Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties, Morphology, and Phase Structure in Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coatings Sprayed by HVOF Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Reliable Coating Methods
3. Study of Structure and Phase Composition
4. Microstructure and Morphology of Coatings
5. Tribological Performance
6. Analysis of Results of Experiments at High Temperatures
7. Conclusions
- Differences in Cr3C2-NiCr coating performance stem from variations in spraying techniques (HVOF, laser cladding), initial powder morphology (spherical, agglomerated, nanomodified), and processing conditions;
- HVOF coatings exhibit high density, uniform phase distribution, and low porosity, contributing to superior wear resistance and adhesion strength;
- Laser cladding enhances coating structure by forming core–shell architectures and composite binder phases, leading to increased hardness and wear resistance;
- The incorporation of rare-earth metals (e.g., Ce) promotes grain refinement and further improves mechanical properties.
- The differences in test results for Cr3C2-NiCr coatings are attributed to various factors, including the deposition method, heat treatment conditions, bonding layer composition, and failure mechanisms;
- HVOF-sprayed coatings exhibit high hardness and wear resistance; however, under increased load (1000 N), cohesive failure and delamination from the substrate occur;
- In contrast, microwave cladding provides a superior metallurgical bond, reduces porosity, and enhances coating adhesion to the substrate.
- Influence of Temperature and Cooling Rate on Phase Composition
- The observed differences between Cr3C2-NiCr coatings obtained by HVOF and HVAF methods stem from variations in the temperature and cooling rate, which significantly impact phase composition and microstructure;
- High spraying temperatures promote the partial decarburization of Cr3C2, leading to the formation of Cr7C3 and Cr23C6, altering mechanical properties;
- The rapid cooling in HVOF promotes the formation of amorphous phases, increasing hardness but reducing ductility, whereas HVAF preserves the original crystalline powder structure, improving wear resistance;
- Prolonged high-temperature exposure leads to carbide coarsening, reducing binder plasticity and negatively affecting erosion resistance.
- HVOF coatings containing 80% Cr3C2 and 20% NiCr exhibited the highest hardness (1410 HV) and the lowest friction coefficient due to their high carbide content;
- Powder production significantly impacts morphology and phase composition, with Woka 7302 powders forming denser microstructures with reduced decarburization compared to Praxair 1375;
- HVAF coatings provide superior wear resistance under high loads, whereas HVOF coatings perform better under mild conditions;
- Modifications in O2/H2 ratios influence mechanical properties, while spraying distance affects the coefficient of friction and wear resistance.
- Heat treatment enhances coating density and hardness by precipitating secondary carbides, with hardness peaking at 600 °C;
- Beyond this temperature, interface weakening and increased porosity are observed;
- Corrosion resistance improves significantly after annealing, particularly at 600 °C, but higher temperatures induce reactions between coating components, such as Ni and Al, which degrade protective properties;
- As temperature increases, elemental interdiffusion intensifies, affecting mechanical and tribological characteristics.
- Optimizing spraying parameters, such as the powder feed rate and oxygen flow rate, can help balance hardness, fracture toughness, and corrosion resistance;
- HVOF is superior to other spraying methods due to its high particle velocity, providing a dense, wear-resistant coating with low porosity and minimal oxidation;
- Unlike plasma and arc spraying, HVOF reduces the risk of thermal damage to the substrate and provides better adhesion;
- Compared to gas thermal spraying, it forms denser coatings with high hardness;
- These characteristics make HVOF the optimal choice for wear and corrosion protection in aviation, power generation, and mechanical engineering.
- Further research in this direction can focus on developing new composite coating compositions and optimizing their spraying parameters to improve performance characteristics;
- Investigating the role of additional alloying elements and nanostructured powders may lead to coatings with enhanced durability and thermal stability for extreme environments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, K.; Zou, Y.; Wu, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Pulsed Laser Re-Melting Supersonic Plasma Sprayed Cr₃C₂-NiCr Coatings for Regulating Microstructure, Hardness, and Corrosion Properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, X.L.; Fu, H.G.; Sun, S.T.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.Y.; Lei, Y.P. Microstructure and Performance of Nb-Bearing Ni60A- Cr3C2 Coatings Manufactured by Laser Cladding. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghimeresht, E.; Markocsan, N.; Nylen, P. Microstructural Characteristics and Corrosion Behavior of HVAF- and HVOF-Sprayed Fe-Based Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 318, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Pan, H.; Yuan, C.; Chen, X. Research on Remanufacturing Strategy for 45 Steel Gear Using H13 Steel Powder Based on Laser Cladding Technology. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 49, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Grewal, J.S.; Gupta, P. Analysis of D-gun Sprayed Coating on Medium Carbon Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1403–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanchenko, O.; Porkuian, O.; Kharlamov, Y.; Sokolov, V.; Krol, O. Research of Features of Oxide Coatings Deposition by D-gun Spraying. In International Conference Innovation in Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhai, H.; Li, W.; Cui, S.; Ning, W.; Qiu, X. Dry Sliding Wear Behaviors of Fe-based Amorphous Metallic Coating Synthesized by D-gun Spray. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 537, 120018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Mishra, S.B.; Mishra, S.; Yadav, P. Comparative Studies on Oxidation Behaviour of Cobalt-based D-gun Coatings on Boiler Steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 474, 130055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Raman, R.K.S.; Berndt, C.C.; Singh, H. Influence of Cold Spray Parameters on Bonding Mechanisms: A Review. Metals 2021, 11, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, A.; Basha, G.M.T.; Venkateshwarlu, B. A Brief Review on Cold Spray Coating Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashar, G.; Vasudev, H. A Comprehensive Review on Sustainable Cold Spray Additive Manufacturing: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, L. Thermally Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings: Improving the Abrasion Resistance; Tampere University of Technology: Tampere, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Xu, L.; Liu, X. Hydrogen-Induced Embrittlement and Degradation of Zirconium Alloys in Nuclear Reactors: A Review. J. Nucl. Mater. 2021, 543, 152536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, L.; Yuan, G.; Wu, G. Effect of Trace Nickel Addition on Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance and Hydrogen Absorption of Zr-4 Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2022, 51, 4488–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, T.S.; Prakash, S.; Agrawal, R.D. State of the Art of HVOF Coating Investigations-A Review. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2005, 39, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, T. Development of Metal-Ceramic Composite Coatings for Zirconium Alloys in Nuclear Reactors. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 402, 126647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, H. Advances in Protective Coating Technology for Zirconium Alloys Used in Nuclear Applications. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 508, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossis, P.; Pecheur, D.; Hanifi, K.; Thomazet, J.; Blat, M. Comparison of the High Burn-Up Corrosion on M5 and Low Tin Zircaloy-4. J. ASTM Int. 2006, 3, 494–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, B.K.; Baek, J.H.; Jeong, Y.H. Effects of Oxide and Hydrogen on the Behavior of Zircaloy-4 Cladding during the Loss of the Coolant Accident (LOCA). Nucl. Eng. Des. 2006, 236, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, A.; Sobieszczyk, S. Hydrogen Enhanced Degradation and Oxide Effects in Zirconium Alloys for Nuclear Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8619–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charit, I. Accident Tolerant Nuclear Fuels and Cladding Materials. JOM 2018, 70, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.T.; Capolungo, L.; Chen, L.Q.; Cinbiz, M.N.; Daymond, M.R.; Koss, D.A.; Lacroix, E.; Pastore, G.; Simon, P.-C.A.; Tonks, M.R.; et al. Hydrogen in Zirconium Alloys: A Review. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 518, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Yang, H.; Satoh, Y.; Murakami, K.; Kano, S.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, J.; Abe, H. Current Status of Materials Development of Nuclear Fuel Cladding Tubes for Light Water Reactors. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2017, 316, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.T.; Chen, L.Q. Hydrogen Embrittlement and High-Temperature Oxidation of Zirconium Alloys in Nuclear Reactors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 77, 411–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y. Development of Metal-Ceramic Composite Coatings to Prevent Hydrogen Uptake and Oxidation of Zirconium Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Carbides of Group IV: Titanium, Zirconium, and Hafnium Carbides; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Technology Roadmap for Generation IV Nuclear Energy Systems; USDOE: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Berger, L.M.; Hermel, W.; Vuoristo, P.; Mäntylä, T.; Lengauer, W.; Ettmayer, P. Structure, Properties and Potentials of WC-Co, Cr3C2-NiCr and TiC-Ni-Based Hardmetal-Like Coatings. In Proceedings of the Thermal Spray 1996: International Thermal Spray Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 7–11 October 1996. ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espallargas, N.; Berget, J.; Guilemany, J.M.; Benedetti, A.V.; Suegama, P.H. Cr3C2-NiCr and WC-Ni Thermal Spray Coatings as Alternatives to Hard Chromium for Erosion-Corrosion Resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, P.S.; Madhavi, Y.; Krishna, L.R.; Rao, D.S.; Padmanabham, G. Thermally-Sprayed WC-Based Cermet Coatings for Corrosion Resistance Applications. JOM 2018, 70, 2636–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Bhagvandas, M.; Berger, L.M. Creation of Modified Cr₃C₂-NiCr Hardmetal Coating Microstructures Through Novel Processing. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 824, 153868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, G.; Berger, L.M.; Bonetti, M.; Lusvarghi, L. Comparative Study of the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of HVOF-Sprayed WC-(W, Cr)2C-Ni and WC-CoCr Hardmetal Coatings. Wear 2014, 309, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, R.; Kamaraj, M.; Sivakumar, G. HVAF vs. Oxygenated HVAF Spraying: Fundamental Understanding to Optimize Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings for Elevated Temperature Erosion Resistant Applications. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2022, 309, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ice, M.; Schoenung, J.M.; Shin, D.H.; Lavernia, E.J. Thermal Stability of Nanostructured Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2001, 10, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghwal, A.; Matthews, S.; Howse, H.; Berndt, C.C.; Ang, A.S.M. Steam and Air Oxidation Behavior of Thermal Spray Chromium Carbide-Based Composite Coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 111, 106088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Hyland, M.; James, B. Long-Term Carbide Development in High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel/High-Velocity Air Fuel Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Heat Treated at 900 °C. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2004, 13, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Ghasemi, R.; Torabi, S.; Mirjani, B.; Memari, M.; Alizadeh, M. Characterization and High-Temperature Fretting Wear Resistance of HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr, CoCrWC and CoCrWNiC Hardfacing Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 2157–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Hussain, T.; McCartney, D.G. High-Temperature Oxidation of HVOF Thermally Sprayed NiCr-Cr3C2 Coatings: Microstructure and Kinetics. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 6808–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.M. Application of Hardmetals as Thermal Spray Coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 49, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, D. Structural Characteristics and Wear, Oxidation, Hot Corrosion Behaviors of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Hardmetal Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 457, 129319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtari Zavareh, M.; Sarhan, A.A.D.M.; Razak, B.B.; Basirun, W.J. The Tribological and Electrochemical Behavior of HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Ceramic Coating on Carbon Steel. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5387–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lavernia, E.J. Precipitation Phenomenon in Nanostructured Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 301, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilemany, J.M.; Miguel, J.M.; Vizcaino, S.; Lorenzana, C.; Delgado, J.; Sánchez, J. Role of Heat Treatments in the Improvement of the Sliding Wear Properties of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 157, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aligizaki, K.K.; Pawlowski, L. Surface Engineering for Corrosion and Wear Resistance; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, D.M. Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Processing, 2nd ed.; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ohring, M. Materials Science of Thin Films: Deposition and Structure, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, A.C. Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pelton, J.F.; Koffskey, J.M. Coating Composition, Method of Application, and Product Thereof. US Patent 3150938 A, 29 September 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, J.D.; Mignogna, R.; Longo, F.N. Plasma- and Vacuum-Plasma-Sprayed Cr3C2 Composite Coatings. Thin Solid Films 1981, 83, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houck, D.L.; Cheney, R.F. Comparison of Properties of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Thermally Sprayed from Pre-Alloyed and Mechanically Mixed Powders. Thin Solid Films 1984, 118, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulianitsky, V.Y.; Batraev, I.S.; Rybin, D.K.; Dudina, D.V.; Shtertser, A.A.; Ukhina, A.V. Detonation Spraying of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings and Their Properties. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2022, 31, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, Z.; Ma, D.; Lu, J.; Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Hao, Z.; Hu, P.; Yao, M.; et al. Investigation of Oxidation Behaviors of Coated Zircaloy as Accident-Tolerant Fuel with CrAlN and CrAlSiN Coatings in High-Temperature Steam. Corros. Sci. 2020, 175, 108896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Sun, S.; You, B.; Dong, T.; Sui, Y.; Wei, S. Evaluation of Wear Resistance of CrN, CrAlN, and TiAlN Coatings Deposited by Multi-Arc Ion Plating on Spinning Components. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 11, 096402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciubotariu, C.R.; Frunzăverde, D.; Mărginean, G.; Șerban, V.A.; Bîrdeanu, A.V. Optimization of the Laser Remelting Process for HVOF-Sprayed Stellite 6 Wear Resistant Coatings. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 77, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, P.H.; Huang, D.N.; Wu, Z.Z.; Yang, T.; Kai, J.J.; Yan, M. Micro-Arc Oxidation for Improving High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Additively Manufacturing Ti2AlNb. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 445, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snizhko, L.; Yerokhin, A.; Pilkington, A.; Gurevina, N.; Misnyankin, D.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. Anodic Processes in Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of Aluminum in Alkaline Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, S.R.; Dahotre, N.B. Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Bio-Implant Applications: Materials, Performance Factors, and Methodologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 66, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Z. Review of the Biocompatibility of Micro-Arc Oxidation Coated Titanium Alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Merino-Millán, D.; Silvestri, A.; Munez, C.; Poza, P. Mechanical Properties Optimization of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Produced by Compact Plasma Spray Process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 465, 129570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbokov, V.A.; Slobodyan, M.; Pavlov, S.; Smolyanskiy, E.; Uglov, V.; Remnev, G.E. Changes in Adhesion of CrN Coatings on Zr-1%Nb Alloy Substrates Preliminary Irradiated with High-Intensity Pulsed Ion Beams. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2022, 26, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lih, W.C.; Yang, S.H.; Su, C.Y.; Huang, S.C.; Hsu, I.C.; Leu, M.S. Effects of Process Parameters on Molten Particle Speed and Surface Temperature and the Properties of HVOF CrC-NiCr Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 133–134, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.C.; Li, C.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, W.Y. Microstructural Characterization and Abrasive Wear Performance of HVOF Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 6749–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robotti, P.; Zappini, G. Thermal Plasma Spray Deposition of Titanium and Hydroxyapatite on Polyaryletheretherketone Implants. In PEEK Biomaterials Handbook; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrani, K.A.; Parish, C.M.; Shin, D.; Pint, B.A. Protection of Zirconium by Alumina- and Chromia-Forming Iron Alloys under High-Temperature Steam Exposure. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 438, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.J.; Berger, L. Long-Term Compositional/Microstructural Development of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings at 500 °C, 700 °C and 900 °C. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 59, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Vogli, E.; Baumann, I.; Kopp, G.; Weihs, C. Desirability-Based Multi-Criteria Optimization of HVOF Spray Experiments to Manufacture Fine Structured Wear-Resistant 75Cr3C2-25(NiCr20) Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2010, 19, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Jayaganthan, R.; Prakash, S. Evaluation of Cyclic Hot Corrosion Behavior of Detonation Gun Sprayed Cr3C2-25% NiCr Coatings on Nickel- and Iron-Based Superalloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, A.; Patnaik, A.; Meena, M.L.; Shringi, D. Role of Micro-Factors on Microstructure and on the Tribological Performance of HVOF Coatings: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1017, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, B.; Matthews, S.; Hyland, M. Microstructural Influence on Erosion Behavior of Thermal-Spray Coatings. Microsc. Microanal. 2005, 11, 1710–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, J.R.; Johnson, W.R. Friction and Wear Behavior of Chromium Carbide Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1987, 32, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bhandari, D.; Goyal, K. Slurry Erosion Behavior of HVOF Sprayed Coatings on Hydro Turbine Steel: A Review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1033, p. 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.K.; Singh, H.; Kumar, H.; Sahni, V. Slurry Erosive Wear Evaluation of HVOF-Spray Cr2O3 Coating on Some Turbine Steels. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2012, 21, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.M. Coatings by Thermal Spray. In Comprehensive Hard Materials; Sarin, V.K., Mari, D., Llanes, L., Nebel, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikanova, T.Y.; Bondar, A.A.; Grytsiv, A.V. The Chromium-Nickel-Carbon (Cr-Ni-C) Phase Diagram. J. Phase Equilib. 1999, 20, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, V.; Bolelli, G.; Koivuluoto, H.; Honkanen, M.; Vippola, M.; Lusvarghi, L.; Vuoristo, P. A Study of Cr3C2-Based HVOF-and HVAF-Sprayed Coatings: Microstructure and Carbide Retention. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2017, 26, 1239–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, V.; Bolelli, G.; Koivuluoto, H.; Sassatelli, P.; Lusvarghi, L.; Vuoristo, P. Sliding wear behavior of HVOF and HVAF sprayed Cr3C2-based coatings. Wear 2017, 388–389, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganvir, A.; Jahagirdar, A.R.; Mulone, A.; Ornfeldt, L.; Björklund, S.; Klement, U.; Joshi, S. Novel utilization of liquid feedstock in high velocity air fuel (HVAF) spraying to deposit solid lubricant reinforced wear resistant coatings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 295, 117203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhadilov, B.; Muktanova, N.; Kengesbekov, A.; Magazov, N. Use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Methods to Analyze Combustion Chamber Processes at HVOF Spraying and Their Comparison with Experimental Data. Modeling 2025, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ying, G.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; Guo, W. Microstructure and cavitation–silt erosion behavior of high-velocity oxygen–fuel (HVOF) sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 225, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.Y. Evaluation of sprayed chromium carbide coatings for gas-cooled reactor applications. Thin Solid Films 1978, 53, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.A.; Overs, M.P.; Quets, J.M.; Tucker, R.C. Development of several new nickel aluminide and chromium carbide coatings for use in high temperature nuclear reactors. Thin Solid Films 1983, 107, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, T.; Chang, C.; Zheng, X. Steam oxidation resistance of plasma sprayed chromium-containing coatings at 1200 °C. Mater. Corros. 2019, 70, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; James, B. Review of thermal spray coating applications in the steel industry: Part 1—Hardware in steel making to the continuous annealing process. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2010, 19, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardelle, A.; Moreau, C.; Akedo, J.; Ashrafizadeh, H.; Berndt, C.C.; Berghaus, J.O.; Boulos, M.; Brogan, J.; Bourtsalas, A.C.; Dolatabadi, A.; et al. The 2016 Thermal Spray Roadmap. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2016, 25, 1376–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhadilov, B.; Muktanova, N.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Satbayeva, Z.; Kassenova, L.; Magazov, N. Investigation of the Influence of Powder Fraction on Tribological and Corrosion Characteristics of 86WC-10Co-4Cr Coating Obtained by HVOF Method. Coatings 2024, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, N.; Sapate, S.G. Abrasive wear maps for High Velocity Oxy Fuel (HVOF) sprayed WC-12Co and Cr3C2-25NiCr coatings. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, N.; Sapate, S.G.; Bagde, P.; Rathod, A.B. Effect of heat treatment on friction and abrasive wear behavior of WC-12Co and Cr3C2-25NiCr coatings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, N.; Khatirkar, S.G.; Sapate, R.K. Tribological behavior of HVOF sprayed WC-12Co, WC-10Co-4Cr and Cr3C2-25NiCr coatings. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, J.K.N.; Venkataraman, B. Abrasive wear behavior of WC–CoCr and Cr3C2-20(NiCr) deposited by HVOF and detonation spray processes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdková, S.; Zahálka, F.; Kašparova, M.; Berger, L.-M. Comparative Study of Thermally Sprayed Coatings Under Different Types of Wear Conditions for Hard Chromium Replacement. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 43, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Q.; Luer, L. The erosion-oxidation behavior of HVOF Cr3C2-NiCr cermet coating. Wear 1994, 174, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; James, B.; Hyland, M. High temperature erosion of Cr3C2-NiCr thermal spray coatings—The role of phase microstructure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lin, Y.; Ke, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhen, Z.; Ge, L. Influence of Process Parameters on High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Sprayed Cr3C2-25%NiCr Coatings. Coatings 2017, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, D.; Legoux, J.G.; Lima, R.S. Engineering HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings: The Effect of Particle Morphology and Spraying Parameters on the Microstructure, Properties, and High Temperature Wear Performance. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2013, 22, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoui, T.; Fenineche, N.E.; Montavon, G.; Coddet, C. Structure and wear behavior of HVOF sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr and WC–Co coatings. Mater. Des. 2003, 24, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, G.; Berger, L.M.; Börner, T.; Koivuluoto, H.; Matikainen, V.; Lusvarghi, L.; Lyphout, C.; Markocsan, N.; Nylén, P.; Sassatelli, P.; et al. Sliding and Abrasive Wear Behavior of HVOF- and HVAF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Hardmetal Coatings. Wear 2016, 358–359, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Deng, C.; Zeng, K. High temperature wear performance of HVOF-sprayed Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo and Cr3C2-NiCr hardmetal coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Duan, D.; Li, S.; Sun, D.; Yong, J.; Jiang, Y.; He, W.; Xu, J. Microstructure and High-Temperature Properties of Cr3C2-NiCr Nanoceramic Coatings Prepared by HVAF. Coatings 2023, 13, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam Kevin, P.; Tiwari, A.; Seman, S.; Beer Mohamed, S.A.; Jayaganthan, R. Erosion-Corrosion Protection Due to Cr3C2-NiCr Cermet Coating on Stainless Steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhadilov, B.; Muktanova, N.; Seitkhanova, A.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Dautbekov, M. Investigation of the Influence of the Oxygen Flow Rate on the Mechanical, Structural and Operational Properties of 86WC-10Co-4Cr Coatings, as Determined Using the High-Velocity Oxyfuel Spraying Method. Coatings 2024, 14, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbanbekov, S.; Rakhadilov, B.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Seitov, B.; Katpaeva, K.; Kurmantayev, A.; Dautbekov, M.; Kengesbekov, A. Research on the Structural–Phase and Physical–Mechanical Characteristics of the Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coating Deposited by the HVOF Method on E110 Zirconium Alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, H.; Bao, C. Corrosive Wear Mechanism of Supersonic Atmospheric Plasma Spray Coating of Hydraulic Supports in Industrial Environment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, G.L.; Wang, H.D.; Kang, J.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Wang, H.J. Structure and wear behavior of NiCr-Cr3C2 coatings sprayed by supersonic plasma spraying and high velocity oxy-fuel technologies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alroy, R.J.; Kamaraj, M.; Sivakumar, G. Influence of processing condition and post-spray heat treatment on the tribological performance of high velocity air-fuel sprayed Cr3C2-25NiCr coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 463, 129498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, M.; Suegama, P.H.; Espallargas, N.; Fugivara, C.S.; Dosta, S.; Guilemany, J.M.; Benedetti, A.V. Corrosion and Wear Studies of Cr3C2-NiCr -HVOF Coatings Sprayed on AA7050 T7 Under Cooling. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.-Y.; Li, F.-Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Wang, L.-M.; Lu, H.-Y.; Ran, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-Y. Influences of plasma arc remelting on microstructure and service performance of Cr3C2-NiCr/ NiCrAl composite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 369, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašparova, M.; Zahálka, F.; Houdková, S. WC-Co and Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings in Low- and High-Stress Abrasive Conditions. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Pauschitz, A.; Bernardi, J.; Koch, T.; Franek, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of HVOF sprayed nanocrystalline Cr3C2-(25Ni20Cr) coating. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2006, 15, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Irfan; Gong, Q.; Wang, H.; Hu, M. Deposition mechanisms and characteristics of nano- modified multimodal Cr3C2-NiCr coatings sprayed by HVOF. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 61, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzuardy, J.; Basuki, E.A.; Martides, E.; Septianissa, S.; Prawara, B.; Junianto, E.; Riyanto, E. Microstructure Characteristics of Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Deposited with the High-Velocity Oxy-Fuel Thermal-Spray Technique. Mater. Technol. 2024, 58, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan; Hu, M.; Meng, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, A. Microstructures and properties of nano- modified multimodal Cr3C2-NiCr coatings made through laser cladding. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 18516–18532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmuga Priyan, M.; Azad, A.; Araffath, S.Y. Influence of HVOF Parameters on the Wear Resistance of Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. J. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 2016, 4, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, P.; Kaur, M. Wear and Friction Characteristics of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 14, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, P.; Shang, L.; He, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Jin, K. Tribological Behaviors of CrN/Cr3C2-NiCr Duplex Coating at Elevated Temperatures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 378, 124926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhadilov, B.; Muktanova, N.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Adilkanova, M.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Abdulina, S. Influence of Varying the Spraying Distance on the Structural-Phase State and Mechanotribological Properties of 86WC-10Co-4Cr-Based Coatings Obtained by the HVOF Method. Coatings 2024, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Du, L.; Zhang, W. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Plasma-Sprayed Self-Lubrication Coating with Clad Powder at Elevated Temperatures up to 800 °C. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2014, 23, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; Kaur, M.; Singh, S. High Temperature Tribological Performance of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coating on H13 Tool Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudenziati, M.; Gazzadi, G.C.; Medici, M.; Dalbagni, G.; Caliari, M. Cr3C2-NiCr HVOF-Sprayed Coatings: Microstructure and Properties Versus Powder Characteristics and Process Parameters. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2010, 19, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahade, S. Investigating Load-Dependent Wear Behavior and Degradation Mechanisms in Cr3C2-NiCr Coatings Deposited by HVAF and HVOF. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4595–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K.; Zhao, L.; Oete, M.; Königstein, T.; Steeger, M. Impact Wear of an HVOF-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Coating. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 70, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Effects of Elevated Temperature Exposure on the Microstructural Evolution of Ni(Cr)-Cr3C2 Coated 304 Stainless Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Yang, F.; Zou, Z.; Gu, L.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xiao, P. A Study of the Zirconium Alloy Protection by Cr3C2-NiCr Coating for Nuclear Reactor Application. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 287, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straffelini, G.; Federici, M. HVOF Cermet Coatings to Improve Sliding Wear Resistance in Engineering Systems. Coatings 2020, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, L.; Norpoth, J.; Eicher, S.; Ripoll, M.R.; Vuoristo, P. Improving the Toughness of Thermally Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr Hardmetal Coatings by Laser Post-Treatment. Mater. Des. 2016, 98, 135–142, 157, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, C.; Hu, K.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Z.; Yang, Y. Improvement in High-Velocity Air-Fuel-Sprayed Cr3C2-NiCr/(NiAl, NiCr) Composite Coatings by Annealing Heat Treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbale, A.M.; Kumar, M.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Ahamad, T.; Kalam, M.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khalid, M. A Comparative Study on Characteristics of Composite (Cr3C2-NiCr) Clad Developed Through Diode Laser and Microwave Energy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, D. On Microstructure and Flexural Strength of Metal-Ceramic Composite Cladding Developed Through Microwave Heating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5583–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Sharma, S. Development of Ni-Based and CeO2-Modified Coatings by Microwave Heating. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, L.; Yun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, X. Comparative Study of HVOF Cr₃C₂-NiCr Coating with Different Bonding Layer on the Interactive Behavior of Fatigue and Corrosion. Coatings 2022, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
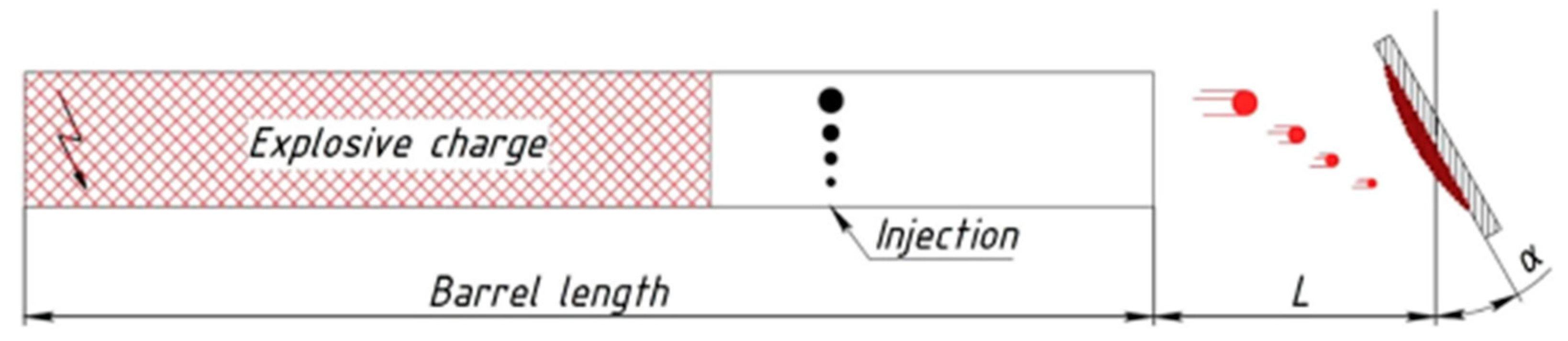
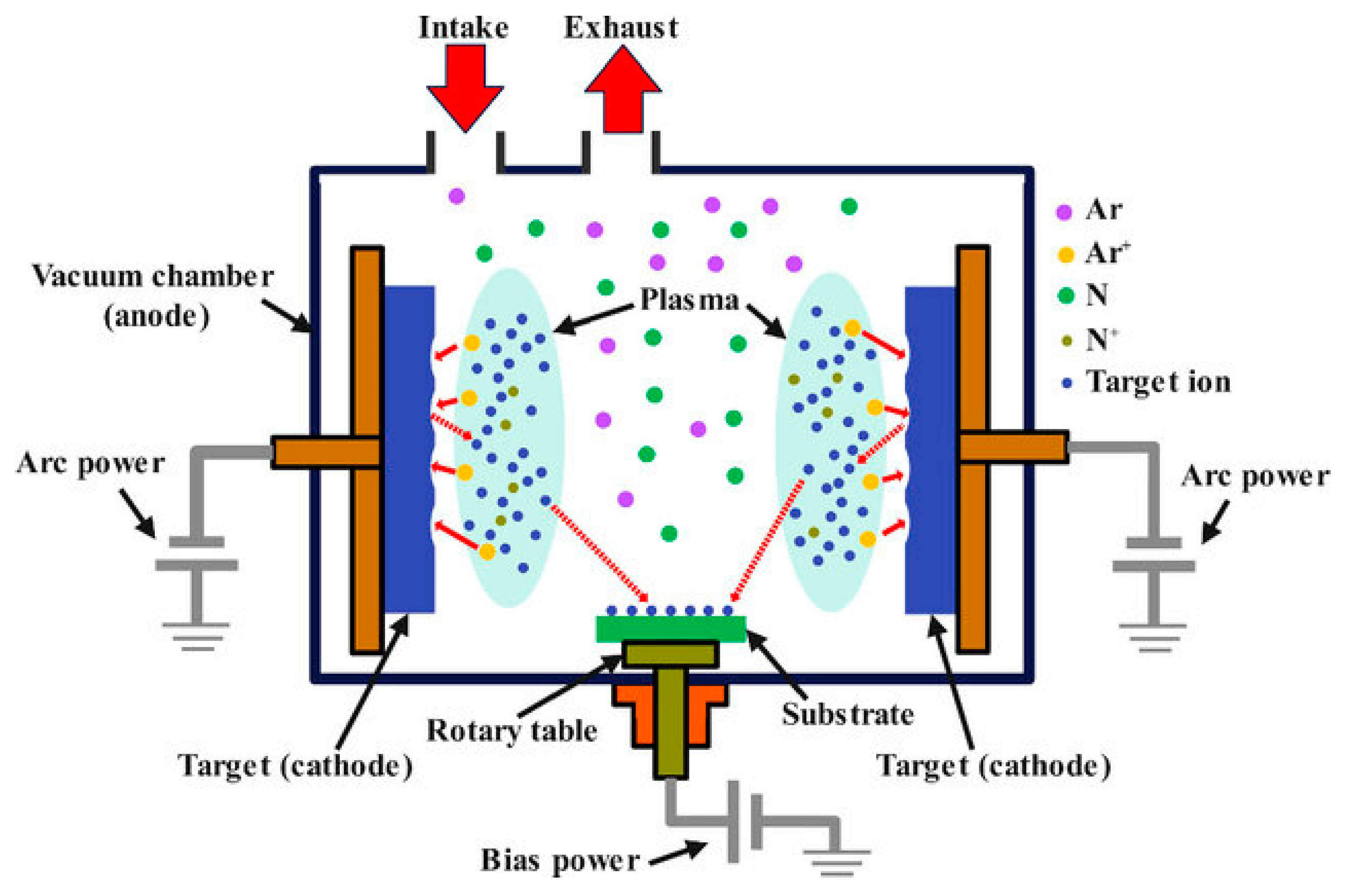
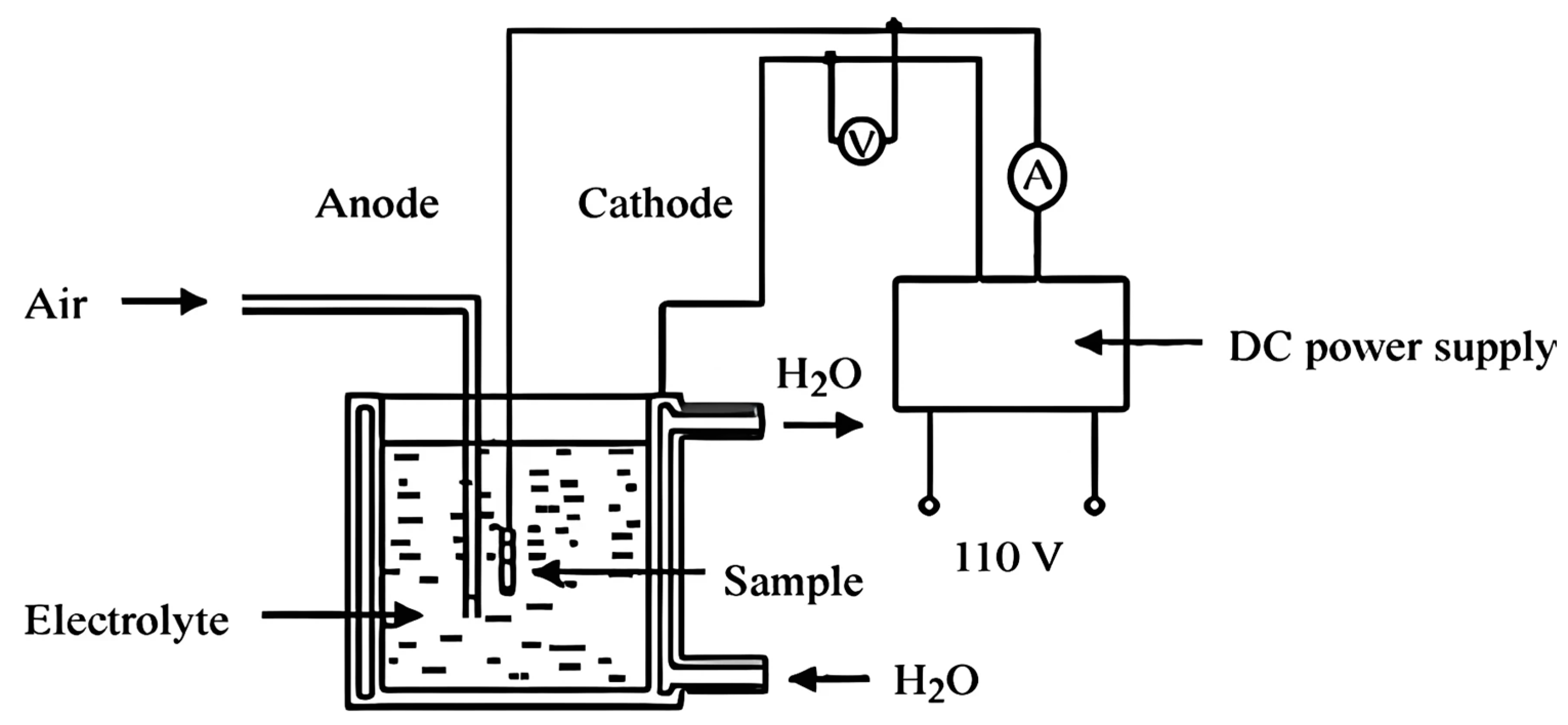
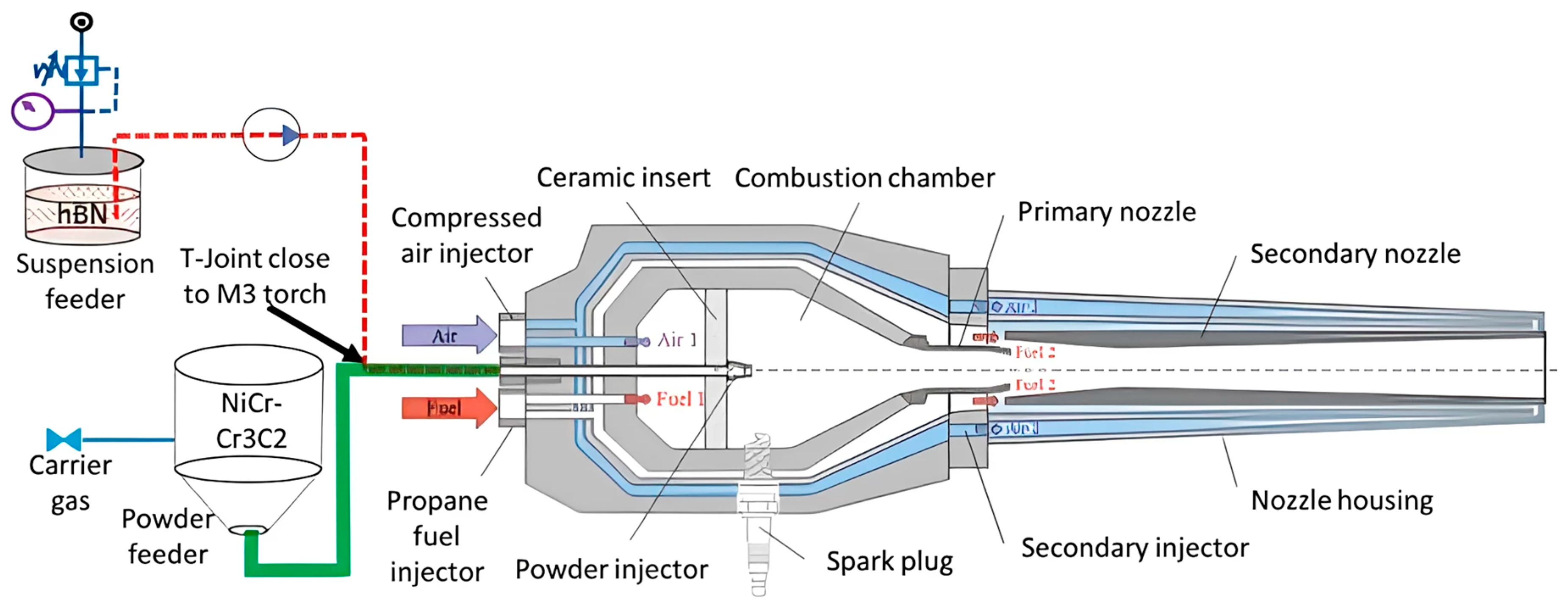

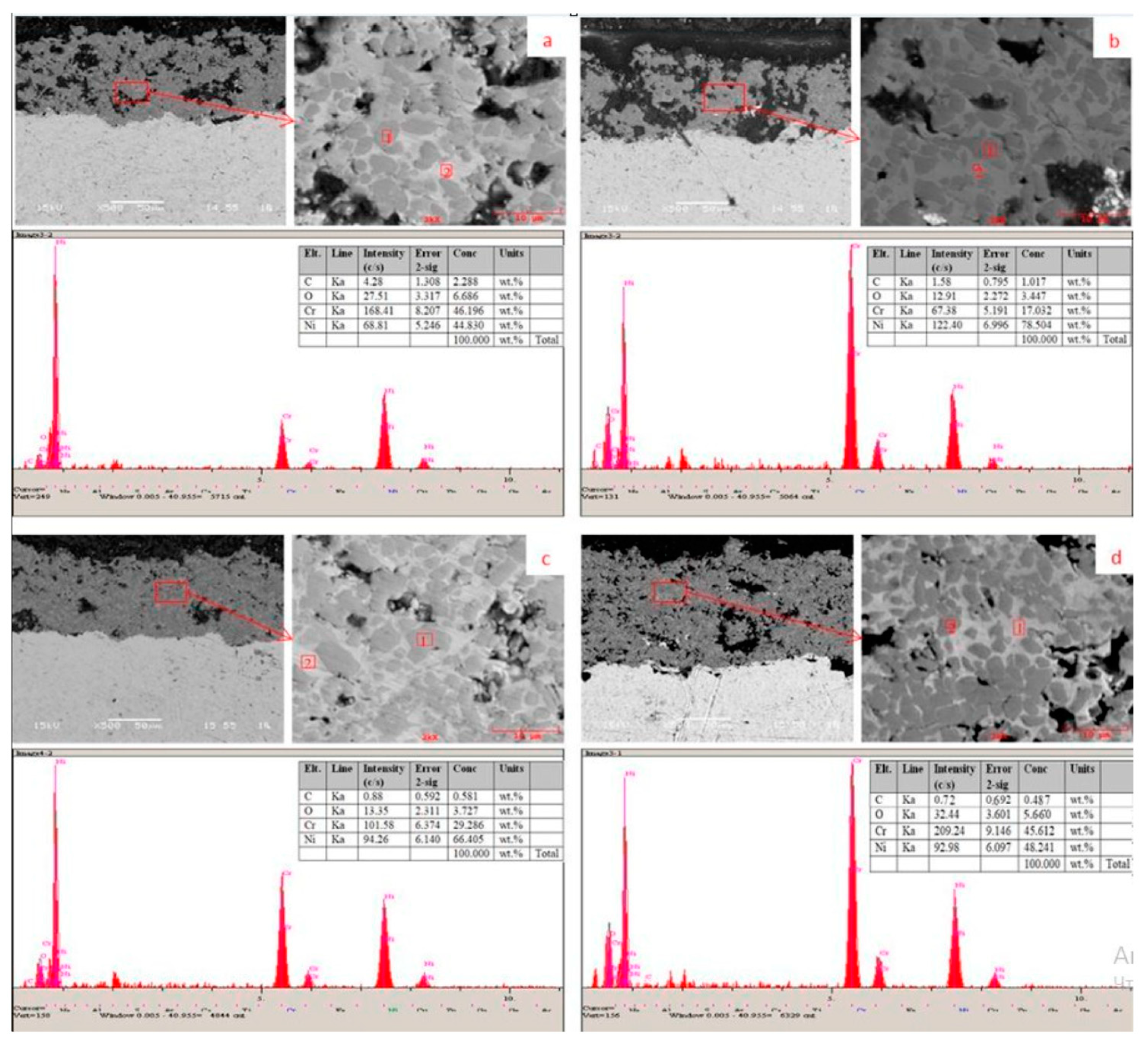
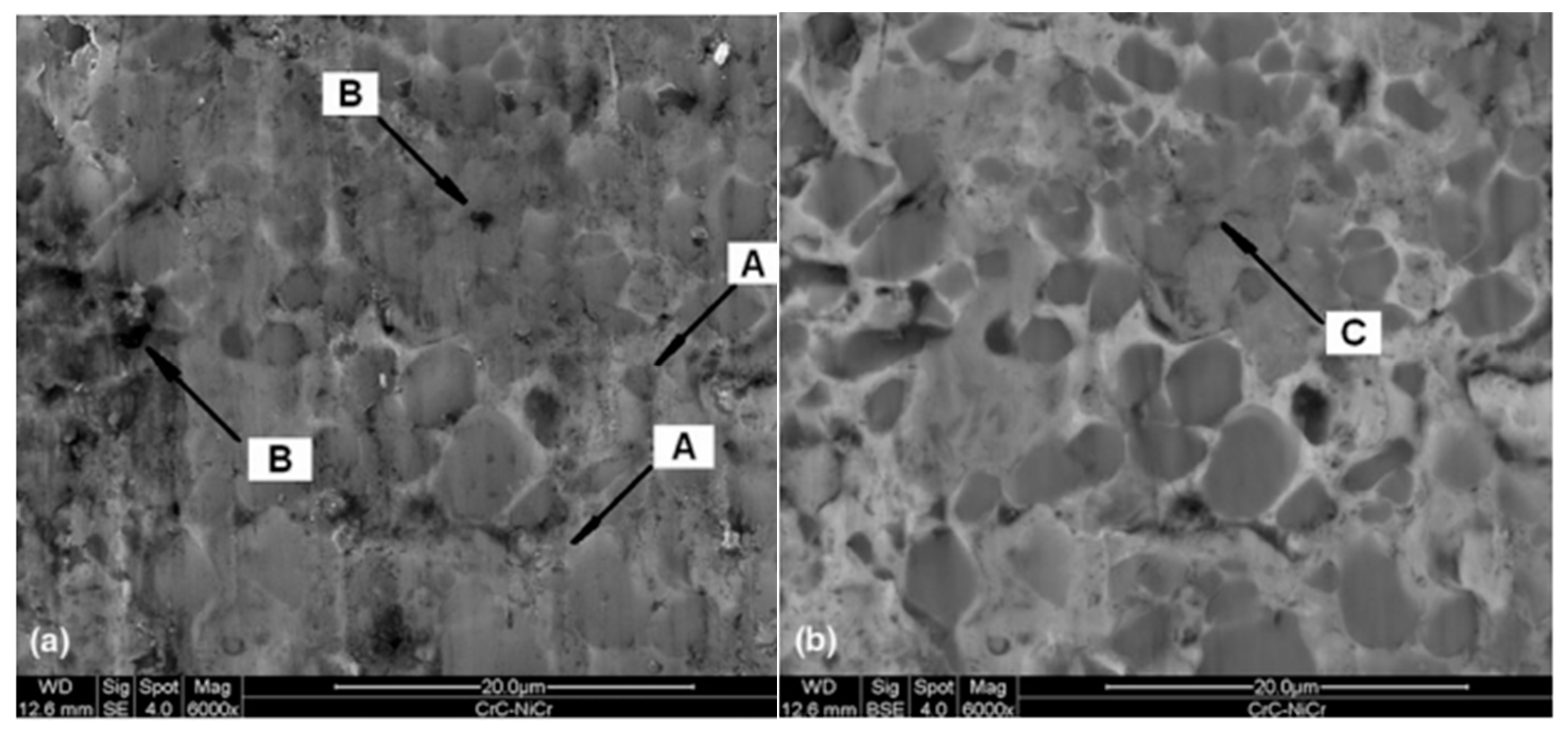
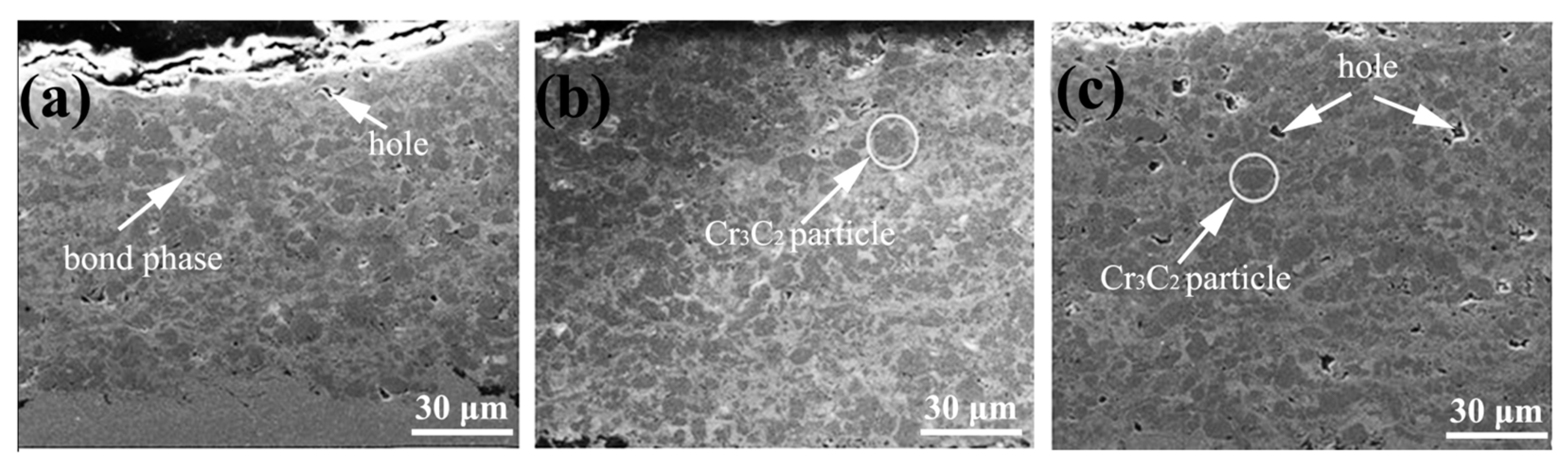




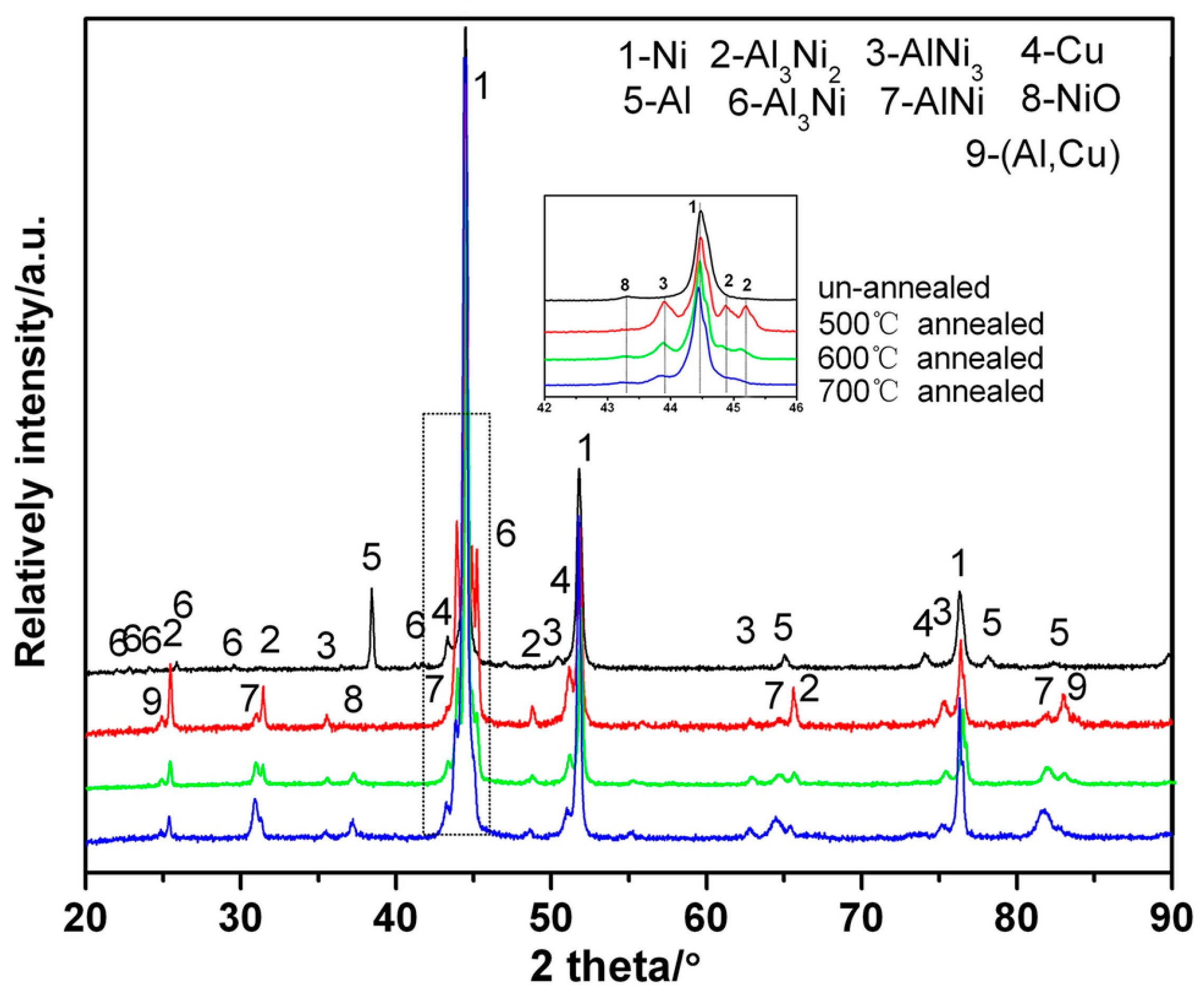
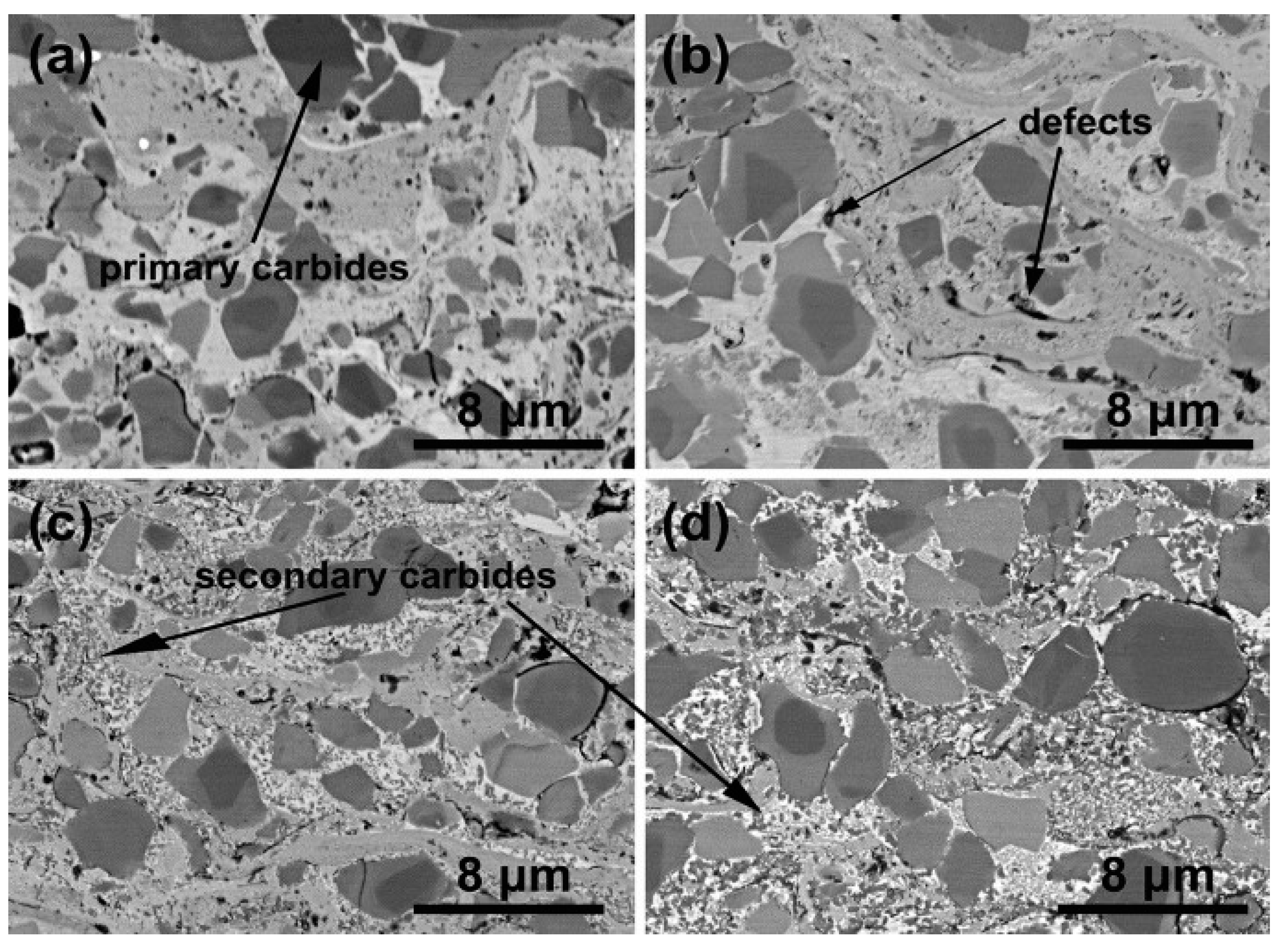


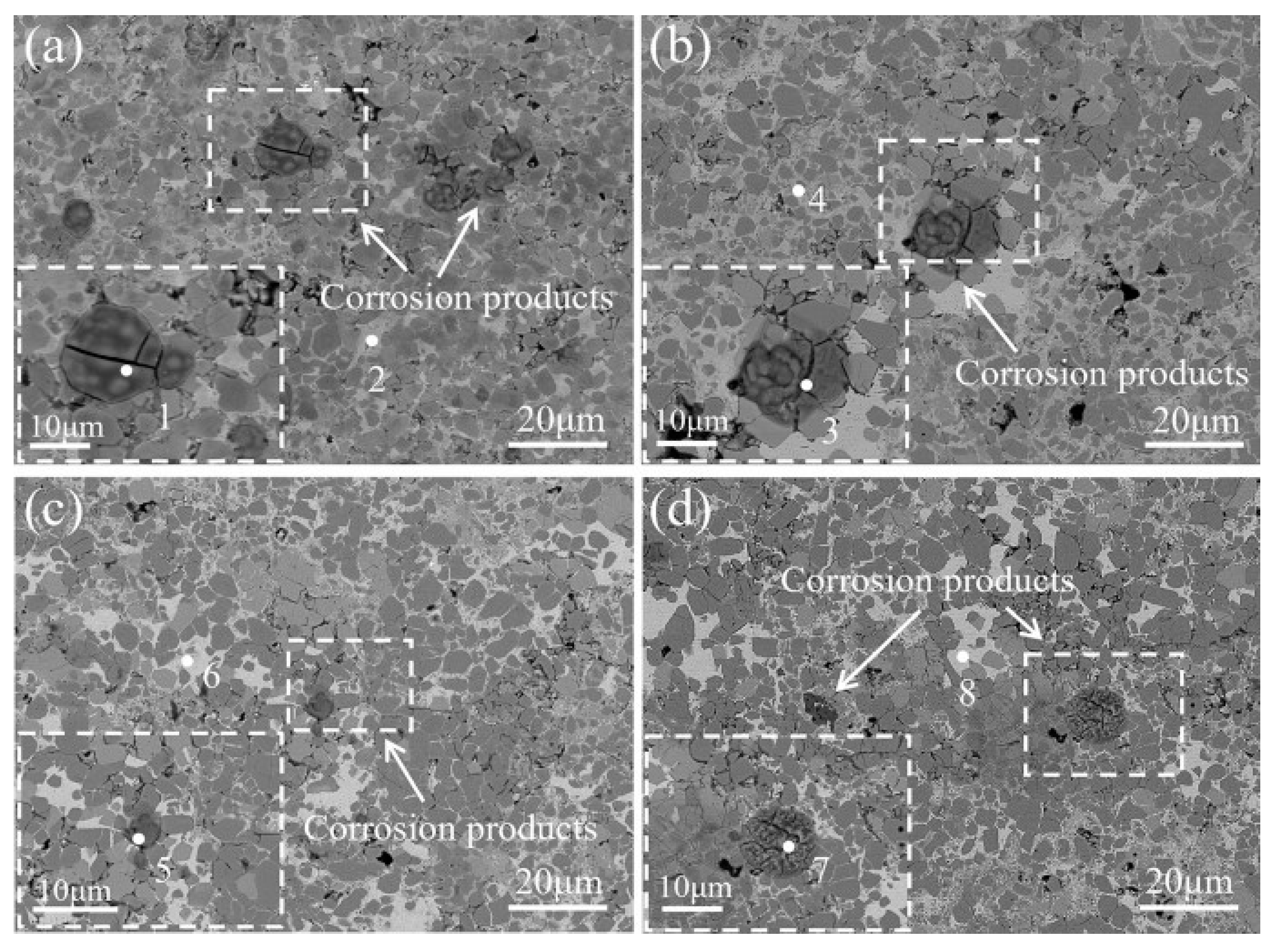
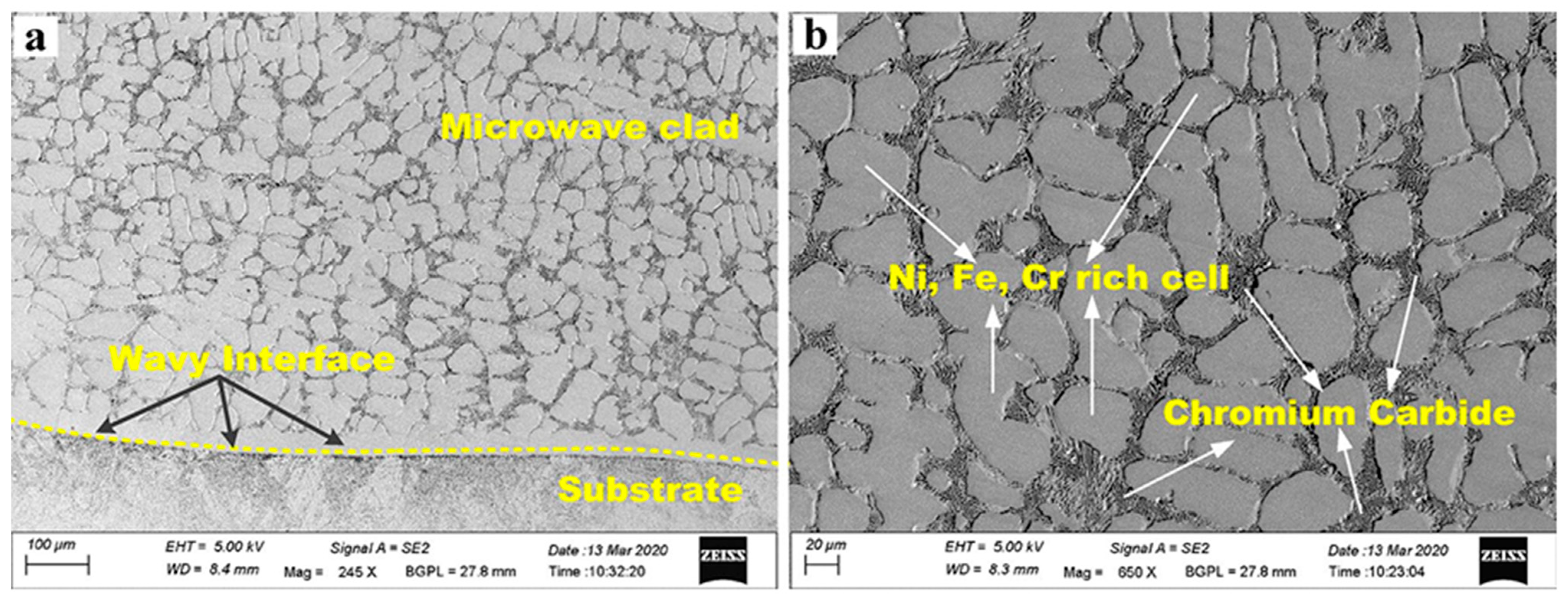
| № | Deposition Method | Deposition Temperature (°C) | Coating Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D-Gun Spraying | 1000–1200 | 100–500 |
| 2 | Cold Spraying | <400 | 50–1000 |
| 3 | Plasma Spraying | 10,000–15,000 (plasma temp.) | 50–500 |
| 4 | HVOF | 1000–3000 | 50–300 |
| 5 | HVAF (High-Velocity Air–Fuel) | 900–1600 | 50–400 |
| 6 | PVD | 100–500 | 0.1–5 |
| 7 | CVD | 500–1100 | 1–10 |
| 8 | Thermal Spray (General) | 500–3000 | 50–500 |
| 9 | Multi-Arc Ion Plating (MAIP) | 400–600 | 1–10 |
| 10 | Micro-Arc Oxidation (MDO) | 200–1000 | 10–100 |
| 11 | Laser Cladding | 800–2500 | 100–2000 |
| 12 | Sol–Gel Coating | Room temperature—800 | 0.1–10 |
| 13 | Magnetron Spraying | Room temperature—500 | 0.1–5 |
