Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nanotechnology Applied to Agriculture
3. Nanofertilizers
4. Nanopesticides
5. Mechanism of Controlled Agrochemical Delivery
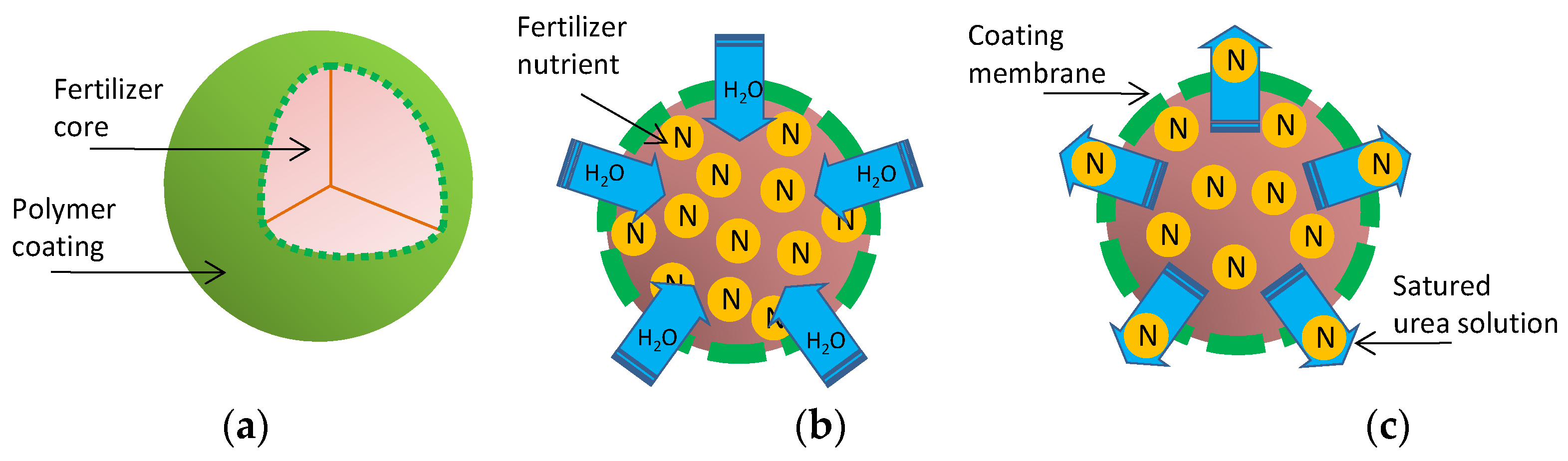
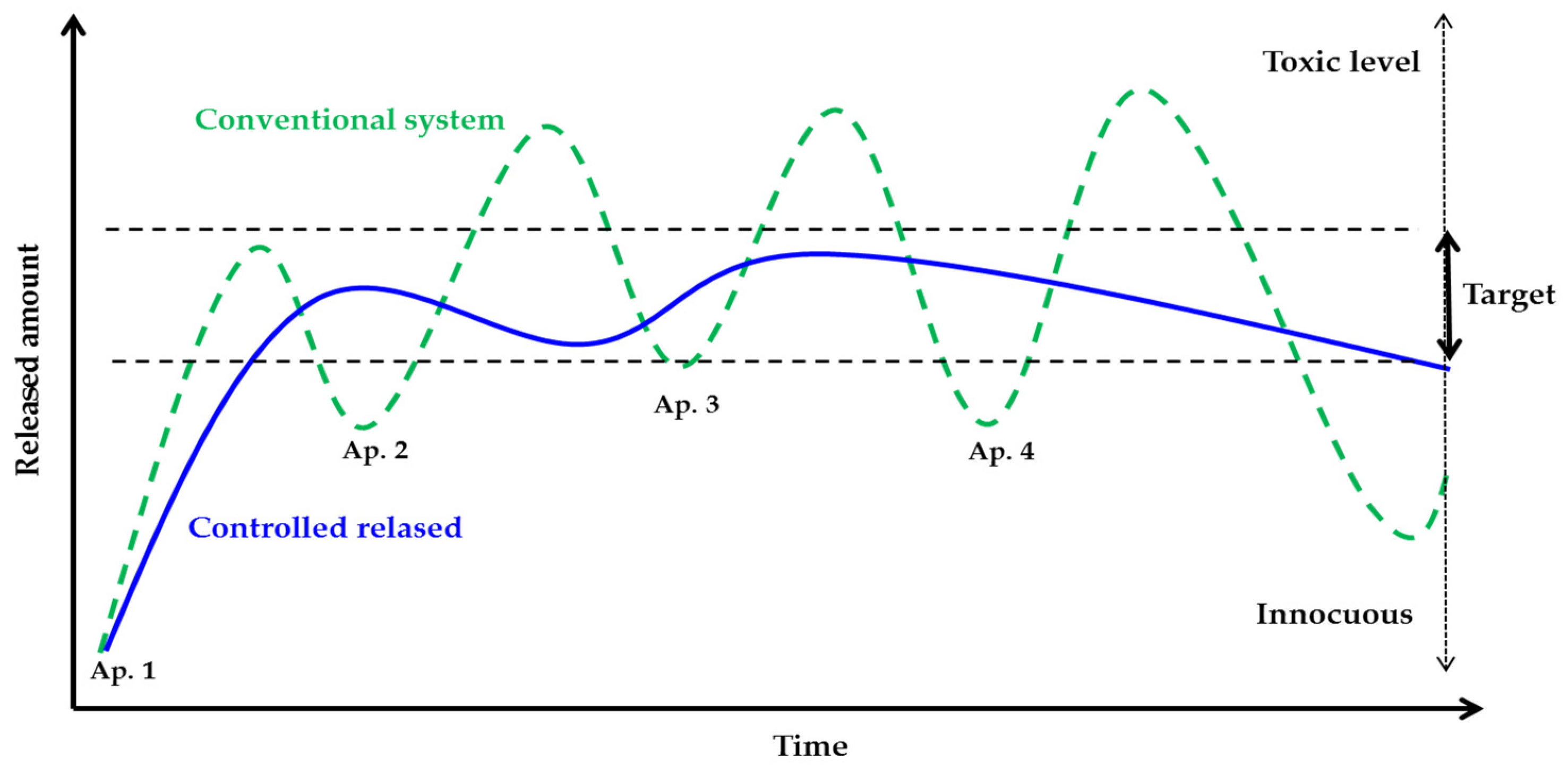
5.1. Slow Release Fertilizers (SRFs)
5.2. Controlled Release Fertilizers (CRFs)
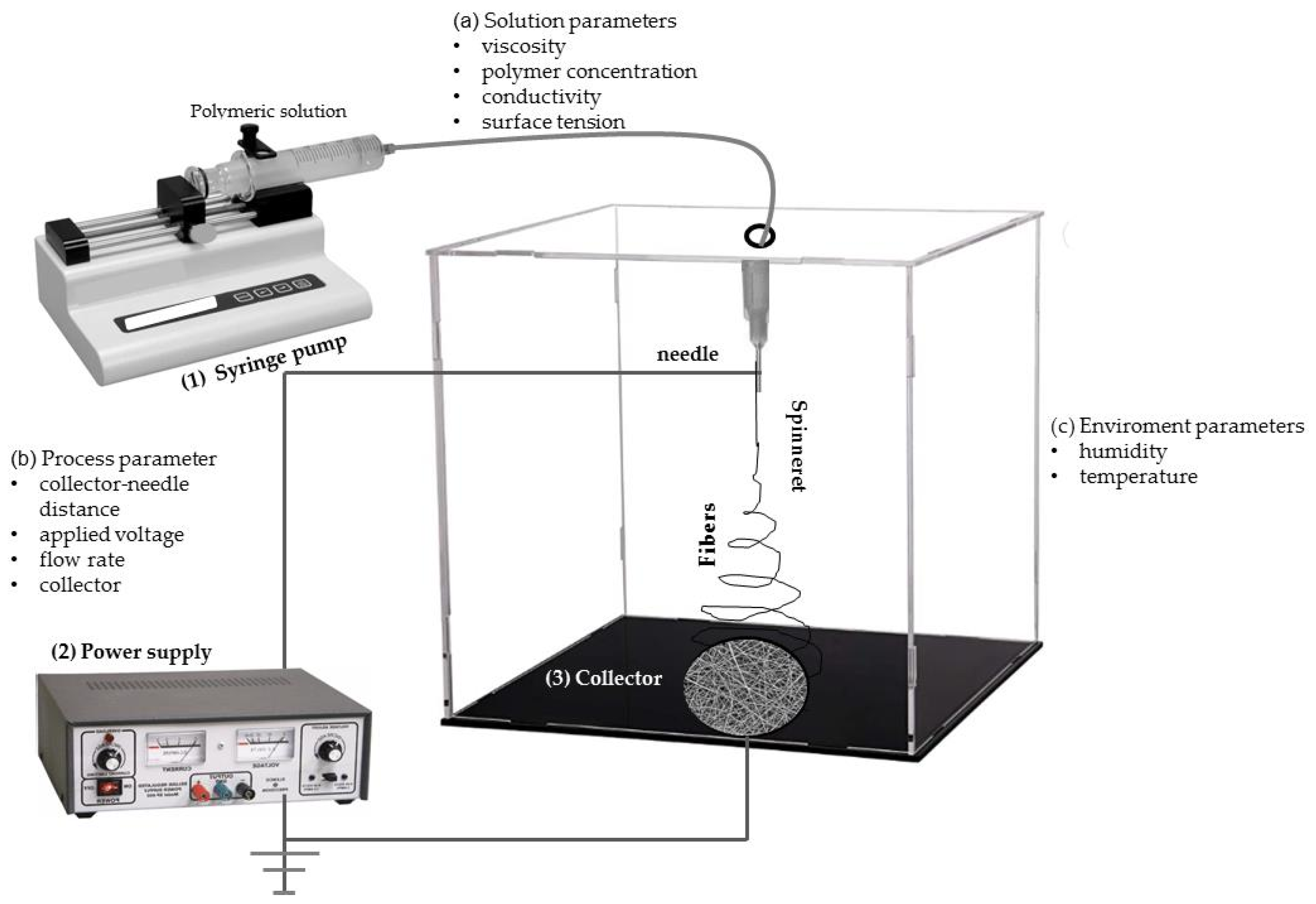
6. Electrospinning Process
| Electrospinning Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | Process | Ambient | ||||||
| Cause | Effect | Reference | Cause | Effect | Reference | Cause | Effect | Reference |
| Increase concentration | Higher diameter and no beads | [96,97] | Increase voltage | Lower fiber diameter | [85,86] | Increase temperature | Lower fiber diameter | [98] |
| Increase viscosity | [89,99] | Increase gap 1 | Lower diameter and no beads | [85,100] | Increase humidity | 2 No defined | [101,102] | |
| Increase molecular weight | No beads | [103,104] | Increase flow rate | Higher fiber diameter | [85,105] | |||
| Decrease surface tension | Fiber formation | [81,106] | ||||||
| Increase conductivity | Lower diameter and no beads | [107,108] | ||||||
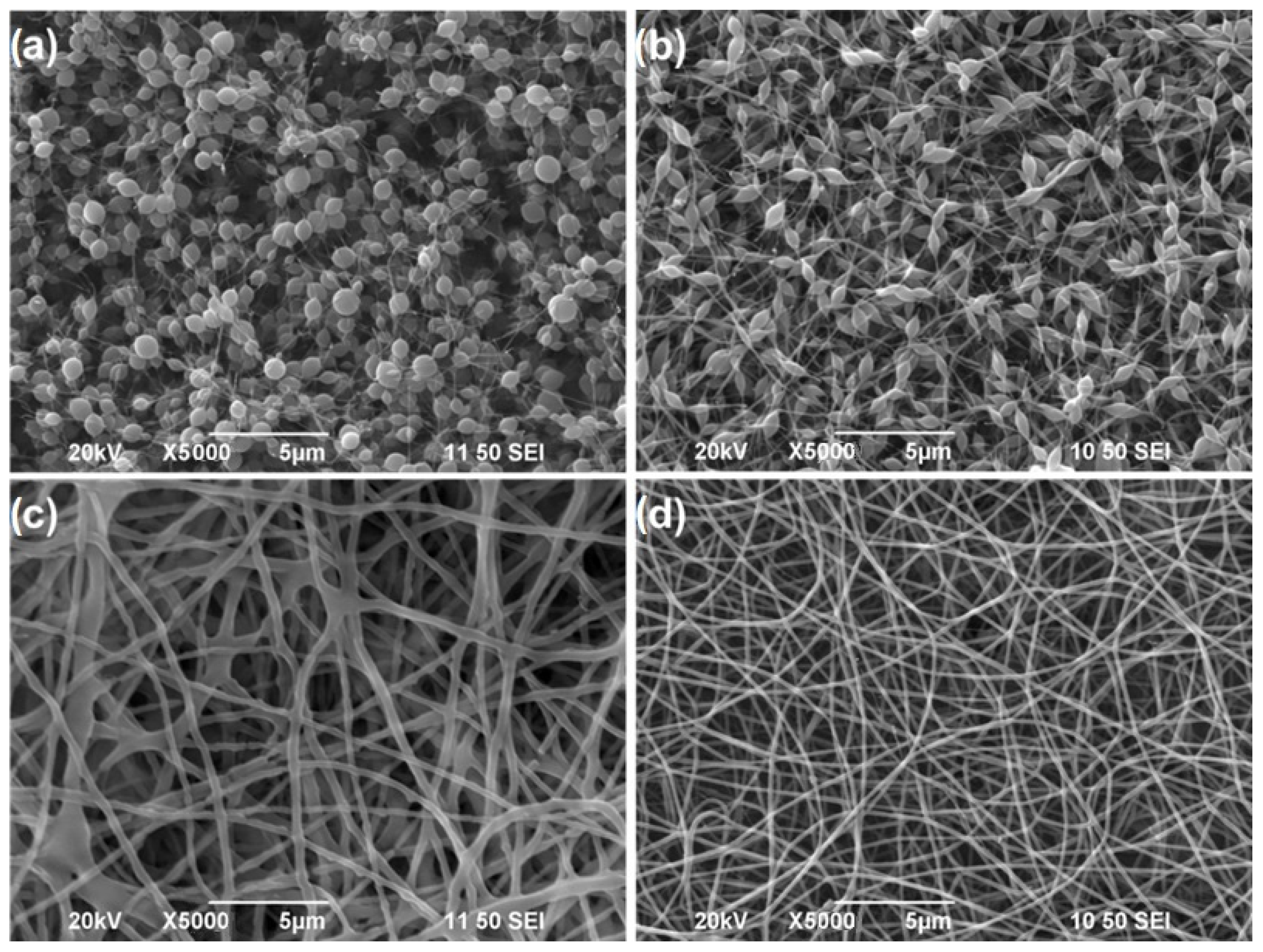
7. Polymers Used in Electrospinning
Polymers-Coated Used in Agriculture
8. Nanofibers as Carriers of Agrochemical
8.1. Nanofibers as Carriers of Fertilizers
| Author | Applied Voltage (kV) | Collector-Tip Distance (cm) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Collector |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castro-Enriquez et al. (2012) [163] | 10–20 | 10, 15 | 0.01 to 0.1 | AF |
| Kampeerapappun and Phanomkate (2013) [165] | 15 | 15 | 0.2–2.2 | AF |
| Krishnamoorthy et al. (2016) [166] | 20 | 15 | 5.0 | AF |
| Bulus et al. (2020) [168] | 30, 35 | 15 | 3.0, 3.5, 5 | ----- |
| Nooeaid, et al. 2021 [169] | 15 | 15 | 0.2, 0.5 | ----- |
| Javazmi et al. (2021) [162] | 12, 20 | 15 | 1.0 | AF |
| Salehi and Kazemikia (2022) [170] | 25 | 10 | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 | AF |
| Ahmad et al. (2023) [171] | ---- | 20 | 0.5 | AF |
| Malafatti et al. (2023) [173] | 16–20 | 5 | 0.6 | ---- |
8.2. Nanofibers as Carriers of Pesticides
| Author | Applied Voltage (kV) | Collector-Tip Distance (cm) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Collector |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thitiwongsawet et al. (2010) [174] | 15 | 15 | 1.0 | --- |
| Xiang et al. (2012) [175] | 15 | 10 | 0.6 | AF |
| Castañeda et al. (2014) [176] | 30 | 16 | 3.0 | ------ |
| Souza et al 2015 [177] | 25 | 12 | 0.4 | ----- |
| Roshani et al. (2016) [178] | 14 | 21 | 0.14 | ----- |
| Latha et al. (2019) [179] | 20 | ----- | 0.3 | ----- |
| Farias et al. (2019) [180] | 12.5 | 15 | 0.5 | AF |
| Ciera et al. (2019) [181] | 12–23 | 14 | 1.0 | AF |
| Gao et al. (2020) [182] | 15–20 | 12–16 | 0.5 | ----- |
| Gao et al. (2021) [183] | 15–20 | 12–16 | 0.5 | AF |
| Ryan et al. (2020) [184] | 15 | 10 | 0.9 | ----- |
| Mukiri et al. (2021) [185] | 15 | ----- | 0.6 | ----- |
| Saileela et al. (2023) [11] | 15 | 15 | 0.6 | ----- |
| Merlini et al. (2023) [187] | 24 | 12 | 0.5 | ----- |
| Reference | Polymers/Solvent | Encapsulated Pesticide | Fibers Morphology/Diameter | Fibers Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thitiwongsawet et al. (2010) [174] | CA/dimethylacetamide (DMA) | 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline | Smooth/241–320 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Xiang et al. (2012) [175] | PLA: cellulose nanocrystal/dimethylformamide (DMF) | CB (model pesticide) Thiomethoxan | Smooth/326 ± 139 nm 335 ± 144 nm 306 ± 90 nm | Design for a controlled-release system control whiteflies |
| Castañeda et al. (2014) [176] | PVP/ethanol, DMF | Vitamax® Thiram® | Fused fibers, beads | Rice seed coating |
| Souza et al. (2016) [177] | PLA/Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) | Linalool | Smooth/176–240 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Roshani et al. (2016) [178] | PLLA/DMF | Thiram | Bead-free/no specific value of diameter | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Latha et al. (2019) [179] | PVA/acetronile organic | Tebuconazole | Beads-free/293–373 nm 405.9–556.7 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Farias et al. (2019) [180] | CDA/acetic acid, DMA | Abamectin (Abm) Fluopyram (Flp) | Smooth, defect-free/335 ± 81 nm, 242 ± 12 nm, 129 ± 28 nm | Soybeans seeds coatings antifungal |
| Ciera et al. (2019) [181] | PVA/water | Permethrin Catnip oil, chili oil, PMD | Bead-like, porous/386 ± 55 nm, 408 ± 67 nm | Repellent |
| Gao et al. (2020) [182] | HPβCD/water | TBZ | Beadless, uniform/370 ± 198 nm | Design for a controlled-release system antifungal activity (Gibberella sp.) |
| Gao et al. (2021) [183] | HPβCD/water | Thiram | Homogeneous, beads-free/270 ± 133 nm | Design for controlled release antifungal activity (Gibberella sp.) |
| Ryan et al. (2020) [184] | Nylon-6,6/formic acid | Picaridin | Defect-free/279 ± 76 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Mukiri et al. (2021) [185] | PVA | Methylobacterium aminovorans | Defect-free/ 93.30 nm–166.1 nm 164.8–218.2 nm 194.4–303.2 nm | Design for controlled release viability microbial |
| Das et al. (2023) [186] | H-PβCD/PVA | ATZ | Homogeneous, bead-free | Design for a controlled-release system activity herbicide (L. sativa) |
| Saileela et al. (2023) [11] | PVA/acetone | Pendimethalin | Bead-free/ 231.6–313.5 nm 182.7–261.2 nm 143.2–210.3 nm | Seed coating (black gram seeds) germination and growth |
