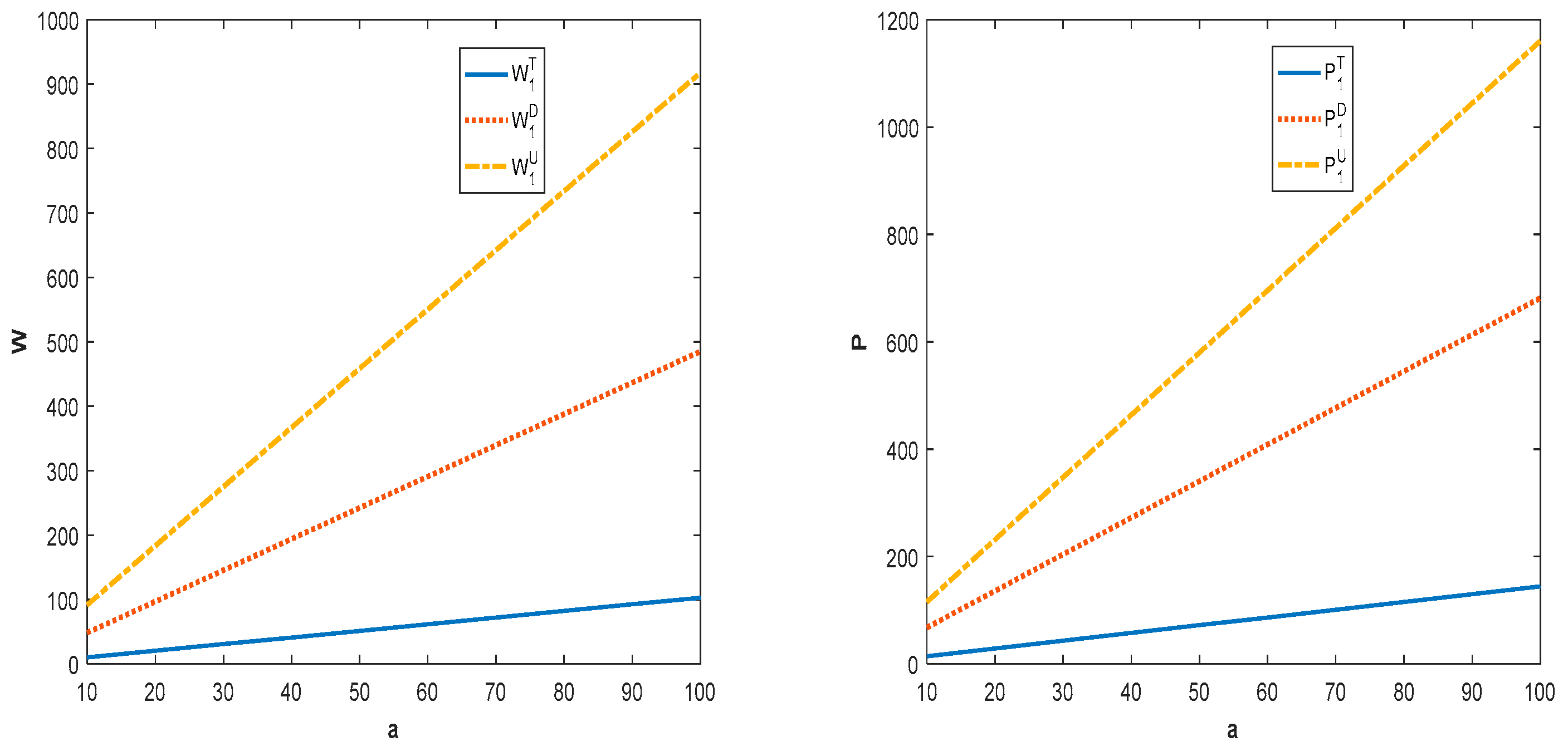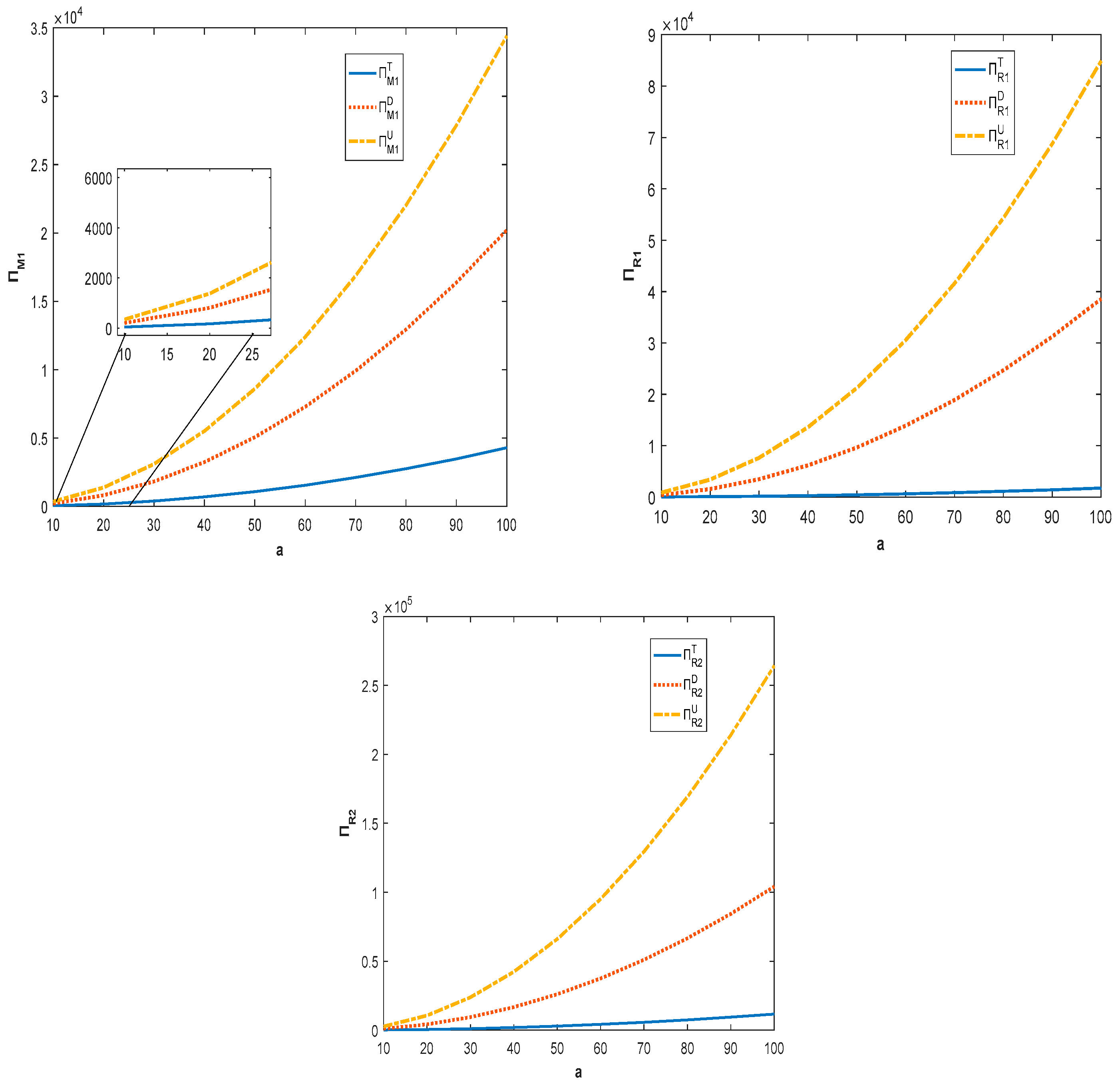Abstract
Product quality is a key factor affecting consumers’ willingness to buy, providing greater advantages to an enterprise than product price. This paper investigates the impact of two factors, price and quality, on the operational decisions of hybrid competing supply chains. Supply chain I, which consists of a manufacturer and a retailer, is a decentralized structure. Supply chain II, where the manufacturer and retailer are integrated, is a centralized structure. Quality investment and vertical shareholding are introduced into the decentralized supply chain. Models are constructed for three different scenarios, examining whether the manufacturer makes a quality investment and whether the retailer holds shares in the quality investment. By comparing the equilibrium results, solved by the Stackelberg game method, the following conclusions are drawn: (1) Quality investment and shareholding can enhance product quality and price. (2) The retail price in a centralized supply chain is consistently lower than that in a decentralized one, leading to generally higher total profits for centralized supply chain. (3) The total profit of the decentralized supply chain only exceeds that of the centralized ones when the degree of substitution between products is lower than 0.6285 and the quality effort cost factor is within a specific range. While centralized supply chain is generally more advantageous, decentralized supply chain can outperform him under specific conditions.
1. Introduction
With the continuous development of the economy, product quality has become the focus of market competition and is a key factor influencing customer choice. From the 1970s to 1990s, in a highly competitive market environment, the Japanese manufacturing industry captured the market share of Europe and the United States in a number of manufacturing industries, such as automobiles and semiconductors, and one of the key reasons for this was that Japanese companies were able to provide better-quality and more reliable products [1]. It is generally accepted that the higher the amount of investment in quality is, the higher the level of product quality will be. It has been found that a high level of product quality increases the rate of repeat purchases by consumers, which in turn increases the market share of the product [2]. Therefore, quality investment is considered to be one of the important strategic decisions for companies. Adopting a quality investment strategy can improve the quality level of and demand for products, but it requires a high level of capital investment [3]. Manufacturers are usually responsible for producing high-quality levels; however investment in quality may benefit other constituents [4,5]. These factors make most enterprises reluctant to participate in product quality research and development. To address the above problems, both upstream and downstream, enterprises in the supply chain should seek deeper strategic cooperation in order to generate win–win situations for both parties. For more examples of quality investments that give companies an edge, readers can refer to the cases of well-known companies such as Apple and Nestle.
