Characterization of a MOB1 Homolog in the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
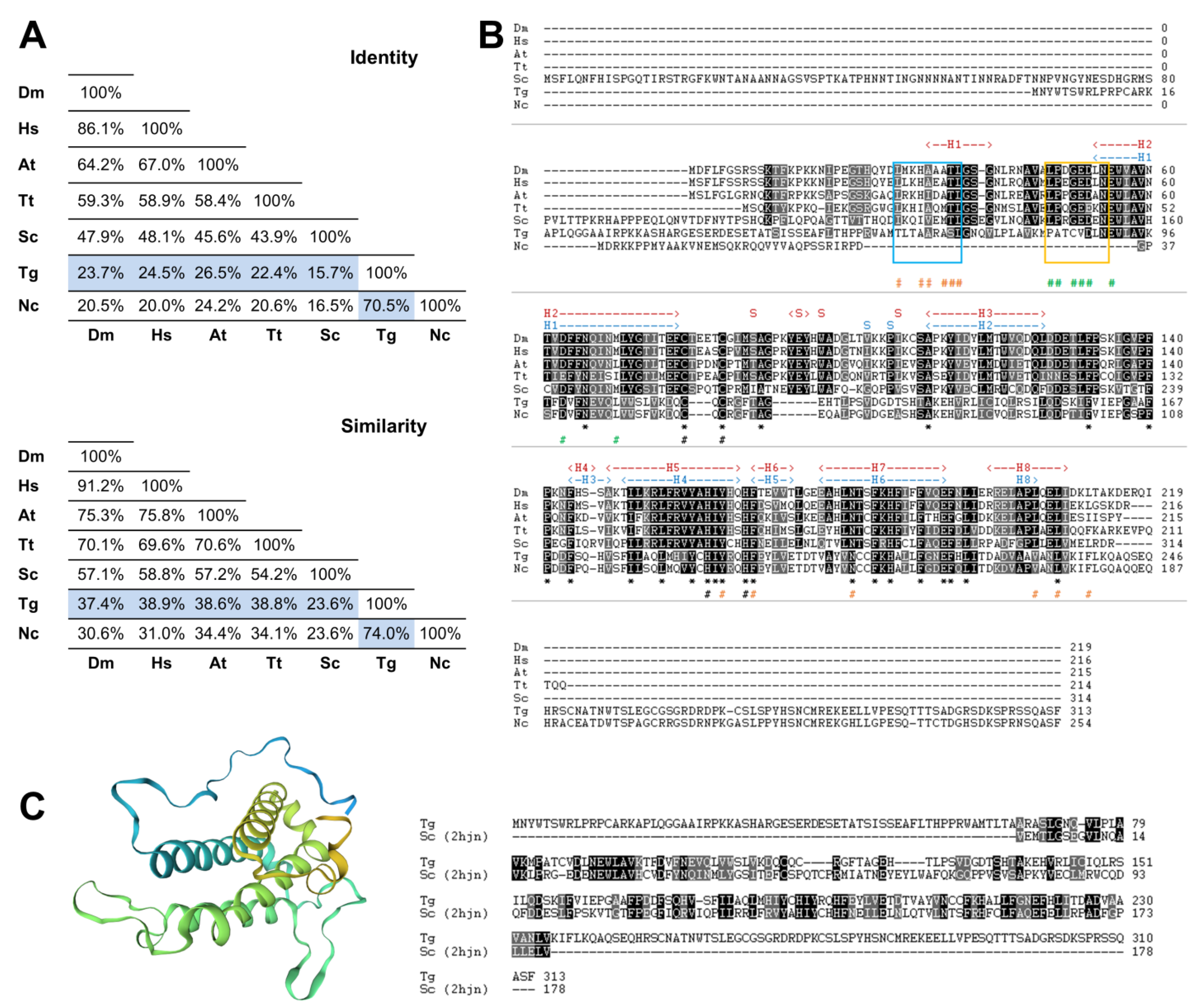
2.1. Deduced Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. DNA Constructs
2.4. Toxoplasma Gondii Strains, Culture, and Transfection
2.5. TgMOB1 Expression Assay
2.6. Invasion and Replication Efficiency Assays
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Biotinylation Assays
2.10. Proteomics
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. The Toxoplasma gondii Genome Encodes a Single MOB1 Protein Homolog
3.2. RNA Expression and Gain-of-Function Analyses Suggest That TgMOB1 Is Maintained at Low Levels in the Intracellular Tachyzoite
3.3. TgMOB1 Loss-of-Function Tachyzoites Do Not Present Compromised Mitotic Exit or Cytokinesis
3.4. Novel Potential MOB1-Interacting Proteins Identified through the TgMOB1 BioID System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, M.W.; Boothroyd, J.C. Lytic Cycle of Toxoplasma Gondii. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomasina, R.; Francia, M.E. The Structural and Molecular Underpinnings of Gametogenesis in Toxoplasma Gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 608291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, F.C.; Winey, M. MOB1, an Essential Yeast Gene Required for Completion of Mitosis and Maintenance of Ploidy. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luca, F.C.; Mody, M.; Kurischko, C.; Roof, D.M.; Giddings, T.H.; Winey, M. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Mob1p Is Required for Cytokinesis and Mitotic Exit. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6972–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammarton, T.C.; Lillico, S.G.; Welburn, S.C.; Mottram, J.C. Trypanosoma Brucei MOB1 Is Required for Accurate and Efficient Cytokinesis but Not for Exit from Mitosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galla, G.; Zenoni, S.; Marconi, G.; Marino, G.; Botton, A.; Pinosa, F.; Citterio, S.; Ruperti, B.; Palme, K.; Albertini, E.; et al. Sporophytic and Gametophytic Functions of the Cell Cycle-Associated Mob1 Gene in Arabidopsis Thaliana L. Gene 2011, 484, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Perdiga, J.; Fesquet, D.; Schiebel, E.; Pines, J.; Tavares, Á.A. Human Mob1 Proteins Are Required for Cytokinesis by Controlling Microtubule Stability. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3085–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavares, A.; Gonçalves, J.; Florindo, C.; Tavares, A.; Soares, H. Mob1: Defining Cell Polarity for Proper Cell Division. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, E.L.; Kurischko, C.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Drubin, D.G.; Luca, F.C. The Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Mob2p—Cbk1p Kinase Complex Promotes Polarized Growth and Acts with the Mitotic Exit Network to Facilitate Daughter Cell—Specific Localization of Ace2p Transcription Factor. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalker, U.L.; Frankel, J. Morphogenesis: A Mob Rules from the Rear. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R700–R702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, J.S.; Kim, S.M.; Jeon, Y.; Sim, J.; Jang, J.Y.; Son, J.; Hong, W.; Park, M.K.; Lee, H. Loss of Mob1a/b Impairs the Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells into the Three Germ Layer Lineages. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Z.-C.; Wei, X.; Shimizu, T.; Ramos, E.; Rohrbaugh, M.; Nikolaidis, N.; Ho, L.