Exploring the Adaptation Process of Huso dauricus to High Temperatures Based on Changes in Intestinal Microbiota
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.3. Processing of Illumina Sequencing Data
2.4. Statistical Analyses
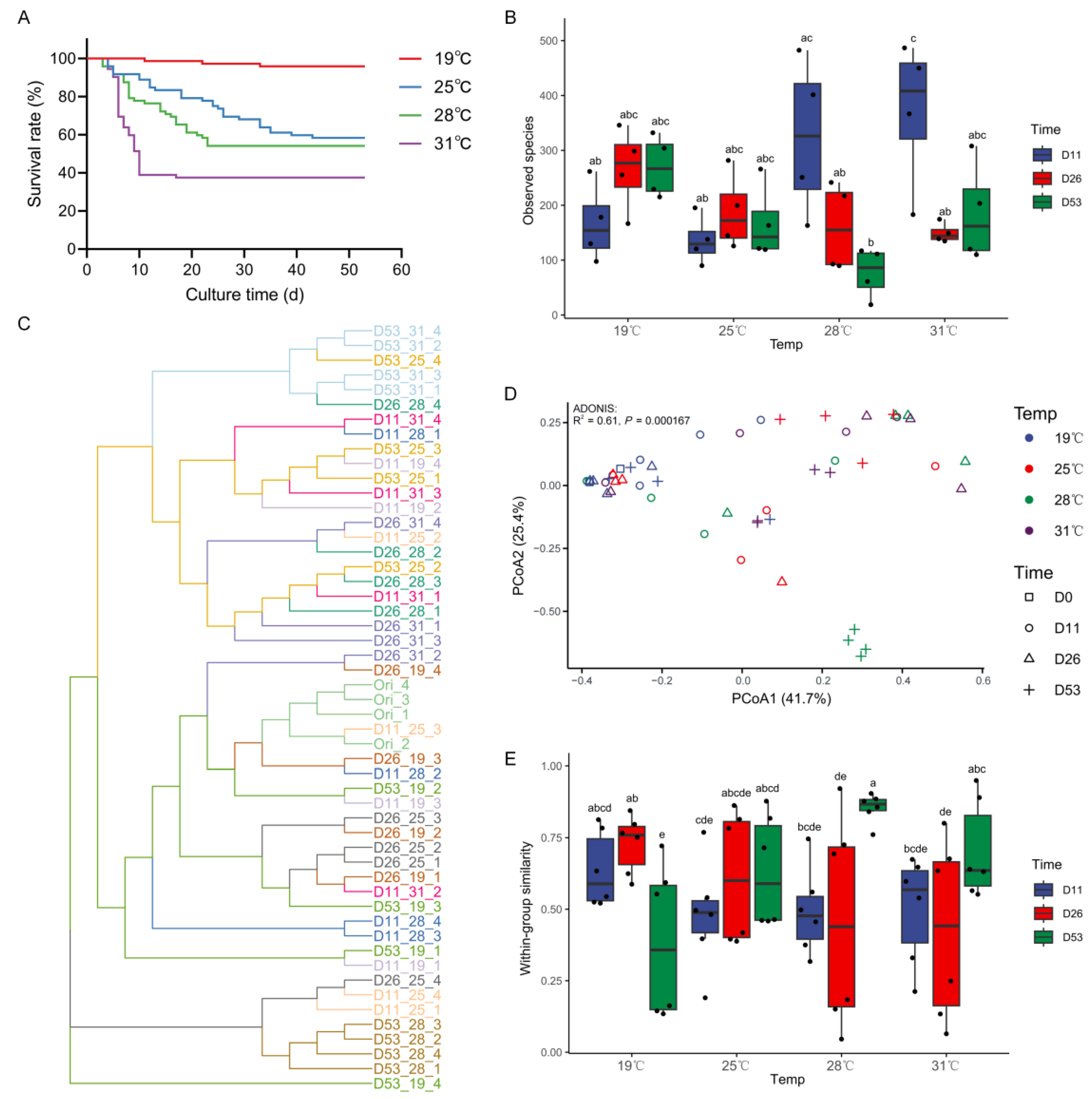
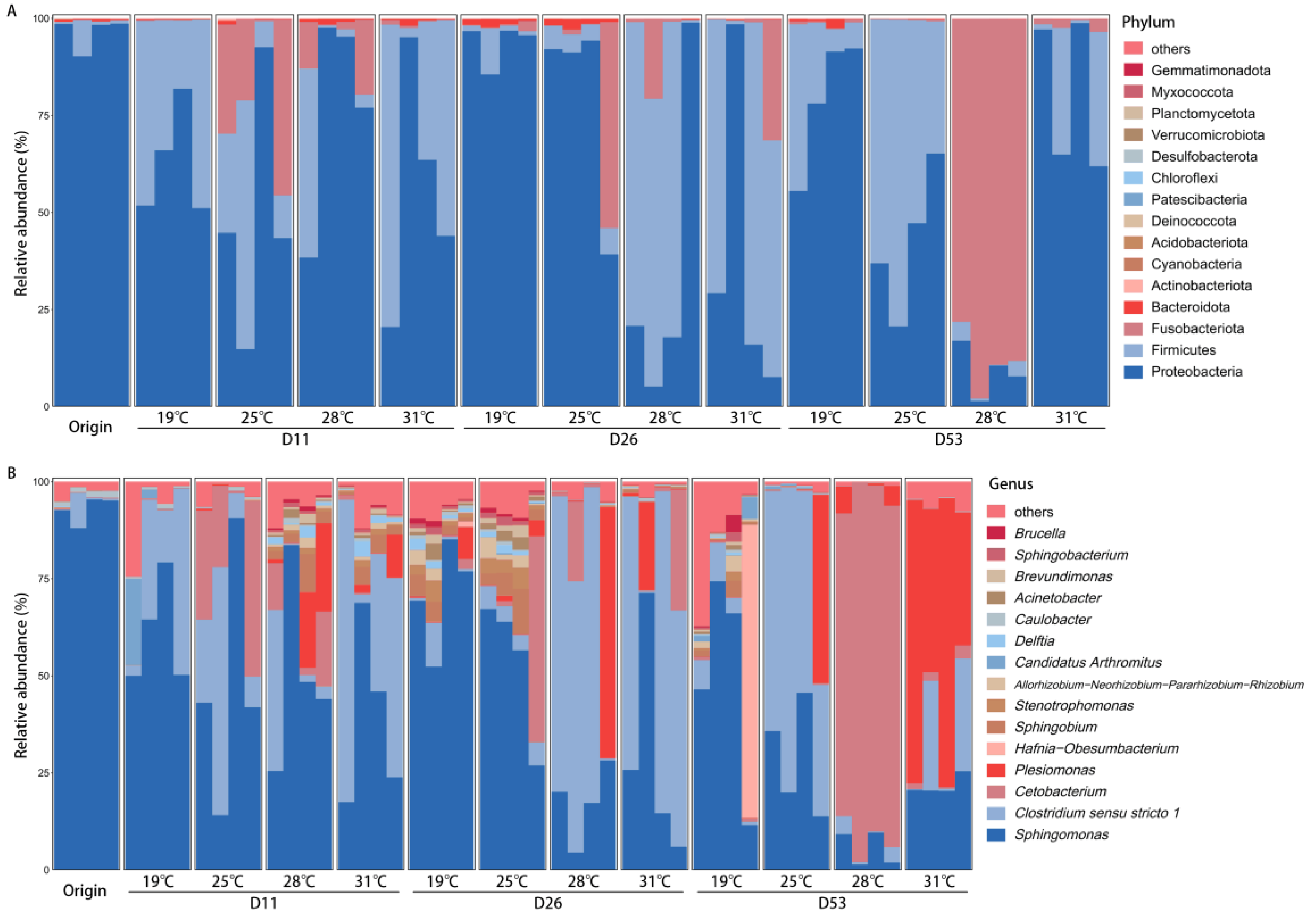
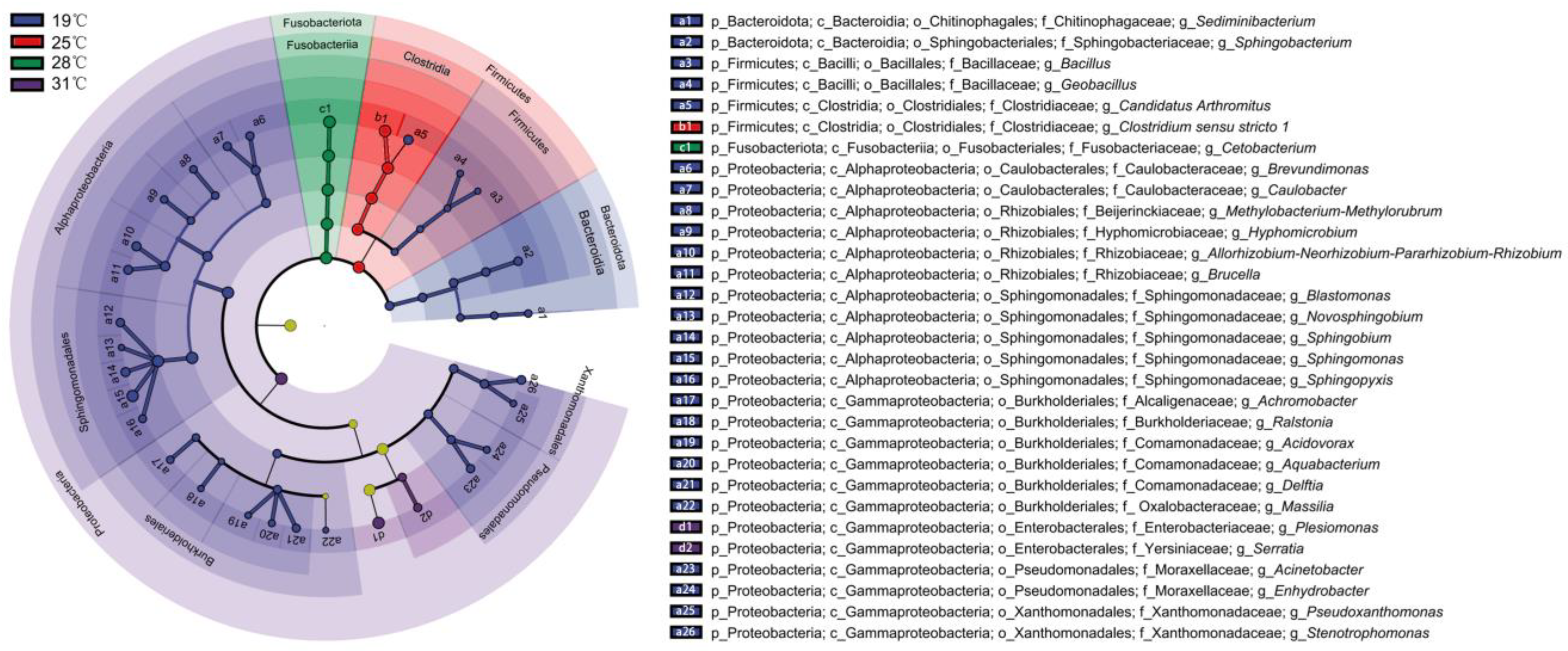
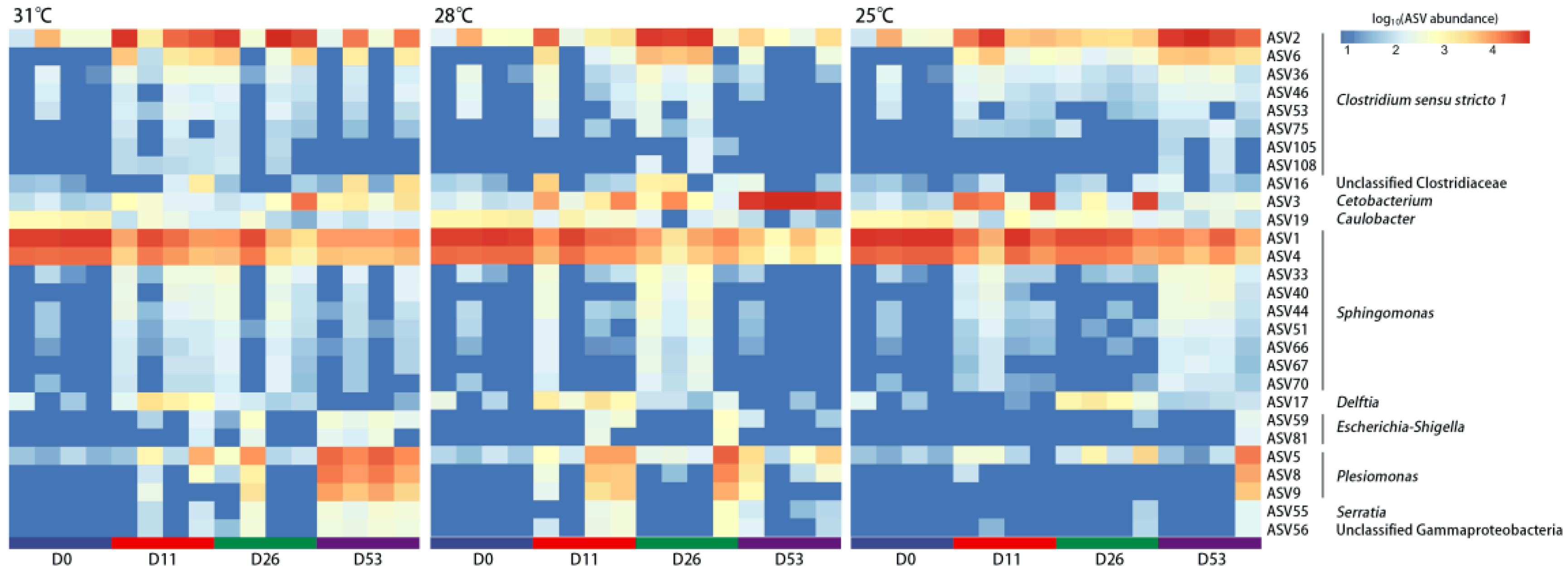
3. Results
3.1. Survival Status Under Different Temperatures
3.2. Diversity of Intestinal Microbiota Under Different Temperatures
3.3. Dominant Bacterial Composition of Intestinal Microbiota Under Different Temperatures
3.4. Differential Bacterial Composition of Intestinal Microbiota Under Different Temperatures
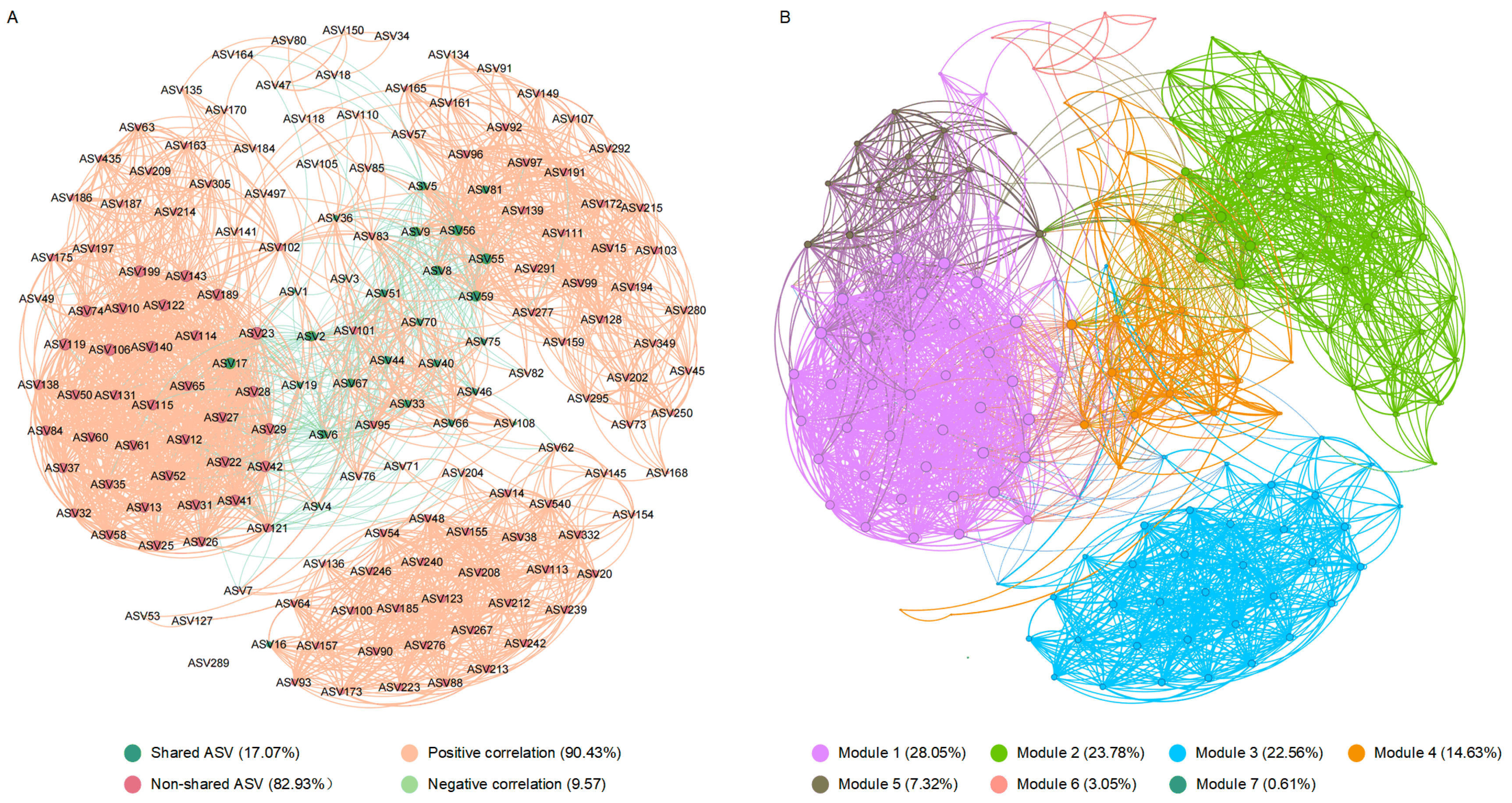
3.5. Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and High-Temperature Adaptability
4. Discussion
4.1. Different Temperatures Shape Intestinal Microbiota with Distinct Characteristics
4.2. Specific Intestinal Bacterial Taxa Are Associated with the Development of High-Temperature Adaptation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfonso, S.; Gesto, M.; Sadoul, B. Temperature increase and its effects on fish stress physiology in the context of global warming. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Lai, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Li, F.; Gong, Q. Integrated biochemical, transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses provide insight into heat stress response in Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 249, 114366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Li, D.; Feng, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Du, Z.; Huang, X. Heat stress decreases intestinal physiological function and facilitates the proliferation of harmful intestinal microbiota in sturgeons. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 755369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Ka, W.