Repurposing of Furin Inhibitors to Reduce Pathogenic E. coli- and Shigella flexneri-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mammalian Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
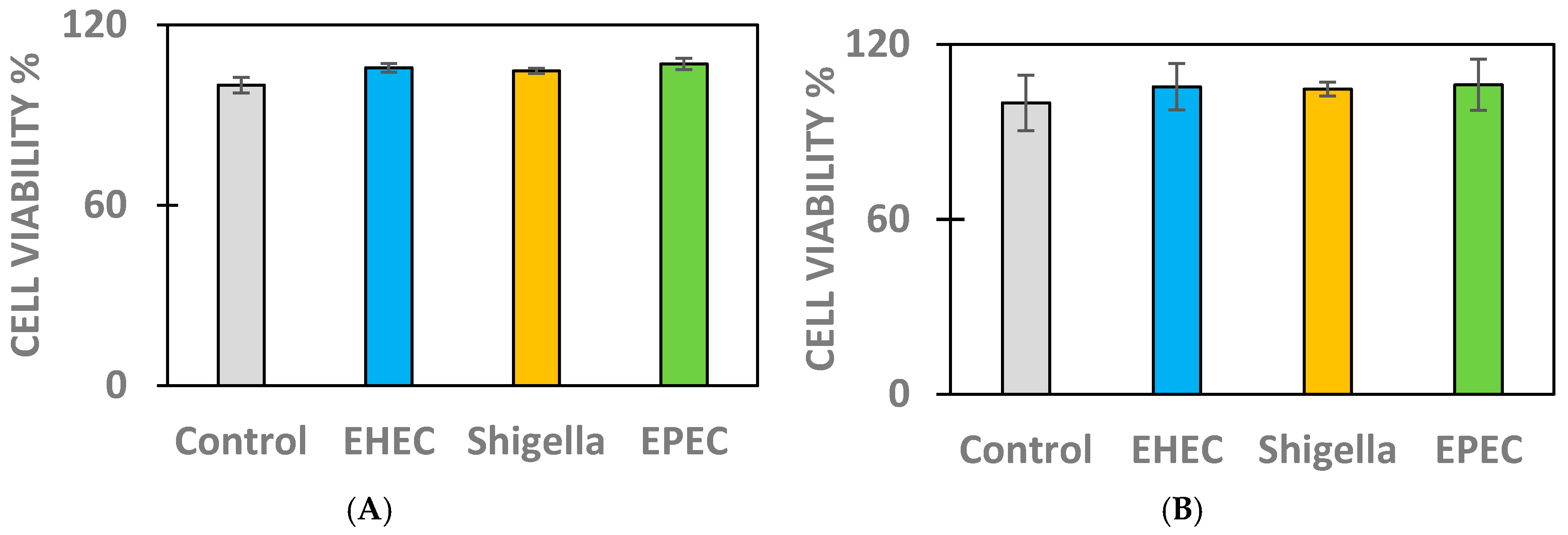
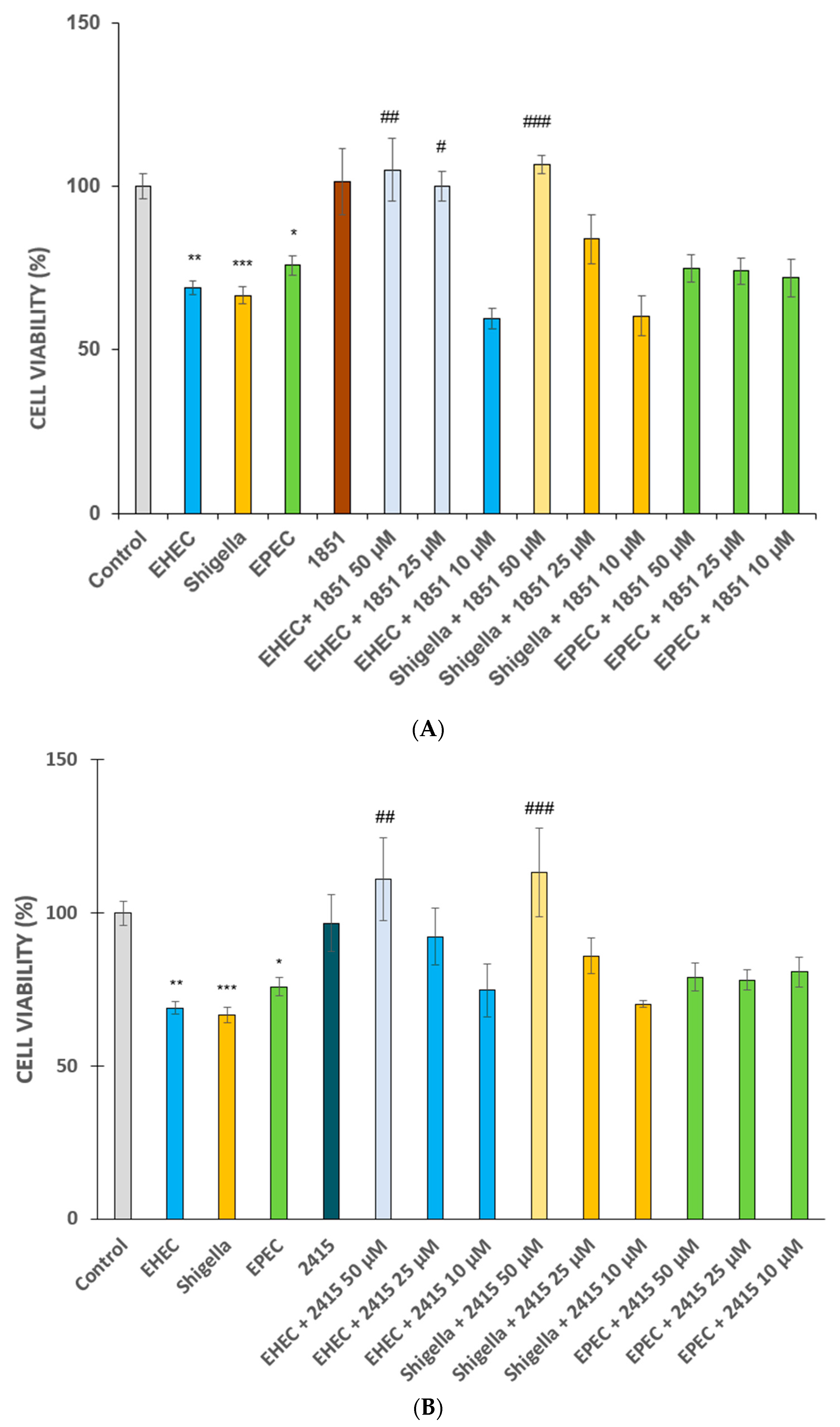
2.1. Cell Viability Measurements in Infected IPEC-J2 and MDCK Cells
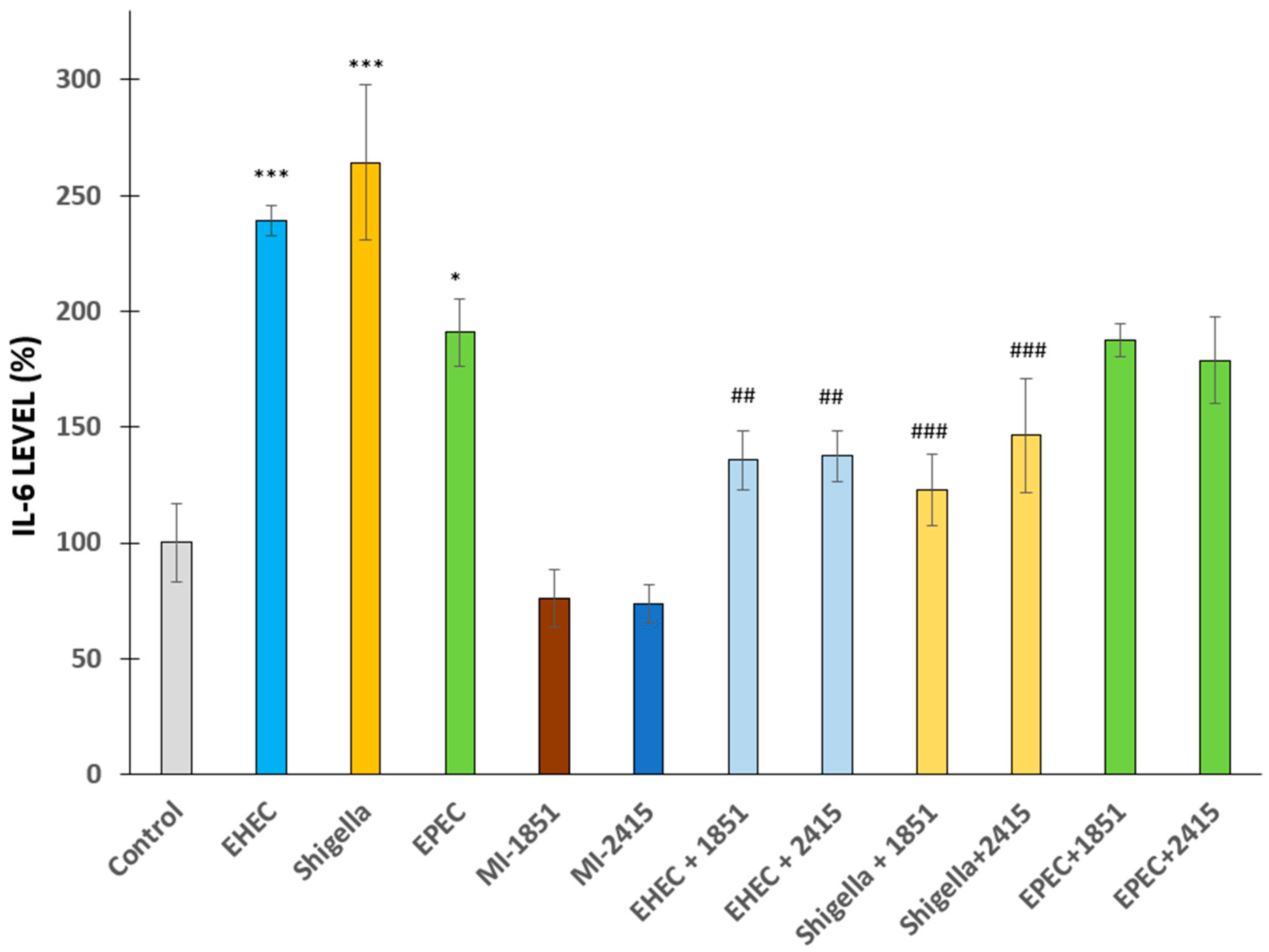
2.2. Changes in Proinflammatory IL-6 Secretion from IPEC-J2 Cells Post-Bacterial Infection
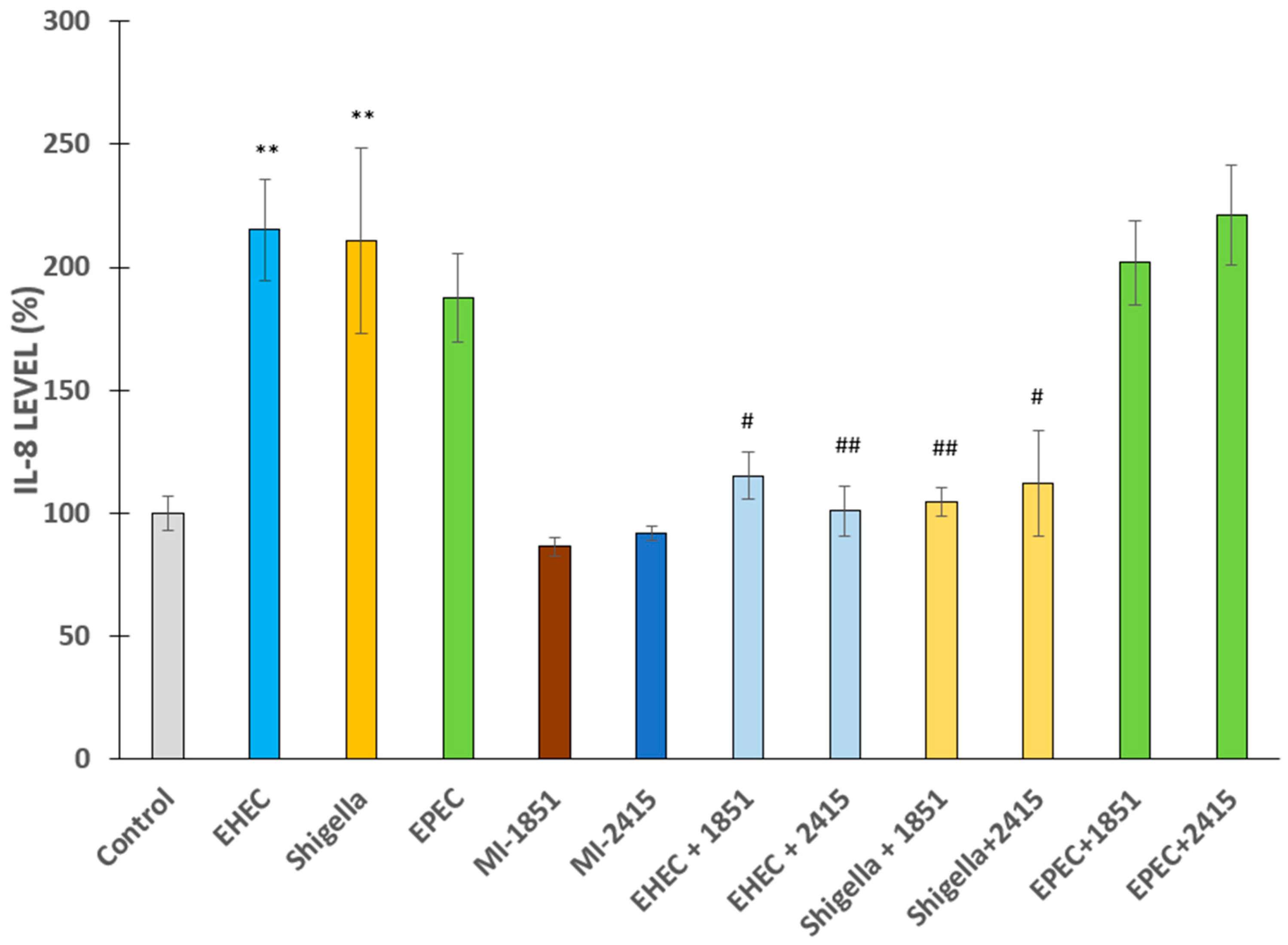
2.3. Proinflammatory IL-8 Production in IPEC-J2 Cells After Bacterial Challenge
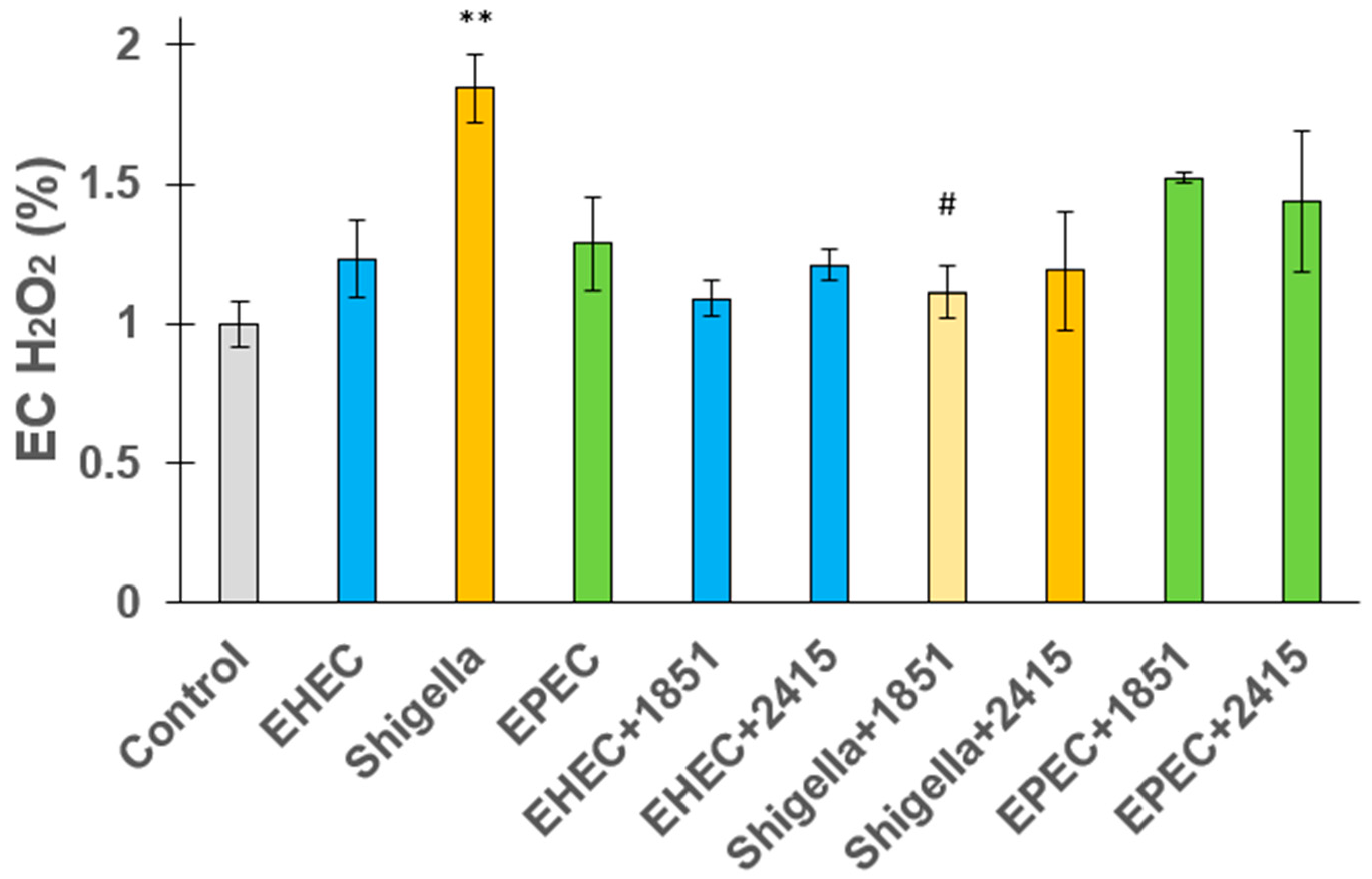
2.4. Extracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Release from Jejunal Epithelial Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Culturing of Epithelial Cells
4.3. Cell Viability Determination of IPEC-J2 and MDCK Cells
4.4. Measurement of IL-6 and IL-8 Production in IPEC-J2 Cells
4.5. Assessment of EC H2O2 Release from IPEC-J2 Cells
4.6. Statistical Evaluation of the Research Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Amba | Amidinobenzylamide |
| Amia | Aminoisoindole |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco modified Eagles medium |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| EC | Extracellular |
| EHEC | Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| EPEC | Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli |
| EspC | E. coli secreted protein C |
| ETA | Exotoxin A |
| ETEC | Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli |
| EU | European Union |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HIOs | Human intestinal organoids |
| HUS | Hemolytic uremic syndrome |
| IL-6/IL-8 | Interleukin-6/-8 |
| IPEC-J2 | Intestinal porcine epithelial cell line |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MDCK | Madin-Darby kidney epithelial cell line |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| Stx1 and Stx2 | Shiga-like toxins |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor—alpha |
References
