Metabonomics Analysis Reveals the Influence Mechanism of Three Potassium Levels on the Growth, Metabolism and Accumulation of Medicinal Components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Experiment
2.2. Determination of Saikosaponin
2.3. Elemental Analysis
2.4. GC−MS Analysis
2.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.6. Experimental Instruments and Reagents
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Analysis of Quality and Traits of Bupleurum Under Different Potassium Levels
3.2. Total Saikosaponins Content Accumulated in Bupleurum Different Tissues Under Three Levels of Potassium Fertilization
3.3. Overview of the Metabolite Profiles in Response to Three Levels of Potassium Fertilization
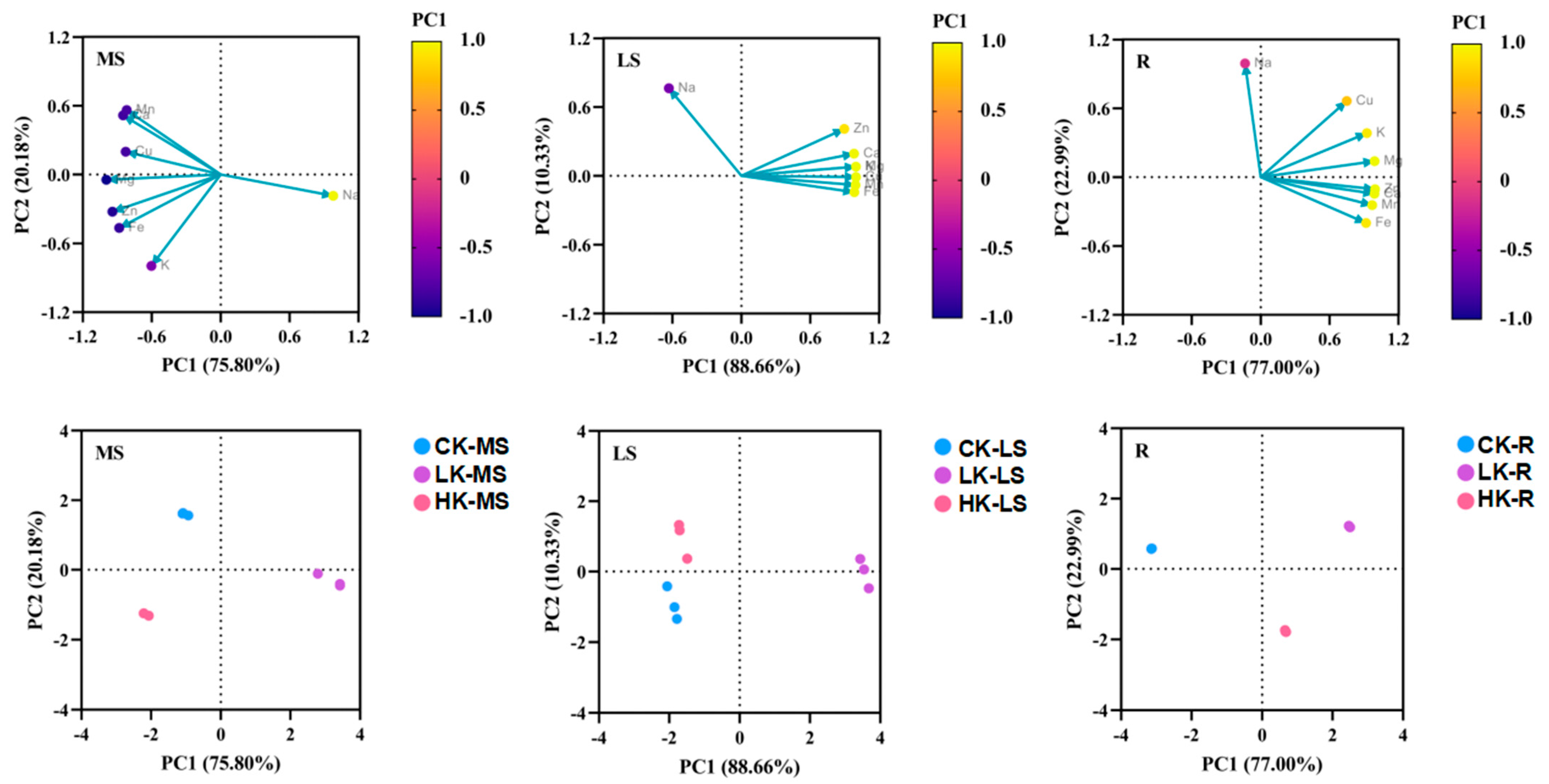
3.4. Effect of Potassium Fertilizer Application on Mineral Elements of Bupleurum
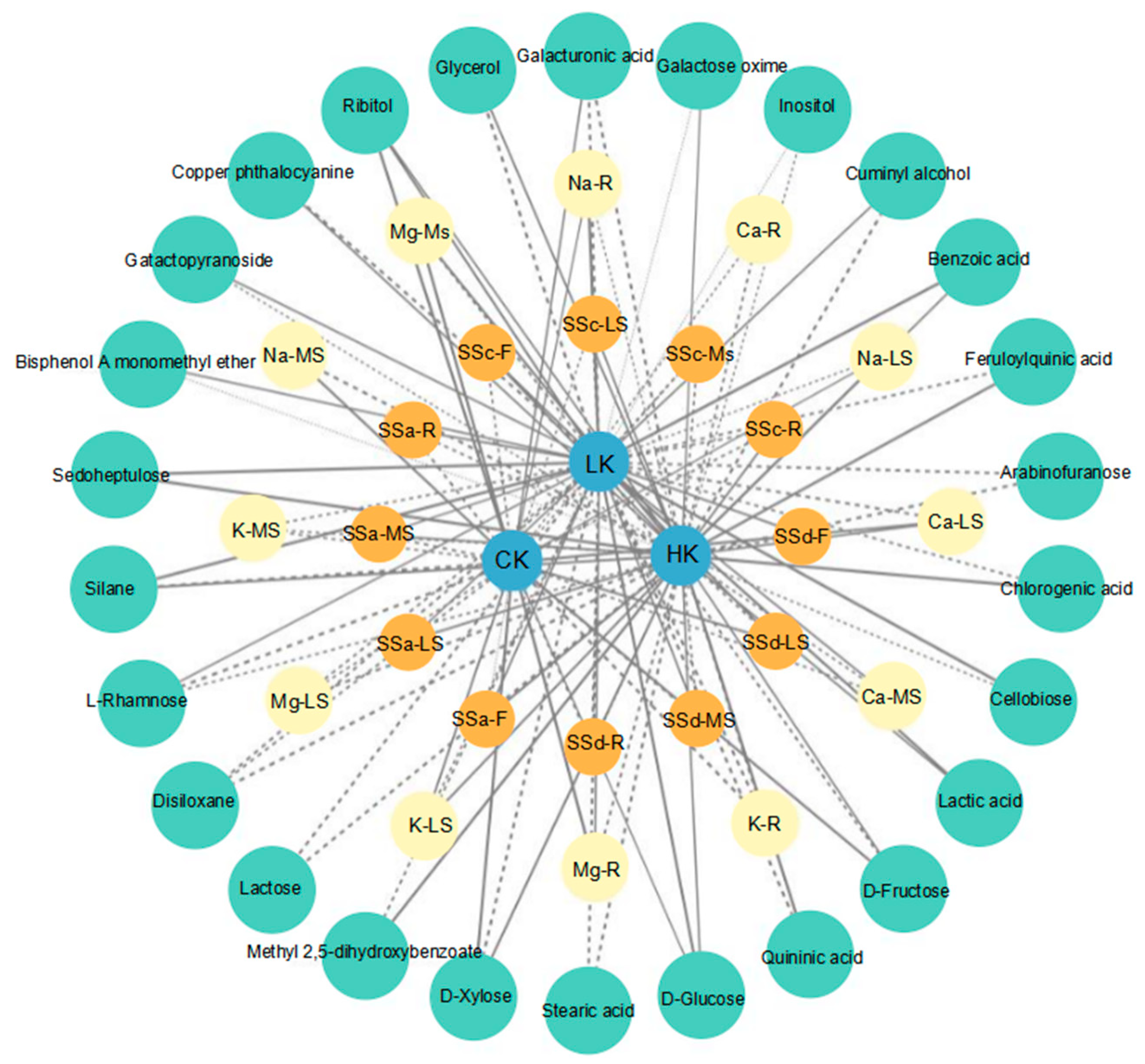
3.5. Volcano Diagram and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Primary Differential Metabolites of Bupleurum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Hao, Z.; et al. Saikosaponins from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. alleviates microglial pyroptosis in depression by binding and inhibiting P2X7 expression. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.N.; Bing, Y.F.; Wu, S.; Luo, L.T.; Sun, Z.W.; Li, W.L.; Qu, Z.Y.; Zou, X. Discovery and verification of anti-inflammatory-related quality markers in the aerial part of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and in RAW 264.7 cells and a zebrafish model. Phytochem. Anal. 2024, 35, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, H.X.; Xia, Y.G. Effects of various processed methods on chemical constituents and anti-hepatitis activity of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. by metabonomics and molecular docking. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 218, 114837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Tuerxun, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, R.; Liu, C. Identification of Bupleurum (Apiaceae) seeds by allele-specific PCR based on ITS sequences. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Song, Z.; Li, R. Sustainability of Maize–Soybean Rotation for Future Climate Change Scenarios in Northeast China. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2025, 211, e70033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhou, B. Response of Crop Yield and Productivity Contribution Rate to Long-Term Different Fertilization in Northeast of China. Plants 2025, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, T.; Liu, K.; Shen, Z.; Daba, N.A.; Tadesse, K.A.; Khan, M.N.; Shah, A.