Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
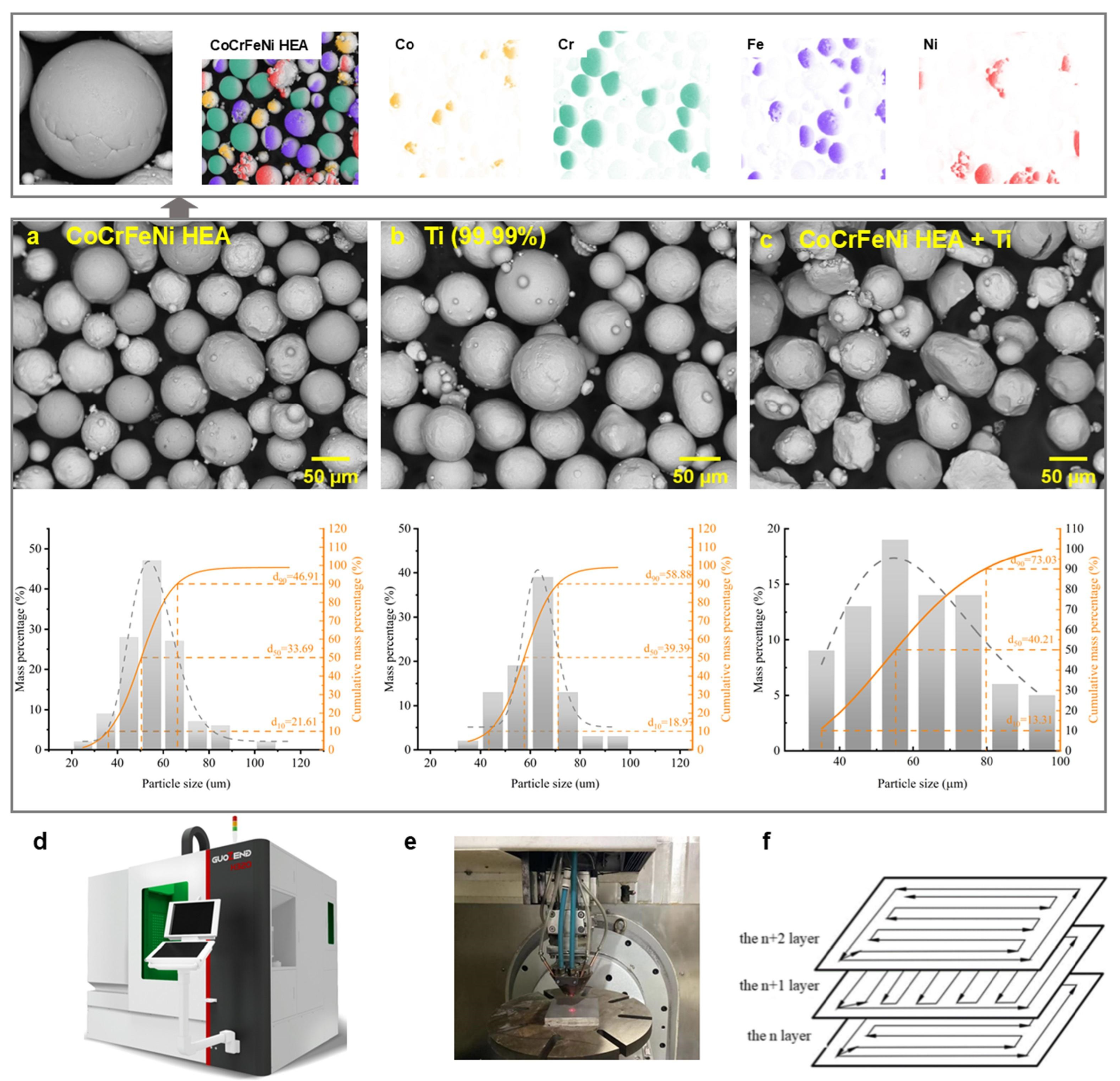
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural and Phase Analysis of CoCrFeNiTix HEAs
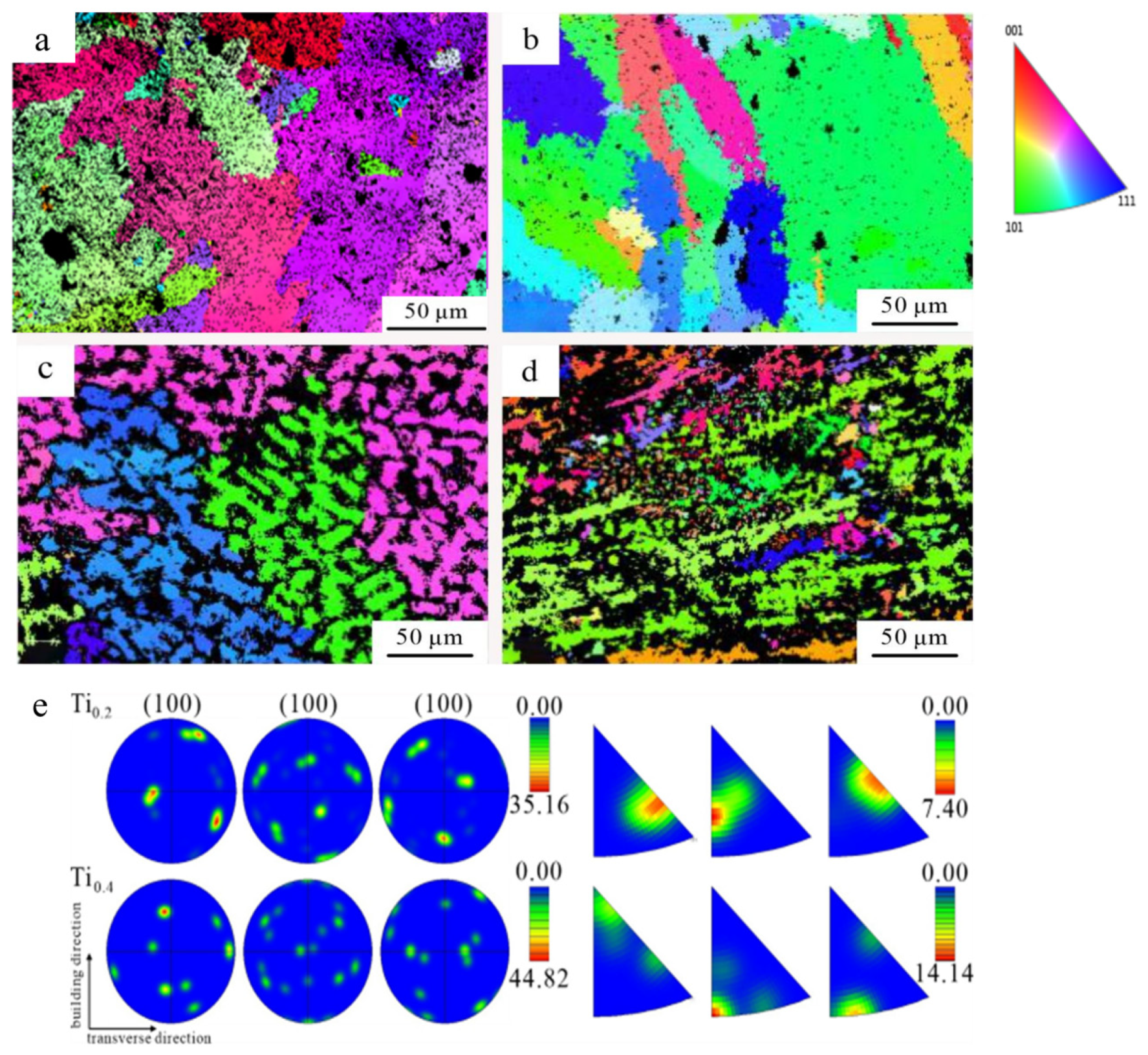
3.1.1. Phase Composition Analysis
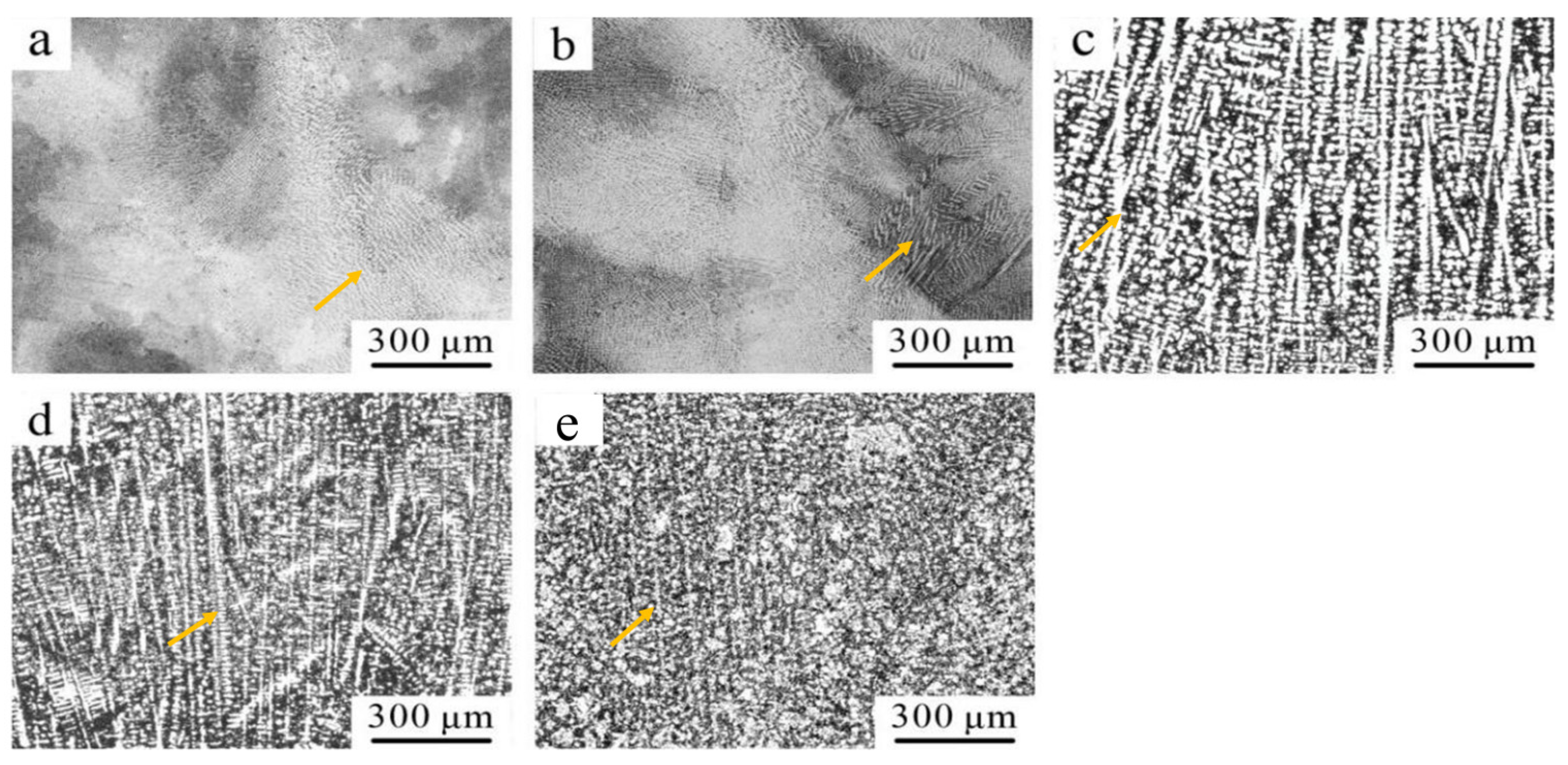
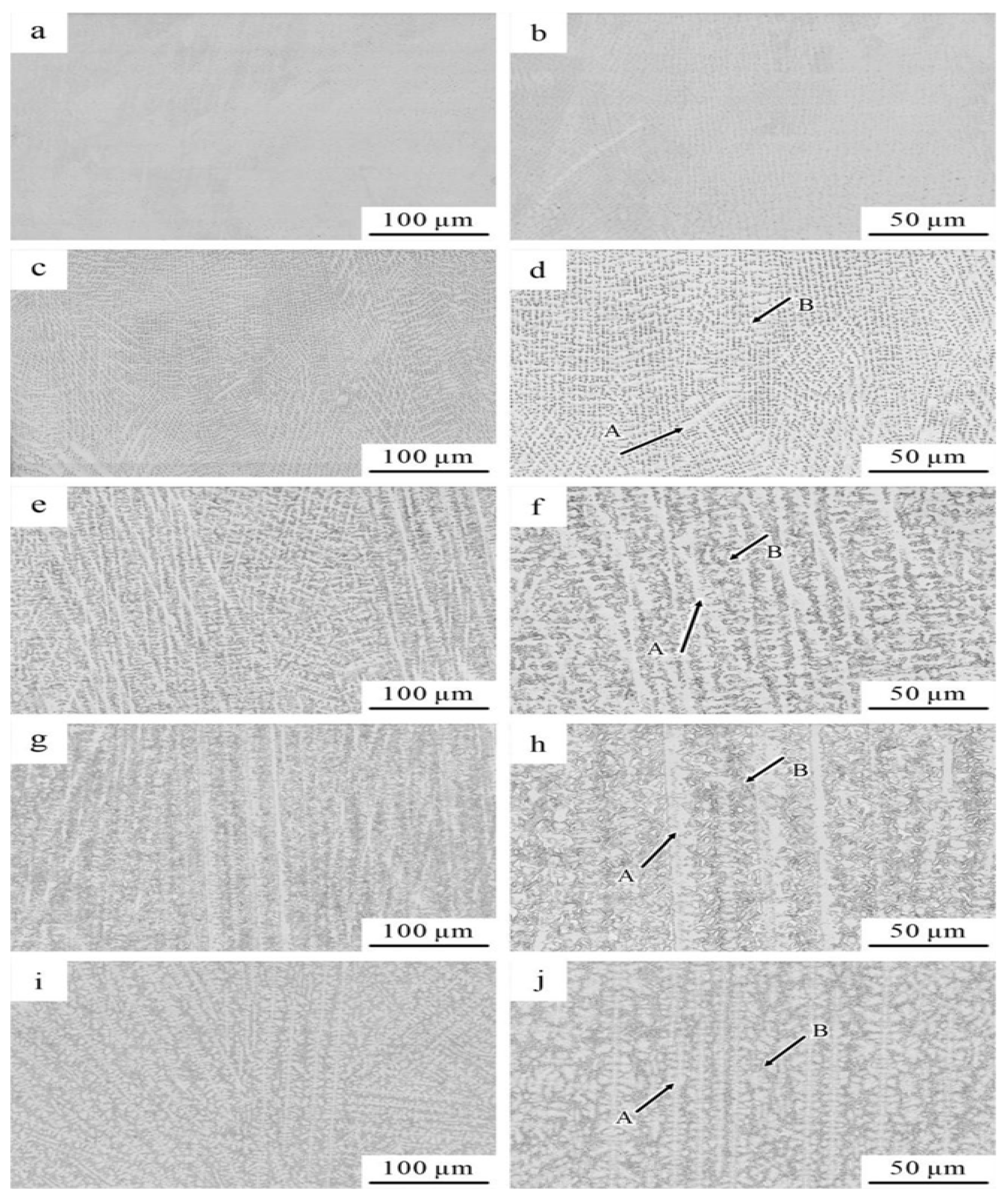
3.1.2. Microstructure and Element Distribution
3.2. Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiTix HEAs
3.2.1. Vickers Microhardness
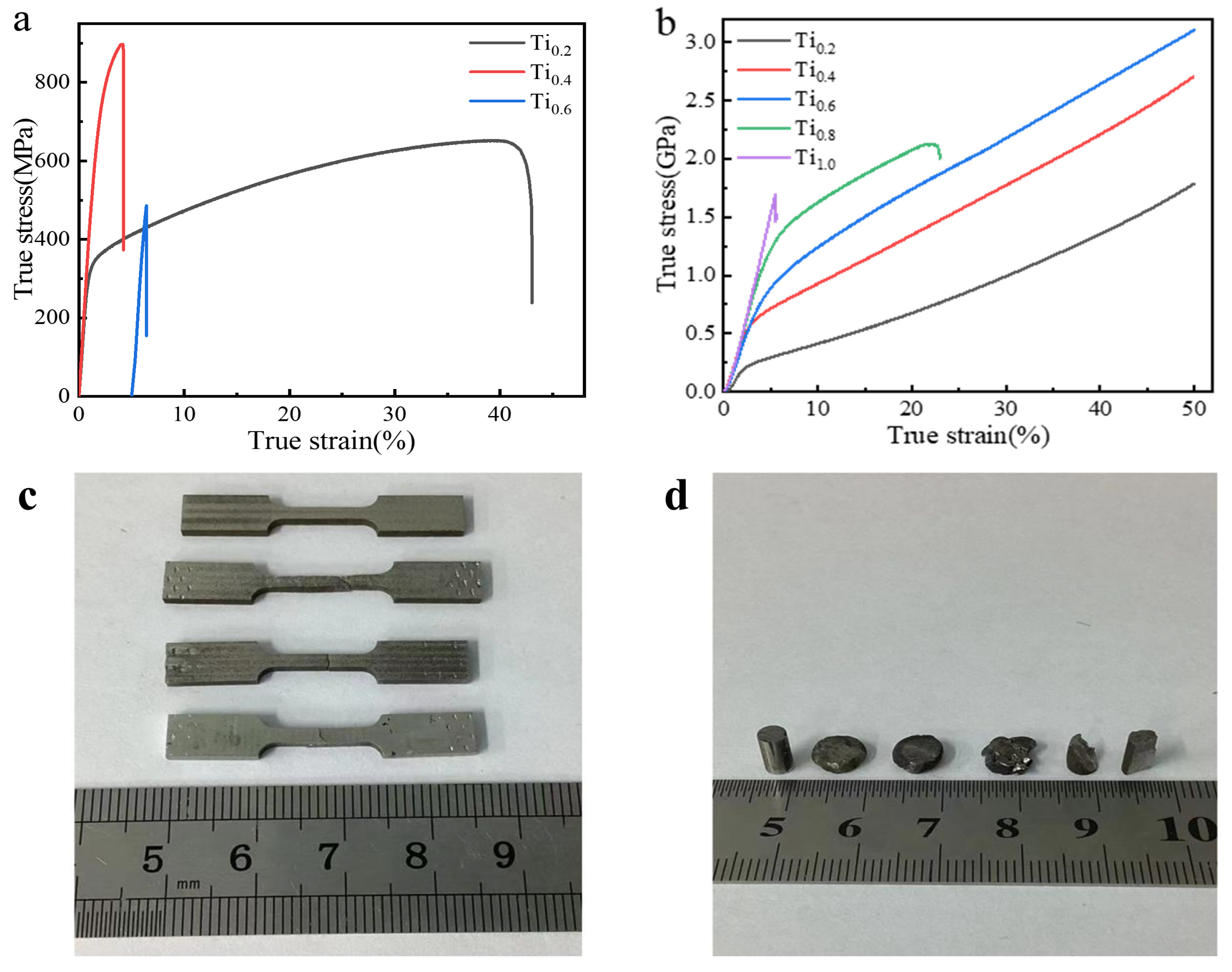
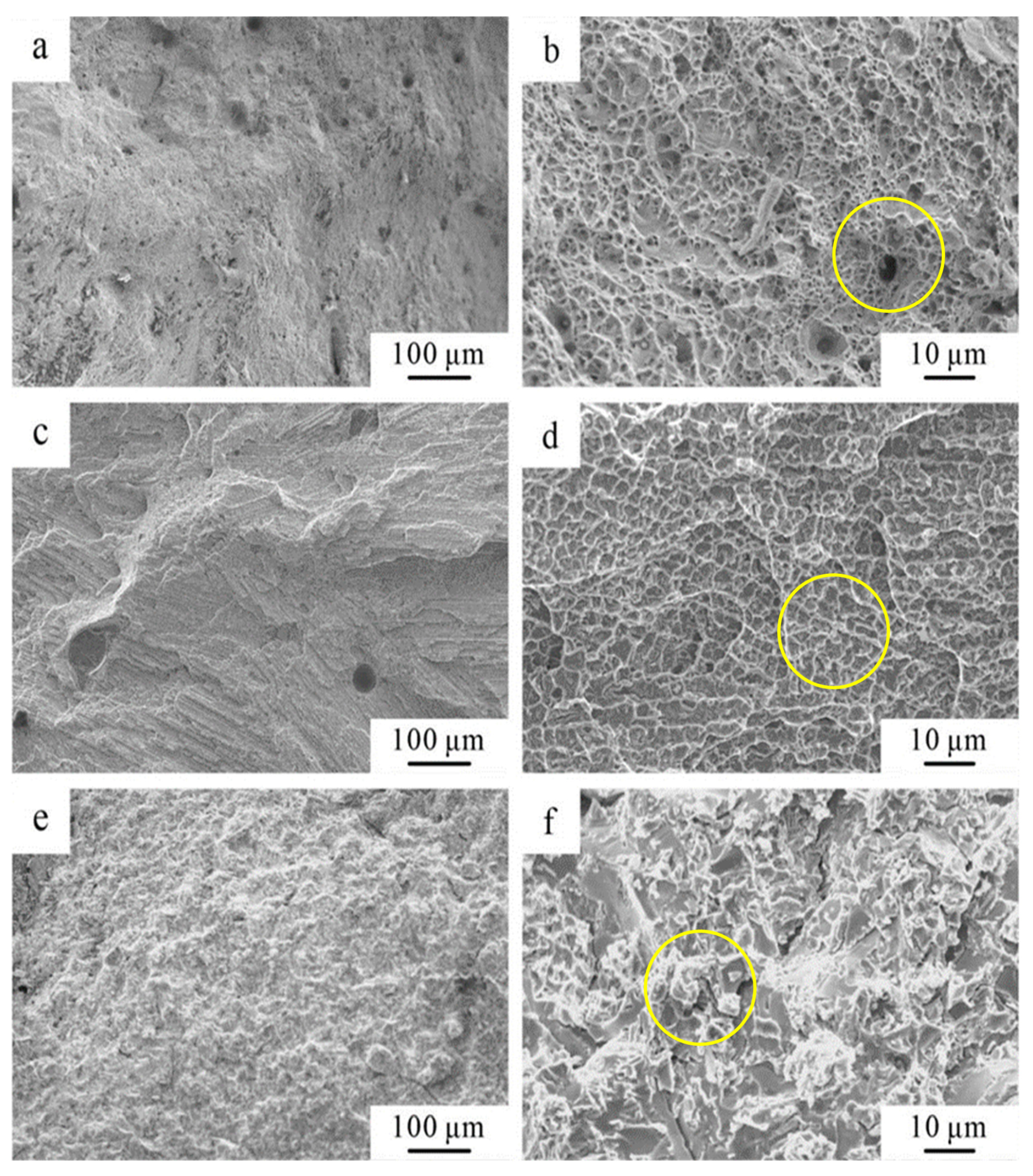
3.2.2. Analysis of Tensile and Compressive Mechanical Properties and Fracture Morphology
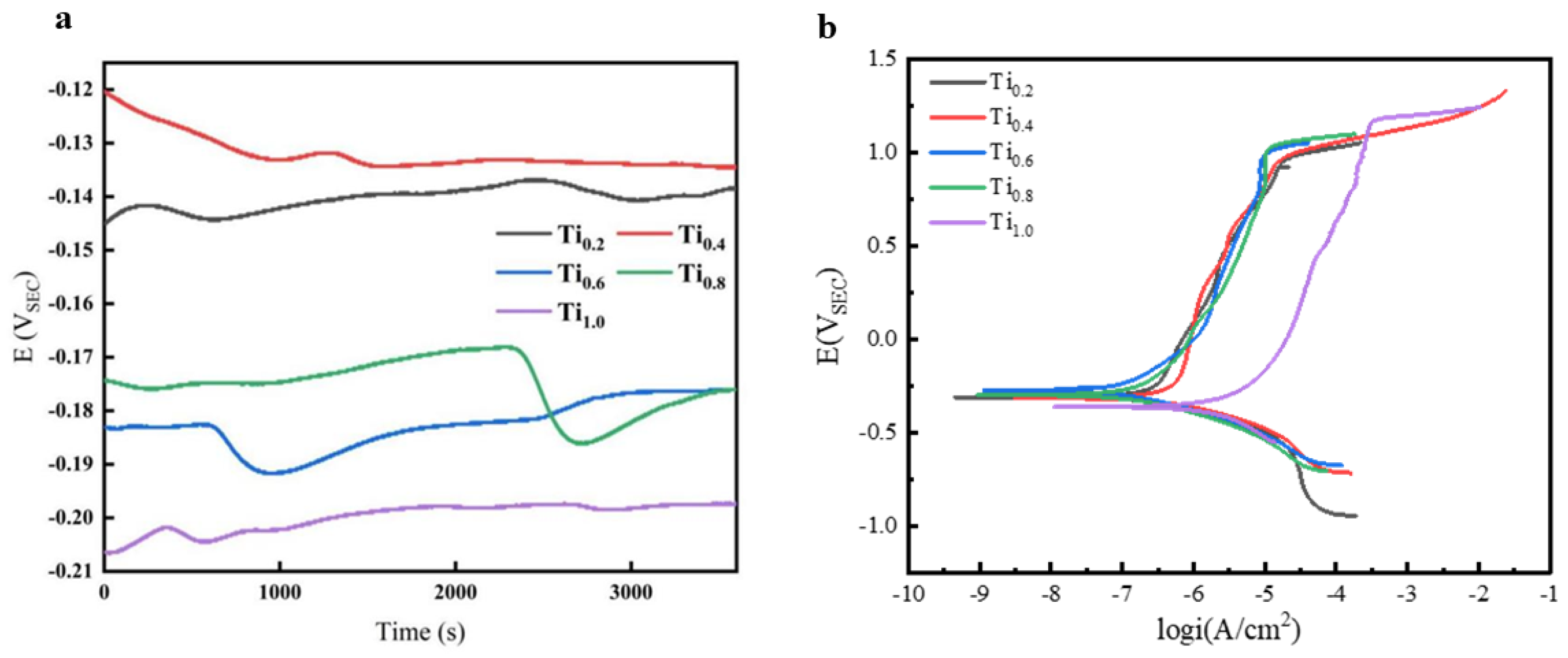
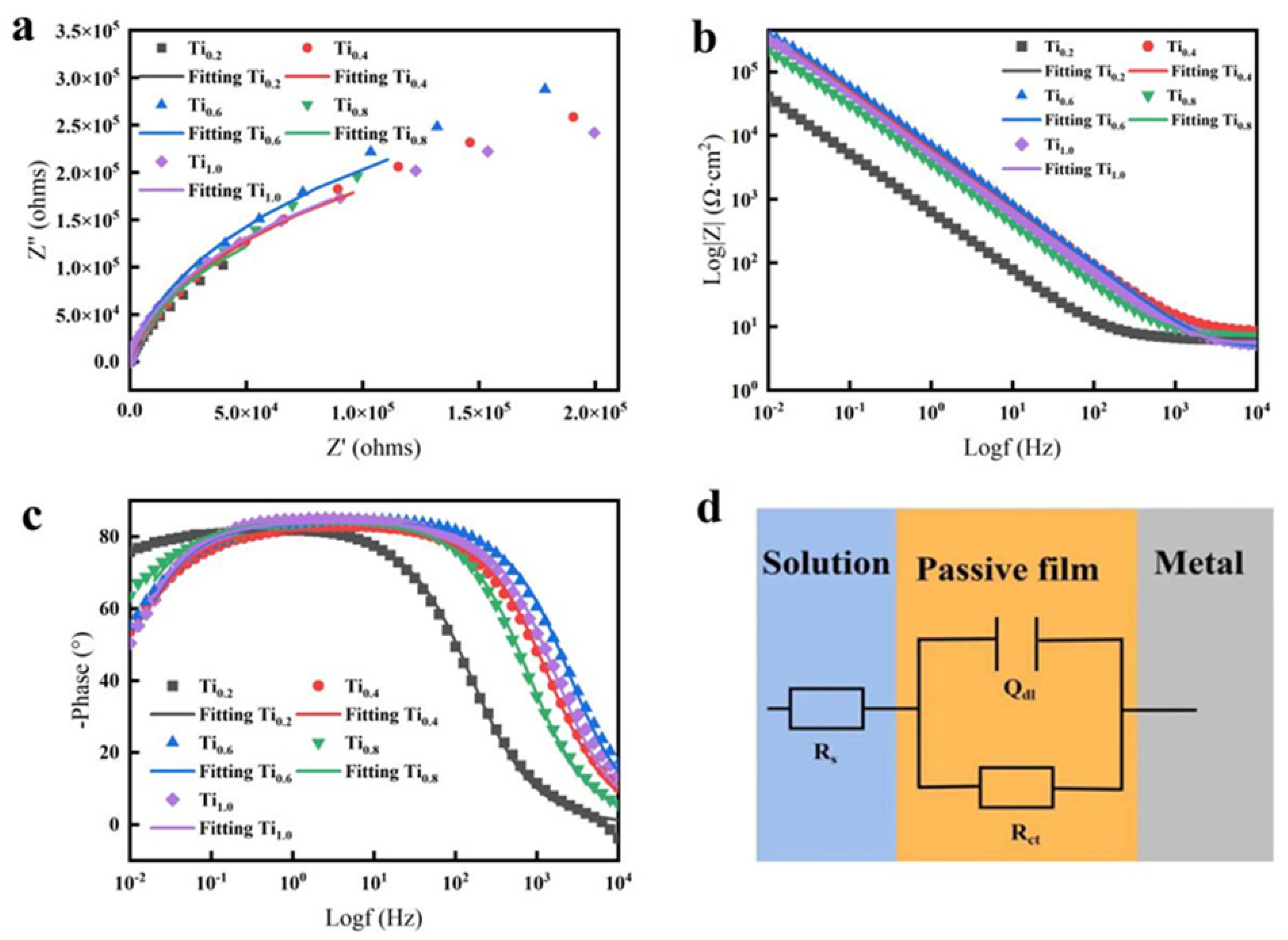
3.3. Analysis of the Corrosion Resistance of CoCrFeNiTix HEAs
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the Ti content was 0.2 at.%, the CoCrFeNiTi0.2 HEA consisted of a single FCC phase. As the Ti content increased, the CoCrFeNiTix HEAs transitioned from a single FCC phase to a dual-phase FCC and BCC structure. With the increase in Ti content, the microstructure of the CoCrFeNiTix HEAs underwent a transformation from an equiaxed to a dendritic morphology, accompanied by grain refinement;
- (2)
- The hardness of the HEA gradually increased with the addition of Ti. The CoCrFeNiTi1.0 HEA exhibited the highest Vickers hardness of 804.5 HV, which was 4.13 times higher than the Vickers hardness of the Ti-free CoCrFeNi HEA (191 HV). This was attributed to solid solution strengthening, grain refinement, and secondary phase strengthening mechanisms. When the Ti content was 0.4 at.%, the CoCrFeNiTix HEA exhibited the optimal mechanical performance, with a yield strength of 412.5 MPa (104.4 MPa higher than CoCrFeNi) and an ultimate tensile strength of 711.2 MPa (136.9 MPa higher than CoCrFeNi). The addition of titanium enhanced the solid solution strengthening, grain refinement strengthening, and secondary phase strengthening capabilities of the alloy, leading to a substantial increase in the microhardness. When the titanium content reached 1.0 at.%, the hardness increased by 4.13 times;
- (3)
- The CoCrFeNiTi0.4 HEA demonstrated the best corrosion resistance in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution, which was likely related to the promotion of the BCC phase formation by the addition of Ti;
