A Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure for Broadband Microwave Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment and Simulation Method
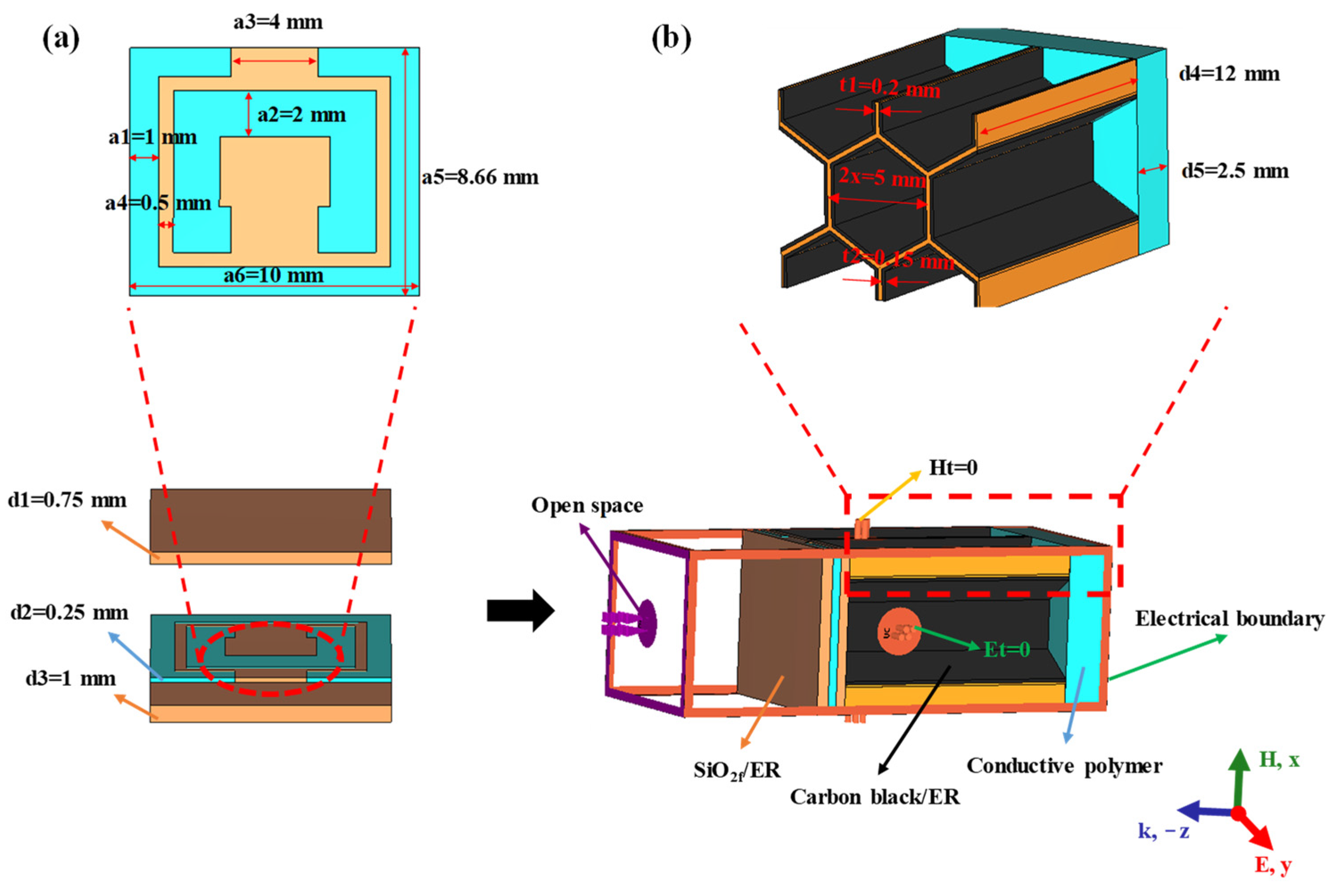
2.1. Material Fabrication
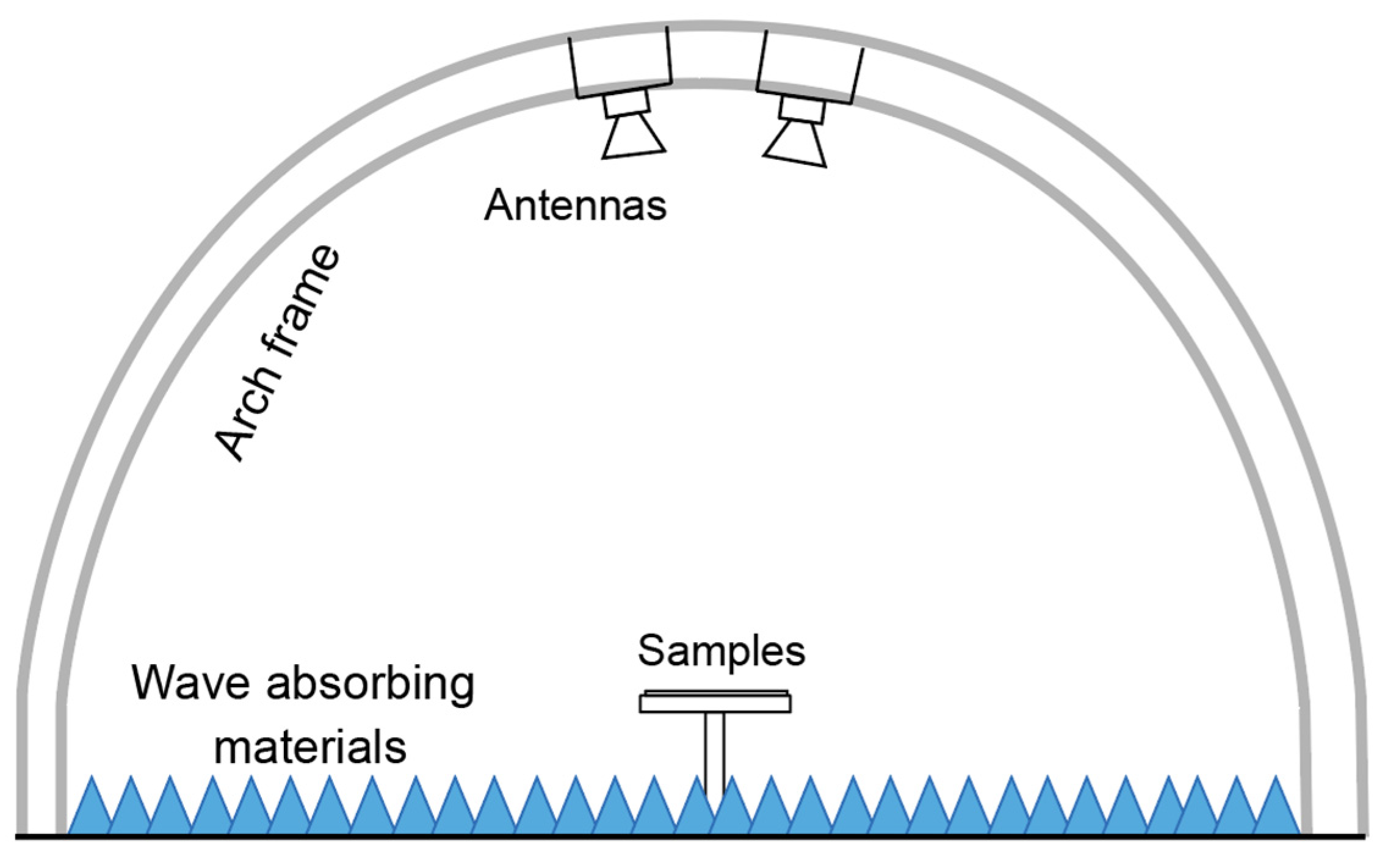
2.2. Characterization, Simulation and Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microwave Absorption Efficiency of Honeycomb with Carbon Black/ER Coating
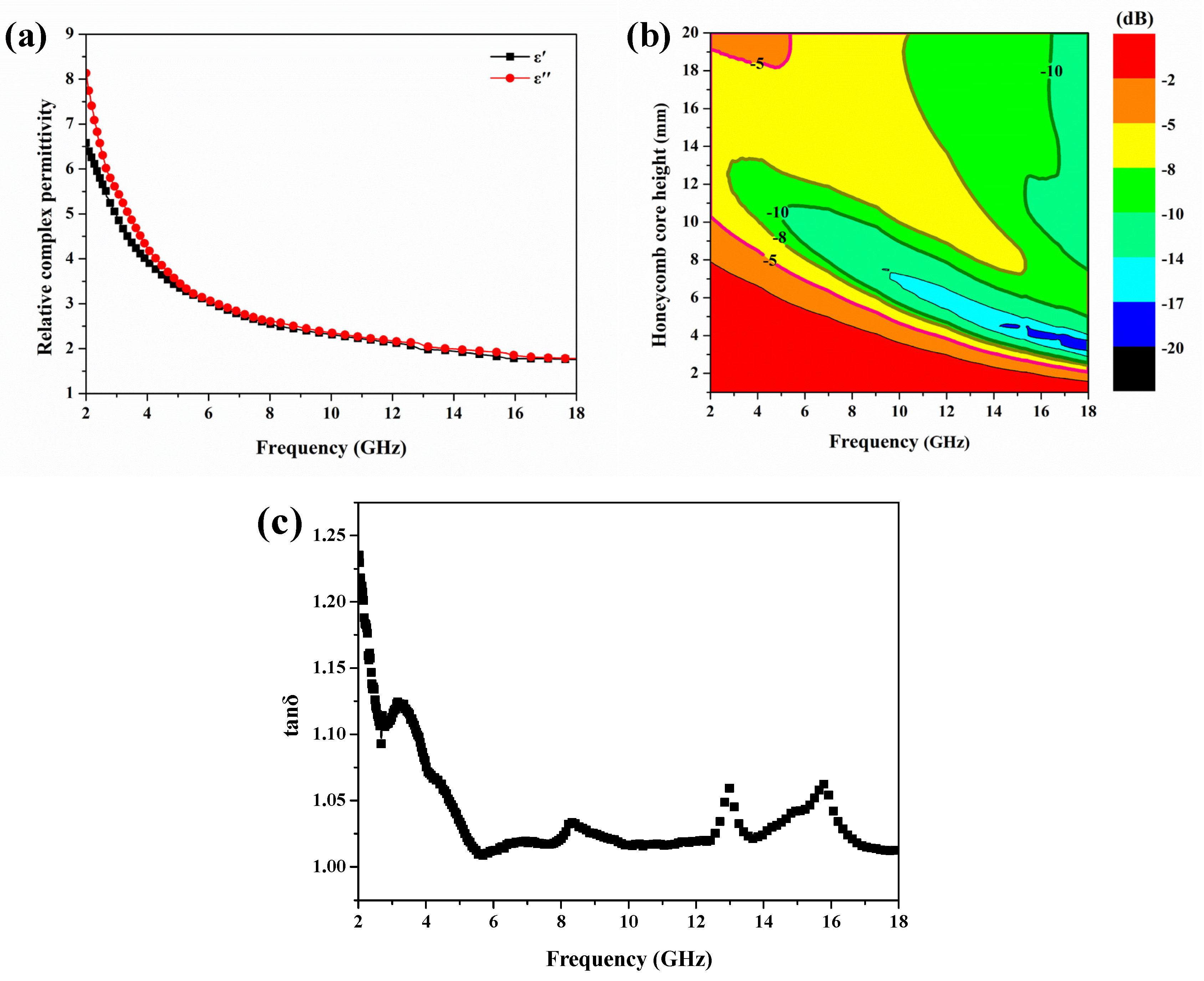
3.2. Microwave Absorption Efficiency of Honeycomb with Bottom Panel Layer
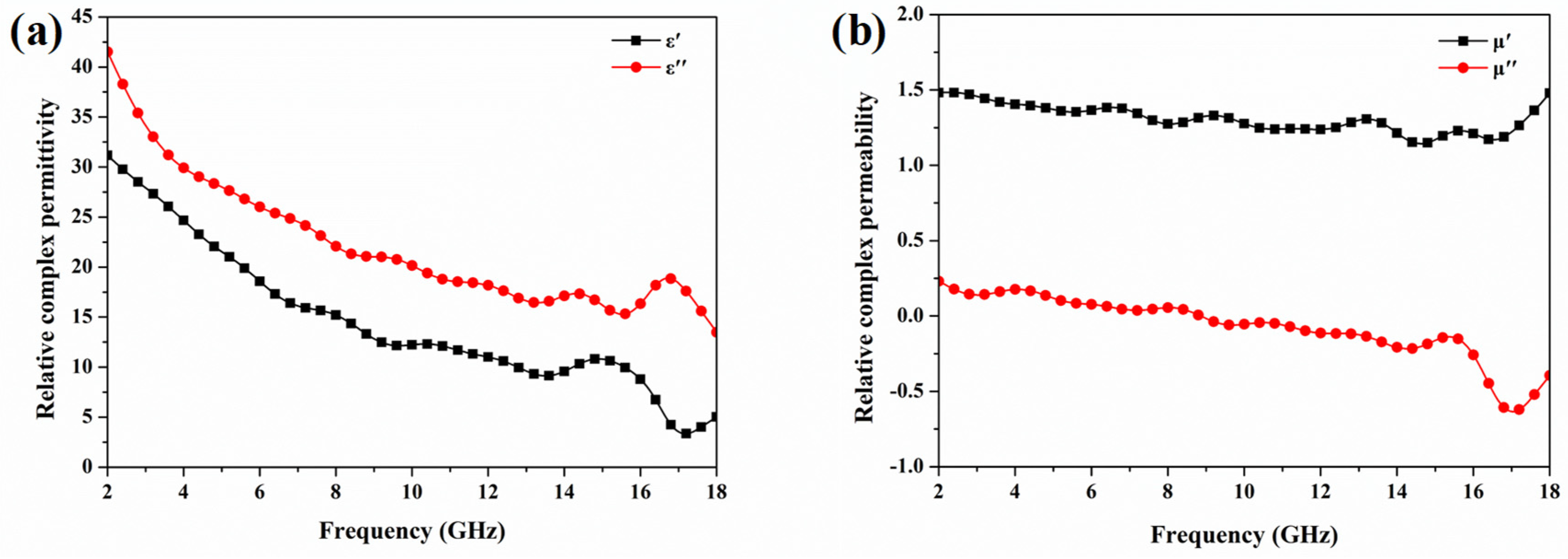
3.3. Microwave Absorption of Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Shan, Y.; Ji, G.; Sun, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, M. Enhanced Microwave-Absorbing Property of Honeycomb Sandwich Structure with a Significant Interface Effect. Materials 2022, 15, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Fang, D. Evolutionary Optimization Design of Honeycomb Metastructure with Effective Mechanical Resistance and Broadband Microwave Absorption. Carbon 2021, 177, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, D.; Vricella, A.; Pastore, R.; Marchetti, M. Synthesis and Electromagnetic Characterization of Frequency Selective Radar Absorbing Materials Using Carbon Nanopowders. Carbon 2014, 77, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, R.G. Official F-19 Stealth Fighter Handbook; Compute: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Xue, B.; Sg, A.; Gu, S.; Ye, F.; Fan, X. Ultra Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing and Scattering Properties of Flexible Sandwich Cylindrical Water-based Metamaterials. Res. Phys. 2022, 38, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainud-Deen, S.H.; Malhat, H.A.; Shabayek, N.A. Reconfigurable RCS Reduction from Curved Structures Using Plasma Based FSS. Plasmonics 2020, 15, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Electromagnetic Properties of Si-C-N Based Ceramics and Composites. Int. Mater. 2014, 59, 326–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhou, M.; Tang, S. Research Progress on Nanostructure Design and Composition Regulation of Carbon Spheres for the Microwave Absorption. Carbon 2022, 189, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Liu, J. Fe-based Material@N-doped Carbon Composites as Environment-Friendly Microwave Absorbers. Carbon 2021, 171, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mahariq, B.; Tran, N. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Dissipation Features of Magnetic Ni Microspheres by Developing Core-Double Shells Structure. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.L.; Choi, Y.L.; Woo, H.J.; Sang, W.K. Microwave Absorption Properties of Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 Composites with Nonmagnetic Nanoferrite Percentages. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 20187–20193. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Cao, Q.; Liu, J.; Guo, B.; Hao, X.; Liu, Q. Hierarchical Cobalt Selenides as Highly Efficient Microwave Absorbers with Tunable Frequency Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. A Frequency Selective Surface Loaded Two-Layer Composite for Tunable Microwave Absorption. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 066301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Panwar, R. Effective Medium Approximation Fused Optimization Strategy Derived New Kind of Honeycomb Microwave Absorbing Structure. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 2501311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.M.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.S. A Study on the Microwave Absorbing Honeycomb Core Embedded with Conductive Periodic Patterned Surfaces for the Effective Dielectric Constant. Compos. Struct. 2022, 289, 115471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Duan, Y.; Dai, Y. The Electromagnetic Response of Composition-Regulated Honeycomb Structural Materials used for Broadband Microwave Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Si, K.; Zha, D.; Li, R.; Jiang, J. Broadband Microwave Absorption Properties of a Frequency-Selective Surface Embedded in a Patterned Honeycomb Absorber. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Electromagnetic and Microwave Absorption Properties of Ti3SiC2/AgNWs/ Acrylic Acid Resin Composite Coatings with FSS Incorporation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 