Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
2.5. The Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization (WISH)
2.6. Immunochemistry Staining in Adult Tissues
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Characterization of Paramyosin
3.2. Protein Structure and Phosphorylation Prediction
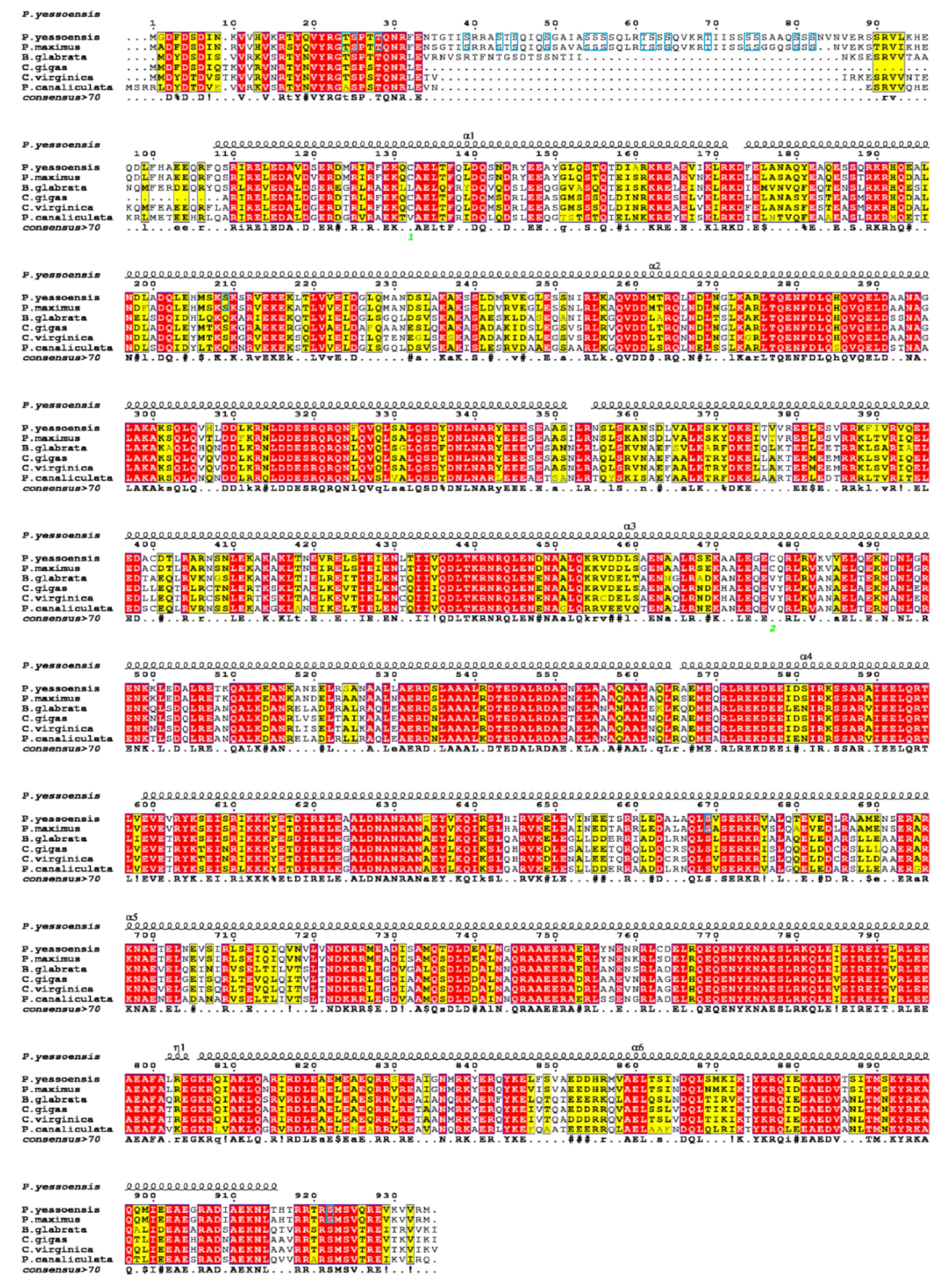
3.3. Multiple Sequence Alignments and Phylogenetic Analysis
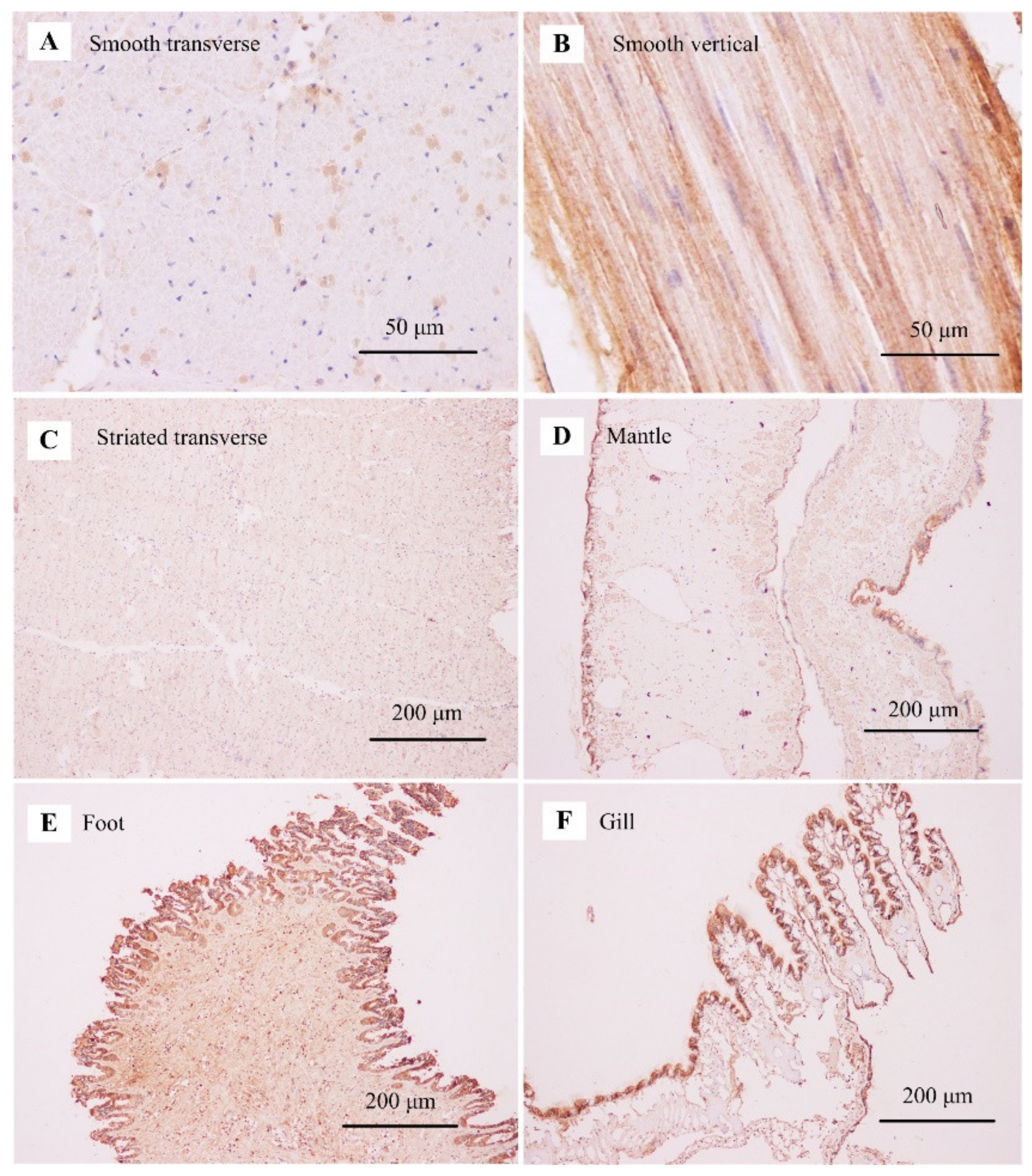
3.4. Tissue-Specific Expression Pattern of Paramyosin
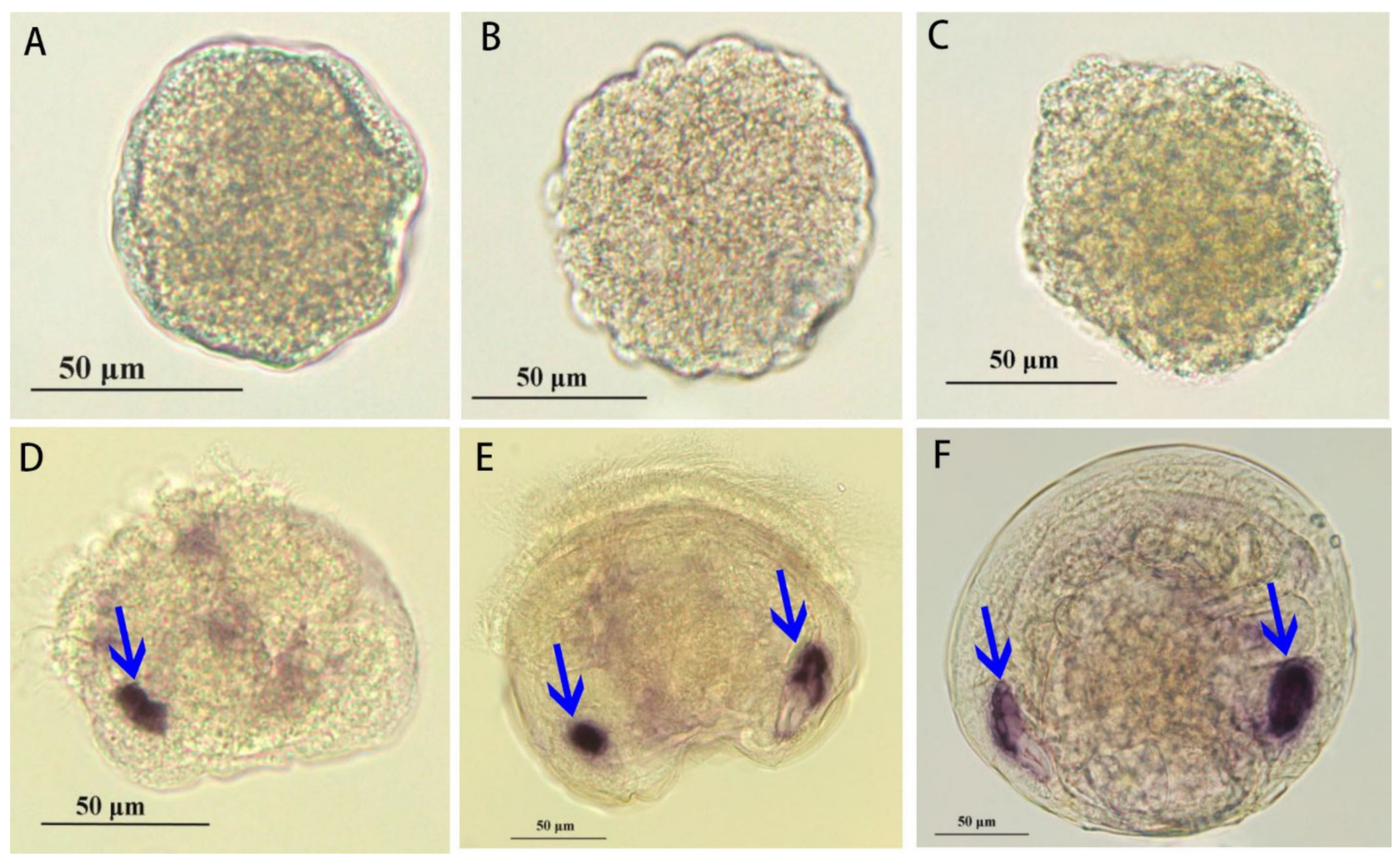
3.5. The Developmental Expression of Paramyosin at Different Stages
4. Discussion
4.1. Sequence Feature of Paramyosin in Molluscs
4.2. Evolution of Paramyosin in Protostomes
4.3. Tissue and Developmental Expression of Paramyosin in Molluscs
4.4. Implication for Catch Mechanism in Molluscs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baylies, M.K.; Michelson, A.M. Invertebrate myogenesis: Looking back to the future of muscle development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Molecular and cellular mechanism of muscle regeneration. In Skeletal Muscle: Form Myogenesis to Clinical Relations; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 4–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, S.L.; Thuma, J.B. Invertebrate muscles: Muscle specific genes and proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1001–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, S.L.; Hobbs, K.H.; Thuma, J.B. Invertebrate muscles: Thin and thick filament structure; molecular basis of contraction and its regulation, catch and asynchronous muscle. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 86, 72–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadot, B.; Gomes, E.R. Skeletal Muscle. Encyclopedia Cell Biol. 2016, 677–682. [Google Scholar]
- Lowy, J.; Millman, B.M.; Hanson, J. Structure and Function in Smooth Tonic Muscles of Lamellibranch Molluscs. P. Roy. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1964, 160, 525–536. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Du, S. Characterization of paramyosin protein structure and gene expression during myogenesis in Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2021, 255, 110594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szent-Györgyi, A.G.; Cohen, C.; Kendrick-Jones, J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan “catch” muscles. II. Native filaments: Isolation and characterization. J. Mol. Biol. 1971, 56, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, S. Molecular basis of the catch state in molluscan smooth muscles: A catchy challenge. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2008, 29, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.J.; Li, H.; Bian, Y.; Zhong, Y. Heat-shock protein 90α1 is required for organized myofibril assembly in skeletal muscles of zebrafish embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M.; Rigby, P.J. Gene regulatory networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis. Dev. Cell. 2014, 28, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyeuns, J.-H.; Hashkimoto, K.; Matsuura, F. Isolation and Characterization of Abalone Paramyosin. Nippon Suisan Gakk. 1973, 39, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Noguchi, S.F.; Tsuchiya, T.; Matsumoto, J.J. Contribution of paramyosin to marine meat gel characteristics. J. Food Sci. 1986, 51, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, Z.E. The Myofibrillar Proteins in Seafoods. In Seafood Proteins; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 40–57. [Google Scholar]
- Levine, R.J.C.; Elfvin, M.; Dewey, M.M.; Walcott, B. Paramyosin in invertebrate muscles. II. Content in relation to structure and function. J. Cell Biol. 1976, 71, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achazi, R.K. Phosphorylation of molluscan paramyosin. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1979, 379, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, L.B.; Johnson, W.H.; Krause, S. Phosphorylation of paramyosin and its possible role in the catch mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Bennett, P.M. Molecular organization of paramyosin in the core of molluscan thick filaments. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 176, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Miller, M.S.; Swank, D.M.; Kronert, W.A.; Maughan, D.W.; Bernstein, S.I. Paramyosin phosphorylation site disruption affects indirect flight muscle stiffness and power generation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10522–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wu, B.; Liu, Z. Identification and characterization of phosphoproteins in the striated and smooth adductor muscles of Yesso scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C. Matching molecules in the catch mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3176–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Zhang, J.C.; Cui, X.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.Z.; Hu, Y.H. Evaluation of immune protection induced by DNA vaccines from Haemaphysalis longicornis paramyosin in rabbits. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhan, B.; Zhu, X. Mapping of the complement C1q binding site on Trichinella spiralis paramyosin. Parasit Vectors 2018, 27, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Ahmad, S.; Walton, S.; Abbasi, S.W. Multi-epitope based vaccine design against Sarcoptes scabiei paramyosin using immunoinformatics approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.M.; Himelbloom, B.; Crapo, C.; Vorholt, C.; Fong, Q.; RaLonde, R. Quality of Alaskan Maricultured Oysters (Crassostrea gigas): A One-Year Survey. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C532–C543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantler, P.D. Chapter 4 scallop adductor muscles: Structure and function. Dev. Aquacult. Fisheries Sci. 2016, 40, 161–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Ding, X.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Khan, M.U.; Lin, H.; Dang, X.; Li, Z. Immunological cross-reactivity involving mollusc species and mite–mollusc and cross-reactive allergen pm are risk factors of mollusc allergy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Burastero, G.J.; Suli, C.; Banerjee, S.; Vrtala, S.; Alessio, M.; Burastero, S.E. Identification by serological proteome analysis of paramyosin as prominent allergen in dust mite allergy. J. Proteomics 2017, 166, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. Purification, Characterization, and Three-Dimensional Structure Prediction of Paramyosin, a Novel Allergen of Rapana venosa. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14632–14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Yang, A. Differences between fast and slow muscles in scallops revealed through proteomics and transcriptomics. BMC Genomics. 2018, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Dan, Z.; Tian, J. Molecular characterization of the myostatin gene and its regulation on muscle growth in yesso scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, L.; Wu, B.; Ge, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, A.; Liu, Z. Cell type diversity in scallop adductor muscles revealed by single-cell RNA-seq. Genomics 2021, 113, 3582–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Biotechnology 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouet, P.; Robert, X.; Courcelle, E. ESPript/ENDscript: Extracting and rendering sequence and 3D information from atomic structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3320–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick-Jones, J.; Cohen, C.; Szent-Gyorgyi, A.G.; Longley, W. Paramyosin: Molecular length and assembly. Science 1969, 163, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick-Jones, J.; Lehman, W.; Szent-Gyorgyi, A.G. Regulation in molluscan muscles. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 54, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteé, N. Paramyosin polarity in the thick filament of molluscan smooth muscles. J. Struct. Biol. 1994, 113, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadota, H.; Mayans, O.; Matsunaga, Y.; McMurry, J.L.; Wilson, K.J.; Kwon, G.E.; Stanford, R.; Deehan, K.; Tinley, T.L.; Ngwa, V.M.; et al. The SH3 domain of UNC-89 (obscurin) interacts with paramyosin, a coiled-coil protein, in Caenorhabditis elegans muscle. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2016, 27, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.; Parry, D.A.D. A conserved C-terminal assembly region in paramyosin and myosin rods. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, P.E.; Waterston, R.H. A region of the myosin rod important for interaction with paramyosin in Caenorhabditis elegans striated muscle. Genet. Soc. Am. 2000, 156, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, H.F.; Aronow, B.J.; Harris, H.E. Interaction of myosin and paramyosin. J. Supramol. Struct. 1975, 3, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, P.; Kraus, J.; Larroux, C.; Hammel, J.U.; Amon-Hassenzahl, A.; Houliston, E.; Wörheide, G.; Nickel, M.; Degnan, B.M.; Technau, U. Independent evolution of striated muscles in cnidarians and bilaterians. Nature 2012, 487, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonobe, H.; Obinata, T.; Minokawa, T.; Haruta, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Wakatsuki, S.; Sato, N. Characterization of paramyosin and thin filaments in the smooth muscle of acorn worm, a member of hemichordates. J. Biochem. 2016, 160, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obinata, T.; Shirao, T.; Murakami, S. Sea urchin paramyosin. Int. J. Biochem. 1975, 6, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, L. Comparative studies of paramyosins. Comp. Biochem Phys. B 1976, 55, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, P.R.; Guthrie, D.M.; Banks, J.R. Paramyosin Muscle in the Notochord of Amphioxus. Nature 1969, 222, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani-Ceresa, L.; Lanzavecchia, G. Isolation and identification of paramyosin from amphioxus notochord. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1982, 3, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolano-Villaverde, I.J.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Rivereo-Espejel, I.A.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Suárez-Jiménez, G.