Development of a Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System for Oxytocin Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Principle of Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System
2.3. Fabrication of Smartphone-Linked Optical Immunosensing Unit
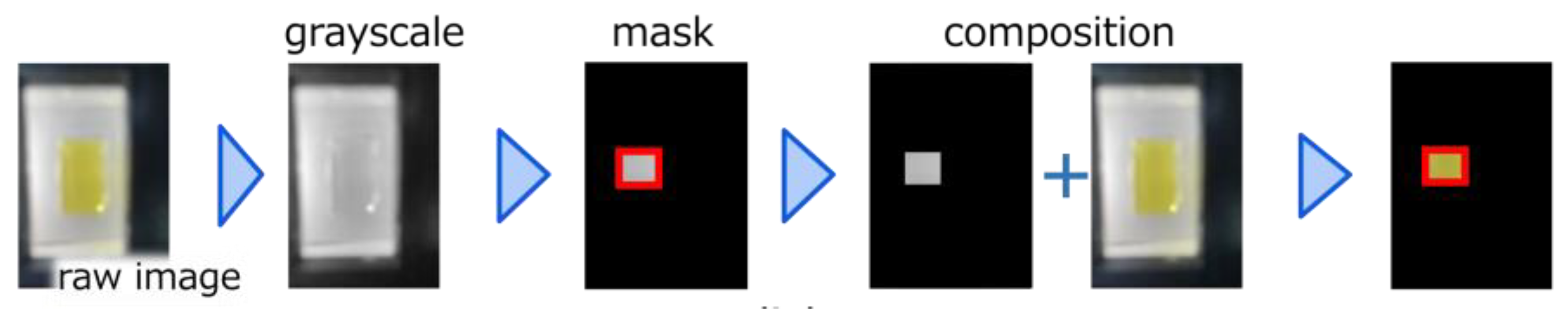
2.4. Development of Image Analysis Software
2.5. Characterization of the Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System
3. Results and Discussion
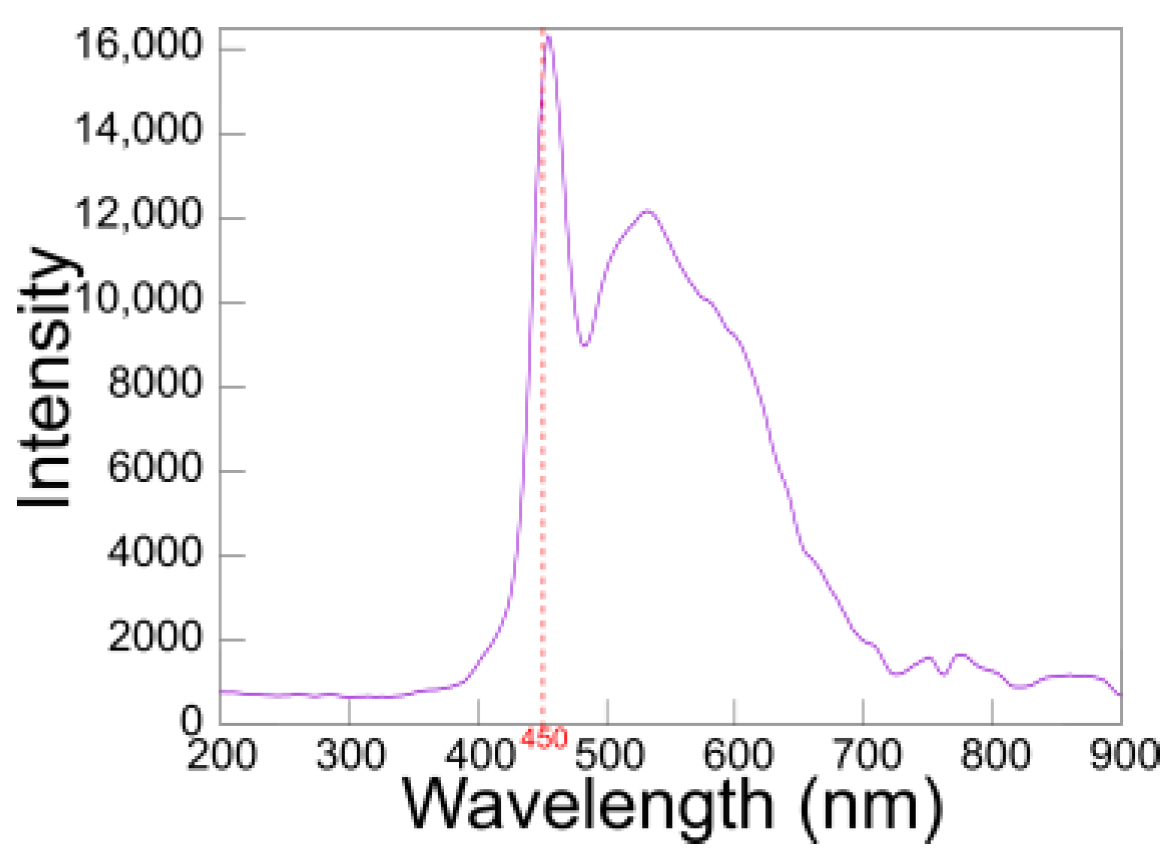
3.1. Determination of TMB Using Spectrophotometry
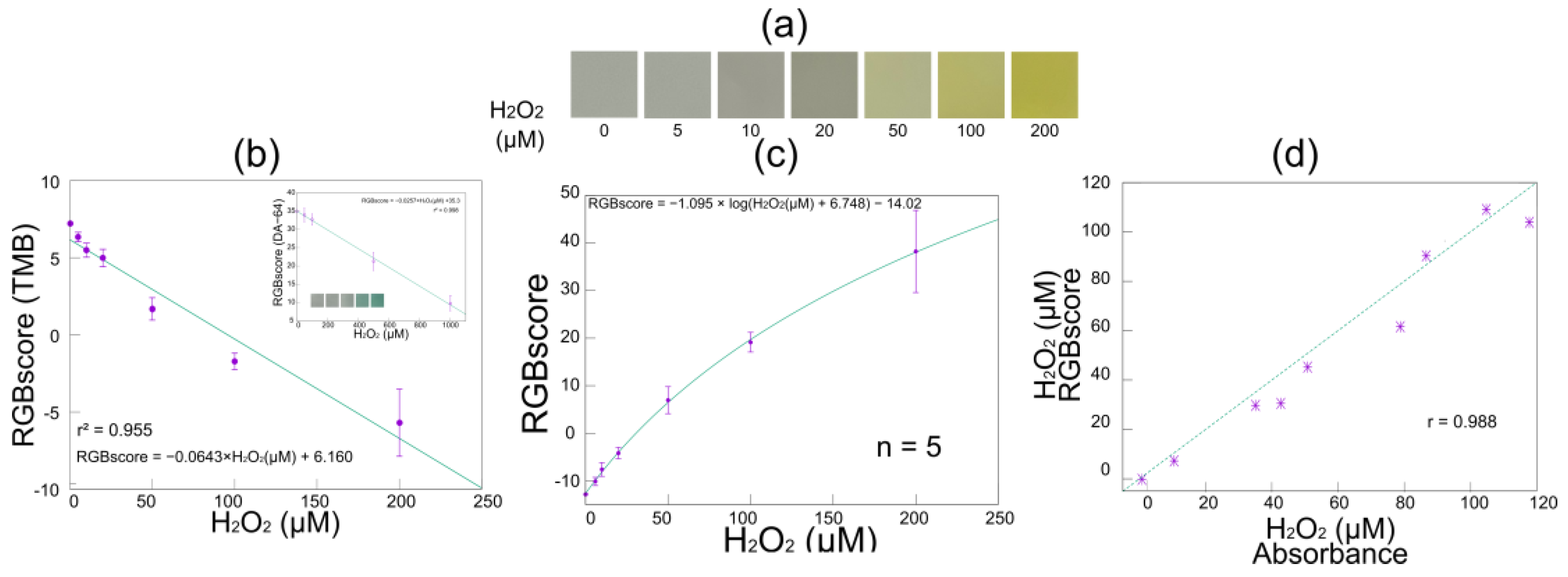
3.2. Characterization of Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System
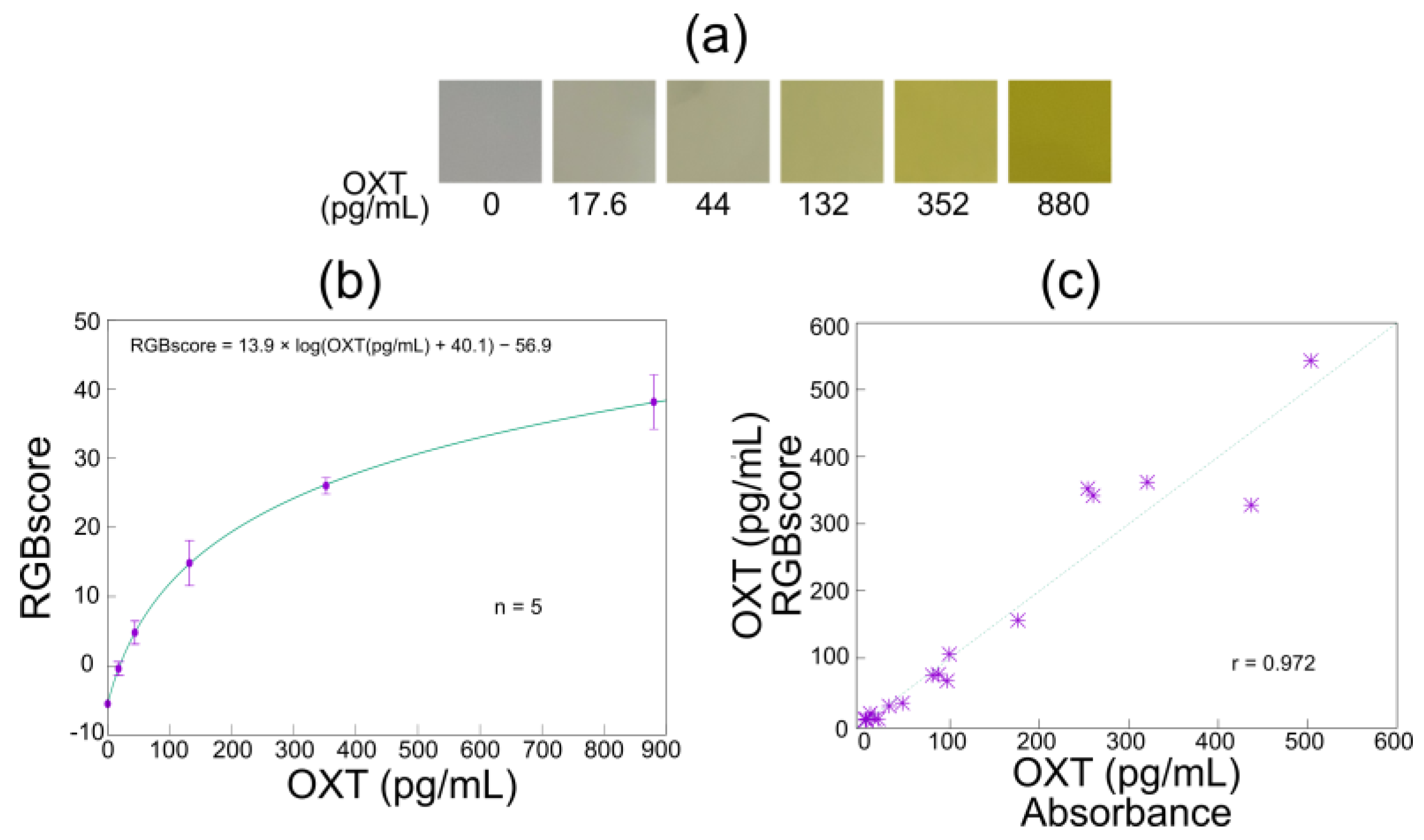
3.3. Application of Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System to OXT Measurement
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vannuccini, S.; Bocchi, C.; Severi, F.M.; Challis, J.R.; Petraglia, F. Endocrinology of Human Parturition. Ann. Endocrinol. 2016, 77, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, W.R.; Armstrong, W.E. Neurochemical regulation of oxytocin secretion in lactation. Endocr. Rev. 1992, 13, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosfeld, M.; Heinrichs, M.; Zak, P.J.; Fischbacher, U.; Fehr, E. Oxytocin increases trust in humans. Nature 2005, 435, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, J.A.; Grewal, N.S.; Ropacki, S.; Perez, P.; Gonzalez, A.; Zak, P.J. Effects of a 10-day oxytocin trial in older adults on health and well-being. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsta, R.; Heinrichs, M. Oxytocin, stress and social behavior: Neurogenetics of the human oxytocin system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A. Oxytocin and human social behavior. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 14, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, B.A.; Leng, G.; Szeto, A.; Parker, K.J.; Verbalis, J.G.; Ziegler, T.E.; Lee, M.R.; Neumann, I.D.; Mendez, A.J. Advances in human oxytocin measurement: Challenges and proposed solutions. