Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbates Esomeprazole-Induced Intestinal Dysmotility While Ameliorating Gastric Dyspepsia in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
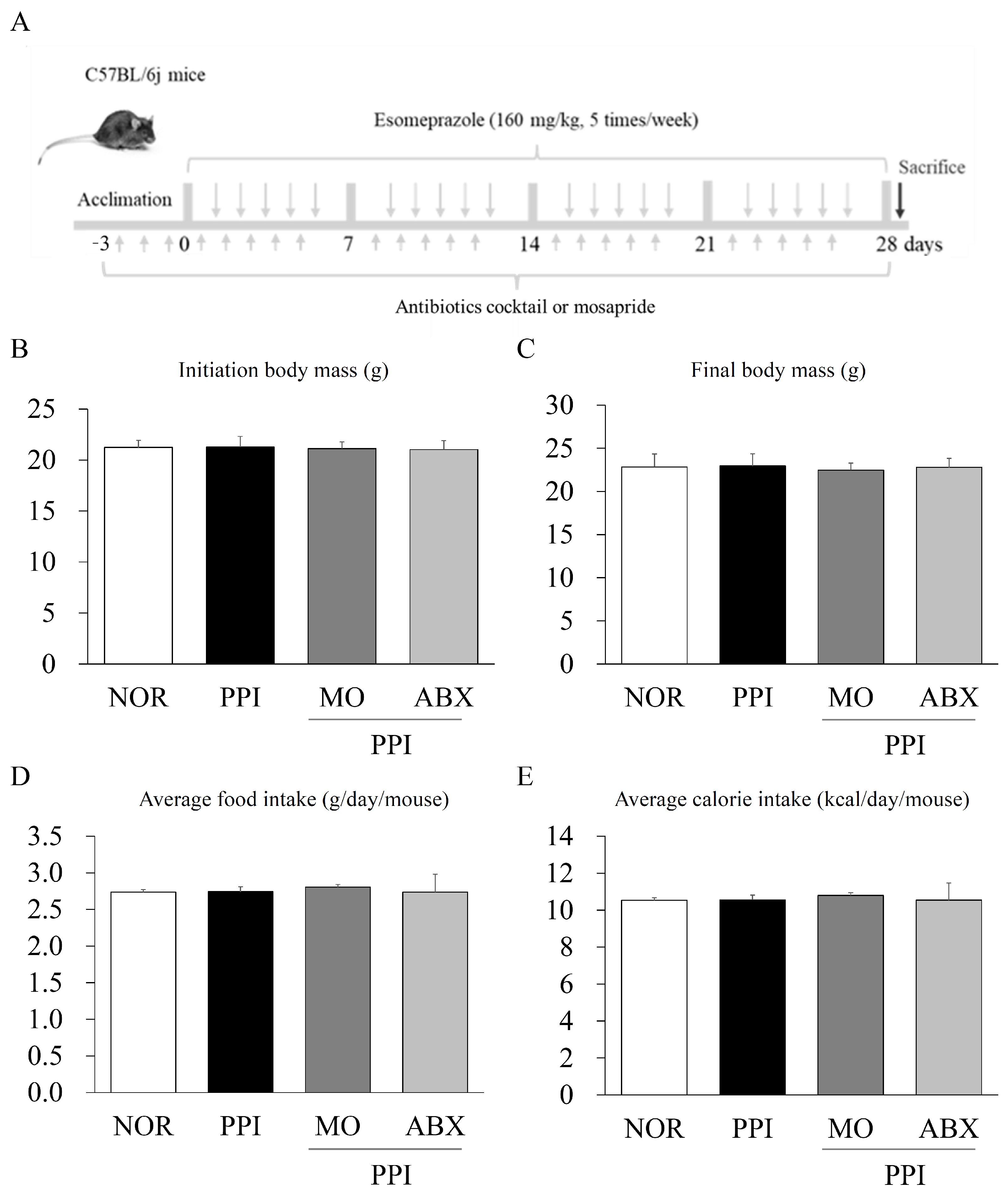
2.1. Long-Term Esomeprazole and Antibiotic Cocktail Administration Did Not Reduce Body Mass or Food Intake
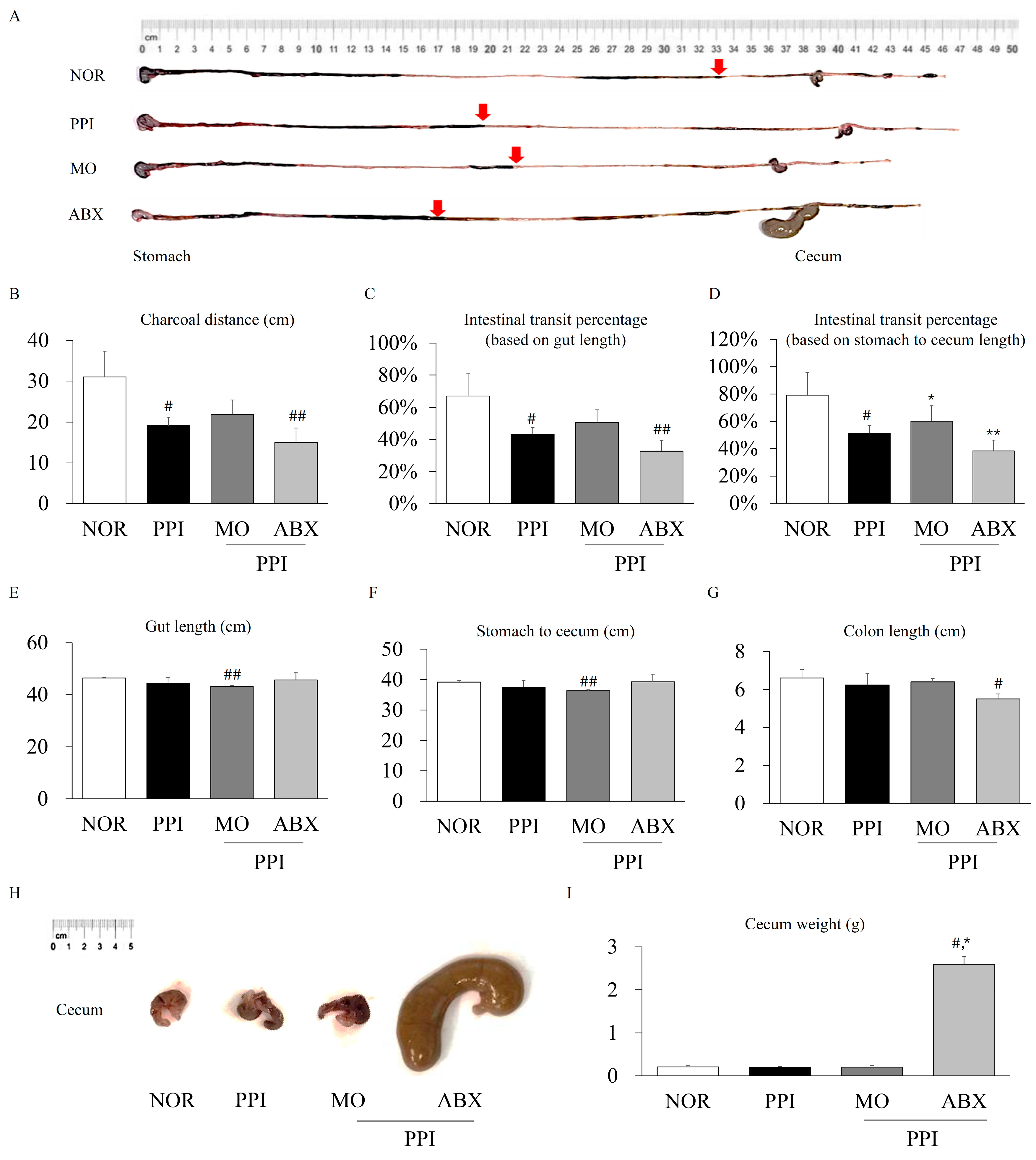
2.2. Antibiotic Cocktail Alleviated the Proton-Pump-Inhibitor-Induced Inhibition of Gastric Motility
2.3. Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbated the Proton-Pump-Inhibitor-Induced Inhibition of Intestinal Motility
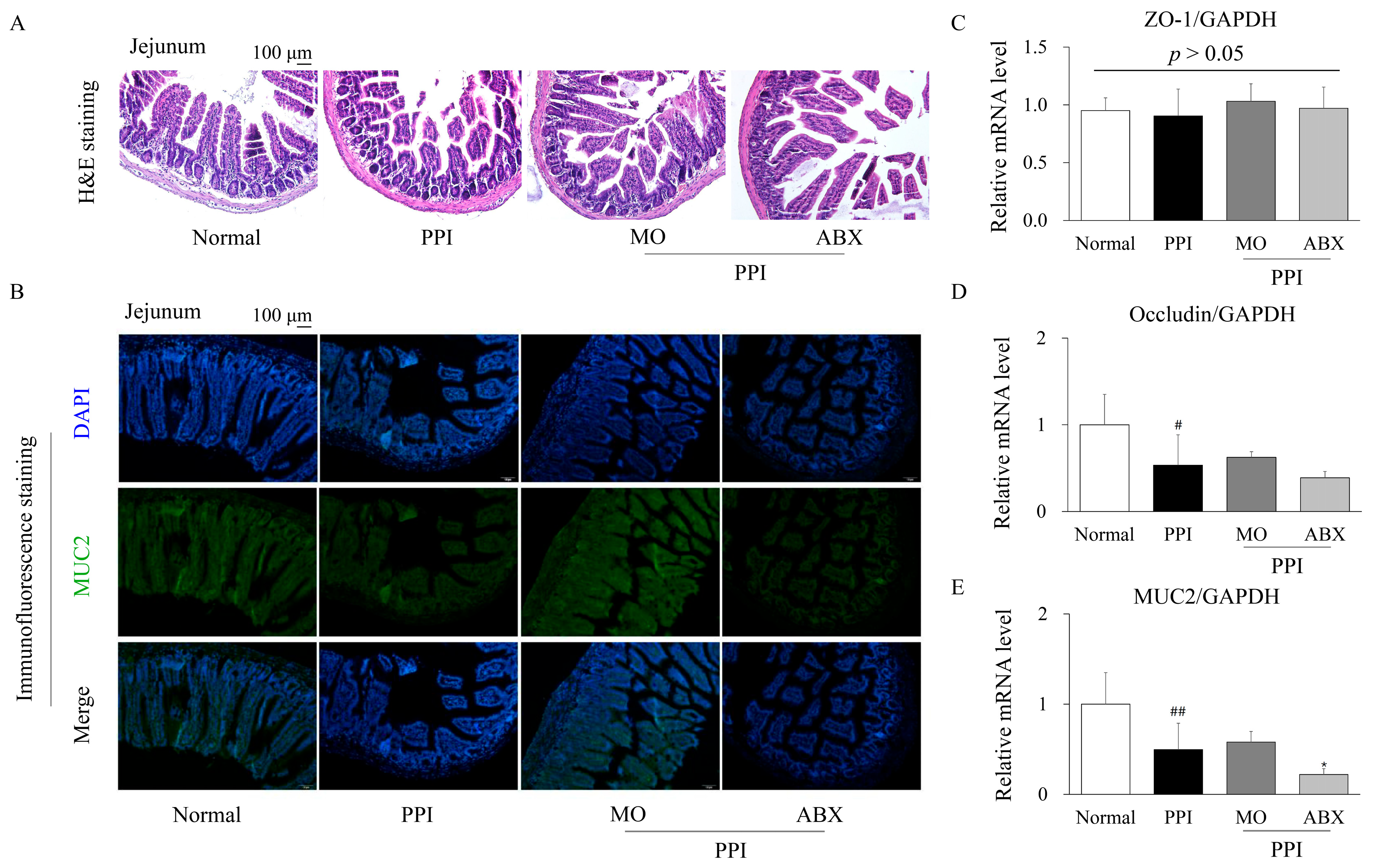
2.4. Antibiotic Cocktail Deteriorated the Proton-Pump-Inhibitor-Induced Injury of Intestinal Integrity
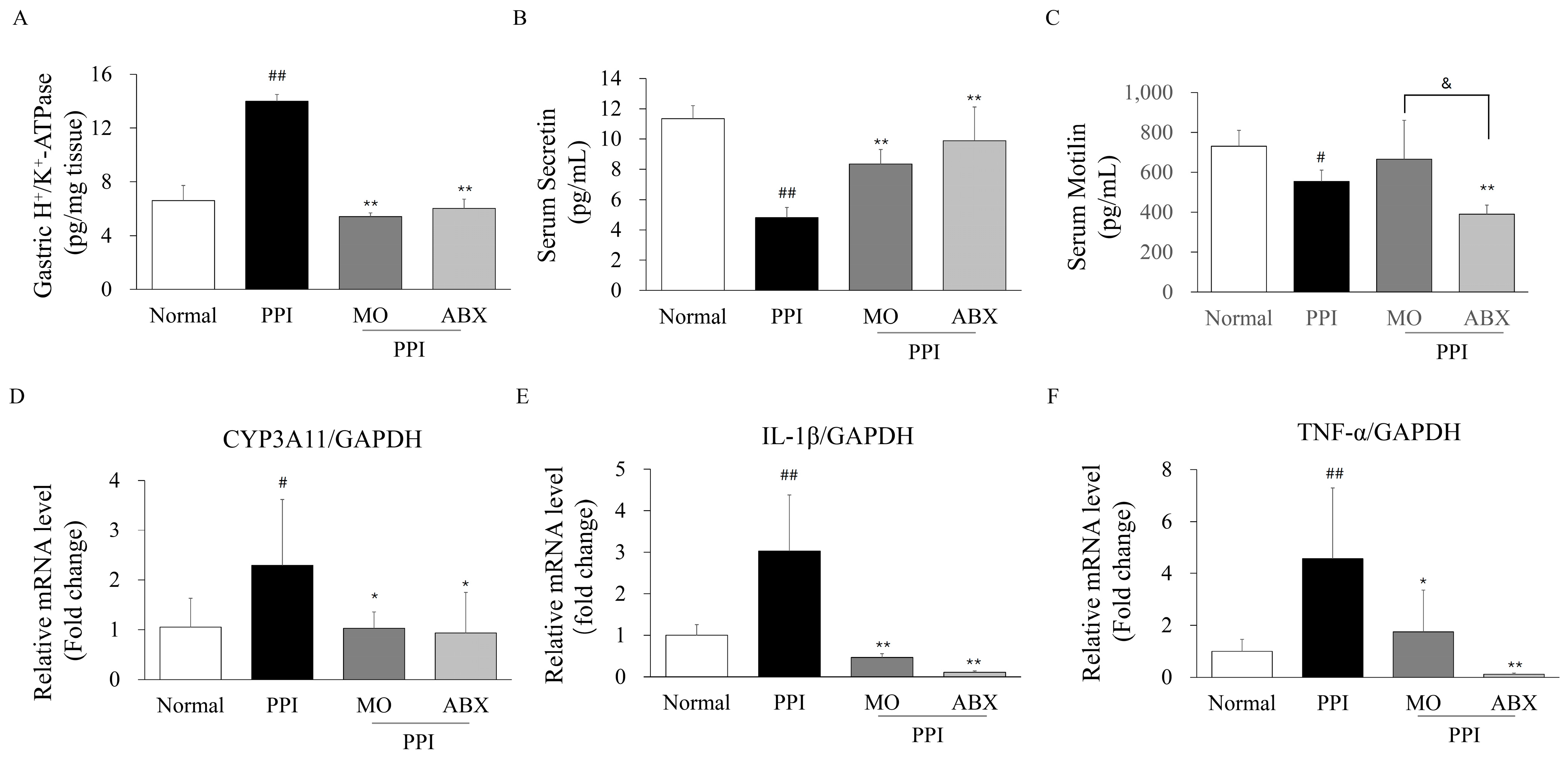
2.5. Antibiotic Cocktail Impacted Proton Pump Inhibitor Metabolic Enzymes, GI Hormones, and Inflammatory Markers
2.6. Antibiotic Cocktail Further Reduced Certain Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids Levels and Related Receptor
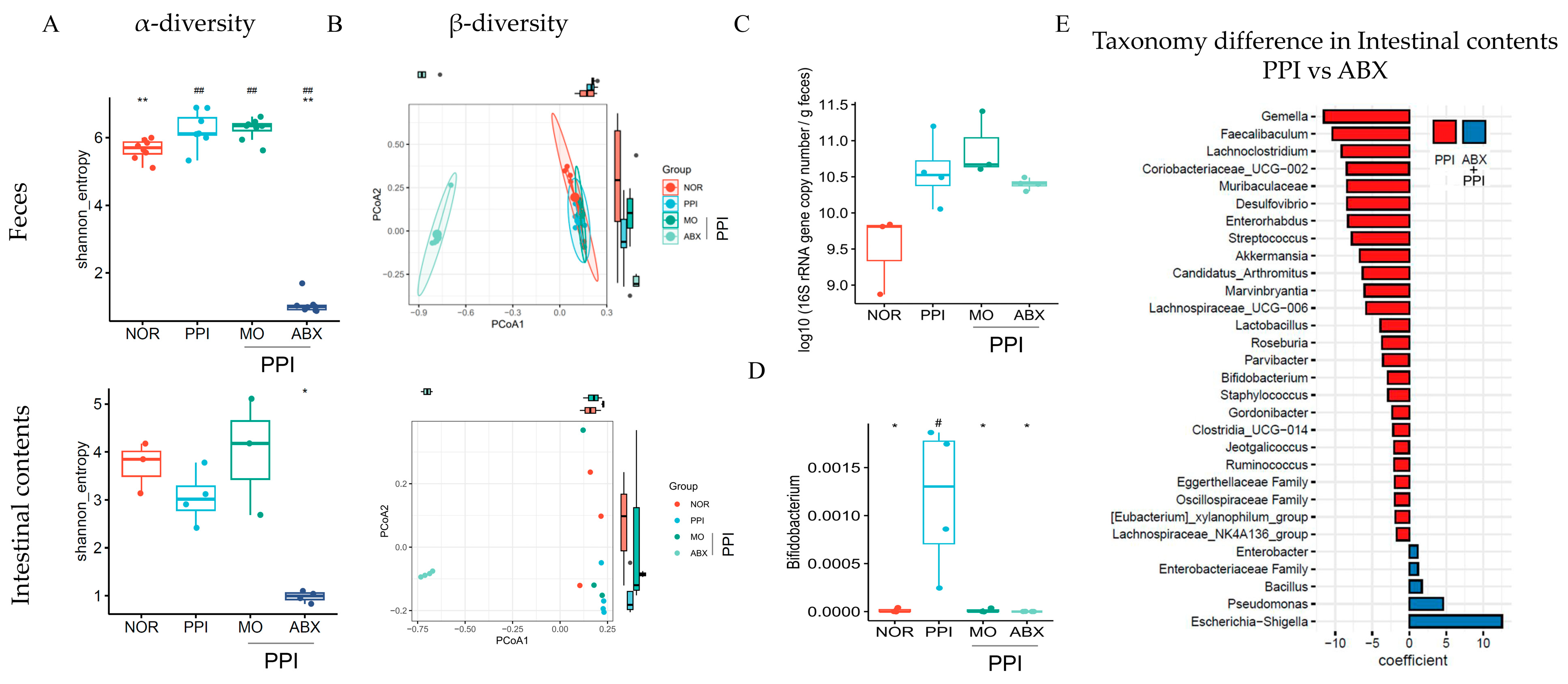
2.7. Antibiotic Cocktail Significantly Reduced Gut Microbiome Diversity but May Increase the Absolute Bacterial Load
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Charcoal Assay for Intestinal Motility Assessment
4.3. Phenol Red Assay for Gastric Emptying Evaluation
4.4. Histopathological Analysis Using Hematoxylin and Eosin and Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Measurement of Gastrointestinal Hormones in Serum by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.6. Quantification of Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids
4.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.8. Fecal and Intestinal Contents 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABX | Antibiotic cocktail |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CMC | Carboxymethylcellulose |
| CYP3A11 | Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily a, polypeptide 11 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| PPI | Proton pump inhibitor |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SIBO | Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth |
References
- Vachhani, R.; Olds, G.; Velanovich, V. Esomeprazole: A proton pump inhibitor. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 3, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Sachs, G. Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2008, 10, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.B.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelbaugh, J.J. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of vitamin and mineral deficiency: Evidence and clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Drug Safety 2013, 4, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vich Vila, A.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.; Coss Adame, E.; Attaluri, A.; Valestin, J.; Rao, S.S. Dysmotility and proton pump inhibitor use are independent risk factors for small intestinal bacterial and/or fungal overgrowth. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maideen, N.M.P. Adverse Effects Associated with Long-Term Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Chonnam Med. J. 2023, 59, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schemann, M. Control of gastrointestinal motility by the “gut brain”—The enteric nervous system. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, S4–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Miwa, H. Role of Gut Microbiota-Gut Hormone Axis in the Pathophysiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Hu, H.; Jin, C.; Yu, X. Efficacy and Safety of Esomeprazole for the Treatment of Reflux Symptoms in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaka, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kuyama, Y. Effects of proton pump inhibitors on gastric emptying: A systematic review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Youn, Y.H.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, B.K.; Park, H. Effects of the Addition of Mosapride to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Patients on Proton Pump Inhibitor: A Prospective Randomized, Double-blind Study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Huang, C.; Fu, W.; Gao, L.; Mi, N.; Bai, M.; Ma, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors may enhance the risk of digestive diseases by regulating intestinal microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1217306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaeddin, N.; Koch, A.; Etteldorf, R.; Stingl, J.C.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Vries, F.M. The impact of proton pump inhibitors on brain health based on cross-sectional findings from the Rhineland Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W. Role of gut microbiota-derived signals in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 961703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, H.K.; Pereira, M.; Bosco, J.; George, J.; Jayaraman, V.; Krishna, K.; Wang, T.; Bei, K.; Rajasekaran, J.J. Gut commensals and their metabolites in health and disease. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1244293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Wei, L.; Bartlett, A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Rajender, S.; Ro, S. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Dysmotility and Metabolic Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavelu, D.; Jog, P. Current understanding of antibiotic-associated dysbiosis and approaches for its management. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, 20499361231154443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Xing, X.; Yang, J. Proton pump inhibitors alter gut microbiota by promoting oral microbiota translocation: A prospective interventional study. Gut 2024, 73, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delungahawatta, T.; Amin, J.Y.; Stanisz, A.M.; Bienenstock, J.; Forsythe, P.; Kunze, W.A. Antibiotic Driven Changes in Gut Motility Suggest Direct Modulation of Enteric Nervous System. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, E.; Losurdo, G.; Fortezza, R.F.; Principi, M.; Barone, M.; Leo, A.D. Optimizing proton pump inhibitors in Helicobacter pylori treatment: Old and new tricks to improve effectiveness. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5097–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanika, L.G.T.; Reynolds, A.; Pattison, S.; Braund, R. Proton pump inhibitor use: Systematic review of global trends and practices. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Furuta, T. Efficacy of esomeprazole in treating acid-related diseases in Japanese populations. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, L.; Hatlebakk, J.; Galmiche, J.P.; Attwood, S.E.; Ell, C.; Fiocca, R.; Persson, T.; Nagy, P.; Eklund, S.; Lind, T. Long-term effect on symptoms and quality of life of maintenance therapy with esomeprazole 20 mg daily: A post hoc analysis of the LOTUS trial. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2015, 31, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, L.; Fennerty, M.B.; Osato, M.; Sugg, J.; Suchower, L.; Probst, P.; Levine, J.G. Esomeprazole-based Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy and the effect of antibiotic resistance: Results of three US multicenter, double-blind trials. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 3393–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullo, A.; Ridola, L.; Francesco, V.D.; Gatta, L.; Hassan, C.; Alvaro, D.; Bellesia, A.; de Nucci, G.; Manes, G. High-dose esomeprazole and amoxicillin dual therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: A proof of concept study. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 448–451. [Google Scholar]
- Keto, Y.; Hirata, T.; Takemoto, Y.; Yamano, M.; Yokoyama, T. Influence of gastric acid on gastric emptying and gastric distension-induced pain response in rats--effects of famotidine and mosapride. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 147-e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougas, G.; Earnest, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Vanderkoy, C.; Rojavin, M. Omeprazole delays gastric emptying in healthy volunteers: An effect prevented by tegaserod. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.; Chela, H.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Rao, D.; Das, K. Long-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor-Induced Gastric Microcystic Glandular Changes Leading to Gastric Wall Thickening. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, S1549–S1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.; Almeida, T.C.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Pereira, C. Linking dysbiosis to precancerous stomach through inflammation: Deeper than and beyond imaging. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1134785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.A.; King, K.Y.; Baldridge, M.T. Mouse Microbiota Models: Comparing Germ-Free Mice and Antibiotics Treatment as Tools for Modifying Gut Bacteria. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.; Nell, S.; Suerbaum, S. Survival in hostile territory: The microbiota of the stomach. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 736–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Lai, S.; Lee, A.; He, X.; Chen, S. Meta-analysis: Proton pump inhibitors moderately increase the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Bustos Fernandez, L.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpetch, W.; Tumwasorn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in feces exacerbate leaky gut in mice with low dose dextran sulfate solution, impacts of specific bacteria. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Brück, T.B. Molecular Mechanisms of Shigella Pathogenesis; Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Dong, Y.; Xie, T.; Chai, Z.; Gao, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, X. The Role of Gut Microbiome in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Implications for Clinical Therapeutics. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, M.S. Escherichia coli Shiga Toxins and Gut Microbiota Interactions. Toxins 2021, 13, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Balas, I.; Robinson, M.J.; Bakdash, G. Border Control: The Role of the Microbiome in Regulating Epithelial Barrier Function. Cells 2024, 13, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornavaca, O.; Chia, M.; Dufton, N.; Almagro, L.O.; Conway, D.E.; Randi, A.M.; Schwartz, M.A.; Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell–cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 508738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherbut, C.; Aubé, A.C.; Blottière, H.M.; Galmiche, J.P. Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Gastrointestinal Motility. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, J. Enteric neuron regulation of gut motility by the microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.A.F.; Magalhães, H.I.R.; Duarte, J.R.L.; Conceição, L.B.; Castelucci, P. Butyrate Protects Myenteric Neurons Loss in Mice Following Experimental Ulcerative Colitis. Cells 2023, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.H. Butyrate producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their intestinal significance with and beyond butyrate, and prospective use as microbial therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Kim, N. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the proton pump inhibitors. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marker, T.; Steimbach, R.R.; Perez-Borrajero, C.; Luzarowski, M.; Hartmann, E.; Schleich, S.; Pastor-Flores, D.; Espinet, E.; Trumpp, A.; Teleman, A.A.; et al. Site-specific activation of the proton pump inhibitor rabeprazole by tetrathiolate zinc centres. Nat. Chem. 2025, 17, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Munson, K.; Vagin, O.; Sachs, G. The gastric HK-ATPase: Structure, function, and inhibition. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2009, 457, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Borjihan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Bai, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y. Complex Probiotics Ameliorate Fecal Microbiota Transplantation-Induced IBS in Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolite Modulation. Nutrients 2025, 17, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, P.; Răzniceanu, V.; Mocrei-Rebrean, Ș.