| Merlini et al. (2023) [187] | PLA/DMF, dichloroethane (DCE) | ILS | 3D, randomly, continuous, porosity rough surfaces/0.55 ± 0.13 μm–1.00 ± 0.20 μm | Aphid-repellent activity (Acyrthosiphon pisum) |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sekhon, B.S. Nanotechnology in agri-food production: An overview. Nanotechnology. Sci. Appl. 2014, 7, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigh, M.; Goswami, S.P.; Ranjitha, G.; Sachan, P.; Sahu, D.K.; Beese, S.; Pandey, S.K. Nanotech for fertlizers and nutrient-improving nutrient use efficiency with nano-enabled fertilizers. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 220–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Ma, C.; Aytac, Z.; Hu, X.; Hg, K.W.; White, J.C.; Demokritou, P. Enhancing agrichemical delivery and seedling development with biodegradable, tunable, biopolymer-based nanofiber seed coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9537–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, T.; Gopal, G.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, A. Nanocomposites for delivering agrochemicals: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, G.; Tan, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, P.; Gao, L.; Rui, Y. Nano-pesticides and fertilizers: Solutions for global food security. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Hasan, M.K.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, M.; Yin, M. Applications of nanotechnology in plant growth and crop protection: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, V.; Tewari, D.; Gaur, M.; Yadav, A.B.; Swaroop, S.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: Bioimaging, biosensing, drug delivery, tissue engineering, antimicrobial, and agro-food applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.; Man, Z.B.; Basit, A.; Thanh, T.H. Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. J. Control Release 2014, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A.A.; Abd-Elhamid, A.I.; Awwad, N.S.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Wu, J.; Mo, X.; Gomha, S.M.; Aly, A.A.; Bräse, S. Review of the Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofibers Applications in Water Purification. Polymers 2022, 14, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.; Roy, K.; Chinnappan, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, W.; Ghosh, R. A Review on electrospun nanofibers based advanced applications: From health care to energy devices. Polymers 2021, 13, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saileela, K.; Bharathi, C.; Raja, K.; Rahale, C.S.; Rajeswari, R. Synthesis, characterization of pendimethalin encapsulated PVA nanofiber and its impact on blackgram. Int. J. Plant Soil. Sci. 2023, 35, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I.I.; Robbie, K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007, 2, MR17–MR71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, R.K.; Rashmi, H.B.; Rao, N.H. Nanotechnology for enhancing food security in India. Food Policy 2011, 36, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Mailapalli, D.R. Nanofertilisers, nanopesticides, nanosensors of pest and nanotoxicity in agriculture. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 19, pp. 307–330. [Google Scholar]
- Duhan, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, P.; Nehra, K.; Duhan, S. Nanotechnology: The new perspective in precision agriculture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bhushan, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Fabrication of nanostructures with bottom-up approach and their utility in diagnostics, therapeutics, and others. In Environmental, Chemical and Medical Sensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 167–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ghormade, V.; Deshpande, M.V.; Paknikar, K.M. Perspectives for nano-biotechnology enabled protection and nutrition of plants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.; Bhargava, A.; Chhipa, H.; Jain, N.; Panwar, J. Nano-fertilizer and their smart delivery system. In Nanotechnologies in Food and Agriculture; Rai, M., Ribeiro, C., Mattoso, L., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 81–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J. The Applications of Nanotechnology in Crop Production. Molecules 2021, 26, 7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, M.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, T.; Noman, M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Rizwan, M.; Chen, J.; Siddique, H.M.; Li, B. Nanobiotechnology to advance stress resilience in plants: Current opportunities and challenges. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 22, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Wu, H.; Xing, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, R. Nano-biotechnology in agriculture: Use of nanomaterials to promote plant growth and stress tolerance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikal, Y.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.M.M. Toxicology and safety aspects of nanosensor on environment, food, and agriculture. In Nanosensors for Environment, Food and Agriculture Vol. 1; Kumar, V., Guleria, P., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Nanoencapsulation, Nano-guard for pesticides: A New window for safe application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1447–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Amari, A.; Osman, H.; Harharah, H.N.; Elboughdiri, N.; Tahoon, M.A. Plant and microbial approaches as green methods for the synthesis of nanomaterials: Synthesis, applications, and future perspectives. Molecules 2023, 28, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A. Nanotechnology in Food and Plant Science: Challenges and future prospects. Plants 2023, 12, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajanan, K.; Tijare, S.N. Applications of nanomaterials. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Pandey, P.; Upadhyay, T.K. Applications of nanotechnology-based agrochemicals in food security and sustainable agriculture: An Overview. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Liu, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, T.; Chen, W. Recent advances in stimuli-response mechanisms of nano-enabled controlled-release fertilizers and pesticides. Eco-Environ. Health 2023, 2, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.K.; Parishwad, G.V.; Husainy, A.S.N.; Patil, A.S. Emerging agriculture applications of silver nanoparticles. ES Food Agrofor. 2021, 3, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arole, V.M.; Munde, S.V. Fabrication of nanomaterials by top-down and bottom-up approaches. An overview. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 1, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, S.S.; Bahuguna, A.; Yadav, B.; Barthwal, A.; Nandan, R.; Khatana, S.; Pandey, A.; Thakur, R.; Jatav, H.S. Nanotechnology: An efficient tool in plant nutrition management. In Ecosystem Services: Types, Management and Benefits; Jatav, H.S., Ed.; Nova Science Publisher, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 165–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sneha, N.; Hosamani, R.; Chandrashekhar, S.S.; Udikeri, S.S. Profenofos loaded nanoliposomes against agricultural insect pest. J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2023, 12, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kah, M.; Beulke, S.; Tiede, K.; Hofmann, T. Nanopesticides: State of knowledge, environmental fate, and exposure modeling. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1823–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Rojas, C.; Pérez-de-Luque, A. Nanobiosensors and nanoformulations in agricultura: New and challengues for sustainable agricultura. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2023, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, A.; Ingle, P.; Nimbalkar, U.; Rai, M.; Raut, R.; Vedpathak, M.; Jagtap, P.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems. Agrochemicals 2023, 2, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilnawaz, F.; Kalaji, M.H.; Misra, A.N. Nanotechnology in improving photosynthesis under adverse climatic conditions: Cell to Canopy action. Plant Nano Biol. 2023, 4, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisa, I.O.; Pullagurala, V.L.R.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Recent advances in nano-enable fertilizers and pesticides: A critical review of mechanisms of action. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2002–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, K.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Exploring the potential of nanofertilizers for a sustainable agriculture. Plant Nano Biol. 2023, 5, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghnia, N.; Janmohammadi, M. Influence of some nano-fertilizers on chickpeas under three irrigation strategies. Plant Nano Biol. 2023, 4, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Hofmann, T. Nanopesticide research: Current trends and future priorities. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, H.; Verheggen, F. Polymer-based nanoinsecticides: Current developments, environmental risks and future challenges. A review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2020, 24, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltnarova, B.; Kubackova, J.; Skoda, J.; Stefela, A.; Smekalova, M.; Svacinova, P.; Pavkova, I.; Dittrich, M.; Scherman, D.; Zbytovska, J. PLGA Based Nanospheres as a Potent Macrophage-Specific Drug Delivery System. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhayay, V.K.; Chitara, M.K.; Mishra, D.; Jha, M.N.; Jaiswal, A.; Kumari, G.; Ghosh, S.; Patel, V.K.; Naitam, M.G.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Synergistic impact of nanomaterials and plant probiotics in agriculture: A tale of two-way strategy for long-term sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1133968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Pérez, K.M.; Avilés-Castrillo, J.I.; Medina, D.I.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Insight into nanoliposomes as smart nanocarriers for greening the twenty-first century biomedical settings. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 579536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundloori, R.V.N.; Singam, A.; Killi, N. Nanobased intravenous and transdermal drug delivery systems. In Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Tomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 551–594. [Google Scholar]
- Badgar, K.; Abdalla, N.; El-Ramady, H.; Prokisch, J. Sustainable Applications of Nanofibers in Agriculture and Water Treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellet, G.; Pilotto, L.; Marchiol, L.; Braidot, E. Tools for nano-enabled agriculture: Fertilizers based on calcium phosphate, silicon, and chitosan nanostructures. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, F.J.; Guagliardi, A.; Masciocchi, N. Nanosized Calcium Phosphates as Novel Macronutrient Nano-Fertilizers. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertahi, S.; Ilsouk, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Recent trends in organic coating based on biopolymers and biomass for controlled and slow release fertilizers. J. Control Release 2021, 330, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rop, K.; Karuku, G.N.; Mbui, D.; Michira, I.; Njomo, N. Formulation of slow release NPK fertilizer (cellulose-graft-poly(acrylamide)/nano-hydroxyapatite/soluble fertilizer) composite and evaluating its N mineralization potential. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2018, 63, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, A.; Maheswari, M.U. Smart fertilizer strategy for better crop production. Agric. Rev. 2021, 42, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; White, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Nano-enabled fertilizers to control the release and use efficiency of nutrient. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 6, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Navarro, M.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A.; Munné-Bosch, S. Nanofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture: Advantages and limitations. Plant Sci. 2019, 289, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lal, R. Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongbet, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Mahanta, S.; Ray, M.K.; Khan, M.; Baek, K.-H.; Chakrabartty, I. Nanofertilizers: A smart and sustainable attribute to modern agricultura. Plants 2022, 11, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronardi, E.; Tsae, P.; Zhang, X.; Monreal, C.; De Rosa, M.C. Strategic role of nanotechnology in fertilizers: Potential and limitations. In Nanotechnologies in Food and Agriculture; Rai, M., Ribeiro, C., Mattoso, L., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juthery, H.W.A.; Lahmod, N.R.; Al-Taee, R.A.H.G. Intelligent, nano-fertilizers: A new technology for improvement nutrient use efficiency (article review). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 735, 012086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junejo, N.; Khanif, M.Y.; Hanfi, M.M.; Yunis, W.M.Z.W.; Drarejo, K.A. Role of inhibitor and biodegradable material in mitigation of nitrogen losses from fertilized lands. Afr. J. Biotech. 2011, 10, 3504–3514. [Google Scholar]