Equity partnerships are important ways for supply chain enterprises to seek strategic cooperation [6]. Specifically, the participating firm receives a portion of the target company’s profits in order to benefit from its operations, and the target company benefits from the participating firm’s incentives to become a better company. It has been found that vertical shareholding can both enhance the robustness of inter-firm cooperation and realize synergies in terms of capital, technology, sales, and innovation, thus gaining more competitive advantages for the supply chain as a whole [7]. Cases of vertical shareholding are common in real life. For example, the largest shareholder of gearbox supplier Aisin Seiki is the downstream Toyota Motor [8]. Xiaomi has established an equity partnership with upstream supplier Amlogic, with the former holding a 3.16 percent stake in the latter. In addition, cases such as Alibaba’s 25.25% stake in Haier Multimedia and Suning’s acquisition of part of TCL’s shares show the prevalence of vertical shareholding. Some studies have investigated how vertical shareholding affects the operational behavior of companies. For example, Gao et al. [9] found that vertical shareholding is similar to knowledge sharing and mutual monitoring and has a positive effect on enterprise innovation. For more examples of vertical shareholding, readers can refer to the cases of well-known companies such as Xerox Printers, Volkswagen, and Porsche.
In addition, increasing international competition and the advancement of economic globalization have led to the evolution of transactional relationships between enterprises. In this context, competition between enterprises is intensifying into competition between supply chains. Most of the literature on competing supply chains assumes that firms must opt for either a centralized (CC) or decentralized (CD) structure. The competing supply chains studied by some scholars have the same structure, i.e., both supply chains are either centralized or decentralized. For example, both Feng et al. [10] and Adnan et al. [11] used the Stackberg game approach to study the impact of green technologies on competing supply chains with the same structure. Some scholars have also considered hybrid structural models where a centralized supply chain competes with a decentralized supply chain. For example, McGuire et al. studied two supply chains with price competition and constructed a hybrid structural model where a centralized supply chain competes with a decentralized supply chain [12]. Li et al. studied competition between a centralized supply chain producing mainstream products and a decentralized supply chain producing bandit products [13]. Hybrid competing supply chain practices also exist at the firm’s operational level. For example, before 2006, Chunlan and CHIGO mainly sold air conditioners through decentralized channels, while Gree sold air conditioners directly to the market through self-built channels. In addition to centralized structure and decentralized structure, partial vertical centralization (PVC) structure is also very common in business practice. That is, a company in the same supply chain holds a certain percentage of shares in the target company and is entitled to that percentage of the target company’s profits. For example, in 2009, Bosideng, China’s largest down jacket maker, acquired a 1.76% stake in downstream department store retailer Dashang Group. In the Israeli telecom and media market, a partial vertical centralized model is preferred over a centralized model [14]. In addition, the phenomenon of double marginalization exists in decentralized supply chain, where members of the supply chain each make independent decisions to maximize their own profits. This generally does not maximize the profits of the entire supply chain [15]. More specifically, they make decisions about inventory or pricing that ultimately result in lower sales across the supply chain than they would have if they were working together. However, this does not mean that centralized supply chains are always better than decentralized ones. Manufacturers are better off using a decentralized distribution system when products are highly substitutable and only price competition is considered [16]. Therefore, the decision of whether to adopt a decentralized or centralized structure in order to face market competition is a very important issue for members of competing supply chains. Considering quality investment and vertical shareholding, we aim to investigate the question of what type of structure firms should adopt in the face of competition. At the same time, we introduce quality investment and vertical shareholding to decentralized supply chain due to the phenomenon of double marginalization. Finally, we develop a model of hybrid competing supply chains model in order to simultaneously compare the total profits of supply chains with those of different structures.
In the existing literature, the impact of quality investment and vertical shareholding on the operational decisions of members of hybrid competing supply chains is seldom considered. This paper examines two competing supply chains with different structures. Supply chain I consists of a manufacturer and a retailer. In supply chain II, the manufacturer and retailer are integrated with each other as a whole. In the model, in addition to deciding the wholesale price, the manufacturer also needs to decide whether to invest in product quality research and development. Then, the retailer needs to decide on the retail price of the product. In addition, the retailer in supply chain I needs to decide whether to take a stake in quality investment. We derived the optimal decisions for competing supply chains by using Stackelberg game-theoretical approaches in a competitive market. Our research aims to address the following questions.
1: What is the optimal wholesale price, retail price, and quality level for a supply chain firm’s products under different game models?
2: How do retailers benefit from shareholding strategies?
3: How do quality investment and vertical shareholding affect retailers’ decisions in centralized supply chains?
4: Do quality investment and vertical holding mitigate the phenomenon of double marginalization? If not, what are the constraints?
The remaining contents of the paper are organized as follows. Section 2 presents the literature review, followed by an outline of problem descriptions and model assumptions in Section 3. We outline model construction and solution analysis in Section 4, present numerical analysis in Section 5, and finally discuss conclusions.
2. Literature Review
This paper is closely related to four major streams of the literature, namely, those on competing supply chains, product quality, vertical shareholding, and game theory. This section reviews the literature related to each stream and highlights the differences between existing research and our work.
2.1. Competing Supply Chains
Supply chains with competitive relationships are one of the hot topics of academic research. Most research on competing supply chain structures assumes that firms must choose between a decentralized and a centralized structure. This study focuses on the impact of different levels of price competition, technological innovation, and information sharing on the profits and decisions of supply chain participants. Zhang et al. investigated the impact of RFID technology and supply chain structure on operational decisions, concluding that supply chains benefit from centralization under the Cournot competition model [17]. Xia et al. analyzed the impact of the intensity of market competition and consumer low-carbon preferences on equilibrium decisions and firm profits, finding low-carbon production insufficient to mitigate the negative effects of increased competition [18]. He et al. developed a framework for manufacturers’ rebate strategies under supply chain competition conditions, finding that increased price competition leads manufacturers to prefer cost-effective rebates [19]. Cai et al. investigated selling effort modes in competing supply chains, finding that members’ preferences vary with different wholesale prices [20]. Zhu et al. investigated green product design in competing supply chains, finding that price competition at the retailer level may positively impact the degree of greenness [21]. McGuire et al. studied two supply chains with price competition and found that choosing a decentralized structure for each supply chain is the optimal strategy when the substitutability of the two products is high [12]. Feng et al. investigated the strategic choice of green product R&D in competing supply chains and found that it was optimal to implement green R&D in the two types of supply chains [10]. Adnan et al. explored operational decision-making in competing electric vehicle supply chains to assist manufacturers in achieving optimal pricing and implementing green investment strategies across market scenarios [11]. Patare et al. investigated the effects of quality production strategies on competing supply chains, finding that increased competition intensity leads to higher product quality [22]. Xue et al. introduced the carbon cap-and-trade mechanism and consumer low-carbon preferences into competing supply chains, showing that carbon quotas provide direct economic profits but do not incentivize investment in carbon reduction technology [23]. Duan et al. investigated the impact of supply chain competition on product recall strategies, and their results revealed the joint impact of product recall strategies across and within channels [24]. Wu et al. examined blockchain technology adoption in competing supply chains, finding that the adoption strategy depends on consumer traceability awareness and the cost sharing of blockchain-based traceability between the manufacturer and retailer [25].
2.2. Product Quality
With the continuous improvement of living standards, product quality has gradually become an important factor affecting consumers’ purchasing intentions. Pal et al. investigated the effect of price competition and product quality on supply chain profitability, finding that profit increases with a higher product quality and substitutability level [26]. Xiao et al. investigated coordinated service quality in supply chain systems under capacity constraints and demand uncertainty, finding that centralized networks do not always provide better service or product quality compared to decentralized networks [27]. Qu et al. investigated the impact of joint decision-making on retail price and quality in a virtual product supply chain with information sharing under two game models, finding that higher levels of quality effort elasticity do not always favor the supplier in a Nash game [28]. Cao et al. investigated the effects of product quality, promotional efforts, and channel structure on supply chain performance and found that retailers are usually willing to participate in promotions regardless of product quality [29]. Ranjan et al. investigated the pricing strategies and coordination mechanisms operational among the members of a dual-channel supply chain under three models and found that the level of green quality was higher under the cooperative model [30]. Li et al. studied the impact of optimal joint decision-making on product quality and price under risk aversion and risk neutrality conditions, finding that firms with higher risk aversion set both the price and quality lower when both are decision variables [31]. Fan et al. studied the impact of responsibility cost sharing on product quality and pricing decisions for units of the low-quality product in a two-echelon supply chain [32]. Zhang et al. compared equilibrium results under bilateral and unilateral information sharing models with unobservable manufacturer quality investment, finding that information leakage discourages retailers from sharing and encourages manufacturers to share information [33]. Gurnani et al. investigated the impact of retailers’ selling effort, product quality, and price on supply chain participants under three different decision structures [34].
2.3. Vertical Shareholding
In reality, vertical shareholding is widely used. This is because it reduces costs for firms and enhances the robustness of inter-firm cooperation. In terms of academic research, the current literature focuses on pricing decisions and profit coordination among the shareholding firms within the supply chain. Fang et al. studied the impact of vertical shareholding on firm performance and found that supplier–customer pairs with vertical shareholding reported higher combined monthly returns since the COVID-19 pandemic [35]. Li et al. introduced a vertical shareholding strategy into a green supply chain and found that retailers’ pricing became more sensitive to market changes compared to a non-shareholding model [36]. Xia et al. studied the effect of cross-shareholding on carbon emission reductions in enterprises and found that cross-shareholding can effectively reduce carbon emissions [37]. Liu et al. investigated the effect of cross-shareholding on the profitability of green supply chains and found that, for supply chain leaders, cross-shareholding always increases their profitability [38]. Ren et al. investigated the effects of three shareholding strategies on green investments, prices, and profits, and found that cross-shareholding is optimal when both forward and backward shareholding are sufficiently low [39]. Xiao et al. investigated the impact of backward shareholding on quality investment in decentralized assembly systems, finding that higher rates of backward shareholding do not always incentivize assemblers to invest more in component development [8]. Sun et al. investigated the impact of cross-shareholding on recycling and emission reductions in a low-carbon closed-loop supply chain, finding that higher cross-shareholding and greater consumer low-carbon awareness enhance recycling rates and reduce carbon emissions [40]. Wang et al. studied the effect of vertical shareholding on consumer surplus and social welfare and found that vertical shareholding leads to higher levels of consumer surplus and social welfare [41]. He et al. investigated the impact of vertical shareholding on supply chain financing strategies and found that there exists a tax-related optimal shareholding ratio which reduces supply chain losses under bank financing conditions [42].
