Improvement Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil of Alpine Sandy Land
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activity Measurement
2.4. 16S rDNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Particle Composition in the Surface Layer of Differentlt Afforested Areas
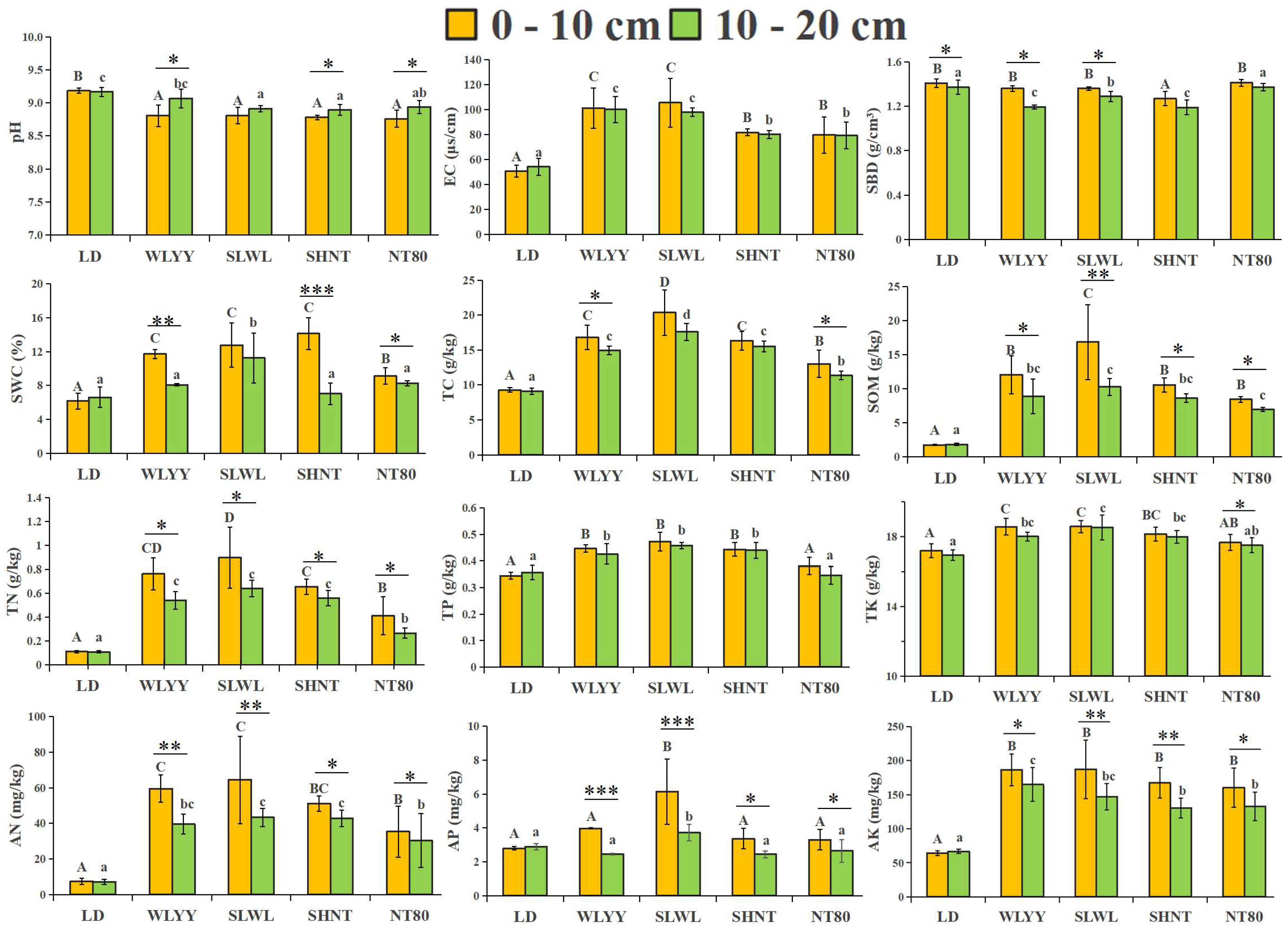
3.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Surface Layer of Differently Afforested Areas
3.3. Enzyme Activity in Surface Soils of Different Afforestation Measures
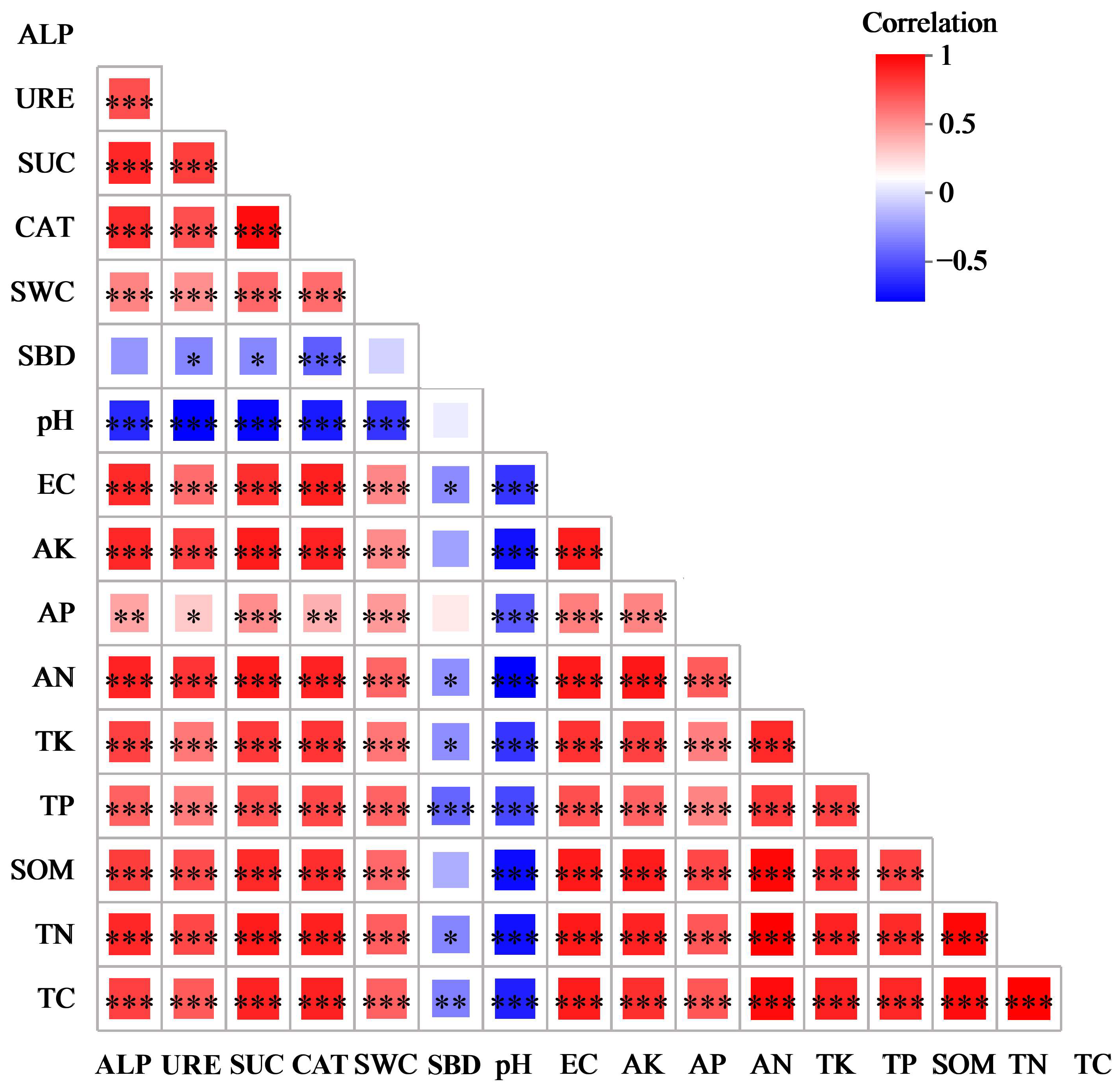
3.4. Correlation Between Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activity
3.5. Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Different Afforestation Measures
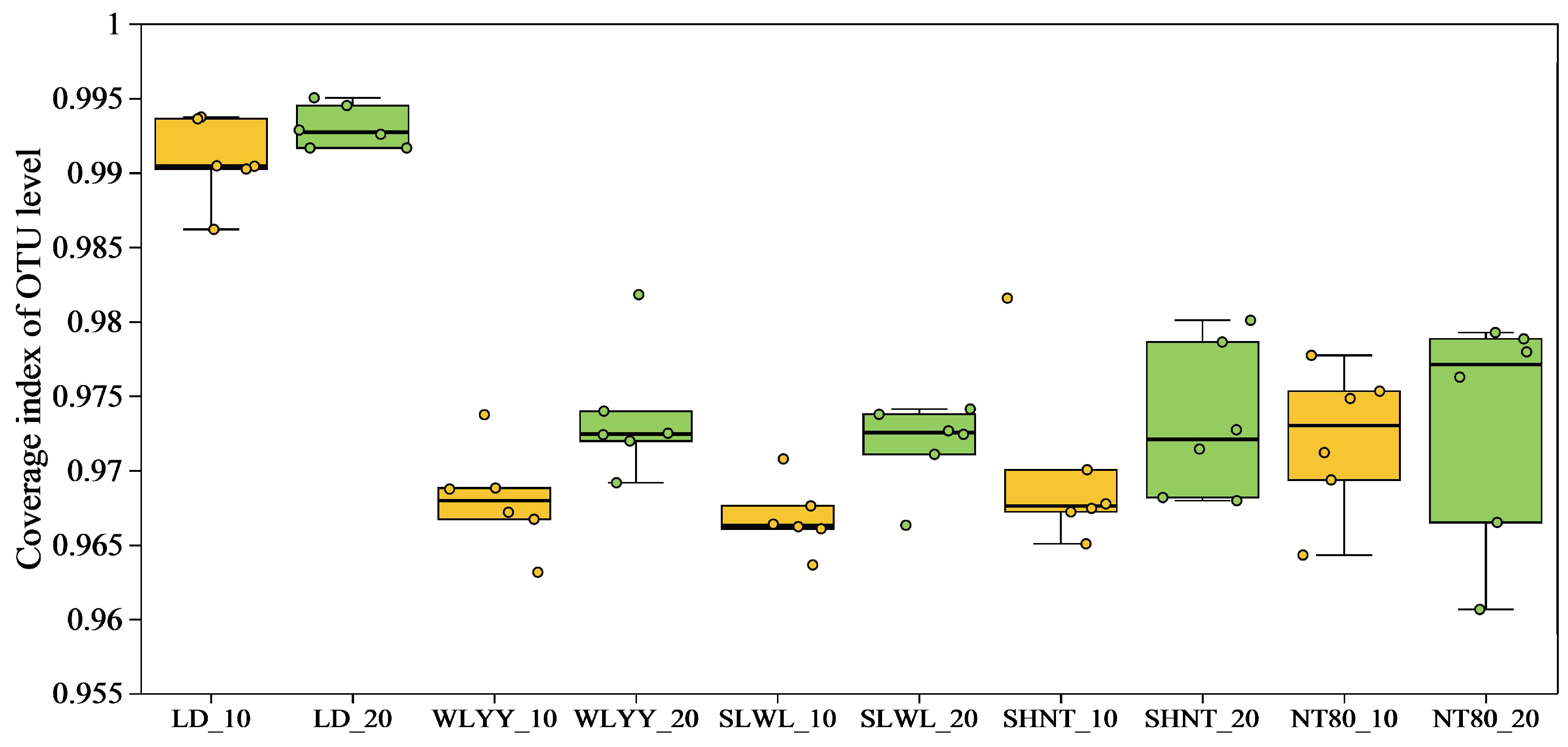
3.5.1. OTUs Statistical Analysis
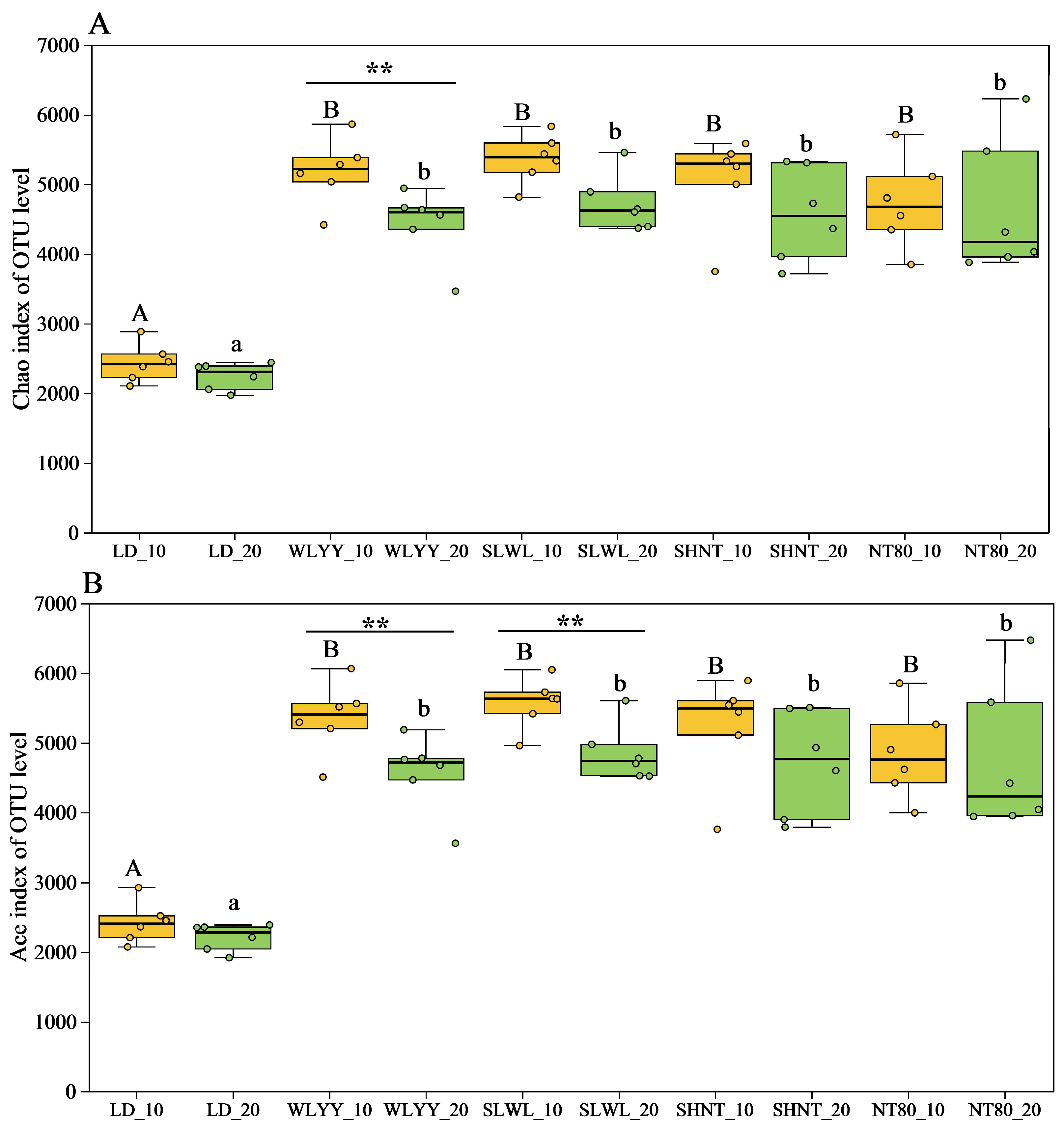
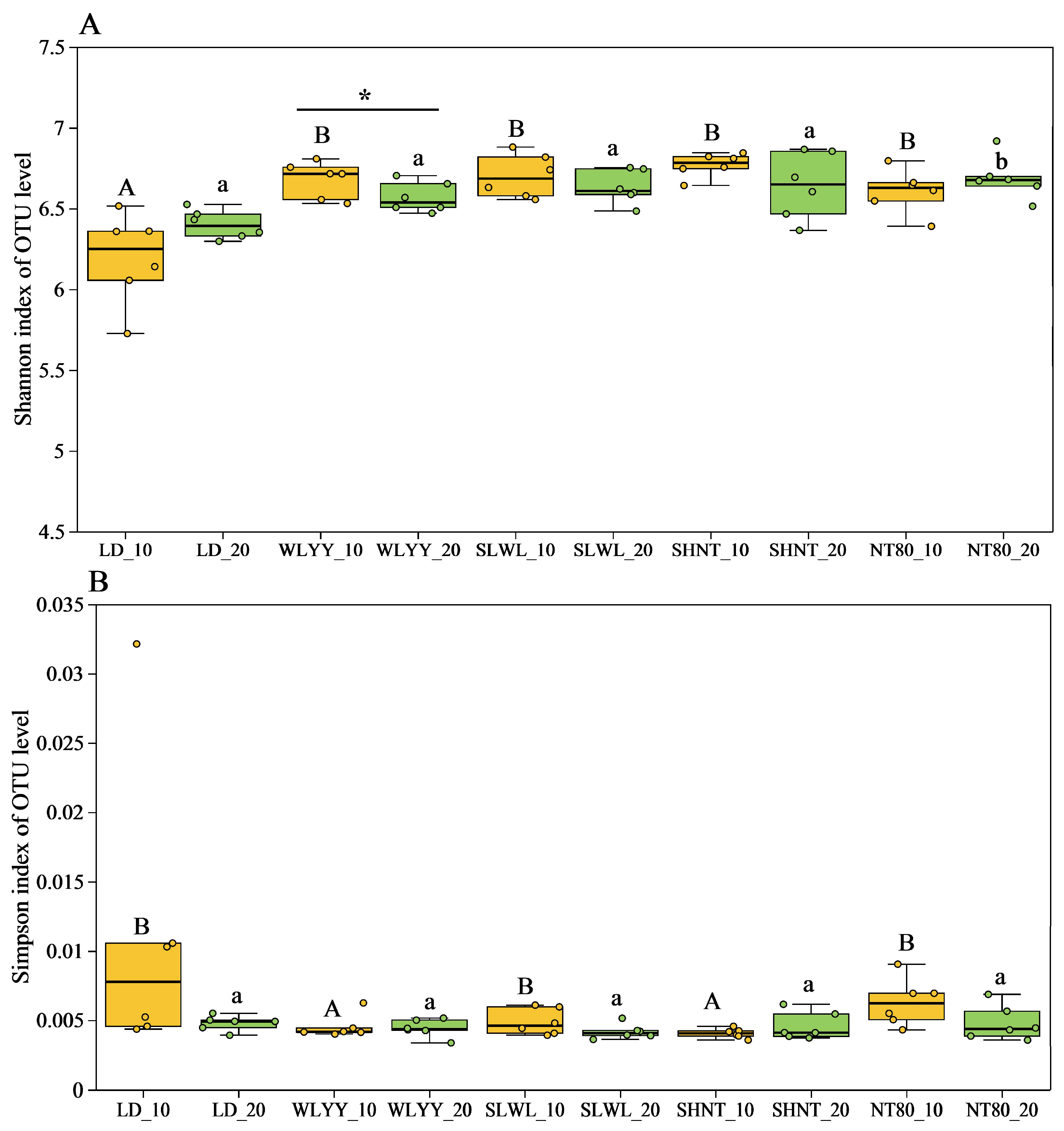
3.5.2. Soil Bacterial Alpha Diversity
3.5.3. Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities
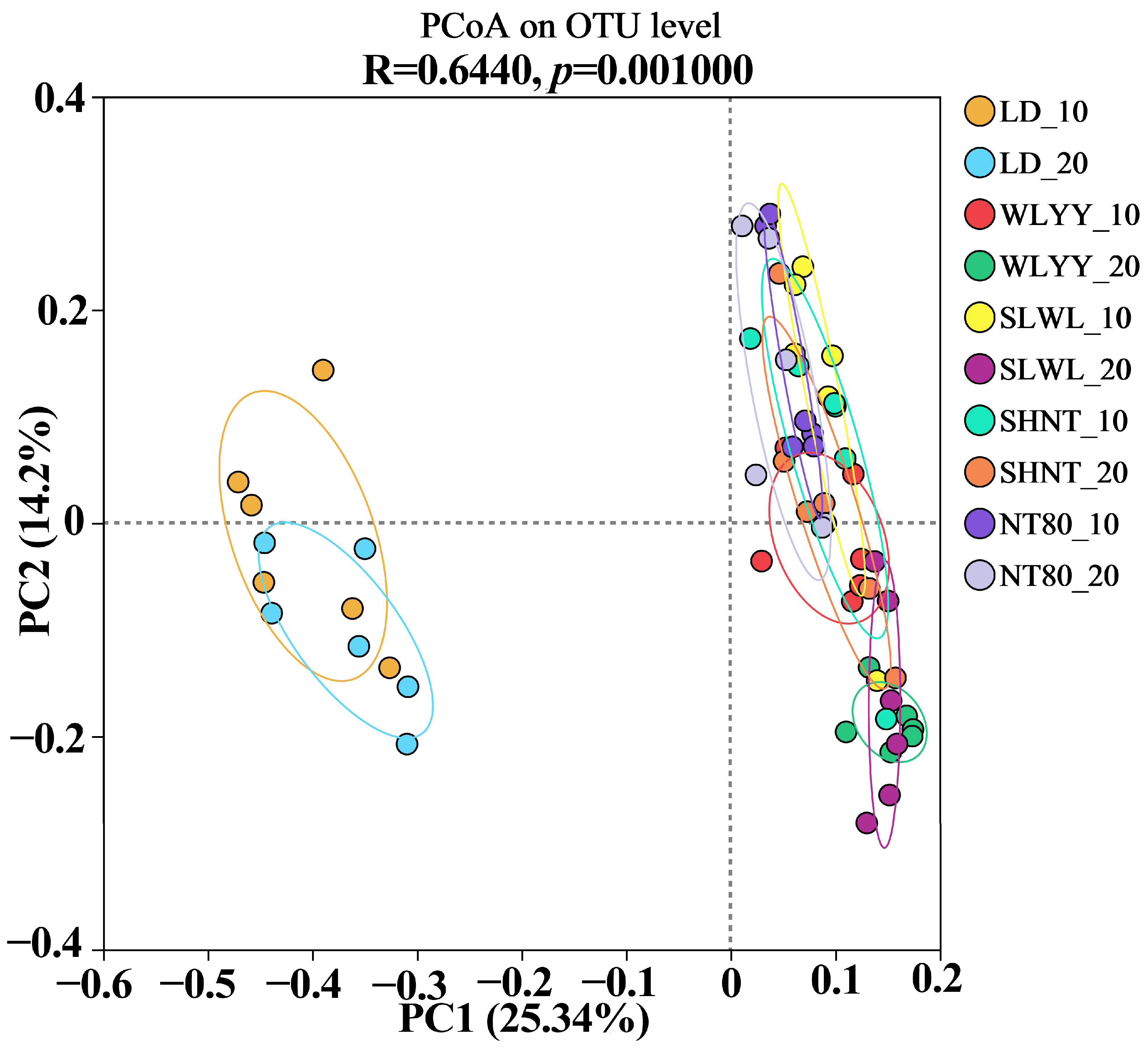
3.5.4. Soil Bacterial Community PCoA Analysis
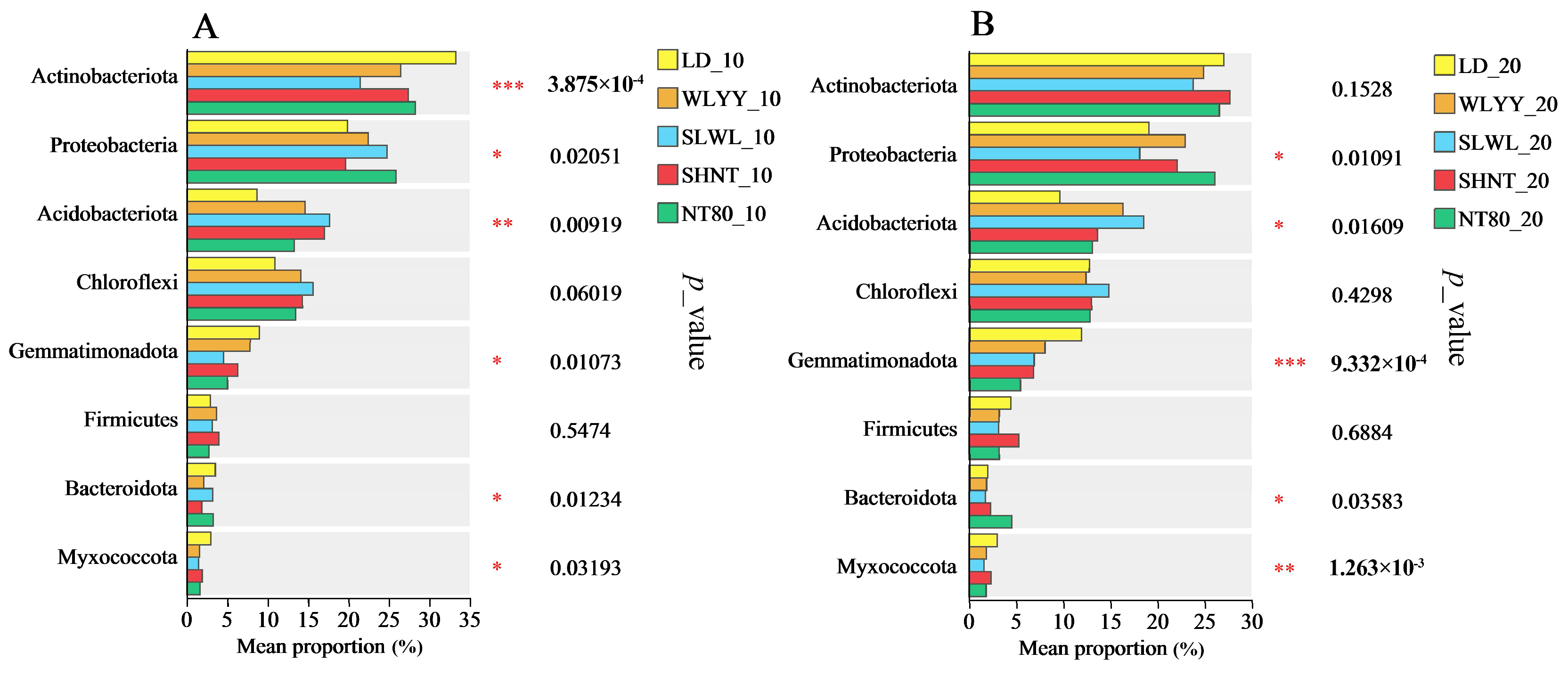
3.5.5. Soil Bacterial Phylum Group Differences
3.6. Correlation Between Soil Physicochemical Properties, Enzyme Activity, and Bacterial Community Structure
3.6.1. Correlation Between Soil Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Community Structure
3.6.2. Correlation Between Soil Enzyme Activity and Bacterial Community Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil Particle Composition
4.2. Impact of Different Afforestation Measures on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activity
4.3. Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil Bacterial Community Structure
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Z. Status and trend of desertification in Northern China. J. Desert Res. 1985, 3, 4–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Zeng, F.; Mao, D.; Jin, Q.; Liu, Y. Oasification: An unable evasive process in fighting against desertification for the sustainable development of arid and semiarid regions of China. Catena 2019, 179, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, R.; Yin, S.; Bao, Y.; Bao, H. Change of Desertification based on MODIS Data in the Mongolia Border Region. In 7th Annu. Meet. Risk Anal. Counc. China Assoc. Disaster Prev. 2016, 128, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Liu, K.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L. Global desert expansion during the 21st century: Patterns, predictors and signals. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, Y. Gully incision as a key factor in desertification in an arid environment, the Negev highlands, Israel. Catena 2005, 63, 185–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bora, S.; Thrall, P.H.; Richardson, A.E. Soil C and N as causal factors of spatial variation in extracellular enzyme activity across grassland-woodland ecotones. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, W.H.; Richardson, C.J.; Vilgalys, R.; Bruland, G.L. Environmental and anthropogenic controls over bacterial communities in wetland soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17842–17847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Z.; Zhao, H.F. Soil properties and plant species in an age sequence of Caragana microphylla plantations in the Horqin Sandy Land, north China. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Meng, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Effects of Different Ages of Salix psammophila forest on soil enzyme activity in Hobq Desert. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xue, X.; Peng, F.; You, Q.; Pan, J.; Li, C.; Lai, C. Effect of human intervention on soil microbial community in desertification grassland of the Yellow River Source Region. Pratacultural Sci. 2019, 36, 970–979. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, N.; Qian, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Effects of different ecological restoration pattern on soil organic nitrogen components in alpine sandy land. Agronomy 2024, 14, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guan, J.; Deng, L. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil moisture changes in sandy vegetation in alpine and semiarid areas. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 5554–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Z.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X. The allocation and cycling characteristics of main nutrients for Caragana intermedia with different stand age on alpine sandy land. For. Res. 2023, 36, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, C.; Song, X.; Xie, J.; Duan, H. Remote sensing investigation of aeolian desertification in Longyangxia Reservoir Region in recent 30 years. J. Desert Res. 2011, 31, 836–841. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Bao, Y.; Yin, S. Influence of soil heterogeneity based on vegetation recovery in alpine sandy land. For. Res. 2016, 29, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y. Effects of artificial sand-fixation vegetation restoration on soil microbial population in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai province. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Comprehensive evaluation and model screening of sand barriers in Gahan Sand District, Qinghai. Qinghai University, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Tatsuno, Y.; Miyasaka, K.; Sasaki, T. Can complementarity in water use help explain diversity-productivity relationships in semi-arid grasslands? J. Arid Environ. 2020, 173, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Zhang, R.; Yang, S. Pedogenic carbonate and soil dehydrogenase activity in response to soil organic matter in Artemisia ordosica community. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Nie, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, E. Correlation between FDA enzyme activity and soil fertility under combining application organic and nitrogen fertilizer in facility vegetable field. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2016, 43, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liang, D.; Liu, J.; Lei, L.; Yu, D. Transformation of heavy metal fractions on soil urease and nitrate reductase activities in copper and selenium co-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mei, W.; Chen, X.; Fang, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, W. Determination of water-soluble sugar in rice by 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Ma, R.; Ma, Y.; Liu, T.; Tian, Y.; Dong, A.; Chai, D. Effects of compound sand control measures on soil bacterial community structure and function. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 33, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.C.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P. Fractal features of soil particle-size distribution and total soil nitrogen distribution in a typical watershed in the source area of the middle Dan River, China. Catena 2013, 101, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, E.; de Vente, J.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Boix-Fayos, C. Exploring particle size distribution and organic carbon pools mobilized by different erosion processes at the catchment scale. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y. Changes of species diversity and productivity in relation to soil properties in sandy grassland in Horqin sand land. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Long-term ecosystem effects of sand-binding vegetation in the Tengger desert, Northern China. Restor. Ecol. 2010, 12, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y. Fractal characteristics of soil retention curve and particle size distribution with different vegetation types in mountain areas of Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15379–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gong, X.; Fang, L.; Jiang, D.; Ala, M.; Bucci, S.; Scholz, F.; Goldstein, G.; Hao, G. Switching of dominant positions between two sand-fixing shrub species during the dune revegetation process is underlain by their contrasting xylem hydraulics and water-use strategies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulaiti, A.; Kimura, R.; Kodama, Y. Effect of flexible and rigid roughness elements on aeolian sand transport. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2017, 31, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kome, G.K.; Enang, R.K.; Tabi, F.O.; Yerima, B.P.K. Influence of clay minerals on some soil fertility attributes: A review. Open J. Soil Sci. 2019, 9, 155–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehlmann, J. Soil particle density as affected by soil texture and soil organic matter:1. Partitioning of SOM in conceptional fractions and derivation of a variable SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Meng, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. The effects of different mixed forest configuration models on the granularity characteristics of the soil and soil of the Kubuqi desert and soil. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 101–109+120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Jiang, D.; Quan, G.; Geng, L.; Cui, Z.; Luo, Y. Soil physical and chemical characters changes of Caragana microphylla plantation for sand fixation in Keerqin sandy land. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 6, 108–111+131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation–soil relationships following vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Plant Soil 2009, 318, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, X.; Yao, D.; Zhang, H.; Yao, K. Effects of fruit tree hole storage bricks on soil improvement and greenhouse pomegranate growth in sandy land of southern Xinjiang. Soils 2024, 56, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siran, M.; Makovnikova, J. Monitoring of soil bulk density in context with its small-scale spatial heterogeneity. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2021, 9, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischetti, G.B.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Epis, T.; Morlotti, E. Root cohesion of forest species in the Italian Alps. Plant Soil 2009, 324, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Ma, R.; Ma, Y.; Niu, D.; He, C.; Tang, W. Effects of the different measures of sandification combatting on the diversity and physicochemical properties of soil bacterial communities. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2023, 31, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.Z. Effects of Haloxylon ammodendron planting on soil physico-chemical properties and soil microorganisms in sandy dunes. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2015, 24, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J. Change of soil properties and related fractal features during forestation and sand fixation by straw checkerboard: A case study in southeast edge of Tengger desert. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 58–65+165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.H.; Liu, X.; Jin, B.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Tian, X.L.; Zhao, X.C. Effects of litter on soil organic carbon fixation in Reaumuria soongorica communities in the Sangong River basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 5339–5347. [Google Scholar]
- Amoo, A.E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Babalola, O.O. Forest plantations reduce soil functioning in terrestrial ecosystems from South Africa. Pedobiologia 2021, 89, 150757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.W.; Peng, C.H.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y.; Xi, T.; Zhang, T. A global meta-analysis of changes in soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur, and stoichiometric shifts after forestation. Plant Soil 2016, 407, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, W.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, W.; He, R.; Yan, B. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization on the growth and physiology of container seedlings of Quercus gilva. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2024, 12, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Awada, T.; Zhou, X.; Shang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Feng, J. Mongolian pine plantations enhance soil physico-chemical properties and carbon and nitrogen capacities in semi-arid degraded sandy land in China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Wu, X.; Duan, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, B. Different life-form plants exert different rhizosphere effects on phosphorus biogeochemistry in subtropical mountainous soils with low and high phosphorus content. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Man, X. Effects of understory vegetation on soil phosphorus morphological and availability in Larix gmelinii forest in the cold temperate zone. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 339–350+363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Run, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G. Effects of inorganic and organic amendment on soil chemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial community and soil quality in yellow clayey soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tian, D.; Zhou, L.; Su, H.; Ma, S.; Feng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ji, C.; Fang, J. Effects of afforestation on soil microbial diversity and enzyme activity: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2022, 423, 115961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.Y.; Ji, C. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, X.; Gao, H.; Lv, R.; Zhang, W. Changes of soil enzyme activities in Mu Us sandy land with aerial seeding afforestation. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 21, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, P.; Xu, C. The influence of the burning soil in the high cold mountainous area on the nutrient content and enzyme activity and the gray association analysis. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1997, 1, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Grinyer, J.; Reich, P.B.; Singh, B.K. Relative importance of soil properties and microbial community for soil functionality: Insights from a microbial swap experiment. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.D.; Joshi, P.K.; Narjary, B.; Sheoran, P.; Jat, H.S.; Chinchmalatpure, A.R.; Yadav, R.K.; Sharma, D.K. Effects of municipal solid waste compost, rice-straw compost and mineral fertilisers on biological and chemical properties of a saline soil and yields in a mustard-pearl millet cropping system. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panke-Buisse, K.; Poole, A.C.; Goodrich, J.; Ley, R.E.; Kao-Kniffin, J. Selection on soil microbiomes reveals reproducible impacts on plant function. ISME J. 2015, 9, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M. Introduction to soil microbiology. Soil Sci. 1977, 125, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Leff, J.W.; Adams, B.J.; Nielsen, U.N.; Bates, S.T.; Lauber, C.; Owens, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Wall, D.H.; Caporaso, J.G. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21390–21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, G.; Rao, L.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y. Afforestation with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica remodelled soil bacterial community and potential metabolic function in the Horqin Desert. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 29, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.J.; Niiu, Z.; Liu, T.N.; Su, Y. Succession of soil bacterial community along a 46-year choronsequence artificial revegetation in an arid oasis-desert ecotone. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, G.; Liu, M.; Gao, G.; Yu, M.; Li, X. Influence of different vegetation types on soil microbial characteristics of typical forest land in Yulin sandy area. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 53, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Ding, Z.; Mao, T.; Zhu, B. Changes in soil total, microbial and enzymatic C-N-P contents and stoichiometry with depth and latitude in forest ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, G. Soil bacterial community composition and diversity response to land conversion is depth-dependent. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, P.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y. Soil bacterial networks in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations of the Hulunbuir Desert. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 40, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Fan, X.; Ren, C.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Doughty, R. Changes of the organic carbon content and stability of soil aggregates affected by soil bacterial community after afforestation. Catena 2018, 171, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, F.; Lin, Y.; Tang, D. Effects of different fertilization rates on yield of Mesona chinensis Benth and soil bacterial diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 40, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W. Research status and prospect of curved viridis. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2020, 60, 1801–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, J. Medium and long term effects of sulfadiazine on soil microorganisms in paddy field. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Bu, L.; Chen, W.; An, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Wang, H. Effects of plantation restoration on chemical properties and bacterial community in soil profiles in Mu Us sandy land. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Song, D.L.; Liang, G.Q.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Maize biochar addition rate influences soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition in a fluvo-aquic soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantidis, G.; Effosse, A.; Potier, P.; Bally, R. Purification and characterization of the first bacterial laccase in the rhizospheric bacterium Azospirillum lipoferum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Plot | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude (m) | Area (m2) | Vegetation Coverage | Plant Spacing | Soil Depth (cm) | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD | 100°14′28.266″ E | 36°13′50.785″ N | 2822 | 273,333 | - | - | 0~10 | LD_10 |
| 10~20 | LD_20 | |||||||
| WLYY | 100°15′19.0″ E | 36°15′20.1″ N | 2829 | 2500 | 82% | 1.5 m × 1.5 m | 0~10 | NL_10 |
| 10~20 | NL_20 | |||||||
| SLWL | 100°14′16.9″ E | 36°14′5.43″ N | 2824 | 33,330 | 69% | 1.5 m × 2 m | 0~10 | SB_10 |
| 10~20 | SB_20 | |||||||
| SHNT | 100°15′8.89″ E | 36°14′41.2″ N | 2817 | 19,998 | 66% | 1.5 m × 1.5 m | 0~10 | NT_10 |
| 10~20 | NT_20 | |||||||
| NT80 | 100°14′7.28″ E | 36°14′55.7″ N | 2,11 | 10,000 | 89% | 1.5 m × 1.5 m | 0~10 | SH_10 |
| 10~20 | SH_20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, S.; Xie, H.; Zhang, G.; Qiao, F.; Geng, G.; E, C. Improvement Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil of Alpine Sandy Land. Biology 2025, 14, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020144
Du S, Xie H, Zhang G, Qiao F, Geng G, E C. Improvement Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil of Alpine Sandy Land. Biology. 2025; 14(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Shaobo, Huichun Xie, Gaosen Zhang, Feng Qiao, Guigong Geng, and Chongyi E. 2025. "Improvement Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil of Alpine Sandy Land" Biology 14, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020144
APA StyleDu, S., Xie, H., Zhang, G., Qiao, F., Geng, G., & E, C. (2025). Improvement Effects of Different Afforestation Measures on the Surface Soil of Alpine Sandy Land. Biology, 14(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020144







