Effects of Toxic Organic Compounds on Tenebrio molitor and Its Parasite Gregarina steini
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
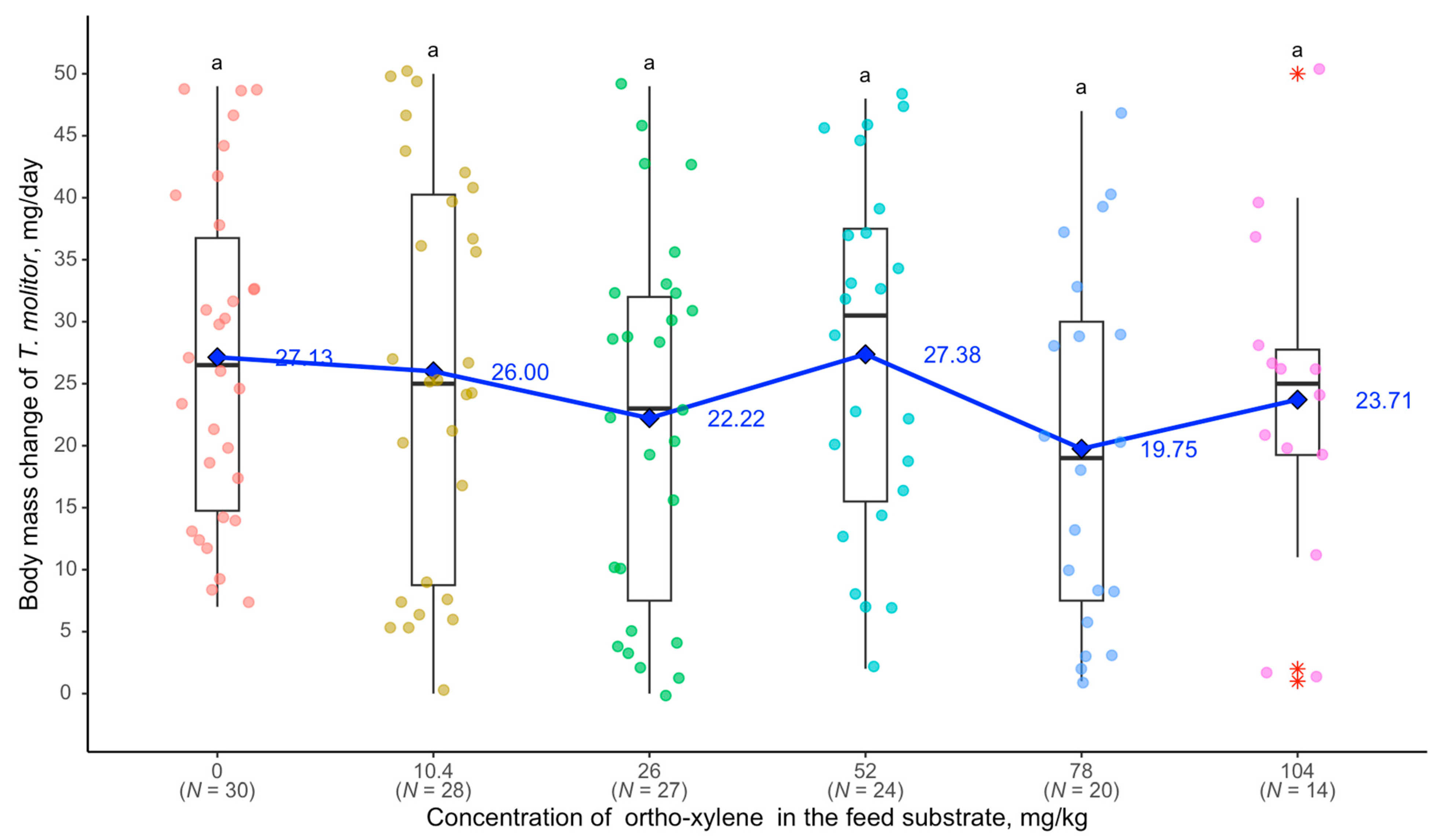
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhind, S.M. Anthropogenic pollutants: A threat to ecosystem sustainability? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ChemAnalyst. Global Formaldehyde Market Analysis: Plant Capacity, Production, Operating Efficiency, Demand & Supply, End-User Industries, Sales Channel, Regional Demand, Foreign Trade, Company Share, 2015–2032. 2022. Available online: https://www.chemanalyst.com/industry-report/formaldehyde-market-627 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Grand View Research. Xylene Market Analysis and Market Trends. 2022. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/xylene-market-analysis-market (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Expert Formaldehyde Market Outlook—Supply and Demand Analysis 2025–2034. 2022. Available online: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/industry-statistics/formaldehyde-market (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- ChemAnalyst. Paraxylene Market Analysis: Industry Market Size, Plant Capacity, Production, Operating Efficiency, Demand & Supply, End-User Industries, Sales Channel, Regional Demand, Foreign Trade, Company Share, Manufacturing Process, Policy and Regulatory Landscape, 2015–2034. 2024. Available online: https://www.chemanalyst.com/industry-report/paraxylene-market-48 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- ChemAnalyst. Aniline Market Analysis: Industry Market Size, Plant Capacity, Production, Operating Efficiency, Demand & Supply, End-User Industries, Sales Channel, Regional Demand, Company Share, Foreign Trade, Manufacturing Process, Policy and Regulatory Landscape, 2015–2032. 