2.4. Game Theory
Game theory is an important theory for the study of group decision-making problems. Some scholars have undertaken research on group decision-making. For example, Qu et al. constructed three robust DFA-MECMs with different degrees of conservatism, obtaining a feasible budget range of robust DFA-MECMs [43]. This section focuses on the Stackelberg game in game theory, which describes the interaction between leaders and followers. In the Stackelberg game, the leader is the forerunner of the game, the one who can consider the responses of the followers and strategize accordingly. The followers choose the best decisions for them based on the leader’s strategy. Similarly, some scholars have studied the Stackelberg game. Liu et al. examined price and delivery lead-time decisions in decentralized supply chains based on the Stackelberg game [44]. Both Mukhopadhyay et al. [45] and Yang et al. [46] studied the influence of the Stackelberg game on supply chains’ operational decisions. To sum up, the Stackelberg game method is well known in supply chain management.
Our study is also interested in most of the papers on competing supply chains, and we provide Table 1, which summarizes the differences between some of the studies that are closely related to our work.

Table 1.
The main differences between our work and existing studies.
In summary, although research exists that examines quality investment, vertical shareholding, and competing supply chains, there is no research that considers all three at the same time. Most of the current literature only considers the impact of the coordination problem of vertical shareholding on the members within the supply chain, with limited exploration of its impact in competing supply chains. In competing supply chains, most studies in the literature focus on decentralized or centralized power structures, and little research discusses partial vertical centralization structures. In addition, most of the current literature only considers the effect of price on consumers’ purchasing decisions. With the ongoing improvement in living standards, integrating the quality factor of product into the demand function is becoming increasingly significant. Overall, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
1: We analyze the characteristics of members’ decisions about product price or product quality level.
2: A partial vertical centralization structure is considered in this study.
3: The question of when the total profit of a decentralized supply chain is higher than the total profit of a centralized supply chain is examined.
4: The equilibrium results of three models in the competing supply chains are compared and some meaningful conclusions and managerial insights are drawn.
3. Problem Description and Modeling Assumptions
This paper studies two supply chains that sell substitutable products. Supply chain I consists of an upstream manufacturer and a downstream retailer, with members making decisions with the goal of maximizing their own profits. Manufacturer and retailer in supply chain II integrate with each other as a whole. The integrated company sets its retail prices to be conditional on the retailer’s prices in order to maximize profits. Referring to the research of [12], we equate a centralized supply chain with a retailer that can produce and sell products by itself. For supply chain I, this paper constructs three models: one where a manufacturer does not invest in quality; one where a manufacturer invests in quality alone; and one where a manufacturer invests in quality and the downstream retailer holds shares. All three models make decisions based on the principle of profit maximization. The main parameters used in this paper are shown in Table 2 below.

Table 2.
Model parameter symbols and their definitions.
This paper makes the following assumptions:
Assumption 1.
Before making quality investment, both supply chains produce homogeneous and substitutable products with a quality level of zero. This is a realistic scenario. For example, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo produce various similar-tasting beverage brands that can be substituted for one another.
Assumption 2.
Referring to the settings of Li et al. [47], let the production cost of unit product be zero. Like the existing marketing literature [10,11] and [37], we set the cost of quality investment to be . This is consistent with the fact that companies often need to invest more money to improve the quality of their products.
Assumption 3.
Similar to Choi et al. [48], the product demand function for the two supply chains is , where . After the manufacturer invests in quality, the quality of the product will change. Drawing on research by [10,11], due to the large room for growth in the current market, a manufacturer’s investment in quality is able to increase the market demand for its own product without decreasing the market demand for the competing product. Two products still influence each other through price competition. Therefore, the product demand functions of the two supply chains are and , respectively.
Assumption 4.
In order to be consistent with the actual situation of the enterprise, set , because when the shareholding ratio exceeds 50%, the control rights of the company will be transferred.
Assumption 5.
This paper also assumes that , where . measures the difficulty of quality investment. A high value of indicates that the difficulty of quality investment is high.
4. Model Construction and Solution Analysis
4.1. Manufacturer Does Not Invest in Quality
The manufacturer does not invest in quality. At this time, the quality level of the two types of products is zero. The demand function is . The model is solved by backward induction. Firstly, the wholesale price of manufacturer M1’s product is given in the first stage. Secondly, in the second stage, two retailers—R1 and R2—simultaneously decide the retail prices, and , of their product in order to maximize their profit, i.e.,
By solving Equations (1)–(3), the optimal decisions of the manufacturer and the retailer can be obtained, as shown in Proposition 1.
Proposition 1.
Under the model where the manufacturer does not invest in quality, the optimal decisions of the manufacturer and the retailer are as follows:
Proposition 1 gives the optimal wholesale price and the optimal retail price of the product in the model where the manufacturer does not invest in quality. From Proposition 1, we can see that both the optimal wholesale price and the optimal retail price monotonically increase with . This is due to the increase in the potential demand for the product, which brings more consumers. Therefore, supply chain participants will appropriately increase the product price to obtain more profits. Substituting , and into Equations (1)–(3), the manufacturer’s profit, retailer’s profit and product demand can be obtained as follows:
The proof of Proposition 1 is provided in Appendix A.
Corollary 1.
The retailer in the centralized supply chain will set a lower retail price than rival retailers to seize more market and thus gain more profits, i.e., , and .
Proof of Corollary 1.
We can obtain the equilibrium solutions’ differences in the following.
□
Intuitively, double marginalization effects that exist in a decentralized supply chain put the retailer at a disadvantage relative to rival retailers in terms of price competition. This means that the optimal price chosen by the retailer in the decentralized supply chain is higher than the optimal price of the retailer in the centralized supply chain. With the advantage of low prices, a homogeneous substitutable product produced by a centralized supply chain can access more markets. As a result, the centralized supply chain is able to achieve higher profits.
4.2. Manufacturer Invests in Quality Alone
Product quality is an important factor influencing customers’ willingness to buy. The higher the quality of the product, the higher the price consumers are willing to pay for the product. Technological innovations, such as the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence, have been shown to enhance product quality and increase supply chain profitability. Consider the case where the manufacturer invests in quality alone and the downstream retailer does not take on shareholding. At this time, the product demand function in supply chain I is , and the product demand function in supply chain II is . In order to make the expression of the equilibrium solution simple and intuitive, let and . The model is solved by backward induction. Firstly, the first stage is given the product quality and the wholesale price of the manufacturer M1. Secondly, in the second stage, two retailers, R1 and R2, simultaneously decide the retail prices, and , of their products to maximize their profit, i.e.,
By solving Equations (4)–(6), the optimal decisions of the manufacturer and the retailer can be obtained, as shown in Proposition 2.
Proposition 2.
Under the model where the manufacturer invests in quality alone, the optimal decisions of the manufacturer and the retailer are as follows:
Proposition 2 gives the optimal wholesale price, the optimal quality, and the optimal retail price of the product under the model where the manufacturer invests in quality alone. Similar to Proposition 1, the result of Proposition 2 shows that the optimal wholesale price and the optimal retail price both increase monotonically with . In addition, the optimal product quality increases with demand. This is because an increase in demand leads manufacturers to invest more in quality in order to capture more of the market and make more profit. Substituting , , and into Equations (4)–(6), the manufacturer’s profit, retailer’s profit and product demand can be obtained as follows:
The proof of Proposition 2 is provided in Appendix A.
Proposition 3.
The quality of the product improves after the manufacturer invests in quality alone. At the same time, the market demand for the product, the wholesale price, the retail price, as well as its own profit and the profit of the downstream retailer all increase, i.e., , , , , , .
For supply chain I, product quality is improved after the manufacturer invests in the quality of the product. At this point, the cost of the investment in quality will show up in the form of higher wholesale and retail prices. However, this does not affect the desire of consumers to buy the product. Product demand increases compared to the case without quality investment. Therefore, the profit of members in supply chain I will increase. This suggests that, as living standards improve, price is not the only determinant of demand. The proof of Proposition 3 is provided in Appendix A.
Proposition 4.
After the manufacturer invests in the quality of the product, the retail price, the demand for the product, and the total profit from sales of the retailer in supply chain II will all increase, i.e., , , . At the same time, the retailer in supply chain I increases the retail price of his product more than the rival retailer does i.e., .
Quality investment requires additional cost inputs, which can lead to an increase in the retail price of the product. Two types of products with quality differences are substitutes for each other. Therefore, a high product price will cause part of the increased aggregate demand in supply chain I to flow to supply chain II. As a result, the demand for products from centralized supply chain will increase. Further, the price of products in the centralized supply chain increases. Additionally, the rational retailer in supply chain II will not increase the price of his product above that in supply chain I, opting instead to leverage the lower price to compensate for the lower quality. The proof of Proposition 4 is provided in Appendix A.
Corollary 2.
After quality investment, the profits of members in the decentralized supply chain all increase. When the product quality effort cost factor
, the increase in the manufacturer’s profit is not less than the increase in the profit of its downstream retailer, i.e., . Conversely, when , the retailer’s profit increase is higher than that of its upstream manufacturer, i.e., , where .
For the manufacturer, the size of their own profit increase will only not be smaller than that of the downstream retailer if the product quality effort cost factor does not fall below the threshold given in Corollary 2. But for manufacturer with limited capital, the excessive cost of technological innovation can easily deter him. When the product quality effort cost factor falls below the threshold given in Corollary 2, the size of the profit increase for the downstream retailer is higher than that for the upstream manufacturer. As a result, the incentive for manufacturer to invest will be hurt. The proof of Corollary 2 is provided in Appendix A.
Corollary 3.