- (4)
- The study of the relationship between the microstructural evolution and the mechanical and corrosion performance of the CoCrFeNiTix HEAs revealed that the alloy properties were primarily influenced by the phase composition (FCC/BCC ratio). When x = 0.4 at.%, the CoCrFeNiTi0.4 HEA with a dual FCC and BCC phase structure likely achieved the optimal FCC-to-BCC ratio.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.W.; Chang, S.Y.; Hong, Y.D.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J. Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of Cu–Ni–Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Si alloy systems with multi-principal elements. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracq, G.; Laurent-Brocq, M.; Perrière, L.; Pirès, R.; Joubert, J.M.; Guillot, I. The fcc solid solution stability in the Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni multi-component system. Acta Mater. 2017, 128, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Choudhuri, D.; Soni, V.; Ren, Y.; Styles, M.; Hwang, J.; Nam, S.; Ryu, H.; Hong, S.H.; Banerjee, R. Cu assisted stabilization and nucleation of L12 precipitates in Al0.3CuFeCrNi2 fcc-based high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 129, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.J.; Middleburgh, S.C.; McGregor, A.G.; Cortie, M.B. Predicting the formation and stability of single phase high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.C.; Diao, H.Y.; Ocelík, V.; Vainchtein, D.; Zhang, C.; Kuo, C.; Tang, Z.; Guo, W.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Secondary phases in AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: An in-situ TEM heating study and thermodynamic appraisal. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Investigation of the phase stabilities in AlNiCoCrFe high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lan, L.; Shi, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, J. The tribological properties of Al0.6CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy with the σ phase precipitation at elevated temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, K.; Qiao, D.; Lu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, T. Effects of Ta addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Hirota, M.; Kato, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Watanabe, S. CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy with superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance achieved by a combination of additive manufacturing using selective electron beam melting and solution treatment. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Mingers, A.M.; Raabe, D. Corrosion behavior of an equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy compared with 304 stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2018, 134, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Hao, J. Effect of Si addition on microstructure and wear behavior of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; Sanaullah, K.; Zhang, C.; Chu, J.; Nian, Y.; Cheng, J. Strengthening mechanisms in high entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Niu, S.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T.; Dang, Y. Strengthening the CoCrFeNiNb0.25 high entropy alloy by FCC precipitate. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 667, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, H.; Xie, Z. Strength and ductility synergy of Nb-alloyed Ni0.6CoFe1.4 alloys. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2023, 30, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.T. Precipitation hardening in CoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, B.; Kabra, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, K.; Lee, P.D.; Liu, Y. Deformation mechanisms of Mo alloyed FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy: In situ neutron diffraction. Acta Mater. 2017, 127, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, H.W.; Xie, Z.M.; Wang, M.M.; Yang, J.F.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F.; et al. Tailoring microstructures and tensile properties of a precipitation-strengthened (FeCoNi)94Ti6 medium-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 828, 154457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Peng, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, S. Enhancing strength-ductility synergy in a casting non-equiatomic NiCoCr-based high-entropy alloy by Al and Ti combination addition. Scr. Mater. 2021, 200, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Luo, H.; Li, J.