Habitat Suitability Shifts of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China Under Climate Change Projections
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Introduction to the Research Region
2.2. Species Distribution Information
2.3. Collection and Evaluation of Environmental Data
2.4. Development of the Model Architecture and Parameter Optimization
2.5. Appropriate Zoning of Eucommia
2.6. Projected Centroid Shift of Eucommia ulmoides Under Future Climate Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation and Selection of Environmental Variables
3.2. Evaluation of Model Accuracy
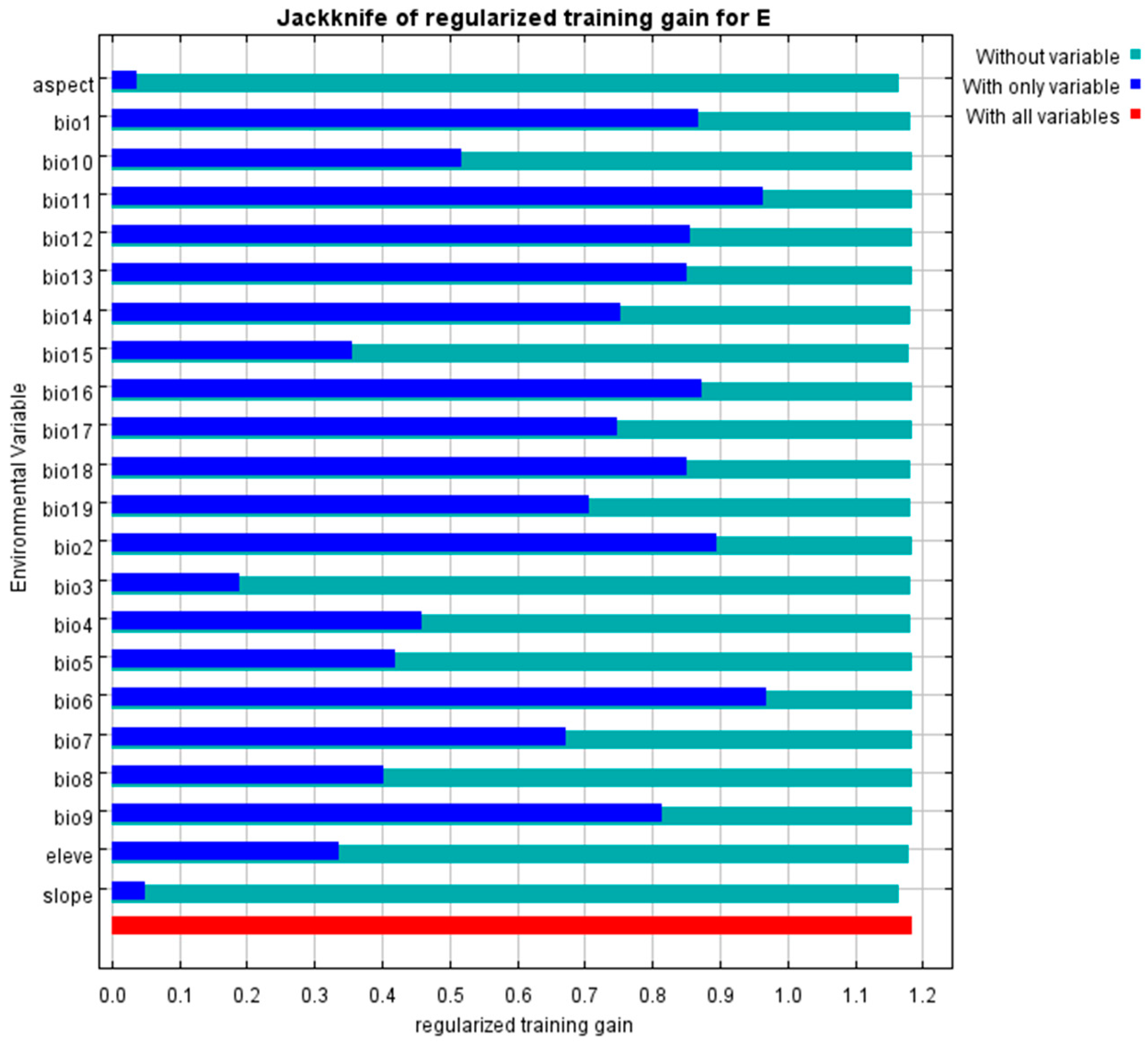
3.3. The Primary Environmental Factors Influencing the Growth of Eucommia ulmoides
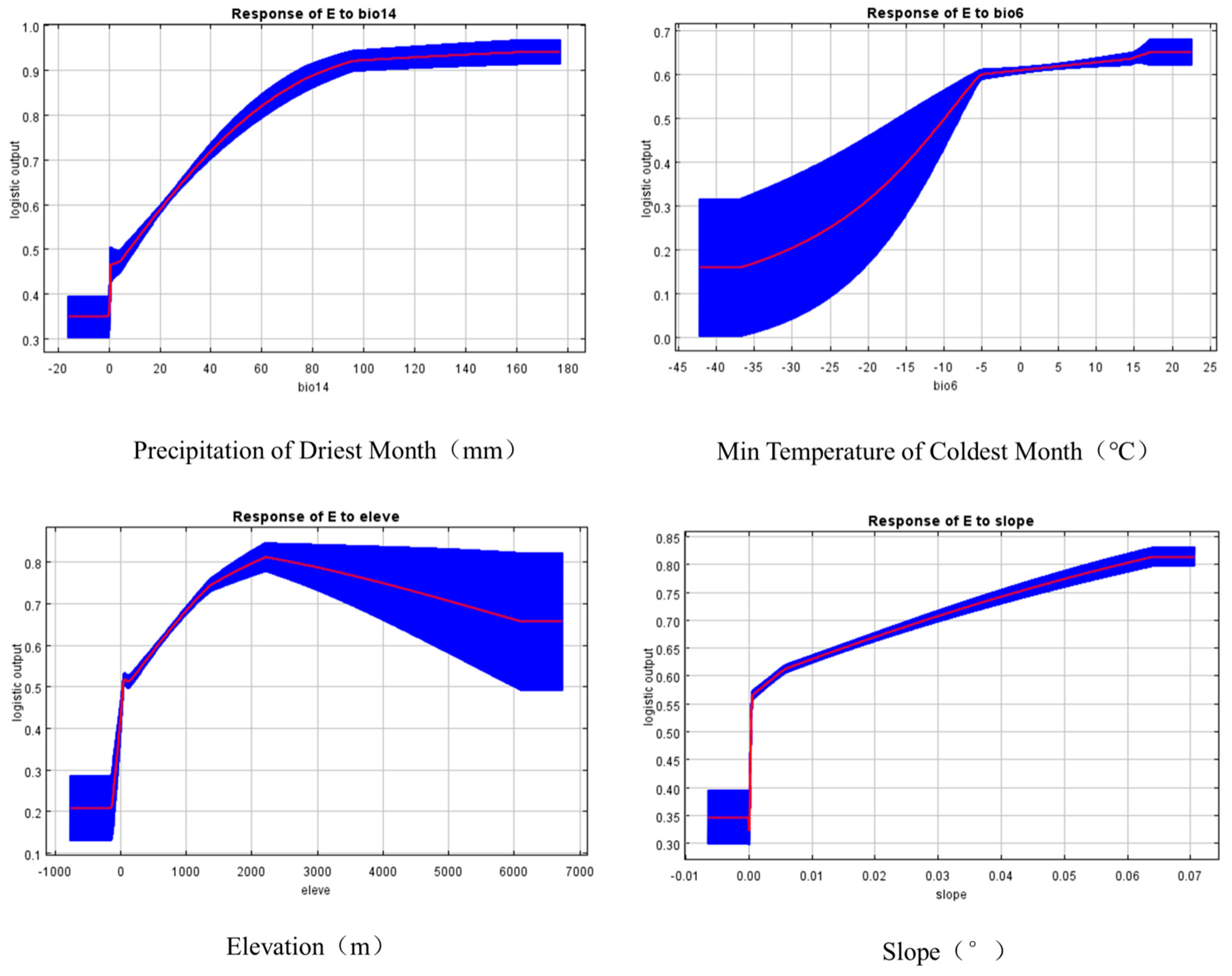
3.4. Correlation Between Eucommia Distribution and Environmental Factors
3.5. Projected Distribution Range of Eucommia ulmoides Under Present Climatic Conditions
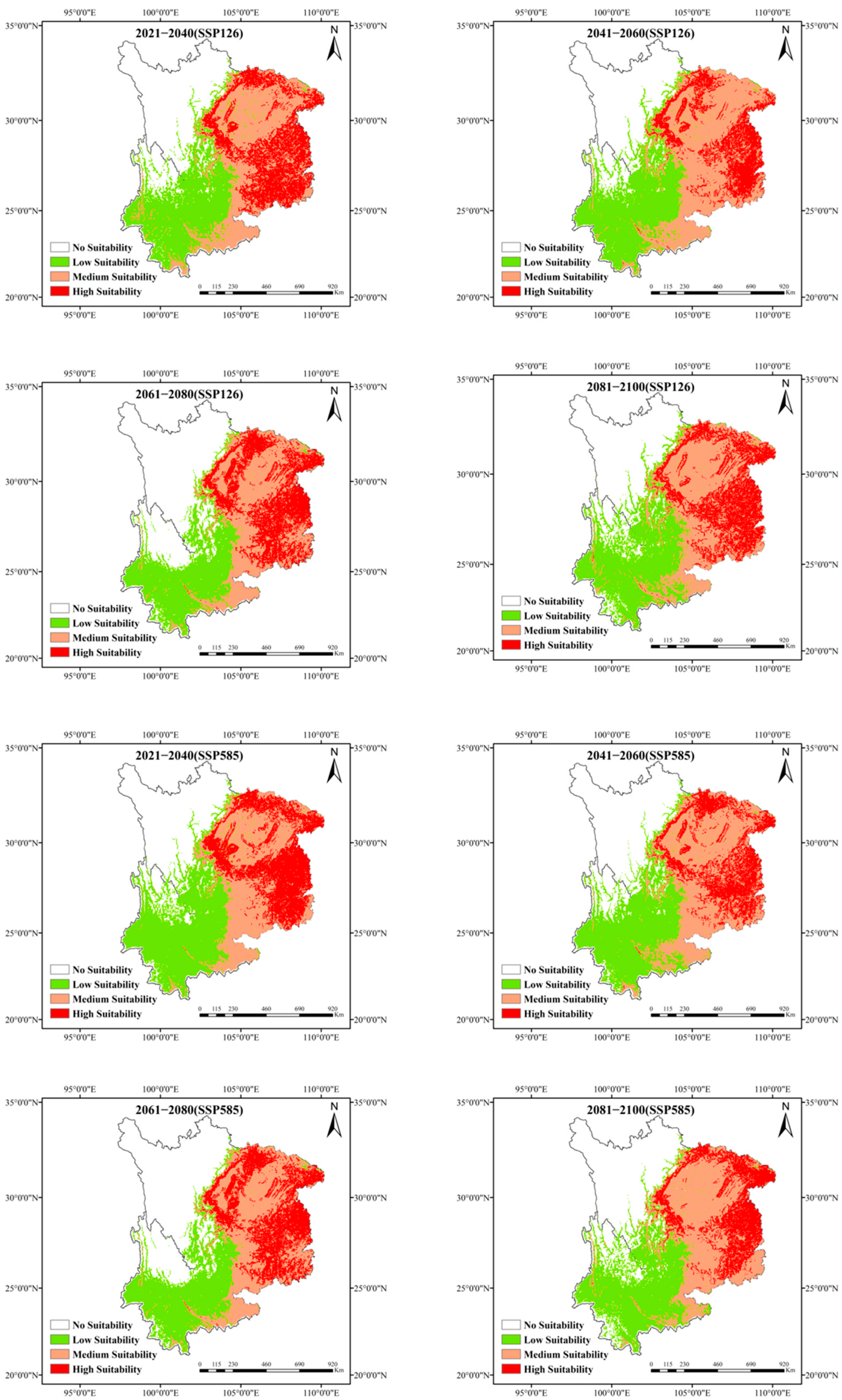
3.6. Projected Distribution Range of Eucommia ulmoides Under Future Climate Scenarios
3.7. Centroid Shift of Eucommia ulmoides Distribution in High-Suitability Regions Under Future Climate Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Potential Suitable Areas for Eucommia ulmoides to Climate Change in Southwest China
4.2. Projected Response of the Potential Habitat Area of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China to Future Climate Scenarios
4.3. The Impact of Climate Change on the Cultivation of Eucommia ulmoides in the Future
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.F. A novel framework for biodiversity systems analysis in response to climate change and land use transformation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 871–884. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Q.; Han, S.; Jin, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Tao, J. Assessing the impact of climate change on three Populus species in China: Distribution patterns and implications. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 50, e02853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.H.; E Waggett, C.; Berenbaum, P.; Bayles, B.R.; Carlson, G.L.; English, R.; Guzmán, C.A.F.; Gartin, M.L.; Grant, L.; Henshaw, T.L.; et al. Planetary health learning objectives: Foundational knowledge for global health education in an era of climate change. Lancet Planet. Health 2024, 8, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, L.S.; Segarra-Medina, C.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; López-Climent, M.F.; Vives-Peris, V.; I Zandalinas, S. Climate change-associated multifactorial stress combination: A present challenge for our ecosystems. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 276, 153764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.L.; Zheng, M.M.