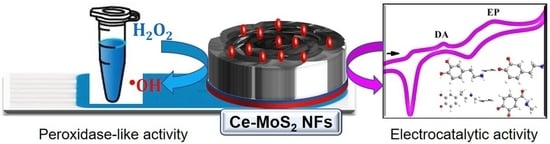
Highly Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Epinephrine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of MoS2 NFs and Ce-MoS2 NFs
2.3. Evaluation of the Peroxidase-like Activity of Ce-MoS2 NFs
2.4. Fabrication of Ce-MoS2 NFs/SPE Biosensors and Electrochemical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Highly-Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 NFs
3.2. Enhanced Peroxidase-like Activity of Ce-MoS2 NFs
3.3. Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance of Ce-MoS2 NFs
3.4. Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of DA and EP Using the Ce-MoS2 NFs/SPE Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatma, S.; Prasad, B.B.; Jaiswal, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, K. Electrochemical simultaneous analysis of dopamine and epinephrine using double imprinted one monomer acryloylated graphene oxide-carbon black composite polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S. N-doped MoS2-nanoflowers as peroxidase-like nanozymes for total antioxidant capacity assay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1180, 338740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fatima Ulbrich, K.; Winiarski, J.P.; Jost, C.L.; Maduro de Campos, C.E. Mechanochemical synthesis of a Ni3−XTe2 nanocrystalline composite and its application for simultaneous electrochemical detection of dopamine and adrenaline. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 183, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; McCracken, S.; Faruk Hossain, M.; Slaughter, G. Electrochemical detection of neurotransmitters. Biosensors 2020, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Mansha, M.; Alsharaa, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Basheer, C. Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of uric acid and ascorbic acid: A review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhurantakam, S.; Karnam, J.B.; Brabazon, D.; Takai, M.; Ahad, I.U.; Balaguru Rayappan, J.B.; Krishnan, U.M. “nano”: An emerging avenue in electrochemical detection of neurotransmitters. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4024–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.M.; Thapliyal, N.; Hussain, K.K.; Goyal, R.N.; Shim, Y.B. Conducting polymer-based electrochemical biosensors for neurotransmitters: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Durairaj, S.; Prins, S.; Chen, A. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of pharmaceutical compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Warner, J.H.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; et al. Photoresponse-bias modulation of a high-performance MoS2 photodetector with a unique vertically stacked 2H-MoS2/1T@2H-MoS2 structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33325–33335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Loh, L.; Nandakumar, D.K.; Lu, W.; Gao, M.; Wee, X.L.C.; Zeng, K.; Bosman, M.; Tan, S.C. Sustainable fuel production from ambient moisture via ferroelectrically driven MoS2 nanosheets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Construction of nanozyme-hydrogel for enhanced capture and elimination of bacteria. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tao, M.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W. Microelectrode-based electrochemical sensing technology for in vivo detection of dopamine: Recent developments and future prospects. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.V.; dos Santos, N.D.; de Almeida, A.K.A.; dos Santos, D.D.E.R.; Santos, A.C.F.; França, M.C.; Lima, D.J.P.; Lima, P.R.; Goulart, M.O.F. A new electrochemical sensor based on oxidized capsaicin/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/glassy carbon electrode for the quantification of dopamine, epinephrine, and xanthurenic, ascorbic and uric acids. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 881, 114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranmai, S.; Kuchi, C.; Sravani, B.; Ƚuczak, T.; Kim, M.J.; Madhavi, G.; Veera Manohara Reddy, Y. Construction of ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor using TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanofibers nanocomposite for epinephrine detection. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 35, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, W.; Fan, Y.Z.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Chemically-modulated turn-on fluorescence for rapid and visual discrimination of norepinephrine and epinephrine and its application for dopamine-β-hydroxylase detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubells, J.F.; Sun, X.; Li, W.; Bonsall, R.W.; McGrath, J.A.; Avramopoulos, D.; Lasseter, V.K.; Wolyniec, P.S.; Tang, Y.L.; Mercer, K.; et al. Linkage analysis of plasma dopamine β-hydroxylase activity in families of patients with schizophrenia. Hum. Genet. 2011, 130, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Dutta, R.K. Ethylene glycol and alanine anhydride based nitrogen doped fluorescent carbon nanoparticles as probe for detection of epinephrine, nor-epinephrine and dopamine. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 203, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.L.; Sadjadi, S.; Schmedes, A. Analysis of catecholamines in urine by unique LC/MS suitable ion-pairing chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1057, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishii, K.; Sousa, K.; Marumoto, K.; Kashibayashi, T.; Fujita, J.; Yokoyama, K. Distinctive regional asymmetry in dopaminergic and serotoninergic dysfunction in degenerative Parkinsonisms. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 423, 117363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas-Ferreira, C.; Silva, A.C.d.J.; Hage-Melim, L.I.d.S.; Faro, L.R.F. Role of voltage-dependent calcium channels on the striatal in vivo dopamine release induced by the organophosphorus pesticide glyphosate. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 104, 104285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, A.; Francis, K.A.; Patel, J.; Jha, S.K.; Basu, S. A decoupler-free simple paper microchip capillary electrophoresis device for simultaneous detection of dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25487–25495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; van Beek, T.A.; Chen, B.; Zuilhof, H.; Salentijn, G.I. Boronate affinity paper spray mass spectrometry for determination of elevated levels of catecholamines in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1235, 340508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, P.B.K.; Dang, T.V.; Kim, M.I. Highly crystalline oxidase-like MnOOH nanowire-incorporated paper dipstick for one-step colorimetric detection of dopamine. