Surface Electromyography-Based Recognition of Electronic Taste Sensations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
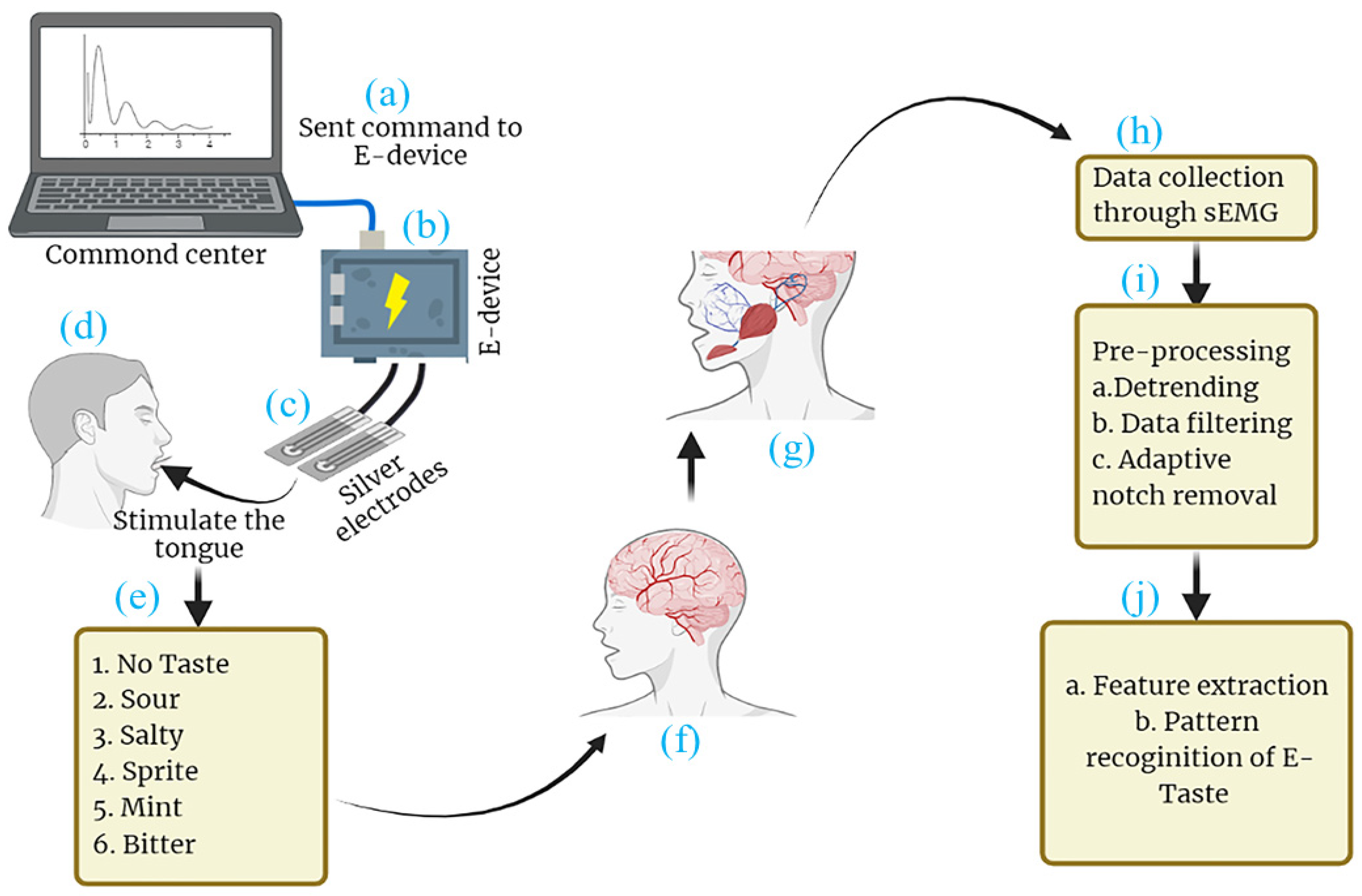
2. System Description
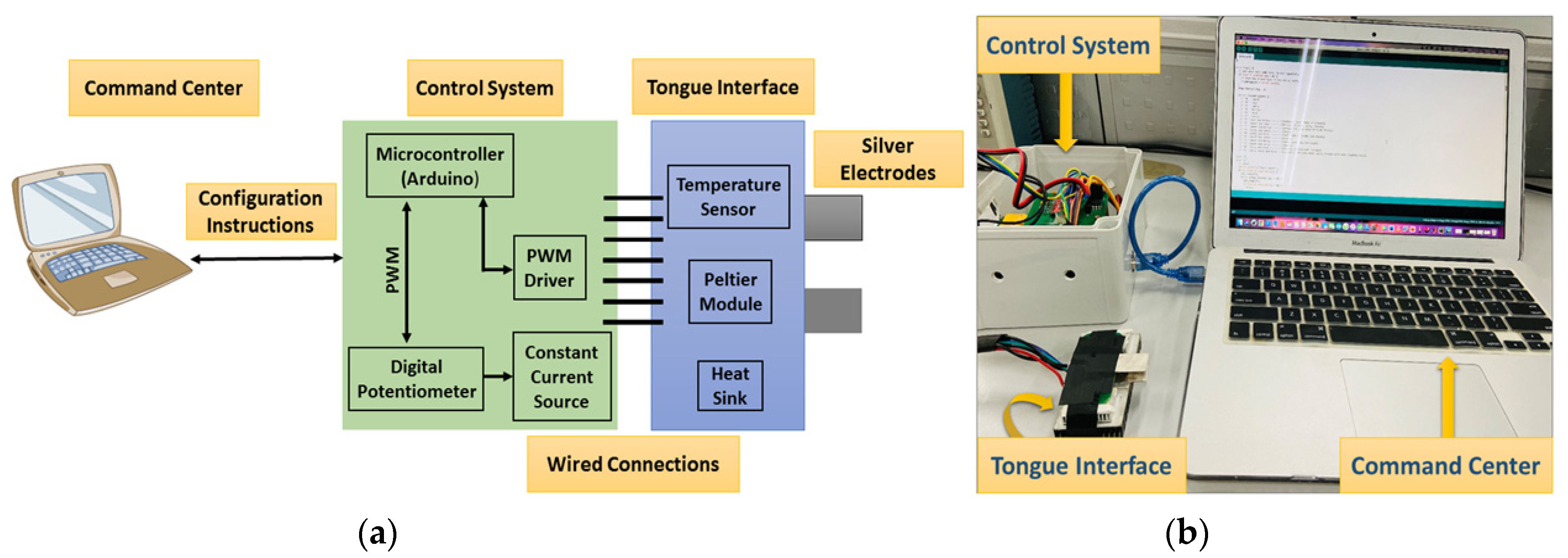
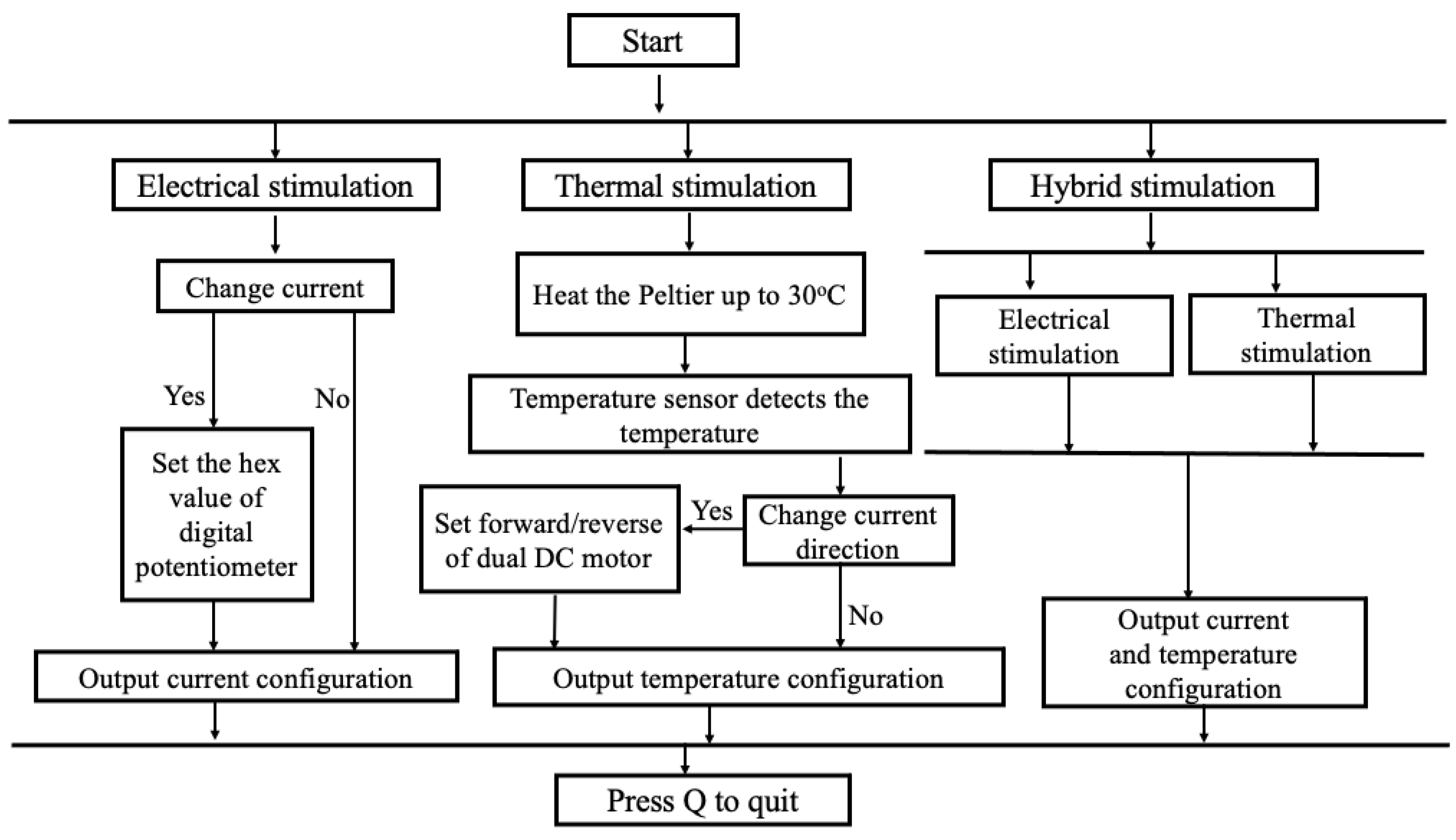
2.1. E-Taste Device