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Optimizing potassium and nitrogen fertilizer strategies to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions in global agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.; Gorelick, J.; Zerahia, R.; Koch, S. Impact of N, P, K, and Humic Acid Supplementation on the Chemical Profile of Medical Cannabis (Cannabis sativa L). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; Tang, Z.; Abozeid, A. Metabolite Profiles Provide Insights into Underlying Mechanism in Bupleurum (Apiaceae) in Response to Three Levels of Phosphorus Fertilization. Plants 2022, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Tang, Z.; Abozeid, A. Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Potential Mechanisms in Bupleurum L. (Apiaceae) Induced by Three Levels of Nitrogen Fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmidi, D.; Muraya, F.; Fizames, C.; Véry, A.A.; Roelfsema, M.R.G. Potassium extrusion by plant cells: Evolution from an emergency valve to a driver of long-distance transport. New Phytol. 2025, 245, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Grauschopf, C.; Hedrich, R.; Dreyer, I.; Konrad, K.R. K+ and pH homeostasis in plant cells is controlled by a synchronized K+/H+ antiport at the plasma and vacuolar membrane. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 1525–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotelle, V.; Leonhardt, N. 14-3-3 Proteins in Guard Cell Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, M.R. Plant Physiology: Redefining the Enigma of Metabolism in Stomatal Movement. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R107–R109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.K.; Xv, B.J.; Si, C.C.; Shi, W.Q.; Ding, G.Z.; Tang, L.X.; Xv, M.; Shi, C.Y.; Liu, H.J. Effect of potassium fertilization on storage root number, yield, and appearance quality of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1298739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakabe, Y.; Arinaga, N.; Umezawa, T.; Katsura, S.; Nagamachi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Ohiraki, H.; Yamada, K.; Seo, S.U.; Abo, M.; et al. Osmotic stress responses and plant growth controlled by potassium transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Persson, S.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, C. At the border: The plasma membrane-cell wall continuum. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves-Cordones, M.; Andrianteranagna, M.; Cuéllar, T.; Chérel, I.; Gibrat, R.; Boeglin, M.; Moreau, B.; Paris, N.; Verdeil, J.L.; Zimmermann, S.; et al. Characterization of the grapevine Shaker K+ channel VvK3.1 supports its function in massive potassium fluxes necessary for berry potassium loading and pulvinus-actuated leaf movements. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil Kumar, S.; Kaniganti, S.; Hima Kumari, P.; Sudhakar Reddy, P.; Suravajhala, P.; P, S.; Kishor, P.B.K. Functional and biotechnological cues of potassium homeostasis for stress tolerance and plant development. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2024, 40, 3527–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefoulon, C. The bare necessities of plant K+ channel regulation. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 2092–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. Potassium transport and signaling in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 451–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyzenga, W.J.; Liu, Z.; Olukayode, T.; Zhao, Y.; Kochian, L.V.; Ham, B.K. Getting to the roots of N, P, and K uptake. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 1784–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. Plant sensing and signaling in response to K+-deficiency. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, A.; Khan, Q.U.; Alem, A.; Hendi, A.A.; Zaman, U.; Khan, S.U.; Rehman, K.U.; Khan, A.A.; Ullah, I.; Anwar, Y.; et al. Zinc and Potassium Fertilizer Synergizes Plant Nutrient Availability and Affects Growth, Yield, and Quality of Wheat Genotypes. Plants 2023, 12, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.F.; Mateus, N.S.; Rosário, M.O.; Garcez, T.B.; Mazzafera, P.; Lavres, J. Enhancing potassium content in leaves and stems improves drought tolerance of eucalyptus clones. Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.Q.; Wang, F.L.; Li, H.; Jing, S.; Yu, M.; Li, J.; Wu, W.H.; Kudla, J.; Wang, Y. The Transcription Factor MYB59 Regulates K+/NO3− Translocation in the Arabidopsis Response to Low K+ Stress. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, L.; Su, X.; Ji, B.; Dong, C. Drought Stress Stimulates the Terpenoid Backbone and Triterpenoid Biosynthesis Pathway to Promote the Synthesis of Saikosaponin in Bupleurum chinense DC. Roots. Molecules 2022, 27, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bu, X.; Gao, D. Integrated physiological, transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis revealed the molecular mechanism of Bupleurum chinense seedlings to drought stress. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Lan, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.; Han, M.; Yang, L.M. Drought stress induces biosynthesis of flavonoids in leaves and saikosaponins in roots of Bupleurum chinense DC. Phytochemistry 2020, 177, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Xia, P.G.; Liang, Z.S.; Liu, S.L.; Liu, Z.L. Expression of key enzyme genes and content of saikosaponin in saikosaponin biosynthesis under drought stress in Bupleurum chinense. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2016, 41, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Hu, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, C. Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Differences Between Bupleurum chinense DC. and Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 933849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, W.-y.; Vanessa, P.; Cheng, F.-q. Synergistic effect of Si and K in improving the growth, ion distribution and partitioning of Lolium perenne L. under saline-alkali stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thor, K. Calcium-Nutrient and Messenger. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.-J.; Luan, S. Rhythms of magnesium. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanikenne, M.; Bouché, F. Iron and zinc homeostasis in plants: A matter of trade-offs. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 5426–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; McDonald, L.M.; Roy, M.; Lanzirotti, A.; Myneni, S.C.B. Uptake and speciation of zinc in edible plants grown in smelter contaminated soils. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, O.A.A.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, Y.; Kuchkarova, N.; Dong, L.; Jiao, J.Y.; Fang, B.Z.; Ma, J.B.; Hatab, S.; Li, W.J. Metabonomic analysis to identify exometabolome changes underlying antifungal and growth promotion mechanisms of endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces albidoflavus for sustainable agriculture practice. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1439798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Kinlock, N.L.; Lučanová, M.; Leitch, I.J.; Pierce, S.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Kreft, H.; et al. Plant invasion and naturalization are influenced by genome size, ecology and economic use globally. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, Z. Maize DLR1/NHX7 Is Required for Root Development Under Potassium Deficiency. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 48, 1329–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, K.; Kubavat, D.; Ghara, K.K.; Kumar, R.; Trivedi, H.; Anand, K.G.V.; Maiti, P.; Ghosh, A. Evaluation of Fertilizer Potential of Different K Compounds Prepared Utilizing Sea Bittern as Feed Stock. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, L. Enhancing Rice Production by Potassium Management: Recommended Reasonable Fertilization Strategies in Different Inherent Soil Productivity Levels for a Sustainable Rice Production System. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchin, A.; Nikel, P.I. Why Nature Chose Potassium. J. Mol. Evol. 2019, 87, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britto, D.T.; Coskun, D.; Kronzucker, H.J. Potassium physiology from Archean to Holocene: A higher-plant perspective. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 262, 153432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Evaluate regional potassium fertilization strategy of winter oilseed rape under intensive cropping systems: Large-scale field experiment analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezui, K.S.; Franke, A.C.; Mando, A.; Ahiabor, B.D.K.; Tetteh, F.M.; Sogbedji, J.; Janssen, B.H.; Giller, K.E. Fertiliser requirements for balanced nutrition of cassava across eight locations in West Africa. Field Crops Res. 2016, 185, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.F.; Ali, A.M.; Azab, M.A.; Lamlom, S.F.; Al-Sayed, H.M. Improved plant yield of potato through exogenously applied potassium fertilizer sources and biofertilizer. AMB Express 2023, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, N.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Kai, G. Estimating Fritillaria thunbergii Miq. yield, quality, and potassium use efficiency in response to potassium application rate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, L. From foe to friend: The role of chloride as a beneficial macronutrient. Plant J. 2019, 99, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero-Flores, J.M.; Franco-Navarro, J.D.; Cubero-Font, P.; Peinado-Torrubia, P.; Rosales, M.A. Chloride as a Beneficial Macronutrient in Higher Plants: New Roles and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xu, E.; Wang, G.; He, D.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, A. Transcriptional and Physiological Analysis Reveal New Insights into the Regulation of Fertilization (N, P, K) on the Growth and Synthesis of Medicinal Components of Dendrobium denneanum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Lankes, C.; Zimmermann, B.F.; Noga, G.; Hunsche, M. Centelloside accumulation in leaves of Centella asiatica is determined by resource partitioning between primary and secondary metabolism while influenced by