The difference in market demand for the products of competing supply chains is related to the degree of substitution between products, the product quality effort cost factor, and consumer sensitivity to product quality in the case a manufacturer invests in quality alone. Meanwhile, the total profit of centralized supply chain and decentralized members has the following relationships:
1: When and , we obtain . When and , we obtain .
2: When and , we obtain , where the specific expression for is and where A and B are, respectively, , .
Proof of Corollary 3.
The difference between the market demand of the centralized supply chain and the market demand of the decentralized supply chain is simplified to obtain the following expression:
We find that when the degree of substitution between products is high, holds. When both the degree of substitution between products and product quality effort cost factor are low, holds.
The difference between the total profit of the centralized supply chain and the total profit of the decentralized supply chain can be simplified to obtain the following expression: . Both A and B are positive, as determined by . Thus, the difference in total profits is closely related to the open upward quadratic equation . Whether the difference in total profits is positive or negative correlates with the function value of . Further analysis results in the following discriminant equation: . When , the function value of the function is constantly positive, which means . When , the function value of the function is constantly 0, which means . When , the function value of the function is always negative, which means . Further, when , we obtain . The function value of the quadratic equation is always positive in the domain , i.e., . When , we obtain . The value of a function of the quadratic equation is always non-negative in the field . The point where the function value of is 0 is . Comparative analysis shows that . Therefore, the quadratic equation f(l) is constantly positive in the domain of definition , i.e.,. In summary, when , we obtain .
When , we obtain , which means can take on a positive, negative, or zero value. The quadratic equation has two roots, denoted as and . According to the analysis, when , we obtain . When , the function value of the quadratic equation does not exceed zero, which means that the total profit of the decentralized supply chain is not less than the total profit of the centralized supply chain. i.e., . When , the function value of the quadratic equation is always positive. This means that the total profit of the centralized supply chain is higher than the total profit of the decentralized supply chain. i.e., . In summary, Corollary 3 is proven. □
After investing in product quality, the demand for centralized supply chain products exceeds that for decentralized supply chain products when product substitution is high. The demand for decentralized supply chain products will be higher than the demand for centralized supply chain products when the degree of substitution between products and the product quality effort cost factor are low. This is because, when the degree of substitution between products is high, there is less product differentiation. From Corollary 1 and Proposition 4, it is clear that products from centralized supply chain with lower prices are more acceptable to consumers. Product differentiation is greater and quality investment is more efficient when both the degree of substitution between products and product quality effort cost factor are low. At this time, the manufacturer is able to improve the quality of his product with lower levels of capital investment and attract more consumers with better-quality product.
In addition, quality investment can make the total profit of decentralized supply chain higher than the total profit of centralized supply chain, but only if competing products are not highly substitutable and the product quality effort cost factor does not exceed a certain interval. The reason behind this is that, when the degree of substitution between products is below 0.6285, product differentiation is high and the squeeze effect is weak. Lower investment in quality and increased product demand can lead to higher total profit in decentralized supply chain than in centralized ones. On the contrary, when the quality investment cost is high, excessive capital investment will make the total profit of the centralized supply chain higher than the total profit of the decentralized supply chain. When the degree of substitution between products is higher than 0.6285, the degree of product differentiation is small. Broadened market demand from quality investment flows more to centralized supply chain where product is sold at lower price. This results in higher total profits in centralized supply chain than in decentralized ones.
4.3. Manufacturer Invests in Quality and the Downstream Retailer Holds Shares
A high degree of capital investment in quality and “free-rider” behavior by downstream retailer discourage manufacturer from investing. In order to change this phenomenon, retailer take on manufacturers’ quality investment costs to ease his financial pressure. Consider the case of a decentralized supply chain in which the retailer holds shares in a manufacturer that invests in quality. Let the shareholding ratio be , and after shareholding, the retailer distributes dividends to the manufacturer’s profits according to the shareholding ratio . In order to make the expression of the equilibrium solution concise and intuitive, we set on the basis of setting . The model is solved by backward induction. Firstly, the first stage is given the product quality and the wholesale price from the manufacturer M1. Secondly, in the second stage, two retailers R1 and R2 simultaneously decide the retail prices and of their product to maximize their profit, i.e.,
By solving Equations (7)–(9), the optimal manufacturer and retailer decisions can be obtained, as shown in Proposition 5.
Proposition 5.
Under the model where the manufacturer invests in quality and the downstream retailer holds shares, the optimal decisions of the manufacturer and the retailer are as follows:
Proposition 5 gives the optimal wholesale price, the optimal quality, and the optimal retail price under the model in which the manufacturer invests in quality and the downstream retailer holds shares. Similar to Proposition 2, the results of Proposition 5 show that the optimal wholesale price, the optimal quantity, and the optimal retail price all increase monotonically with . Substituting , , , and into Equations (7)–(9) increased manufacturer’s profit, retailer’s profit, and product demand, respectively:
The proof of Proposition 5 is similar to the proofs of Propositions 1 and 2, and so it will not be stated.
Proposition 6.
When the shareholding ratio α is less than a certain threshold, the retailer will hold shares in the upstream manufacturer that implements the quality investment.
Proof of Proposition 6.
Ensure that the following four cases hold, which are as follows: there is a negative characterization of the Hessian matrix, the retail price is higher than the wholesale price, the retailer’s profit does not decrease after the shareholding, and the shareholding ratio 0 is within the assumed constraint. Combining the relevant conditions in the paper, the constraint function on the shareholding ratio is obtained:
Solving these four constraints yields . Here, is associated with the condition that the retailer’s profit does not decrease after shareholding. We focus on analyzing the conditions under which the third inequality holds. From this analysis, we obtain a quadratic function on the percentage of holdings and solve it to obtain two roots and . The specific expressions are , . Here , .
The specific solution process is as follows:
Letting the numerator of the fraction be greater than zero gives us the condition we want. This means that . By simplifying this equation, we obtain a quadratic function about . Finally, we use the rooting formula to solve for . □
Retailer will hold shares as a reasonable proportion of the funds invested in quality. This can not only enhance the robustness of supply chain enterprises, but also ensure the normal development of transactions between upstream and downstream enterprises. Because the retailer has limited funds, controlling the shareholding ratio within a certain range is also in line with actual situations.
Proposition 7.
The downstream retailer’s shareholding in quality investment within a certain percentage range leads to a sustained improvement in product quality, as compared to a situation where the manufacturer invests in quality alone. As the demand for and selling price of the product have increased, the manufacturer is able to make more profit. i.e., , , , , .
The implementation of the shareholding strategy can see the retailer share the financial pressure of the manufacturer and also enhance the quality level of the product. The high quality level of the product increases the market demand for the product and increased demand leads to an increase in the price of the product. As a result, the profit of all members of the decentralized supply chain is increased.
Corollary 4.
The demand for product in the centralized supply chain will rise and the retailer will raise the selling price of his product appropriately to gain more profit. i.e., , , , .
As market demand expands, the demand for products from centralized supply chains with relatively cheaper retail prices will also increase. Therefore, retailer in a centralized supply chain will appropriately raise the prices of his product to gain more profit.
Corollary 5.
The effect of shareholding on quality, selling price, and demand is as follows: , , , , , .
Corollary 5 shows that the level of product quality in the decentralized supply chain continues to improve as the shareholding increases. The reason for this is that a higher shareholding level means a deeper degree of equity collaboration between the manufacturer and the retailer. This will allow retailer to share more of the cost pressures of quality investment on behalf of manufacturer, thereby increasing the incentive for manufacturer to invest in quality. As a result, the level of product quality will increase. The improvement of quality level will not only broaden the market demand for a product, but also increase the cost of quality investment. It can lead to an increase in product pricing for members of the decentralized supply chain as the shareholding rises. From Corollary 4, it can be seen that the retail price of the product in the centralized supply chain is lower than that in the decentralized supply chain. Excessively high product pricing in the decentralized supply chain can cause the demand for a product in the centralized supply chain to increase as shareholding rises. As a result, the product price of the centralized supply chain will also increase with the increase in the shareholding ratio.
Corollary 6.
The total profit of the centralized supply chain is always higher than that of the decentralized supply chain, regardless of the value of the product quality effort cost factor, when the manufacturer invests in quality and the downstream retailer holds shares. i.e., .
Proof of Corollary 6.
The difference between the total profit of the centralized supply chain and the total profit of the decentralized supply chain is simplified to obtain the following expression: , where the expressions for and are, respectively, , . Clearly, is greater than zero. Thus, the difference in total supply chain profits is an open-ended quadratic function of the product quality effort cost factor. The discriminant of the quadratic equation is . Further, we obtain . Combined with the set range of constraints, we know that and . Therefore, the quadratic equation discriminant is always negative. That is, the total profit of the decentralized supply chain is lower than the total profit of the centralized supply chain. □
Corollary 6 arises because the product quality level improves more when the retailer shares in the quality investment, compared to when only the manufacturer invests. However, higher levels of quality mean that members of a decentralized supply chain will invest more. In addition, there is “free-riding” by retailer in centralized supply chain. These reasons can cause the total profit of a decentralized supply chain to be lower than the total profit of a centralized supply chain.
5. Numerical Analysis
In this section, some of the propositions and corollaries are verified by numerical analysis. Referring to Feng et al. [10] and Gurnani et al. [34], who studied the parameter settings, the basic parameters of this paper are set as follows: , , . According to Assumption 5, where the influence factor of cost is always greater than that of the quality sensitivity factor, we set the product quality effort cost factor . According to Proposition 6, the retailer’s shareholding in the manufacturer ranges from 0 to 0.212. Next, when the basic parameter is analyzed separately, the rest of the parameters are fixed and the analyzed factor becomes a ranges of values.
5.1. Impact of Potential Demand for the Product on the Competing Supply Chains
In this subsection, the specific parameters are set as , , , , .