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.; Yao, J. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and electrochemical investigation of the passive behavior of high-entropy FeCoCrNiMox alloys in sulfuric acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 499, 143903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Duval, T.; Hung, U.D.; Yeh, J.W.; Shih, H.C. Microstructure and electrochemical properties of high entropy alloys—A comparison with type-304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2257–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-C.; Lu, H.-N.; Tsai, M.-H.; Wu, B.-W.; Lo, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Chang, S.-Y.; Yen, S.-K. Corrosion mechanism of annealed equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi tri-phase high-entropy alloy in 0.5 M H2SO4 aerated aqueous solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 157, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhao, T.; Du, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of molybdenum content on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of FeCoCrNiMox high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 46, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-J.; Chiang, W.-C.; Wu, J.-K. Corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCrCux high-entropy alloys in 3.5% sodium chloride solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 92, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Xie, X.; Brechtl, J.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion of Al CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: Al-content and potential scan-rate dependent pitting behavior. Corros. Sci. 2017, 119, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Niu, T.; Li, H. Effect of Ti on the corrosion behavior of (FeCrCoNi)100−xTix alloy. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Xia, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qu, N.; Zhu, J. Unraveling microstructure evolution during isothermal annealing treatment in dual-phase FeNiCr0.8Al0.8 high entropy alloy and its effect on corrosion behavior. Corros. Sci. 2024, 237, 112287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-T.; Cheng, K.-C.; Chen, S.