- Raliya, R.; Saharan, V.; Dimkpa, C.; Biswas, P. Nanofertilizer for precision and sustainable agriculture: Current state and future perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6487–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliyarsingh, B.; Pradhan, C.K. Prospects of plant-derived metallic nanopesticides against storage pests—A review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratovcic, A.; Hikal, W.M.; Said-Al Ahl, H.A.H.; Tkachenko, K.G.; Baeshen, R.S.; Sabra, A.S.; Sany, H. Nanopesticides and nanofertilizers and agricultural development: Scopes, advances and applications. Open J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Sohrawardy, H.; Mahmud, N.U.; Roy, P.C.; Islam, T. Nanopesticides for crop protection. In Agricultural Nanobiotechnology Biogenic Nanoparticles, Nanofertilizers and Nanoscale Biocontrol Agents, 1st ed.; Ghosh, S., Thongmee, S., Kumar, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 389–438. [Google Scholar]
- Hayles, J.; Johnson, L.; Worthley, C.; Losic, D. Nanopesticides: A review of current research and perspectives. In New Pesticides and Soil Sensors, 1st ed.; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 193–225. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Su, X.; Yan, S.; Shen, J. Multifunctional nanoparticles and nanopesticides in agricultural application. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Saleh, N.B.; Byro, A.; Zepp, R.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Luxton, T.P.; Ho, K.T.; Burguess, R.M.; Flury, M.; White, J.C.; et al. Nano-enabled pesticides for sustainable agriculture and global food security. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Singh, S.K.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K. Controlled pesticide release from biodegradable polymers. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, G.G.; Carroll, J.P. Controlled release delivery of agrochemicals: Looking back and looking forward. In International Atomic Energy Agency, Research and Development of Controlled Release Formulations of Pesticides -Development and Evaluation of Controlled Release Formulations of Pesticides; FAO/IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv. Agron. 2000, 71, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempeho, S.I.; Kim, H.T.; Mubofu, E.; Hilonga, A. Meticulous overview on the controlled release fertilizers. Adv. Chem. 2014, 363071, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, M.E.; Salama, D.M.; Morsi, S.M.; Youssef, A.M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A. Development of polymer composites and encapsulation technology for slow-release fertilizers. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow- and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture, 2nd ed.; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2010; pp. 14–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, A.; Sharma, S.P.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, H. Novel nanocomposite-based controlled-release fertilizer and pesticide formulations: Prospects and challenges. In Micro and Nano Technologies, Multifunctional Hybrid Nanomaterials for Sustainable Agri-Food Ecosystems, Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.I.; Giroto, A.S.; Bortolin, A.; Yamamoto, C.F.; Marconcini, J.M.; de Campos Bernardi, A.C.; Ribeiro, C. Perspectives in nanocomposites for the slow and controlled release of agrochemicals: Fertilizers and pesticides. In Nanotechnologies in Food and Agriculture, 1st ed.; Rai, M., Ribeiro, C., Mattoso, L., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopeña, F.; Maqueda, C.; Morillo, E. Controlled release formulations of herbicides base on micro-encapsulation. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2009, 35, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraz-Dávila, S.; Pérez-García, C.E.; Feregrino-Perez, A.A. Challenges and advantages of electrospun nanofibers in agriculture: A review. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenot, A.; Chronakis, I.S. Polymer nanofibers assembled by electrospinning. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: Reinventing the wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.-R.; Layman, J.M.; Watkins, J.R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Matthews, J.A.; Simpson, D.G.; Wnek, G.E. Electrospinning of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) fibers. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fawal, G.F. Polymer nanofibers electrospinning: A review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesson, I.; Taylor, R.M.; Reifsnider, K. Mechanical and dielectric properties of aligned electrospun fibers. Fibers 2021, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Ryu, B.-Y.; Choi, J.; Jo, B.; Farris, R.J. The morphology and mechanical properties of sodium alginate based electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Stylios, G. Effect of experimental parameters on the morphology of electropsun nylon 6 fibres. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennessey, S.F.; Farris, J. Fabrication of aligned and molecularly oriented electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers and the mechanical behavior of their twisted yarns. Polymer 2004, 45, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.S.S.; Fong, K.C.; Eleyas, A.; Nazeri, M.F.M. Effect of voltage and flow rate electrospinning parameters on polyacrylonitrile electrospun fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 318, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Sheng, J. Study on morphology of electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) mats. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Ren, J.; Vancso, G.J. Process optimization and empirical modeling for electrospun polyaccrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber precursor of carbon nanofiber. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 42, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yördem, O.S.; Papila, M.; Menceloglu, Y.Z. Effects of electrospinning parameters on polyacrylonitrile nanofiber diameter: An investigation by response surface methodology. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, S.; Çetiner, S.; Saraç, A.S. Polymer Nanofibers Via Electrospinning: Factors Affecting Nanofiber Quality. J. Eng. Sci. 2013, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kailasa, S.; Reddy, M.S.B.; Rani, B.G.; Maurya, M.R.; Rao, K.V.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Electrospun Nanofibers: Materials, synthesis parameters and their role in sensing applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anup, N.; Chavan, T.; Chavan, S.; Polanka, S.; Kalyane, D.; Abed, S.N.; Venugopala, K.N.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Reinforced electrospun nanofiber compossites for drug delivery applicactions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2021, 109, 2036–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Bonakdar, M.; Rodrigue, D. Electrospinning: Processes, Structures, and Materials. Macromol 2024, 4, 58–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Downes, S. Acetone, a Sustainable Solvent for Electrospinning Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Fibres: Effect of varying parameters and solution concentrations on Fibre Diameter. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Ren, J. Process optimization and empirical modeling for electrospun poly(D,L-lactide) fibers using response surface methodology. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagstrom, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The Effect of Temperature and Humidity on Electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Jin, X. Controlling the surface structure, mechanical properties, crystallinity, and piezoelectric properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibers by maneuvering molecular weight. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.Y. Effect of Needle Length, Electrospinning Distance, and Solution Concentration on Morphological Properties of Polyamide-6 Electrospun Nanowebs. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Stachewicz, U. The impact of relative humidity on electrospun polymer fibers: From structural changes to fiber morphology. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icoglu, H.I.; Ogulata, R.T. Effect of ambient parameters on morphology of electrospun polyetherimide (PEI) fibers. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2013, 23, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Mwiiri, F.K.; Daniels, R. Influence of PVA molecular weight and concentration on electrospinnability of birch bark extract-loaded nanofibrous scaffolds intended for enhanced wound healing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Shivkumar, S. Bead-to-fiber transition in electrospun polystyrene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 155892501200700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Electrospun metal oxide nanofibers and their conductometric gas sensor application. Part 1: Nanofibers and features of their forming. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Effect of salt concentration in spinning solution on fiber diameter and mechanical property of electrospun styrene-butadiene-styrene tri-block copolymer membrane. Polymer 2018, 153, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Haoqing, H.; Schaper, A.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Poly-L-lactide nanofibers by electrospinning—Influence of solution viscosity and electrical conductivity on fiber diameter and fiber morphology. e-Polymers 2003, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colín, O.J. Synthesis of Nanofibers from Biomaterials by Electrospinning as Component Active Carriers. Ph.D. Thesis, National Polytechnic Institute, Mexico City, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.K.; Dutta, J.; Tripathi, V. Chitin and chitosan: Chemistry, properties and applications. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2004, 63, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, S.; Wang, L.-F.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparations and characterization of alginate/silver composite films: Effect of types of silver particles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Cha, D.; Kim, H.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H. Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: Processing optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Gao, C.; Feng, X.X.; Chen, J.C.; Ye, J.; Gou, Z. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: The favorable effect of metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, K.; Henrist, C.; Jérôme, C.; Aqil, A.; Maté, J.I.; Cloots, R. Effect of nonionic surfactant and acidity on chitosan nanofibers with different molecular weights. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutan, N.; Terzi, P.; Altay, F. Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Silk fibroin nanofiber. Electrospinning and structure. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, K.; Maleki, H.; Samadian, H.; Shahsavari, S.; Sarrafzadeh, M.H.; Larijani, B.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Haghpanah, V.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery systems: Applications and recent advances. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wróblewska-Krepsztu, J.; Rydzkowski, T.; Michalska-Pozoga, I.; Thakur, V.K. Biopolymers for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications: Recent advances and overview of alginate electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, R.