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Long, R.; Wang, J. Association of gut microbiota with metabolism in rainbow trout under acute heat stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 846336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Rosa, F.; Rossi, N.; Martin, T.C.; Mohney, R.P.; Li, W.; de Rinaldis, E.; Bell, J.T.; Venter, J.C. Interplay between the human gut microbiome and host metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Clarke, J.L.; Xie, S. The fish microbiota: Research progress and potential applications. Engineering 2023, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K. Recent progress in the understanding of the gut microbiota of marine fishes. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Ren, W.; Zheng, S.; Ren, Y. Histological, immune, and intestine microbiota responses of the intestine of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to high temperature stress. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Park, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, C.Y. Impact of water temperature on oxidative stress and intestinal microbiota in pearl-spot chromis, Chromis notata (Temminck & Schlegel, 1843). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 275, 111029. [Google Scholar]
- Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O.; Bohmann, K.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Do vertebrate gut metagenomes confer rapid ecological adaptation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macke, E.; Tasiemski, A.; Massol, F.; Callens, M.; Decaestecker, E. Life history and eco-evolutionary dynamics in light of the gut microbiota. Oikos 2017, 126, 508–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakisahneh, S.; Zhang, X.; Nouri, Z.; Wang, D. Gut microbiota and host thermoregulation in response to ambient temperature fluctuations. Msystems 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, C.; Villegas-Ríos, D.; Moland, E.; Olsen, E.M. Sea temperature effects on depth use and habitat selection in a marine fish community. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, D. Temperature acclimation alters the thermal tolerance and intestinal heat stress response in a Tibetan fish Oxygymnocypris Stewarti. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 898145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.H.; Ivey, K.; Cornwall, M.B.; Herr, K.; Rede, J.; Taylor, E.N.; Gunderson, A.R. The lizard gut microbiome changes with temperature and is associated with heat tolerance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01181-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the International Aaai Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, G.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Gut microbiota of two invasive fishes respond differently to temperature. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1087777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, J.; Moeller, A.H. The effects of temperature on animal gut microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassenrück, C.; Reinwald, H.; Kunzmann, A.; Tiedemann, I.; Gärdes, A. Effects of thermal stress on the gut microbiome of juvenile milkfish (Chanos chanos). Microorganisms 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Bu, X.; Shen, J.; Tao, Z.; Zeng, T.; Du, X.; Lu, L. High-temperature exposure alters the community structure and functional features of the intestinal microbiota in Shaoxing ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2662–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rui, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, N.; Zhan, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, X. Ambient temperature alters body size and gut microbiota of Xenopus tropicalis. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.; Yan, C.; Zhang, J.; Lai, J.; Yan, T.; He, Z.; Du, X. Resveratrol improves the digestive ability and the intestinal health of Siberian sturgeon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, T.P.; Wynne, J.W.; Weyrich, L.S.; Oxley, A.P. A microbial sea of possibilities: Current knowledge and prospects for an improved understanding of the fish microbiome. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1101–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhong, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, H.; Wang, L. Acute temperature stresses trigger liver transcriptome and microbial community remodeling in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Razak, S.; Bauman, J.M.; Marsh, T.L.; Scribner, K.T. Changes in lake sturgeon gut microbiomes relative to founding origin and in response to chemotherapeutant treatments. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüst, P.K.; Horn, M.A.; Drake, H.L. Clostridiaceae and Enterobacteriaceae as active fermenters in earthworm gut content. Isme J. 2011, 5, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Lv, Y.; Hou, L.; Jia, Z.; Lin, S.; Wang, S.; He, X.; Hou, J. Effect of acute temperature stress on energy metabolism, immune performance and gut microbiome of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Fish. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maiuta, N.; Schwarzentruber, P.; Schenker, M.; Schoelkopf, J. Microbial population dynamics in the faeces of wood-eating loricariid catfishes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kessel, M.A.; Dutilh, B.E.; Neveling, K.; Kwint, M.P.; Veltman, J.A.; Flik, G.; Jetten, M.S.; Klaren, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J. Pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons to study the microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Amb Express 2011, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Olsen, R.E.; Ringø, E.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Stabilized fermentation product of Cetobacterium somerae improves gut and liver health and antiviral immunity of zebrafish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.T.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Zheng, H.; Aweya, J.J.; Wen, X.; Li, S. Progress and perspectives of short-chain fatty acids in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, T.; Alba, C.; Aparicio, M.; de Andrés, J.; Santa Quiteria, J.A.R.