-H. Effect of heat treatment on the phase evolution and mechanical properties of atomized AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 803, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yi, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P. Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Kong, X.; Chen, X. Fabrication of bulk Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloy using combined cable wire arc additive manufacturing (CCW-AAM): Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 74, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Arvind Singh, R. Investigation of the Effect of the Thermo-Mechanical Processing of Additively Manufactured CoCrFeNiAl0.4 High-Entropy Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, C.T.; Zhang, Z.; Liaw, P.K. Nanoprecipitate-Strengthened High-Entropy Alloys. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Chen, M.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Watanabe, S. Mechanical and corrosion properties of CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy additive manufactured using selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.A.; Noble, N.; Radhika, N.; Saleh, B. A comprehensive review on advances in high entropy alloys: Fabrication and surface modification methods, properties, applications, and future prospects. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 109, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cui, T.; Guo, H.; Lv, W.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Laser additively manufacturing of Al0.5CoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloys with increased resistances to corrosion 3.5% NaCl and oxidation at 1000 °C. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 10148–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, B.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Jia, C. Comparison of CoCrFeNi coatings prepared via high-speed laser cladding and normal laser cladding on microstructure and properties. Intermetallics 2023, 153, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.R.; Qi, W.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, X.; Xie, L.; Li, D.Y.; Xiang, Y.H. Superior corrosion resistance-dependent laser energy density in (CoCrFeNi)95Nb5 high entropy alloy coating fabricated by laser cladding. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Bei, H.; Gao, Y. Strengthening in Al-, Mo- or Ti-doped CoCrFeNi high entropy alloys: A parallel comparison. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 94, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, Q.S.; Lu, Y.P.; Zhang, P.C.; Li, T.J. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and hardness of CoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 789, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Corbin, M.; Yung, C. High throughput synthesis of CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloys via directed energy deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 916, 165469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, X.; Tian, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Fu, S.; Gao, Y.; Wan, M.; Wang, X. Corrosion behavior of a non-equiatomic CoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy: A comparison with 304 stainless steel in simulated body fluids. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 163036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Huang, D.; Zhuang, Y. Significant evolutions of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.3CoCrFeNiTix high-entropy alloys under annealing treatment. Vacuum 2022, 204, 111350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Fu, H.G.; Ma, T.J.; Wang, K.M.; Yang, X.J.; Lin, J. Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNi-WC/TiC composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 194, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y. On enhancing wear resistance of titanium alloys by laser cladded WC-Co composite coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 107, 105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Sheng, Q.X.; Sun, C.F. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding and CoCr2.5FeNi2Tix high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152986. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, G.; Lei, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, K.; Tan, P.; Yi, J. A Study of the Microstructure and Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys Additive-Manufactured Using Laser Metal Deposition. Coating 2023, 13, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Li, C.; Hao, J.; Li, X.; Dong, C.; Nieh, T. Controlled formation of coherent cuboidal nanoprecipitates in body-centered cubic high-entropy alloys based on Al2(Ni,Co,Fe,Cr)14 compositions. Acta Mater. 