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, J.X. Progress on ancient DNA investigation of Late Quaternary mammals in China. Yi Chuan 2025, 47, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Niu, F.; Lu, S.; Du, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. Impacts of Climate Change on the Potential Suitable Ecological Niches of the Endemic and Endangered Conifer Pinus bungeana in China. Forests 2025, 16, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, S.; Trivedi, A.; Chaudhary, K.B.; Ghadiali, J. Global Climate Change and Its Effects on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants: A Review Article. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, L.K.; Robertson, M.P.; Barker, N.P. Range contraction to a higher elevation: The likely future of the montane vegetation in South Africa and Lesotho. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 28, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.Y.; Zhang, M.M.; Su, H.J.; Zhang, H.B. Application of niche model in habitat selection of species. J. Econ. Anim. 2014, 18, 47–52+58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Duan, Y.X.; Jin, L.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Peng, M.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Ma, Y.F. Prediction of historical, present and future distribution of Quercus sect. Heterobalanus based on the optimized MaxEnt model in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6590–6604. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, S.; Kong, L.; Dou, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, J. Study on the Distribution Range and Influencing Factors of Salix oritrepha Schneid. and Picea crassifolia Kom. in the Watershed of the Yellow River Under Future Climate Models. Forests 2025, 16, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Guéguen, M.; Georges, D.; Bonet, R.; Chalmandrier, L.; Garraud, L.; Renaud, J.; Roquet, C.; Van Es, J.; Zimmermann, N.E.; et al. Are different facets of plant diversity well protected against climate and land cover changes? A test study in the French Alps. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Schapire, R.E.; Blair, M.E. Opening the black box: An open-source release of Maxent. Ecography 2017, 40, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; He, M.; Wang, M.; Chu, G.; Yang, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhou, M.; Hui, Y.; Ding, J. Assessing Habitat Suitability for Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. turkestanica Amid Climate Change Using the MaxEnt Model. Forests 2025, 16, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Jin, L.; Wei, S.; Yang, H.; Cao, Z.; Peng, J.; Luo, Y. Prediction of the Future Evolution Trends of Prunus sibirica in China Based on the