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Gibello, A. Abundant bacteria in the proximal and distal intestine of healthy Siberian sturgeons (Acipenser baerii). Aquaculture 2019, 506, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Mu, Z.; Lv, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J. Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Citrobacter freundii isolated from the endangered Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Wang, R.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. Gut bacterial consortium enriched in a biofloc system protects shrimp against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Microbiome 2023, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, A.L.; Zhang, V.; Lamberti, L.; Jones, E.W.; Obadia, B.; Korasidis, N.; Gavryushkin, A.; Carlson, J.M.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Ludington, W.B. Microbiome interactions shape host fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11951–E11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, X.; Wang, Q.; Peng, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z.; Qi, R. Clostridium sporogenes increases fat accumulation in mice by enhancing energy absorption and adipogenesis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e04116-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Al-Masqari, Z.A.; Yan, M.; Wang, G.; Dong, P.; Gao, F.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D. Survival status of Penaeus vannamei is associated with the homeostasis and assembly process of the intestinal bacterial community. Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Verdegem, M.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, S. Co-occurrence patterns in biofloc microbial communities revealed by network analysis and their impact on the host. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthagaray, A.I.; Arim, M.; Marquet, P.A. Inferring species roles in metacommunity structure from species co-occurrence networks. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Sciellour, M.; Zemb, O.; Hochu, I.; Riquet, J.; Gilbert, H.; Giorgi, M.; Billon, Y.; Gourdine, J.; Renaudeau, D. Effect of chronic and acute heat challenges on fecal microbiota composition, production, and thermoregulation traits in growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 3845–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labussière, E.; Achard, C.; Dubois, S.; Combes, S.; Castex, M.; Renaudeau, D. Saccharomyces cerevisiae boulardii CNCM I-1079 supplementation in finishing male pigs helps to cope with heat stress through feeding behaviour and gut microbiota modulation. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Z.; Cao, D.; Sun, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B. Exploring the Adaptation Process of Huso dauricus to High Temperatures Based on Changes in Intestinal Microbiota. Biology 2024, 13, 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121045
Wang R, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang S, He Z, Cao D, Sun Z, Wang N, Zhang Y, Ma B. Exploring the Adaptation Process of Huso dauricus to High Temperatures Based on Changes in Intestinal Microbiota. Biology. 2024; 13(12):1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121045
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruoyu, Yutao Li, Yining Zhang, Sihan Wang, Zheng He, Dingchen Cao, Zhipeng Sun, Nianmin Wang, Ying Zhang, and Bo Ma. 2024. "Exploring the Adaptation Process of Huso dauricus to High Temperatures Based on Changes in Intestinal Microbiota" Biology 13, no. 12: 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121045
APA StyleWang, R., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., He, Z., Cao, D., Sun, Z., Wang, N., Zhang, Y., & Ma, B. (2024). Exploring the Adaptation Process of Huso dauricus to High Temperatures Based on Changes in Intestinal Microbiota. Biology, 13(12), 1045. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121045