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 11070382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, L.; Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Sun, L.P.; Guan, B.O. Optofluidic laser sensor for the detection of dopamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 133941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desagani, D.; Ben-Yoav, H. Chemometrics meets electrochemical sensors for intelligent in vivo bioanalysis. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanakumar, M.; Nesakumar, N.; Kulandaisamy, A.J.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Principles and recent developments in optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine: A comprehensive review. Measurement 2021, 183, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bortoli, L.S.; Vanoni, C.R.; Jost, C.L.; Mezalira, D.Z.; Fredel, M.C. Stable and ligand-free gold nanoparticles produced by laser ablation as efficient electrocatalysts for electrochemical sensing of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 947, 117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamilselvan, A.; Rajagopal, V.; Suryanarayanan, V. Highly sensitive and selective amperometric determination of BPA on carbon black/f-MWCNT composite modified GCE. J Alloys. Compd. 2019, 786, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamilselvan, A.; Manivel, P.; Rajagopal, V.; Nesakumar, N.; Suryanarayanan, V. Improved electrocatalytic activity of Au@Fe3 O4 magnetic nanoparticles for sensitive dopamine detection. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Yu, J.; Lv, F.; Yan, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Functionalized nano-MoS2 with peroxidase catalytic and near-infrared photothermal activities for safe and synergetic wound antibacterial applications. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11000–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarinathan, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Harish, S. Cerium-doped MoS2 layered nanostructures for enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 33, 13988–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malleshappa, J.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C.; Vidya, Y.S.; Anantharaju, K.S.; Prashantha, S.C.; Daruka Prasad, B.; Raja Naika, H.; Lingaraju, K.; Surendra, B.S. Leucas aspera mediated multifunctional CeO2 nanoparticles: Structural, photoluminescent, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 149, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Miao, F.; Wang, K.; Lu, N.; Liu, Y. 3D MoS2 nanosheet/TiO2 nanofiber heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity under UV irradiation. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 686, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincotto, F.H.; Canevari, T.C.; Campos, A.M.; Landers, R.; Machado, S.A.S. Simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine by electrochemical reduction on the hybrid material SiO2/graphene oxide decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 2014, 139, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinoth, V.; Natarajan, L.N.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Valdés, H.; Anandan, S. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and epinephrine using gold nanocrystals capped with graphene quantum dots in a silica network. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Sun, D.M. Simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine with poly(l-arginine) modified electrode. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 35, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivel, P.; Thamilselvan, A.; Rajagopal, V.; Nesakumar, N.; Suryanarayanan, V. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of Ni-CNT nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of epinephrine and dopamine. Electroanal 2019, 31, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Palleschi, G.; Morales, E.L.; Orlanducci, S.; Tamburri, E.; Terranova, M.L. Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes modified microsensors for the selective response of epinephrine in presence of ascorbic acid. Electroanal 2007, 19, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, B.O.; Vilakazi, S.L.; Ozoemena, K.I. Electrochemistry at cobalt(II)tetrasulfophthalocyanine-multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode: A sensing platform for efficient suppression of ascorbic acid in the presence of epinephrine. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.M.; Costa, M.; Pereira, C.; Bachiller-Baeza, B.; Rodríguez-Ramos, I.; Guerrero-Ruiz, A.; Freire, C. Novel electrochemical sensor based on N-doped carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 432, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Catalyst | Km (mM) | Vm (10−8 M s−1) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMB | H2O2 | TMB | H2O2 | ||
| HRP | 0.434 | 3.7 | 10 | 8.71 | [34] |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles | 0.098 | 154 | 3.44 | 9.78 | [34] |
| N-MoS2 NFs | 0.065 | 3.13 | 10.76 | 16.06 | [2] |
| Ce-MoS2 NFs | 0.25 | 0.52 | 10.5 | 17.81 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thamilselvan, A.; Dang, T.V.; Kim, M.I. Highly Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Epinephrine. Biosensors 2023, 13, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121015
Thamilselvan A, Dang TV, Kim MI. Highly Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Epinephrine. Biosensors. 2023; 13(12):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121015
Chicago/Turabian StyleThamilselvan, Annadurai, Thinh Viet Dang, and Moon Il Kim. 2023. "Highly Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Epinephrine" Biosensors 13, no. 12: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121015
APA StyleThamilselvan, A., Dang, T. V., & Kim, M. I. (2023). Highly Conductive Peroxidase-like Ce-MoS2 Nanoflowers for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Dopamine and Epinephrine. Biosensors, 13(12), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121015