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, S. Fabrication and biocompatibility of agarose acetate nanofibrous membrane by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ghosh, K.; Shu, X.Z.; Li, B.; Sokolov, J.C.; Prestwich, G.D.; Clark, R.A.; Rafailovich, M.H. Electrospun three-dimensional hyaluronic acid nanofibrous scaffolds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3782–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, G.; Fang, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Nie, J. Effects of solution properties and electric field on the electrospinning of hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Lugo, A.-C.; Lim, L.-T. Electrospinning of soy protein isolate nanofibers. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2008, 2, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Ocio, M.J.; Lagaron, J.M. Novel antimicrobial ultrathin structures of zein/chitosan blends obtained by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M. Novel route to stabilization of bioactive antioxidants by encapsulation in electrospun fibers zein prolamine. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafaya, P.B.; Silva, G.A.; Reis, R.L. Natural–origin polymers as carriers and scaffolds for biomolecules and cell delivery in tissue engineering applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Thomas, N.L. Fabricating porous poly(lactic acid) fibres via electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Jin, K.; Liu, W.; Qiu, X.; Li, C. Fabrication of functional PLGA-based electrospun scaffolds and their applications in biomedical engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Jung, S.M.; Kang, M.; Shin, H.S.; Youk, J.H. Preparation of hydrophilic PCL nanofiber scaffolds via electrospinning of PCL/PVP- b -PCL block copolymers for enhanced cell biocompatibility. Polymer 2015, 69, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Min, B.-M.; Lee, S.J.; Park, W.H. Preparation of porous ultrafine PGA fibers via selective dissolution of electrospun PGA/PLA blend fibers. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Salick, M.R.; Cordie, T.; Mi, H.-Y.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Electrospinning Homogeneous nanofibrous poly(propylene carbonate)/gelatin composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. Industrial & engineering. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9391–9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Reda, M.M.; Klingner, A. Preparation and characterization of green carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS)—Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) electrospun nanofibers containing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and its potential use as biomaterials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.-G.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.Z. Electrospun Janus zein–PVP nanofibers provide a two-stage controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mirzaei, A.; Bonyani, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Advances in electrospun nanofiber fabrication for polyaniline (PANI)-based chemoresistive sensors for gaseous ammonia. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Hosseini Salekdeh, S.S.; Solouk, A.; Yousefzadeh, M. Electrospun polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibrous conduit for biomedical application. Poly. Adv. Technol. 2019, 31, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Sardroud, H.A.; Allafasghari, S.; Yazdanpanah, Z.; Naghieh, S.; Gorji, M.; Chen, X. Electropinning of polyurethane/grapheme oxide for skin wound dressing and its in vitro characterization. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindasamy, K.; Dahlan, N.A.; Janarthanan, P.; Goh, K.L.; Chai, S.-P.; Pasbakhsh, P. Electrospun chitosan/polyethylene-oxide (PEO)/halloysites (HAL) membranes for bone regeneration applications. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2020, 190, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, K.; Hou, H. Electrospun polyimide nonwovens with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties by addition of trace plasticizer. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5667–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, B.-H. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile/cyclodextrin-derived hierarchical porous carbon nanofiber/MnO2 composites for supercapacitor applications. Carbon 2020, 164, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Nie, J. Preparation of gelatin/PVA nanofibers and their potential application in controlled release of drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.W.; Zhu, Y.L.; Guo, Z.X.; Hu, P.; Yu, J. Electrospinning of sodium alginate with poly (ethylene oxide). Polymer 2006, 47, 8026–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation and properties of electrospun soy protein isolate/polyethylene oxide nanofiber membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4331–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.X.; Xu, X.X.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.M.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Lou, X. Preparation and characterization of electrospun PLGA/gelatin nanofibers as a potential drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluigi, A.; Vineis, C.; Varesano, A.; Mazzuchetti, G.; Ferrero, F.; Tonin, C. Structure and properties of keratin/PEO blend nanofibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, P.; França, D.; Balieiro, A.G.; Faez, R. Polymers and its applications in agriculture. Polymers 2017, 27, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizka, H.; Armin, F.; Djamaan, A. Utilization od polystyrene waste as coting material for slow-release urea fertilizer. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2020, 15, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Cao, B.