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Effect of temperature on the actomyosin-paramyosin structure from giant squid mantle (Dosidicus gigas). J. Sci. Food Agr. 2019, 99, 5377–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Vasquez, A.E.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Huerta-Ocampo, J.Á.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.; Torres-Arreola, W. Proteomic identification and physicochemical characterisation of paramyosin and collagen from octopus (Octopus vulgaris) and jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas). Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 55, 3246–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, M.; Arredondo, J.J.; Ferreres, R.M. Paramyosin and Miniparamyosin; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Chapter 6; pp. 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Obinata, T.; Amemiya, S.; Takai, R.; Ichikawa, M.; Toyoshima, Y.Y.; Sato, N. Sea lily muscle lacks a troponin-regulatory system, while it contains paramyosin. Zoologicalence 2014, 31, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Mardahldumesnil, M.; Sweeney, S.T.; O’Kane, C.J.; Bernstein, S.I. Drosophila paramyosin is important for myoblast fusion and essential for myofibril formation. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A. The arrangement of myosin on the surface of paramyosin filaments in the white adductor muscle of Crassostrea angulata. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1974, 186, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J. Protein distribution and physicochemical properties in striated muscle and smooth muscle of Patinopecten yessoensis. J. Fish. China 2017, 41, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Watabe, S.; Iwasaki, K.; Funabara, D.; Hirayama, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Kikuchi, K. Complete amino acid sequence of Mytilus anterior byssus retractor paramyosin and its putative phosphorylation site. J. Exp. Zool. Part A 2000, 286, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, T.; Wu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tian, J.; Yang, A. Developmental dynamics of myogenesis in Yesso Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2019, 228, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsova, N.; Dyachuk, V.; Kiselev, K.; Shelud’ko, N. Expression of thick filament proteins during ontogenesis of the mussel Mytilus trossulus (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B. 2006, 144, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachuk, V.A.; Plotnikov, S.V.; Odintsova, N.A. Appearance of muscle proteins in ontogenesis of the mussel Mytilus trossulus (bivalvia). Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2005, 31, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, C.M.; Murphy, R.A. Cross-bridge phosphorylation and regulation of latch state in smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 254, C99–C106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.M.; Marston, S.B. Calcium regulated thin filaments from molluscan catch muscles contain a caldesmon-like regulatory protein. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1990, 11, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halina, I.F.; Eugene, S.; Helen, P.; Inna, M.S. The Role of Reversible Protein Phosphorylation in Regulation of the Mitochondrial Electron Transport System During Hypoxia and Reoxygenation Stress in Marine Bivalves. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 467. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M.; Allred, S.C.; Peifer, M. Abelson kinase’s intrinsically disordered region plays essential roles in protein function and protein stability. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, C.S.; Deitiker, P.R.; Epstein, H.F. Assembly-dependent phosphorylation of myosin and paramyosin of native thick filaments in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 186, 1528–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Bodor, O.; Gohr, L.; Kunz, W. Paramyosin isoforms of Schistosoma mansoni are phosphorylated and localized in a large variety of muscle types. Parasitology 1996, 112, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primer Name | Sequences | Product Size(bp) | Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| paramyosin-full_F1 | AGCTCCATTTCGTGATTTCCT | 3763 | PCR |
| paramyosin-full_R1 | CACGTGTCCTCCATACAAACA | PCR | |
| Paramyosin-F | ACATTACAAGGGCTAGTATTTAAAGCATTCGT | 1520 | PCR |
| Paramyosin-R | CTGTCTGTTCCTCTTGGTGAGATCC | PCR | |
| Paramyosin_qPCR_F | GAGTCTGTCAGGAGGAAGTTT | 158 | qPCR |
| Paramyosin_qPCR_R | ACGATGATGGTGAGGTTTT | qPCR | |
| Paramyosin_F | TGGATGACGAGTCTAGGCAA | 611 | in situ hybridization |
| Paramyosin_R | GGCTTTGTTGGCTTCCTTGA | in situ hybridization | |
| wish_Paramyosin_F | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGGATGACGAGTCTAGGCAA | 611 | in situ hybridization |
| wish_Paramyosin_R | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGGCTTTGTTGGCTTCCTTGA | in situ hybridization | |
| UBQ_F | TCGCTGTAGTCTCCAGGATTGC | 184 | internal control |
| UBQ_R | TCGCCACATACCCTCCCAC | internal control |
