dsAMP and dsAMPGAN: Deep Learning Networks for Antimicrobial Peptides Recognition and Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
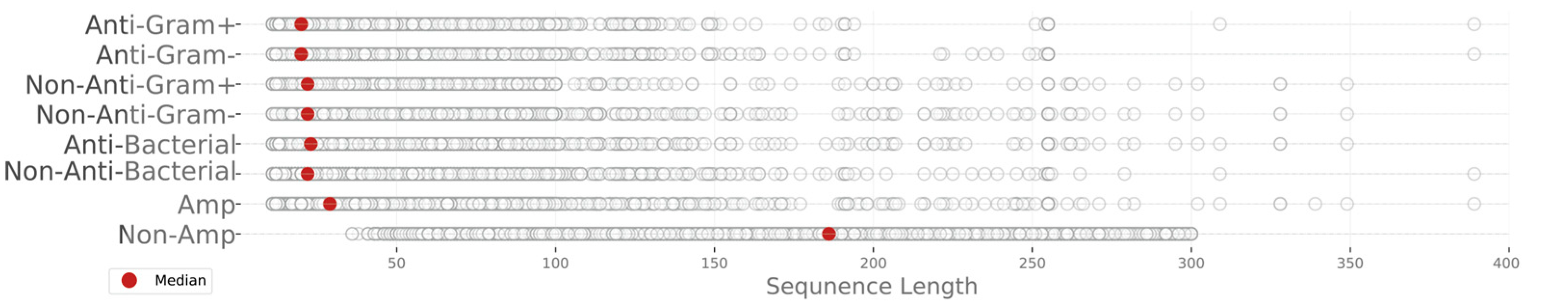
2.1. Sequence Analysis of the Datasets
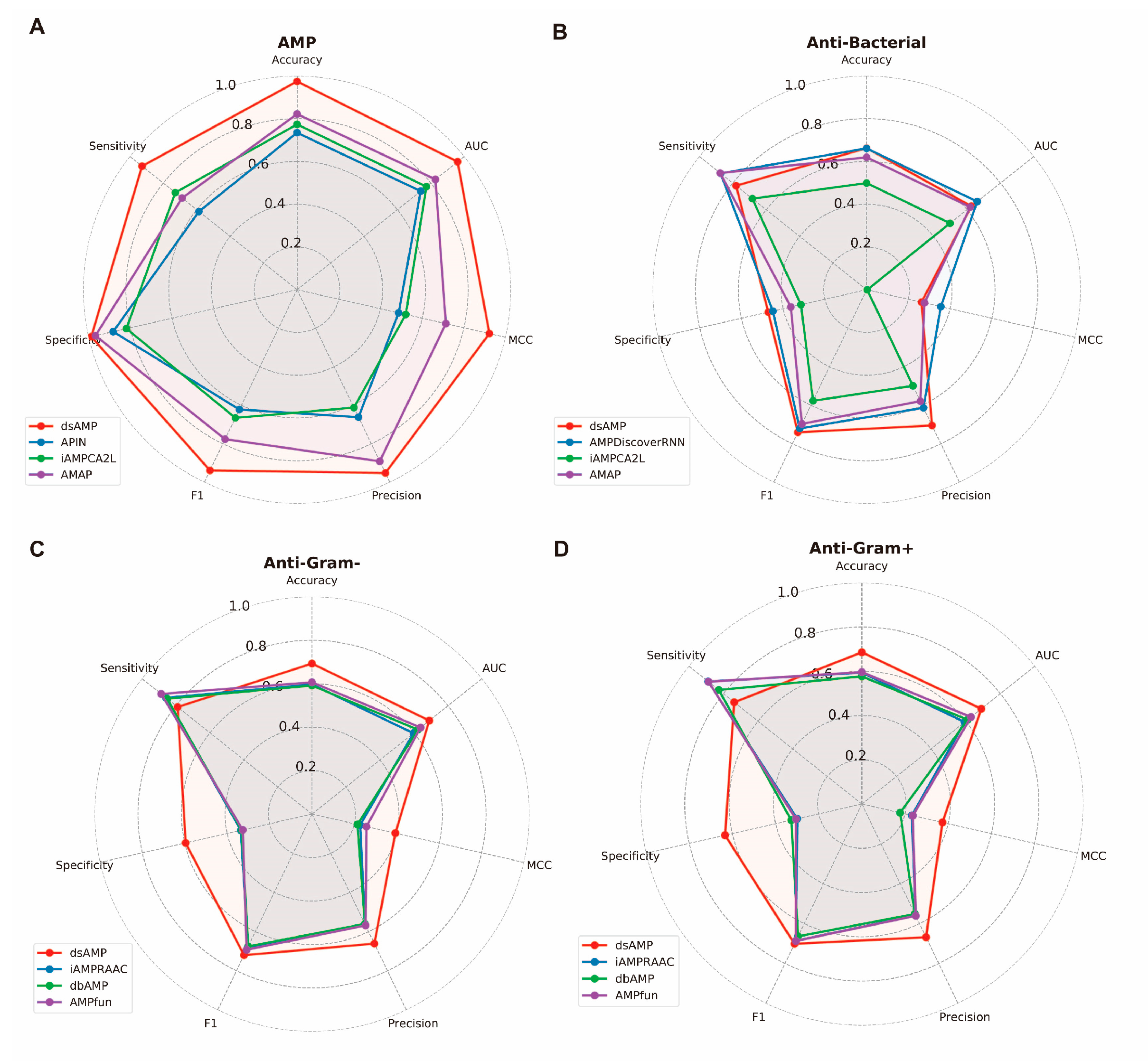
2.2. Comparison of Different ML Methods on AMP Prediction
2.3. Performance of Transfer Learning AMP Prediction Network Targeting Different Bacteria
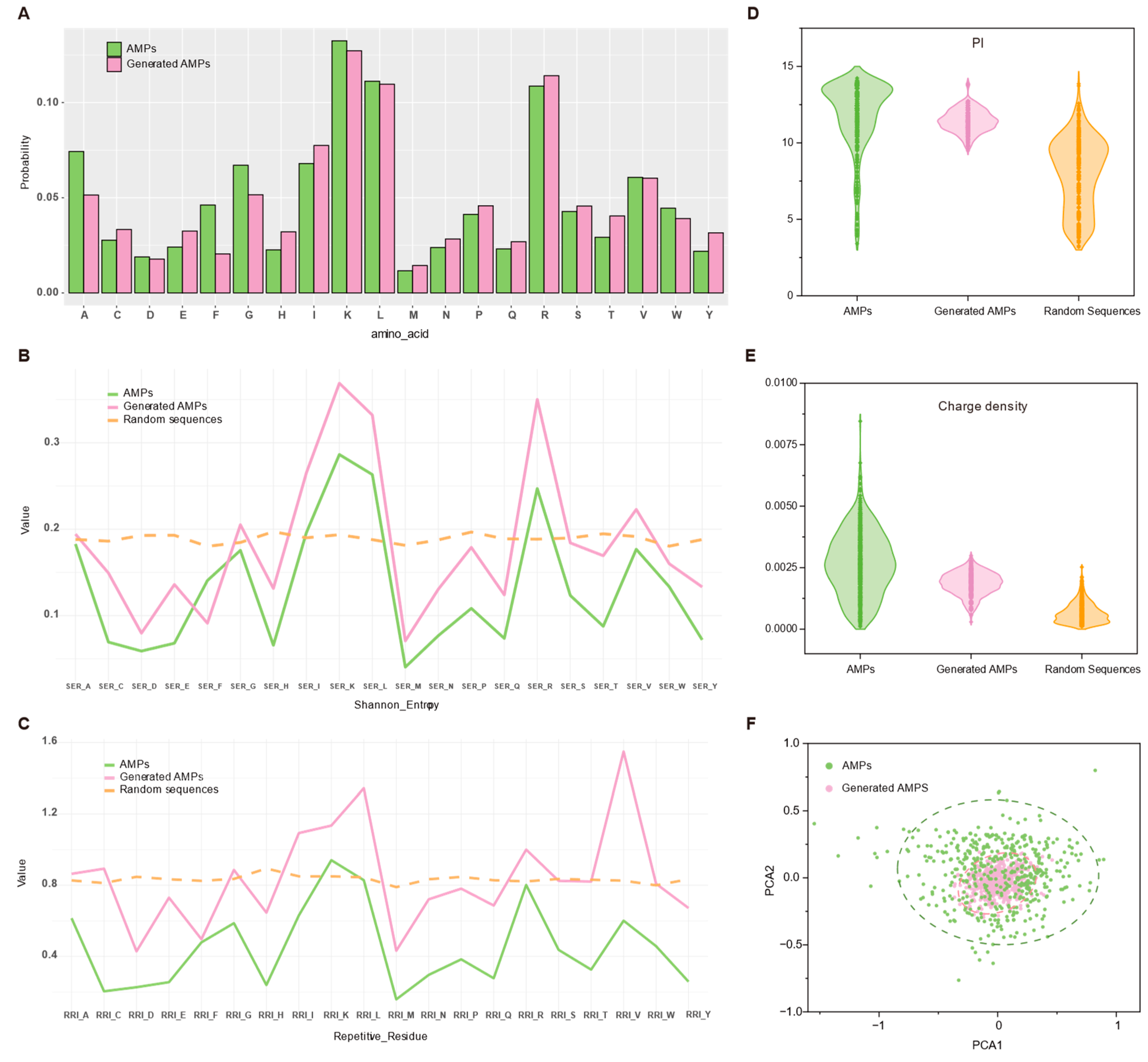
2.4. Evaluating GAN-Designed Peptides
3. Discussion
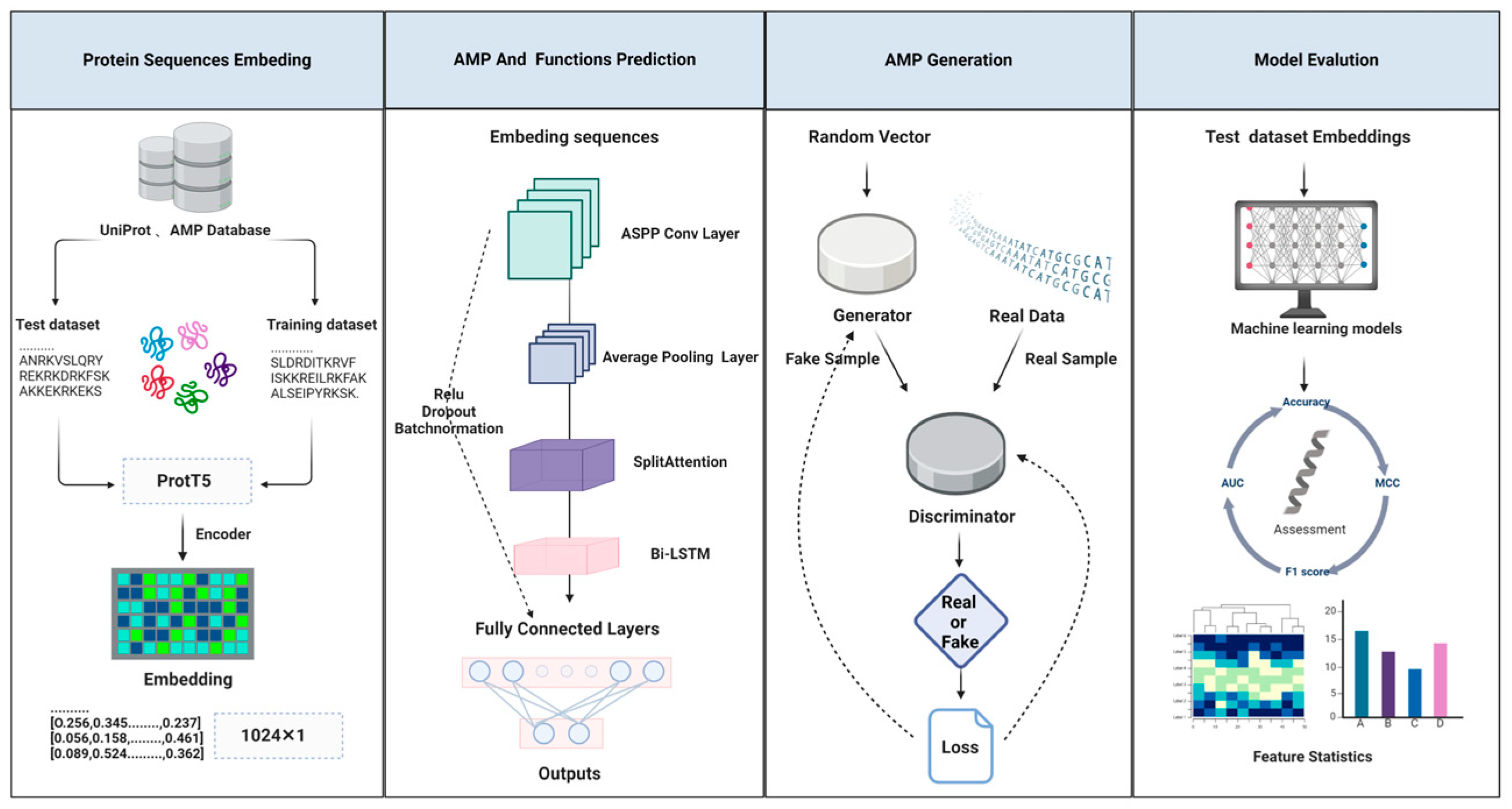
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
4.2. Protein-Encoding Method
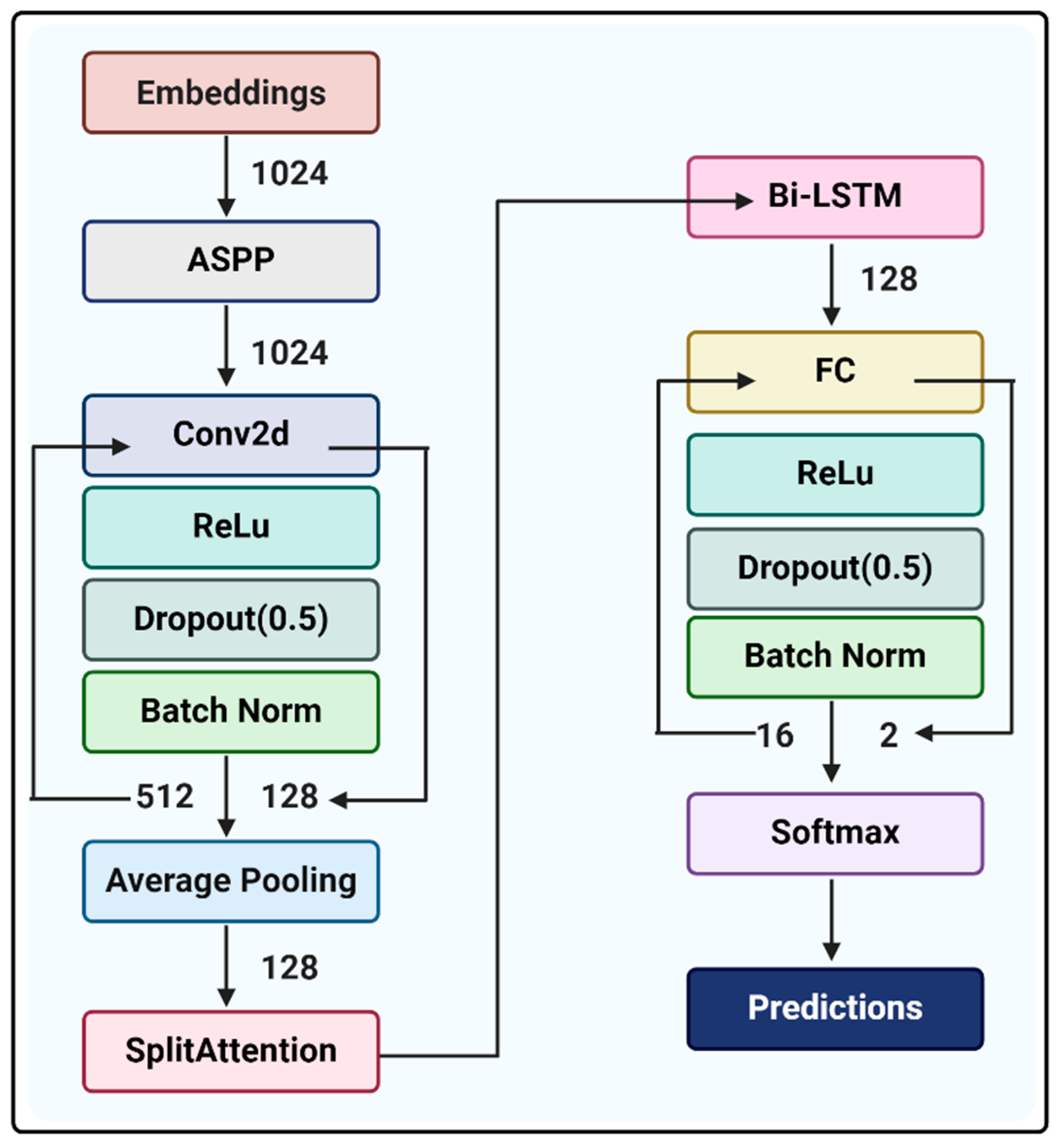
4.3. AMP Predictor Model Construction
4.4. Transfer Learning for AMP Predictive Modelling
4.5. AMP GAN Model Construction
4.6. Model Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: Functions and clinical potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Yan, Z.B.; Meng, Y.M.; Hong, X.Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, X.R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.R.; Kuo, T.R.; Wu, L.C.; Lee, T.Y.; Horng, J.T. Characterization and identification of antimicrobial peptides with different functional activities. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1098–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The value of antimicrobial peptides in the age of resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, L.; Liu, G.; Jiang, N.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Tan, M.; Chen, Z.; et al. Prediction of antimicrobial peptides based on sequence alignment and feature selection methods. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Qureshi, A.; Kumar, M. AVPpred: Collection and prediction of highly effective antiviral peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W199–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Ananth, V.; Shelke, K.; Sehgal, D.; Deepak, J. Classification of anti hepatitis peptides using Support Vector Machine with hybrid Ant Colony Optimization. Bioinformation 2016, 12, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, T.T.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, C.T.; Cheng, W.C.; Lu, I.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, S.H. AI4AVP: An antiviral peptides predictor in deep learning approach with generative adversarial network data augmentation. Bioinform. Adv. 2022, 2, vbac080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Huo, Y.; Dong, G. iAMP-Attenpred: A novel antimicrobial peptide predictor based on BERT feature extraction method and CNN-BiLSTM-Attention combination model. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. APD3: The antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1087–D1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhong, J.H.; Yao, L.; Pang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chung, C.R.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Luo, M.; Ma, R.; et al. dbAMP 2.0: Updated resource for antimicrobial peptides with an enhanced scanning method for genomic and proteomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D460–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Dong, F.; Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Lao, X.; Zheng, H. DRAMP 2.0, an updated data repository of antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, H.; Li, G.; Huang, Q. LAMP: A Database Linking Antimicrobial Peptides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, J.; Kamau, P.M.; Thuku, R.C.; Lai, R. Design methods for antimicrobial peptides with improved performance. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Lv, Z. Using the Random Forest for Identifying Key Physicochemical Properties of Amino Acids to Discriminate Anticancer and Non-Anticancer Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.N.; Walper, S.A. Variational Autoencoder for Generation of Antimicrobial Peptides. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20746–20754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.T.; Hiss, J.A.; Schneider, G. Recurrent Neural Network Model for Constructive Peptide Design. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (NIPS 2014); Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; NIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tucs, A.; Tran, D.P.; Yumoto, A.; Ito, Y.; Uzawa, T.; Tsuda, K. Generating Ampicillin-Level Antimicrobial Peptides with Activity-Aware Generative Adversarial Networks. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22847–22851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.T.; Yang, L.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Wang, C.T.; Lai, C.W.; Ko, C.F.; Shih, Y.H.; Chen, S.H. Intelligent De Novo Design of Novel Antimicrobial Peptides against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, M.; Jiang, B.; Gao, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, T. Antimicrobial Peptides Prediction method based on sequence multidimensional feature embedding. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1069558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Lin, T.T.; Cheng, W.C.; Lu, I.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, S.H. Peptide-Based Drug Predictions for Cancer Therapy Using Deep Learning. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.B.; Chou, K.C. PseAAC: A flexible web server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, A.; Heinzinger, M.; Dallago, C.; Rehawi, G.; Wang, Y.; Jones, L.; Gibbs, T.; Feher, T.; Angerer, C.; Steinegger, M.; et al. ProtTrans: Toward Understanding the Language of Life Through Self-Supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 7112–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liao, L.; Cai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. IVS2vec: A tool of Inverse Virtual Screening based on word2vec and deep learning techniques. Methods 2019, 166, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.; González, M.S.; Boto, A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M. Prediction of Antifungal Activity of Antimicrobial Peptides by Transfer Learning from Protein Pretrained Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirtskhalava, M.; Amstrong, A.A.; Grigolava, M.; Chubinidze, M.; Alimbarashvili, E.; Vishnepolsky, B.; Gabrielian, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Hurt, D.E.; Tartakovsky, M. DBAASP v3: Database of antimicrobial/cytotoxic activity and structure of peptides as a resource for development of new therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D288–D297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosa, G.H.; Papa, J.P. A survey on text generation using generative adversarial networks. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 119, 108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellouki, O.E.; Khedher, M.I.; El-Yacoubi, M.A. Abstract Layer for LeakyReLU for Neural Network Verification Based on Abstract Interpretation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 33401–33413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. CCNet: Criss-Cross Attention for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, M.; Werner, A.; Palt, M. The Proposal of Undersampling Method for Learning from Imbalanced Datasets. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 159, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.T.; Gabernet, G.; Hiss, J.A.; Schneider, G. modlAMP: Python for antimicrobial peptides. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2753–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, A.; Patiyal, S.; Lathwal, A.; Arora, C.; Kaur, D.; Dhall, A.; Mishra, G.; Kaur, H.; Sharma, N.; Jain, S.; et al. Pfeature: A Tool for Computing Wide Range of Protein Features and Building Prediction Models. J. Comput. Biol. 2023, 30, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.E.M.; González-Garcia, M.; Diaz Pico, E.; Moreno-Castillo, E.; Garay, H.E.; Rosi, P.E.; Jimenez, A.M.; Campos-Delgado, J.A.; Rivera, D.G.; Chinea, G.; et al. Design of a helical-stabilized, cyclic, and nontoxic analogue of the peptide cm-p5 with improved antifungal activity. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19081–19095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.F.; Zheng, L.; Huang, S.H.; Gao, J.; Zuo, Y.C. Amino Acid Reduction Can Help to Improve the Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Functional Activities. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 669328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, S.; Shamim, N.; Minhas, F. AMAP: Hierarchical multi-label prediction of biologically active and antimicrobial peptides. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 107, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinacho-Castellanos, S.A.; García-Jacas, C.R.; Gilson, M.K.; Brizuela, C.A. Alignment-Free Antimicrobial Peptide Predictors: Improving Performance by a Thorough Analysis of the Largest Available Data Set. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3141–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, C.F.; Chang, T.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Liao, Y.D. Oligomerization and insertion of antimicrobial peptide TP4 on bacterial membrane and membrane-mimicking surfactant sarkosyl. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.G.; Bartlett, G.J.; Crump, M.P.; Sessions, R.B.; Linden, N.; Faul, C.F.J.; Woolfson, D.N. Local and macroscopic electrostatic interactions in single α-helices. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridyard, K.E.; Overhage, J. The Potential of Human Peptide LL-37 as an Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, S.; Todorov, P.; Staneva, D.; Grozdanov, P.; Nikolova, I.; Grabchev, I. Metal–Peptide Complexes with Antimicrobial Potential for Cotton Fiber Protection. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Y.; Tu, C.H.; Yip, B.S.; Chen, H.L.; Cheng, H.T.; Huang, K.C.; Lo, H.J.; Cheng, J.W. Easy strategy to increase salt resistance of antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4918–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieślik, M.; Bagińska, N.; Górski, A.; Jończyk-Matysiak, E. Human β-Defensin 2 and Its Postulated Role in Modulation of the Immune Response. Cells 2021, 10, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.F.; Hao, Y.D.; Wang, T.Y.; Cai, P.L.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, K.J.; Lin, H.; Lv, H. Prediction of blood-brain barrier penetrating peptides based on data augmentation with Augur. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, T.P.; Loureiro, R.B.; Lisboa, F.V.N.; Peixoto, R.M.; Guimarães, G.A.S.; Cruz, G.O.R.; Araujo, M.M.; Santos, L.L.; Cruz, M.A.S.; Oliveira, E.L.S.; et al. Bias and Unfairness in Machine Learning Models: A Systematic Review on Datasets, Tools, Fairness Metrics, and Identification and Mitigation Methods. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, S.; Arora, P.; Singh, D.; Sahasrabuddhe, D.; Valadi, J. PandoraGAN: Generating antiviral peptides using Generative Adversarial Network. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Shao, Y.T.; Cheng, X.; Stamatovic, B. iAMP-CA2L: A new CNN-BiLSTM-SVM classifier based on cellular automata image for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghu, F.H.; Gopi, L.; Barai, R.S.; Ramteke, P.; Nizami, B.; Idicula-Thomas, S. CAMP: Collection of sequences and structures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1154–D1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Landersdorfer, C.; Shen, H.H.; Peleg, A.Y.; Li, J.; Imoto, S.; Yao, J.; et al. iAMPCN: A deep-learning approach for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional activities. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-T.; Yang, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-T.; Lai, G.-W.; Ko, C.-F.; Shih, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. Discovering Novel Antimicrobial Peptides in Generative Adversarial Network. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathe, M.; Wieprecht, T. Structural features of helical antimicrobial peptides: Their potential to modulate activity on model membranes and biological cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1462, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

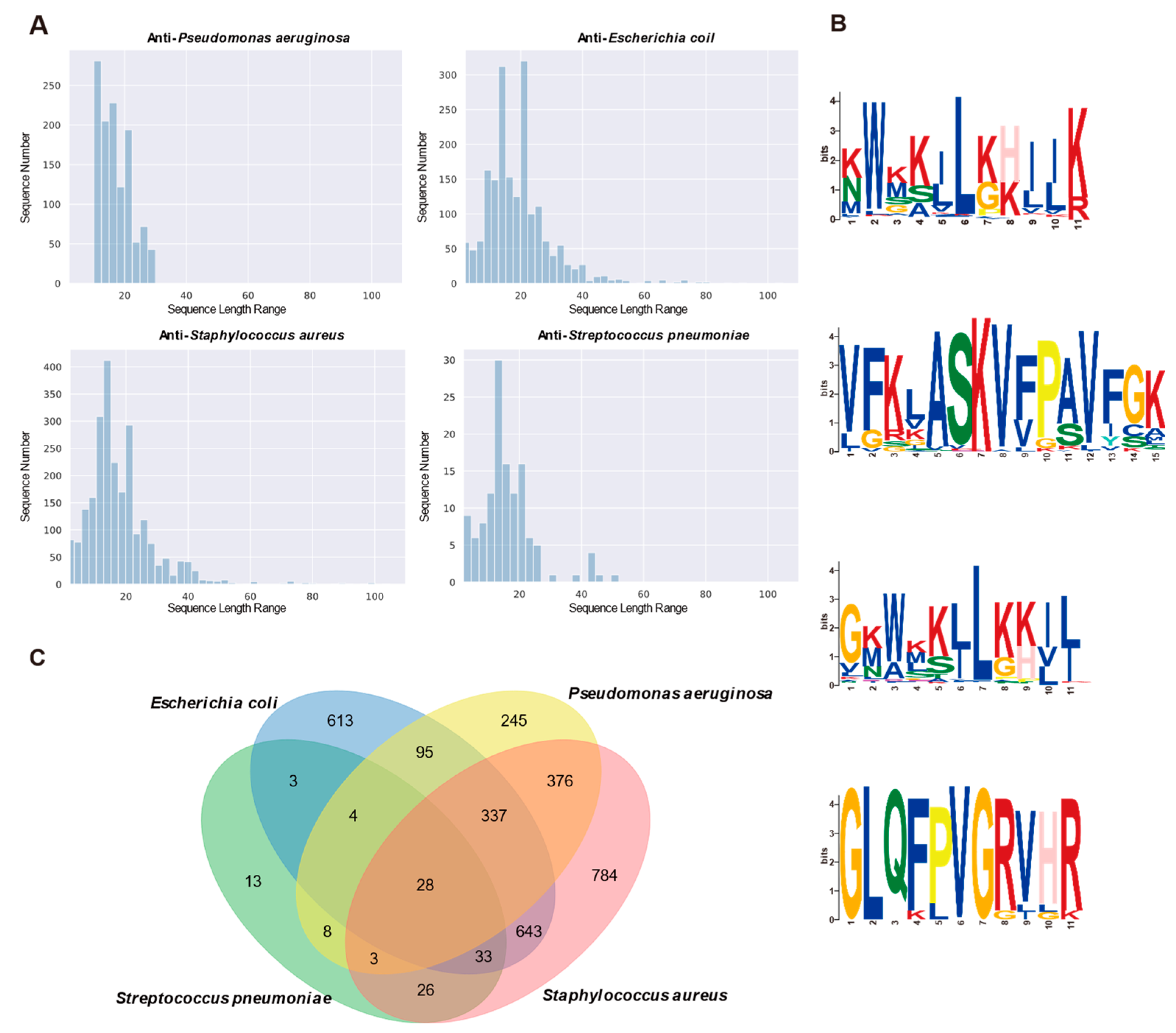
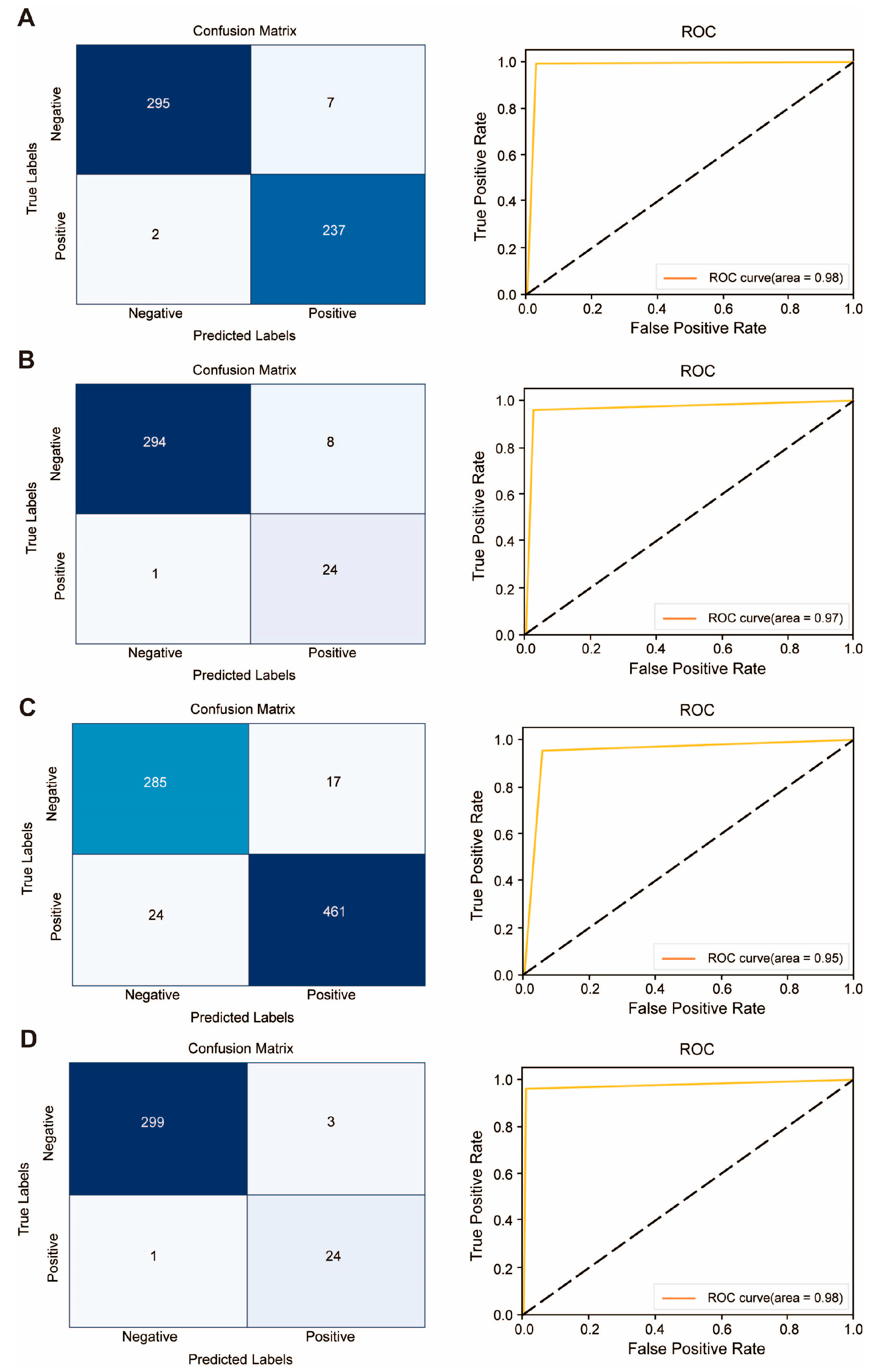