- Nash, J.H.; Villegas, A.; Kropinski, A.M.; Aguilar-Valenzuela, R.; Konczy, P.; Mascarenhas, M.; Ziebell, K.; Torres, A.G.; Karmali, M.A.; Coombes, B.K. Genome Sequence of Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli and Comparative Genomic Analysis with Other E. coli Pathotypes. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnenberg, M. (Ed.) Escherichia coli: Pathotypes and Principles of Pathogenesis, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-0-12-397048-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W.A. Virulence Factors of Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattock, E.; Blocker, A.J. How Do the Virulence Factors of Shigella Work Together to Cause Disease? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Parsons, B.D.; Szelewicki, J.; Yuen, Y.T.K.; Fach, P.; Delannoy, S.; Li, V.; Ferrato, C.; Freedman, S.B.; Lee, B.E.; et al. Identification of Shiga-Toxin-Producing Shigella Infections in Travel and Non-Travel Related Cases in Alberta, Canada. Toxins 2021, 13, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G. Furin at the Cutting Edge: From Protein Traffic to Embryogenesis and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivachtchenko, A.V.; Khvat, A.V.; Shkil, D.O. Development and Prospects of Furin Inhibitors for Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, E.; Sauter, D. Furin-Mediated Protein Processing in Infectious Diseases and Cancer. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2019, 8, e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenk, H.D.; Rott, R. The Molecular Biology of Influenza Virus Pathogenicity. Adv. Virus Res. 1988, 34, 247–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, L.V.; Hamilton, A.M.; Friling, T.; Whittaker, G.R. A Novel Activation Mechanism of Avian Influenza Virus H9N2 by Furin. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestle, D.; Heindl, M.R.; Limburg, H.; Van Lam van, T.; Pilgram, O.; Moulton, H.; Stein, D.A.; Hardes, K.; Eickmann, M.; Dolnik, O.; et al. TMPRSS2 and Furin Are Both Essential for Proteolytic Activation of SARS-CoV-2 in Human Airway Cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Molina, B.; Lick, A.N.; Blanco, E.H.; Posada-Salgado, J.A.; Martinez-Mayorga, K.; Johnson, A.T.; Jiao, G.-S.; Lindberg, I. Identification of Potent and Compartment-Selective Small Molecule Furin Inhibitors Using Cell-Based Assays. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 96, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmanova, A.; Llorente, A.; Polesskaya, A.; Garred, O.; Olsnes, S.; Kozlov, J.; Sandvig, K. Structural Requirements for Furin-Induced Cleavage and Activation of Shiga Toxin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanenko, V.; Malyukova, I.; Hubbard, A.; Delannoy, M.; Boedeker, E.; Zhu, C.; Cebotaru, L.; Kovbasnjuk, O. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection Stimulates Shiga Toxin 1 Macropinocytosis and Transcytosis across Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C1140–C1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garred, O.; Dubinina, E.; Holm, P.K.; Olsnes, S.; van Deurs, B.; Kozlov, J.V.; Sandvig, K. Role of Processing and Intracellular Transport for Optimal Toxicity of Shiga Toxin and Toxin Mutants. Exp. Cell Res. 1995, 218, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garred, O.; van Deurs, B.; Sandvig, K. Furin-Induced Cleavage and Activation of Shiga Toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10817–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardes, K.; Ivanova, T.; Thaa, B.; McInerney, G.M.; Klokk, T.I.; Sandvig, K.; Künzel, S.; Lindberg, I.; Steinmetzer, T. Elongated and Shortened Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of the Proprotein Convertase Furin. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, M.; Fryling, C.M.; Pastan, I.; FitzGerald, D.J. Cell-Mediated Cleavage of Pseudomonas Exotoxin between Arg279 and Gly280 Generates the Enzymatically Active Fragment Which Translocates to the Cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 25396–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachran, C.; Leppla, S.H. Tumor Targeting and Drug Delivery by Anthrax Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacle, A.G.; Gawlik, K.; Golubkov, V.S.; Cadwell, G.W.; Liddington, R.C.; Cieplak, P.; Millis, S.Z.; Desjardins, R.; Routhier, S.; Yuan, X.W.; et al. Selective and Potent Furin Inhibitors Protect Cells from Anthrax without Significant Toxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, M.S.; Peinado, J.R.; Leppla, S.H.; Lindberg, I. Protection