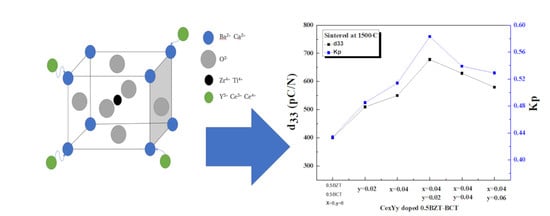
Ce and Y Co-Doping Effects for (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
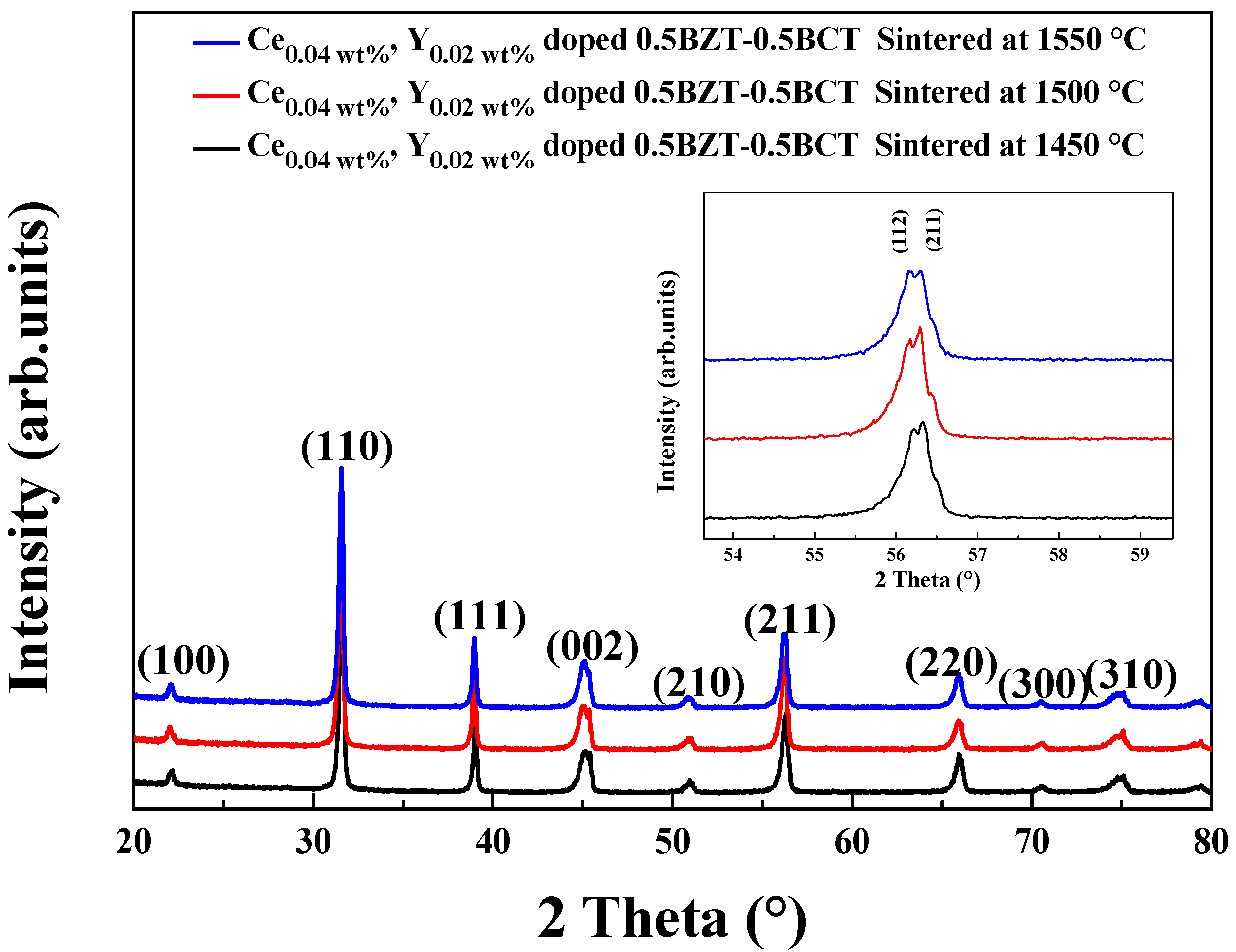
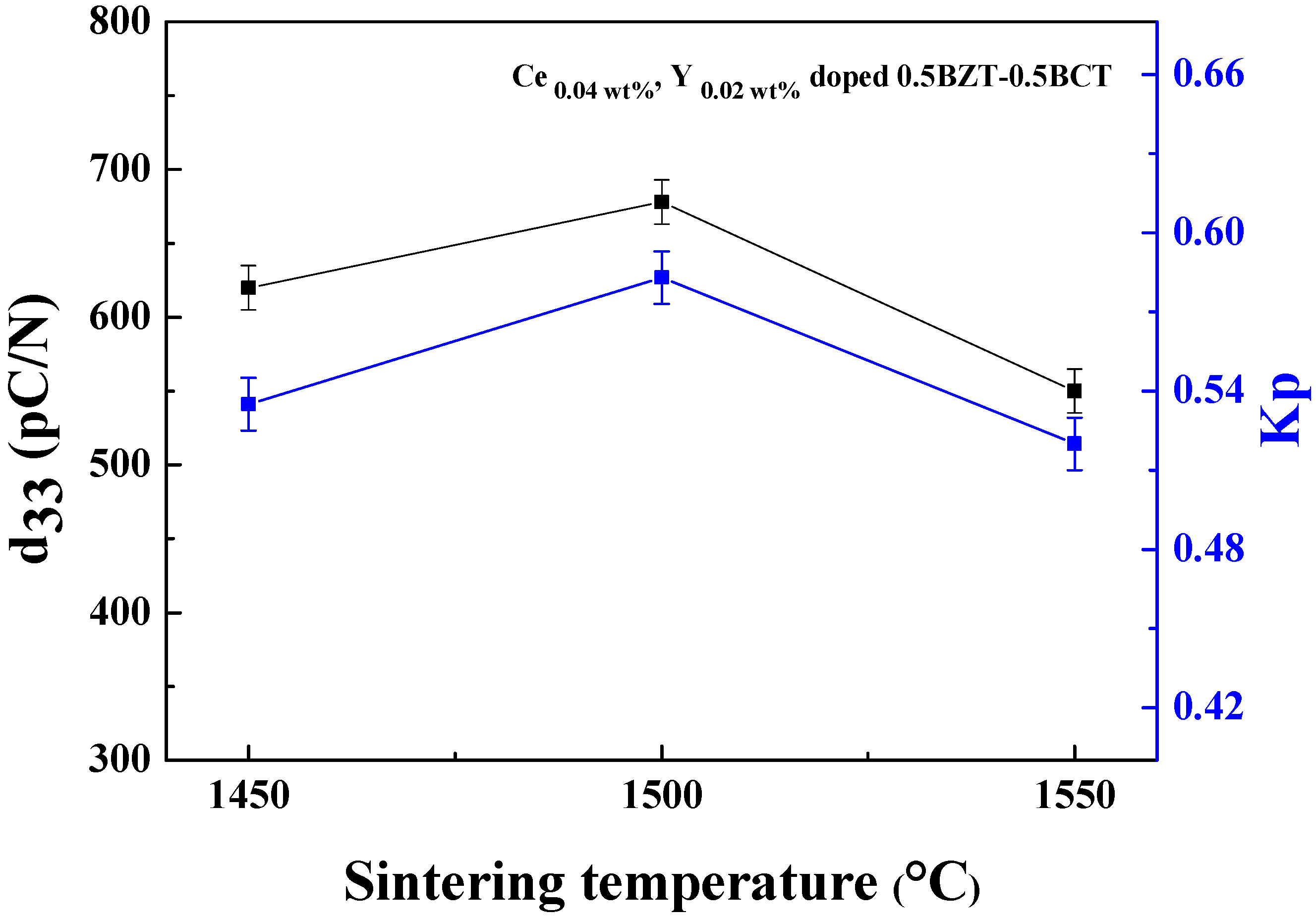
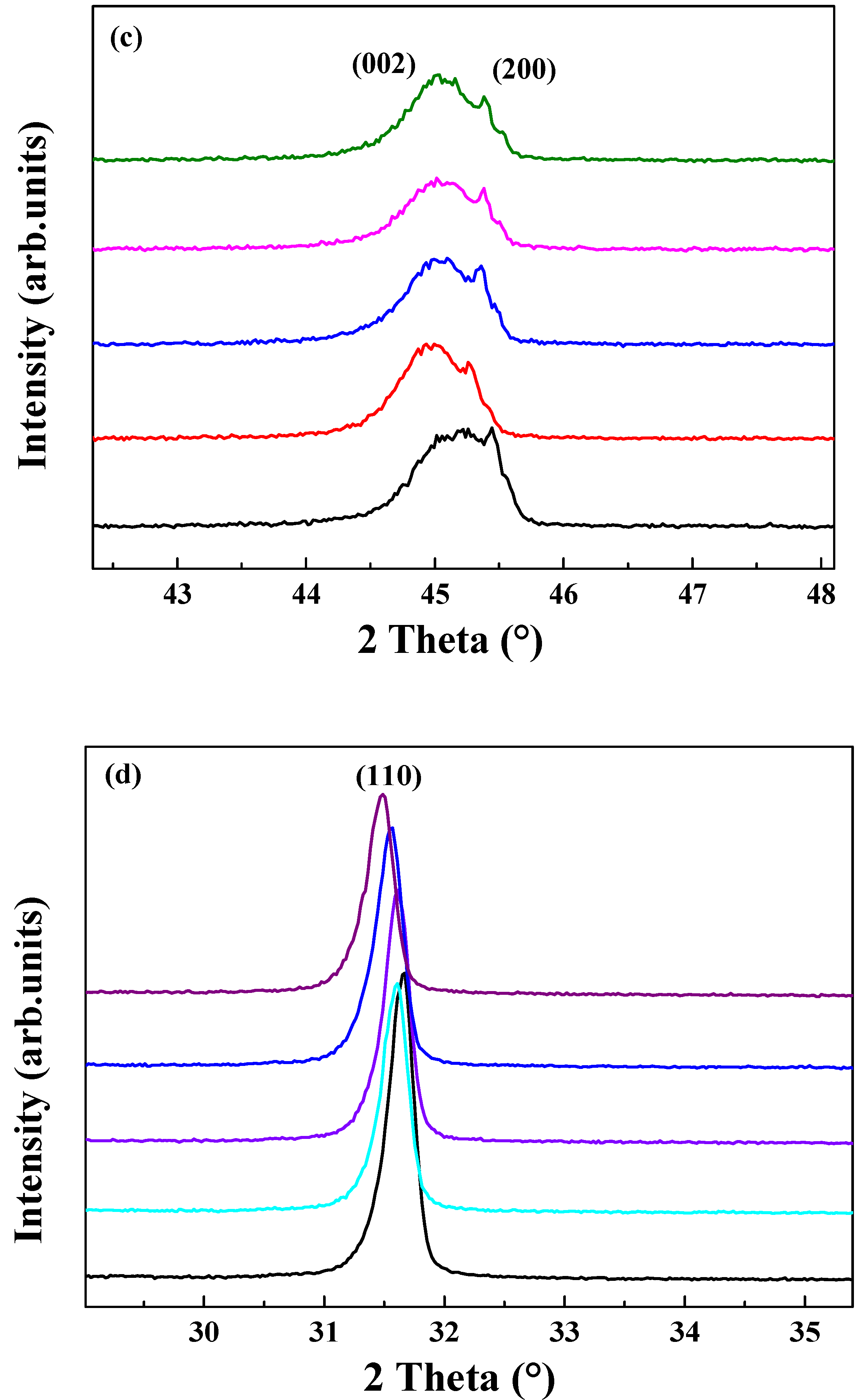
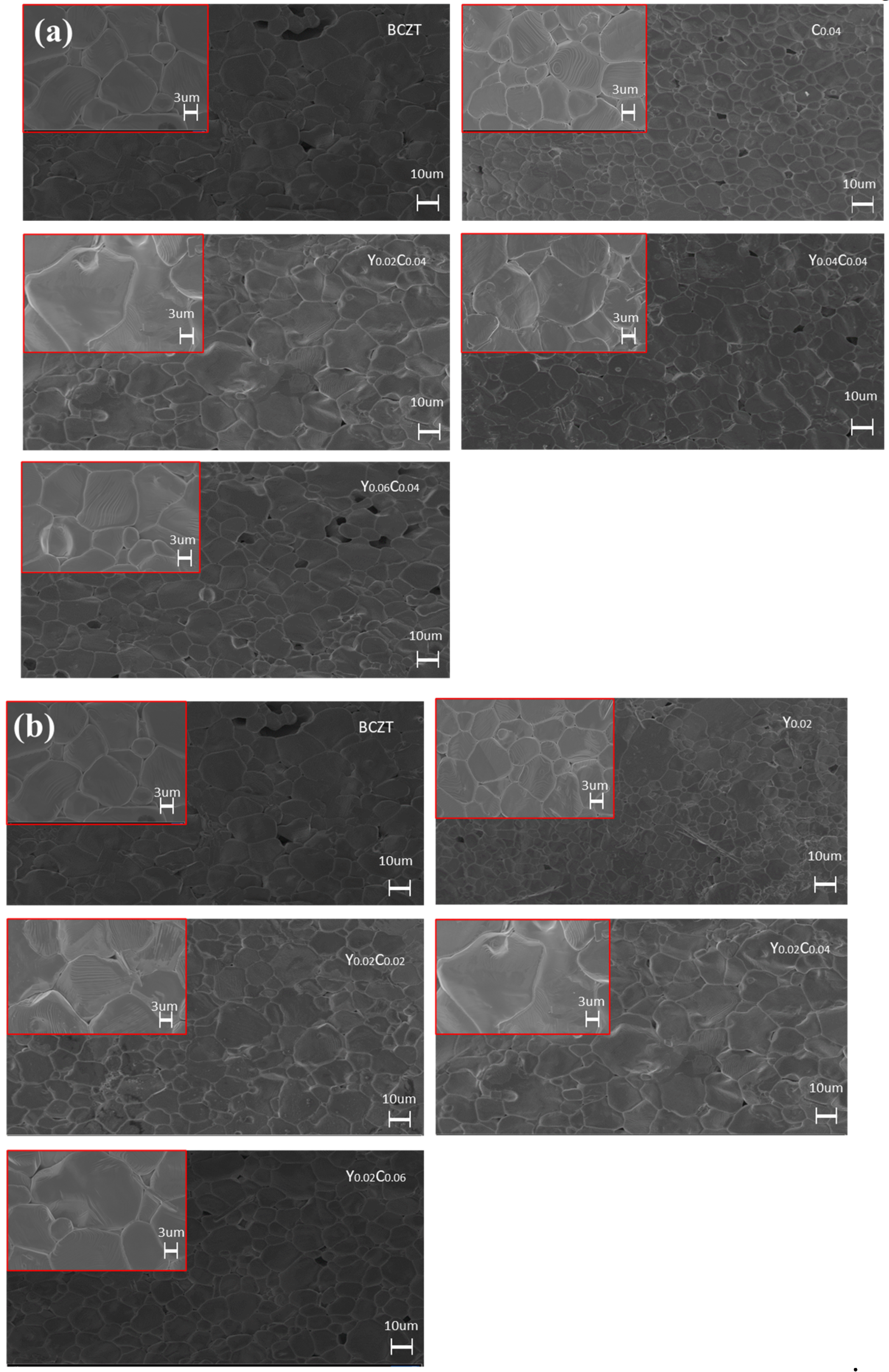
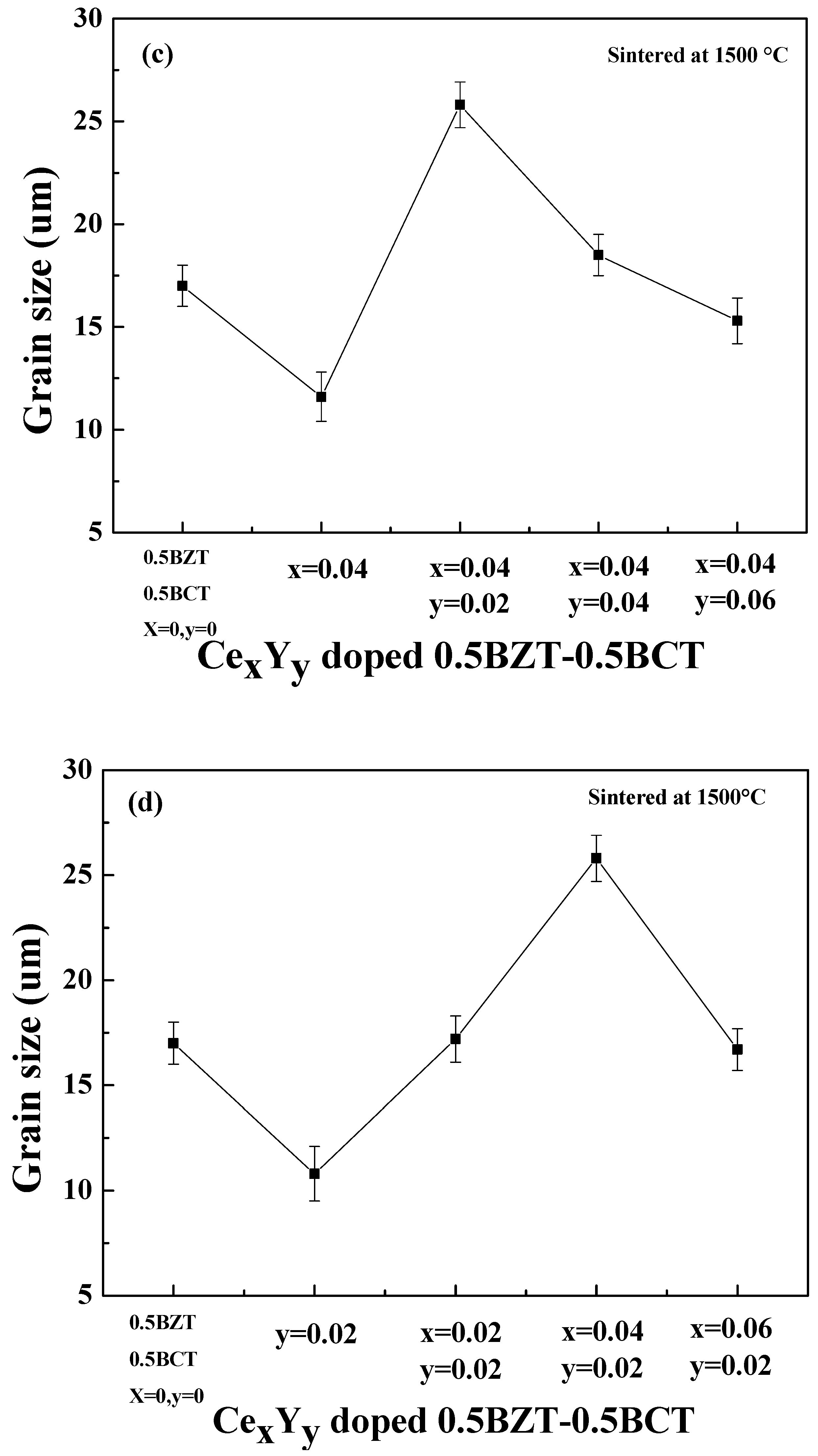
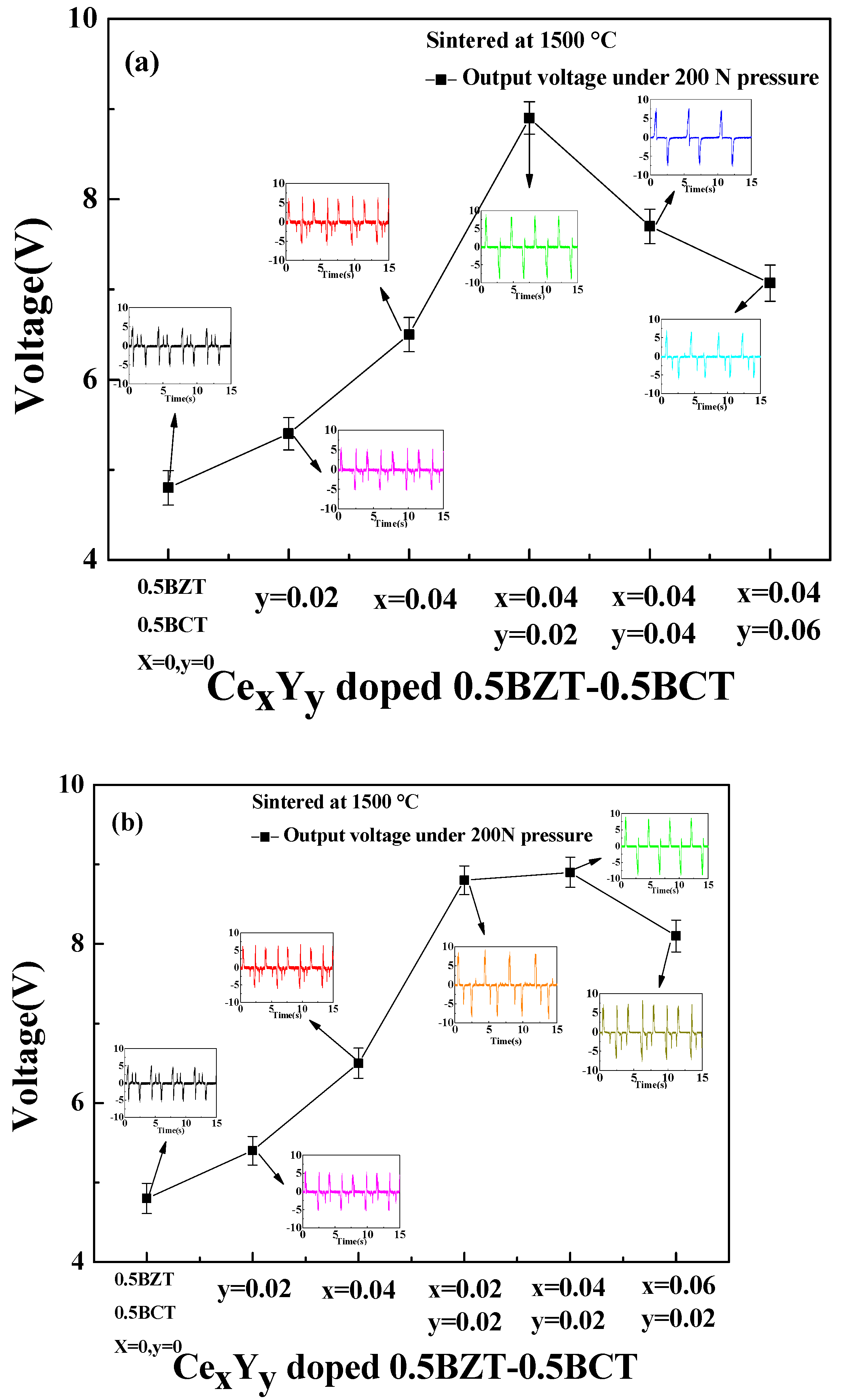
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haertling, H.K. Ferroelectric ceramics: History and technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 797–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, K.P. Review: Environmental friendly lead-free piezoelectric materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rödel, J.; Jo, W.; Seifert, K.T.P.; Anton, E.M.; Granzow, T. Perspective on the development of lead-free piezoceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1153–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, T.R.; Zhang, S.J. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT? J. Electroceram. 2007, 19, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clementi, G.; Margueron, S.; Suarez, M.A.; Baron, T.; Dulmet, B.; Bartasyte, A. Piezoelectric and pyroelectric energy harvesting from lithium niobate films. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1407, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuldina, G.; Turdakyn, N.; Abay, I.; Medeubayev, A.; Nurpeissova, A.; Adair, D.; Bakenov, Z. A Review of Piezoelectric PVDF Film by electrospinning and its applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.; Novak, N.; Rojas, V.; Patel, S.; Vaish, R.; Koruza, J.; Rossetti, G.A., Jr.; Rodel, J. BaTiO3-based piezoelectrics: Fundamentals, current status, and perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 041305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariello, M.; Fachechi, L.; Guido, F.; Vittorio, M.D. Multifunctional sub-100 µm thickness flexible piezo/triboelectric hybrid water energy harvester based on biocompatible AlN and soft parylene C-PDMS-Ecoflex™. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 2211–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariello, M.; Qualtieri, A.; Mele, G.; Vittorio, M.D. Metal-free multilayer hybrid peng based on soft electrospun/sprayed membranes with cardanol additive for harvesting energy from surgical face masks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20606–20621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.R.; Yuan, C.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Shan, X. Lead-free (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3-Y2O3 ceramics with large piezoelectric coefficient obtained by low-temperature sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Chu, R.; Fu, P.; Peng, A. Effect of Ho doping on piezoelectric properties of BCZT ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 4353–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, X. Large Piezoelectric Effect in Pb-Free Ceramics. PRL 2009, 103, 257602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Wang, C.B.; Harumoto, T.; Zhang, S.; Tu, R.; She, Q.; Shi, J. Structure and electrical properties of BCZT ceramics derived from microwave-assisted sol–gel-hydrothermal synthesized powders. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parjansri, P.; Intatha, U.; Eitssayeam, S. Dielectric, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of Nb5+ doped BCZT ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 65, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bai, W.; Zhao, X.; Ding, Y.; Wu, S.; Zheng, P.; Li, P.; Zhai, J. Influences of rare earth site engineering on piezo electric and electromechanical response of (Ba0.85Ca0.15) (Zr0.1Ti0.9) O3 lead-free ceramics. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 6560–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Fang, B.; Ding, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Luo, H. Enhancing piezoelectric properties of BCZT ceramics by Sr and Sn co-doping. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 640, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.N. Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bijalwan, V.; Hughes, H.; Pooladvand, H.; Tofel, P.; Nan, B.; Holcmanc, V.; Bai, Y.; Buttona, T.W. The effect of sintering tem perature on the microstructure and functional properties of BCZT-xCeO2 lead free ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 114, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Kwok, K.W.; Lin, D.; Chan, H.L.W. Microstructure, electrical properties of CeO2-doped (K0.5Na0.5) NbO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramic. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsur, Y.; Ddunbar, T.D.; Randall, C.A. Crystal and defect chemistry of rare earth cations in BaTiO3. J. Electroceram. 2001, 7, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Hong, R.Z.; Tian, C.S. Tolerance factor and the stability discussion of ABO3-type ilmenite. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 20, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.L. Elsevier Sintering, Densification, Grain Growth and Microstructure; Butterworth-Heinemann Publication: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 89–135. [Google Scholar]
- Buatip, N.; Promsawat, N.; Pisitpipathsin, N.; Namsar, O.; Pawasri, P.; Ounsung, P.; Phabsimma, K.; Rattanachan, S.T.; Janphuang, P.; Projprapai, S. Investigation on electrical properties of BCZT ferroelectric ceramics prepared at various sintering condition. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 187, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, X.; Shan, X.; Li, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, C. Lead-free (Ba0.85Ca0.15) (Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3–CeO2 ceramics with high piezoelectric coefficient obtained by low-temperature sintering. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 4761–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnar, P.; Khansur, N.H.; Webber, K.G.; Kungl, H.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Hinterstein, M. Grain size effects in donor doped lead zirconate titanate ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 214105. [Google Scholar]
- Ştefan, Ţ. Micro and Nanoscale Characterization of Three Dimensional Surfaces. Basics and Applications; Napoca Star Publishing House: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2015; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Sakata, A.; Carter, J.; Thomas, P.A.; Han, H.; Nino, J.C.; Jones, J.L. Domain wall displacement is the origin of superior permittivity and piezoelectricity in BaTiO3 at Intermediate grain sizes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, G.; Wei, F.; Li, W.; Chen, N. Co-doping effects of A-site Y3+ and B-site Al3+ on the microstructures and dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 4653–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-D.; Zheng, M.-P.; Zhu, M.; Hou, Y.-D. Soft and hard piezoelectric ceramics for vibration energy harvesting. Crystals 2020, 10, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.J.; Kim, J.-W.; Koh, J.H. Piezoelectric properties of (1-x)BZT-xBCT system for energy harvesting applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4395–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Baek, J.-S.; Koh, J.-H. Ce and Y Co-Doping Effects for (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics. Coatings 2021, 11, 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101248
Li C, Baek J-S, Koh J-H. Ce and Y Co-Doping Effects for (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics. Coatings. 2021; 11(10):1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101248
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chao, Jin-Su Baek, and Jung-Hyuk Koh. 2021. "Ce and Y Co-Doping Effects for (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics" Coatings 11, no. 10: 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101248
APA StyleLi, C., Baek, J.-S., & Koh, J.-H. (2021). Ce and Y Co-Doping Effects for (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O3 Lead-Free Ceramics. Coatings, 11(10), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101248