Optimized Copper-Based Microfeathers for Glucose Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and Chemicals
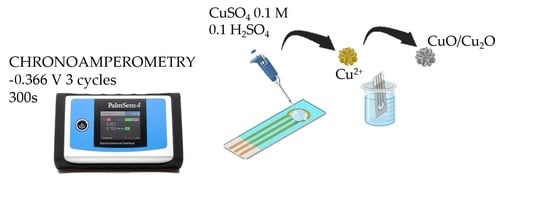
2.2. Electrode Synthesis and Preparation
2.3. Taguchi Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
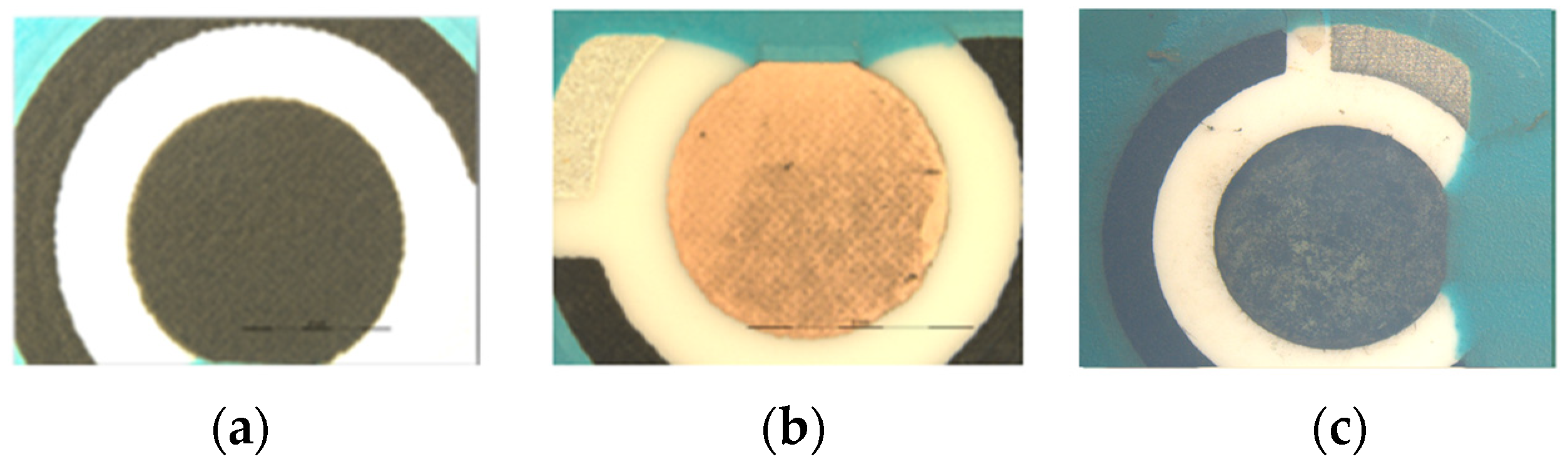
3.1. Optimization of the Synthesis Method
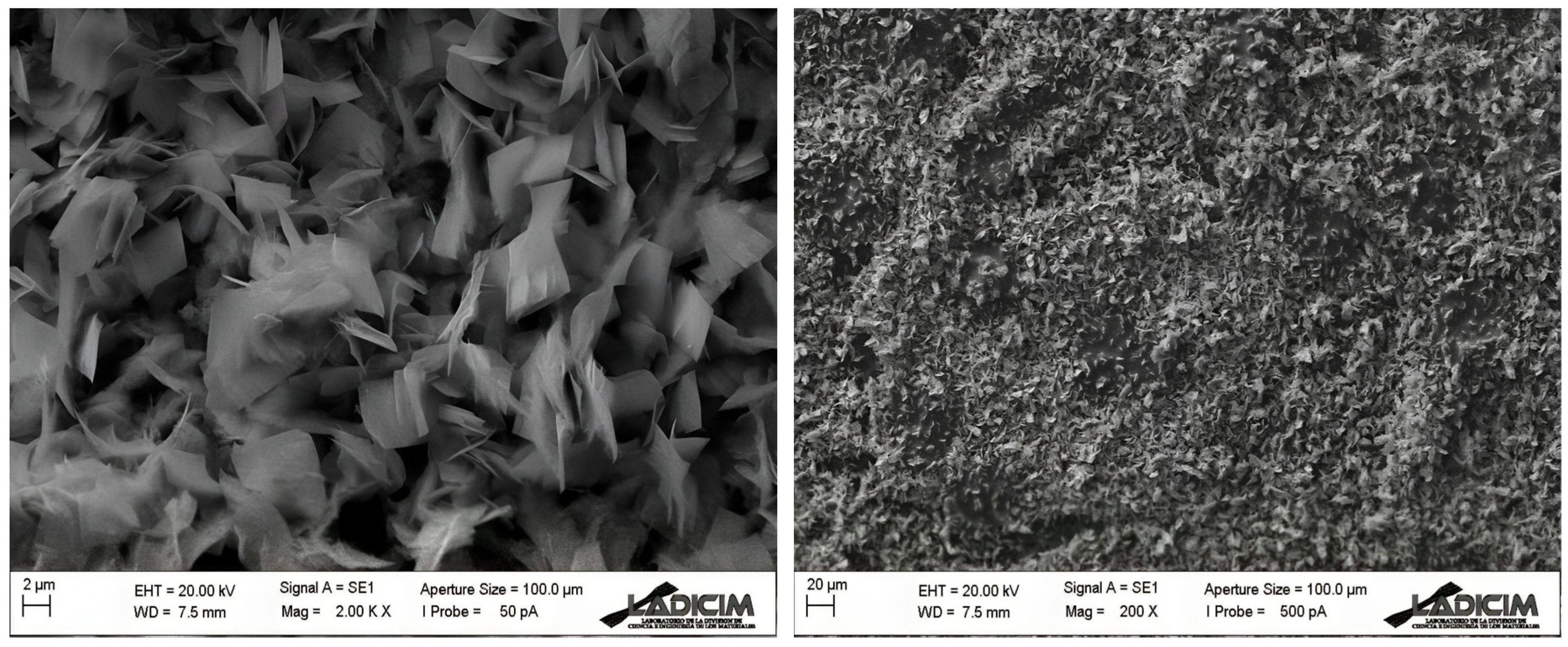
3.2. Electrode Characterization and Active Area
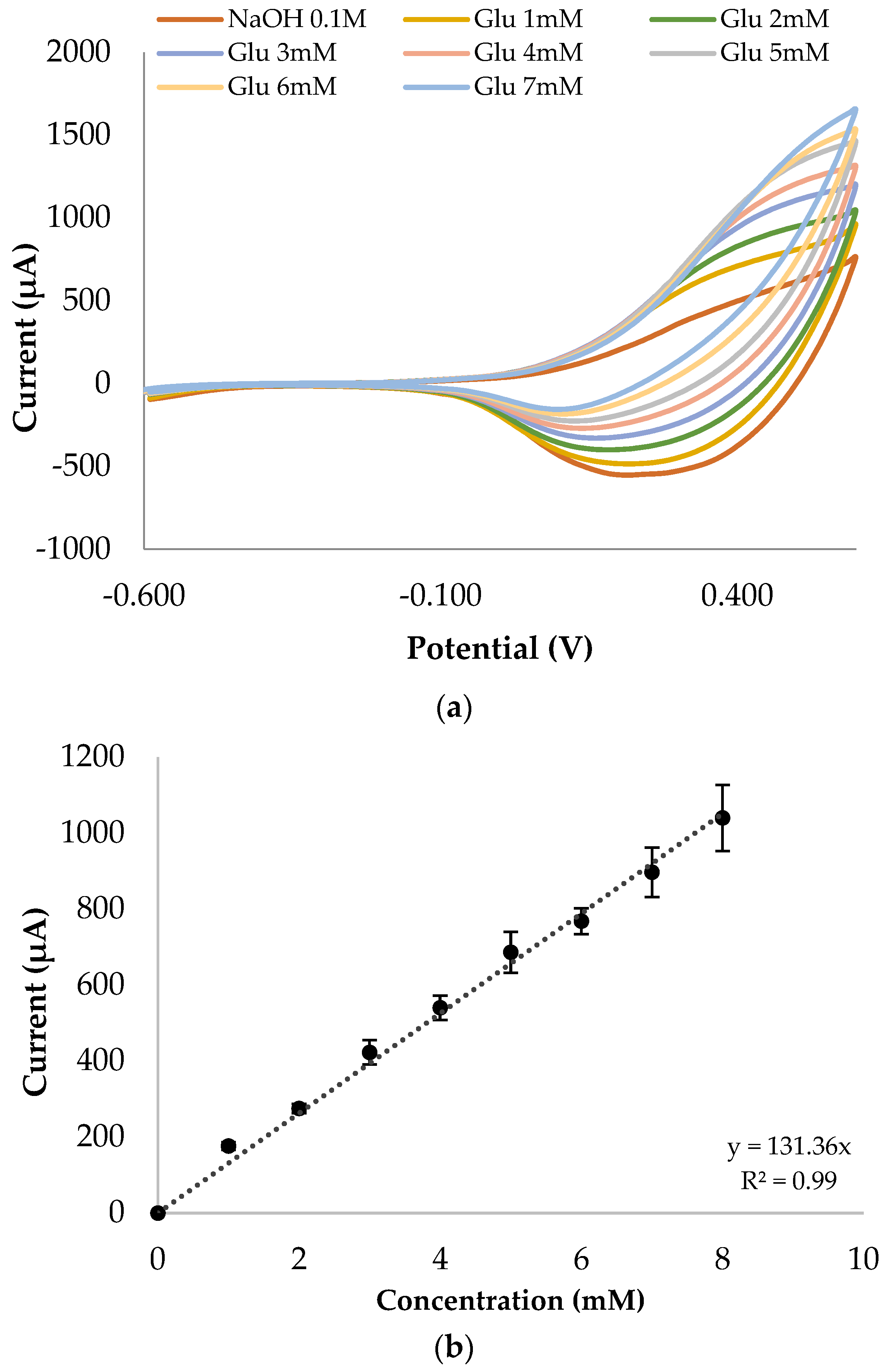
3.3. Linear Range
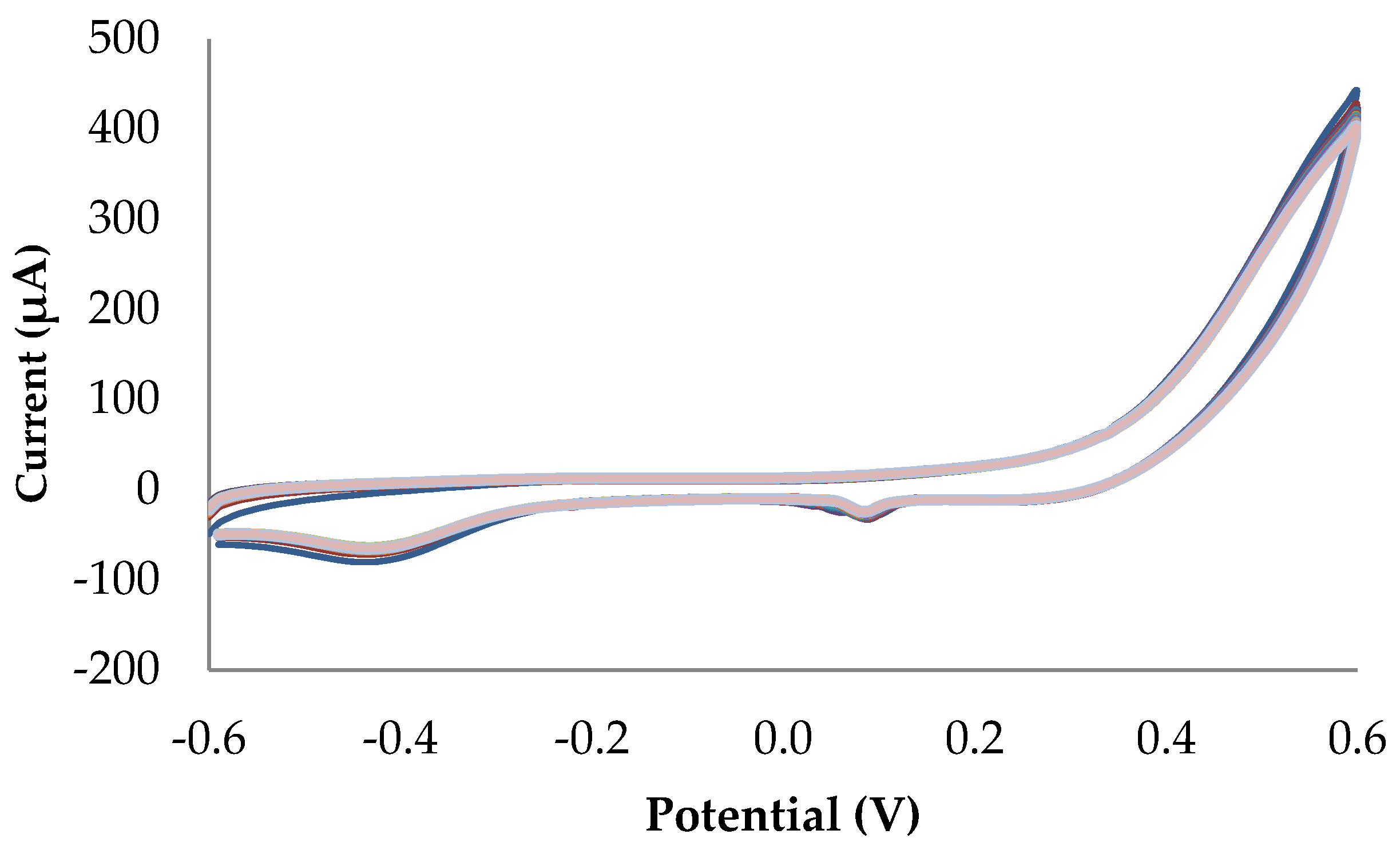
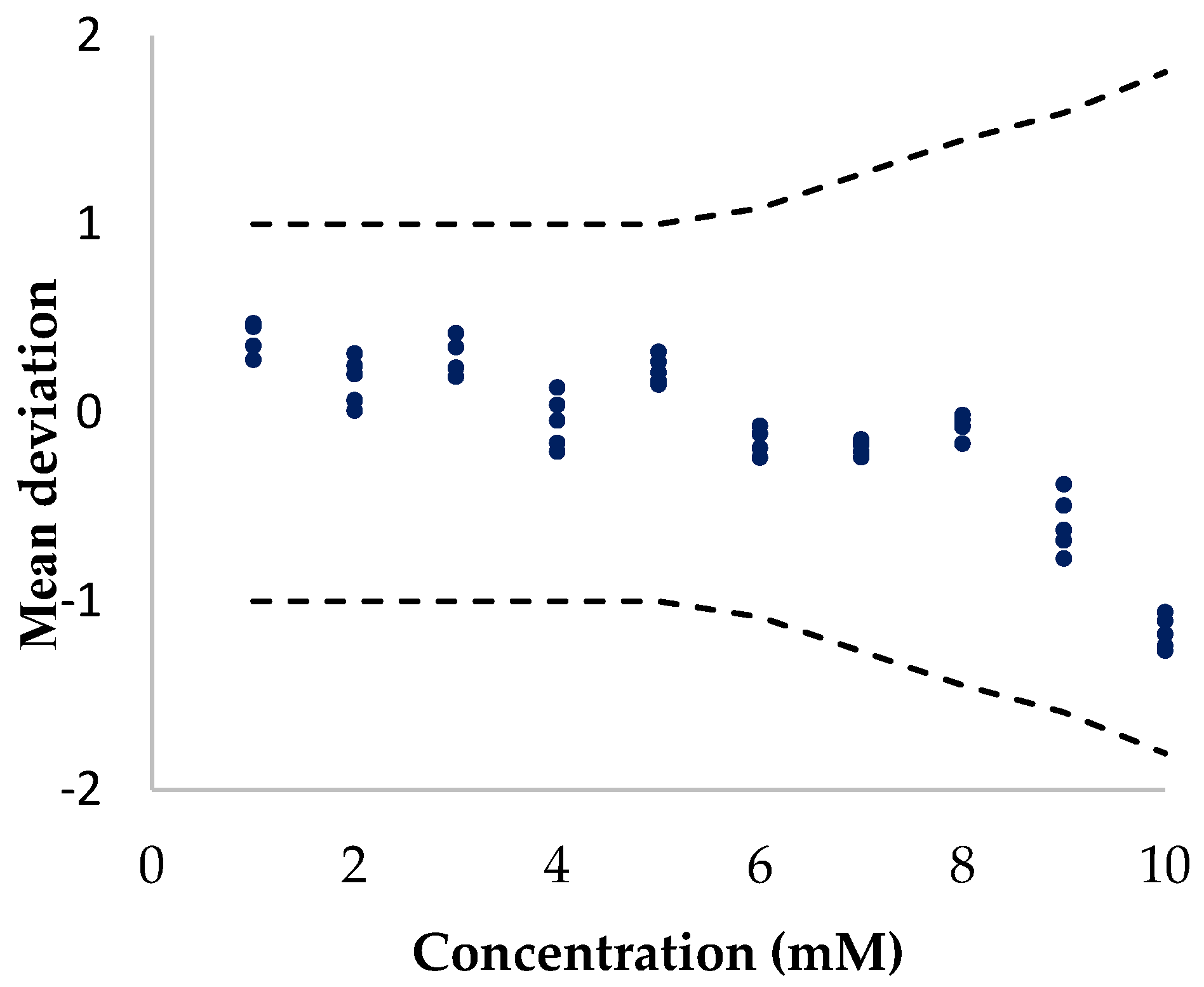
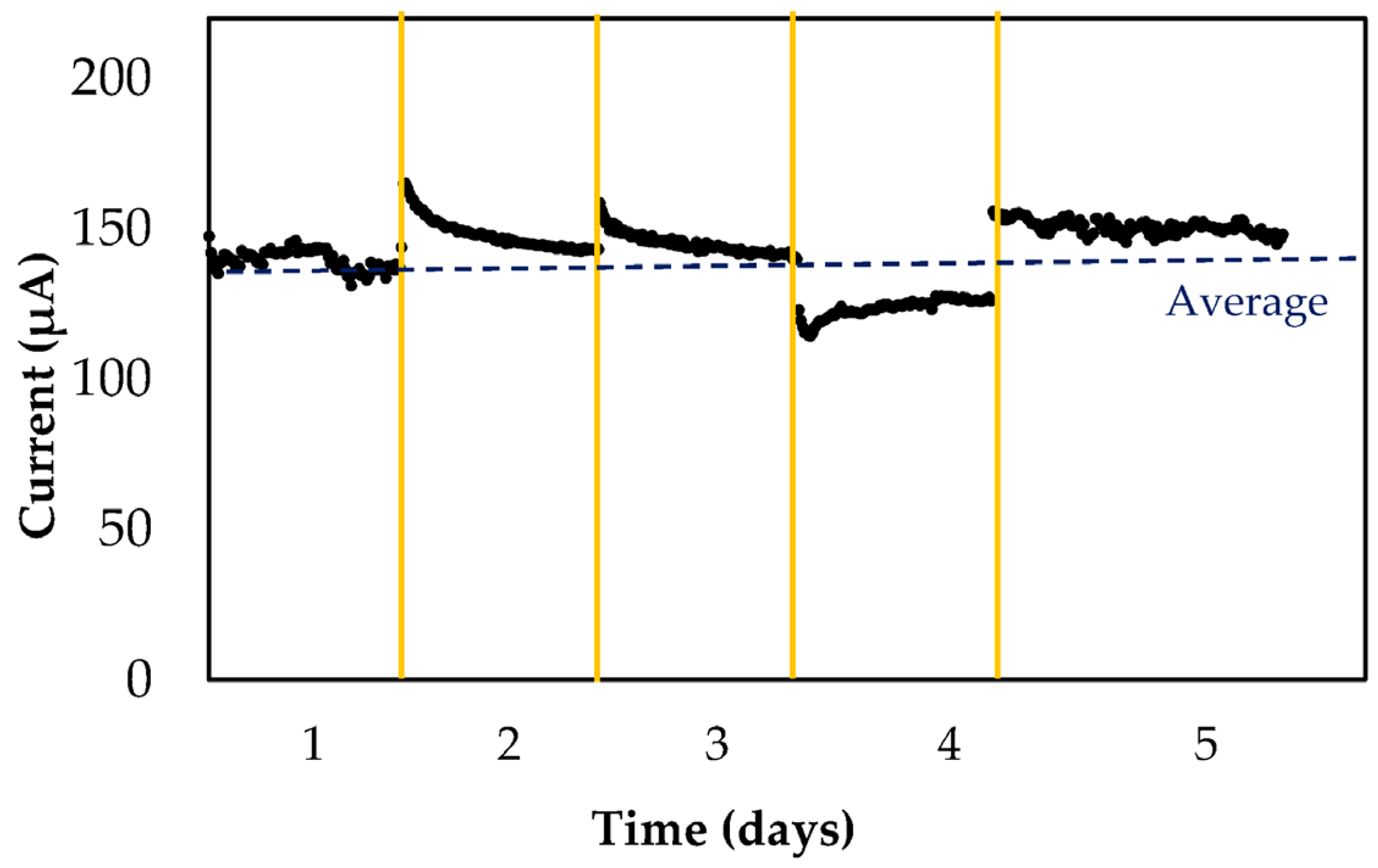
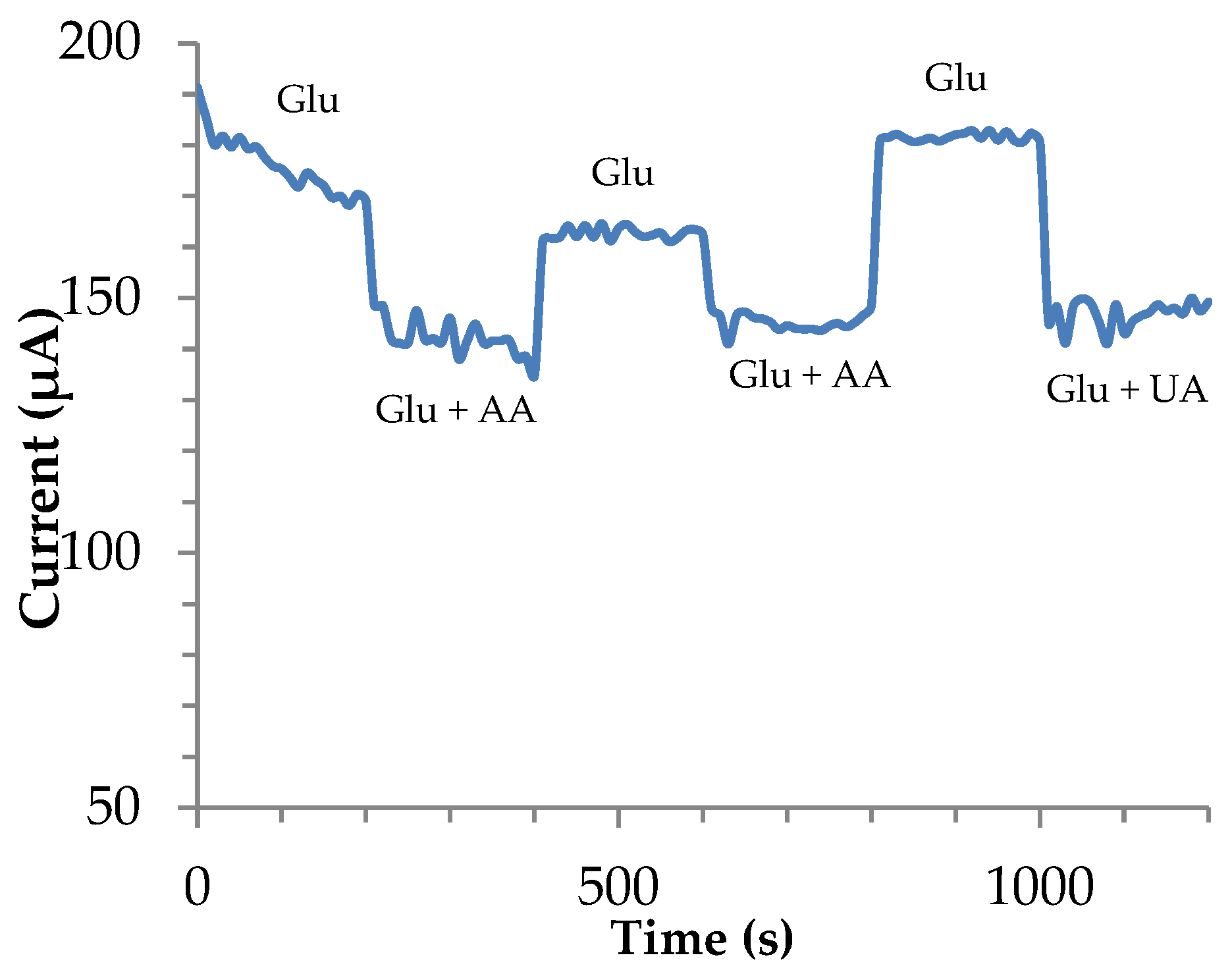
3.4. Reproducibility, Repeatability, and Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Good Health and Well-Being. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals/good-health (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- World Health Organization, Sustainable Development Goal 3. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/about-us/our-work/sustainable-development-goals/targets-of-sustainable-development-goal-3 (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Yang, W.; Dall, T.M.; Halder, P.; Gallo, P.; Kowal, S.L.; Hogan, P.F.; Petersen, M. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, D.; Meng, Q.B.; Wu, S.; Song, X.M. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Supported Methylene Blue Nanocomposite as a Glucose Oxidase-Mimetic for Electrochemical Glucose Sensing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32565–32573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.H.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Compatibility of Nitric Oxide Release with Implantable Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Osmium (III/II) Mediated Electrochemistry. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, N.; Gopal, T.M.; Muthuraamamoorthy, M.; Alobaidi, A.; Alsaigh, R.A.; Aldosary, M.; Pandiaraj, S.; Almutairi, M.; Nirmala Grace, A.; Alodhayb, A. Cu2O/MXene/Rgo Ternary Nanocomposites as Sensing Electrodes for Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensors. Appl. Nanomater. 2023, 6, 12271–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical Glucose Sensors and Their Applications in Diabetes Management. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanovic, G.M. Comprehensive Review on Wearable Sweat-Glucose Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guati, C.; Gomez-Coma, L.; Fallanza, M.; Oritz, I. Progress on the influence of non-enzymatic electrodes characteristics on the response to glucose detection: A review (2016–2022). Rev. Chem. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, C.; Roy, K.; Chinnappan, A.; Narayan, R.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ghosh, R. Recent Advancement in Biofluid-Based Glucose Sensors Using Invasive, Minimally Invasive, and Non-Invasive Technologies: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkogianni, K.; Nikita, K.S. Special Issue on Emerging Technologies for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollmar, S.; Fernandez Schrunder, A.; Birgersson, U.; Kristoffersson, T.; Rusu, A.; Thorsson, E.; Hedenqvist, P.; Manell, E.; Rydén, A.; Jensen-Waern, M.; et al. A battery-less implantable glucose sensor based on electrical impedance spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.; Kim, S.-H. Toward Long-Term Implantable Glucose Biosensors for Clinical Use. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitare, Y.M.; Jadhav, S.B.; Pawaskar, P.N.; Magdum, V.V.; Gunjakar, J.L.; Lokhande, C.D. Metal Oxide-Based Composites in Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 18195–18217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.J. Can Nanozymes Have an Impact on Sensing? ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2213–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalil Oglou, R.; Ulusoy Ghobadi, T.G.; Ozbay, E.; Karadas, F. Electrodeposited Cobalt Hexacyanoferrate Electrode as a Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor under Neutral Conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1188, 339188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cao, X.; Chang, K.; Xiang, H.; Wang, R. A Novel Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Au Nanoparticle-Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode and Boronate Affinity. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 368, 137603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.Y.; Lee, P.Y.; Chu, T.F.; Peng, C.I.; Wang, G.J. Neutral Nonenzymatic Glucose Biosensors Based on Electrochemically Deposited Pt/Au Nanoalloy Electrodes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5551–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuchamy, N.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.P. Highly Selective Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Titanium Dioxide Nanowire-Poly(3-Aminophenyl Boronic Acid)-Gold Nanoparticle Ternary Nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Salim, H.; Hassan, I.U.; Awan, T.; Arshad, F.; Pedram, M.Z.; Ahmed, W.; Qurashi, A. Recent Advances in Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Metal and Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Diabetes Management—A Review. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Lakshmy, S.; Santhosh, S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Chakraborty, B.; Rout, C.S. Recent Developments and Future Perspective on Electrochemical Glucose Sensors Based on 2D Materials. Biosensors 2022, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, X. Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14553–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xiong, D.; Gu, M.; Lu, C.; Yi, F.Y.; Ma, X. MOF-Derived Bimetallic CoFe-PBA Composites as Highly Selective and Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Hydrogen Peroxide and Nonenzymatic Glucose in Human Serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35365–35374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ju, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, H. Nonenzymatic Wearable Sensor for Electrochemical Analysis of Perspiration Glucose. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayranci, R.; Demirkan, B.; Sen, B.; Şavk, A.; Ak, M.; Şen, F. Use of the Monodisperse Pt/Ni@rGO Nanocomposite Synthesized by Ultrasonic Hydroxide Assisted Reduction Method in Electrochemical Nonenzymatic Glucose Detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Ambedkar, A.K.; Sharma, K.; Gautam, Y.K.; Singh, B.P. Metal oxide nanomaterial-based sensors for monitoring envioronmental NO2 and its impact on the planet ecosystem: A review. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakosas, X.; Selberg, J.; Pansodtee, P.; Yonas, N.; Manapongpun, P.; Teodorescu, M.; Rolandi, M. A non-enzymatic glucose sensor enabled by bioelectronic pH control. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Saucedo, G.; Cuevas-Muñiz, F.M.; Sanchez-Fraga, R.; Mejia, I.; Alcantar-Peña, J.J.; Urbiola-Chavez, I.R. Cellulose microfluidic pH boosting on copper oxide non-enzymatic glucose sensor strip for neutral pH samples. Talanta 2023, 253, 123926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupin, D.D.; Abelit, A.A.; Mereshchenko, A.S.; Panov, M.S.; Ryazantsev, M.N. Copper–Ruthenium Composite as Perspective Material for Bioelectrodes: Laser-Assisted Synthesis, Biocompatibility Study, and an Impedance-Based Cellular Biosensor as Proof of Concept. Biosensors 2022, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, S.G.; Han, L.; Ling, Y.; Liao, L.L.; Mo, S.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Copper Nanoclusters with Strong Fluorescence Emission as a Sensing Platform for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Picric Acid. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4251–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Lv, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, M.; Zhao, C.; Yang, P.; Fu, Y. Biomimetic Nanoarchitectonics of Hollow Mesoporous Copper Oxide-Based Nanozymes with Cascade Catalytic Reaction for Near Infrared-II Reinforced Photothermal-Catalytic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 40645–40658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guati, C.; Gomez-Coma, L.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, I. Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Glucose Screen-Printed Sensors Based on Copper and Copper Oxide Particles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Miao, L.; Qiu, D.; Chen, S. Co3O4-Chitosan/Biomass-Derived Porous Carbon Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Integrated Electrode for Selective Detection of Glucose. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 23137–23144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, D. Petal-like CuO Nanostructures Prepared by a Simple Wet Chemical Method, and Their Application to Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshroo, A.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Taran, M.; Fattahi, A. Electrochemical System Designed on a Copper Tape Platform as a Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.J. Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engineering, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-07053958-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, T.; Ahmadi, S.; Ahmadi, E.; Bavil Olyai, M.R.T.; Khodadadi, Z. Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode with Graphene Quantum Dots, Chitosan and Nickel Molybdate Nanocomposites for Diazinon and Optimal Design by the Taguchi Method. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, M.; Natarajan, K.; Mobin, S.M. Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Sensing of Glucose by Employing Sucrose Templated Microspheres of Copper Oxide (CuO). Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5833–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emran, M.Y.; Shenashen, M.A.; El Sabagh, A.; Selim, M.M.; El-Safty, S.A. Enzymeless Copper Microspheres@carbon Sensor Design for Sensitive and Selective Acetylcholine Screening in Human Serum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 210, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Arrigan, D.W.M.; Silvester, D.S. Mechanical Polishing as an Improved Surface Treatment for Platinum Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2016, 9, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.G.M.; Foster, C.W.; Kelly, P.J.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Determination of the Electrochemical Area of Screen-Printed Electrochemical Sensing Platforms. Biosensors 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, M.; Lee, Y. Nonenzymatic Amperometric Glucose Sensor Based on a Composite Prepared from CuO, Reduced Graphene Oxide, and Carbon Nanotube. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fernández, B.; Martín-Yerga, D.; Costa-García, A. Galvanostatic Electrodeposition of Copper Nanoparticles on Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes and Their Application for Reducing Sugars Determination. Talanta 2017, 175, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Fan, G.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, M.; Sun, P.; Fu, Y.; Han, D.; Cui, G. A Portable Micro Glucose Sensor Based on Copper-Based Nanocomposite Structure. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 7806–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, H.R.; Memarzadeh, F.; Ardakani, M.M.; Namazian, M.; Golabi, S.M. Norepinephrine-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for the Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid and Uric Acid. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE ISO 15197:2015; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus (ISO 15197:2013). AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2015.