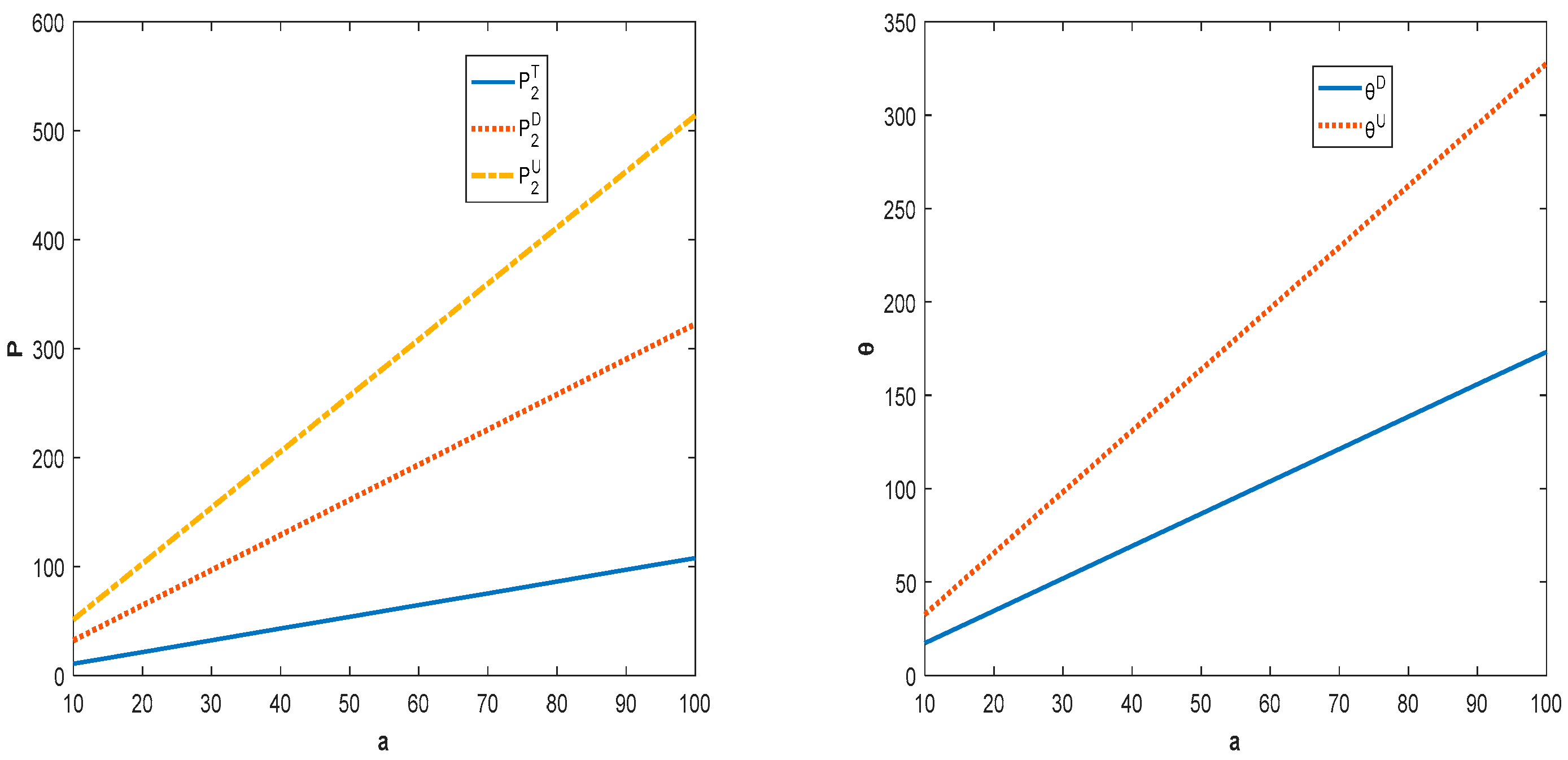
Figure 1 shows that, as the potential demand for the product increases, the wholesale price, product quality level, and retail price will all increase. With the increase in demand, supply chain members will appropriately increase the pricing of a product to obtain more profit. At the same time, manufacturer also tends to improve the level of product quality in order to develop the market to increase his profit. In addition, along with the implementation of the quality investment and shareholding strategy, the pricing of the products of the supply chain members will increase. This is because the increase in investment costs and market demand will eventually show up in the form of higher market prices.
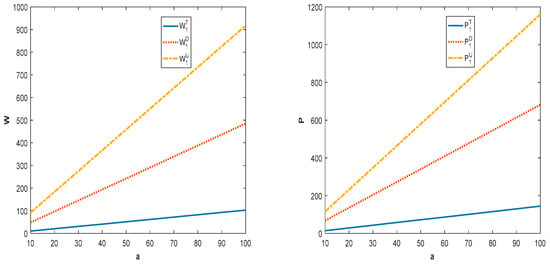
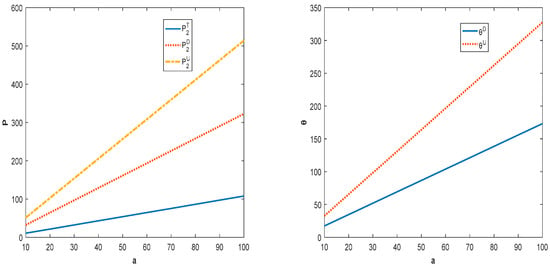
Figure 1.
Impact of potential demand for product on price and product quality.
It can be seen from Figure 2 that, with the increase in the potential demand for product, the members of the competing supply chains can obtain more profit. In addition, decentralized supply chain members have incentives to pursue quality investment and shareholding strategies. This is because, in both models, the profit of members can grow continuously and realize Pareto improvement. Combining Figure 1 and Figure 2, we can see that the retail price of a product in the centralized supply chain is lower than the price of product in the decentralized supply chain. This is because centralized supply chain member has lower costs in terms of acquiring parts and is more inclined to set lower prices than his competitor in order to capture the market.
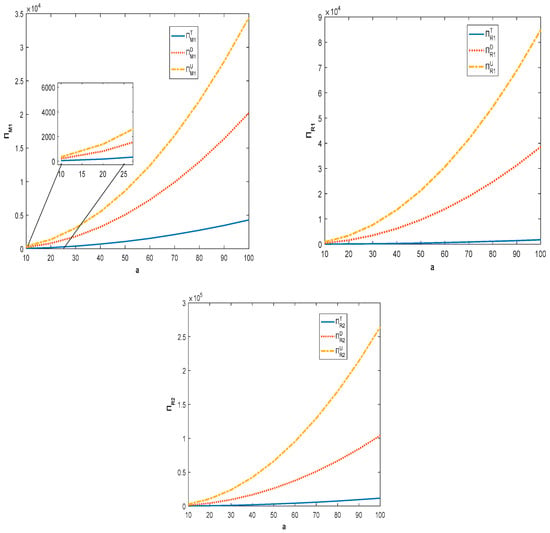
Figure 2.
Impact of potential demand for product on profit of supply chain members.
5.2. Impact of Product Quality Effort Cost Fator on Total Supply Chain Profit
5.2.1. Low Level of Degree of Substitution between Products
In this subsection, the specific parameters are set as , , , .
5.2.2. High Level of Degree of Substitution between Products
In this subsection, the specific parameters are set as , , , .
