Thermoplastic Zinc-Infused Polymer for Chairside Socket Seal Abutments Enhances Antimicrobial and Tissue-Integrative Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
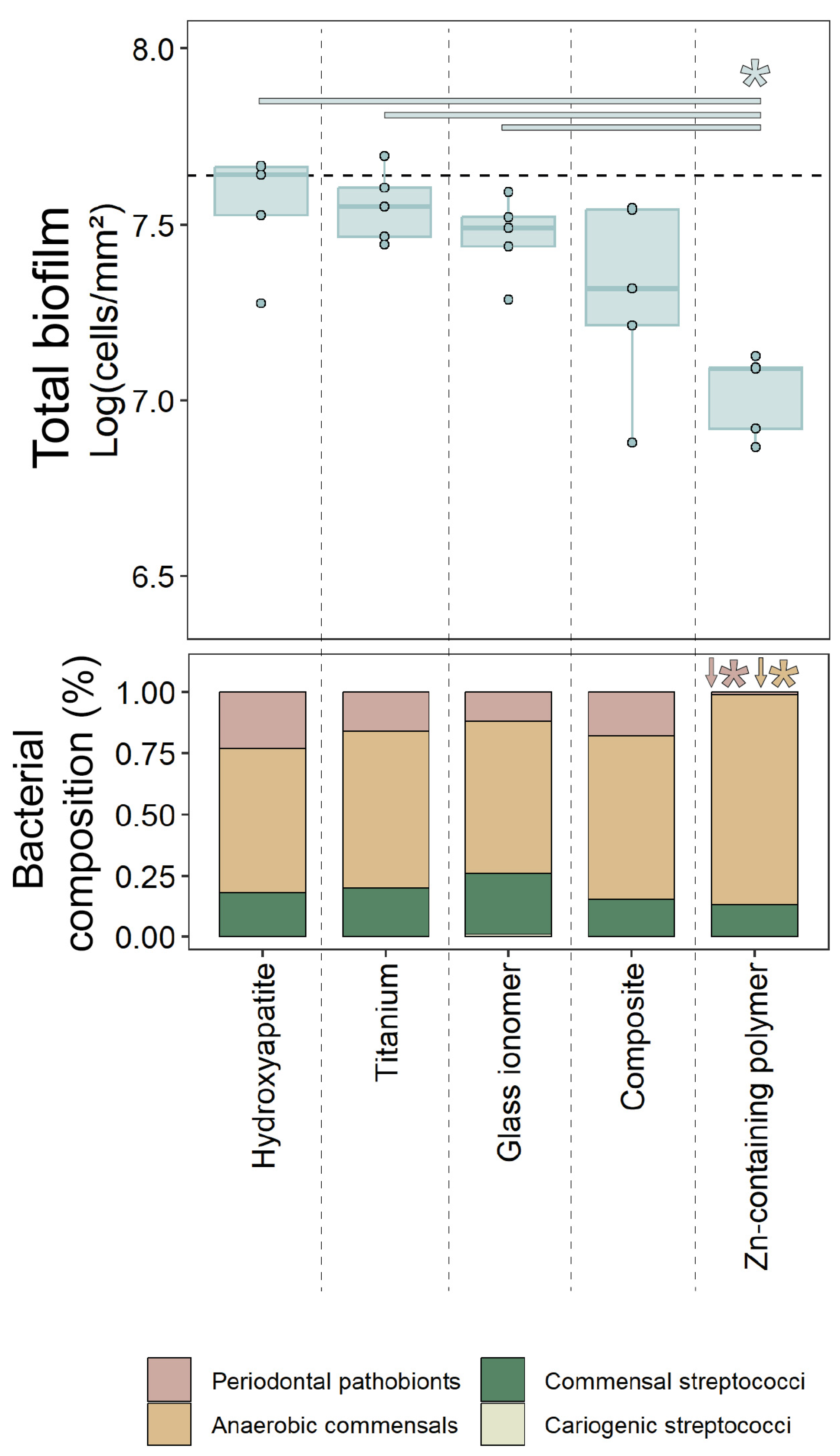
2.1. Oral Biofilm Growth
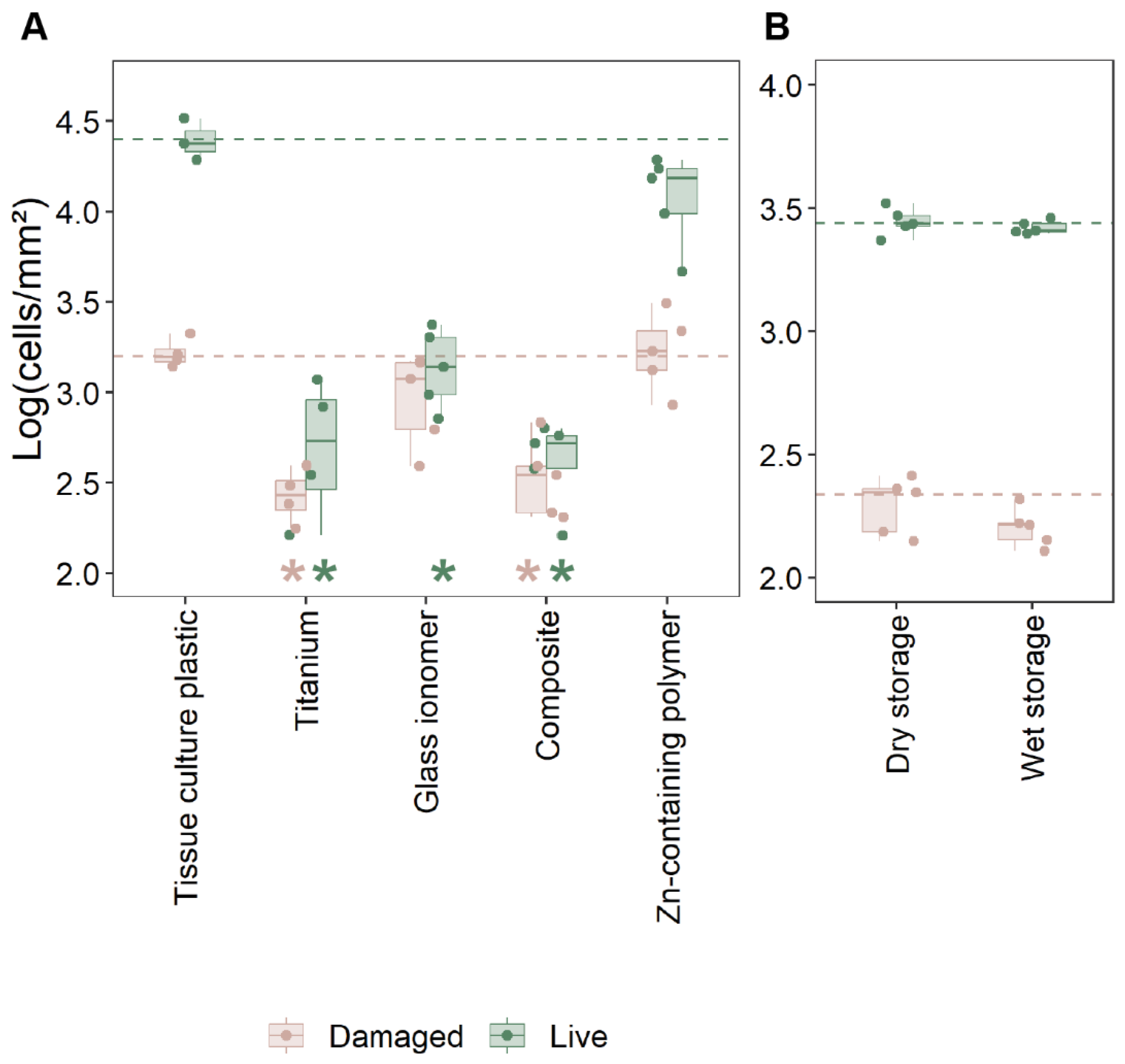
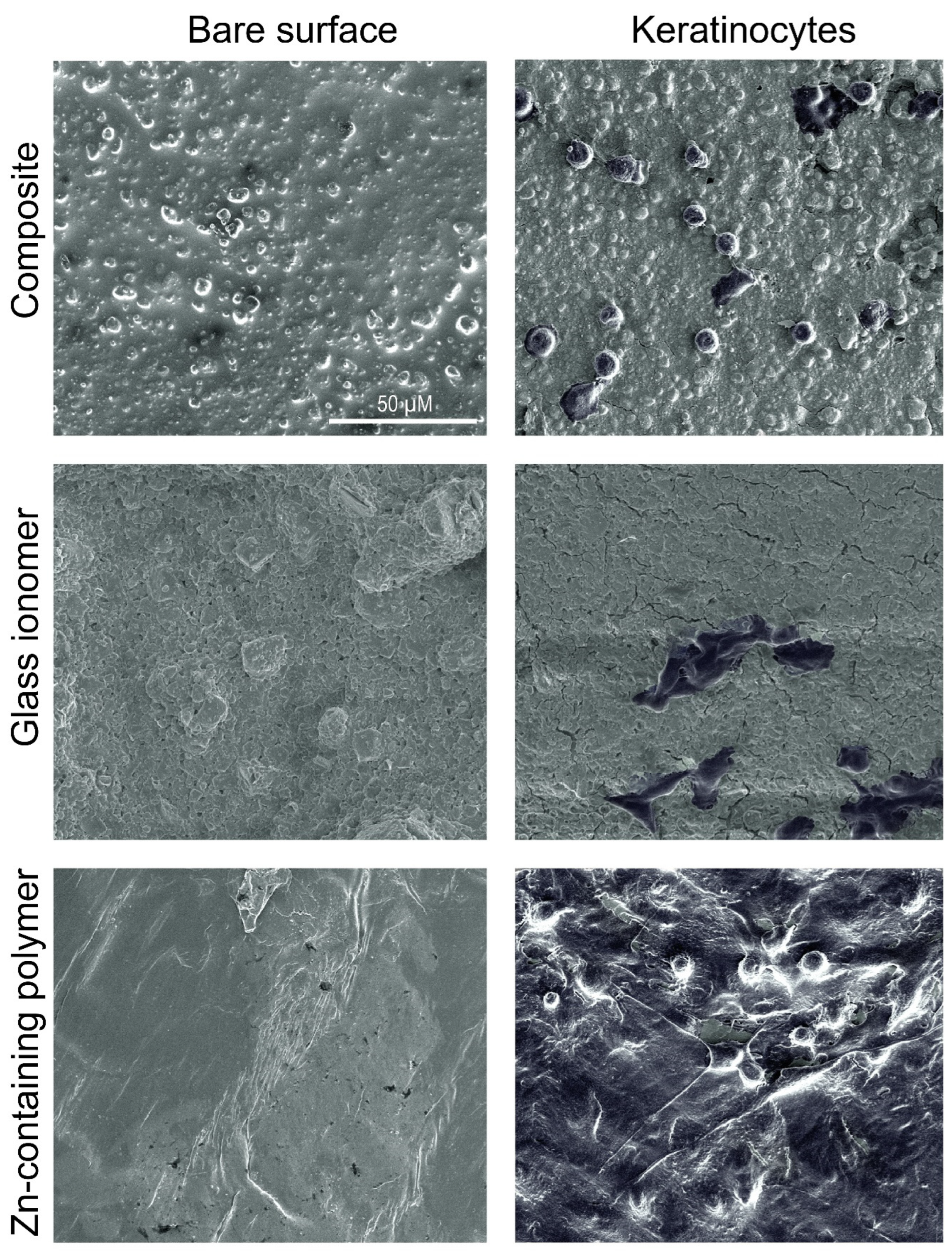
2.2. Cell Adhesion and Viability
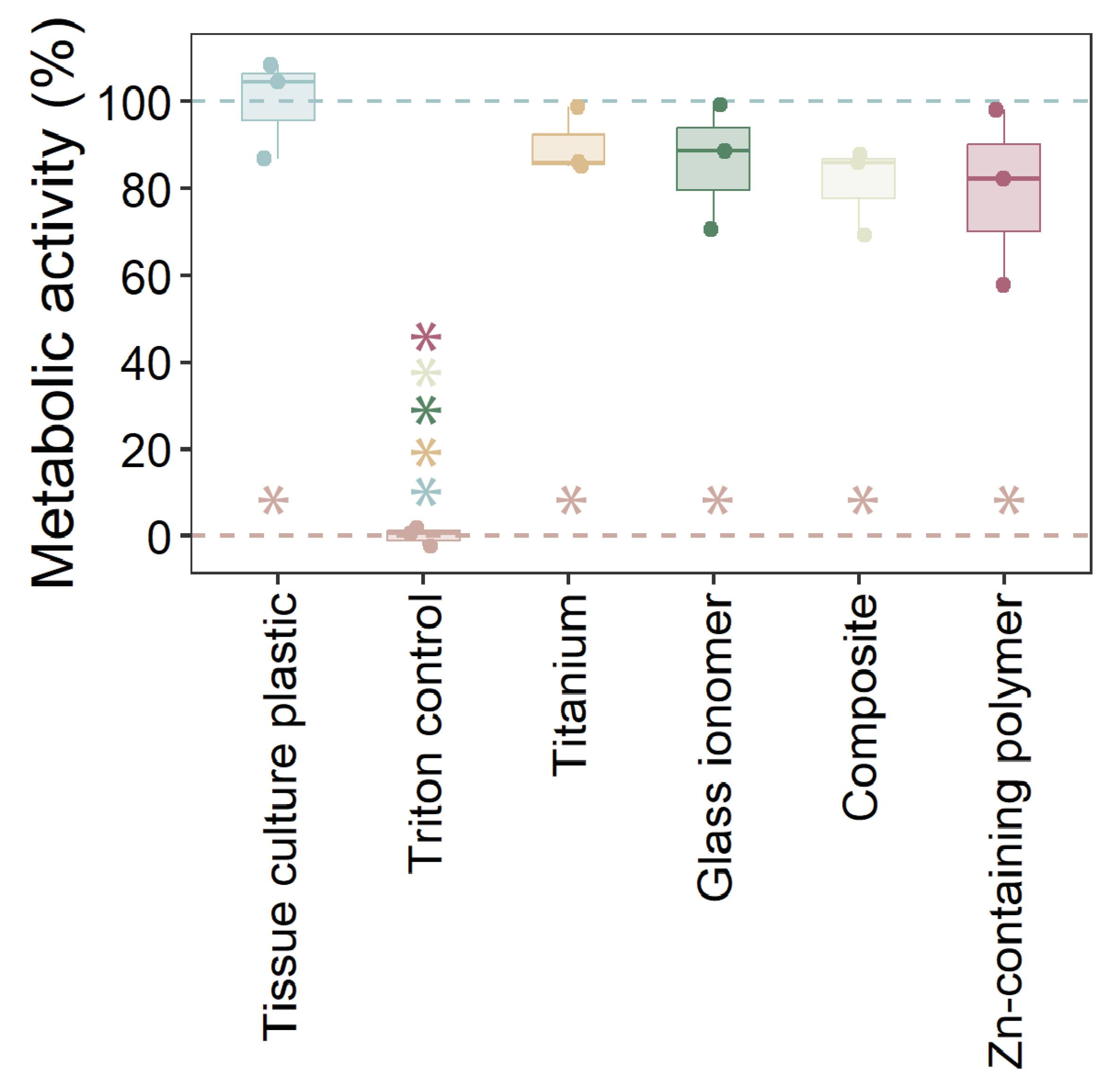
2.3. Cytotoxicity of Materials
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
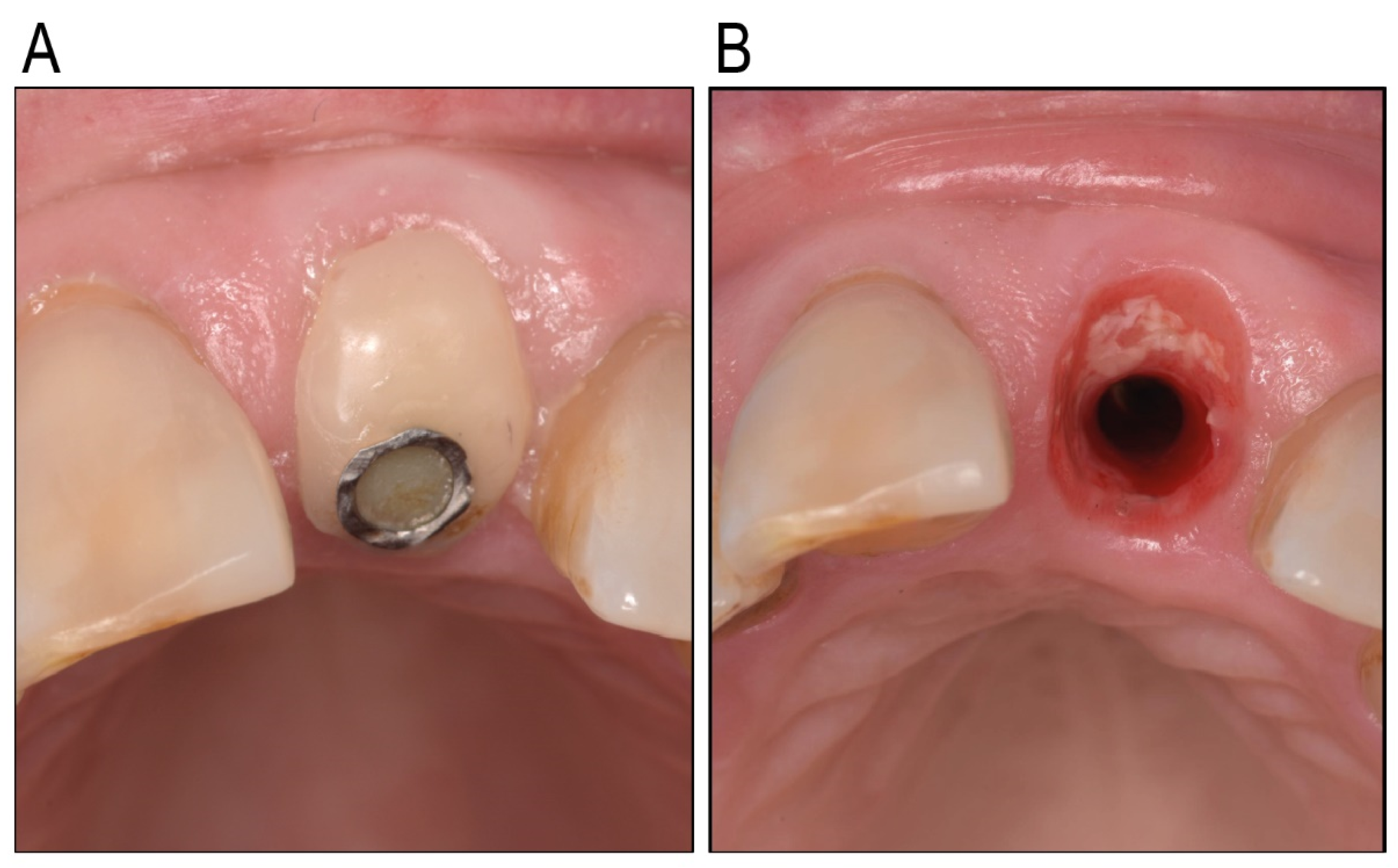
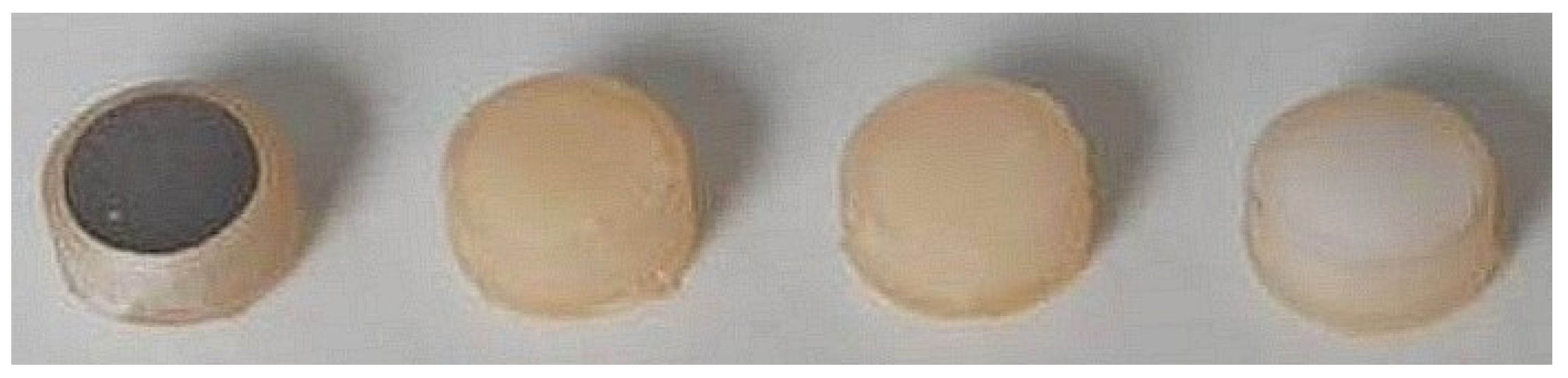
4.1. Investigated Materials
4.2. Bacterial and Biofilm Growth on the Materials
4.3. Epithelial Cells
4.4. Cell Adhesion to Materials—Cell Viability
4.5. Cytotoxicity of Materials—Metabolic Activity
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Zn | Zinc |
| HOK-18A | Human oral keratinocyte cell line |
| SSA | Socket seal abutments |
| v-qPCR | Viability quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Cooper, L.F.; Reside, G.J.; Raes, F.; Garriga, J.S.; Tarrida, L.G.; Wiltfang, J.; Kern, M.; De Bruyn, H. Immediate provisionalization of dental implants placed in healed alveolar ridges and extraction sockets: A 5-year prospective evaluation. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyn, H.; Raes, F.; Cooper, L.F.; Reside, G.; Garriga, J.S.; Tarrida, L.G.; Wiltfang, J.; Kern, M. Three-years clinical outcome of immediate provisionalization of single Osseospeed(™) implants in extraction sockets and healed ridges. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihali, S.F.P.C.; Bratu, E.A. Maintaining Tissue Architecture in Immediate Implant Placement Following Extraction of Natural Teeth Using Custom Healing Screw. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchini-Fabris, G.B.; Crespi, R.; Toti, P.; Crespi, G.; Rubino, L.; Covani, U. A 3-year retrospective study of fresh socket implants: CAD/CAM customized healing abutment vs cover screws. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2020, 23, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finelle, G.; Popelut, A.; Knafo, B.; Martín, I.S. Sealing Socket Abutments (SSAs) in Molar Immediate Implants with a Digitalized CAD/CAM Protocol: Soft Tissue Contour Changes and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2021, 41, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, R. A New Concept in Maintaining the Emergence Profile in Immediate Posterior Implant Placement: The Anatomic Harmony Abutment. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finelle, G.; Lee, S.J. Guided Immediate Implant Placement with Wound Closure by Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Assisted Manufacture Sealing Socket Abutment: Case Report. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, e63–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, R.; Colombo, M.; Rizzo, K.; Di Cristofaro, A.; Poggio, C.; Pietrocola, G. Cytotoxicity of Different Composite Resins on Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell Lines. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Van Noort, R.; Brook, I.M.; Scutt, A.M. Cytotoxicity of resin monomers on human gingival fibroblasts and HaCaT keratinocytes. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichl, F.X.; Esters, M.; Simon, S.; Seiss, M.; Kehe, K.; Kleinsasser, N.; Folwaczny, M.; Glas, J.; Hickel, R. Cell death effects of resin-based dental material compounds and mercurials in human gingival fibroblasts. Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.S.; Jung, U.W.; Gil, A.; Kim, M.J.; Paeng, K.W.; Jung, R.E.; Fickl, S. The effects of hard and soft tissue grafting and individualization of healing abutments at immediate implants: An experimental study in dogs. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2019, 49, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Ramanauskaite, A. It is all about peri-implant tissue health. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms Committee of the Academy of Prosthodontics. The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms: Ninth Edition. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 117, e1–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Z. Comparing the Clinical Outcome of Peri-implant Hard and Soft Tissue Treated with Immediate Individualized CAD/CAM Healing Abutments and Conventional Healing Abutments for Single-Tooth Implants in Esthetic Areas Over 12 Months: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokaree, P.; Poovarodom, P.; Chaijareenont, P.; Yavirach, A.; Rungsiyakull, P. Biomaterials and Clinical Applications of Customized Healing Abutment-A Narrative Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokaree, P.; Poovarodom, P.; Chaijareenont, P.; Rungsiyakull, P. Effect of Customized and Prefabricated Healing Abutments on Peri-Implant Soft Tissue and Bone in Immediate Implant Sites: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennes, M.E.; Naumann, M.; Peroz, S.; Beuer, F.; Schmidt, F. Antibacterial Effects of Modified Implant Abutment Surfaces for the Prevention of Peri-Implantitis-A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B.; Mirastschijski, U.; Stubbs, N.; Scanlon, E.; Agren, M.S. Zinc in wound healing: Theoretical, experimental, and clinical aspects. Wound Repair. Regen. 2007, 15, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; You, Y.; Cheng, G.W.; Lan, Z.; Zou, K.L.; Mai, Q.Y.; Han, Y.H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yu, G.T. Advanced materials and technologies for oral diseases. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2023, 24, 2156257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bauman, L.; Nogueira, C.L.; Aucoin, M.G.; Anderson, W.A.; Zhao, B. Antimicrobial polymeric composites for high-touch surfaces in healthcare applications. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 22, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaya, B.; Kayhan, H.G.; Temmerman, A.; Haytac, M.C.; Teughels, W. Pre-operative, chair-side Zn-containing surgical stents affect morbidity and wound healing after free gingival graft harvesting: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2023, 27, 5519–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welander, M.; Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T. The mucosal barrier at implant abutments of different materials. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutouzis, T.; Richardson, J.; Lundgren, T. Comparative soft and hard tissue responses to titanium and polymer healing abutments. J. Oral. Implant. 2011, 37, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, I.; Berglundh, T.; Glantz, P.O.; Lindhe, J. The mucosal attachment at different abutments. An experimental study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, S.; Lee, R. Comparison of peri-implant and periodontal marginal soft tissues in health and disease. Periodontol. 2000 2018, 76, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Scutt, A.M.; Thornhill, M.H.; Van Noort, R. Mucotoxicity of dental composite resins on a tissue-engineered human oral mucosal model. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.W.; Sakong, J.; Kang, S. Cytotoxicity of dental self-curing resin for a temporary crown: An in vitro study. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2023, 40 (Suppl.), S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.I.; Condos, S.; Deutsch, A.S.; Musikant, B.L. Comparison of the shear bond strength of a titanium composite resin material with dentinal bonding agents versus glass ionomer cements. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 68, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilselvam, S.; Divyanand, M.J.; Neelakantan, P. Biocompatibility of a conventional glass ionomer, ceramic reinforced glass ionomer, giomer and resin composite to fibroblasts: In vitro study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2013, 37, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothdurft, F.P.; Fontana, D.; Ruppenthal, S.; May, A.; Aktas, C.; Mehraein, Y.; Lipp, P.; Kaestner, L. Differential Behavior of Fibroblasts and Epithelial Cells on Structured Implant Abutment Materials: A Comparison of Materials and Surface Topographies. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Dan, P.; Sosnik, A.; Kalarikkal, N.; Tran, N.; Vincent, B.; Thomas, S.; Menu, P.; Rouxel, D. Electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/zinc oxide nanocomposite tissue engineering scaffolds with enhanced cell adhesion and blood vessel formation. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3358–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Hu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Quan, L.; Yang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ye, W. Improved Blood Compatibility and Endothelialization of Titanium Oxide Nanotube Arrays on Titanium Surface by Zinc Doping. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2072–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.-X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, D. Enhanced cytocompatibility and antibacterial property of zinc phosphate coating on biodegradable zinc materials. Acta Biomater. 2019, 98, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, D. Endothelial Cellular Responses to Biodegradable Metal Zinc. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Su, J. Double-edged effects and mechanisms of Zn(2+) microenvironments on osteogenic activity of BMSCs: Osteogenic differentiation or apoptosis. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14915–14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, D.; Wolfgarten, M.; Enkling, N.; Helfgen, E.H.; Frentzen, M.; Probstmeier, R.; Winter, J.; Stark, H. In-vitro cytocompatibility of dental resin monomers on osteoblast-like cells. J. Dent. 2017, 65, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuajungco, M.P.; Ramirez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Zinc: Multidimensional Effects on Living Organisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Labrie, J.; Tremblay, Y.D.; Haine, D.; Mourez, M.; Jacques, M. Zinc as an agent for the prevention of biofilm formation by pathogenic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.M.; Maia, M.R.G.; Pinna, C.; Biagi, G.; Matos, E.; Segundo, M.A.