- Hagel, A.F.; Albrecht, H.; Dauth, W.; Hagel, W.; Vitali, F.; Ganzleben, I.; Schultis, H.W.; Konturek, P.C.; Stein, J.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Plasma Concentrations of Ascorbic Acid in a Cross Section of the German Population. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, E.P.; Burini, R.C. High Plasma Uric Acid Concentration: Causes and Consequences. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2012, 4, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Maurya, M.R.; Al-maadeed, S.; Muthalif, A.A.; Sadasivuni, K.K. High-Precision Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensing Based on CNTs/CuO Nanocomposite. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznowicz, M.; Rębiś, T.; Jędrzak, A.; Nowaczyk, G.; Szybowicz, M.; Jesionowski, T. Glucose Determination Using Amperometric Non-Enzymatic Sensor Based on Electroactive Poly(Caffeic Acid)@MWCNT Decorated with CuO Nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiela, M.; Wysokowski, M.; Galinski, M.; Jesionowski, T.; Stepniak, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Copper Oxide-Chitosan Nanocomposites for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.F.; Hogg, R.A.; Manjakkal, L. Cu2O-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Non-Invasive and Portable Glucose Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Wan, Q.; Yang, N. Morphology-Dependent Sensing Performance of CuO Nanomaterials. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1171, 338663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Peng, H. Pt/MXene-Based Flexible Wearable Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor for Continuous Glucose Detection in Sweat. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13290–13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.W.; Chinnamani, M.V.; Lee, E.; Lee, N.-E. Stretchable Non-Enzymatic Fuel Cell-Based Sensor Patch Integrated with Thread-Embedded Microfluidics for Self-Powered Wearable Glucose Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