2018, 147, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ou, N. Powder plasma arc additive manufacturing of CoCrFeNiWx high-entropy alloys: Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 922, 166245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; He, F.; Han, B.; Wu, Q.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Kai, J.J. Synergistic effect of Ti and Al on L12-phase design in CoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2019, 110, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| HEA | CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | CoCrFeNiTi0.4 | CoCrFeNiTi0.6 | CoCrFeNiTi0.8 | CoCrFeNiTi1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal plane spacing/nm | 0.2076 | 0.2079 | 0.2081 | 0.2089 | 0.2093 |
| lattice constant/nm | 0.3596 | 0.3601 | 0.3604 | 0.3619 | 0.3625 |
| HEA | Area | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | nominal | 23.81 | 23.81 | 23.81 | 23.81 | 4.76 |
| 21.51 | 22.54 | 24.97 | 22.29 | 3.72 | ||
| CoCrFeNiTi0.4 | nominal | 22.72 | 22.72 | 22.72 | 22.72 | 9.12 |
| 20.93 | 21.83 | 21.98 | 21.53 | 7.84 | ||
| CoCrFeNiTi0.6 | nominal | 21.74 | 21.74 | 21.74 | 21.74 | 13.04 |
| A | 18.13 | 22.12 | 23.39 | 21.63 | 9.25 | |
| B | 19.63 | 19.09 | 19.37 | 23.43 | 13.81 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.8 | nominal | 20.83 | 20.83 | 20.83 | 20.83 | 16.68 |
| A | 18.96 | 25.49 | 26.79 | 16.69 | 7.24 | |
| B | 18.51 | 26.63 | 19.35 | 19.27 | 13.11 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi1.0 | nominal | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| A | 19.06 | 25.06 | 23.64 | 13.37 | 13.59 | |
| B | 18.30 | 7.83 | 10.62 | 37.36 | 19.89 |
| HEA | CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | CoCrFeNiTi0.4 |
|---|---|---|
| grain size/μm | 6.56 ± 2.10 | 12.60 ± 5.38 |
| HEA | Measuring Method | Yield Strength (MPa) | Strength of Extension (MPa) | Extend Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | stretch | 308.9 | 652.7 | 43.09 |
| compress | 337.6 | - | >50 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.4 | stretch | 647.2 | 897.5 | 4.2 |
| compress | 513.8 | - | >50 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.6 | stretch | 486.2 | 486.2 | 1.4 |
