Predicting Climate Change Impact on the Habitat Suitability of the Schistosoma Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Occurrence Data for Oncomelania hupensis
2.2.2. Environmental Data
Environmental Data of Snail Current Distribution
Future Climatic Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Establishment and Evaluation of the Species Distribution Model for O. hupensis
2.3.2. Change in Potential Distribution and Centroids
2.3.3. Regionalization and Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Establishment and Effect of the Model
3.1.1. Filtering of Environment Variables
3.1.2. Evaluation of Models
3.2. The Influence of Environmental Factor
3.3. Current Prediction of O. hupensis Distribution
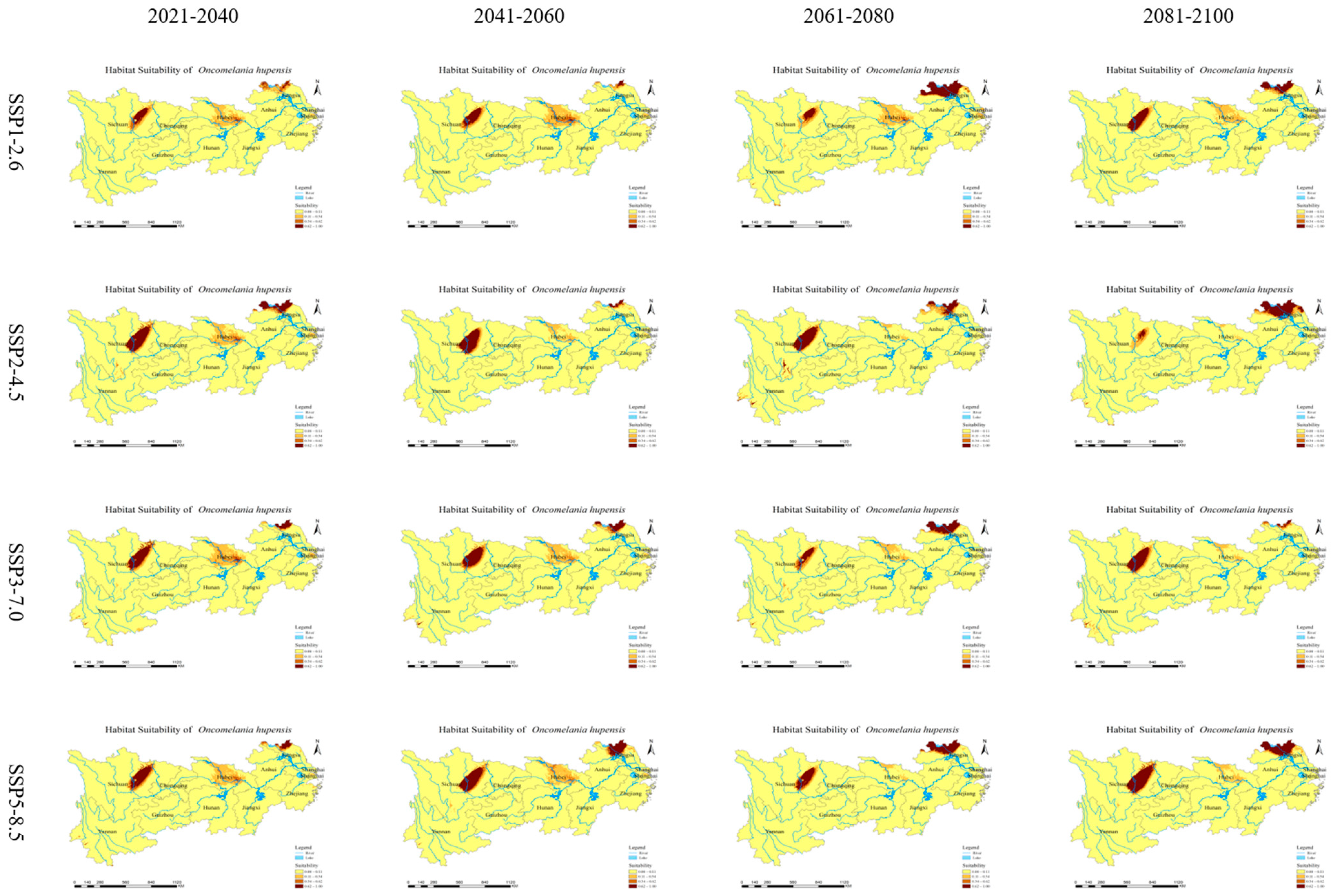
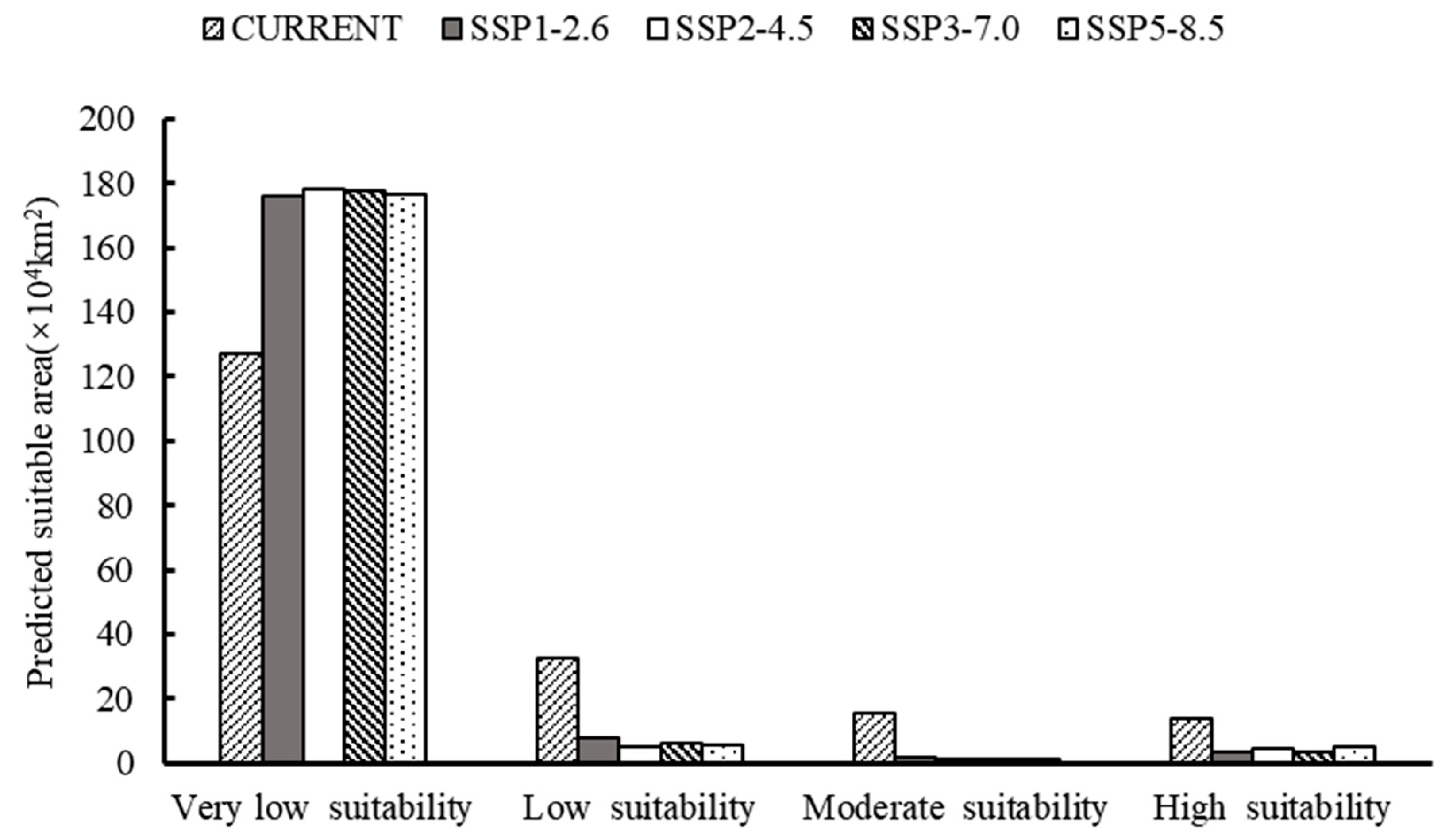
3.4. Future Prediction of O. hupensis Distribution
3.5. Directional Analysis of O. hupensis’ Distribution Centroid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X. Distribution and control of schistosomiasis in China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2007, 12, 3766–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloo, A. Schistosomiasis Elimination: Refocusing on Snail Control to Sustain Progress. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/25-03-2020-schistosomiasis-elimination-refocusing-on-snail-control-to-sustain-progress (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Qin, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, C. Environment factors and spatial characters of distribution of Oncomcelania Snails in islet and beach of Dongting Lake area. J. Nat. Disasters 2008, 4, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.-J.; Zhou, X.-N.; Sun, L.-P.; Wu, F.; Zhong, B.; Qiu, D.-C.; Utzinger, J.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Compensatory density feedback of Oncomelania hupensis populations in two different environmental settings in China. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Lü, S.; Li, S. Progress of the national programme and achievements of scientific researches on schistosomiasis elimination in China. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 2019, 23, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Yang, K. Identifying the determinants of distribution of Oncomelania hupensis based on geographically and temporally weighted regression model along the Yangtze River in China. Pathogens 2022, 11, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Li, C. The measures of the environment construction to kill snails and their effect on controlling Schistosomiasis. Chin. J. Endem. 2002, 21, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Lin, D.-D.; Wu, X.-H.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Q.-Z.; Lv, S.-B.; Yang, G.-J.; Han, Y.-Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Retrospective investigation on national endemic situation of schistosomiasis. III. Changes of endemic situation in endemic rebounded counties after transmission of schistosomiasis under control or interruption. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2011, 23, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Yang, K. Progresses of research on patterns and monitoring approaches of Oncomelania hupensis spread. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2020, 32, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, A.S. Yangtze River Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China. China Water Resour. 