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; Cabrita, A.R.J. Effects of Zinc Source and Enzyme Addition on the Fecal Microbiota of Dogs. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 688392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Krieg, T.; Zinser, M.; Schroder, K.; Kroger, N. An Overview of Scaffolds and Biomaterials for Skin Expansion and Soft Tissue Regeneration: Insights on Zinc and Magnesium as New Potential Key Elements. Polymers 2023, 15, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Ngoc Le, T.T.; Nguyen, A.T.; Thien Le, H.N.; Pham, T.T. Biomedical materials for wound dressing: Recent advances and applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5509–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, P.; Bosco, F.; Mollea, C.; Onida, B. Antimicrobial Nano-Zinc Oxide Biocomposites for Wound Healing Applications: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado-Prone, G.; Silva-Bermudez, P.; Rodil, S.E.; Ganjkhani, Y.; Moradi, A.R.; Mendez, F.J.; Garcia-Macedo, J.A.; Bazzar, M.; Almaguer-Flores, A. ZnO nanoparticles-modified polycaprolactone-gelatin membranes for guided/bone tissue regeneration, antibacterial and osteogenic differentiation properties. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2023, 9, 035011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, D.; Novakovic, K.; Hilkens, C.M.U.; Ferreira, A.M. Interplay between biomaterials and the immune system: Challenges and opportunities in regenerative medicine. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreth, J.; Merritt, J.; Pfeifer, C.S.; Khajotia, S.; Ferracane, J.L. Interaction between the Oral Microbiome and Dental Composite Biomaterials: Where We Are and Where We Should Go. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktan, M.K.; Van der Gucht, M.; Hendrix, H.; Vande Velde, G.; Baert, K.; Hauffman, T.; Killian, M.S.; Lavigne, R.; Braem, A. Anti-infective DNase I coatings on polydopamine functionalized titanium surfaces by alternating current electrophoretic deposition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1218, 340022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, V.; Herrero, E.R.