| Evaluation Indicators | Anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Anti- Escherichia coil | Anti-Staphylococcus aureus | Anti-Streptococcus pneumoniae |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9834 | 0.9368 | 0.9479 | 0.9878 |
| Sensitivity | 0.9916 | 0.9499 | 0.9505 | 0.9610 |
| Specificity | 0.9768 | 0.9205 | 0.9437 | 0.9901 |
| Precision | 0.9713 | 0.9375 | 0.9644 | 0.8889 |
| F1 | 0.9814 | 0.9436 | 0.9574 | 0.9230 |
| MCC | 0.9665 | 0.8720 | 0.8905 | 0.9172 |
| Dataset | Negative Samples | Positive Samples |
|---|---|---|
| AMP | 13,560 | 63,838 |
| Anti-Bacterial AMP | 12,055 | 10,573 |
| Anti-Gram+ AMP | 6607 | 10,835 |
| Anti-Gram- AMP | 6745 | 10,730 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, L.Z. dsAMP and dsAMPGAN: Deep Learning Networks for Antimicrobial Peptides Recognition and Generation. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13100948
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Wang M, Ma LZ. dsAMP and dsAMPGAN: Deep Learning Networks for Antimicrobial Peptides Recognition and Generation. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(10):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13100948
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Min, Yu Zhang, Maolin Wang, and Luyan Z. Ma. 2024. "dsAMP and dsAMPGAN: Deep Learning Networks for Antimicrobial Peptides Recognition and Generation" Antibiotics 13, no. 10: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13100948
APA StyleZhao, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., & Ma, L. Z. (2024). dsAMP and dsAMPGAN: Deep Learning Networks for Antimicrobial Peptides Recognition and Generation. Antibiotics, 13(10), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13100948