2.2. Surface Electromyography
3. Experimental Procedure
3.1. Validation of E-Taste Device
3.2. sEMG Acquisition System
3.3. Placement of Electrodes
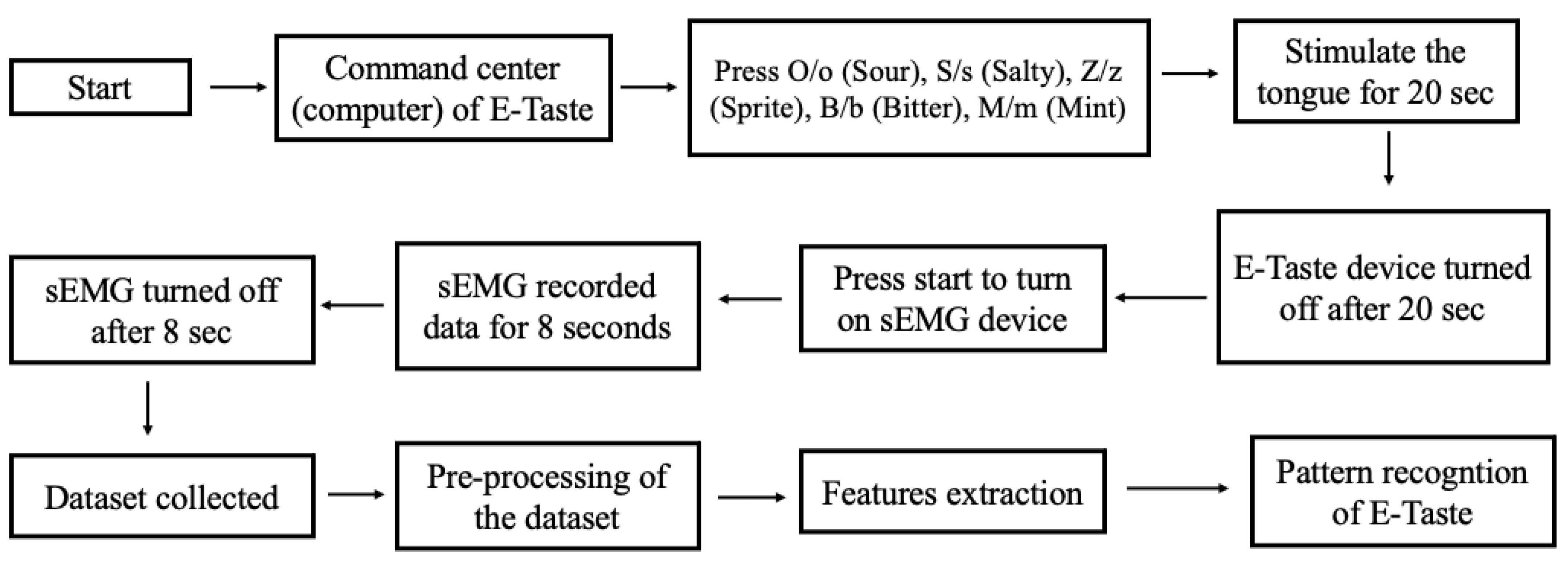
3.4. Data Collection
- The E-Taste and sEMG devices were examined before the experiment began.