2023. Available online: https://www.chemanalyst.com/industry-report/aniline-market-282 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Rajan, S.T.; Malathi, N. Health hazards of xylene: A literature review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Xylene; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, G.A.; McLean, S. Biological monitoring of low-level occupational xylene exposure and the role of recent exposure. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2003, 47, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Meng, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q. Environmental behaviour and eco-toxicity of xylene in aquatic environments: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, L.C. Toxicological and environmental impact of xylene on aquatic invertebrates. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 410–425. [Google Scholar]
- Anjalin, M.; Suganthi, A.R. A brief review on aniline and its derivatives. Mater. Today 2020, 33, 4751–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Mekala, P.; Chintalapati, S.; Ramana, C. New insights into aniline toxicity: Aniline exposure triggers envelope stress and extracellular polymeric substance formation in Rubrivivax benzoatilyticus JA2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.J.; Schiestl, R.H. Aniline and its metabolites generate free radicals in yeast. Mutagenesis 1997, 12, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Soman, K.V.; Ansari, G.A.S.; Khan, M.F. Aniline-induced nitrosative stress in rat spleen: Proteomic identification of nitrated proteins. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 255, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Yun, S.H.; Choi, C.W.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.I. Proteogenomic characterisation of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation pathways in the aniline-degrading bacterium Burkholderia sp. K24. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Saito, H.; Niikura, Y.; Nakano, Y. Embryonic development assay with Daphnia magna: Application to toxicity of aniline derivatives. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, P.J.; Daniels, K.L.; Cushman, R.M.; Kazlow, G.A. Acute toxicity of a synthetic oil, aniline and phenol to laboratory and natural populations of chironomid (Diptera) larvae. Environ. Pollut. A 1984, 34, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, H.A.; Casanova, M.; Starr, T.B. Formaldehyde toxicity—New understanding. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1990, 20, 397–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, L.; Barbosa, E.; Charão, M.F.; Brucker, N. Formaldehyde toxicity reports from in vitro and in vivo studies: A review and updated data. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 45, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chénier, R. An ecological risk assessment of formaldehyde. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 483–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordiean, A.; Krzyźaniak, M.; Stolarski, M.J.; Czachorowski, S.; Peni, D. Will yellow mealworm become a source of safe proteins for Europe? Agriculture 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. The influence of synthetic food additives and surfactants on the body weight of larvae of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae). Biosyst. Divers. 