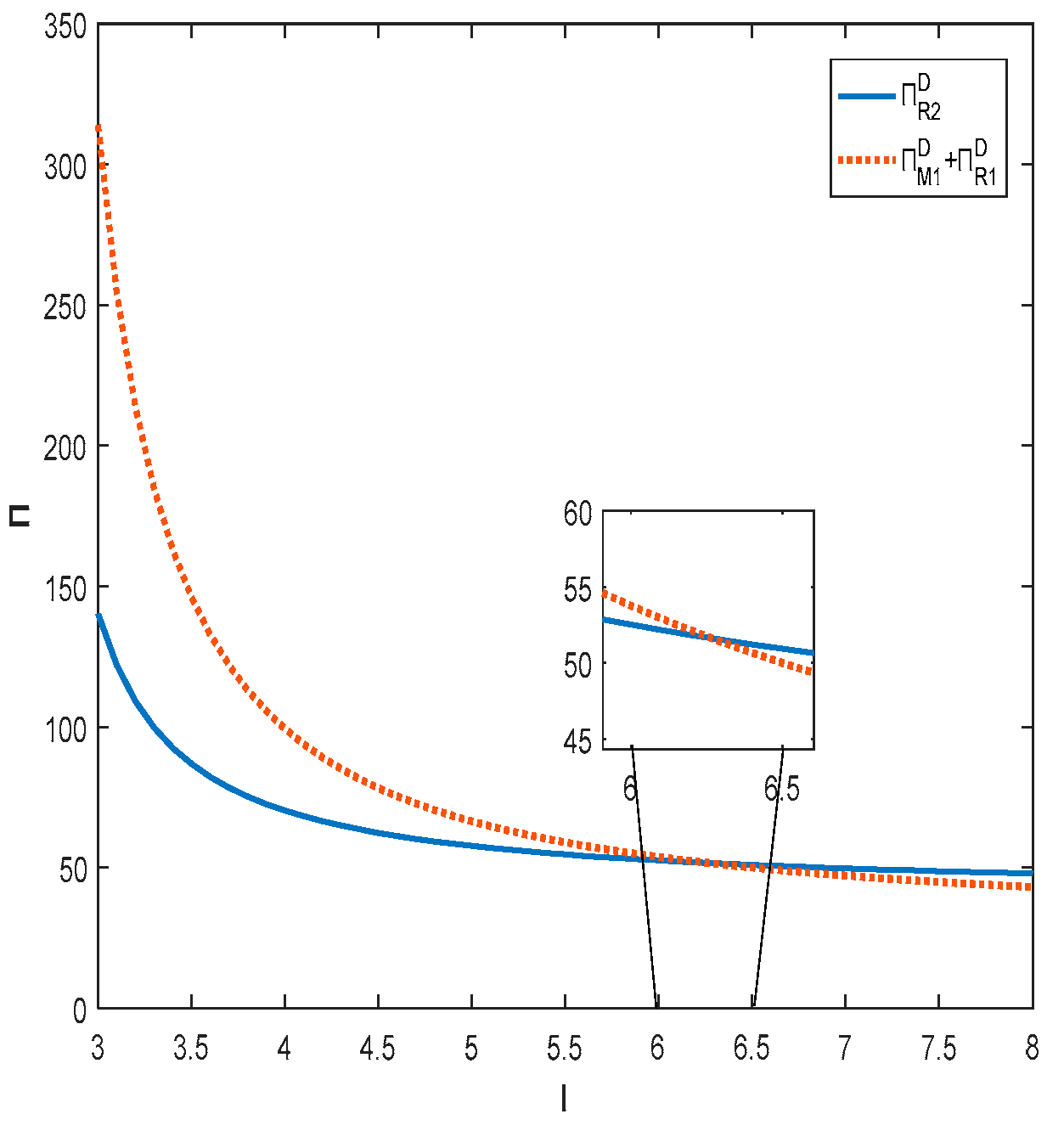
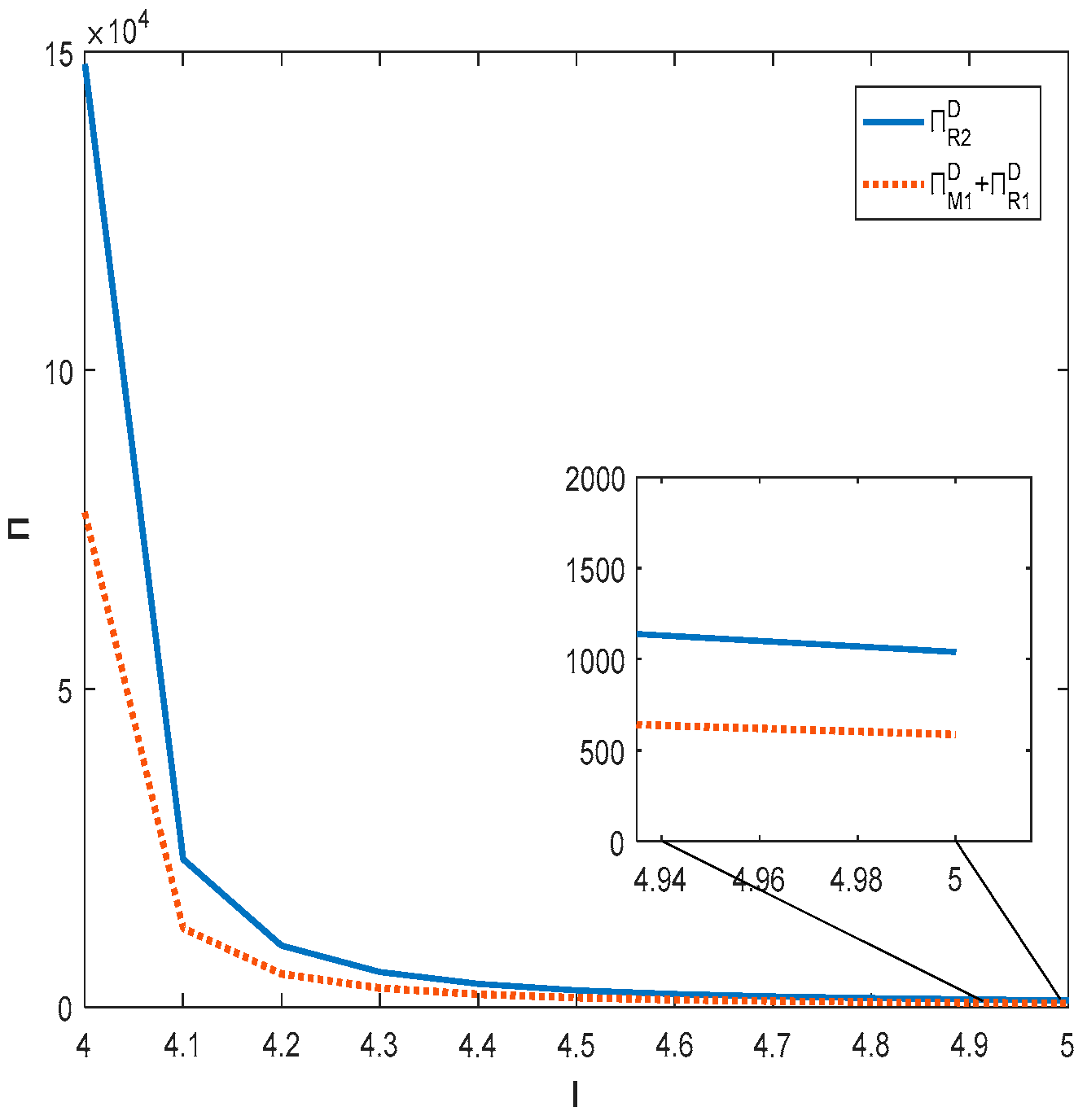
Figure 3 and Figure 4 together show that only when the degree of substitution between products is not high and the product quality effort cost factor is within a certain range, the total profit of the decentralized supply chain will be higher than that of the centralized supply chain. When the degree of substitution between products is high or the product quality effort cost factor is high, the total profit of the centralized supply chain will be higher than the total profit of the decentralized supply chain. This is the same result as that obtained for Corollary 3.
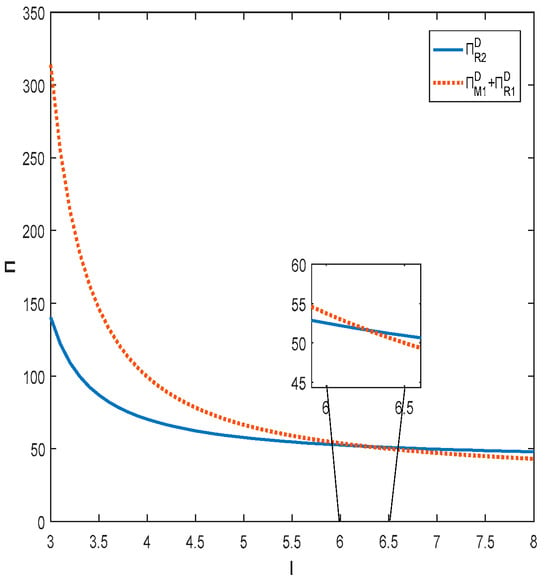
Figure 3.
Impact of product quality effort cost factor on total supply chain profit.
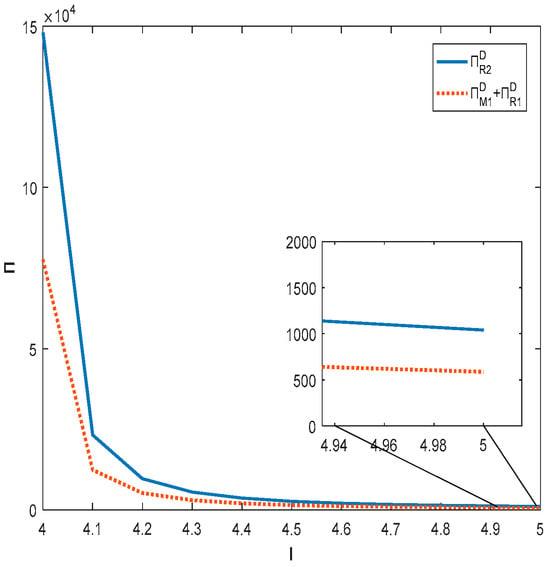
Figure 4.
Impact of product quality effort cost factor on total supply chain profit.