-M.; Neculicioiu, V.S.; Dragoș, H.M.; Costache, C.; Filip, G.A. The Effect of Gut Microbiota-Targeted Interventions on Neuroinflammation and Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Animal Models-A Systematic Review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 3946–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.; Lee, J.; Ko, K.; Sikora, A.G.; Bonnen, M.D.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Ghebre, Y.T. Therapeutic Efficacy of Esomeprazole in Cotton Smoke-Induced Lung Injury Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Gong, J.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; You, J.; He, J.; Wu, S. Evaluation of an Antibiotic Cocktail for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Mouse. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 918098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, N.T.; Schmidt, A.W.; Venkataraman, A.; Kim, K.S.; Waldron, C.; Schmidt, T.M. Dynamics of Human Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Response to Dietary Interventions with Three Fermentable Fibers. mBio 2019, 10, e02566-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahori, K.; Qu, N.; Kuramasu, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Kiyoshima, D.; Suyama, K.; Hayashi, S.; Sakabe, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Itoh, M. Changes in Expression of Specific mRNA Transcripts after Single- or Re-Irradiation in Mouse Testes. Genes 2022, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, P.P.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, G.H.; Yuan, B.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, T.T.; Wang, M.Y.; et al. GPR43 deficiency protects against podocyte insulin resistance in diabetic nephropathy through the restoration of AMPKα activity. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4728–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoine, D.; Petit, M.; Pilote, S.; Picard, F.; Drolet, B.; Simard, C. Modulation of CYP3A expression and activity in mice models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2014, 2, e00082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Lu, T.; Chen, Q.; Hu, A. Conditional Knockout of IL-1R1 in Endothelial Cells Attenuates Seizures and Neurodegeneration via Inhibiting Neuroinflammation Mediated by Nrf2/HO-1/NLRP3 Signaling in Status Epilepticus Model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 4289–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, D.; Han, R.; Zhang, C.; Jin, W.N.; Wood, K.; Liu, Q.; Shi, F.D.; Hao, J. Acetylcholine-producing NK cells attenuate CNS inflammation via modulation of infiltrating monocytes/macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6202–E6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-H.; Han, S.-Y.; Lee, K.; Han, U.; Cho, S.-K.; Kim, H. Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbates Esomeprazole-Induced Intestinal Dysmotility While Ameliorating Gastric Dyspepsia in Mice. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050442
Wang J-H, Han S-Y, Lee K, Han U, Cho S-K, Kim H. Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbates Esomeprazole-Induced Intestinal Dysmotility While Ameliorating Gastric Dyspepsia in Mice. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(5):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050442
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing-Hua, Song-Yi Han, Kyungjae Lee, Uijeong Han, Si-Kyung Cho, and Hojun Kim. 2025. "Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbates Esomeprazole-Induced Intestinal Dysmotility While Ameliorating Gastric Dyspepsia in Mice" Antibiotics 14, no. 5: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050442
APA StyleWang, J.-H., Han, S.-Y., Lee, K., Han, U., Cho, S.-K., & Kim, H. (2025). Antibiotic Cocktail Exacerbates Esomeprazole-Induced Intestinal Dysmotility While Ameliorating Gastric Dyspepsia in Mice. Antibiotics, 14(5), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14050442