against anthrax toxemia by hexa-d-arginine in vitro and in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, M.S.; Cameron, A.; Lindberg, I. The furin inhibitor hexa-d-arginine blocks the activation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 7136–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.B.; van de Kar, N.C.A.J.; Tarr, P.I. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and the Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthc. Basel Switz. 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, E.S.; Odoom, A.; Osman, A.-H.; Darkwah, S.; Kotey, F.C.N. A Systematic Review on Antimicrobial Resistance in Ghana from a One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husna, A.; Rahman, M.; Badruzzaman, A.T.M.; Sikder, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, T.; Alam, J.; Ashour, H.M. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBL): Challenges and Opportunities. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.; Müller, A.; Grabowski, N.T.; Kehrenberg, C.; Muylkens, B.; Al Dahouk, S. Foodborne Diseases Do Not Respect Borders: Zoonotic Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Food Products of Animal Origin Illegally Imported into the European Union. Vet. J. Lond. Engl. 1997 2019, 244, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Treatment Strategies for Infections with Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, D.; Grif, K.; Zimmerhackl, L.B.; Würzner, R. Prevention and Treatment of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infections in Humans. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2008, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, M.E.; Patfield, S.; Hughes, A.C.; Hernlem, B.; He, X. A Novel Shiga Toxin 2a Neutralizing Antibody Therapeutic with Low Immunogenicity and High Efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2024, 68, e0059823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palócz, O.; Pászti-Gere, E.; Gálfi, P.; Farkas, O. Chlorogenic Acid Combined with Lactobacillus Plantarum 2142 Reduced LPS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in IPEC-J2 Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palkovicsné