| No. | Authors | Method | Type of Coating | Phases | Structure | Lattice Period, Å | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xie M. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr7C3, NiCr | - | - | [93] |
| 2 | Poirier D. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-NiCr (7102) | Cr23C6, Cr7C3, Cr3C2, Cr, Ni | - | - | [94] |
| Cr3C2-NiCr (7305) | Cr23C6, Cr7C3, Cr3C2, Cr, Ni | ||||||
| 3 | Sahraoui T. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-25NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr3Ni2, Cr | - | - | [95] |
| 4 | Bolelli G. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-25NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr2O3, γ-Ni | f.c.c. | - | [96] |
| HVAF | Cr3C2, Cr2O3, Cr7C3, γ-Ni | ||||||
| 5 | Zhou W. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr7C3, NiCr | - | - | [97] |
| Cr3C2-WC-NiCoCrMo | WC, Cr3C2, Cr7C3, Niss amorphous | ||||||
| 6 | Zhou Z. et al. | HVAF | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr7C3, Ni, Cr | - | - | [98] |
| 7 | Selvam Kevin et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr3C2, NiCr, Cr7C3, Cr23C6, Ni, Cr | - | [99] | |
| 8 | Rakhadilov B. et al. | HVOF | 86WC-10Co-4Cr | (A1) WC | - | a = 2.9005 c = 2.8330 | [100] |
| W2C | a = 2.9614 c = 4.6884 | ||||||
| CoO | a = 4.2507 | ||||||
| (A2) WC | a = 2.9011 c = 2.8328 | ||||||
| W2C | a = 2.9554 c = 4.6641 | ||||||
| CoO | a = 4.2451 | ||||||
| (A3) WC | a = 2.9027 c = 2.8345 | ||||||
| W2C | a = 2.9624 c = 4.6924 | ||||||
| CoO | a = 4.2506 | ||||||
| 9 | Kurbanbekov S. et al. | HVOF | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr23C6 | Cr23C6 (cubic, Fm-3m) | a = 10.6600 | [101] |
| Cr3C2 | Cr3C2 (orthorhombic, Pnma) | a = 5.5400 b = 2.8330 c = 11.4940 | |||||
| CrNi3 | CrNi3 (cubic, Fm-3m) | a = 3.5400 | |||||
| NiCrO4 | NiCrO4 Tetragonal lattice (space group I41/amd) |
a = 5.5380 b = 5.5380 c = 8.4350 | |||||
| 10 | Zhang C. et al. | SAPS | Cr3C2-NiCr | Cr3C2, Cr23C6, NiCr, (Ni,Cr)7C3 and Ni | - | - | [102] |
| No. | Distance, mm | Fuel, bar | Air, bar | Oxygen, bar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample (a) | 350 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.8 |
| Sample (b) | 350 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 2.8 |
| Sample (c) | 350 | 1.7 | 3.7 | 2.8 |
| Sample (d) | 350 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 2.8 |
| No. | Authors | Method | Coating | Load (N) | Coefficient of Friction (f)/T, ℃ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shunmuga Priyan et al. | HVOF | 80%Cr3C2 + 20%NiCr | 10 | 0.2018 | [112] |
| 20 | 0.2155 | |||||
| 30 | 0.2346 | |||||
| 75%Cr3C2 + 25%NiCr | 10 | 0.2161 | ||||
| 20 | 0.2341 | |||||
| 30 | 0.2516 | |||||
| 2 | Pankaj Chhabra et al. | APS | Cr3C2-NiCr | 25 | 0.63 (RT) | [113] |
| 0.37 (400 °C) | ||||||
| 0.43 (800 °C) | ||||||
| 50 | 0.51 (RT) | |||||
| 0.36 (400 °C) | ||||||
| 0.41 (800 °C) | ||||||
| 3 | Li W. et al. | HVOF | CrN | 316 | 0.6 (25 °C) | [114] |
| 0.6–0.2 (150 °C) | ||||||
| 0.4 (350 °C) | ||||||
| 0.3 (550 °C) | ||||||
| CrN/Cr3C2-NiCr | 316 | 0.6 (25 °C) | ||||
| 0.3 (150 °C) | ||||||
| 0.4 (350 °C) | ||||||
| 0.3 (550 °C) | ||||||
| 4 | Rakhadilov B et al. | HVOF | 86WC-10Co-4Cr | - | 0.488–0.463 | [115] |
| 5 | Huang C. et al. | APS | NiCr/(Cr3C2-BaF2CaF2) | - | 0.8–0.25 (0–800 °C) | [116] |
| 6 | Chhabra P. et al. | APS | Cr3C2-NiCr | 25 | 0.59 (RT) | [117] |
| 0.39 (400 °C) | ||||||
| 0.42 (400 °C) | ||||||
| 50 | 0.58 (RT) | |||||
| 0.34 (400 °C) | ||||||
| 0.38 (400 °C) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seitov, B.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Baltabayeva, D.; Kakimzhanov, D.; Katpayeva, K.; Temirbekov, A.; Bekbayev, S.; Mussakhan, N. Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties, Morphology, and Phase Structure in Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coatings Sprayed by HVOF Method. Coatings 2025, 15, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040479
Seitov B, Kurbanbekov S, Baltabayeva D, Kakimzhanov D, Katpayeva K, Temirbekov A, Bekbayev S, Mussakhan N. Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties, Morphology, and Phase Structure in Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coatings Sprayed by HVOF Method. Coatings. 2025; 15(4):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040479
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeitov, Bekbolat, Sherzod Kurbanbekov, Dilnoza Baltabayeva, Dauir Kakimzhanov, Karakoz Katpayeva, Alisher Temirbekov, Sattar Bekbayev, and Nurken Mussakhan. 2025. "Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties, Morphology, and Phase Structure in Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coatings Sprayed by HVOF Method" Coatings 15, no. 4: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040479
APA StyleSeitov, B., Kurbanbekov, S., Baltabayeva, D., Kakimzhanov, D., Katpayeva, K., Temirbekov, A., Bekbayev, S., & Mussakhan, N. (2025). Review of Physical and Mechanical Properties, Morphology, and Phase Structure in Cr3C2-NiCr Composite Coatings Sprayed by HVOF Method. Coatings, 15(4), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15040479