| compress | 702.2 | - | >50 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.8 | stretch | - | - | - |
| compress | 1045.4 | 2125.5 | 22.9 | |
| CoCrFeNiTi1.0 | stretch | - | - | - |
| compress | 1696.6 | 1696.6 | 5.5 |
| HEA | CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | CoCrFeNiTi0.4 | CoCrFeNiTi0.6 | CoCrFeNiTi0.8 | CoCrFeNiTi1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| icorr/A/cm2 | 2.3246 × 10−7 | 2.1933 × 10−7 | 0.8348 × 10−7 | 1.1543 × 10−7 | 1.5367 × 10−6 |
| Ecorr/V | −0.3081 | −0.3010 | −0.2732 | −0.2957 | −0.3653 |
| ipass/A/cm2 | 1.4825 × 10−5 | 1.3173 × 10−5 | 0.9027 × 10−5 | 1.0402 × 10−5 | 2.9367 × 10−4 |
| Epit/V | −0.9047 | −0.9203 | −0.9654 | −0.9995 | −1.1444 |
| HEA | Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPE (Ω−1·cm2·Sn) | n | Rct (Ω·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrFeNiTi0.2 | 6.409 | 3.6696 × 10−7 | 0.90858 | 4.3627 × 105 |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.4 | 8.367 | 2.9600 × 10−5 | 0.91404 | 6.1911 × 105 |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.6 | 4.710 | 2.5983 × 10−5 | 0.93263 | 7.3187 × 105 |
| CoCrFeNiTi0.8 | 7.082 | 5.0146 × 10−5 | 0.93325 | 5.4944 × 105 |
| CoCrFeNiTi1.0 | 5.328 | 3.2603 × 10−5 | 0.93645 | 5.4619 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Song, D.; Li, L.; Shao, G.; Mi, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, C.; Tan, P. Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Additive Manufacturing. Coatings 2024, 14, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091171
Wang K, Song D, Li L, Shao G, Mi Y, Hu H, Liu C, Tan P. Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Additive Manufacturing. Coatings. 2024; 14(9):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091171
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kai, Daliang Song, Likun Li, Guanghui Shao, Yingye Mi, Huiping Hu, Chuan Liu, and Ping Tan. 2024. "Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Additive Manufacturing" Coatings 14, no. 9: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091171
APA StyleWang, K., Song, D., Li, L., Shao, G., Mi, Y., Hu, H., Liu, C., & Tan, P. (2024). Microstructure and Properties of CoCrFeNiTix High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Additive Manufacturing. Coatings, 14(9), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14091171