- sEMG electrodes were placed on the participant’s face, as shown in Figure 5, while he was instructed to sit back and relax.
- The participant was instructed to put the tongue’s tip between the Ag/Pt electrodes of the E-Taste device.
- Various taste sensations were generated on the tongue’s tip, as mentioned in Table 1. The time duration of the tongue’s stimulation was 20 s.
- sEMG signal was captured from the facial muscles for 8 s after generating the taste on the tongue.
- The participant was told to wash their mouth or drink water and take a one-minute break during each taste sensation.
- After finishing all six taste sensations, the participant was instructed to take a five-minute break.
- After the five-minute pause, another session was started.
- All the above steps were repeated for each participant.
4. Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
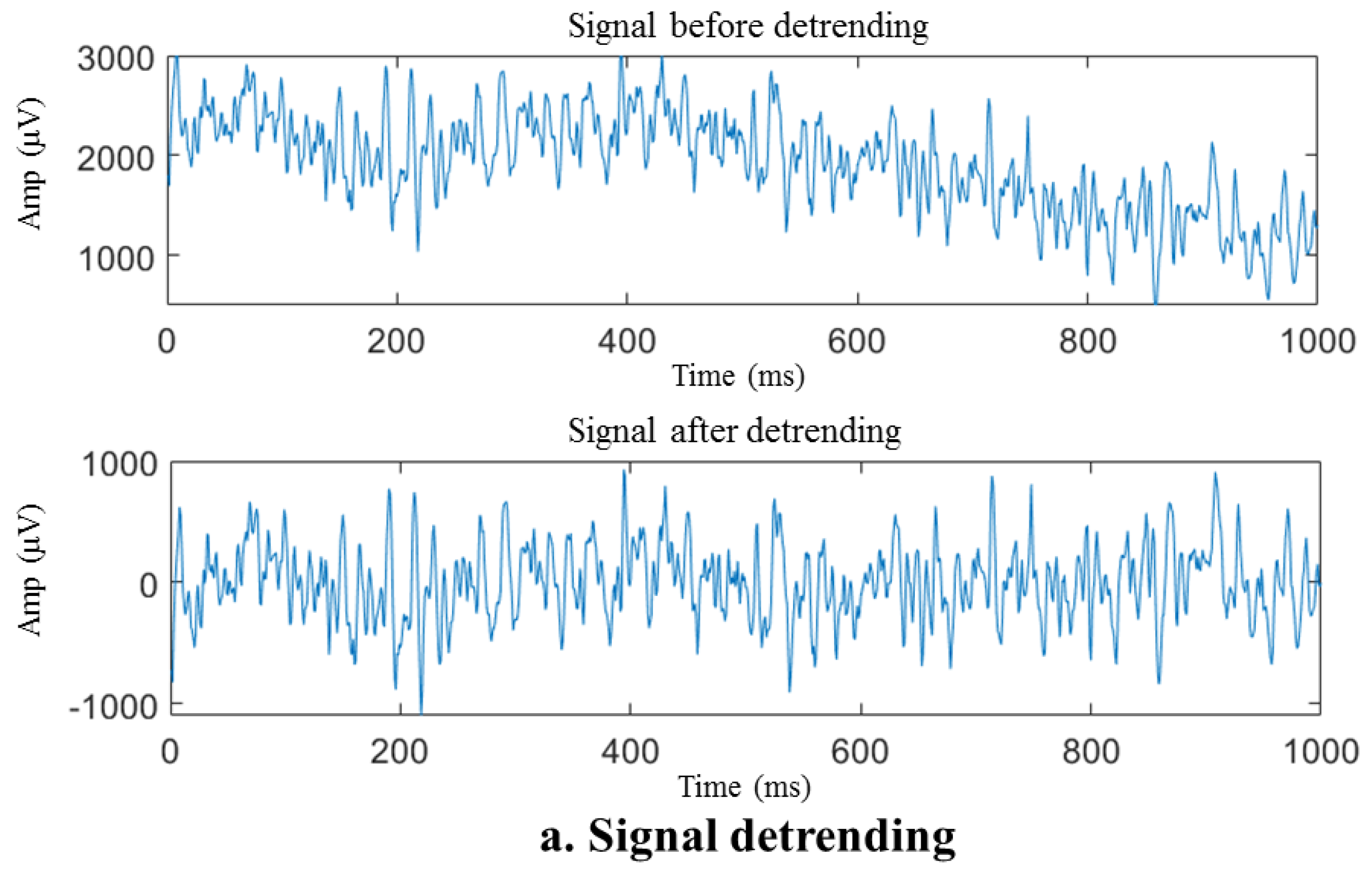
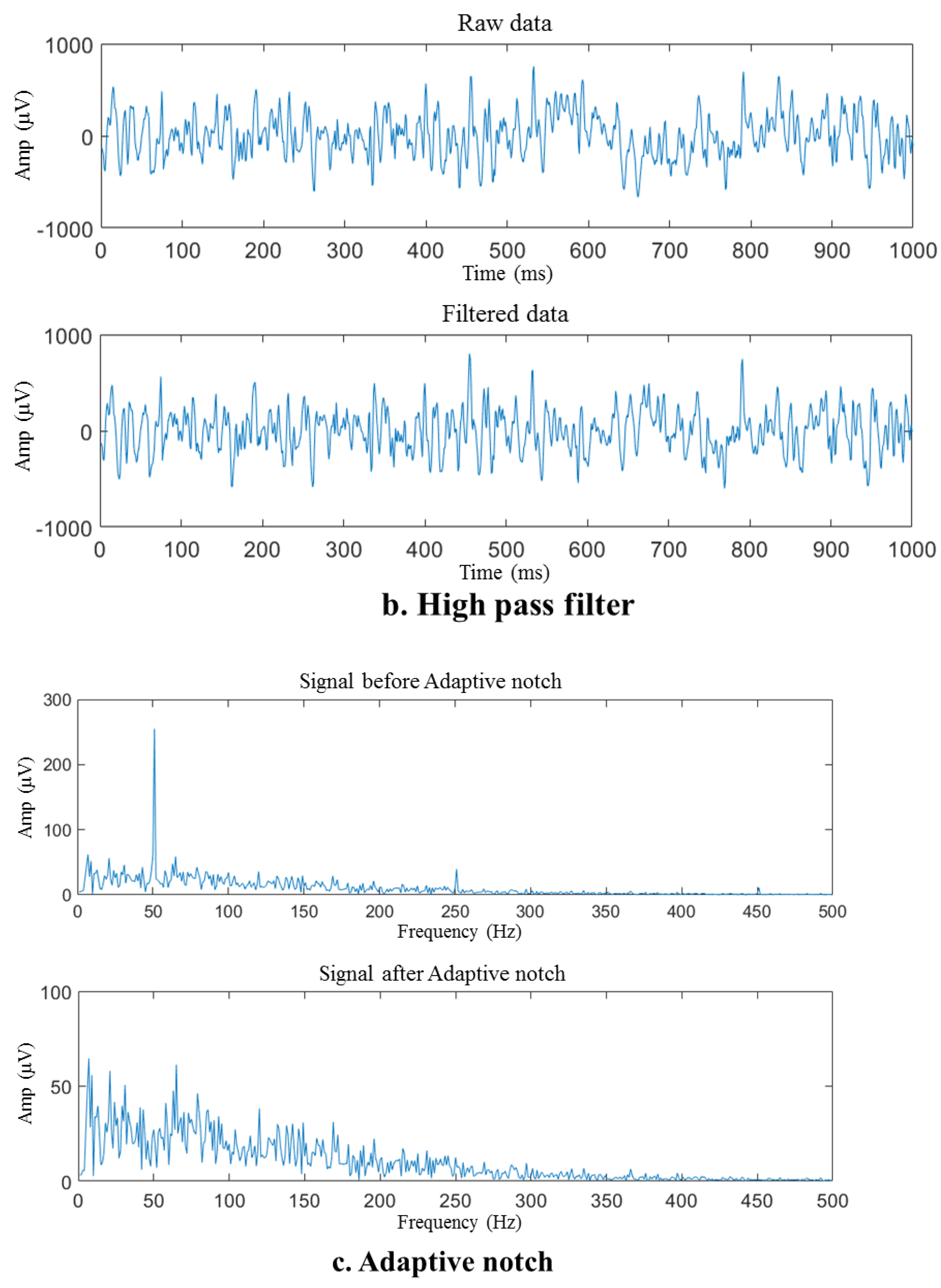
4.1. Data Filtration
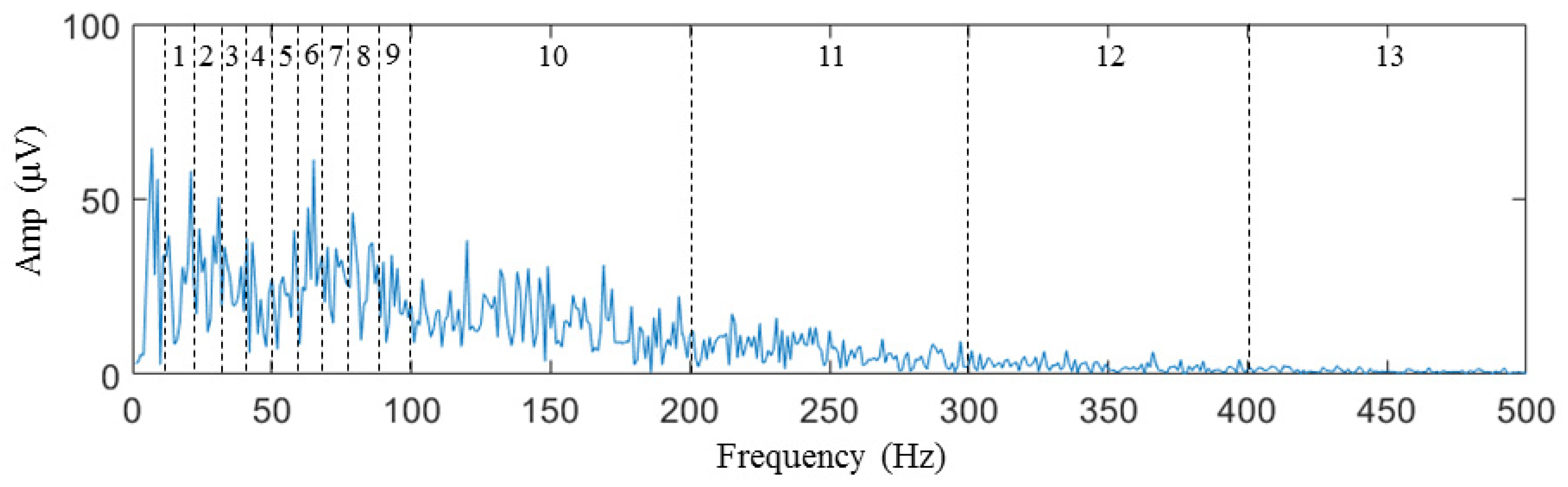
4.2. Features Extraction
5. Classification
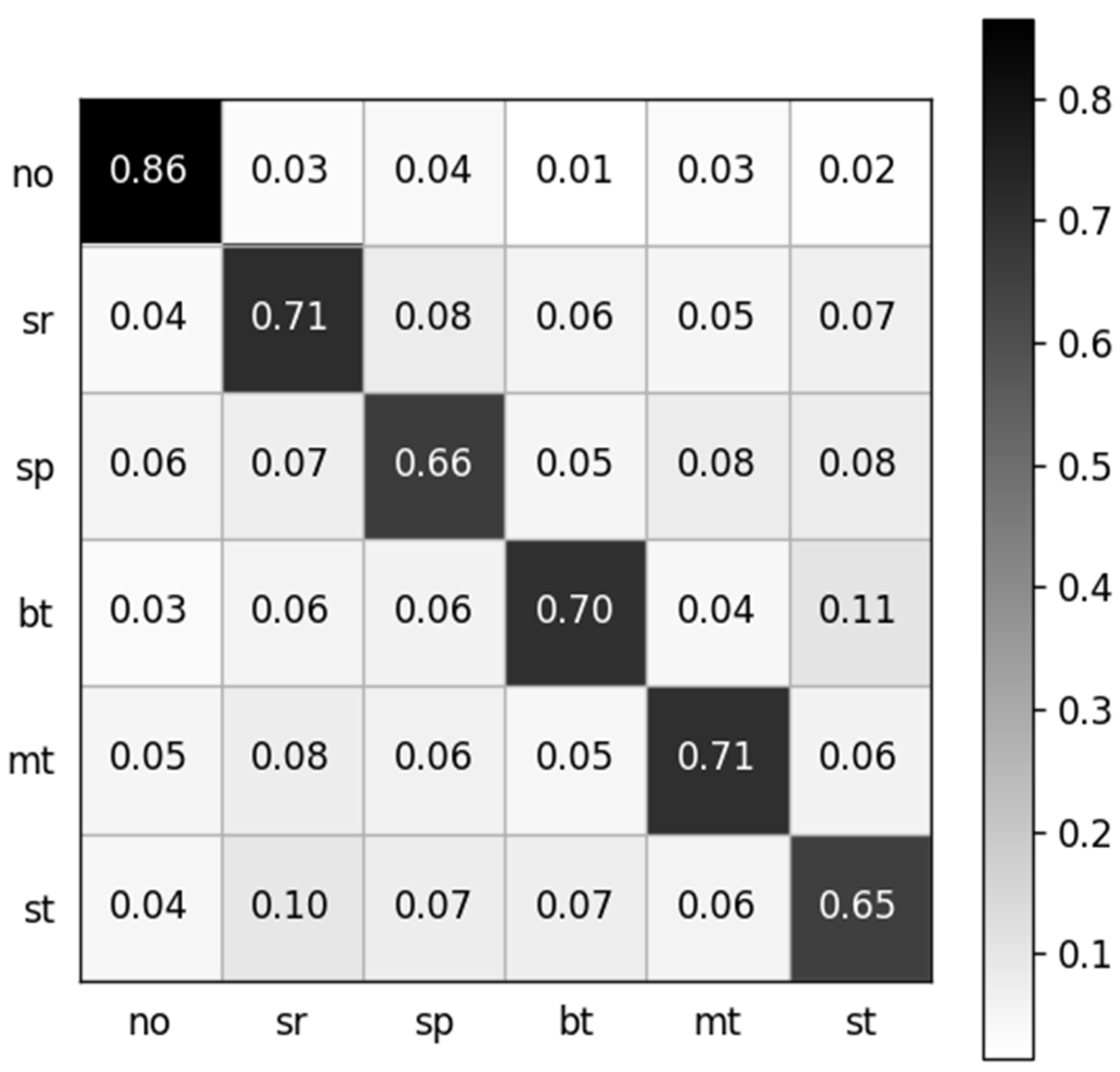
5.1. Results and Discussion
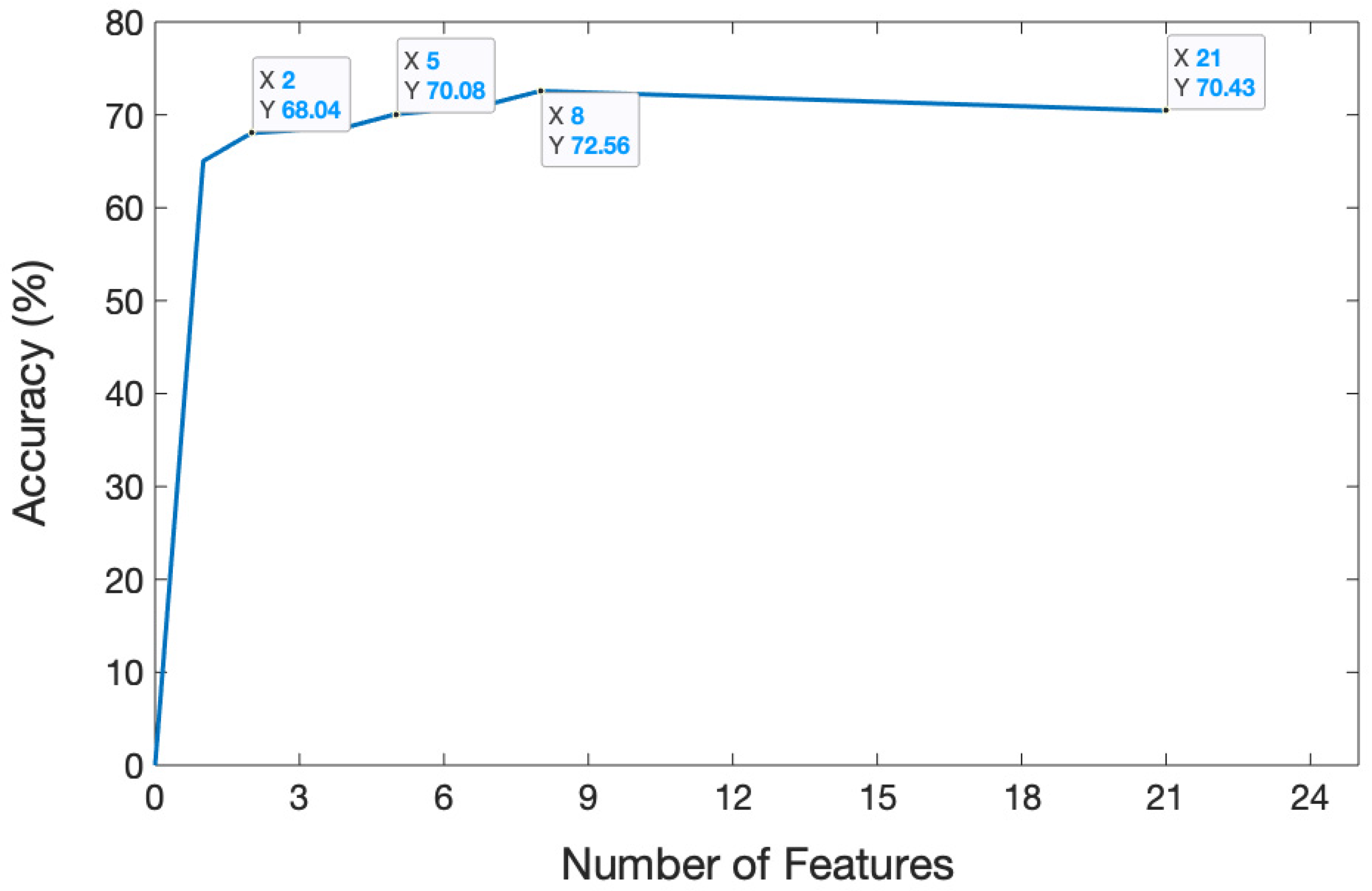
5.1.1. Feature Selection
5.1.2. Participant’s Grouping
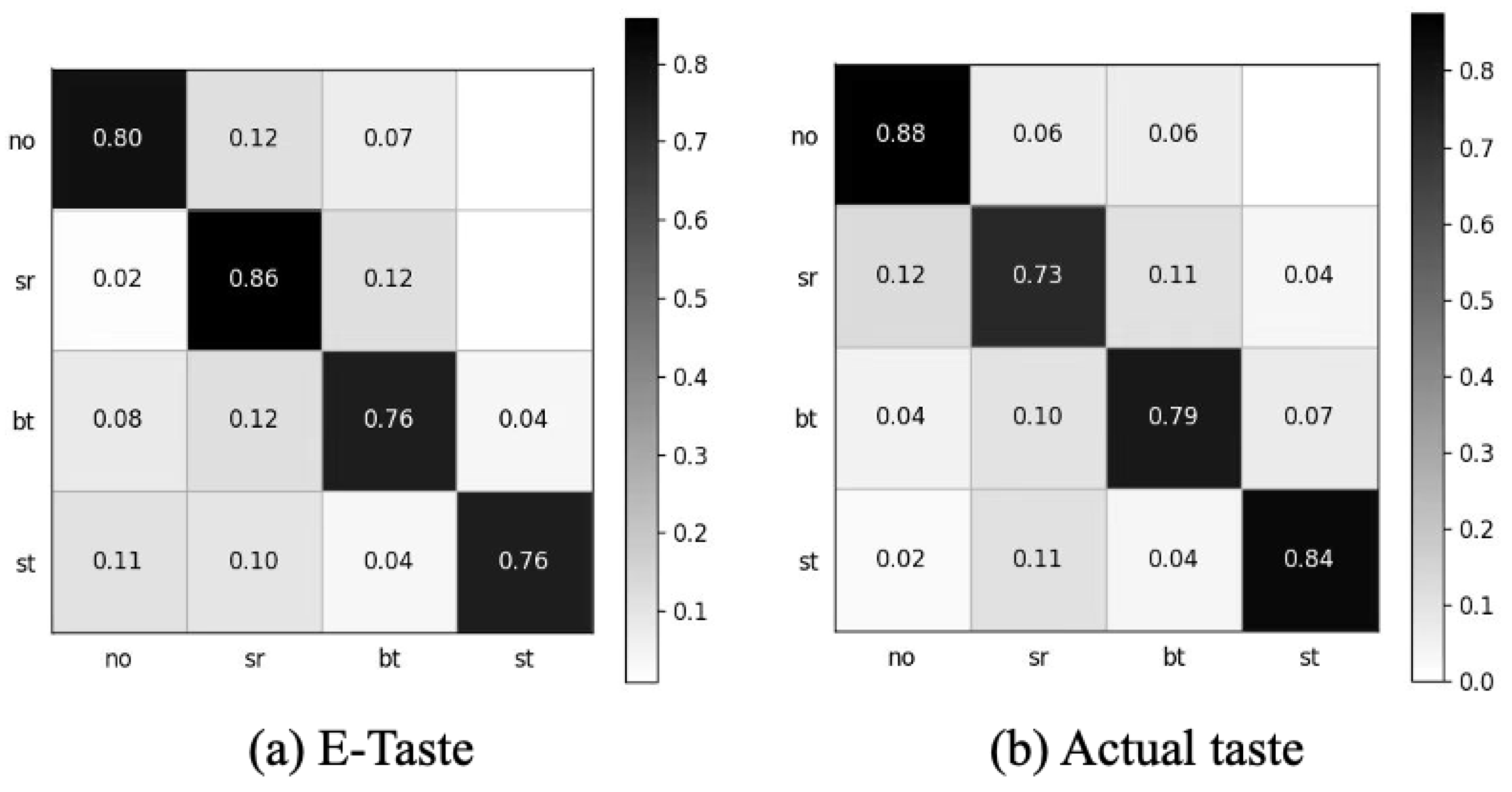
5.1.3. Comparison of E-Taste and Real Taste Sensation
5.2. Limitations and Directions for Further Research
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drewnowski, A. Taste preferences and food intake. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department, F.M.I.R.; Corporation, O.R. Trends in the United States: Consumer Attitudes & the Supermarket; Research Department, Food Marketing Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Logue, A.W. The Psychology of Eating and Drinking; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjur, D. Social and Cultural Perspectives in Nutrition; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, H.R. Taste and food technology: Acceptability, aesthetics, and preference. Handb. Percept. 1978, 1, 157–194. [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski, A. Fats and food texture: Sensory and hedonic evaluations. In Food Texture; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 251–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, H.R. Texture in dairy products and its sensory evaluation. In Food Texture; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 217–250. [Google Scholar]
- Linforth, R.S.T. Developments in instrumental techniques for food flavour evaluation: Future prospects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 2044–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Roy, A.; Franks, A.T.; Joseph, P.V. A systematic review of taste differences among people with eating disorders. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2020, 22, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Era, V.; Farri, F.; Garzaro, G.; Gatto, M.; Aluffi Valletti, P.; Garzaro, M. Smell and taste disorders during COVID-19 outbreak: Cross-sectional study on 355 patients. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewys, W.D.; Walters, K. Abnormalities of taste sensation in cancer patients. Cancer 1975, 36, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, A.; Riedl, M.; Luger, A.; Hummel, T.; Mueller, C.A. Clinical significance of smell and taste disorders in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2010, 267, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbarasan, R.; Gomez Carmona, D.; Mahendran, R. Human Taste-Perception: Brain Computer Interface (BCI) and Its Application as an Engineering Tool for Taste-Driven Sensory Studies. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 408–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, C.; Kobayakawa, T.; Saito, S.; Ogawa, H. Gustatory evoked cortical activity in humans studied by simultaneous EEG and MEG recording. Chem. Senses 2002, 27, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, D.; Hogervorst, M.; Toet, A.; van Erp, J.B.; Kallen, V.; Brouwer, A.-M. Explicit and implicit responses to tasting drinks associated with different tasting experiences. Sensors 2019, 19, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallroth, R.; Höchenberger, R.; Ohla, K. Delta activity encodes taste information in the human brain. Neuroimage 2018, 181, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horio, T. EMG activities of facial and chewing muscles of human adults in response to taste stimuli. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2003, 97, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, A.; Prinster, A.; Cantone, E.; Ponticorvo, S.; Russo, A.G.; Di Salle, F.; Esposito, F. Intensity-related distribution of sweet and bitter taste fMRI responses in the insular cortex. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 3631–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, C.; Rocha-Rego, V. Investigating the predictive value of functional MRI to appetitive and aversive stimuli: A pattern classification approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Manian, V. Eeg and deep learning based brain cognitive function classification. Computers 2020, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, O. Olfactory recognition based on EEG gamma-band activity. Neural Comput. 2017, 29, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q. Olfactory EEG signal classification using a trapezoid difference-based electrode sequence hashing approach. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 2050011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Maglione, A.G.; Rossi, D.; Modica, E.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; Colosimo, A. EEG-based approach-withdrawal index for the pleasantness evaluation during taste experience in realistic settings. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 3228–3231. [Google Scholar]