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.; Trivedi, H.M.; Daep, C.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Oral prebiotics and the influence of environmental conditions in vitro. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holm, W.; Carvalho, R.; Delanghe, L.; Eilers, T.; Zayed, N.; Mermans, F.; Bernaerts, K.; Boon, N.; Claes, I.; Lebeer, S.; et al. Antimicrobial potential of known and novel probiotics on in vitro periodontitis biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, N.; Figueiredo, J.; Van Holm, W.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.; Teughels, W. Mode of killing determines the necrotrophic response of oral bacteria. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2184930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holm, W.; Ghesquiere, J.; Boon, N.; Verspecht, T.; Bernaerts, K.; Zayed, N.; Chatzigiannidou, I.; Teughels, W. A Viability Quantitative PCR Dilemma: Are Longer Amplicons Better? Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0265320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, E.R.; Slomka, V.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.; Hernandez-Sanabria, E.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Dysbiosis by neutralizing commensal mediated inhibition of pathobionts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.H.; Min, B.M.; Cherrick, H.M.; Park, N.H. Combined effects of human papillomavirus-18 and N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine on the transformation of normal human oral keratinocytes. Mol. Carcinog. 1994, 9, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliepen, I.; Van Damme, J.; Van Essche, M.; Loozen, G.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Microbial interactions influence inflammatory host cell responses. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Name |
|---|---|