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valstad, M.; Alvares, G.A.; Egknud, M.; Matziorinis, A.M.; Andreassen, O.A.; Westlye, L.T.; Quintana, D.S. The correlation between central and peripheral oxytocin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 78, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, I.D. Brain oxytocin: A key regulator of emotional and social behaviours in both females and males. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Kagerbauer, S.M.; Gempt, J.; Podtschaske, A.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Schneider, G. Oxytocin levels in saliva correlate better than plasma levels with concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients in neurocritical care. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Arjona, M.; Botia, M.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Ceron, J.J. Oxytocin measurements in saliva: An analytical perspective. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Zuo, R.; Zheng, H.; Dang, J.; Wang, Z. Exploring associations between postpartum depression and oxytocin levels in cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and saliva. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 315, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewen, K.M.; Davenport, R.E.; Light, K.C. An investigation of plasma and salivary oxytocin responses in breast-and formula-feeding mothers of infants. Psychophysiology 2010, 47, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Birmingham, W.; Light, K.C. The influence of depressive symptomatology and perceived stress on plasma and salivary oxytocin before, during and after a support enhancement intervention. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mera, J.C.C.; Molano, M.A.C.; López, C.C.G.; Triana, C.A.; Cotrina, J.M. Discussions and perspectives regarding oxytocin as a biomarker in human investigations. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue Carter, C.; POURNAJAFI-NAZARLOO, H.; Kramer, K.M.; Ziegler, T.E.; WHITE-TRAUT, R.; Bello, D.; Schwertz, D. Oxytocin: Behavioral associations and potential as a salivary biomarker. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1098, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M.; Keresteš, O.; Žáková, J. A 3D-Printed Do-It-Yourself ELISA Plate Reader as a Biosensor Tested on TNFα Assay. Biosensors 2024, 14, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumburg, F.; Pujato, N.; Peverengo, L.M.; Marcipar, I.S.; Berli, C.L.A. Coupling ELISA to smartphones for POCT of chronic and congenital Chagas disease. Talanta 2023, 256, 124246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogirala, T.; Eapen, A.; Salvante, K.G.; Rapaport, T.; Nepomnaschy, P.A.; Parameswaran, A.M. Smartphone-based colorimetric ELISA implementation for determination of women’s reproductive steroid hormone profiles. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelis, J.L.D.; Bura, L.; Zhao, Y.; Burkin, K.M.; Rafferty, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. The efficiency of color space channels to quantify color and color intensity change in liquids, pH strips, and lateral flow assays with smartphones. Sensors 2019, 19, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, K.; Xu, H.; Liao, Z.; Wang, H.; Chang, J. A smartphone-based quantitative detection platform of mycotoxins based on multiple-color upconversion nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15865–15874.v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taron, W.; Phooplub, K.; Sanchimplee, S.; Piyanamvanich, K.; Jamnongkan, W.; Techasen, A.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Klanrit, P.; Namwat, N.; Khuntikeo, N. Smartphone-based fluorescent ELISA with simple fluorescent enhancement strategy for Opisthorchis viverrini (Ov) antigen detection in urine samples. Sens. Actuators B 2021, 348, 130705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I. Point-of-care colorimetric detection with a smartphone. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4240–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbach, S.; Jiang, N.; Moreddu, R.; Dong, X.; Kurz, W.; Wang, C.; Dong, J.; Yin, Y.; Butt, H.; Brischwein, M. Smartphone-based colorimetric detection system for portable health tracking. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, V.; Horzum, N.; Solmaz, M.E. From sophisticated analysis to colorimetric determination: Smartphone spectrometers and colorimetry. In Color Detection; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-Y. 13. Immunosensors in Introduction to Biosensors, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Ratterman, M.; Klotzkin, D.; Papautsky, I. A CMOS optical detection system for point-of-use luminescent oxygen sensing. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 155, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nonno, S.; Ulber, R. Smartphone-based optical analysis systems. Analyst 2021, 146, 2749–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Canning, J. Developments and Drivers of Low-Cost Smartphone Instrumentation. Adv. Devices Instrum. 2024, 5, 0068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Regression Model | α | β | γ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.200 | −0.300 | 0.150 | 0.955 | |
| 0.100 | −0.250 | 0.150 | 0.999 | |
| −0.500 | −0.050 | 0.200 | 0.784 |
| Regression Model | α | β | γ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.00 | 0.900 | 0.150 | 0.994 | |
| 0.100 | −0.450 | 0.400 | 0.999 | |
| −0.900 | −0.800 | 0.550 | 0.784 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarubo, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Numazaki, Y.; Kudo, H. Development of a Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System for Oxytocin Determination. Biosensors 2025, 15, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040261
Sarubo M, Suzuki Y, Numazaki Y, Kudo H. Development of a Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System for Oxytocin Determination. Biosensors. 2025; 15(4):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarubo, Miku, Yoka Suzuki, Yuka Numazaki, and Hiroyuki Kudo. 2025. "Development of a Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System for Oxytocin Determination" Biosensors 15, no. 4: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040261
APA StyleSarubo, M., Suzuki, Y., Numazaki, Y., & Kudo, H. (2025). Development of a Smartphone-Linked Immunosensing System for Oxytocin Determination. Biosensors, 15(4), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040261