Key Climate Factors Using MaxEnt Modeling. Biology 2024, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.J.; Zhang, D.F.; Guo, X.D. Analysis and prediction of suitable areas of Malus sinensis in the context of climate change. J. Qinghai Univ. 2023, 41, 24–31+47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, L. Assessing the quality ecology of endemic tree species in China based on machine learning models and UPLC methods: The example of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.P.; Yan, B.B.; Zhang, X.B.; Peng, Z.; Guo, X.Z.; Sun, J.H.; Zhan, W.L.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.P.; et al. Discussion on Ecological Planting of Eucommia ulmoides and Its Enlightenment to Development of Health Industry. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 905–912. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Li, Y. A new historical opportunity for the development of Eucommia industry was published in The National Eucommia ulmoides Industry Development Plan (2016–2030). China For. Ind. 2017, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, X.; Lin, H.; Peng, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, H. Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological Effect, and Product Development of Eucommia ulmoides with Both Medicinal and Edible Values: A Review. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2024, 30, 190–202. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; Ying, L.; Zhuo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. miR-200a suppresses cell growth and migration by targeting MACC1 and predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, D.; Lu, X.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Zhan, Z. Herbal Textual Research on Eucommiae Cortex in Famous Classical Formulas. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2023, 29, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Duzhong Industry Research Task Group. Current Situation and Prospects of Duzhong Biological Industry Development. China For. Ind. 2022, 11, 18–47. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.F.; Wang, L.; Du, Q.X.; Du, L.Y. Estimation of potential suitable distribution area and the ecological characteristics of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5674–5684. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Yuan, X.; Shu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wu, T.; Xiao, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of the potentially suitable areas of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver in China under climate change based on optimized Biomod2 and MaxEnt models. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1359271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Xu, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.S. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Temperature in Southwest China during the Past Century. J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 37, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Chen, Z.J. Wind speed changes and its influencing factors in Southwestern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Mo, J.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Yan, H. Study on the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of forest NEP in Southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Deng, H. Heterogeneous Impacts of Human Activity Intensity on Regional Ecological Security Patterns. Case Southwest China 2024, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Q. Characteristics and the constraint relationship between ecosystem services and vegetation coverage in the Southwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2253–2270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.F.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, S.Y. Predicting the potential habitat suitability of Saussurea species in China under future climate scenarios using the optimized Maximum Entropy (MaxEnt) model. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 474, 143552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Chen, F.L.; Chen, H.B.; Ding, Z.T.; Wu, G.Y.; Luo, X.; Huang, S. Future Temperature and Precipitation Trend Analysis and Runoff Simulation in the Kaiduhe River Basin Based on BCC-CSM2-MR Model. Water Resour. Power 2024, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Jiamahate, A.; Yang, H.; Cao, L.; Dang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Bozorov, T.A.; Wang, X. Potential Ecological Distribution of the Beetle Agrilus mali Matsumura (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in China under Three Climate Change Scenarios, with Consequences for Commercial and Wild Apple Forests. Biology 2024, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.-G.; Wu, T.-W.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.-P.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Jie, Y.; Ji, W.-H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Li, J.-L.; et al. Introduction of BCC models and its participation in CMIP6. Clim. Change Res. 2019, 15, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Dong, P.; Wang, L.; Ke, X.; Hao, X.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F. Predicting the Potential Distribution of Hypericum perforatum under Climate Change Scenarios Using a Maximum Entropy Model. Biology 2024, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cao, G.C.; Rong, Z.L.; Li, H.F. Prediction of potential distribution of Ophiocordyceps sinensis in Chain based on Maxent model. Ecol. Sci. 2023, 42, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, B.; Wan, F.; Xiao, Q.; Dai, L. Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodivers. Sci. 2007, 15, 365. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, W.K.; Xiao, C.H.; Xie, Y. Study on Ecological Suitability Regionalization of Eucommia ulmoides in Gui-zhou. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2014, 37, 760–766. [Google Scholar]