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, S.; Mi, C.; Li, K.; Wang, M. Structure and properties of bio-based polyurethane coatings for controlled-release fertilizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, e50179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaee, S.; Mirabeddini, M.; Farnood, R.; Alizadegan, F. Development of self-healing coatings on urea-formaldehyde/polyurethane microcapsules containing epoxy resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Preparation of urea-containing starch castor oil superabsorbent polyurethane coated urea and investigation of controlled nitrogen release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, P. Preparation and characterization of polyurethane-/MMT nanocimposite-coated as controlled-release fertilizers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasson, E.; Malka, E.; Caspi, A.; Kanovsky, N.; Margel, S. Engineered thin coating of cross-linked silane polymers with urea group onto polypropylene fabrics for controlled release of thymol against molds in hay. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 37, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Mahanwar, P.A. Superabsorbent polymers in agriculture and other applications: A review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 59, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers: A Review on Coating Materials and Mechanism of Release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanek, I.; Cvek, M.; Rogacz, D.; Żarski, A.; Lewicka, K.; Sedlarik, V.; Rychter, P. Degradation of Polylactic Acid/Polypropylene Carbonate Films in Soil and Phosphate Buffer and Their Potential Usefulness in Agriculture and Agrochemistry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, H.; Lu, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Preparation and ppplication of degradable lignin/poly (vinyl alcohol) polymers as urea slow-release coating materials. Molecules 2024, 29, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmelshue, c.; Goggi, A.S.; Cademartiri, R. The use of biological seed coatings based on bacteriophages and polymers against Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. Nebraskensis in maize seeds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnopeeva, E.L.; Panova, G.G.; Yakimansky, A.V. Agricultural Applications of Superabsorbent Polymer Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, A. Water and fertilizer integrated hydrogel derived from the polymerization of acrylic and urea as a slow-release N fertilizer and water retention in agriculture. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2018, 66, 5762–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, A.; Chen, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, S. Influence of super absorbent polymer on soil water retention, seed germination and plant survivals for rocky slopes eco-engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javazmi, L.; Young, A.; Ash, G.J.; Low, T. Kinetics of slow release of nitrogen fertiliser from multi-layered nanofibrous structures. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Enríquez, D.D.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; Torres-Chávez, P.I.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Rodríguez-Félix, D.E.; Armenta-Villegas, L.; Ledesma-Osuna, A.I. Preparation, characterization and release of urea from wheat gluten electrospun membranes. Materials 2012, 5, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Jing, X. Controlled release of urea encapsulated by starch-g-poly(L-lactide). Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampeerapappun, P.; Phanomkate, N. Slow release fertilizer from core-shell electrospun fibers. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013, 40, 775–782. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Elumalai, G.; Rajiv, S. Environment friendly synthesis of polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers and their potential use as seed coats. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cesare, F.; Pietrini, F.; Zacchini, M.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Macagnano, A. Catechol-loading nanofibrous membranes for eco-friendly iron nutrition of Plants. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulus, E.; Sakarya Bulus, G.; Yakuphanoglu, F. Production and characterization of novel nature-friendly organic fertilizer covers based on nanotechnology for the agricultural sector. J. Mater. Electron. Device 2020, 5, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nooeaid, P.; Chuysinuan, P.; Pitakdantham, W.; Aryuwananon, D.; Techasakul, S.; Dechtrirat, D. Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/polylactic acid core/shell structured fibers as controlled-release fertilizers for sustainable agriculture. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.A.; Kazemikia, F. Chemical fertilizer release control using encapsulation in polymer matrix by electrospinning. Sci. Iran. 2022, 29, 3198–3207. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Zou, Z.; Awais, M.; Munsif, F.; Khan, A.; Nepal, J.; Ahmad, M.; Akbar, S.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.S.; et al. Seed-Primed and foliar oxozinc nanofiber application increased wheat production and zn biofortification in calcareous-alkaline soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.B.; Husted, S. The Biochemical Properties of manganese in plants. Plants 2019, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafatti, J.O.D.; Ruellas, T.M.O.; Sciena, C.R.; Paris, E.C. PLA/starch biodegradable fibers obtained by the electrospinning method for micronutrients mineral release. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2023, 10, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitiwongsawet, P.; Ouykul, P.; Khaoroppan, A. 2,6-Dicholoro-4-nitroaniline-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats and their release characteristics. ASEAN J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 2, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Taylor, A.G.