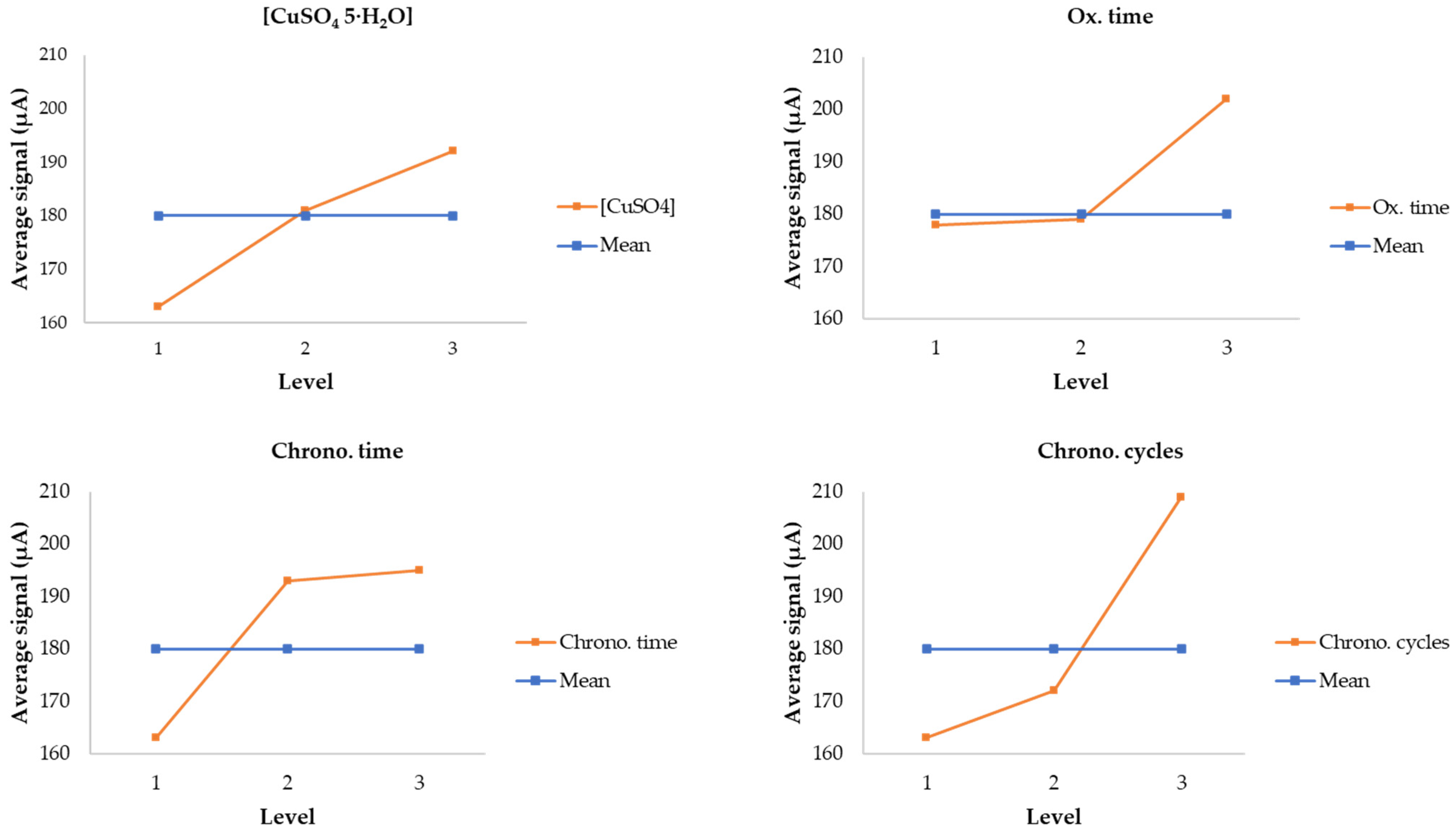

| Variable | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (I) | 0.01 M | 0.1 M | 1 M |
| Chrono. Cycles (II) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Chrono. Time (III) | 200 s | 300 s | 400 s |
| Oxidation time (IV) | 2 days | 3 days | 4 days |
| Electrode | Linear Range (mM) | Reproducibility STD (%) | Sensitivity (μA·mM−1·cm−2) | Media NaOH | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO/CNTs | 5–100 μM | 1.07 | 15300 | 0.1 M | [49] |
| CuO/rGO/CNT | 10–1000 μM | 4.1 | 9278 | 0.1 M | [42] |
| CuO/PCA /MWCNT | 0.002–9 | 4.6 | 2412 | 0.1 M | [50] |
| CuO/CS | 0.05–1 | 3.0 | 503 | 0.1 M | [51] |
| Cu2O/GCE | 0.1–1 | N/A | 1082.5 | 0.1 M | [52] |
| CuO microfeathers | 0.03–8 | 7 | 1091 | 0.1 M | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guati, C.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, I. Optimized Copper-Based Microfeathers for Glucose Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121032
Guati C, Gómez-Coma L, Fallanza M, Ortiz I. Optimized Copper-Based Microfeathers for Glucose Detection. Biosensors. 2023; 13(12):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121032
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuati, Carlota, Lucía Gómez-Coma, Marcos Fallanza, and Inmaculada Ortiz. 2023. "Optimized Copper-Based Microfeathers for Glucose Detection" Biosensors 13, no. 12: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121032
APA StyleGuati, C., Gómez-Coma, L., Fallanza, M., & Ortiz, I. (2023). Optimized Copper-Based Microfeathers for Glucose Detection. Biosensors, 13(12), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13121032