-L.; Li, Y. Control of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis by Mob as Tumor Suppressor, Mats. Cell 2005, 120, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmeth, L.J.; Shrestha, S.; Montaño, G.; Rashe, J.; Shuster, C.B. Mutual Dependence of Mob1 and the Chromosomal Passenger Complex for Localization during Mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardin, A.J.; Amon, A.; Medical, H.H. Men and sin: what’s the difference? Nature 2001, 2, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotz, M.; Barral, Y. The Mitotic Exit Network: New Turns on Old Pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergovich, A. Hippo Signaling in Mitosis: An Updated View in Light of the MEN Pathway; Monje-Casas, F., Queralt, E., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1505, ISBN 9781493965021. [Google Scholar]
- Duhart, J.C.; Raftery, L.A. Mob Family Proteins: Regulatory Partners in Hippo and Hippo-Like Intracellular Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebé-Pedrós, A.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Trillo, I.; Pan, D. Premetazoan Origin of the Hippo Signaling Pathway. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hergovich, A. MOB Control: Reviewing a Conserved Family of Kinase Regulators. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Seo, G.; Vargas, R.E.; Yang, B.; Chuc, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W. Systematic Analysis of the Hippo Pathway Organization and Oncogenic Alteration in Evolution. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitulo, N.; Vezzi, A.; Galla, G.; Citterio, S.; Marino, G.; Ruperti, B.; Zermiani, M.; Albertini, E.; Valle, G.; Barcaccia, G. Characterization and Evolution of the Cell Cycle-Associated Mob Domain-Containing Proteins in Eukaryotes. Evol. Bioinform. 2007, 3, 121–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hehl, A.B.; Basso, W.U.; Lippuner, C.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Okoniewski, M.; Walker, R.A.; Grigg, M.E.; Smith, N.C.; Deplazes, P. Asexual Expansion of Toxoplasma Gondii Merozoites Is Distinct from Tachyzoites and Entails Expression of Non-Overlapping Gene Families to Attach, Invade, and Replicate within Feline Enterocytes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Maier, S.; Walker, R.A.; Rehrauer, H.; Joekel, D.E.; Winiger, R.; Basso, W.U.; Grigg, M.E.; Hehl, A.B.; Deplazes, P.; et al. An Experimental Genetically Attenuated Live Vaccine to Prevent Transmission of Toxoplasma Gondii by Cats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, K.R.; Fritz, H.M.; Chen, X.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Rocke, D.M.; Ferguson, D.J.; Conrad, P.A.; Boothroyd, J.C. Identification of Tissue Cyst Wall Components by Transcriptome Analysis of in Vivo and in Vitro Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoites. Eukaryot. Cell 2011, 10, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Grech, J.; Stortz, J.F.; Gow, M.; Periz, J.; Meissner, M.; Jimenez-Ruiz, E. A Phenotypic Screen Using SplitCas9 Identifies Essential Genes Required for Actin Regulation during Host Cell Egress and Invasion by Toxoplasma Gondii. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.H.; Carruthers, V.B. Tagging of Endogenous Genes in a Toxoplasma Gondii Strain Lacking Ku80. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roux, K.J.; Kim, D.I.; Raida, M.; Burke, B. A Promiscuous Biotin Ligase Fusion Protein Identifies Proximal and Interacting Proteins in Mammalian Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stothard, P. The Sequence Manipulation Suite: JavaScript Programs for Analyzing and Formatting Protein and DNA Sequences. Biotechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studer, G.; Rempfer, C.; Waterhouse, A.M.; Gumienny, R.; Haas, J.; Schwede, T. QMEANDisCo—Distance Constraints Applied on Model Quality Estimation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Bienert, S.; Biasini, M.; Johner, N.; Schwede, T. ProMod3—A Versatile Homology Modelling Toolbox. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrkobrada, S.; Boucher, L.; Ceccarelli, D.F.J.; Tyers, M.; Sicheri, F. Structural and Functional Analysis of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Mob1. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 362, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.W.; Gogl, G.; Bálint, M.; Hetényi, C.; Reményi, A.; Weiss, E.L. Ndr/Lats Kinases Bind Specific Mob-Family Coactivators through a Conserved and Modular Interface. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Armougom, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Higgins, D.G.; Jongeneel, C.V.; Notredame, C. The M-Coffee Web Server: A Meta-Method for Computing Multiple Sequence Alignments by Combining Alternative Alignment Methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. TrimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2-A Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillary, W.; Lin, S.-H.; Upton, C. Base-By-Base Version 2: Single Nucleotide-Level Analysis of Whole Viral Genome Alignments. Microb. Inform. Exp. 2011, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. Europe PMC Funders Group ProtTest 3: Fast Selection of Best-Fit Models of Protein Evolution. Bioinformatics 2017, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herm-Götz, A.; Agop-Nersesian, C.; Münter, S.; Grimley, J.S.; Wandless, T.J.; Frischknecht, F.; Meissner, M. Rapid Control of Protein Level in the Apicomplexan Toxoplasma Gondii. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gubbels, M.-J.; Vaishnava, S.; Boot, N.; Dubremetz, J.-F.; Striepen, B. A MORN-Repeat Protein Is a Dynamic Component of the Toxoplasma Gondii Cell Division Apparatus. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, D.; Tarleton, R. EuPaGDT: A Web Tool Tailored to Design CRISPR Guide RNAs for Eukaryotic Pathogens. Microb. Genom. 2015, 1, e000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donald, R.G.K.; Carter, D.; Ullman, B.; Roos, D.S. Insertional Tagging, Cloning, and Expression of the Toxoplasma Gondii Hypoxanthine-Xanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyltransferase Gene: Use as a Selectable Marker for Stable Transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14010–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Team R Development Core A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Found. Stat. Comput. 2018, 2. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-Pot, Solid-Phase-Enhanced Sample Preparation for Proteomics Experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supek, F.; Bošnjak, M.; Škunca, N.; Šmuc, T. Revigo Summarizes and Visualizes Long Lists of Gene Ontology Terms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, I.L.S.; Carmona, B.; Nolasco, S.; Santos, D.; Leitão, A.; Soares, H. Mob: Pivotal Conserved Proteins in Cytokinesis, Cell Architecture and Tissue Homeostasis. Biology 2020, 9, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabodnick, M.M.; Ruby, J.G.; Dunn, J.G.; Feldman, J.L.; DeRisi, J.L.; Marshall, W.F. The Kinase Regulator Mob1 Acts as a Patterning Protein for Stentor Morphogenesis. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, J.S.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, M.K.; Kim, I.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Lim, D.S.; Lee, H. Depletion of MOB1A/B Causes Intestinal Epithelial Degeneration by Suppressing Wnt Activity and Activating BMP/TGF-β Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.L.; Kim, E.W.; Toh, J.Y.; Vashisht, A.A.; Rashoff, A.Q.; Van, C.; Huang, A.S.; Moon, A.S.; Bell, H.N.; Bentolila, L.A.; et al. Novel Components of the Toxoplasma Inner Membrane Complex Revealed by BioID. MBio 2015, 6, e02357-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nadipuram, S.M.; Thind, A.C.; Rayatpisheh, S.