2021, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J. Challenges and prospects of Oncomelania snail control via mollusciciding in China in the new era. J. Trop. Dis. Parasitol. 2022, 20, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.M.; Rojas, B.H.; Samset, K.; Cobb, A.; Diongue Niang, P.; Edwards, S.; Emori, S.H.; Faria, E.; Hawkins, P.; Hope, P.; et al. 2021: Framing, Context, and Methods. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 147–286. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H. Impact of air temperature on annual runoff of batang station in the headstream of Yangtze river. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Pang, H.; Hu, H.; Xie, C.; Qiu, L.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hong, Q.; Zhou, X. Prediction of snail habitats in the marshland along the yangtze river affected by flood in 1998 by remote sensing. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2000, 6, 337–339+386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Hong, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, G.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y. Prediction of the Impact of Climate Warming on Transmission of Schistosomiasis in China. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2004, 22, 8–11+67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Impact of Water Level and Climatic Factors on the Distribution of Schistosoma japonicum Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis and the Identification of Snail Habitats in Eastern Dongting Lake Areas. Master’s Thesis, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Chang, A.; Peng, J. Research on the response of the intermediate host—Snail to the meteorological factors in Dongting Lake area. J. Public Health Prev. 2015, 26, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Yi, Z.; Li, S.; Xiao, L. Maxent modeling for predicting the potentially geographical distribution of Miscanthus nudipes under different climate conditions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 8297–8305. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Wei, C.; Liang, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Future climatic adaption of 12 dominant tree species in Northeast China under 3 climatic scenarios by using MaxEnt modeling. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 9712–9725. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Sun, T.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Identification of potential distribution area for Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis by the MaxEnt model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Oso, O.G.; Sunday, J.O.; Odaibo, A.B. Models for predicting bulinids species habitats in southwestern Nigeria. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2022, 18, e00256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaniz, A.J.; Carvajal, M.A.; Quiroz, M.; Vergara, P.M.; Marquet, P.A.; Fierro, A.; Sieving, K.E.; Moreira-Arce, D.; Hidalgo-Corrotea, C.; Rodríguez-San Pedro, A. Unravelling the cavity-nesting network at large spatial scales: The biogeographic role of woodpeckers as ecosystem engineers. J. Biogeogr. 2024, 51, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosso, L.; Panzuto, R.; Balestrieri, R.; Smeraldo, S.; Chiusano, M.L.; Raffini, F.; Canestrelli, D.; Musco, L.; Gili, C. Integrating citizen science and spatial ecology to inform management and conservation of the Italian seahorses. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Tao, B.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, Q. Spatial pattern of schistosomiasis in Xingzi, Jiangxi Province, China: The effects of environmental factors. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-B.; Liang, S.; Chen, G.-X.; Rea, C.; Han, S.-M.; He, Z.-G.; Li, Y.-P.; Wei, J.-G.; Zhao, G.-M.; Jiang, Q.-W. Spatial-temporal variations of Schistosoma japonicum distribution after an integrated national control strategy: A cohort in a marshland area of China. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Huang, X.-B.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shan, X.-w.; Zhang, J.; Cai, S.-X.; Liu, J.-B. Spatial Analysis of Schistosomiasis in Hubei Province, China: A GIS-Based Analysis of Schistosomiasis from 2009 to 2013. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Cai, S.-X.; Liu, J.-B.; Tu, Z.-W.; Xia, J.; Shan, X.-W.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, L.; et al. A spatial analysis of human Schistosoma japonicum infections in Hubei, China, during 2009–2014. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, S. Schistosomiasis transmission and control in China. Acta Trop. 2015, 143, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, J. Spatio-temporal variations of land vegetation gross primary production in the Yangtze River Basin and correlation with meteorological factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 6949–6959. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Gao, X.; Luo, Y. Projected changes in temperature and precipitation extremes over the Yangtze River Basin of China in the 21st century. Quat. Int. 2009, 208, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G. Study on the conservation of aquatic biodiversity in Yangtze River. Resour. Econ. Environ. 2023, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Sun, Y.; Yin, S.; Wei, X.; Ou, Y. Spatial-temporal variations of vegetation coverage and its driving factors in the Yangtze River Basin from 2000 to 2019. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 798–811. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Zuo, L.; Yang, W.; Li, C. Generating pseudo-absence samples of invasive species based on the similarity of geographical environment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Biodivers. Sci. 2023, 31, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cao, W.; Yang, X. Spatial-temporal Dynamics and Influencing Factors of Ecological Security in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: Based on Three-dimensional Ecological Footprint Expansion Model. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2023, 46, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Tong, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, N.; Yin, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; et al. Three Gorges Dam: The changing trend of snail density in the Yangtze River basin between 1990 and 2019. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Sun, F.; Ao, X.; Geng, S.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Evaluation and projection of temperature and precipitation change in the Liaohe River Basin based on BCC-CSM2-MR model CMIP6 test. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2022, 38, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L. Biases and improvements in three dynamical downscaling climate simulations over China. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Dai, Y.; Hu, G. Climate Sensitivity and Feedbacks of BCC-CSM to Idealized CO2 Forcing from CMIP5 to CMIP6. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Phillips, S.J.; Hastie, T.; Dudík, M.; Chee, Y.E.; Yates, C.J. A statistical explanation of MaxEnt for ecologists. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, B.W.; Robertson, M.P.; Erasmus, B.F.; Van Rensburg, B.J.; Thuiller, W. Ensemble models predict Important Bird Areas in southern Africa will become less effective for conserving endemic birds under climate change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.-A.; Haines-Young, R.; Watkins, C. Species presence in fragmented landscapes: Modelling of species requirements at the national level. Biol. Conserv. 2002, 108, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Study on the Movement of Population and Economic Gravity Center in Chongqing from 1999 to 2010. J. Chongqing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 29, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, P.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X. An evaluation of four threshold selection methods in species occurrence modelling with random forest: Case studies with Davidia involucrata and Cunninghamia lanceolata. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Ding, L.; Yuan, L.; Xia, M.; Tang, L.; Ren, G.; Wang, J.; Wei, G. Impact of environmental changes on Oncomelania snail distribution in Dongting Lake beach. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2012, 24, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, L.; Liang, J.; Ang, Y.; Yang, D.; Cai, B.; et al. Relationship between natural extinction of Oncomelania hupensis snails and water chemical properties in Eastern Dongting Lake areas. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2019, 31, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.-N.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.-H.; Yao, Z.-Q.; Wang, T.-P.; Yang, G.-J.; Yang, Y.-J.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Wang, J. Strategy formulation for schistosomiasis japonica control in different environmental settings supported by spatial analysis: A case study from China. Geospat. Health 2007, 1, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M. Distribution characteristics of snails in Wuhan and its relationship with elevation. J. Public Health Prev. 2018, 29, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.R.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.N.; Yang, G.J. Ecological Model to Predict Potential Habitats of Oncomelania hupensis, the Intermediate Host of Schistosoma japonicum in the Mountainous Regions, China. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, D.; Zhuang, D.; Wang, Y. The influence of natural factors on the spatio-temporal distribution of Oncomelania hupensis. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wei, F.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, W. Impact of Future Climate Change on Potential Distribution of Oncomelania in Hubei Province. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 13, 606–613. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C. Biology of Schistosome and Control of Schistosomiasis; People’s Health Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Medical Malacology; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993; 157p. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Xiao, J. Relative importance of meteorological and geographical factors in the distribution of Fasciola hepatica infestation in farmed sheep in Qinghai province, China. Parasite 2016, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, P.; Claxton, J. Epidemiology and control. Fasciolosis 1999, 113, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Studies of Water, Heat and CO2, Fluxes over a Beach Snail Control and Schistosomiasis Prevention Forests in Yueyang City, Hunan Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cordellier, M.; Pfenninger, M. Inferring the past to predict the future: Climate modelling predictions and phylogeography for the freshwater gastropod Radix balthica (Pulmonata, Basommatophora). Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; He, Q.; Pan, X.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Predicting current potential distribution and the range dynamics of Pomacea canaliculata in China under global climate change. Biology 2022, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zou, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Distribution change and protected area planning of Tilia amurensis in China: A study of integrating the climate change and present habitat landscape pattern. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 43, e02438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Tibatá, J.; Salaman, P.; Graham, C.H. Effects of climate change on species distribution, community structure, and conservation of birds in protected areas in Colombia. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Dai, J.; Ye, J.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, B.; Liao, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J. Field observations on the survival and multiplication of Oncomelania snails in the different latitude regions in China. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 1996, 8, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Sun, L.; Hong, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, R.; Hua, Z. Potential impact of global warming on schistosomiasis transmission. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 78, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Q.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, G.; Yang, K.; Huang, Y. Impact of Global Warming on Transmission of Schistosomiasis in China Ⅳ Accumulated Temperature for Development of Generations of Oncomelania hupensis in Natural Environment. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2003, 4, 269–271. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, E.Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-G.; Hubbard, A.; Holt, A.; Davis, G.M. Impact of changing water levels and weather on Oncomelania hupensis populations, the snail host of Schistosoma japonicum, downstream of the Three Gorges Dam. Ecohealth 2008, 5, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z. Response of Holocene flood to southwest monsoon change in upper reaches of Yangtze River. Geogr. Res. 2009, 28, 592–600. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, R.; Luo, S.; Chen, L. The relationship between monsoon circulation in midsummer and precipitation in China. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1982, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Cen, S.; Lai, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, S. Prediction of Rainstorm in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on CMIP6 Multi-Model Ensemble. Plateau Meteorol. 2024, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, T.; Chang, Y.; Yin, Z. Trend Analysis of Future Temperature and Precipitation in Shule River Basin based on BCC-CSM2-MR Model. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 535–546. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Quan, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Su, T.; Yan, P. Evaluation of the ability of BCC-CSM2-MR global climate model in simulating precipitation and temperature in East Asia. J. Arid Meteorol. 2023, 41, 984–996. [Google Scholar]
- Di Febbraro, M.; Bosso, L.; Fasola, M.; Santicchia, F.; Aloise, G.; Lioy, S.; Tricarico, E.; Ruggieri, L.; Bovero, S.; Mori, E. Different facets of the same niche: Integrating citizen science and scientific survey data to predict biological invasion risk under multiple global change drivers. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 5509–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Peng, H.; Xiao, S. Evaluation of precipitation in CMIP6 over the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Sturrock, R.F.; Kariuki, H.C.; Hamburger, J. Transmission control for schistosomiasis—Why it matters now. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

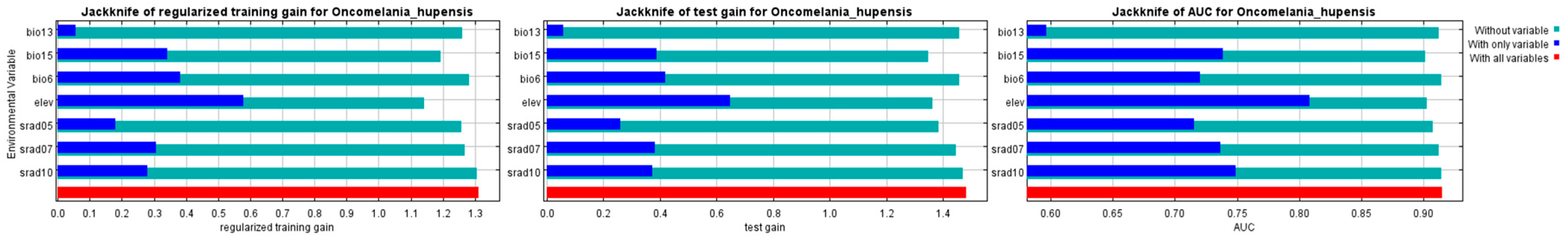




| Code | Environmental Variable | Percent Contribution | Permutation Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| elev | Elevation | 40.1 | 46.8 |
| bio6 | Min. Temperature of Coldest Month | 18.1 | 13.3 |
| bio13 | Precipitation of Wettest Month | 11.9 | 6.5 |
| srad07 | Solar radiation in July | 11.3 | 17.9 |
| srad05 | Solar radiation in May | 8.7 | 7.9 |
| bio15 | Precipitation Seasonality | 8.0 | 6.3 |
| srad10 | Solar radiation in October | 1.9 | 1.4 |
| Accuracy Measure | Result |
|---|---|
| AUC | 0.915 |
| TSS | 0.688 |
| Overall Accuracy | 0.898 |
| Sensitivity | 0.790 |
| Specificity | 0.898 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, R.; Rebi, A.; Shi, Z.; Mao, A.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, J. Predicting Climate Change Impact on the Habitat Suitability of the Schistosoma Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Biology 2024, 13, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070480
Li Y, Guo M, Jiang J, Dai R, Rebi A, Shi Z, Mao A, Zheng J, Zhou J. Predicting Climate Change Impact on the Habitat Suitability of the Schistosoma Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Biology. 2024; 13(7):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yimiao, Mingjia Guo, Jie Jiang, Renlong Dai, Ansa Rebi, Zixuan Shi, Aoping Mao, Jingming Zheng, and Jinxing Zhou. 2024. "Predicting Climate Change Impact on the Habitat Suitability of the Schistosoma Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China" Biology 13, no. 7: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070480
APA StyleLi, Y., Guo, M., Jiang, J., Dai, R., Rebi, A., Shi, Z., Mao, A., Zheng, J., & Zhou, J. (2024). Predicting Climate Change Impact on the Habitat Suitability of the Schistosoma Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Biology, 13(7), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070480