supply levels of either nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, J.; Saxena, J.; Sanwal, P.; Maddela, N.R.; Nain, L.; Prasad, R. Improving the Growth and Productivity of Macrotyloma uniflorum Medicinal Plant by the Co-inoculation of P, Zn and K-Solubilizing Fungi Under Field Conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Lei, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Jiang, C. Photosynthate transport rather than photosynthesis rate is critical for low potassium adaptation of two cotton genotypes. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2015, 66, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidong, W.; Zhu, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Rengel, Z.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Potassium starvation affects biomass partitioning and sink–source responses in three sweet potato genotypes with contrasting potassium-use efficiency. Crop Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



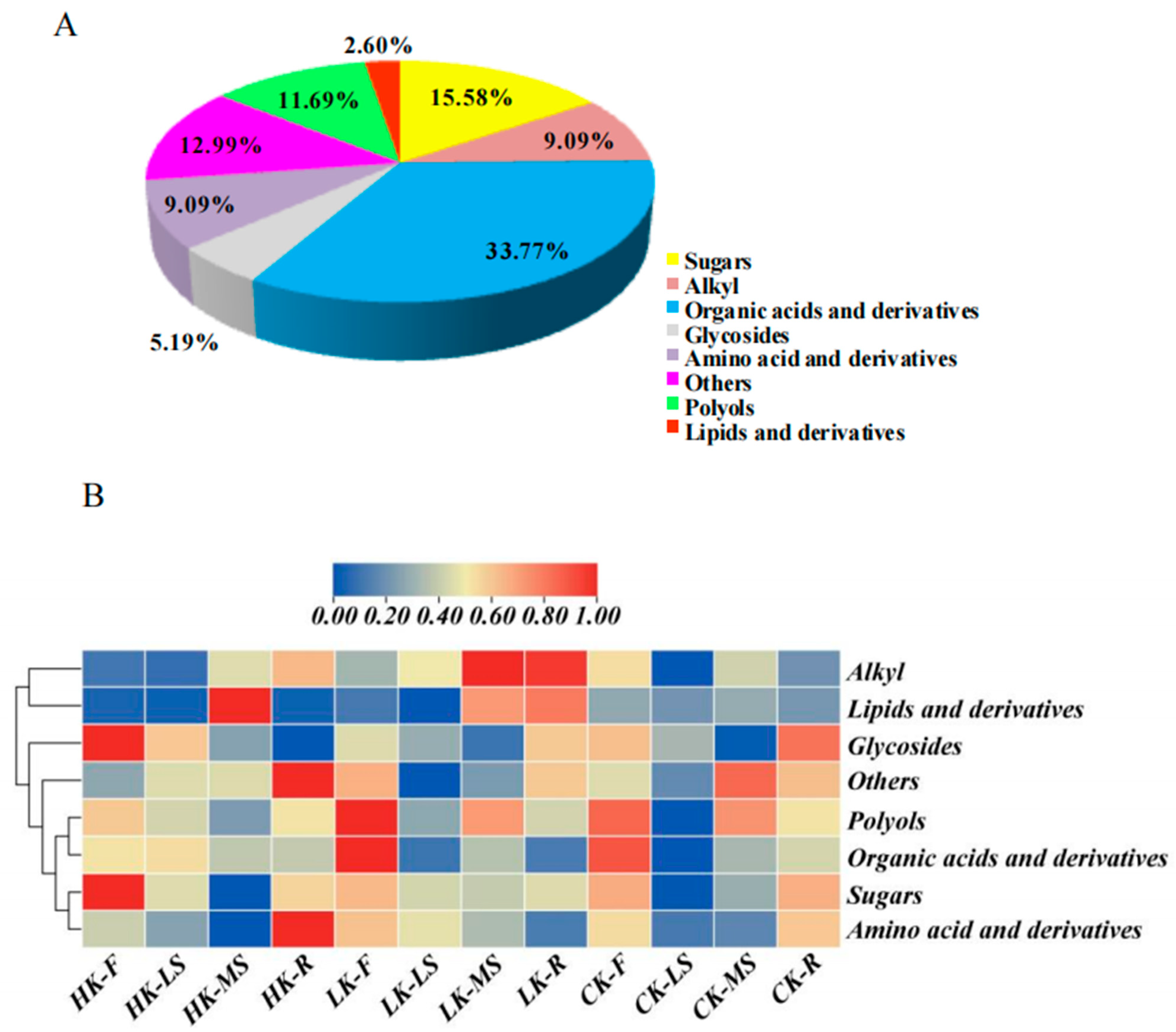



| Classification | Metabolites | Classification | Metabolites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugars (12) | α-Mannobiose | Organic acids and Derivatives (26) | Galactaric acid |
| Arabinofuranose | Aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid | ||
| d-Cellobiose | Aminobutanoic acid | ||
| d-Fructose | Feruloylquinic acid | ||
| d-Glucose | Benzoic acid | ||
| d-Xylose | Butanedioic acid | ||
| Lactose | Caffeic acid | ||
| Levoglucosan | Butanoic acid | ||
| l-Rhamnose | Chlorogenic acid | ||
| Sedoheptulose | Citric acid | ||
| Sucrose | Gallic acid | ||
| d-Mannose | Glyceric acid | ||
| Glycosides (4) | β-d-Galactofuranoside | Isophthalic acid | |
| α-d-Galactopyranoside | Lactic acid | ||
| α-d-Glucopyranoside | Malic acid | ||
| α-d-Lyxofuranoside | Palmitic acid | ||
| Polyols (9) | d-Mannitol | Pentanedioic acid | |
| Erythritol | Propanedioic acid | ||
| Ribitol | Protocatechoic acid | ||
| Inositol | Quininic acid | ||
| Ethenediol | Stearic acid | ||
| Benzenediol | Succinic acid | ||
| Cuminyl alcohol | Sulfurous acid | ||
| Benzylaminooctanol | 2-Butenedioic acid | ||
| Silanol | 2-Propenoic acid | ||
| Amino acid and Derivatives (7) | l-5-Oxoproline | Phosphoric acid | |
| Valine | Lipids and Derivatives (2) | Glycerol | |
| Butylamine | Glycerol monostearate | ||
| Androst-2-en-17-amine | Others (10) | Cyclohexene | |
| Ethanolamine | Heptabarbital | ||
| Urea | Monopalmitin | ||
| Copper phthalocyanine | Benzene | ||
| Alkyl (7) | Decane | Ether | |
| Disiloxane | Isoquinolinium | ||
| Heptane | Phenol | ||