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Frey, M.W. Controlled release of nonionic compounds from poly(lactic acid)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 127, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.M.F.; Genro, C.; Roggia, I.; Bender, S.S.; Bender, R.J.; Preira, C.N. Innovate rice seed coatong (Oryza Sativa) with polymer nanofibres and microparticles using the electrspinning method. J. Res. Updates Polym. Sci. 2014, 3, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.A.; Oliveira, J.E.; Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Controlled release of linalool using nanofibrous membranes of poly(lactic acid) obtained by electrospinning and solution blow spinning: A comparative study. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 5628–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshani, B.; Tavanai, H.; Morshed, M.; Khajehali, J. Controlled release of thiram pesticide from poly(L-lactic acid) nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 108, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, M.; Raja, K.; Subramanian, K.; Karthikeyan, M.; Lakshmanan, A. Fabrication and characterization of tebuconazole loaded PVA nanofiber. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 8514–8517. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, B.V.; Pirzada, T.; Mathew, R.; Sit, T.L.; Opperman, C.; Khan, S.A. Electrospun polymer nanofibers as seed coatongs for crop protection. ACA Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19848–19856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciera, L.; Beladjal, L.; Landuyt, L.V.; Menger, D.; Holdinga, M.; Mertens, J.; Langenhove, L.V.; De Clerk, K.; Gheysens, T. Electrospinning repellents in polyvinyl alcohol-nanofibres for obtaining mosquito-repelling fabrics. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F. Encapsulation of thiabendazole in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin nanofibers via polymer-free electrospinning and its characterization. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, L. Thiram/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex electrospun nanofibers for a fast dissolving water-based drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 201, 111625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.J.; Casalini, R.; Orlicki, J.A.; Lundin, J.G. Controlled release of the insect repellent picaridin from electrospun nylon-6,6 nanofibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiri, C.; Raja, K.; Senthilkumar, M.; Subramanian, K.S.; Govindaraju, K.; Pradeep, D.; Ranjan, S. Immovilization of beneficial microbe Methylobacterium aminovorans in electrospun nanofibre as germination and growth of groundnut Arachis hypogaea. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 97, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.P.; Singh, P.; Satapathy, B.K. Nanofibrous-substrate-based controlled herbicidal release systems: Atrazine/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex loaded PVA agro-augmenting electrospun mats. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 6, 111586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, C.; Lacotte, V.; Castro, V.O.; Perli, G.; Da Silva, P.; Livi, S. Novel aphid-repellent fiber mats based on poly(lactic acid)-containing ionic liquids. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5406–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Polymers/Solvent | Encapsulated Fertilizer | Fibers Morphology/Diameter | Fibers Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castro-Enriquez et al. (2012) [163] | WG Acetic acid/ethanol/1-propanol/ 2-propanol/acetone /2-mercaptoethanol | Urea | Smooth and porous/ 0.683 to 5.45 μm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Kampeerapappun and Phanomkate, (2013) [165] | PLA/dimethylformamide (DMF) PHB/Choloform | NPK 21-21-21 | Core-shell/3.9 to 4.5 μm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Krishnamoorthy et al. (2016) [166] | urea–PVP–CoNPs/ ethanol and chloroform | Urea-CoNPs | Smooth surface, aligned and continuous/ 0.43–1.5 μm; 0.8–1.6 μm, and 0.06–0.8 μm | Coatings cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) |
| De Cesare et al. (2018) [167] | PCL/PHB | Catechol(CL-NMs) | Mean diameter 0.502 ± 0.173 μm | Coating duckweeds (Lemma minor L.) |
| Bulus et al. (2020) [168] | PCL/DMF | Liquid fertilizer | Smooth, thinner/ 150–300 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Nooeaid, et al., 2021 [169] | PVA/deionized PLA/DMF/Dichloromethane (DCM) | NPK | Core-shell/ 0.1–0.3 μm; 0.2–0.5 μm | Growth of green cos lettuce and red cos lettuce |
| Javazmi et al. (2021) [162] | PLLA/chloroform: acetone PHB/DMF: chloroform | Urea (N-P-K; 46-0-0) | Smooth fibers/PLLA 496–782 nm PHB/428 ± 64 nm. | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Salehi and Kazemikia (2022) [170] | CA/acetic acid, distilled water | Urea | Continuous, uniform fibers/87 nm | Design for a controlled-release system |
| Ahmad et al. (2023) [171] | PVA | Zn nanoparticles | Round, irregular, and hexagonal shape/not explicitly valor | Foliar application, seed priming, seed coating to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) |
| Malafatti et al. (2023) [173] | PLA/starch/chloroform, DMF | MnCO3 | Homogeneity and smooth structure/not explicitly valor diameter | Design for a controlled-release system |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colín-Orozco, J.; Colín-Orozco, E.; Valdivia-Barrientos, R. Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical. Fibers 2024, 12, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12080064
Colín-Orozco J, Colín-Orozco E, Valdivia-Barrientos R. Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical. Fibers. 2024; 12(8):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12080064
Chicago/Turabian StyleColín-Orozco, Julia, Elena Colín-Orozco, and Ricardo Valdivia-Barrientos. 2024. "Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical" Fibers 12, no. 8: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12080064
APA StyleColín-Orozco, J., Colín-Orozco, E., & Valdivia-Barrientos, R. (2024). Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical. Fibers, 12(8), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib12080064