| No. | Position | Residue | Sequence Context | Score | Kinase | Positive Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | T | HVKRTYQVY | 0.65 | PKC | YES |
| 2 | 28 | T | TSPTTQNRF | 0.53 | DNAPK | YES |
| 3 | 39 | S | TGTISRRAS | 0.80 | PKC | YES |
| 4 | 49 | S | SQIQSGAIA | 0.59 | PKC | YES |
| 5 | 56 | S | IASSSSQLR | 0.60 | PKC | YES |
| 6 | 61 | T | SQLRTSSSQ | 0.54 | PKC | YES |
| 7 | 64 | S | RTSSSQVKR | 0.75 | PKC | YES |
| 8 | 69 | T | QVKRTIISS | 0.66 | PKC | YES |
| 9 | 74 | S | IISSSSSAA | 0.74 | PKC | YES |
| 10 | 80 | S | SAAQSSSNV | 0.52 | cdc2 | YES |
| 11 | 82 | S | AQSSSNVNV | 0.60 | cdc2 | YES |
| 12 | 155 | T | GLQSTQTDI | 0.59 | DNAPK | YES |
| 13 | 157 | T | QSTQTDIAR | 0.88 | PKC | YES |
| 14 | 181 | Y | ANAQYEAQE | 0.50 | EGFR | YES |
| 15 | 187 | S | AQESSQRKR | 0.69 | PKC | YES |
| 16 | 233 | S | MANDSLAKA | 0.56 | PKC | YES |
| 17 | 240 | S | KAKSSLDMR | 0.71 | PKA | YES |
| 18 | 251 | S | GLESSNIRL | 0.52 | cdc2 | YES |
| 19 | 362 | S | SKANSDLVA | 0.58 | cdc2 | YES |
| 20 | 418 | T | KAKLTNEVR | 0.53 | PKC | YES |
| 21 | 439 | T | VQDLTKRNR | 0.87 | PKC | YES |
| 22 | 468 | S | AALRSEKAA | 0.71 | PKC | YES |
| 23 | 535 | S | AERDSLAAA | 0.63 | PKA | YES |
| 24 | 609 | S | KSEISRIKK | 0.71 | PKC | YES |
| 25 | 617 | T | KKYETDIRE | 0.57 | CKII | YES |
| 26 | 642 | S | KQIRSLHIR | 0.53 | PKA | YES |
| 27 | 701 | T | KNAETELNE | 0.56 | CKII | YES |
| 28 | 736 | T | SAMQTDLDE | 0.66 | CKII | YES |
| 29 | 893 | Y | TMSKYRKAQ | 0.52 | EGFR | YES |
| 30 | 915 | T | EKNLTHTRR | 0.71 | PKC | YES |
| 31 | 917 | T | NLTHTRRTR | 0.76 | PKC | YES |
| 32 | 920 | T | HTRRTRSMS | 0.65 | PKC | YES |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Wu, B.; Yu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, X. Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop. Biology 2022, 11, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030453
Yang Y, Zhao D, Zhou L, Zhang T, Liu Z, Wu B, Yu T, Zheng Y, Sun X. Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop. Biology. 2022; 11(3):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030453
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yumin, Dan Zhao, Liqing Zhou, Tianshi Zhang, Zhihong Liu, Biao Wu, Tao Yu, Yanxin Zheng, and Xiujun Sun. 2022. "Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop" Biology 11, no. 3: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030453
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhao, D., Zhou, L., Zhang, T., Liu, Z., Wu, B., Yu, T., Zheng, Y., & Sun, X. (2022). Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop. Biology, 11(3), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030453