- Pagan, K.M.; Giraldi, J.D.M.E.; Maheshwari, V.; de Paula, A.L.D.; de Oliveira, J.H.C. Evaluating cognitive processing and preferences through brain responses towards country of origin for wines: The role of gender and involvement. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2021, 33, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Looney, D.; Mandic, D.P. Estimating human response to taste using EEG. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 6331–6334. [Google Scholar]
- Abidi, I.; Farooq, O.; Beg, M. Sweet and sour taste classification using EEG based brain computer interface. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.; Yadav, S.; Veer, K. A comprehensive assessment of Brain Computer Interfaces: Recent trends and challenges. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Ullah, A.; Zhang, M.; Gao, H.; Hu, R.; Li, G. Qualitative recognition of primary taste sensation based on surface electromyography. Sensors 2021, 21, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Ashida, I.; Inagaki, D.; Kawakami, S.Y. Differentiation of activity patterns in the suprahyoid muscles during swallowing of foods with five taste qualities. J. Sens. Stud. 2005, 20, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Parker, P.J. Electromyography: Physiology, Engineering, and Non-Invasive Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cifrek, M.; Medved, V.; Tonković, S.; Ostojić, S. Surface EMG based muscle fatigue evaluation in biomechanics. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.E. Human facial expressions in response to taste and smell stimulation. In Advances in Child Development and Behavior; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; Volume 13, pp. 257–295. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, C.; Pedersen, A.L.; Villa, A.; Ekström, J.; Proctor, G.B.; Vissink, A.; Aframian, D.; McGowan, R.; Aliko, A.; Narayana, N. The functions of human saliva: A review sponsored by the World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Negro, F.; Felici, F.; Farina, D. Associations between motor unit action potential parameters and surface EMG features. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 123, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, P.; Mańkowski, T.; Tomczyński, J. putEMG—A surface electromyography hand gesture recognition dataset. Sensors 2019, 19, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, N.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Cazorla, M. An semg-controlled 3D game for rehabilitation therapies: Real-time time hand gesture recognition using deep learning techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, R.; Gao, H.; Yang, M.; Luo, Z.; Li, G. Silent speech decoding using spectrogram features based on neuromuscular activities. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, N.