899, 163327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, P.A.; Westphal, W.B.; Von Hippel, A. Dielectric Spectroscopy of Ferromagnetic Semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 279–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Suetake, K. Application of Ferrite to Electromagnetic Wave Absorber and its Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1971, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Schultz, S.; Markos, P. Determination of Effective Permittivity and Permeability of Metamaterials from Reflection and Transmission Coefficients. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 195104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koschny, T.; Markos, P.; Smith, D.R. Resonant and Antiresonant Frequency Dependence of the Effective Parameters of Metamaterials. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 065602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linden, S.; Enkrich, C.; Wegener, M. Magnetic Response of Metamaterials at 100 Terahertz. Science 2004, 306, 1351–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsarakis, N.; Koschny, T.; Kafesaki, M.; Economou, N.E. Electric Coupling to the Magnetic Resonance of Split Ring Resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

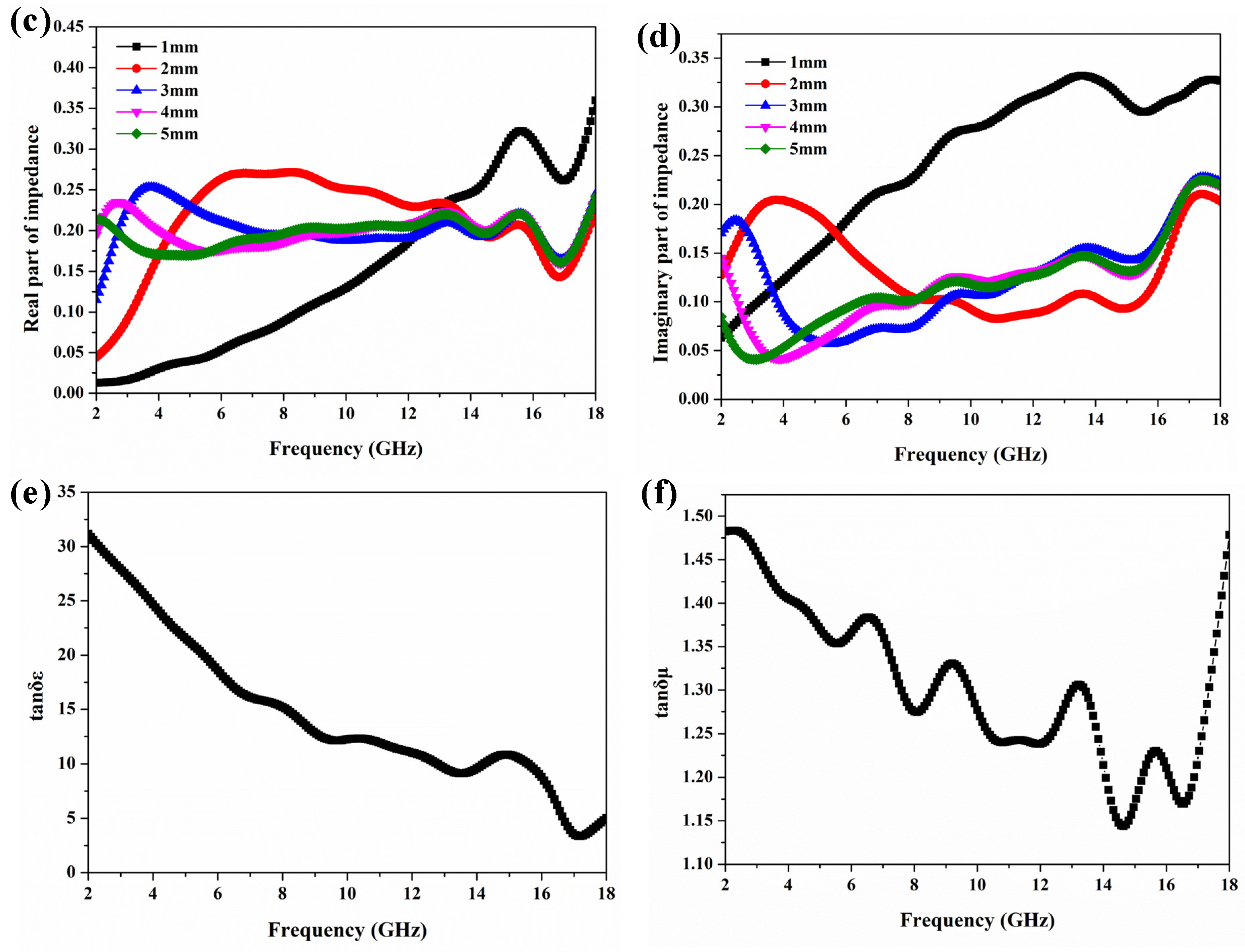

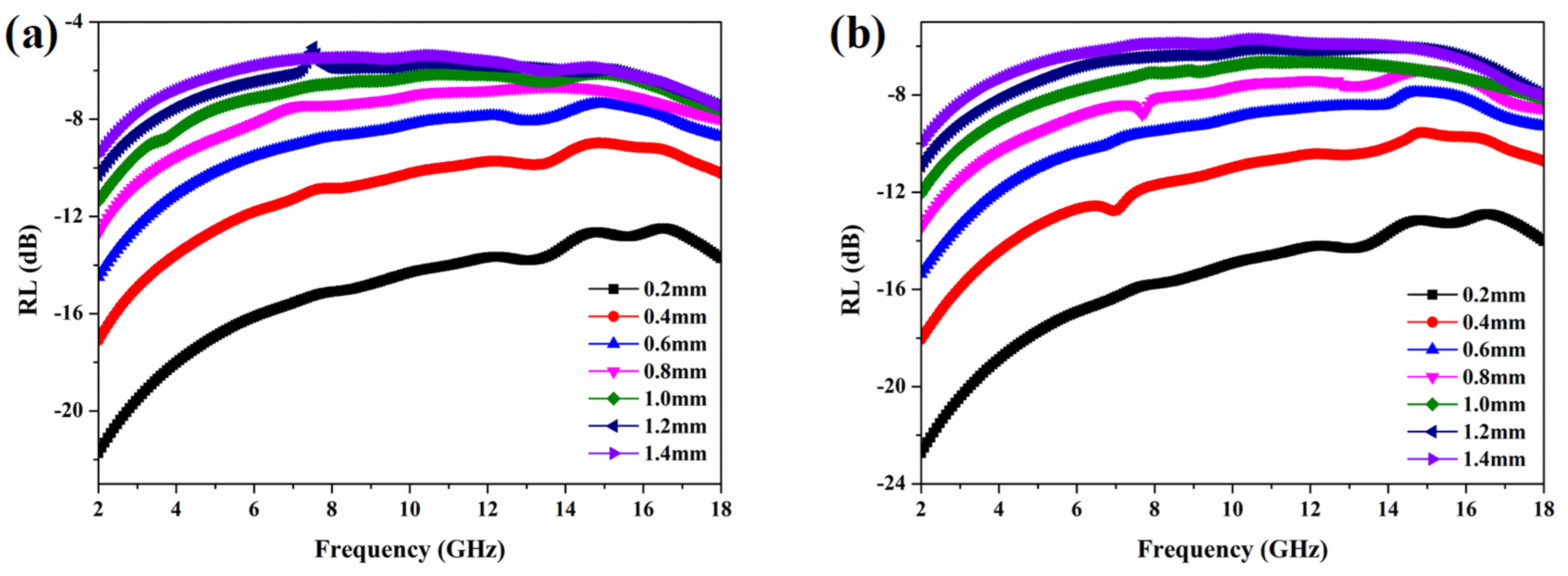
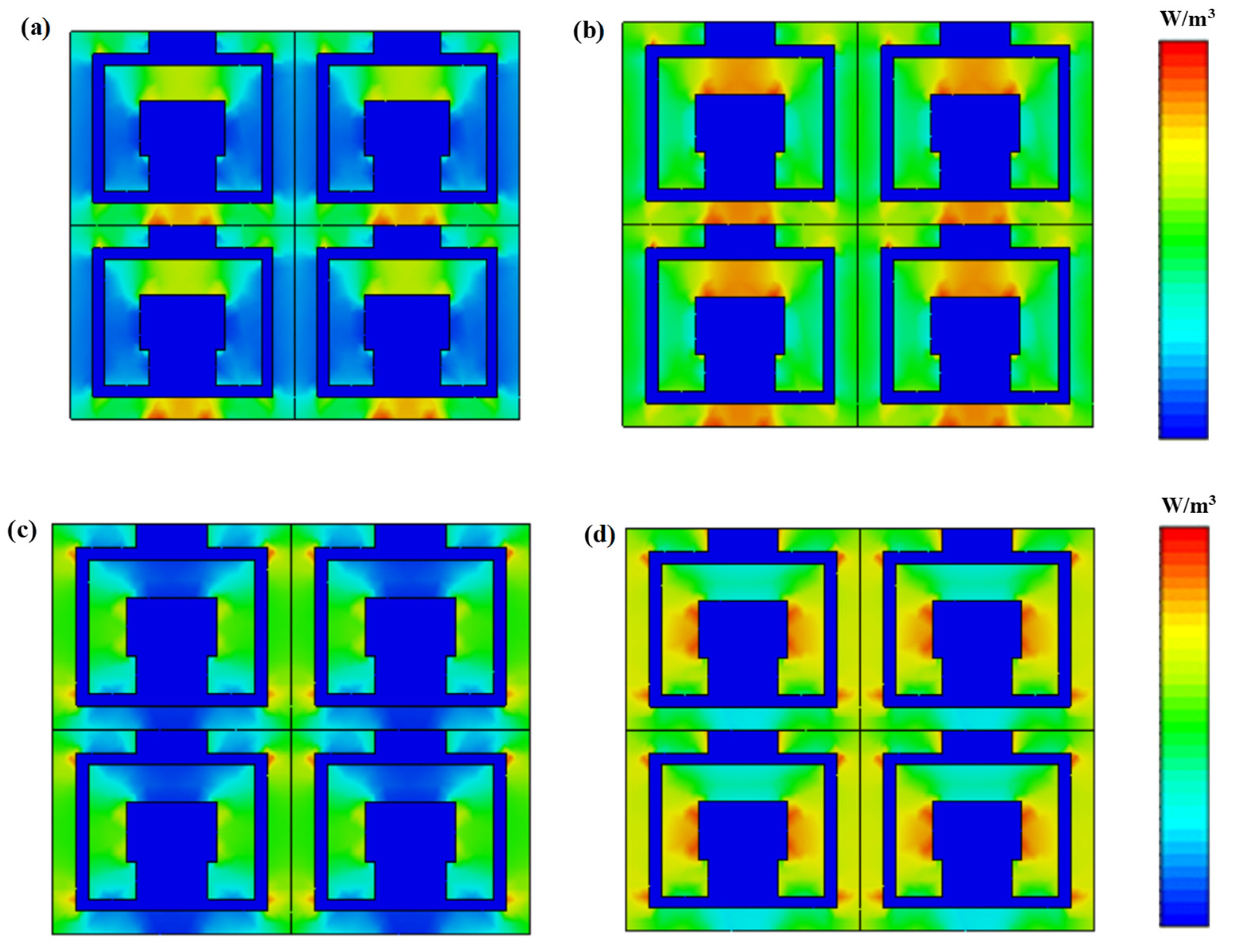
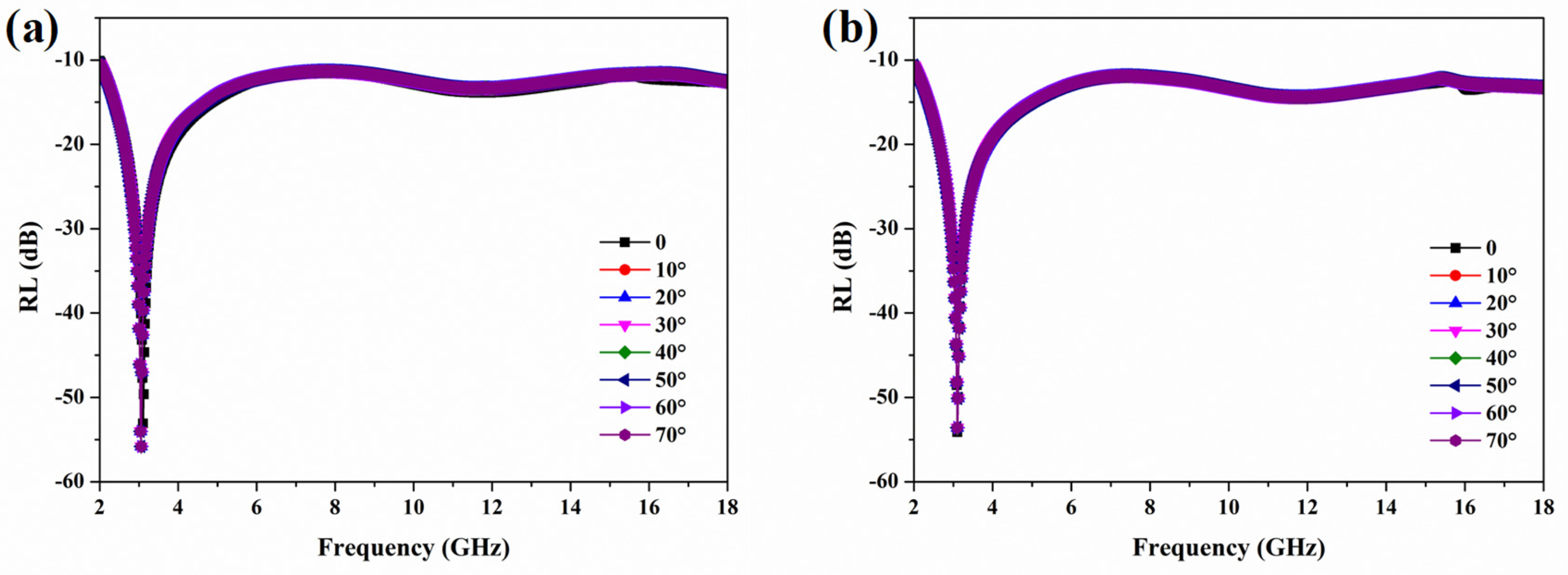
| Frequency Ranges (GHz) | Dimensions of Samples (mm) |
|---|---|
| 1.72–2.61 | 54.46 × 108.92 × (8.0–12.0) |
| 2.60–3.95 | 33.89 × 71.84 × (8.0–12.0) |
| 3.94–5.99 | 22.0 × 47.25 × (8.0–12.0) |
| 5.38–8.2 | 15.75 × 34.70 × (2.0–6.0) |
| 8.2–12.4 | 22.9 × 10.2 × (2.0–6.0) |
| 12.4–18 | 15.9 × 8.03 × (2.0–4.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Ji, G.; Mo, R. A Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Coatings 2022, 12, 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111706
Zhao Y, Liu Q, Xu Z, Ji G, Mo R. A Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Coatings. 2022; 12(11):1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111706
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yiming, Qingwei Liu, Zhonghao Xu, Guoliang Ji, and Ran Mo. 2022. "A Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure for Broadband Microwave Absorption" Coatings 12, no. 11: 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111706
APA StyleZhao, Y., Liu, Q., Xu, Z., Ji, G., & Mo, R. (2022). A Split-Ring Resonator-Loaded Honeycomb Sandwich Structure for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Coatings, 12(11), 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111706






