
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans | CIP 52106T | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, 5% CO2 | |
| Prevotella intermedia | CIP 103607 | Columbia agar + 5% sheep blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis | |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | CIP 103683 | Wilkins Chalgren + 5% horse blood | 36 °C, anaerobiosis |
| Technique | SEM | Calotest | AFM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | ||||
| 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | - | 0.97 ± 0.04 | |
| 1 | 2 ± 1 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.07 ± 0.04 | |
| 2 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | - | 2.15 ± 0.06 | |
| 5 | 9 ± 2 | 6.0 ± 0.5 | >3.6 | |
| 10 | 13 ± 3 | 7.4 ± 0.7 | >3.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pierre, C.; Bertrand, G.; Pavy, I.; Benhamou, O.; Rey, C.; Roques, C.; Combes, C. Antibacterial Electrodeposited Copper-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Dental Implants. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010020
Pierre C, Bertrand G, Pavy I, Benhamou O, Rey C, Roques C, Combes C. Antibacterial Electrodeposited Copper-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Dental Implants. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010020
Chicago/Turabian StylePierre, Camille, Ghislaine Bertrand, Iltaf Pavy, Olivier Benhamou, Christian Rey, Christine Roques, and Christèle Combes. 2023. "Antibacterial Electrodeposited Copper-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Dental Implants" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010020
APA StylePierre, C., Bertrand, G., Pavy, I., Benhamou, O., Rey, C., Roques, C., & Combes, C. (2023). Antibacterial Electrodeposited Copper-Doped Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Dental Implants. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010020