2017, 25, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1372 of 17 August 2021 amending Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the prohibition to feed non-ruminant farmed animals, other than fur animals, with protein derived from animals. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32021R1372&qid=1745312887371 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Urbanek, A.K.; Rybak, J.; Wróbel, M.; Leluk, K.; Mirończuk, A.M. A comprehensive assessment of microbiome diversity in Tenebrio molitor fed with polystyrene waste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 2020, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnson, S. Natural enemies of mass-reared predatory mites (family Phytoseiidae) used for biological pest control. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 46, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Hladkyi, O.Y.; Kolombar, T.M.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. Impact of essential oil from plants on migratory activity of Sitophilus granarius and Tenebrio molitor. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2019, 10, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. The impact of some inorganic substances on change in body mass of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae) larvae in a laboratory experiment. Folia Oecol. 2018, 45, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health: Xylenes (Mixed Isomers); CCME: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2004; Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/res/xylenes-canadian-soil-quality-guidelines-for-the-protection-of-environmental-and-human-health-en.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Formaldehyde Environmental Exposure Assessment; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2025-01/7.-formaldehyde-.-environmental-exp-assessment-.-public-release-.-hero-.-dec-2024.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Rebelo, D.; Antunes, S.C.; Rodrigues, S. The silent threat: Exploring the ecological and ecotoxicological impacts of chlorinated aniline derivatives and the metabolites on the aquatic ecosystem. J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clopton, R.E.; Janovy, J. Host stadium specificity in the gregarine assembly parasitising Tenebrio molitor. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopton, R.E.; Janovy, J. Developmental niche structure in the gregarine assembly parasitising Tenebrio molitor. J. Parasitol. 1993, 79, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geus, A. Sporentierchen, Sporozoa: Die Gregarinida der land- und süßwasserbewohnenden Arthropoden Mitteleuropas. In Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile nach Ihren Merkmalen und Nach Ihrer Lebensweise; Dahl, F., Ed.; VEB Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Desportes, I.; Schrével, J. Treatise on Zoology—Anatomy, Taxonomy, Biology: The Gregarines; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 1–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazurska, V.; Brygadyrenko, V. Effects of organic xenobiotics on Tenebrio molitor larvae and their parasite Gregarina polymorpha. Biology 2024, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brai, A.; Poggialini, F.; Vagaggini, C.; Pasqualini, C.; Simoni, S.; Francardi, V.; Dreassi, E. Tenebrio