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Bradley, P.J. Proximity Biotinylation Reveals Novel Secreted Dense Granule Proteins of Toxoplasma Gondii Bradyzoites. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Williamson, A.; Banerjee, S.; Philipp, I.; Rape, M. Mechanism of Ubiquitin-Chain Formation by the Human Anaphase-Promoting Complex. Cell 2008, 133, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.-Y.; Maier, W.; Baumeister, R.; Joachimiak, E.; Ruan, Z.; Kannan, N.; Clarke, D.; Louka, P.; Guha, M.; Frankel, J.; et al. Two Antagonistic Hippo Signaling Circuits Set the Division Plane at the Medial Position in the Ciliate Tetrahymena. Genetics 2019, 211, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salimova, E.; Sohrmann, M.; Fournier, N.; Simanis, V. The S. Pombe Orthologue of the S. Cerevisiae Mob1 Gene Is Essential and Functions in Signalling the Onset of Septum Formation. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidik, S.M.; Huet, D.; Ganesan, S.M.; Huynh, M.-H.; Wang, T.; Nasamu, A.; Thiru, P.; Saeij, J.P.; Carruthers, V.B.; Niles, J.C.; et al. A Genome-Wide CRISPR Screen in Toxoplasma Identifies Essential Apicomplexan Genes. Cell 2016, 166, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lignitto, L.; Arcella, A.; Sepe, M.; Rinaldi, L.; Donne, R.D.; Gallo, A.; Stefan, E.; Bachmann, V.A.; Oliva, M.A.; Storlazzi, C.T.; et al. Proteolysis of MOB1 by the Ubiquitin Ligase Praja2 Attenuates Hippo Signalling and Supports Glioblastoma Growth. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Wang, T.; Chi, X.; Wei, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, M.; He, H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Du, J.; et al. Kindlin-2 Inhibits the Hippo Signaling Pathway by Promoting Degradation of MOB1. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3664–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Han, X.; Zou, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y.; Xu, X.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Gong, A. PTEN–GSK3β–MOB1 Axis Controls Neurite Outgrowth in Vitro and in Vivo. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4445–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.A.; Beli, P.; Weinert, B.T.; Schölz, C.; Kelstrup, C.D.; Young, C.; Nielsen, M.L.; Olsen, J.V.; Brakebusch, C.; Choudhary, C. Proteomic Analyses Reveal Divergent Ubiquitylation Site Patterns in Murine Tissues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akimov, V.; Barrio-hernandez, I.; Hansen, S.V.F.; Hallenborg, P.; Pedersen, A.; Bekker-jensen, D.B.; Puglia, M.; Christensen, S.D.K.; Vanselow, J.T.; Nielsen, M.M.; et al. UbiSite Approach for Comprehensive Mapping of lysine and N-terminal ubiquitination sites. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, A.C.; Kyrousi, C.; Einsiedler, M.; Burtscher, I.; Drukker, M.; Markie, D.M.; Kirk, E.P.; Götz, M.; Robertson, S.P.; Cappello, S. Mob2 Insufficiency Disrupts Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cortex. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, K.; Conery, A.R.; Litovchick, L.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Settleman, J.; Harlow, E.; Dyson, N. A Kinase ShRNA Screen Links LATS2 and the PRB Tumor Suppressor. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 814–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degoutin, J.; Milton, C.C.; Yu, E.; Tipping, M.; Bosveld, F.; Bellaiche, Y.; Veraksa, A.; Harvey, K.F. Riquiqui and Minibrain, New Regulators of the Hippo Pathway Downstream of Dachsous. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Cho, Y.S.; Wang, X.; Park, O.; Ma, X.; Kim, H.; Gan, W.; Jho, E.-H.; Cha, B.; Jeung, Y.; et al. Hippo Signaling Is Intrinsically Regulated during Cell Cycle Progression by APC/CCdh1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9423–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, V.; Gundogdu, R.; Gomez, M.; Hoa, L.; Panchal, N.; O’Driscoll, M.; Hergovich, A. Regulation of DNA Damage Responses and Cell Cycle Progression by HMOB2. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamson, B.; Smogorzewska, A.; Sigoillot, F.D.; King, R.W.; Elledge, S.J. A Genome-Wide Homologous Recombination Screen Identifies the RNA-Binding Protein RBMX as a Component of the DNA Damage Response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Q.; Hong, W. The Emerging Role of the Hippo Pathway in Cell Contact Inhibition, Organ Size Control, and Cancer Development in Mammals. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Tumaneng, K.; Guan, K. The Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Regeneration and Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, V.; Hansen, C.G. The Hippo Pathway, YAP/TAZ, and the Plasma Membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidpeter, J.; Dahl, M.; Hofmann, J.; Koch, C. ChMob2 Binds to ChCbk1 and Promotes Virulence and Conidiation of the Fungal Pathogen Colletotrichum Higginsianum. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delbac, F.; Sänger, A.; Neuhaus, E.M.; Stratmann, R.; Ajioka, J.W.; Toursel, C.; Herm-Götz, A.; Tomavo, S.; Soldati, T.; Soldati, D. Toxoplasma Gondii Myosins B/C: One Gene, Two Tails, Two Localizations, and a Role in Parasite Division. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Citterio, S.; Piatti, S.; Albertini, E.; Aina, R.; Varotto, S.; Barcaccia, G. Alfalfa Mob1-like Proteins Are Involved in Cell Proliferation and Are Localized in the Cell Division Plane during Cytokinesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.W.; Suvorova, E.S. Apicomplexa Cell Cycles: Something Old, Borrowed, Lost, and New. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Mann, T.; Striepen, B.; Beckers, C.J.M.; Roos, D.S.; Murray, J.M. Daughter Cell Assembly in the Protozoan Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, H.M.; Buchholz, K.R.; Chen, X.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Rocke, D.M.; Conrad, P.A.; Boothroyd, J.C. Transcriptomic Analysis of Toxoplasma Development Reveals Many Novel Functions and Structures Specific to Sporozoites and Oocysts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Genova, B.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Knoll, L.J. Intestinal Delta-6-Desaturase Activity Determines Host Range for Toxoplasma Sexual Reproduction. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE Database and Related Tools and Resources in 2019: Improving Support for Quantification Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| MOB1 | Control | Total Proteins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unique peptides (#) | 494 | 608 | 27,163 |
| Identified proteins (#) | |||
| FDR confidence high (in MOB1 pulldown only) | 84 (39) | 80 | 3128 |
| FDR confidence medium | 12 | 18 | 141 |
| FDR confidence low | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| total | 97 | 98 | 3274 |
| Accession | Annotation | Abundance (×105) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SD | ||
| TGME49_309890 | Uncharacterized protein | 102.45 | 18.13 |
| TGME49_206540 | Uncharacterized protein | 15.77 | 0.63 |
| TGME49_263140 | SWI2/SNF2-containing protein RAD26 | 11.17 | 2.65 |