| Nonane | Galactose oxime | ||
| Silane | Methyl benzoate | ||
| Trisiloxane | Carbamate | ||
| Silatrane |
| R2X (cum) | R2Y (cum) | Q2 (cum) | R2Y-Q2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLS-DA (F) | 0.427 | 0.814 | 0.273 | 0.541 |
| PLS-DA (LS) | 0.598 | 0.934 | 0.550 | 0.384 |
| PLS-DA (MS) | 0.190 | 0.422 | −0.006 | 0.481 |
| PLS-DA (R) | 0.713 | 0.999 | 0.879 | 0.120 |
| MS | PC1 | PC2 | LS | PC1 | PC2 | R | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 0.979 | −0.186 | Na | −0.631 | 0.763 | Na | −0.137 | 0.991 |
| K | −0.604 | −0.797 | K | 0.997 | 0.080 | K | 0.924 | 0.383 |
| Ca | −0.850 | 0.516 | Ca | 0.980 | 0.193 | Ca | 0.989 | −0.145 |
| Mg | −0.996 | −0.046 | Mg | 0.997 | 0.079 | Mg | 0.990 | 0.139 |
| Mn | −0.819 | 0.562 | Mn | 0.993 | −0.081 | Mn | 0.970 | −0.244 |
| Cu | −0.827 | 0.199 | Cu | 0.997 | −0.011 | Cu | 0.748 | 0.663 |
| Zn | −0.943 | −0.324 | Zn | 0.895 | 0.409 | Zn | 0.994 | −0.106 |
| Fe | −0.884 | −0.466 | Fe | 0.983 | −0.143 | Fe | 0.916 | −0.400 |
| Total variation explained | 75.80% | 20.18% | 88.66% | 10.33% | 77.00% | 22.99% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Wu, J.; Nasr, A.; Tang, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, W. Metabonomics Analysis Reveals the Influence Mechanism of Three Potassium Levels on the Growth, Metabolism and Accumulation of Medicinal Components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae). Biology 2025, 14, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050452
Sun J, Wu J, Nasr A, Tang Z, Liu W, Liu X, Ma W. Metabonomics Analysis Reveals the Influence Mechanism of Three Potassium Levels on the Growth, Metabolism and Accumulation of Medicinal Components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae). Biology. 2025; 14(5):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050452
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jialin, Jianhao Wu, Alyaa Nasr, Zhonghua Tang, Weili Liu, Xiubo Liu, and Wei Ma. 2025. "Metabonomics Analysis Reveals the Influence Mechanism of Three Potassium Levels on the Growth, Metabolism and Accumulation of Medicinal Components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae)" Biology 14, no. 5: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050452
APA StyleSun, J., Wu, J., Nasr, A., Tang, Z., Liu, W., Liu, X., & Ma, W. (2025). Metabonomics Analysis Reveals the Influence Mechanism of Three Potassium Levels on the Growth, Metabolism and Accumulation of Medicinal Components of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae). Biology, 14(5), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050452