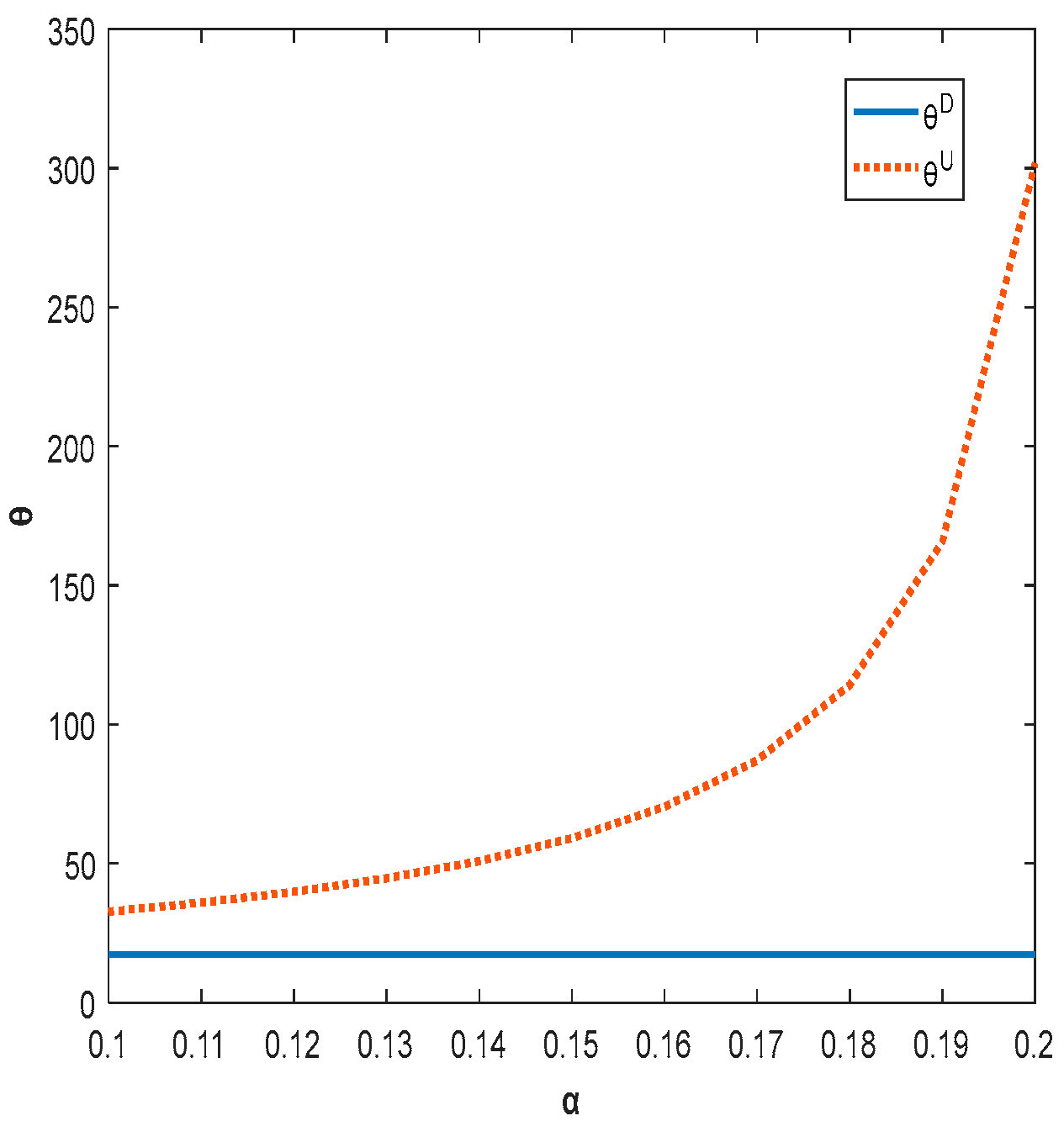
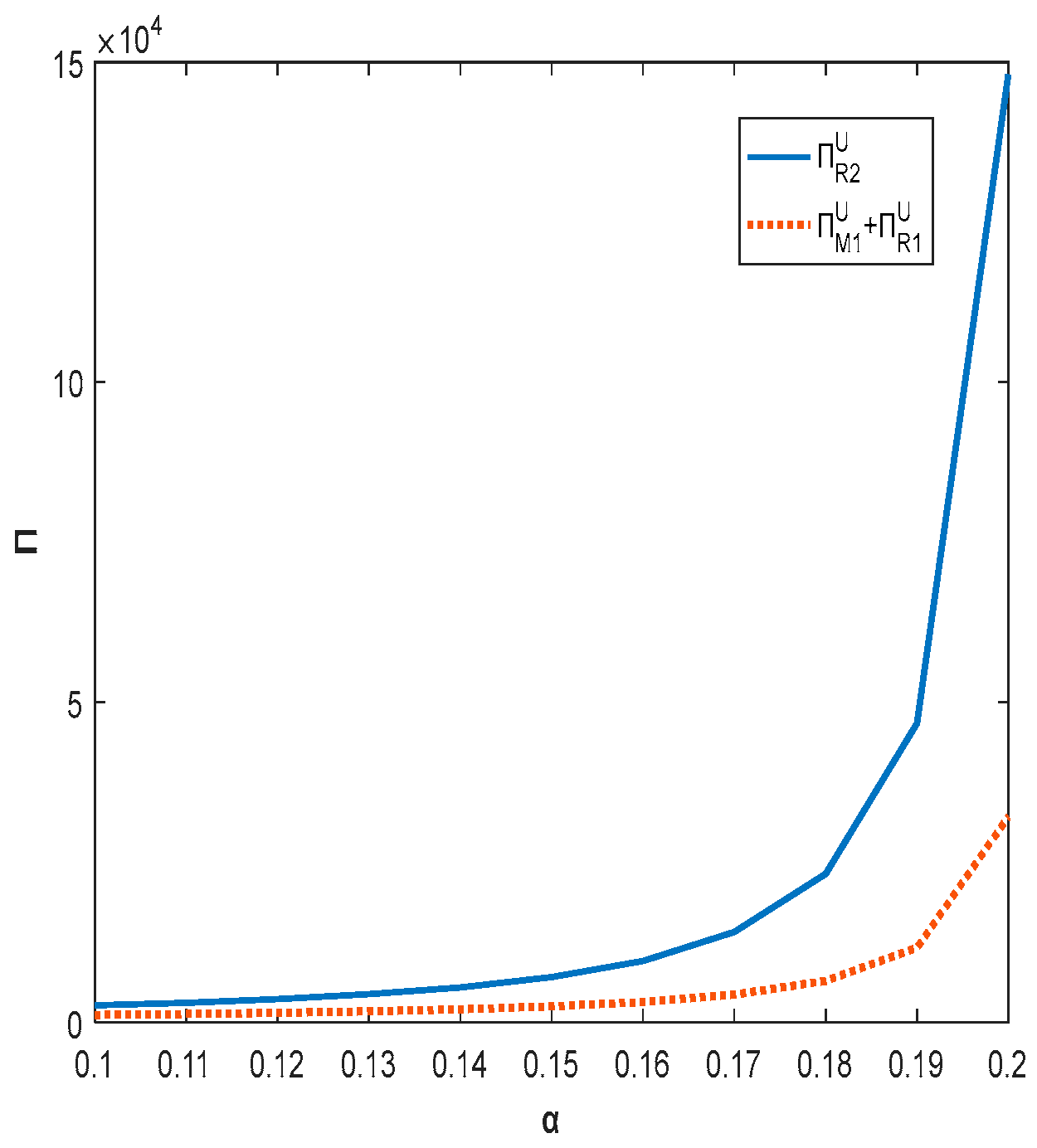
5.3. Impact of Shareholding Ratio on Product Quality and Total Profit of Supply Chain
In this subsection, the specific parameters are set as , , , , .
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show that both product quality and total supply chain profit increase with increased shareholding when the shareholding strategy is implemented. The higher the shareholding ratio in the range, the higher the profit of the firm. In order to improve the overall benefit of chain enterprises, the government can encourage enterprises to increase their shareholding ratio through policy support or economic subsidies. Currently, the total profit of the decentralized supply chain is always lower than that of the centralized supply chain due to high capital investment and the phenomenon of “free riding”.
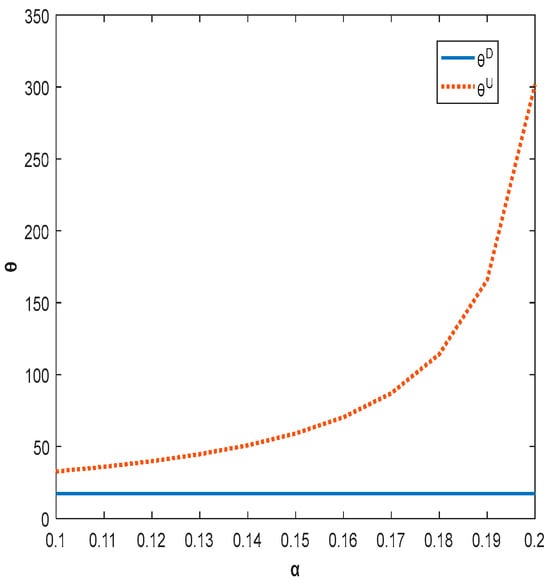
Figure 5.
The impact of shareholding ratio on product quality.
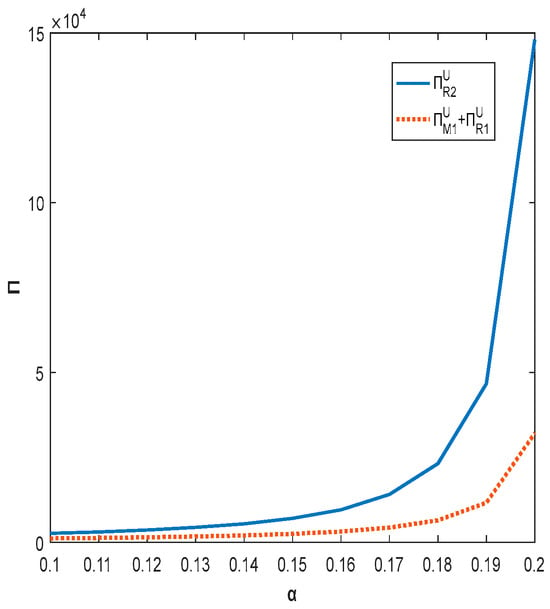
Figure 6.
The impact of shareholding ratio on total supply chain profit.
6. Conclusions
This paper investigates the effects of quality investment and vertical shareholding on the operational decisions of members of hybrid competing supply chains. Using dynamic game theory, we obtain equilibrium solutions for the members in the competing supply chains and compare the profit of the members under three different scenarios. Finally, through theoretical analysis and numerical experiments, the following conclusions were obtained.
From the point of view of theoretical analysis, we drew the following conclusions.
(1) After the manufacturer in the decentralized supply chain invests individually in product quality, the overall quality level improves. Quality investment can enhance the profit of members in competing supply chains. However, this investment behavior may also result in increased profit for downstream retailer, creating a “free riding” phenomenon. Additionally, it is important to note that when the degree of product substitution is high and the cost factor of quality effort remains within a specific range, the total profit of a decentralized supply chain may surpass that of a centralized supply chain. Therefore, quality investment can be advantageous for decentralized supply chain under certain conditions.
(2) The level of product quality, price, and market demand will continue to improve with the increase in shareholding. “Free-riding” by downstream retailer has improved as manufacturer in decentralized supply chains has become more profitable. In general, the shareholding strategy not only realizes the Pareto improvement of corporate decision-making and performance, but also enhances the polarity of the manufacturer’s quality investment product. There is no doubt that the holding strategy facilitates the promotion of product quality investment. The important thing to note here is that the holding strategy leads to an increase in the cost of quality investments, which can lead to an increase in the price of the product. As a result, some of the total market demand broadened by quality investments will flow to centralized supply chain with lower prices. At this point, the total profit of the centralized supply chain will always be higher than the total profit of the decentralized supply chain.
From the point of view of regulatory and policy implications, we obtain the following conclusions.
(3) The price and profit of supply chain participants and the optimal level of quality of the product are positively correlated with the potential demand in the market. Both the manufacturer and retailer benefit from consumer sensitivity to quality levels. For members of the decentralized supply chain, it is necessary to implement quality investment and vertical ownership strategies, which can allow them to obtain greater profits.