- Msadek, J.; Tlili, A.; Chouikhi, F.; Ragkos, A.; Tarhouni, M. Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change Scenarios on Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index in North African Arid Montane Rangeland: Case of Toujane Region. Climate 2025, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.M. Activity Rhythm and Potential Distribution Prediction of Silver Pheasant (Lophura nycthemera) in Hunan Province in Hunan Province. Master’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry & Technology, Changsha, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.F.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Su, N.; Kong, Y.H.; Xing, X.H. Chemical constituents, biological functions and pharmacological effects for comprehensive utilization of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhu, W.Q.; Li, P.X. Potential distributions of Alsophila spinulosa under different climates in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6105–6117. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Li, Q.Q.; Yang, Y.R.; Zhang, L.Y. Dynamic change of forest fire with topographic factors in Southwest China from 2003 to 2020 based on MODIS data. Ecol. Sci. 2024, 43, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Luo, G.G.; Tang, H.Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.R. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Features of Winter Temperature in Southwestern China. J. Southwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 33, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.Q. Climatic Variation of Rainfall and Rain Day in Southwest China for Last 48 Years. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 372–383. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liang, S.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, J. Predicting the Potential Distribution of Aralia chinensis L. (Wild Vegetable) in China Under Different Climate Change Scenarios. Biology 2024, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.A.; Bin, L.I.; Zhen, F.E.; Xiao, Z. Global Climate Change and Geological Disaster Response Analysis. J. Geomech. 2017, 23, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Hu, Y.W.; Wang, Y. Prediction of future change of persistent climate event in Southwest China. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2020, 40, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, C.R. Impact of Climate Change on Geological Disaster in Southwest China. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 40, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; He, M.Z.; Wang, L. Effects of precipitation control on plant diversity and biomass in a desert region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liang, F.N.; Sun, Y.W.; Han, F.; Zhou, Y.; Rong, Y.F.; Qiu, F.; Ding, L.Q. Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical application of Eucommia ulmoides. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 4740–4761. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.F.; Liu, B.S.; Yan, P.P.; Li, B.X.; Zhang, X.F.; Zheng, Y.; Song, Y.G.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Miao, M.S. Review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects, and quality control status of Eucommiae Cortex and prediction of its Q-markers. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2025, 50, 946–958. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.Y.; Zhang, T.; Tian, J.Y.; Li, J.Z.; Feng, P. Ecological risk assessment in the Ziya watershed under the influences of land use change and water resource shortage. CATENA 2024, 244, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.T.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.P.; Zhao, C.L.; Jiang, Q.S.; Cheng, Z.Q. Ecosystem health assessment based on AHP-DPSR model and impacts of climate change and human disturbances: A case study of Liaohe River Basin in Jilin Province. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.W.; Jin, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.T. Vulnerability and driving mechanism of four typical grasslands in China under the coupled impacts of climate change and human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.P.; Qiao, H.J. Impact of MaxEnt model complexity on species potential distribution prediction. Biodivers. Sci. 2016, 24, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljevic, A.; Anderson, R.P. Making better MAXENT models of species distributions: Complexity, overfitting and evaluation. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| bio1 | Annual Mean Temperature (°C) |
| bio2 | Mean Diurnal Range (Mean of monthly (max temp − min temp) (°C) |
| bio3 | Isothermality (bio2/bio7) (×100) (bio2/bio7) (×100) |
| bio4 | Temperature Seasonality (standard deviation ×100) |
| bio5 | Max Temperature of Warmest Month (°C) |
| bio6 | Min Temperature of Coldest Month (°C) |
| bio7 | Temperature Annual Range (bio5–bio6) |
| bio8 | Mean Temperature of Wettest Quarter (°C) |
| bio9 | Mean Temperature of Driest Quarter (°C) |
| bio10 | Mean Temperature of Warmest Quarter (°C) |
| bio11 | Mean Temperature of Coldest Quarter (°C) |
| bio12 | Annual Precipitation (mm) |
| bio13 | Precipitation of Wettest Month (mm) |