| Periodontal pathobionts | Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans ATCC 43718 |
| Prevotella intermedia ATCC 25611 | |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 | |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum ATCC 20482 | |
| Anaerobic commensals | Actinomyces viscosus DSM 43327 |
| Actinomyces naeslundii ATCC 51655 | |
| Veillonella parvula DSM 2008 | |
| Cariogenic streptococci | Streptococcus mutans ATCC 20523 |
| Streptococcus sobrinus ATCC 20742 | |
| Commensal streptococci | Streptococcus oralis DSM 20627 |
| Streptococcus sanguinis LM14657 | |
| Streptococcus gordonii ATCC 49818 | |
| Streptococcus mitis DSM 12643 | |
| Streptococcus salivarius TOVE-R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Holm, W.; Vandamme, K.; Hadisurya, J.; Pamuk, F.; Zayed, N.; Aktan, M.K.; Braem, A.; Temmerman, A.; Teughels, W. Thermoplastic Zinc-Infused Polymer for Chairside Socket Seal Abutments Enhances Antimicrobial and Tissue-Integrative Properties. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050441
Van Holm W, Vandamme K, Hadisurya J, Pamuk F, Zayed N, Aktan MK, Braem A, Temmerman A, Teughels W. Thermoplastic Zinc-Infused Polymer for Chairside Socket Seal Abutments Enhances Antimicrobial and Tissue-Integrative Properties. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050441
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Holm, Wannes, Katleen Vandamme, Jill Hadisurya, Ferda Pamuk, Naiera Zayed, Merve Kübra Aktan, Annabel Braem, Andy Temmerman, and Wim Teughels. 2025. "Thermoplastic Zinc-Infused Polymer for Chairside Socket Seal Abutments Enhances Antimicrobial and Tissue-Integrative Properties" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050441
APA StyleVan Holm, W., Vandamme, K., Hadisurya, J., Pamuk, F., Zayed, N., Aktan, M. K., Braem, A., Temmerman, A., & Teughels, W. (2025). Thermoplastic Zinc-Infused Polymer for Chairside Socket Seal Abutments Enhances Antimicrobial and Tissue-Integrative Properties. Antibiotics, 14(5), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050441