(4) From the perspective of overall supply chain profitability, quality investment is the preferred option, as it can lead to higher total profits for decentralized supply chains under specific conditions. When product differentiation is high and quality investment is less challenging, firms should prioritize quality investment to rapidly capture market demand. In this scenario, the decentralized structure is preferred over the centralized structure.
(5) From the perspective of supply chain participants’ profitability, quality investment and shareholding are the preferred solutions, as these strategies lead to increased profits for supply chain members. At this time, the centralized structure is superior to the partial vertical centralization structure, which in turn is better than the decentralized structure.
(6) In general, the total profit of the centralized supply chain is higher. Therefore, the competitive advantage of the supply chain that completes the integration of upstream and downstream enterprises in advance is more obvious. Therefore, business consolidation should be oriented towards the goal of setting lower prices than competitors. For example, companies may consider supply chain efficiency optimization to reduce product procurement costs.
There are several directions for further research following this paper. First, only two supply chains are considered in this paper, while the supply chain system in reality is intricate and complex. Therefore, exploring the impact of quality investment and shareholding strategies on supply chain networks is a highly relevant research question. Secondly, demand is influenced by many factors in reality and this cannot be easily portrayed. Subsequently, the model can be extended to use in study in a stochastic demand environment. Finally, in practice, information about manufacturer and retailer is not always completely symmetrical. Therefore, how quality investment and stockholding strategies under asymmetric information conditions affect the decision-making of members of a hybrid competitive supply chain is also a scientific question that deserves to be explored further.
Author Contributions
Methodology, S.X. and T.Z.; formal analysis, S.X. and T.Z.; Investigation, S.X. and T.Z.; Conceptualization, T.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Z.; Supervision, S.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Foundation, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China, grant number 22YJCZH221; and the Key Project of the Hunan Provincial Department of Education, grant number 23A0254; and the General Project of Hunan Provincial Water Resources Department, grant number XSKJ2023059-39.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the readability of Table 2. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Appendix A
Proof of Proposition 1.
By backward induction, the second-order partial derivatives of and are obtained according to Equations (2) and (3):
Thus, is a concave function with respect to . is a concave function with respect to . This implies that there exists a unique optimal retail price for the two retailers. Therefore, let and . The first-order conditional solutions of Equations (2) and (3) are obtained as follows:
Solve (A1) to obtain
Substituting the solved (A2) into Equation (1) and taking the second-order partial derivative with respect to , we find that is a strictly concave function with respect to . The first-order conditional solution is obtained as
by making .
Bringing (A3) to (A4) yields
Obviously , , . Therefore, we obtain the equilibrium solution of the model, and the profit of supply chain members can be obtained from (A3) and (A4). □
Proof of Proposition 2.
By backward induction, the second-order partial derivatives of and are obtained according to Equations (2) and (3):
Thus, is a concave function with respect to . is also a concave function with respect to . This implies that there exists a unique optimal retail price for the two retailers. Therefore, let and . Then, the first-order conditional solutions of Equations (5) and (6) are obtained as follows:
Solve (A5) to obtain
Substituting the solved (A6) into Equation (4) and taking the second-order partial derivatives of and , we obtain
Obviously, the results of both equations in (A7) are less than zero, and a second-order mixed partial derivative of the profit function yields
Therefore, the Hessian matrix of Equation (4) is
According to this assumption, the determinant of the Hessian matrix 18 is less than zero. That is, the profit function of manufacturer is a joint concave function with respect to and . Solving for yields the first-order conditional solution of
Solving this set of equations for (A10) yields
Substituting (A11) into (15) yields and , respectively, as
From (A11) and (A12), the profits of supply chain members can be obtained. □
Proof of Proposition 3.
The difference between the optimal solutions can be obtained.
According to Assumption 5 and the constraints, the difference equations are non-negative. Increases in demand and product price mean that the profit of manufacturer and retailer will also increase as a result of investments in quality, i.e., , . □
Proof of Proposition 4.
The difference between the optimal solutions can be obtained.
According to Assumption 5 and the constraints, the difference equations are non-negative. Increases in demand and product price mean that the profit of retailer will also increase as a result of investments in quality, i.e., . □
Proof of Corollary 2.
The difference between the optimal solutions can be obtained.
When , we obtain . The solution is obtained . The condition is obtained by the same reasoning. □
Proof of Proposition 5.
The proof is similar to Proposition 2. □
Proof of Proposition 7.
The proof is similar to Proposition 3 and Proposition 4. □
Proof of Corollary 4.
The proof is similar to Proposition 3 and Proposition 4. □
Proof of Corollary 5.
According to the Assumptions and the constraints, we know that these derivative values are all positive. □
References
- Banker, R.D.; Khosla, I.; Sinha, K.K. Quality and competition. Manag. Sci. 1998, 44, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranton, R.E. Competition and the incentive to produce high quality. Economica 2003, 70, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.-B.; You, T.-H.; Ou, C.X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, C.-Y. Optimizing payment schemes in a decentralized supply chain: A Stackelberg game with quality investment and bank credit. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 168, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q. Quality investment, and the contract manufacturer’s encroachment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 279, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xin, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Q. Differential dynamic decision-making model for multi-stage investment of scenic area. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 2819–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, J.; Faulkner, D. Strategies of Cooperation: Managing Alliances, Networks, and Joint Ventures; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, C.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Y. Institutional cross-ownership and corporate strategy: The case of mergers and acquisitions. J. Corp. Financ. 2018, 48, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, K.; Fu, H. Quality investment in a decentralized assembly system with backward shareholding. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 242, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Shen, H.; Gao, X.; Chan, K.C. The power of sharing: Evidence from institutional investor cross-ownership and corporate innovation. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2019, 63, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, T. Selection strategy and coordination of green product R&D in sustainable competitive supply chain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, Z.H.; Chakraborty, K.; Bag, S.; Wu, J.S. Pricing and green investment strategies for electric vehicle supply chain in a competitive market under different channel leadership. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, T.W.; Staelin, R. An industry equilibrium analysis of downstream vertical integration. Mark. Sci. 1983, 2, 161–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sethi, S.P.; Zhang, J. Competing with bandit supply chains. Ann. Oper. Res. 2016, 240, 617–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilo, D.; Spiegel, Y. Partial vertical integration in telecommunication and media markets in Israel. Isr. Econ. Rev. 2011, 9, 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Coordination of information sharing in a supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 143, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Bao, Y. Price competition with integrated and decentralized supply chains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 200, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-H.; Wang, S.-S.; Chang, L.-Y. Radio-frequency Identification (RFID) adoption and chain structure decisions in competing supply chains: Bertrand competition versus Cournot competition. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 336, 1777–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Wang, Y.; Lv, L.; Shen, L.; Cheng, T. Financing decisions of low-carbon supply chain under chain-to-chain competition. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 6153–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ai, X.; Wang, G.; Zhong, L. Manufacturer rebate strategy under chain to chain competition. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2023, 74, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Dong, R.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, X. Supply chain competition models with strategic customers considering sales effort. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 172, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; He, Y. Green product design in supply chains under competition. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 258, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patare, S.; Venkataraman, S.V. Strategies in supply chain competition: A game theoretic approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 180, 109242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Sun, G. Impacts of supply chain competition on firms’ carbon emission reduction and social welfare under cap-and-trade regulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Xu, J. Remanufacturing and Product Recovery Strategies Considering Chain-to-Chain Competition and Power Structures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Fan, Z.-P.; Li, G. Strategic analysis for adopting blockchain technology under supply chain competition. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2023, 26, 1384–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Guin, S.; Chaudhuri, K. Pricing and quality competition between two substitute products in a closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2023, 10, 2259294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-X.; Zhang, R.-Q. Supply chain network equilibrium considering coordination between after-sale service and product quality. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 175, 108848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Meng, C.; Hu, B. Pricing and quality decisions in virtual product supply chains with information sharing. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2023, 74, 1746–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, M. Optimizing hybrid-channel supply chains with promotional effort and differential product quality: A game-theoretic analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Jha, J. Pricing and coordination strategies of a dual-channel supply chain considering green quality and sales effort. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, X. On pricing and quality decisions with risk aversion. Omega 2021, 98, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ni, D.; Fang, X. Liability cost sharing, product quality choice, and coordination in two-echelon supply chains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 284, 514–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, W.; Zaccour, G.; Zhang, J. Should a manufacturer give up pricing power in a vertical information-sharing channel? Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 276, 910–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnani, H.; Erkoc, M.; Luo, Y. Impact of product pricing and timing of investment decisions on supply chain co-opetition. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 180, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhang, R.-Z. Vertical shareholding during supply chain shocks. Econ. Lett. 2024, 235, 111566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; He, J.; Shi, Y. Firms’ shareholding behavior in green supply chains: Carbon emissions reduction, power structures, and technology spillovers. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Zhi, B.; Wang, X. The role of cross-shareholding in the green supply chain: Green contribution, power structure and coordination. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 234, 108037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Song, Z.; Fan, Y. The impact of cross-shareholding under different power structures considering green investment and green marketing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22249–22261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Guo, R.; Lan, Y.; Shang, C. Shareholding strategies for selling green products on online platforms in a two-echelon supply chain. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 149, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Shao, T.; Yao, F. Modelling low-carbon closed-loop supply chain considering channel power structures and cross-shareholding. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 2023, 57, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.F. Vertical shareholding, vertical product differentiation and social welfare. Metroeconomica 2023, 74, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kang, K.; Mu, X. Impact of tax difference and asset structure on a capital-constrained vertical equity holding transnational supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 3606–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z. Robust maximum expert consensus modeling with dynamic feedback mechanism under uncertain environments. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Parlar, M.; Zhu, S.X. Pricing and lead time decisions in decentralized supply chains. Manag. Sci. 2007, 53, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Yue, X.; Zhu, X. A Stackelberg model of pricing of complementary goods under information asymmetry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 134, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Pricing and carbon emission reduction decisions in supply chains with vertical and horizontal cooperation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 191, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Shi, V.; Zhai, S. Partial vertical centralization in competing supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 224, 107565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.C. Price competition in a channel structure with a common retailer. Mark. Sci. 1991, 10, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).