Pézsa, N.; Kovács, D.; Gálfi, P.; Rácz, B.; Farkas, O. Effect of Enterococcus Faecium NCIMB 10415 on Gut Barrier Function, Internal Redox State, Proinflammatory Response and Pathogen Inhibition Properties in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palkovicsné Pézsa, N.; Kovács, D.; Somogyi, F.; Karancsi, Z.; Móritz, A.V.; Jerzsele, Á.; Rácz, B.; Farkas, O. Effects of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus DSM7133 on Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cells. Animals 2023, 13, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; He, W. The Application of Organoids in Cancers Associated with Pathogenic Infections. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, C.C.H.; Lambert, M.; Rogers, K.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Van Oijen, A.M.; Keighley, C.; Taxis, K.; Robertson, H.; Pont, L.G. One Health Determinants of Escherichia coli Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans in the Community: An Umbrella Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. The Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in the WHO European Region in 2019: A Cross-Country Systematic Analysis. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e897–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouma, M.; Madec, J.-Y.; Laxminarayan, R. Colistin: From the Shadows to a One Health Approach for Addressing Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 61, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, B.; Ebrahimi, A.; Hariri, B.; Sokouti, Z.; Kazemi, N.; Moradi, N. Frequencies of Mobilized Colistin Resistance (Mcr-1, 2) Genes in Clinically Isolated Escherichia coli; a Cross Sectional Study. BMC Res. Notes 2023, 16, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.T.; Cunha, M.V.; Araujo, D.; Ferreira, H.; Fonseca, C.; Palmeira, J.D. Emergence of Colistin Resistance Genes (Mcr-1) in Escherichia coli among Widely Distributed Wild Ungulates. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2021, 291, 118136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardes, K.; Becker, G.L.; Lu, Y.; Dahms, S.O.; Köhler, S.; Beyer, W.; Sandvig, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Lindberg, I.; Walz, L.; et al. Novel Furin Inhibitors with Potent Anti-Infectious Activity. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluck, S.; Bobrovsky, R.; Poór, M.; Lange, R.W.; Steinmetzer, T.; Jerzsele, Á.; Adorján, A.; Bajusz, D.; Rácz, A.; Pászti-Gere, E. In Vitro Evaluation of Antipseudomonal Activity and Safety Profile of Peptidomimetic Furin Inhibitors. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavaliauskiene, S.; Dyve Lingelem, A.B.; Skotland, T.; Sandvig, K. Protection against Shiga Toxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.L.; Lu, Y.; Hardes, K.; Strehlow, B.; Levesque, C.; Lindberg, I.; Sandvig, K.; Bakowsky, U.; Day, R.; Garten, W.; et al. Highly Potent Inhibitors of Proprotein Convertase Furin as Potential Drugs for Treatment of Infectious Diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21992–22003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zhai, J.-L.; Wang, Y.-T.; Guo, P.-T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.-K.; Jin, L.; Gao, Y.-Y. Potassium Diformate Alleviated Inflammation of IPEC-J2 Cells Infected with EHEC. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 291, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chu, B.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, D. Exopolysaccharides from Bifidobacterium Animalis Ameliorate Escherichia coli-Induced IPEC-J2 Cell Damage via Inhibiting Apoptosis and Restoring Autophagy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Donato, K.A.; Shen-Tu, G.; Gordanpour, M.; Sherman, P.M. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Strain GG Prevents Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-Induced Changes in Epithelial Barrier Function. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.W.; El-Nezami, H.; Shah, N.P. The Protective Effects of Enriched Citrulline Fermented Milk with Lactobacillus Helveticus on the Intestinal Epithelium Integrity against Escherichia coli Infection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingspor, S.; Bondzio, A.; Martens, H.