molitor as a simple and cheap preclinical pharmacokinetic and toxicity model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, J. Taste: Invertebrates. In Encyclopedia of Animal Behaviour; Breed, M.D., Moore, J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.F.; Wu, X.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Boor, P.J.; Ansari, G.A.S. Acute haematopoietic toxicity of aniline in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 1997, 92, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songur, A.; Ozen, O.A.; Sarsilmaz, M. The toxic effects of formaldehyde on the nervous system. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 203, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Nachev, M. Effects of multiple stressors in fish: How parasites and contaminants interact. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brázová, T.; Miklisová, D.; Barčák, D.; Uhrovič, D.; Šalamún, P.; Orosová, M.; Oros, M. Hazardous pollutants in the environment: Fish host-parasite interactions and bioaccumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, R. Relation of Gregarines to Growth and Longevity in the Mealworm Tenebrio molitor L. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1936, 29, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, B.; Dong, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, H. Can closed artificial ecosystem have an impact on insect microbial community? A case study of yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 86, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.N.; Duarte, R.M.; Silva, A.R.R.; Prodana, M.; Góis, A.; Silva, P.V.; Mostafaie, A.; Pinto, J.; Brandão, P.F.; Lopes, I.G.; et al. Edible insects: Understanding benzo(a)pyrene toxicokinetics in yellow mealworms for safe and sustainable consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, R.; van Huis, A. Insect food in space. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

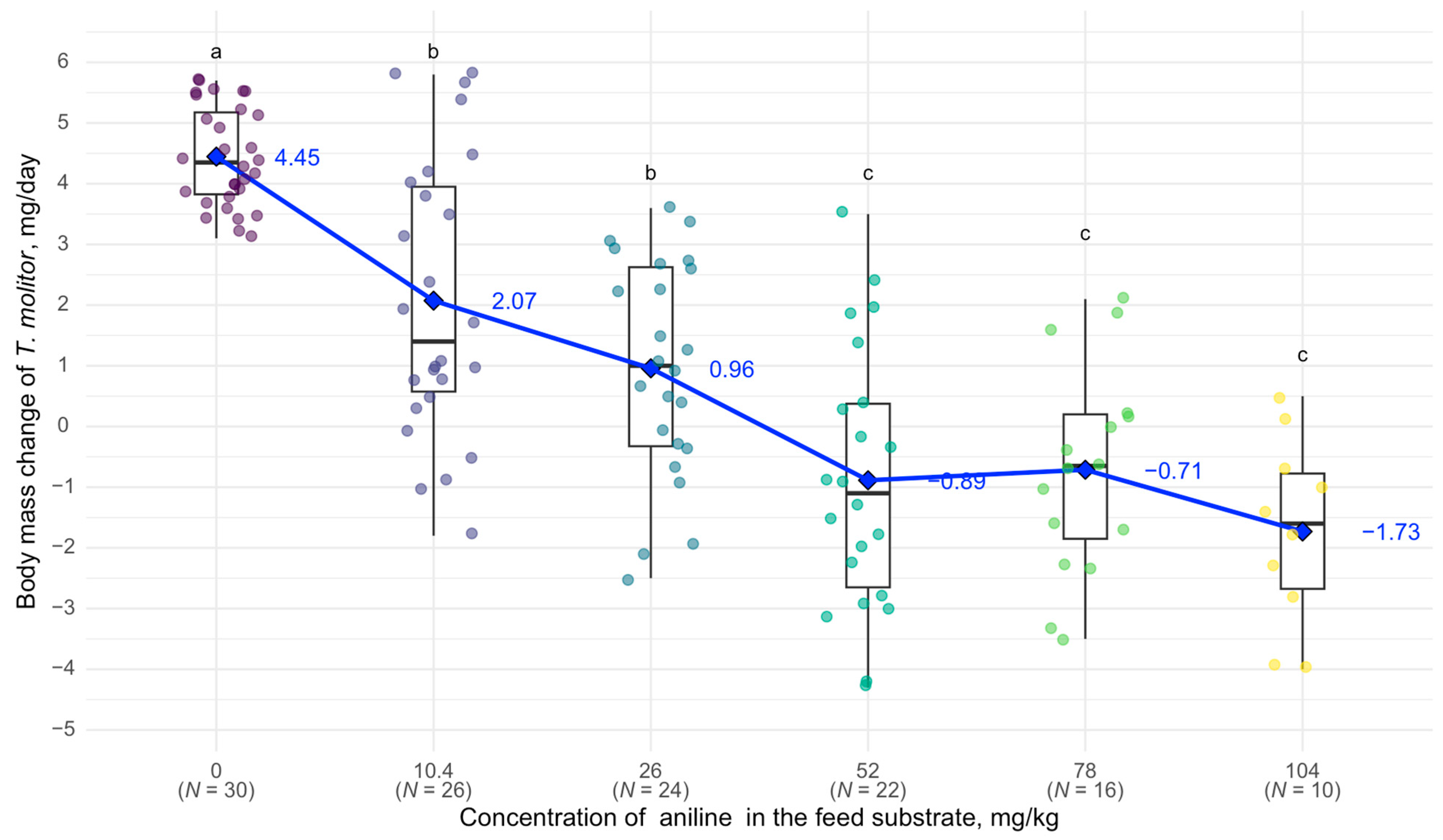

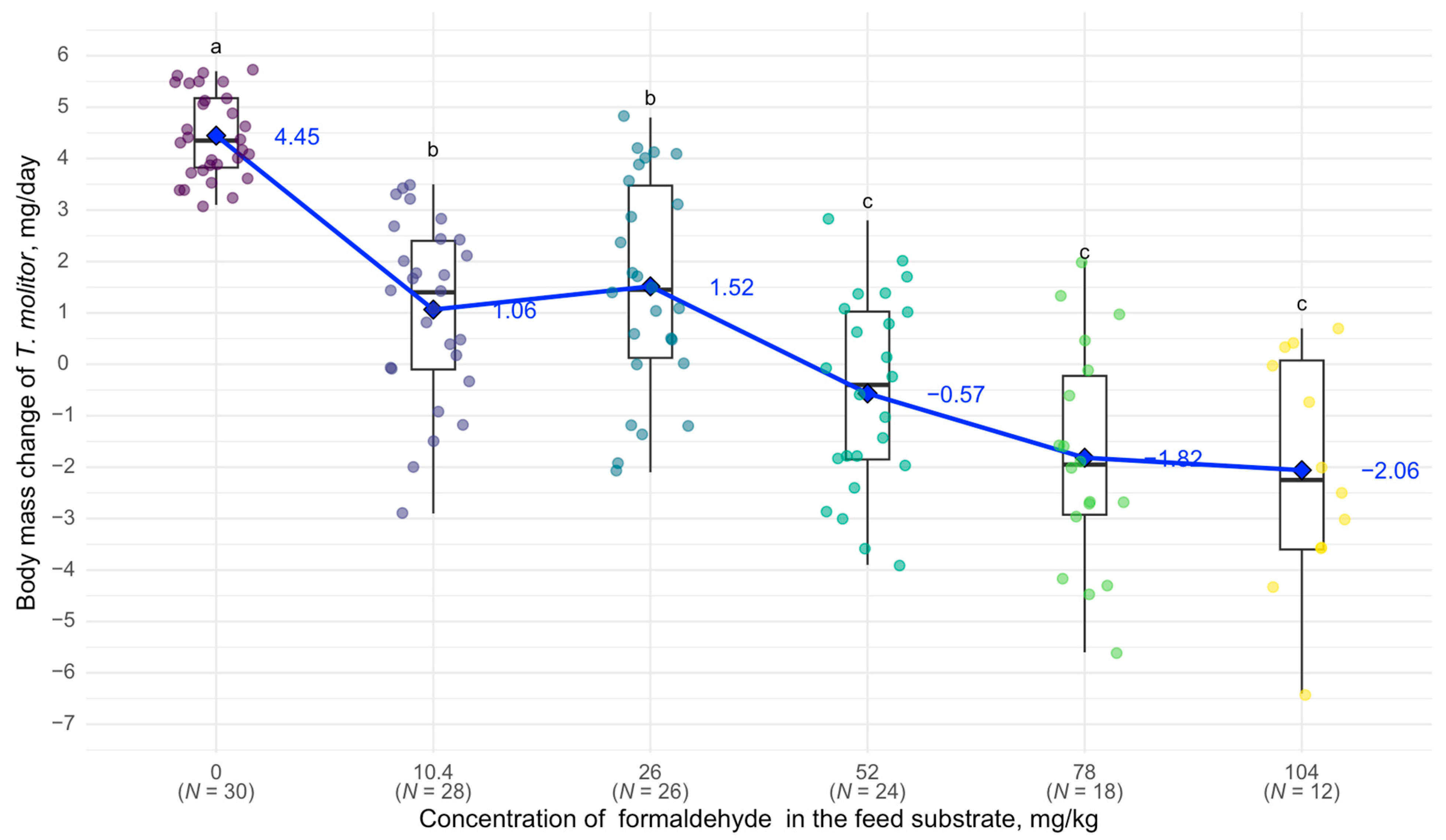
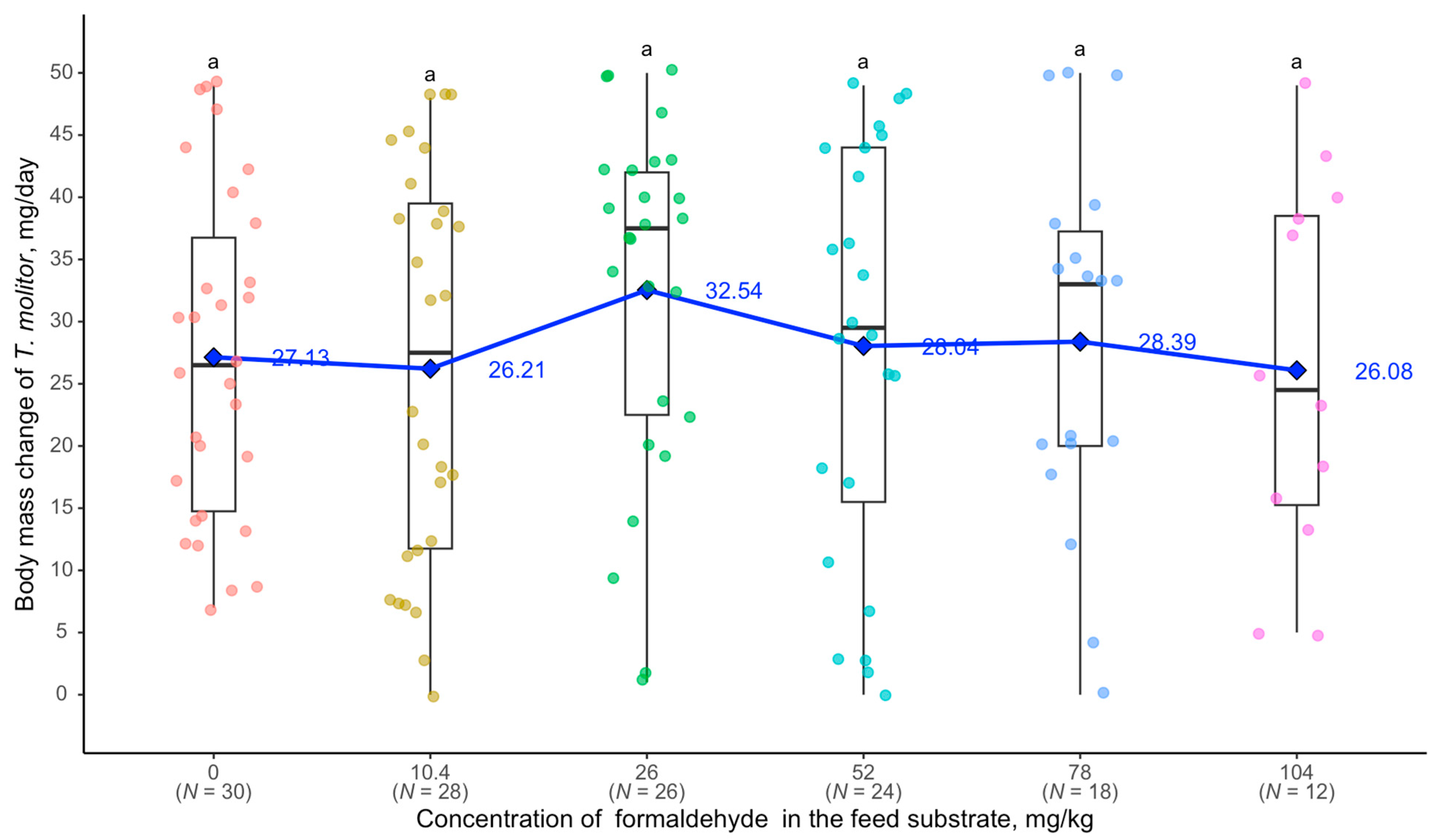
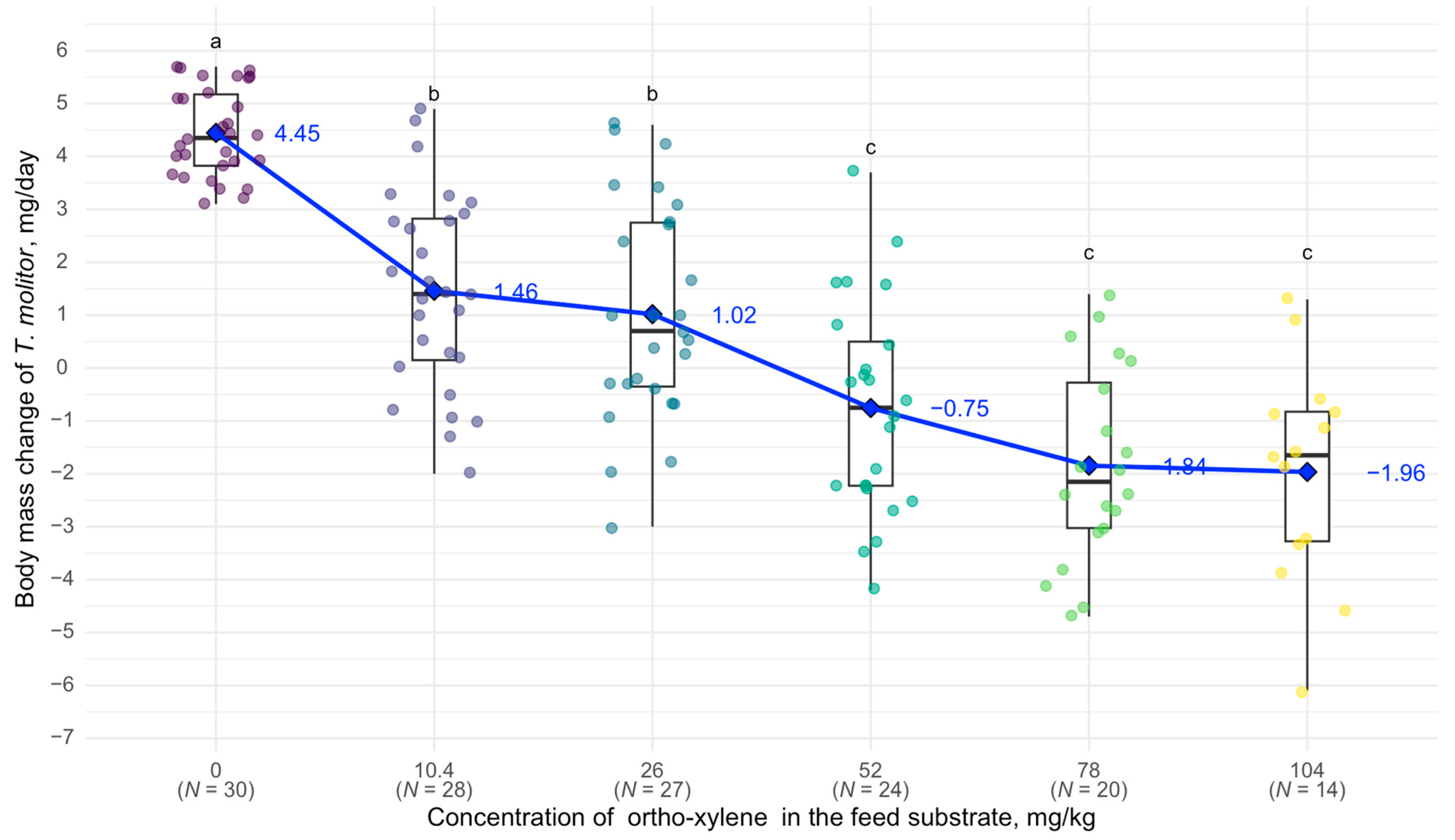
| Substance | Concentration of the Studied Compounds, mg/kg | χ2 | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10.4 | 26 | 52 | 78 | 104 | |||
| Aniline | 0 | 13.0 | 20.0 | 26.7 | 46.7 | 66.7 | 172.89 | <0.001 |
| Formaldehyde | 0 | 6.7 | 13.3 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 60.0 | 104.52 | <0.001 |
| O-xylene | 0 | 6.7 | 13.3 | 20.0 | 33.3 | 53.3 | 75.43 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rybalka, D.; Brygadyrenko, V. Effects of Toxic Organic Compounds on Tenebrio molitor and Its Parasite Gregarina steini. Biology 2025, 14, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050453
Rybalka D, Brygadyrenko V. Effects of Toxic Organic Compounds on Tenebrio molitor and Its Parasite Gregarina steini. Biology. 2025; 14(5):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050453
Chicago/Turabian StyleRybalka, Denis, and Viktor Brygadyrenko. 2025. "Effects of Toxic Organic Compounds on Tenebrio molitor and Its Parasite Gregarina steini" Biology 14, no. 5: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050453
APA StyleRybalka, D., & Brygadyrenko, V. (2025). Effects of Toxic Organic Compounds on Tenebrio molitor and Its Parasite Gregarina steini. Biology, 14(5), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14050453