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Gomez-Donoso, F.; Cazorla, M. Inferring static hand poses from a low-cost non-intrusive sEMG sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, W.; Minemoto, K.; Ikegami, A.; Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Fushiki, T. Facial EMG correlates of subjective hedonic responses during food consumption. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Morita, Y.; Koizumi, H.; Shingai, T. Effects of taste solutions, carbonation, and cold stimulus on the power frequency content of swallowing submental surface electromyography. Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, Y.; Kodama, N.; Maeda, N.; Minagi, S. Effect of food properties and chewing condition on the electromyographic activity of the posterior tongue. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynes-Aminzade, D. Edible bits: Seamless interfaces between people, data and food. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’05)-Extended Abstracts, Portland, OR, USA, 2–7 April 2005; pp. 2207–2210. [Google Scholar]
- Rolls, E.T. Brain mechanisms underlying flavour and appetite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajduković, D. The relationship between electrode area and sensory qualities in electrical human tongue stimulation. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1984, 98, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardello, A.V. Comparison of taste qualities elicited by tactile, electrical, and chemical stimulation of single human taste papillae. Percept. Psychophys. 1981, 29, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettaneh, A.; Pariès, J.; Stirnemann, J.; Steichen, O.; Eclache, V.; Fain, O.; Thomas, M. Clinical and biological features associated with taste loss in internal medicine patients. A cross-sectional study of 100 cases. Appetite 2005, 44, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.; Green, B.G. Thermal stimulation of taste. Nature 2000, 403, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawless, H.T.; Stevens, D.A.; Chapman, K.W.; Kurtz, A. Metallic taste from electrical and chemical stimulation. Chem. Senses 2005, 30, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talavera, K.; Ninomiya, Y.; Winkel, C.; Voets, T.; Nilius, B. Influence of temperature on taste perception. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, R.A.N. Digitally Stimulating the Sensation of Taste through Electrical and Thermal Stimulation. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Karunanayaka, K.; Johari, N.; Hariri, S.; Camelia, H.; Bielawski, K.S.; Cheok, A.D. New thermal taste actuation technology for future multisensory virtual reality and internet. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 24, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, N.; Cheok, A.D.; Fernando, O.N.N.; Nii, H.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Digital taste: Electronic stimulation of taste sensations. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–18 November 2011; pp. 