| bio14 | Precipitation of Driest Month (mm) |
| bio15 | Precipitation Seasonality (Coefficient of Variation) |
| bio16 | Precipitation of Wettest Quarter (mm) |
| bio17 | Precipitation of Driest Quarter (mm) |
| bio18 | Precipitation of Warmest Quarter (mm) |
| bio19 | Precipitation of Coldest Quarter (mm) |
| elevation | Elevation (m) |
| aspect | Aspect |
| slope | Slope (°) |
| Environment Variable | Percent Contribution (%) | Permutation Importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| bio14 | 27.2 | 5.90 |
| bio6 | 22.1 | 11.0 |
| bio13 | 14.90 | 0.40 |
| bio12 | 10.40 | 7.10 |
| bio11 | 4.20 | 20.0 |
| slope | 3.0 | 5.20 |
| bio9 | 2.20 | 0.10 |
| elevation | 1.90 | 7.30 |
| Environment Variable | Threshold |
|---|---|
| bio14 | 12.6 mm ≤ bio14 ≤ 96.5 mm |
| bio6 | 4 °C ≤ bio6 ≤ 6 °C |
| bio13 | bio13 mm ≤ 184 mm; bio13 ≥ 345 mm |
| bio12 | bio12 ≤ 216 mm; bio12 ≥ 970 mm |
| bio11 | 0.7 °C ≤ bio11 ≤ 9.8 °C; bio11 ≥18 °C |
| bio9 | 3 ≤ bio9 ≤ 11.7; bio9 ≥ 17 |
| elevation | 13.9 m ≤ elevation ≤ 756 m |
| slope | Slope ≥ 0.002° |
| Suitable Area/km2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction Period | Low Suitable Area | Mid-Natural Area | High Fitness Area | Total Suitable Area | |
| Current | 9342 | 12,334 | 7255 | 28,931 | |
| SSP1-2.6 | 2021–2040 | 12,264 | 12,580 | 8411 | 33,255 |
| 2041–2060 | 14,944 | 19,078 | 1916 | 35,938 | |
| 2061–2080 | 13,665 | 14,497 | 10,664 | 38,826 | |
| 2081–2100 | 14,458 | 16,103 | 10,082 | 40,643 | |
| SSP5-8.5 | 2021–2040 | 15,781 | 14,625 | 11,212 | 41,618 |
| 2041–2060 | 15,552 | 17,605 | 8679 | 41,836 | |
| 2061–2080 | 13,662 | 14,480 | 10,633 | 38,775 | |
| 2081–2100 | 15,959 | 16,849 | 8594 | 41,402 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Xue, J.; Shi, P.; Liang, S. Habitat Suitability Shifts of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China Under Climate Change Projections. Biology 2025, 14, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040451
Liu Q, Liu L, Xue J, Shi P, Liang S. Habitat Suitability Shifts of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China Under Climate Change Projections. Biology. 2025; 14(4):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040451
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qi, Longjiang Liu, Juan Xue, Peiyao Shi, and Shanshan Liang. 2025. "Habitat Suitability Shifts of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China Under Climate Change Projections" Biology 14, no. 4: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040451
APA StyleLiu, Q., Liu, L., Xue, J., Shi, P., & Liang, S. (2025). Habitat Suitability Shifts of Eucommia ulmoides in Southwest China Under Climate Change Projections. Biology, 14(4), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040451