| TGME49_254600 | Ubiquitin family protein | 8.27 | 1.15 |
| TGME49_225120 | Uncharacterized protein | 7.34 | 0.45 |
| TGME49_265010 | Glutamate 5-kinase domain-containing protein | 7.33 | 2.20 |
| TGME49_224110 | Adhesion regulating molecule region protein, putative | 5.53 | 0.15 |
| TGME49_312410 | Uncharacterized protein | 4.27 | 0.36 |
| TGME49_215420 | SNARE protein | 3.40 | 1.27 |
| TGME49_216920 | Mediator complex subunit MED8 | 3.07 | 0.48 |
| TGME49_260450 | DEAD/DEAH box helicase domain-containing protein | 3.03 | 0.57 |
| TGME49_223510 | AB hydrolase-1 domain-containing protein | 3.01 | 0.50 |
| TGME49_271600 | Uncharacterized protein | 2.90 | 0.88 |
| TGME49_272670 | Peptidase family M3 protein | 2.82 | 0.95 |
| TGME49_272230 | Heat shock protein hslv, putative | 2.78 | 1.76 |
| TGME49_203710 | AP2 domain transcription factor AP2VIIa-4 | 2.59 | 1.15 |
| TGME49_297970 | Aspartyl aminopeptidase | 2.55 | 0.75 |
| TGME49_215250 | Thiamine diphosphokinase | 2.49 | 0.17 |
| TGME49_309050 | Uncharacterized protein | 2.45 | 0.15 |
| TGME49_262780 | FHA domain-containing protein | 2.18 | 0.35 |
| Accession | Annotation | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|
| TGME49_234560 | Uncharacterized protein | 25.00 |
| TGME49_275410 | Anaphase-promoting complex subunit1 | 16.67 |
| TGME49_243590 | Endonuclease/exonuclease/phosphatase family protein | 13.70 |
| TGME49_229500 | Uncharacterized protein | 13.33 |
| TGME49_204280 | Cell-cycle-associated protein kinase DYRK, putative | 12.50 |
| TGME49_268320 | Uncharacterized protein | 10.64 |
| TGME49_313600 | DDHD domain-containing protein | 9.43 |
| TGME49_222090 | Uncharacterized protein | 9.17 |
| TGME49_264030 | Aminotransferase, putative | 8.77 |
| TGME49_210778 | Hemimethylated DNA binding domain-containing protein | 8.62 |
| TGME49_281400 | Phosphofructokinase domain-containing protein | 8.26 |
| TGME49_210345 | Uncharacterized protein | 7.75 |
| TGME49_265390 | Uncharacterized protein | 7.63 |
| TGME49_246990 | Uncharacterized protein | 6.99 |
| TGME49_204160 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A | 6.62 |
| TGME49_254210 | RNA recognition motif-containing protein | 6.41 |
| TGME49_213415 | Uncharacterized protein | 6.37 |
| TGME49_305610 | Uncharacterized protein | 6.33 |
| TGME49_310790 | Uncharacterized protein | 5.71 |
| TGME49_228630 | Uncharacterized protein | 5.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado, I.L.S.; Tavares, A.; Francisco, S.; Santos, D.; Coelho, J.; Basto, A.P.; Zúquete, S.; Müller, J.; Hemphill, A.; Meissner, M.; et al. Characterization of a MOB1 Homolog in the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Biology 2021, 10, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121233
Delgado ILS, Tavares A, Francisco S, Santos D, Coelho J, Basto AP, Zúquete S, Müller J, Hemphill A, Meissner M, et al. Characterization of a MOB1 Homolog in the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121233
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado, Inês L. S., Alexandra Tavares, Samuel Francisco, Dulce Santos, João Coelho, Afonso P. Basto, Sara Zúquete, Joachim Müller, Andrew Hemphill, Markus Meissner, and et al. 2021. "Characterization of a MOB1 Homolog in the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii" Biology 10, no. 12: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121233
APA StyleDelgado, I. L. S., Tavares, A., Francisco, S., Santos, D., Coelho, J., Basto, A. P., Zúquete, S., Müller, J., Hemphill, A., Meissner, M., Soares, H., Leitão, A., & Nolasco, S. (2021). Characterization of a MOB1 Homolog in the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Biology, 10(12), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121233