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. E-Taste: Taste Sensations and Flavors Based on Tongue’s Electrical and Thermal Stimulation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, R.; Gao, H.; Ai, Q.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Remote control system of spherical robot based on silent speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, G. Feature selection of mime speech recognition using surface electromyography data. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 3173–3178. [Google Scholar]
- Karthick, P.; Ghosh, D.M.; Ramakrishnan, S. Surface electromyography based muscle fatigue detection using high-resolution time-frequency methods and machine learning algorithms. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 154, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis Rocha, R.A.; Reis Rocha, L.C.; Ribeiro, M.N.; Lima Ribeiro, A.P.; Alves da Rocha, R.; Souza Carneiro, J.d.D. Effect of the food matrix on the capacity of flavor enhancers in intensifying salty taste. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Luo, Z.; Li, G. Gender Differences in Taste Sensations Based on Frequency Analysis of Surface Electromyography. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2023, 130, 938–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castroflorio, T.; Farina, D.; Bottin, A.; Piancino, M.; Bracco, P.; Merletti, R. Surface EMG of jaw elevator muscles: Effect of electrode location and inter-electrode distance. J. Oral Rehabil. 2005, 32, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Botter, A.; Troiano, A.; Merlo, E.; Minetto, M.A. Technology and instrumentation for detection and conditioning of the surface electromyographic signal: State of the art. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.; Ali, M.A.B.M.; Bakar, A.A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T.G. Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, E.A.; Morin, E.L.; Merletti, R. Sampling, noise-reduction and amplitude estimation issues in surface electromyography. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2002, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: Detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, K.G.; Farina, D.; Merletti, R.; Enoka, R.M. Influence of motor unit properties on the size of the simulated evoked surface EMG potential. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 169, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J.; Gilmore, L.D.; Kuznetsov, M.; Roy, S.H. Filtering the surface EMG signal: Movement artifact and baseline noise contamination. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotte, F.; Bougrain, L.; Cichocki, A.; Clerc, M.; Congedo, M.; Rakotomamonjy, A.; Yger, F. A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces: A 10 year update. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 031005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Qin, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhai, M.; Shi, W. Feature extraction and classification of lower limb motion based on sEMG signals. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132882–132892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.; Scott, R.N. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, S. Temporal information in speech: Acoustic, auditory and linguistic aspects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1992, 336, 367–373. [Google Scholar]

| Tastes and Flavors | Stimulation’s Range | Number of Participants Recognizing Taste Sensation |
|---|---|---|
| No Taste | Nil | |
| Sour | 60–180 µA | 13/17 |
| Salty | 40–70 µA | 12/17 |
| Sprite | 60–180 µA and 30–20 °C | 12/17 |
| Bitter | 60–140 µA | 10/17 |
| Mint | Below 25 °C | 13/17 |
| Electrodes | Electrode Type | Muscle | Detailed Placement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Differential | Masseter | Below the right ear |
| 2 | Differential | Masseter | In line and beneath channel 1 |
| 3 | Single | Depressor anguli oris | Mouth’s lower right corner |
| 4 | Single | Depressor labium | Under the lower lip |
| 5 | Single | Masseter | Below the left ear |
| 6 | Single | Masseter | In line and beneath channel 5 |
| B | Bias | Mastoid bone | Behind left ear |
| R | Reference | Mastoid bone | Behind right ear |
| Name | Feature’s Domain | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| Spectrum average amplitude | Frequency | 13 |
| RVF | Frequency | 1 |
| FC | Frequency | 1 |
| RMSF | Frequency | 1 |
| MAV | Time | 1 |
| Sk | Time | 1 |
| RMS | Time | 1 |
| Ku | Time | 1 |
| ZCR | Time | 1 |
| Number of Participants | Dataset | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1680 | 84.79 |
| 2 | 3360 | 82.75 |
| 3 | 5040 | 80.61 |
| 4 | 6720 | 79.52 |
| 5 | 8400 | 75.36 |
| 6 | 10,080 | 72.82 |
| 7 | 11,760 | 71.49 |
| 8 | 13,440 | 70.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, A.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Riaz, W.; Li, G. Surface Electromyography-Based Recognition of Electronic Taste Sensations. Biosensors 2024, 14, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080396
Ullah A, Zhang F, Song Z, Wang Y, Zhao S, Riaz W, Li G. Surface Electromyography-Based Recognition of Electronic Taste Sensations. Biosensors. 2024; 14(8):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080396
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Asif, Fengqi Zhang, Zhendong Song, You Wang, Shuo Zhao, Waqar Riaz, and Guang Li. 2024. "Surface Electromyography-Based Recognition of Electronic Taste Sensations" Biosensors 14, no. 8: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080396
APA StyleUllah, A., Zhang, F., Song, Z., Wang, Y., Zhao, S., Riaz, W., & Li, G. (2024). Surface Electromyography-Based Recognition of Electronic Taste Sensations. Biosensors, 14(8), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14080396