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Bratz, K.; Tedin, K.; Einspanier, R.; Lodemann, U. Enterococcus Faecium NCIMB 10415 Modulates Epithelial Integrity, Heat Shock Protein, and Proinflammatory Cytokine Response in Intestinal Cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 304149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriendt, B.; Stuyven, E.; Verdonck, F.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Cox, E. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (K88) Induce Proinflammatory Responses in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwaba, S.E.; Costa, D.V.S.; Bolick, D.T.; Giallourou, N.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Swann, J.R.; Traore, A.N.; Potgieter, N.; Nataro, J.P.; Guerrant, R.L. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Induces Diarrhea, Intestinal Damage, Metabolic Alterations, and Increased Intestinal Permeability in a Murine Model. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 595266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karancsi, Z.; Kovács, D.; Palkovicsné Pézsa, N.; Gálfi, P.; Jerzsele, Á.; Farkas, O. The Impact of Quercetin and Its Methylated Derivatives 3-o-Methylquercetin and Rhamnazin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Porcine Intestinal Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-García, F.; Canizalez-Roman, A.; Sui, B.Q.; Nataro, J.P.; Azamar, Y. The serine protease motif of EspC from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli produces epithelial damage by a mechanism different from that of Pet toxin from enteroaggregative E. coli. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3609–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilapitiya, A.U.; Hor, L.; Pan, J.; Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Pike, R.N.; Leyton, D.L.; Paxman, J.J.; Heras, B. The crystal structure of the toxin EspC from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli reveals the mechanism that governs host cell entry and cytotoxicity. Gut Microbes. 2025, 17, 2483777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, R.; Abderrazek, B.; Sana, F.; Ahmed, S.; Mariem, Z.; Lamia, K.; Asma, F.; Ben Slama, M.R.; Ilhem, B.B.B. Molecular Mechanisms Impact on Fluoroquinolone Resistance among E. coli from Enteric Carriage Monitoring before Prostate Biopsy and Earliest Description of qnrB81. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam van, T.V.; Heindl, M.R.; Schlutt, C.; Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, E.; Bartenschlager, R.; Klebe, G.; Brandstetter, H.; Dahms, S.O.; Steinmetzer, T. The Basicity Makes the Difference: Improved Canavanine-Derived Inhibitors of the Proprotein Convertase Furin. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.W.; Bloch, K.; Heindl, M.R.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Weiss, M.S.; Brandstetter, H.; Klebe, G.; Falcone, F.H.; Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, E.; Dahms, S.O.; et al. Fragment-Based Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of Aminoisoindole-Derived Furin Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rumer, I.; Tóth, L.; Wohlert, A.; Adorján, A.; Jerzsele, Á.; Lange, R.W.; Steinmetzer, T.; Gere-Pászti, E. Repurposing of Furin Inhibitors to Reduce Pathogenic E. coli- and Shigella flexneri-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mammalian Epithelial Cells. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050431
Rumer I, Tóth L, Wohlert A, Adorján A, Jerzsele Á, Lange RW, Steinmetzer T, Gere-Pászti E. Repurposing of Furin Inhibitors to Reduce Pathogenic E. coli- and Shigella flexneri-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mammalian Epithelial Cells. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050431
Chicago/Turabian StyleRumer, Isabella, Lilla Tóth, Annelie Wohlert, András Adorján, Ákos Jerzsele, Roman W. Lange, Torsten Steinmetzer, and Erzsébet Gere-Pászti. 2025. "Repurposing of Furin Inhibitors to Reduce Pathogenic E. coli- and Shigella flexneri-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mammalian Epithelial Cells" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050431
APA StyleRumer, I., Tóth, L., Wohlert, A., Adorján, A., Jerzsele, Á., Lange, R. W., Steinmetzer, T., & Gere-Pászti, E. (2025). Repurposing of Furin Inhibitors to Reduce Pathogenic E. coli- and Shigella flexneri-Induced Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mammalian Epithelial Cells. Antibiotics, 14(5), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050431






